Molnupiravir Inhibits Replication of Multiple Alphacoronavirus suis Strains in Feline Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2. Viruses
2.3. Compounds
2.4. Cytotoxic Effects of Compounds
2.5. Plaque Reduction Assay
2.6. Molnupiravir Treatment and Sample Collection
2.7. Virus Titration
2.8. Quantification of Intracellular FCoV 3′-UTR Expression
2.9. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA) for the Detection of Viral Antigens
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
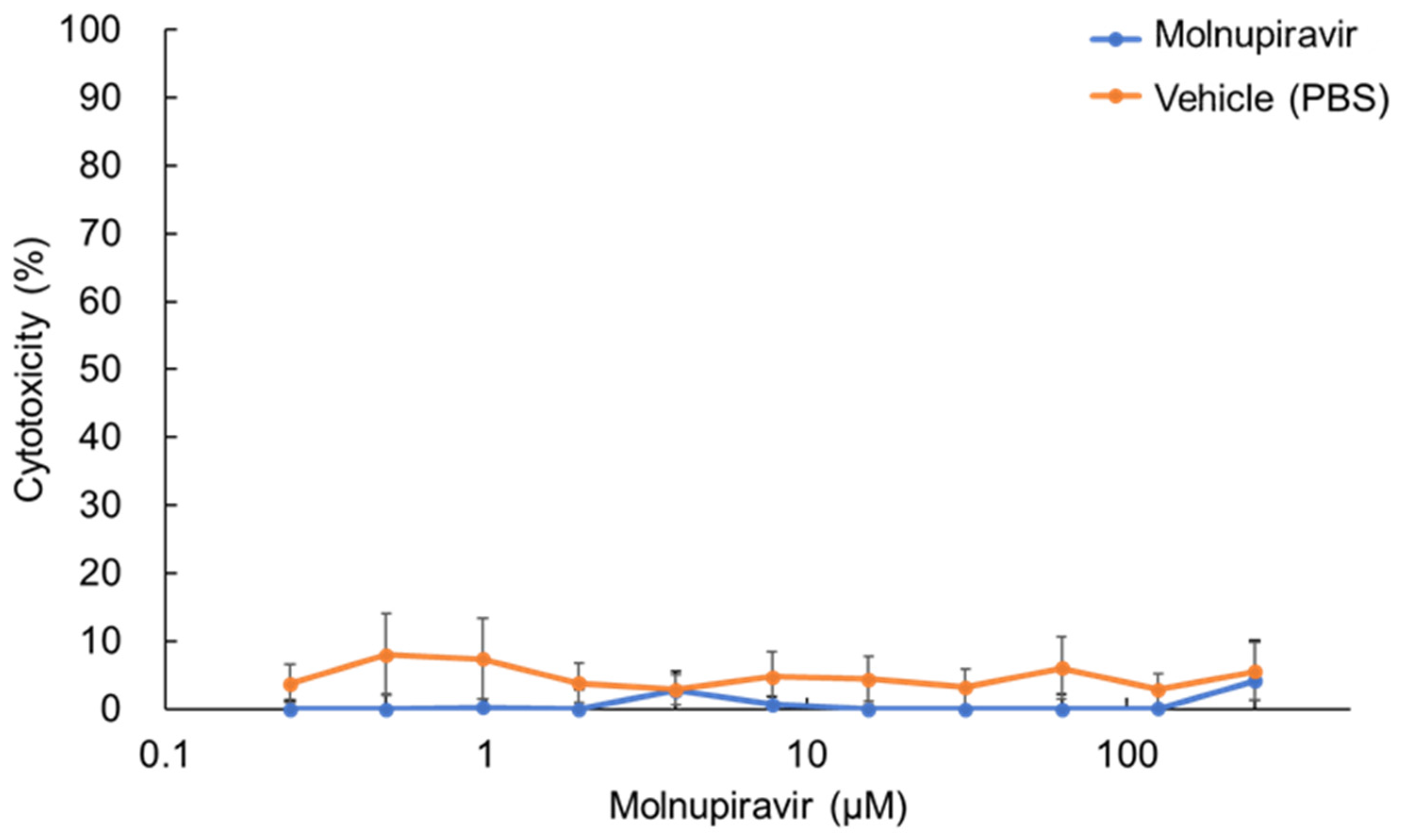
3.1. Cytotoxicity of Molnupiravir in fcwf-4 Cells
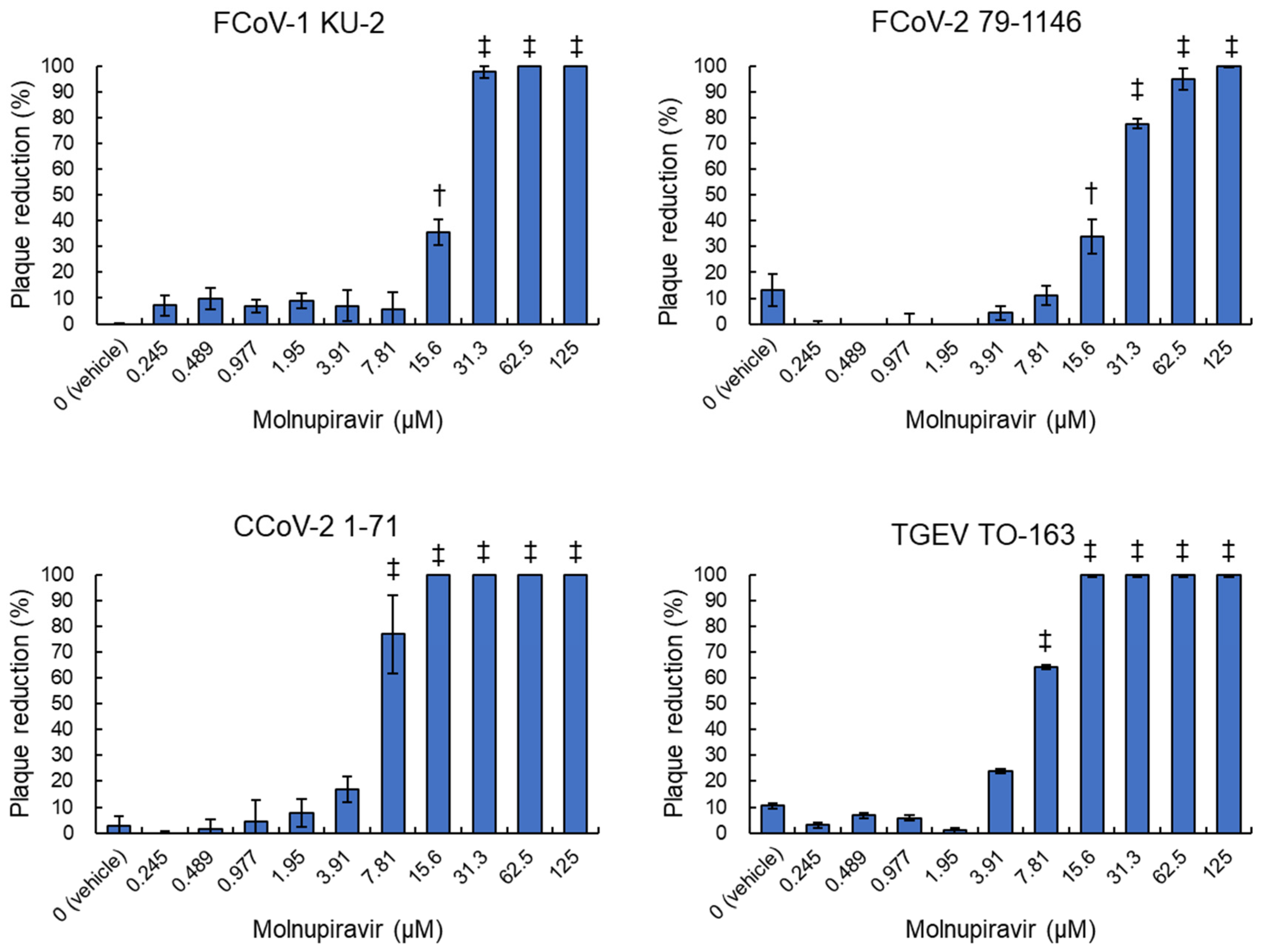
3.2. Plaque Reduction Activity of Molnupiravir Against Alphacoronavirus suis
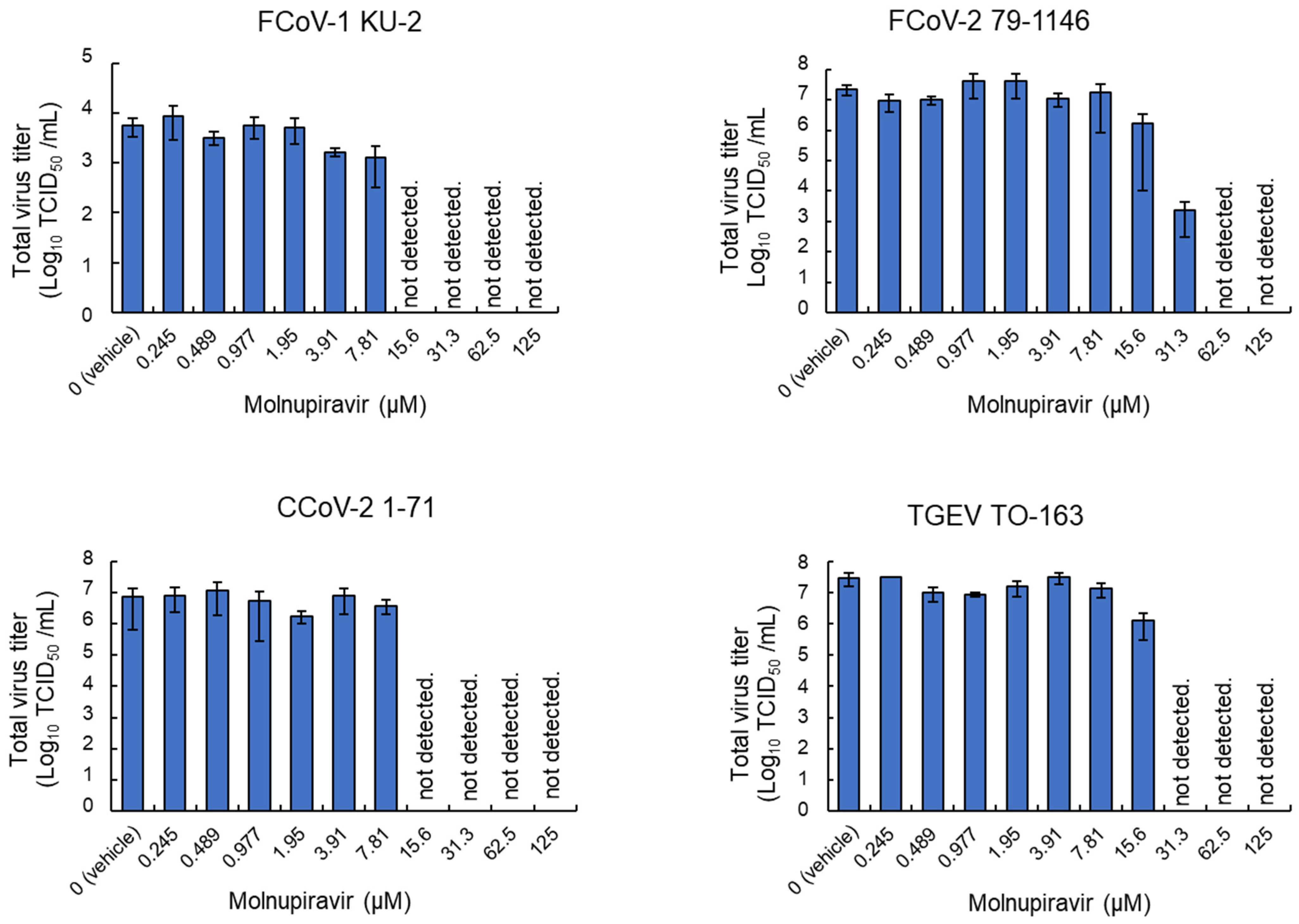
3.3. Inhibitory Effects of Molnupiravir on Viral Replication
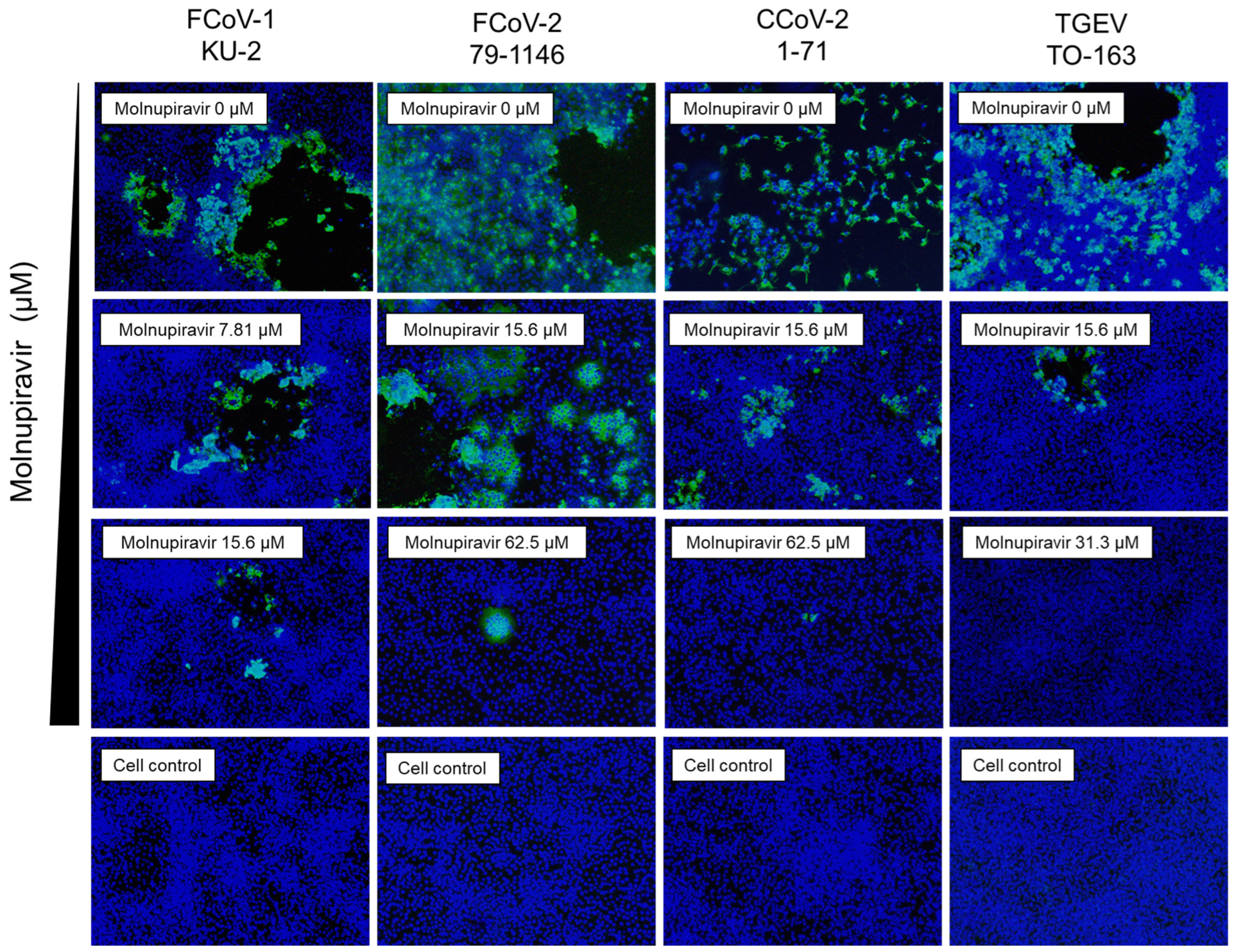
3.4. Suppression of Viral Antigen Expression by Molnupiravir
3.5. Molnupiravir Inhibits Viral Release and Genome Replication
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neuman, B.W.; Buchmeier, M.J. Supramolecular Architecture of the Coronavirus Particle. Adv. Virus Res. 2016, 96, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brant, A.C.; Tian, W.; Majerciak, V.; Yang, W.; Zheng, Z.M. SARS-CoV-2: From Its Discovery to Genome Structure, Transcription, and Replication. