Pathological Characteristics of the Emerging Recombinant African Swine Fever Virus Genotypes I and II in Vietnam
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statements
2.2. Virus Strain
2.3. Animals
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. DNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
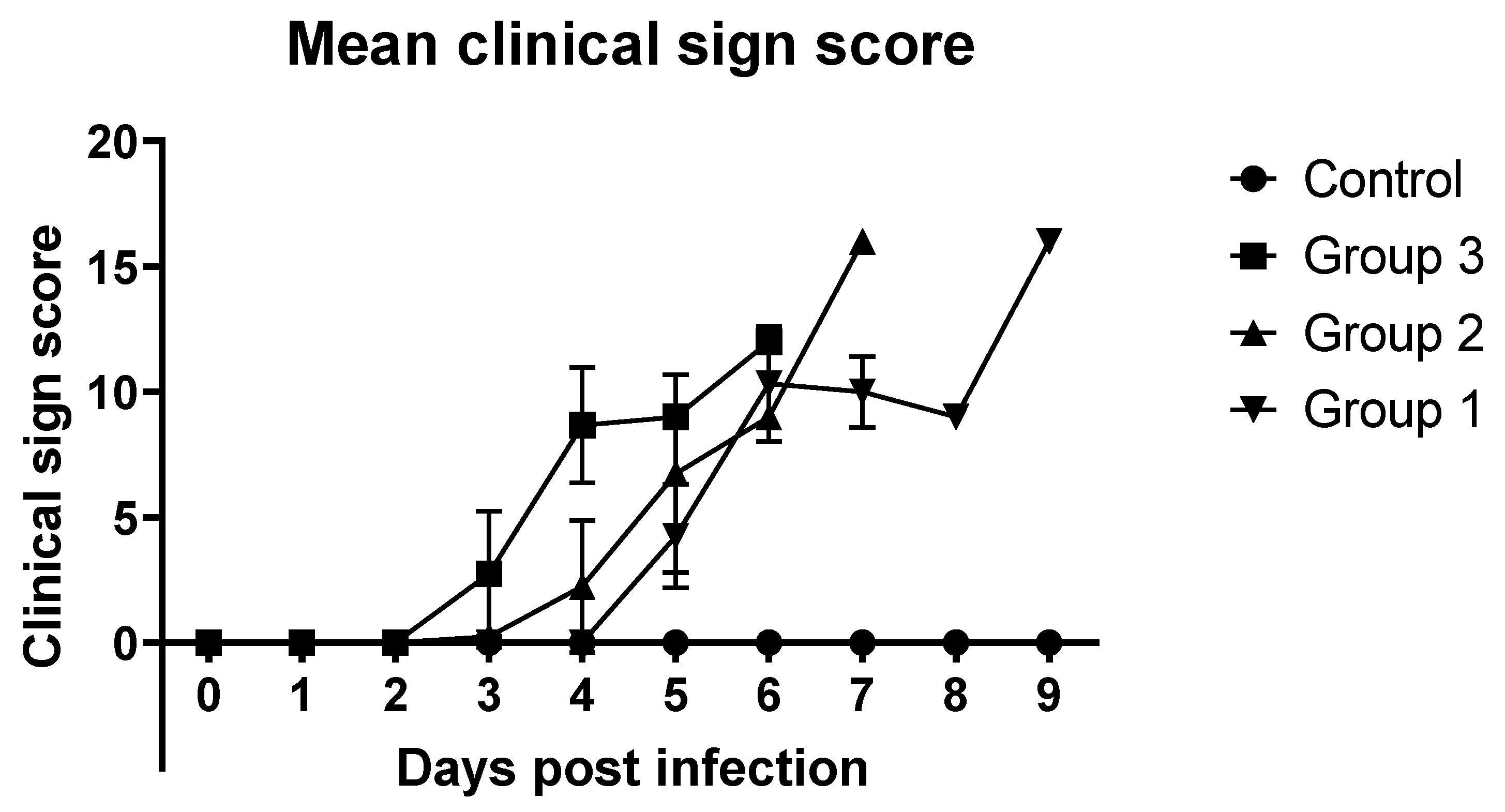
2.6. Scoring of ASF Clinical Signs
3. Results
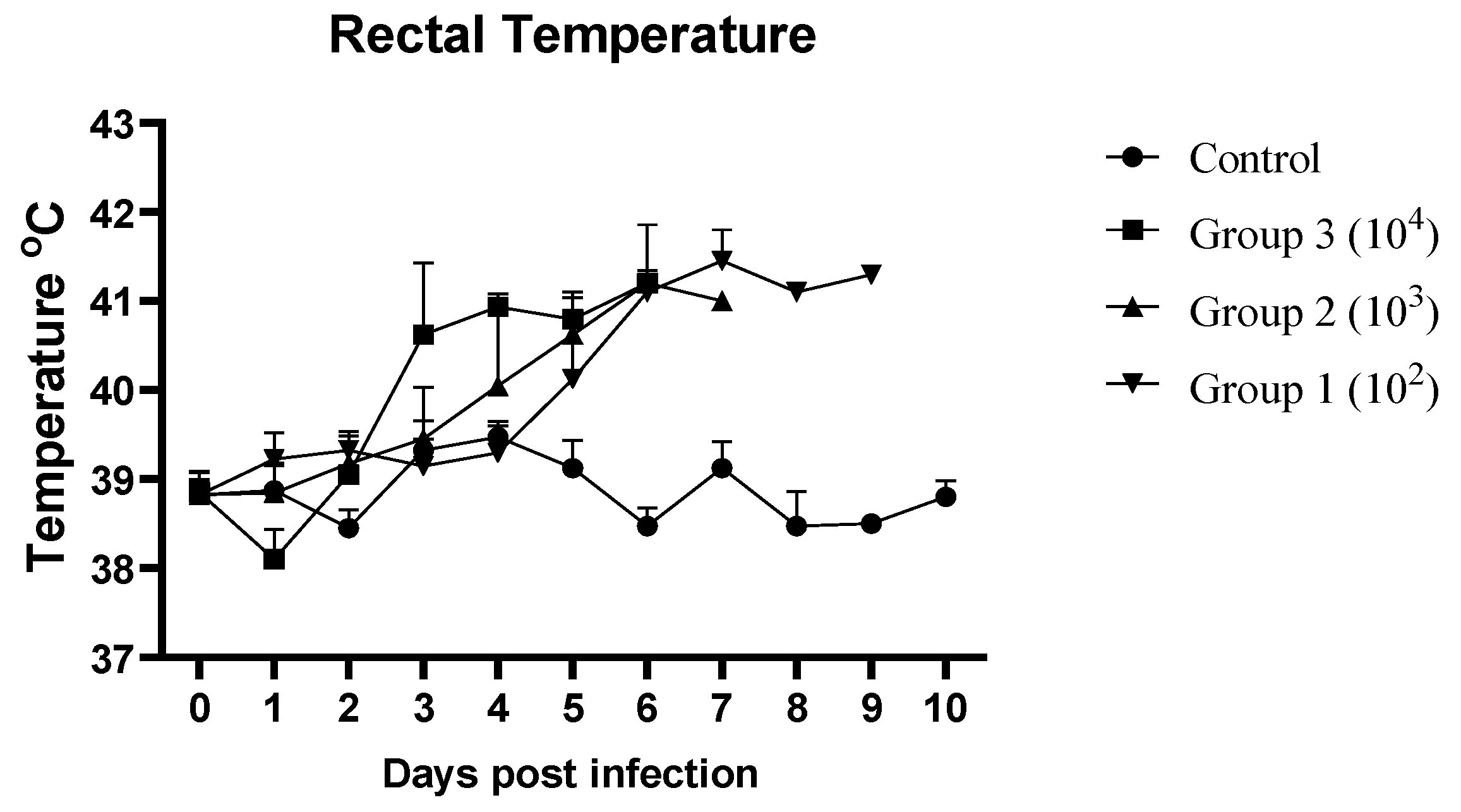
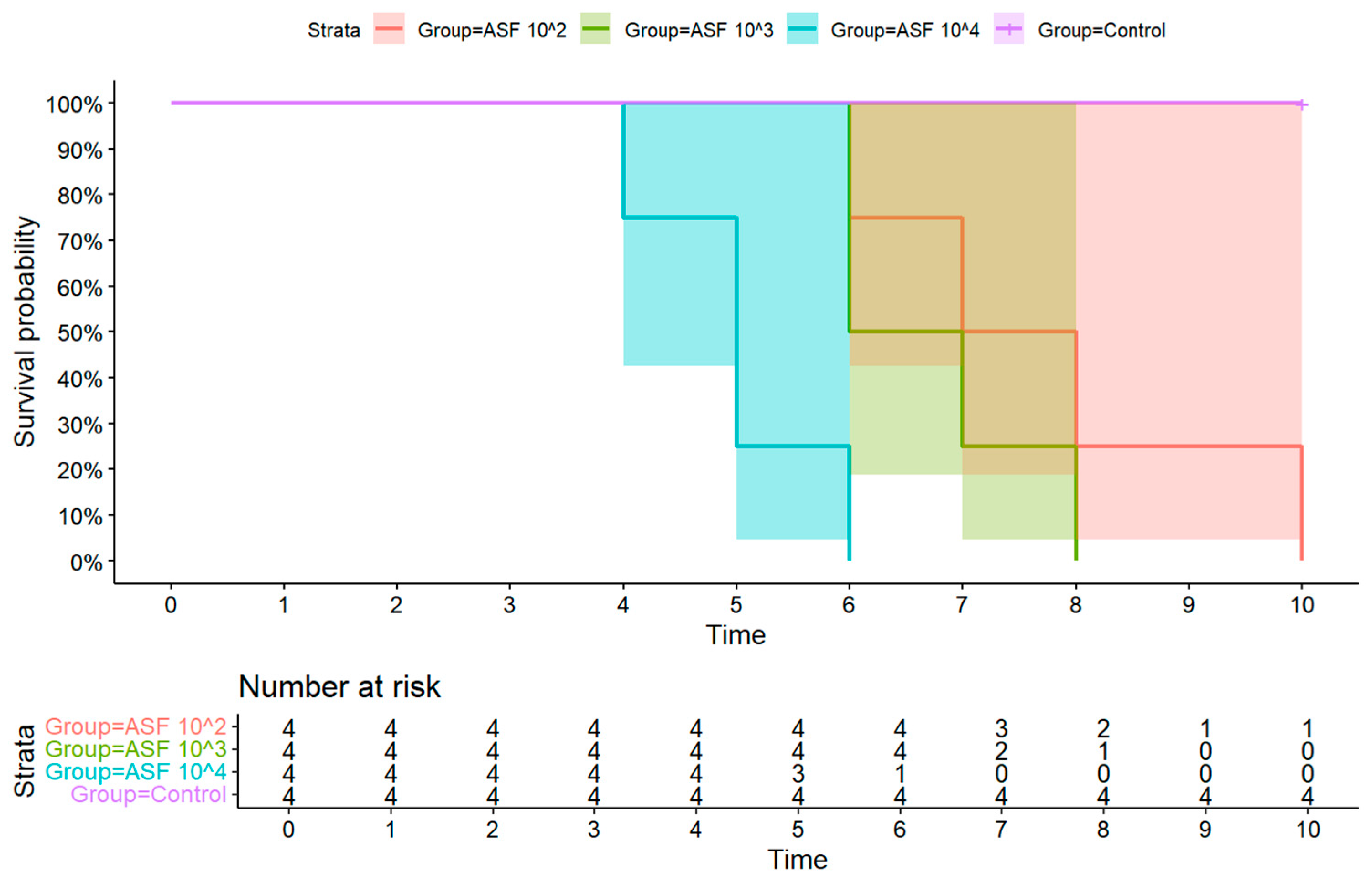
3.1. Clinical Signs
3.2. Detection of ASFV Genomic Material in Whole Blood and Oral Fluid
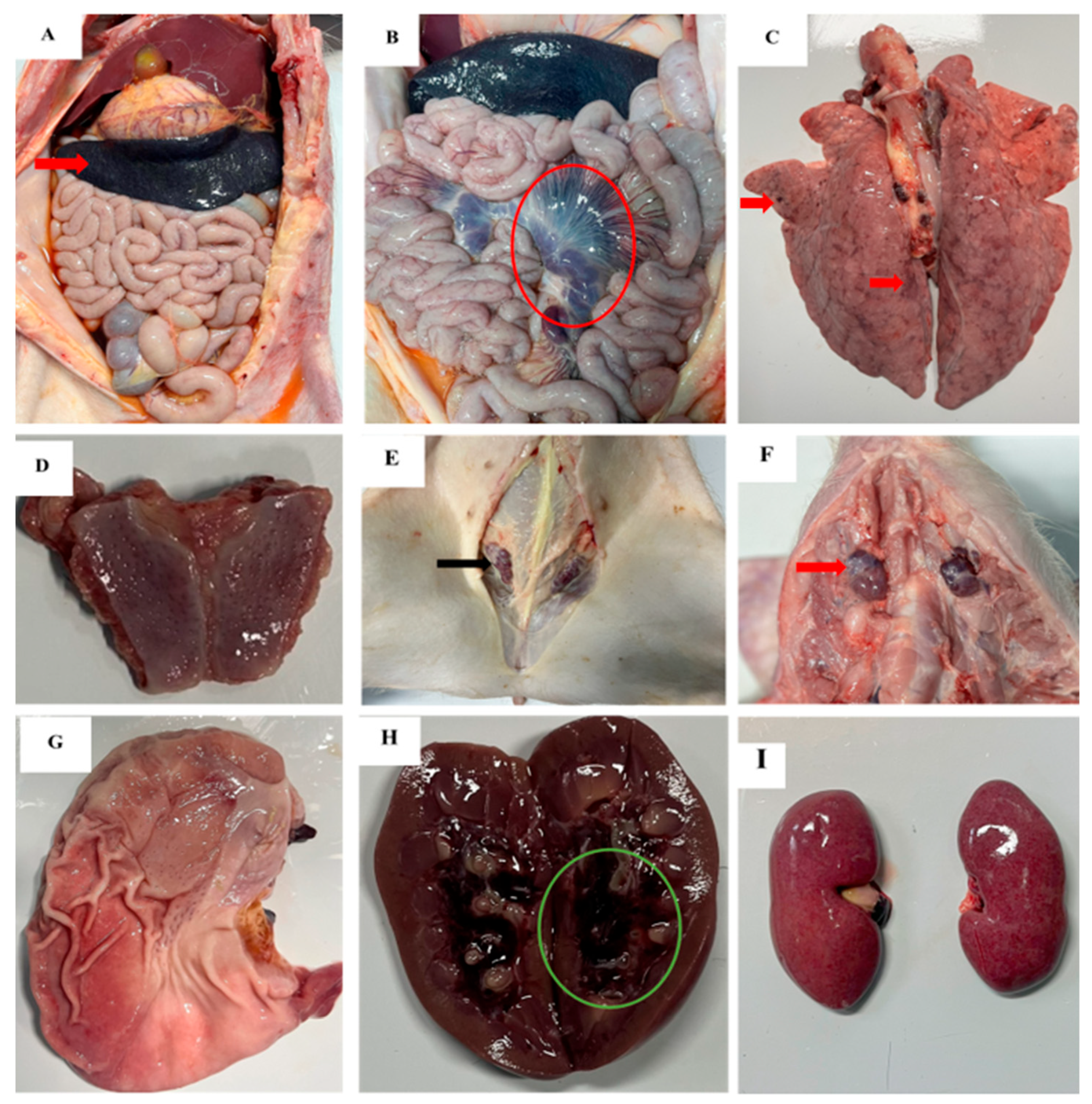
3.3. Gross Pathological Findings
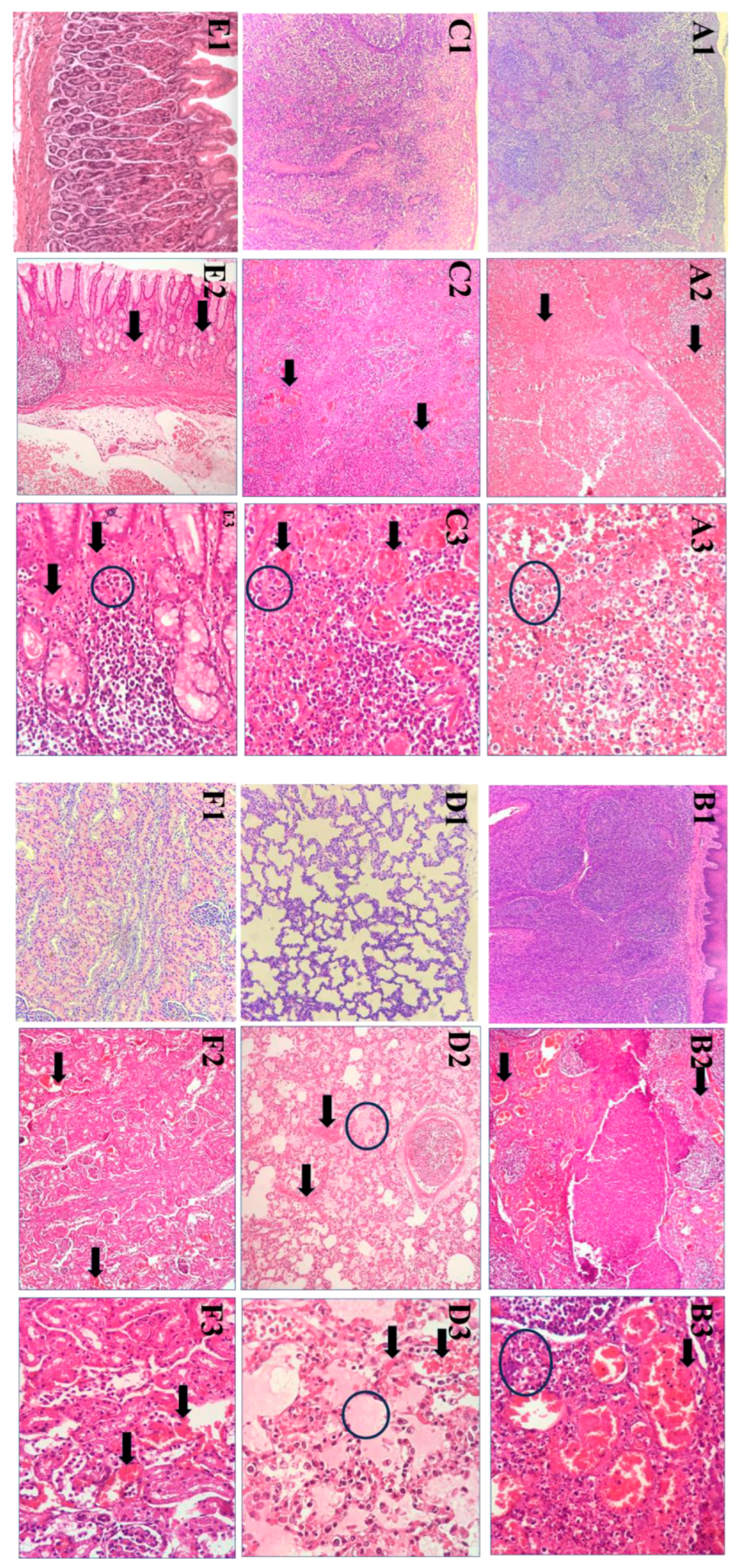
3.4. Histopathological Lesions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dixon, L.K.; Chapman, D.A.; Netherton, C.L.; Upton, C. African swine fever virus replication and genomics. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quembo, C.J.; Jori, F.; Vosloo, W.; Heath, L. Genetic characterization of African swine fever virus isolates from soft ticks at the wildlife/domestic interface in Mozambique and identification of a novel genotype. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Cardiel, I.; Ballester, M.; Solanes, D.; Nofrarias, M.; Lopez-Soria, S.; Argilaguet, J.M.; Lacasta, A.; Accensi, F.; Rodriguez, F.; Segales, J. Standardization of pathological investigations in the framework of experimental ASFV infections. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; et al. Replication and virulence in pigs of the first African swine fever virus isolated in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, E.; Huang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Huo, H.; Wang, W.; Huangfu, H.; et al. Genotype I African swine fever viruses emerged in domestic pigs in China and caused chronic infection. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhenzhong, W.; Chuanxiang, Q.; Shengqiang, G.; Jinming, L.; Yongxin, H.; Xiaoyue, Z.; Yan, L.; Naijun, H.; Xiaodong, W.; Zhiliang, W.; et al. Genetic variation and evolution of attenuated African swine fever virus strain isolated in the field: A review. Virus Res. 2022, 319, 198874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Sun, E.; Huang, L.; Ding, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shen, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, T.; et al. Highly lethal genotype I and II recombinant African swine fever viruses detected in pigs. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igolkin, A.; Mazloum, A.; Zinyakov, N.; Chernyshev, R.; Schalkwyk, A.V.; Shotin, A.; Lavrentiev, I.; Gruzdev, K.; Chvala, I. Detection of the first recombinant African swine fever virus (genotypes I and II) in domestic pigs in Russia. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, V.P.; Jeong, D.G.; Yoon, S.W.; Kwon, H.M.; Trinh, T.B.N.; Nguyen, T.L.; Bui, T.T.N.; Oh, J.; Kim, J.B.; Cheong, K.M.; et al. Outbreak of African Swine Fever, Vietnam, 2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1433–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambagala, A.; Goonewardene, K.; Kanoa, I.E.; Than, T.T.; Nguyen, V.T.; Lai, T.N.H.; Nguyen, T.L.; Erdelyan, C.N.G.; Robert, E.; Tailor, N.; et al. Characterization of an African Swine Fever Virus Field Isolate from Vietnam with Deletions in the Left Variable Multigene Family Region. Viruses 2024, 16, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, V.P.; Nguyen, V.T.; Le, T.B.; Mai, N.T.A.; Nguyen, V.D.; Than, T.T.; Lai, T.N.H.; Cho, K.H.