Encapsulation of Disease-Causing and Commensal Mitis Group Non-Pneumococcal Streptococci
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Organisms
2.2. Electron Microscopy
2.3. Research and Publication Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Molecular and Genetic Characterization
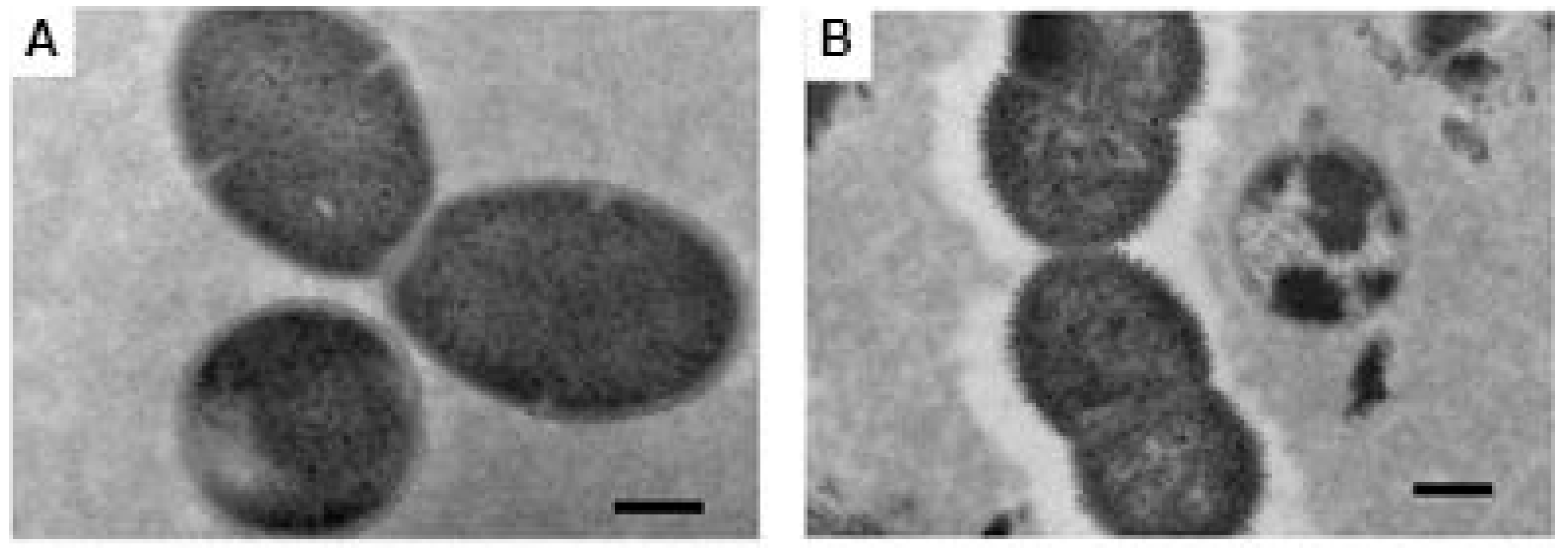
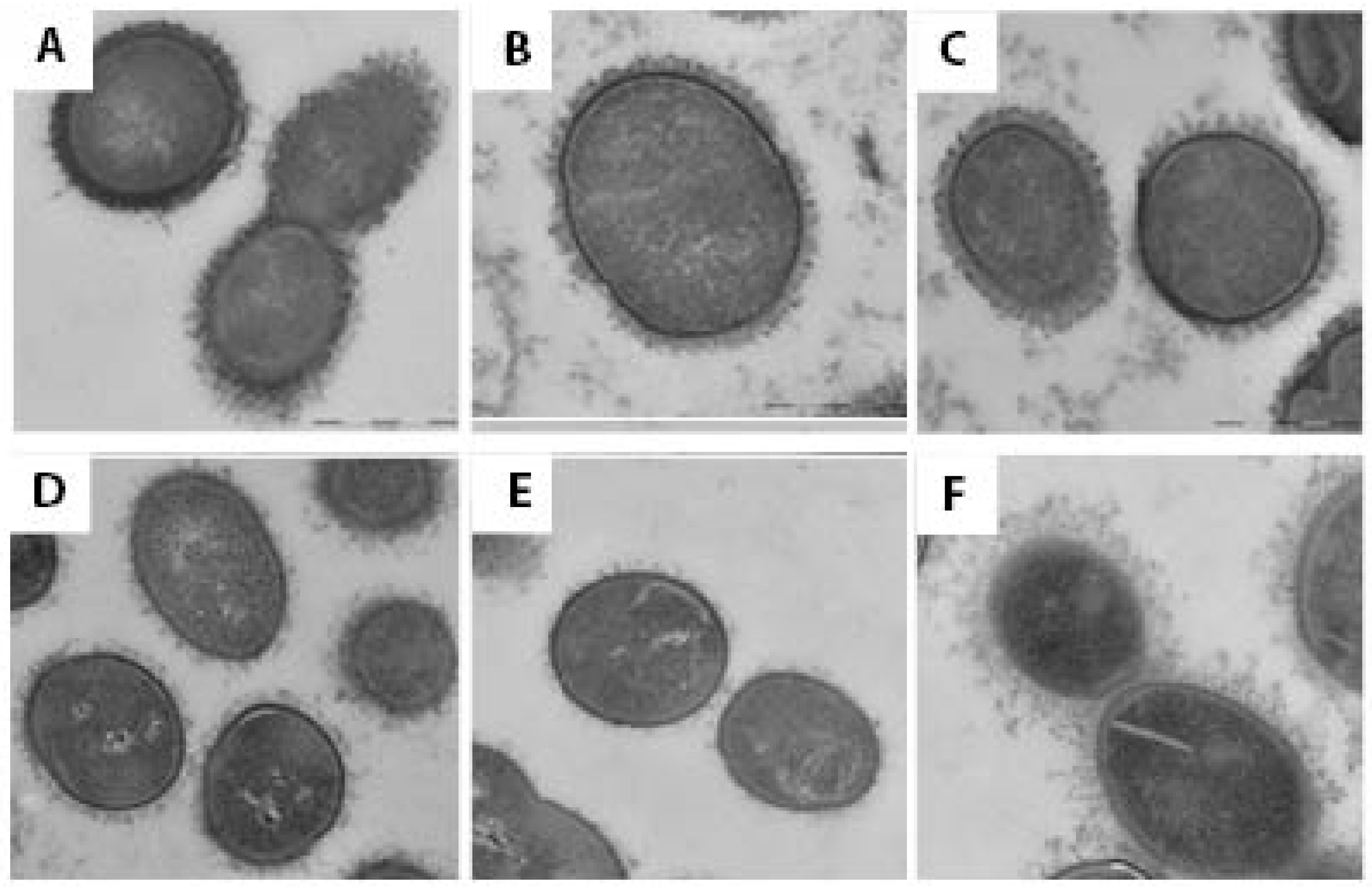
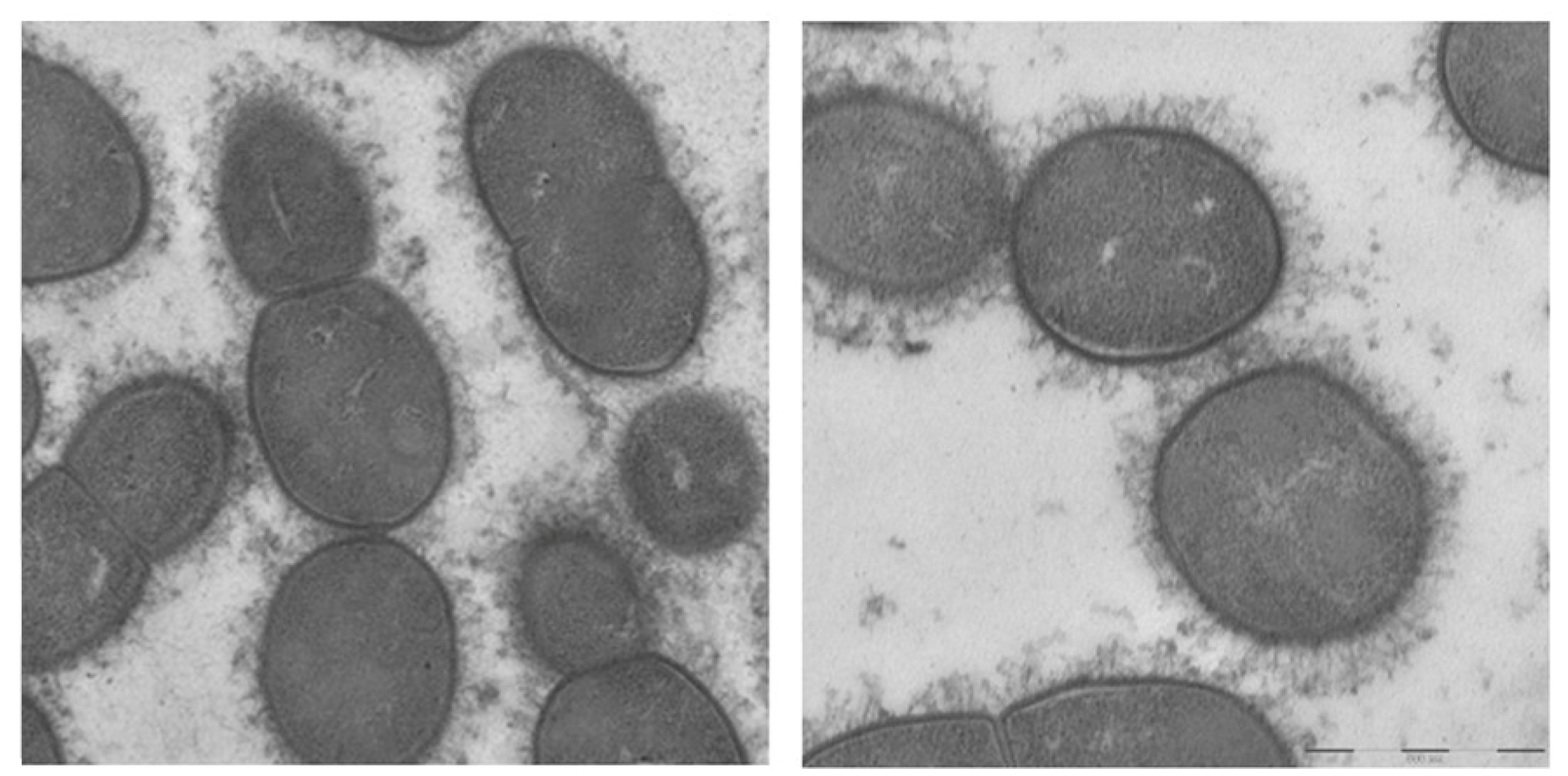
3.2. Electron Microscopy
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kilian, M.; Tettelin, H. Identification of Virulence-Associated Properties by Comparative Genome Analysis of Streptococcus pneumoniae, S. pseudopneumoniae, S. mitis, Three S. oralis Subspecies, and S. infantis. mBio 2019, 10, e01985-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffron, R. Pneumonia with Special Reference to Pneumococcus Lobar Pneumonia; The Commonwealth Fund: New York, NY, USA, 1939. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, D.A.; Musher, D.M.; Jacobson, J.W.; Verhoef, J. A brief history of the pneumococcus in biomedical research: A panoply of scientific discovery. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1993, 17, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denapaite, D.; Bruckner, R.; Nuhn, M.; Reichmann, P.; Henrich, B.; Maurer, P.; Schahle, Y.; Selbmann, P.; Zimmermann, W.; Wambutt, R.; et al. The genome of Streptococcus mitis B6—What is a commensal? PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J. Streptococcus mitis: Walking the line between commensalism and pathogenesis. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2011, 26, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.Y.; Kamana, M.; Rolston, K.V. Viridans streptococci isolated by culture from blood of cancer patients: Clinical and microbiologic analysis of 50 cases. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochud, P.Y.; Calandra, T.; Francioli, P. Bacteremia due to viridans streptococci in neutropenic patients: A review. Am. J. Med. 1994, 97, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelburne, S.A.; Sahasrabhojane, P.; Saldana, M.; Yao, H.; Su, X.; Horstmann, N.; Thompson, E.; Flores, A.R. Streptococcus mitis strains causing severe clinical disease in cancer patients. