The Role of Anisakis sp. in α-Gal Sensitization: Implications for Parasitic-Induced Meat Allergy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protein Crude Extract Preparation
2.2. Serum Samples
2.3. Detection of α-Gal Epitopes in Anisakis sp. Crude Protein Extract via Indirect ELISA
2.4. Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Measurement of Anti-Anisakis sp.-Specific Antibody Levels by ELISA
2.7. Anti-Alpha Gal-Specific IgM, IgG, IgG4, IgA, and IgE Antibodies
2.8. Inhibition ELISA
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
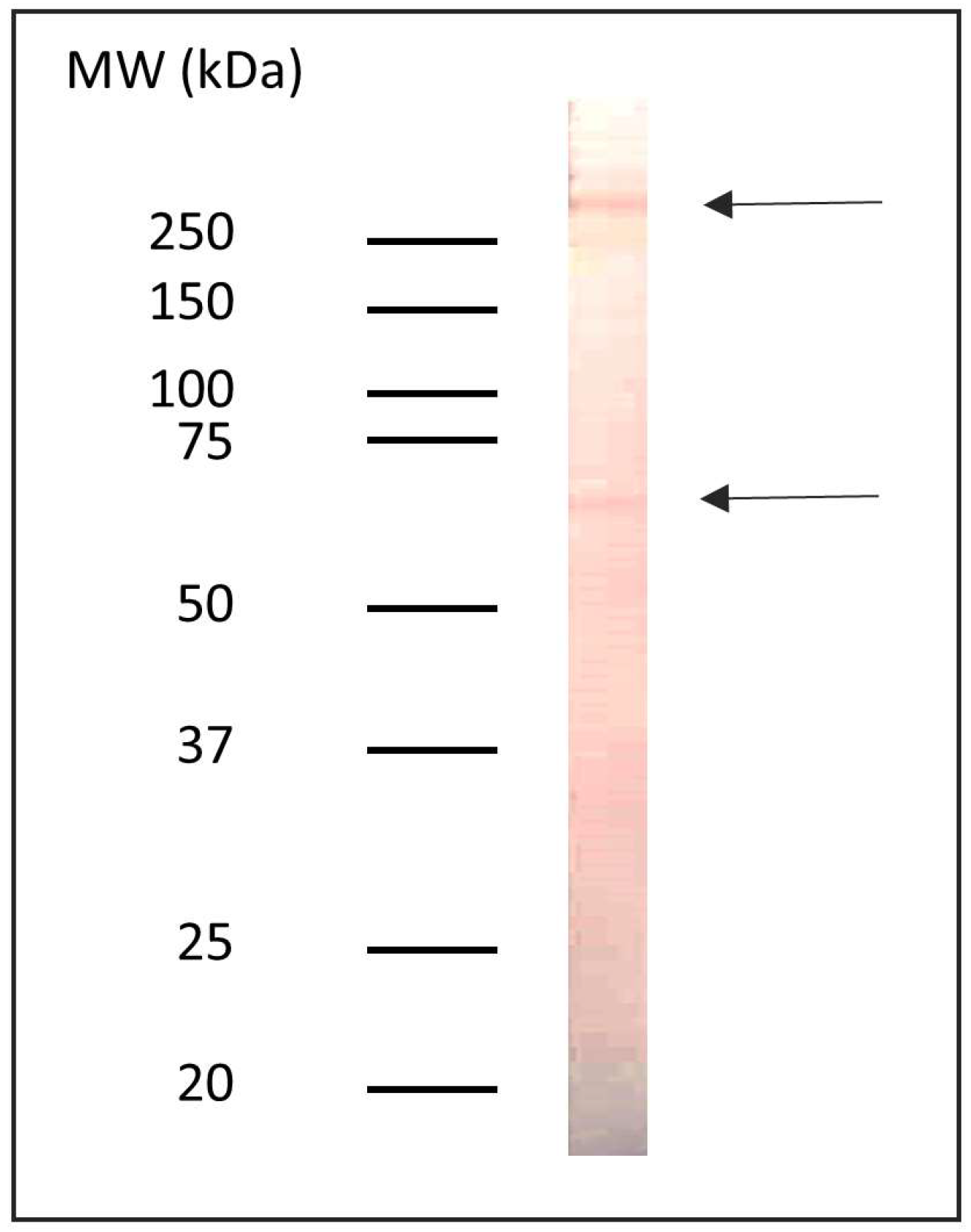
3.1. Detection of Proteins with α-Gal Epitopes in the Non-Delipidated Extract of Anisakis sp.
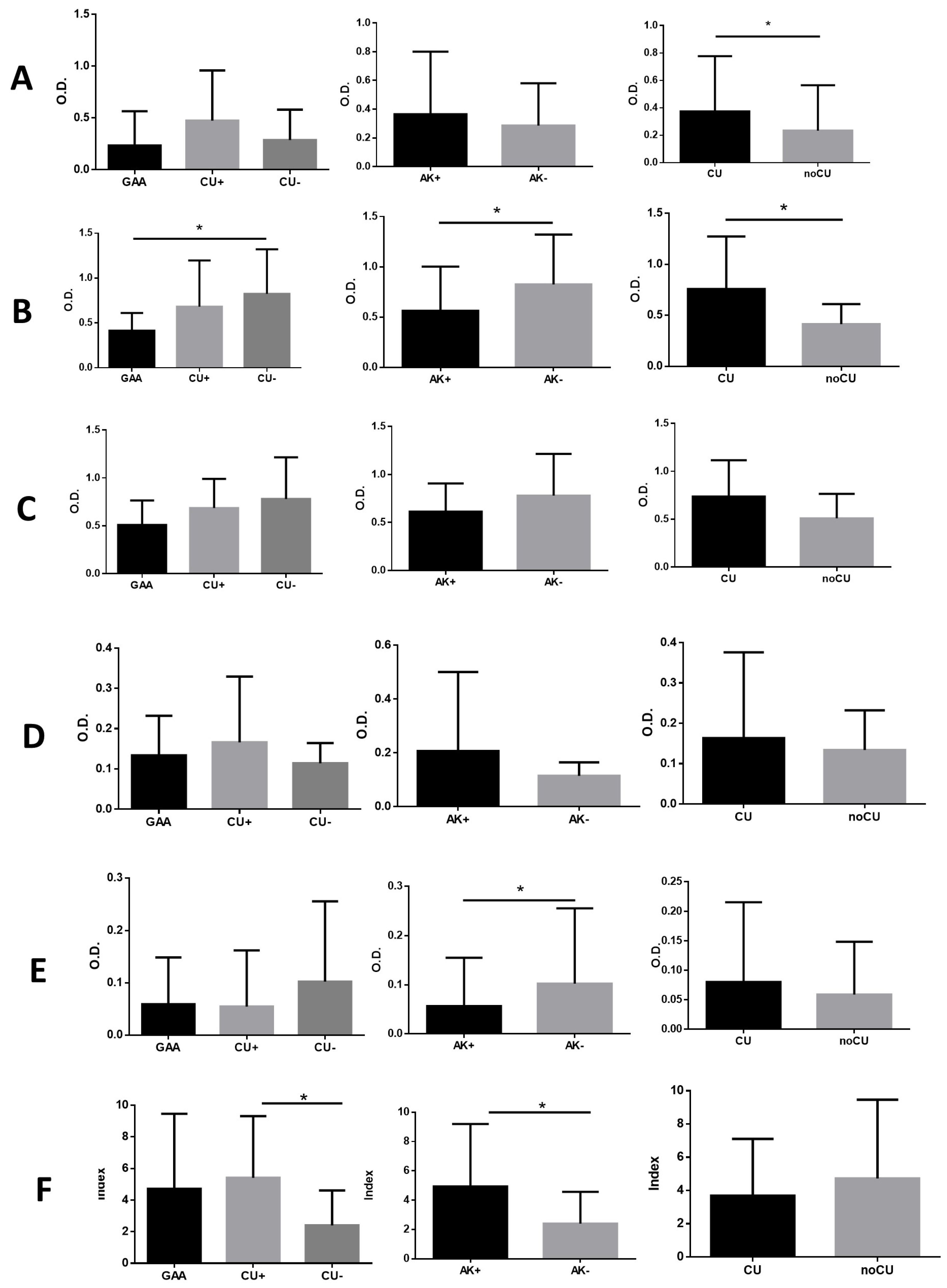
3.2. Anti-Anisakis sp. Specific Antibodies
3.3. Anti-α-Gal Specific Antibodies
3.4. Detection of IgG, IgE, and IgG4 Antibodies Against Proteins Present in Mammalian Muscle Tissue
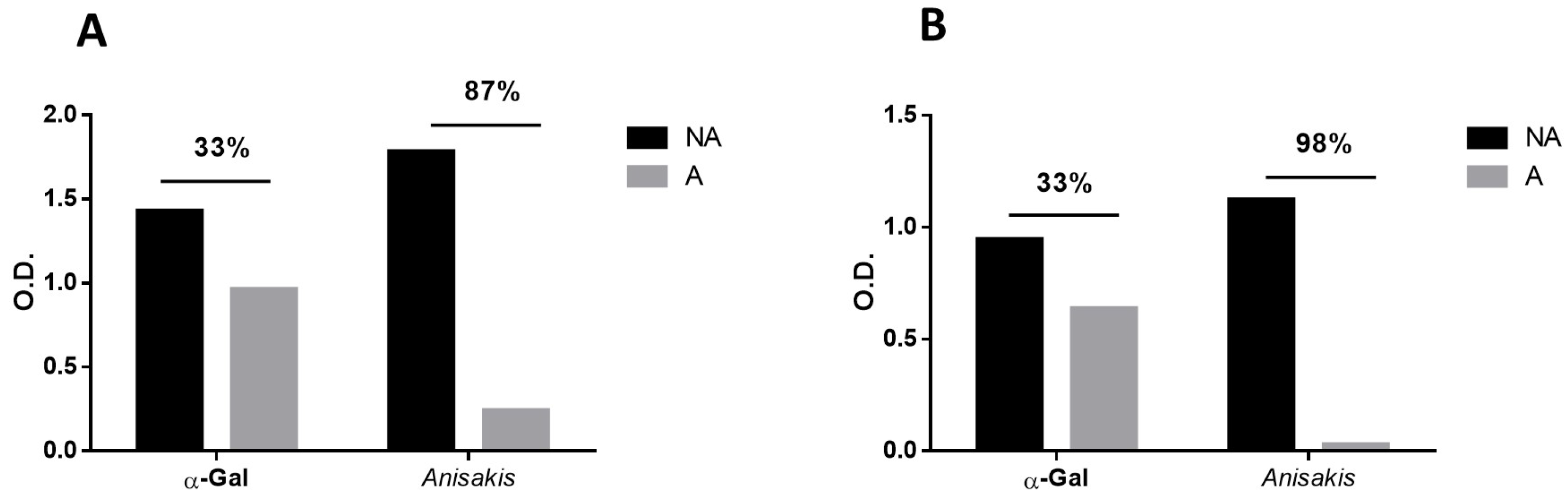
3.5. Inhibition ELISA for the Detection of Anti-Anisakis sp. and Anti-α-Gal Antibodies in Serum Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macher, B.A.; Galili, U. The Galalpha1,3Galbeta1,4GlcNAc-R (alpha-Gal) epitope: A carbohydrate of unique evolution and clinical relevance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1780, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, G.; Qi, P.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of alpha-Gal epitope, anti-Gal antibody, alpha1,3 galactosyltransferase and its clinical exploitation (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galili, U. Biosynthesis of alpha-Gal Epitopes (Galalpha1-3Galbeta1-4GlcNAc-R) and Their Unique Potential in Future alpha-Gal Therapies. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 746883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galili, U. Significance of the evolutionary alpha1,3-galactosyltransferase (GGTA1) gene inactivation in preventing extinction of apes and old world monkeys. J. Mol. Evol. 2015, 80, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commins, S.P.; James, H.R.; Kelly, L.A.; Pochan, S.L.; Workman, L.J.; Perzanowski, M.S.; Kocan, K.M.; Fahy, J.V.; Nganga, L.W.; Ronmark, E.; et al. The relevance of tick bites to the production of IgE antibodies to the mammalian oligosaccharide galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 1286–1293.