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, Y.H.; et al. Detection of Recombinant African Swine Fever Virus Strains of p72 Genotypes I and II in Domestic Pigs, Vietnam, 2023. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, N.V.; Duc, N.V.; Ngoc, N.T.; Dang, V.X.; Tiep, T.N.; Nguyen, V.D.; Than, T.T.; Maydaniuk, D.; Goonewardene, K.; Ambagala, A.; et al. Genotype II Live-Attenuated ASFV Vaccine Strains Unable to Completely Protect Pigs against the Emerging Recombinant ASFV Genotype I/II Strain in Vietnam. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmquist, W.A.; Hay, D. Hemadsorption and cytopathic effect produced by African Swine Fever virus in swine bone marrow and buffy coat cultures. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1960, 21, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.S.; Bui, V.N.; Dao, D.T.; Bui, N.A.; Le, T.D.; Kieu, M.A.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Tran, L.H.; Roh, J.H.; So, K.M.; et al. Pathogenicity of an African swine fever virus strain isolated in Vietnam and alternative diagnostic specimens for early detection of viral infection. Porcine Health Manag. 2021, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.H.; Nguyen, V.T.; Le, P.N.; Mai, N.T.A.; Dong, V.H.; Bui, T.A.D.; Nguyen, T.L.; Ambagala, A.; Le, V.P. Pathological Characteristics of Domestic Pigs Orally Infected with the Virus Strain Causing the First Reported African Swine Fever Outbreaks in Vietnam. Pathogens 2023, 12, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Cho, K.H.; Mai, N.T.A.; Park, J.Y.; Trinh, T.B.N.; Jang, M.K.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Vu, X.D.; Nguyen, T.L.; Nguyen, V.D.; et al. Multiple variants of African swine fever virus circulating in Vietnam. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Vu, T.T.H.; Yeom, M.; Nguyen, V.D.; Than, T.T.; Nguyen, V.T.; Jeong, D.G.; Ambagala, A.; Le, V.P.; Song, D. Molecular characterization of emerging recombinant African swine fever virus of genotype I and II in Vietnam, 2023. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2404156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, X.H.; Le, T.T.P.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Do, T.T.; Nguyen, V.D.; Gay, C.G.; Borca, M.V.; Gladue, D.P. African swine fever virus vaccine candidate ASFV-G-DeltaI177L efficiently protects European and native pig breeds against circulating Vietnamese field strain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e497–e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, D.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Cao, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Cheng, T.; Ren, W.; Xu, F.; et al. In Vivo Study of Inoculation Approaches and Pathogenicity in African Swine Fever. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.H.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, D.Y.; Jang, M.K.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.; Kim, E.M.; Park, J.H.; Suh, T.Y.; Choi, J.G.; et al. Pathogenicity and Pathological Characteristics of African Swine Fever Virus Strains from Pig Farms in South Korea from 2022 to January 2023. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, L.; Bautista, M.J.; Gomez-Villamandos, J.C.; Martin de las Mulas, J.; Chacon, M.d.L.F.; Wilkinson, P.J.; Sierra, M.A. Development of microscopic lesions in splenic cords of pigs infected with African swine fever virus. Vet. Res. 1997, 28, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Salguero, F.J.; Sanchez-Cordon, P.J.; Nunez, A.; Fernandez de Marco, M.; Gomez-Villamandos, J.C. Proinflammatory cytokines induce lymphocyte apoptosis in acute African swine fever infection. J. Comp. Pathol. 