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, M.; Patel, N.R.; Elshaboury, R.; Kubiak, D.W.; Hammond, S.P. Risk of Infective Endocarditis in Streptococcus mitis Bloodstream Infections Among Patients with Neutropenia from Hematologic Malignancies. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, ofae063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musher, D.M.; Jesudasen, S.S.; Barwatt, J.W.; Cohen, D.N.; Moss, B.J.; Rodriguez-Barradas, M.C. Normal Respiratory Flora as a Cause of Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukke, H.V.; Kalluru, R.S.; Repnik, U.; Gerlini, A.; Jose, R.J.; Periselneris, J.; Marshall, H.; Griffiths, G.; Oggioni, M.R.; Brown, J.S.; et al. Protective role of the capsule and impact of serotype 4 switching on Streptococcus mitis. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 3790–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov Sorensen, U.B.; Yao, K.; Yang, Y.; Tettelin, H.; Kilian, M. Capsular Polysaccharide Expression in Commensal Streptococcus Species: Genetic and Antigenic Similarities to Streptococcus pneumoniae. mBio 2016, 7, e01844-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessa, F.C.; Milucky, J.; Rouphael, N.G.; Bennett, N.M.; Talbot, H.K.; Harrison, L.H.; Farley, M.M.; Walston, J.; Pimenta, F.; Gertz, R.E.; et al. Streptococcus mitis Expressing Pneumococcal Serotype 1 Capsule. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimenta, F.; Gertz, R.E., Jr.; Park, S.H.; Kim, E.; Moura, I.; Milucky, J.; Rouphael, N.; Farley, M.M.; Harrison, L.H.; Bennett, N.M.; et al. Streptococcus infantis, Streptococcus mitis, and Streptococcus oralis strains with highly similar cps5 loci and antigenic relatedness to serotype 5 pneumococci. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gertz, R.E., Jr.; Pimenta, F.C.; Chochua, S.; Larson, S.; Venero, A.K.; Bigogo, G.; Milucky, J.; Carvalho, M.D.G.; Beall, B. Nonpneumococcal strains recently recovered from carriage specimens and expressing capsular serotypes highly related or Identical to pneumococcal serotypes 2, 4, 9A, 13, and 23A. mBio 2021, 12, e01037-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.; Morita, M.; Nariai, A.; Kasahara, K.; Kakutani, A.; Ogawa, M.; Ohnishi, M.; Oishi, K. Invasive Streptococcus oralis expressing serotype 3 pneumococcal capsule, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 1720–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukke, H.V.; Hegna, I.K.; Petersen, F.C. Identification of a functional capsule locus in Streptococcus mitis. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2012, 27, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, H.; Aguayo, S.; Kilian, M.; Petersen, F.; Bozec, L.; Brown, J. In Vivo Relationship between the Nano-Biomechanical Properties of Streptococcal Polysaccharide Capsules and Virulence Phenotype. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganaie, F.A.; Beall, B.W.; Yu, J.; van der Linden, M.; McGee, L.; Satzke, C.; Manna, S.; Lo, S.W.; Bentley, S.D.; Ravenscroft, N.; et al. Update on the evolving landscape of pneumococcal capsule types: New discoveries and way forward. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2025, 38, e0017524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerschmidt, S.; Rohde, M. Electron Microscopy to Study the Fine Structure of the Pneumococcal Cell. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1968, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, B.J.; Gertz, R.E., Jr.; Gladstone, R.A.; Walker, H.; Sherwood, L.K.; Jackson, D.; Li, Z.; Law, C.; Hawkins, P.A.; Chochua, S.; et al. Strain features and distributions in pneumococci from children with invasive disease before and after 13-valent conjugate vaccine implementation in the USA. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 60.e9–60.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, C.L.; Kapatai, G.; Broughton, K.; Schaefer, U.; Hannah, M.; Litt, D.J.; Fry, N.K. Clinical streptococcal isolates, distinct from Streptococcus pneumoniae, but containing the beta-glucosyltransferase tts gene and expressing serotype 37 capsular polysaccharide. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.Y.; Tipton, K.A.; Farokhyfar, M.; Burd, E.M.; Weiss, D.S.; Rather, P.N. A high-frequency phenotypic switch links bacterial virulence and environmental survival in Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, B.M.; Musher, D.M. The history of pneumococcal disease. In Pneumococcal Vaccines: The Impact of Conjugate Vaccine; Siber, G.R., Klugman, K.P., Makela, P., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho Mda, G.; Pimenta, F.C.; Moura, I.; Roundtree, A.; Gertz, R.E., Jr.; Li, Z.; Jagero, G.; Bigogo, G.; Junghae, M.; Conklin, L.; et al. Non-pneumococcal mitis-group streptococci confound detection of pneumococcal capsular serotype-specific loci in upper respiratory tract. PeerJ 2013, 1, e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, B.M.; Converse, G.M., 3rd; Dillon, H.C., Jr. Epidemiologic studies of Streptococcus pneumoniae in infants: Acquisition, carriage, and infection during the first 24 months of life. J. Infect. Dis. 1980, 142, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musher, D.M.; Groover, J.E.; Reichler, M.R.; Reido, F.X.; Schwartz, B.; Watson, D.A.; Baughn, R.E.; Breiman, R. Emergence of antibody to capsular polysaaccharides of Streptococcus pneumoniae during outbreaks of pneumonia: Association with nasopharyngeal colonization. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 24, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhar, S.; Khan, R.; Schenck, K.; Petersen, F.C. Intranasal Immunization with the Commensal Streptococcus mitis Confers Protective Immunity against Pneumococcal Lung Infection. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02235-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, C.; Munro, N.C.; Jeffery, P.K.; Mitchell, T.J.; Andrew, P.W.; Boulnois, G.J.; Guerreiro, D.; Rohde, J.A.; Todd, H.C.; Cole, P.J.; et al. Pneumolysin induces the salient histologic features of pneumococcal infection in the rat lung in vivo. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1991, 5, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.E.; Lock, R.A.; Peeters, C.C.; Poolman, J.T.; Andrew, P.W.; Mitchell, T.J.; Hansman, D.; Paton, J.C. Immunization of mice with pneumolysin toxoid confers a significant degree of protection against at least nine serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 5683–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalizang’oma, A.; Richard, D.; Kwambana-Adams, B.; Coelho, J.; Broughton, K.; Pichon, B.; Hopkins, K.L.; Chalker, V.; Beleza, S.; Bentley, S.D.; et al. Population genomics of Streptococcus mitis in UK and Ireland bloodstream infection and infective endocarditis cases. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musher, D.M.; Alexandraki, I.; Graviss, E.A.; Yanbeiy, N.; Eid, A.; Inderias, L.A.; Phan, H.M.; Solomon, E. Bacteremic and nonbacteremic pneumococcal pneumonia. A prospective study. Medicine 2000, 79, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.J.; Forte, S.; Thompson, C.M.; Anderson, P.W.; Malley, R. Protection against Pneumococcal colonization and fatal pneumonia by a trivalent conjugate of a fusion protein with the cell wall polysaccharide. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2076–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Musher, D.M.; Müsken, M.; Hicks, M.J.; McGee, L.; Beall, B. Encapsulation of Disease-Causing and Commensal Mitis Group Non-Pneumococcal Streptococci. Pathogens 2025, 14, 876. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090876
Musher DM, Müsken M, Hicks MJ, McGee L, Beall B. Encapsulation of Disease-Causing and Commensal Mitis Group Non-Pneumococcal Streptococci. Pathogens. 2025; 14(9):876. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090876
Chicago/Turabian StyleMusher, Daniel M., Mathias Müsken, M. John Hicks, Lesley McGee, and Bernard Beall. 2025. "Encapsulation of Disease-Causing and Commensal Mitis Group Non-Pneumococcal Streptococci" Pathogens 14, no. 9: 876. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090876
APA StyleMusher, D. M., Müsken, M., Hicks, M. J., McGee, L., & Beall, B. (2025). Encapsulation of Disease-Causing and Commensal Mitis Group Non-Pneumococcal Streptococci. Pathogens, 14(9), 876. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090876