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Hodzic, A.; Roman-Carrasco, P.; Mateos-Hernandez, L.; Duscher, G.G.; Sinha, D.K.; Hemmer, W.; Swoboda, I.; Estrada-Pena, A.; de la Fuente, J. Environmental and Molecular Drivers of the alpha-Gal Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.; Iweala, O.I. ‘Doc, will I ever eat steak again?’: Diagnosis and management of alpha-gal syndrome. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2020, 32, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.R.; Karim, S. Tick Saliva and the Alpha-Gal Syndrome: Finding a Needle in a Haystack. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 680264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perusko, M.; Grundstrom, J.; Eldh, M.; Hamsten, C.; Apostolovic, D.; van Hage, M. The alpha-Gal epitope—The cause of a global allergic disease. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1335911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perusko, M.; Grundstrom, J.; Eldh, M.; Reinhardt, A.; Fuhrmann, V.; Duzakin, M.; Hamsten, C.; Starkhammar, M.; Apostolovic, D.; van Hage, M. Allergenic potency of various foods of mammalian origin in patients with alpha-Gal syndrome. Allergy 2025, 80, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.R.; Choudhary, S.K.; Vorobiov, J.; Commins, S.P.; Karim, S. Tick bite-induced alpha-gal syndrome and immunologic responses in an alpha-gal deficient murine model. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1336883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalcaci, M. Mysterious Allergy Caused by Tick Bite: Alpha-Gal Syndrome. Turk. Parazitol. Derg. 2024, 48, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.N.; Franco, P.F.; Rodrigues, H.; Santos, L.C.B.; McKay, C.S.; Sanhueza, C.A.; Brito, C.R.N.; Azevedo, M.A.; Venuto, A.P.; Cowan, P.J.; et al. Amblyomma sculptum tick saliva: Alpha-Gal identification, antibody response and possible association with red meat allergy in Brazil. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Quintela, A.; Dam Laursen, A.S.; Vidal, C.; Skaaby, T.; Gude, F.; Linneberg, A. IgE antibodies to alpha-gal in the general adult population: Relationship with tick bites, atopy, and cat ownership. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2014, 44, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, M.; Lobera, T.; Sebastian, A.; Portillo, A.; Oteo, J.A. IgE to alpha-Gal in Foresters and Forest Workers From La Rioja, North of Spain. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 28, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo Borrega, M.B.; Garcia, B.; Larramendi, C.H.; Azofra, J.; Gonzalez Mancebo, E.; Alvarado, M.I.; Alonso Diaz de Durana, M.D.; Nunez Orjales, R.; Dieguez, M.C.; Guilarte, M.; et al. IgE-Mediated Sensitization to Galactose-alpha-1,3- Galactose (alpha-Gal) in Urticaria and Anaphylaxis in Spain: Geographical Variations and Risk Factors. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 29, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.H.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.M.; Ock, M.; Park, M.I.; Goo, J.Y. A case of acute gastric anisakiasis provoking severe clinical problems by multiple infection. Korean J. Parasitol. 2003, 41, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Audicana, M.T.; Kennedy, M.W. Anisakis simplex: From obscure infectious worm to inducer of immune hypersensitivity. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 360–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravettoni, V.; Primavesi, L.; Piantanida, M. Anisakis simplex: Current knowledge. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 44, 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura, Y.; Muwanwella, N.; Chandran, S.; Kandel, G.; Marcon, N. Common Symptoms from an Uncommon Infection: Gastrointestinal Anisakiasis. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2016, 5176502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuizen, N.E.; Lopata, A.L. Anisakis—A food-borne parasite that triggers allergic host defences. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murangi, T.; Prakash, P.; Moreira, B.P.; Basera, W.; Botha, M.; Cunningham, S.; Facey-Thomas, H.; Halajian, A.; Joshi, L.; Ramjith, J.; et al. Ascaris lumbricoides and ticks associated with sensitization to galactose alpha1,3-galactose and elicitation of the alpha-gal syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 698–707.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodzic, A.; Mateos-Hernandez, L.; Frealle, E.; Roman-Carrasco, P.; Alberdi, P.; Pichavant, M.; Risco-Castillo, V.; Le Roux, D.; Vicogne, J.; Hemmer, W.; et al. Infection with Toxocara canis Inhibits the Production of IgE Antibodies to alpha-Gal in Humans: Towards a Conceptual Framework of the Hygiene Hypothesis? Vaccines 2020, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perteguer, M.J.; Cuellar, C. Isotype-specific immune responses in murine experimental anisakiasis. Zent. Vet. B 1998, 45, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perteguer, M.J.; Raposo, R.; Cuellar, C. In vitro study on the effect of larval excretory/secretory products and crude extracts from Anisakis simplex on blood coagulation. Int. J. Parasitol. 