2005, 132, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Masujin, K.; Kameyama, K.I.; Yamazoe, R.; Kubo, T.; Iwata, K.; Tamura, A.; Hibi, H.; Shiratori, T.; Koizumi, S.; et al. Experimental infection of pigs with different doses of the African swine fever virus Armenia 07 strain by intramuscular injection and direct contact. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 82, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzati, U.Z.; Inanaga, M.; Hoa, N.T.; Nueangphuet, P.; Myint, O.; Truong, Q.L.; Lan, N.T.; Norimine, J.; Hirai, T.; Yamaguchi, R. Pathological investigation and viral antigen distribution of emerging African swine fever in Vietnam. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 2039–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinat, C.; Reis, A.L.; Netherton, C.L.; Goatley, L.; Pfeiffer, D.U.; Dixon, L. Dynamics of African swine fever virus shedding and excretion in domestic pigs infected by intramuscular inoculation and contact transmission. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, C.D.; Bold, D.; Trujillo, J.D.; Meekins, D.A.; Keating, C.; Cool, K.; Kwon, T.; Madden, D.W.; Artiaga, B.L.; Balaraman, V.; et al. Experimental Infection of Domestic Pigs with African Swine Fever Virus Isolated in 2019 in Mongolia. Viruses 2022, 14, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Hong, S.-K.; Kim, D.-Y.; Sohn, H.-J.; Yoo, D.-S.; Kang, H.-E.; Kim, Y.-H. Disease Course of Korean African Swine Fever Virus in Domestic Pigs Exposed Intraorally, Intranasally, Intramuscularly, and by Direct Contact with Infected Pigs. Viruses 2024, 16, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, C.; Soler, A.; Nieto, R.; Cano, C.; Pelayo, V.; Sanchez, M.A.; Pridotkas, G.; Fernandez-Pinero, J.; Briones, V.; Arias, M. Experimental Infection of Domestic Pigs with African Swine Fever Virus Lithuania 2014 Genotype II Field Isolate. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Vizcaino, J.M.; Mur, L.; Gomez-Villamandos, J.C.; Carrasco, L. An update on the epidemiology and pathology of African swine fever. J. Comp. Pathol. 2015, 152, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietschmann, J.; Guinat, C.; Beer, M.; Pronin, V.; Tauscher, K.; Petrov, A.; Keil, G.; Blome, S. Course and transmission characteristics of oral low-dose infection of domestic pigs and European wild boar with a Caucasian African swine fever virus isolate. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhao, D.; He, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Shan, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. A seven-gene-deleted African swine fever virus is safe and effective as a live attenuated vaccine in pigs. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, V.; Holinka, L.G.; Krug, P.W.; Gladue, D.P.; Carlson, J.; Sanford, B.; Alfano, M.; Kramer, E.; Lu, Z.; Arzt, J.; et al. African Swine Fever Virus Georgia 2007 with a Deletion of Virulence-Associated Gene 9GL (B119L), when Administered at Low Doses, Leads to Virus Attenuation in Swine and Induces an Effective Protection against Homologous Challenge. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8556–8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group | Pig No. | Date of Onset of Clinical Signs in Pigs After ASFV Infection | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fever | Depression | Anorexia | Diarrhea | Recumbency | Dead | Onset of Viremia (Ct Value) | ||
| Group 3 (104 HAD50) | 5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 3 (21.36) |
| 6 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 (18.41) | ||