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Current ICTV Taxonomy Release | ICTV. Available online: https://ictv.global/taxonomy (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Jaimes, J.A.; Millet, J.K.; Stout, A.E.; André, N.M.; Whittaker, G.R. A Tale of Two Viruses: The Distinct Spike Glycoproteins of Feline Coronaviruses. Viruses 2020, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, B.; Duhamel, G.; Whittaker, G. Canine Enteric Coronaviruses: Emerging Viral Pathogens with Distinct Recombinant Spike Proteins. Viruses 2014, 6, 3363–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Allen, C.E.; Lyons, L.A. Pathogenesis of Feline Enteric Coronavirus Infection. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2008, 10, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C. An Update on Feline Infectious Peritonitis: Virology and Immunopathogenesis. Vet. J. 2014, 201, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duijvestijn, M.; Mughini-Gras, L.; Schuurman, N.; Schijf, W.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Egberink, H. Enteropathogen Infections in Canine Puppies: (Co-)Occurrence, Clinical Relevance and Risk Factors. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 195, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonavoglia, C.; Decaro, N.; Martella, V.; Elia, G.; Campolo, M.; Desario, C.; Castagnaro, M.; Tempesta, M. Canine Coronavirus Highly Pathogenic for Dogs. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, F.; Fusco, G.; Mari, V.; Occhiogrosso, L.; Miletti, G.; Brunetti, R.; Galiero, G.; Desario, C.; Cirilli, M.; Decaro, N. Circulation of Pantropic Canine Coronavirus in Autochthonous and Imported Dogs, Italy. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1991–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, H.Y. Porcine Enteric Coronaviruses: An Updated Overview of the Pathogenesis, Prevalence, and Diagnosis. Vet. Res. Commun. 2021, 45, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesheh, M.M.; Hosseini, P.; Soltani, S.; Zandi, M. An Overview on the Seven Pathogenic Human Coronaviruses. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, A.N.; Toh, T.H.; Lee, J.S.Y.; Poovorawan, Y.; Davis, P.; Azevedo, M.S.P.; Lednicky, J.A.; Saif, L.J.; Gray, G.C. Animal Alphacoronaviruses Found in Human Patients with Acute Respiratory Illness in Different Countries. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.S.; Mullis, L.B.; Pereira, O., Jr.; Saif, L.J.; Vlasova, A.; Zhang, X.; Owens, R.J.; Paulson, D.; Taylor, D.; Haynes, L.M.; et al. Human Respiratory Coronaviruses Detected in Patients with Influenza-Like Illness in Arkansas, USA. Virol. Mycol. 