1996, 26, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuellar, C.; Daschner, A.; Valls, A.; de Frutos, C.; Fernandez-Figares, V.; Anadon, A.M.; Rodriguez, E.; Garate, T.; Rodero, M.; Ubeira, F.M. Ani s 1 and Ani s 7 recombinant allergens are able to differentiate distinct Anisakis simplex-associated allergic clinical disorders. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2012, 304, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Fernández, J.; Ullate, L.; Fernandez-Figares, V.; Rodero, M.; Daschner, A.; Cuellar, C. Serum IgA contributes to the comprehension of Anisakis simplex associated chronic urticaria. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 129, 111602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcarcel, A.; Montero, A.B.; Rodero, M.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, J.; Olmeda, A.S.; Valcarcel, F.; Cuellar, C. Alpha-Gal, epitope responsible for allergy to red meat, in the Mediterranean tick Hyalomma lusitanicum. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2024, 38, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daschner, A.; Cuellar, C.; Sanchez-Pastor, S.; Pascual, C.Y.; Martin-Esteban, M. Gastro-allergic anisakiasis as a consequence of simultaneous primary and secondary immune response. Parasite Immunol. 2002, 24, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, R.; Cuellar, C. Immunoglobulins anti-Anisakis simplex in patients with gastrointestinal diseases. J. Helminthol. 2002, 76, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinuki, Y.; Ishiwata, K.; Yamaji, K.; Takahashi, H.; Morita, E. Haemaphysalis longicornis tick bites are a possible cause of red meat allergy in Japan. Allergy 2016, 71, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Espinosa, P.J.; Alberdi, P.; Simo, L.; Valdes, J.J.; Mateos-Hernandez, L.; Contreras, M.; Rayo, M.V.; de la Fuente, J. Tick galactosyltransferases are involved in alpha-Gal synthesis and play a role during Anaplasma phagocytophilum infection and Ixodes scapularis tick vector development. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkestal, K.; Sibanda, E.; Thors, C.; Troye-Blomberg, M.; Mduluza, T.; Valenta, R.; Gronlund, H.; van Hage, M. Impaired allergy diagnostics among parasite-infected patients caused by IgE antibodies to the carbohydrate epitope galactose-alpha 1,3-galactose. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, K.H.; Chatterjee, D.; Caulfield, J.P.; Morris, H.R.; Dell, A. Structural mapping of the glycans from the egg glycoproteins of Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma japonicum: Identification of novel core structures and terminal sequences. Glycobiology 1997, 7, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.S.; Morris, H.R.; Dell, A.; Appleton, J.A.; Haslam, S.M. Protein glycosylation in Parelaphostrongylus tenuis—First description of the Galalpha1-3Gal sequence in a nematode. Glycobiology 2006, 16, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- van Stijn, C.M.; van den Broek, M.; Vervelde, L.; Alvarez, R.A.; Cummings, R.D.; Tefsen, B.; van Die, I. Vaccination-induced IgG response to Galalpha1-3GalNAc glycan epitopes in lambs protected against Haemonchus contortus challenge infection. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olajiga, O.M.; Maldonado-Ruiz, L.P.; Fatehi, S.; Cardenas, J.C.; Gonzalez, M.U.; Gutierrez-Silva, L.Y.; Londono-Renteria, B.; Park, Y. Association of dengue infection with anti-alpha-gal antibodies, IgM, IgG, IgG1, and IgG2. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1021016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Pacheco, I. Alpha-gal syndrome: Challenges to understanding sensitization and clinical reactions to alpha-gal. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platts-Mills, T.A.; Schuyler, A.J.; Tripathi, A.; Commins, S.P. Anaphylaxis to the carbohydrate side chain alpha-gal. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2015, 35, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Mateos-Hernandez, L.; Chmelar, J.; Villar, M.; de la Fuente, J. Salivary Prostaglandin E2: Role in Tick-Induced Allergy to Red Meat. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, J.L.; Cox, K.M.; Erickson, L.D. B Cell Responses in the Development of Mammalian Meat Allergy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joral, A.; Azketa, N.; Sanchez, P.; Velez-Del-Burgo, A.; Aranzabal-Soto, M.A.; Lizarza, S.; Martinez, J.; Postigo, I. The Quantification of IgG Specific to alpha-Gal Could Be Used as a Risk Marker for Suffering Mammalian Meat Allergy. Foods 2022, 11, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Lazaro, J.; Nunez-Orjales, R.; Gonzalez-Guzman, L.A.; Gonzalez, M.T.; Boquete, M.; Carballada, F. Galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose (alpha-gal) allergy: First pediatric case in a series of patients in Spain. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2020, 48, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iweala, O.I.; Choudhary, S.K.; Addison, C.T.; Batty, C.J.; Kapita, C.M.; Amelio, C.; Schuyler, A.J.; Deng, S.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M.; et al. Glycolipid-mediated basophil activation in alpha-gal allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tordesillas, L.; Cubells-Baeza, N.; Gomez-Casado, C.; Berin, C.; Esteban, V.; Barcik, W.; O’Mahony, L.; Ramirez, C.; Pacios, L.F.; Garrido-Arandia, M.; et al. Mechanisms underlying induction of allergic sensitization by Pru p 3. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 47, 1398–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyonouchi, S.; Abraham, V.; Orange, J.S.; Spergel, J.M.; Gober, L.; Dudek, E.; Saltzman, R.; Nichols, K.E.; Cianferoni, A. Invariant natural killer T cells from children with versus without food allergy exhibit differential responsiveness to milk-derived sphingomyelin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 102–109.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E. alpha-Gal and other recent findings that have informed our understanding of anaphylaxis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 124, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodero, M.; Romero, S.; Valcárcel, Á.; González-Fernández, J.; Olmeda, A.S.; Valcárcel, F.; Daschner, A.; Cuéllar, C. The Role of Anisakis sp. in α-Gal Sensitization: Implications for Parasitic-Induced Meat Allergy. Pathogens 2025, 14, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080789
Rodero M, Romero S, Valcárcel Á, González-Fernández J, Olmeda AS, Valcárcel F, Daschner A, Cuéllar C. The Role of Anisakis sp. in α-Gal Sensitization: Implications for Parasitic-Induced Meat Allergy. Pathogens. 2025; 14(8):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080789
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodero, Marta, Sara Romero, Ángela Valcárcel, Juan González-Fernández, A. Sonia Olmeda, Félix Valcárcel, Alvaro Daschner, and Carmen Cuéllar. 2025. "The Role of Anisakis sp. in α-Gal Sensitization: Implications for Parasitic-Induced Meat Allergy" Pathogens 14, no. 8: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080789
APA StyleRodero, M., Romero, S., Valcárcel, Á., González-Fernández, J., Olmeda, A. S., Valcárcel, F., Daschner, A., & Cuéllar, C. (2025). The Role of Anisakis sp. in α-Gal Sensitization: Implications for Parasitic-Induced Meat Allergy. Pathogens, 14(8), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080789