| 7 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 3 (18.95) | ||
| 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 3 (21.15) | ||
| Group 2 (103 HAD50) | 9 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 3 (23.67) | |
| 10 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 3 (18.46) | ||
| 11 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 3 (33.96) | |
| 12 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 3 (29.38) | |
| Group 1 (102 HAD50) | 13 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 3 (30.4) | |
| 14 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 3 (33.18) | ||
| 15 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 6 (18.36) | |
| 16 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 6 (15.34) | ||
| Dpi | Viral Load (Ct Value) of the ASFV in Oral Fluids | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control Group | Group 3 (104 HAD50) | Group 2 (103 HAD50) | Group 1 (102 HAD50) | |
| 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 1 | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | 35.59 | - | - |
| 3 | - | 39.74 | - | - |
| 4 | - | NS | 37.41 | - |
| 5 | - | NS | 33.84 | 37.4 |
| Gross Lesions | Group 3 (104 HAD50) | Group 2 (103 HAD50) | Group 1 (102 HAD50) | Total Frequency | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |||
| Lymph nodes | Enlargement | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 12/12 (100%) |
| Hemorrhage | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 12/12 (100%) | |
| Spleen | Enlargement | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 12/12 (100%) |
| Congestion | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 12/12 (100%) | |
| Tonsils | Erythema | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 12/12 (100%) |
| Lung | Pneumonia | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | 11/12 (92%) |
| Kidneys | Hemorrhage | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | 11/12 (92%) |
| Stomach | Hyperemia | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 11/12 (92%) |
| Intestine | Hemorrhage | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | 7/12 (58%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, V.D.; Nguyen, T.V.H.; Vu, N.D.; Than, T.T.; Tran, T.C.G.; Vu, T.T.H.; Nguyen, T.L.; Kim, Y.H.; Ambagala, A.; Le, V.P. Pathological Characteristics of the Emerging Recombinant African Swine Fever Virus Genotypes I and II in Vietnam. Pathogens 2025, 14, 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090875
Nguyen VD, Nguyen TVH, Vu ND, Than TT, Tran TCG, Vu TTH, Nguyen TL, Kim YH, Ambagala A, Le VP. Pathological Characteristics of the Emerging Recombinant African Swine Fever Virus Genotypes I and II in Vietnam. Pathogens. 2025; 14(9):875. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090875
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Viet Dung, The Viet Hoang Nguyen, Ngoc Duong Vu, Thi Tam Than, Thi Chau Giang Tran, Thi Thu Hang Vu, Thi Lan Nguyen, Yeon Hee Kim, Aruna Ambagala, and Van Phan Le. 2025. "Pathological Characteristics of the Emerging Recombinant African Swine Fever Virus Genotypes I and II in Vietnam" Pathogens 14, no. 9: 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090875
APA StyleNguyen, V. D., Nguyen, T. V. H., Vu, N. D., Than, T. T., Tran, T. C. G., Vu, T. T. H., Nguyen, T. L., Kim, Y. H., Ambagala, A., & Le, V. P. (2025). Pathological Characteristics of the Emerging Recombinant African Swine Fever Virus Genotypes I and II in Vietnam. Pathogens, 14(9), 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090875