2014, 2014, 004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lednicky, J.A.; Tagliamonte, M.S.; White, S.K.; Blohm, G.M.; Alam, M.M.; Iovine, N.M.; Salemi, M.; Mavian, C.; Morris, J.G. Isolation of a Novel Recombinant Canine Coronavirus from a Visitor to Haiti: Further Evidence of Transmission of Coronaviruses of Zoonotic Origin to Humans. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, E1184–E1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabinger, F.; Stiller, C.; Schmitzová, J.; Dienemann, C.; Kokic, G.; Hillen, H.S.; Höbartner, C.; Cramer, P. Mechanism of Molnupiravir-Induced SARS-CoV-2 Mutagenesis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, B.M.; Strizki, J.; Miller, R.R.; Kumar, S.; Brown, M.; Johnson, M.G.; Cheng, M.; De Anda, C.; Rizk, M.L.; Stone, J.A. Molnupiravir: Mechanism of Action, Clinical, and Translational Science. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2024, 17, e13732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.; Wittenburg, L.; Yan, V.C.; Theil, J.H.; Castillo, D.; Reagan, K.L.; Williams, S.; Pham, C.D.; Li, C.; Muller, F.L.; et al. An Optimized Bioassay for Screening Combined Anticoronaviral Compounds for Efficacy against Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus with Pharmacokinetic Analyses of GS-441524, Remdesivir, and Molnupiravir in Cats. Viruses 2022, 14, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barua, S.; Kaltenboeck, B.; Juan, Y.C.; Bird, R.C.; Wang, C. Comparative Evaluation of GS-441524, Teriflunomide, Ruxolitinib, Molnupiravir, Ritonavir, and Nirmatrelvir for In Vitro Antiviral Activity against Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sase, O. Molnupiravir Treatment of 18 Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis: A Case Series. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2023, 37, 1876–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagan, K.L.; Brostoff, T.; Pires, J.; Rose, A.; Castillo, D.; Murphy, B.G. Open Label Clinical Trial of Orally Administered Molnupiravir as a First-Line Treatment for Naturally Occurring Effusive Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2024, 38, 3087–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.M.; Coggins, S.J.; Korman, R.; King, J.; Malik, R. Treatment of Feline Infectious Peritonitis in Cats with Molnupiravir: Clinical Observations and Outcomes for 54 Cases. Aust. Vet. J. 2025, 103, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Solanki, K.; Li, Y.; Ma, Z.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Baig, M.S.; Pan, Q. Viral Polymerase Binding and Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Activity of Molnupiravir against Human Seasonal Coronaviruses. Virology 2021, 564, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusell, S.M.; Schittone, S.A.; Holmes, K.V. Mutational Analysis of Aminopeptidase N, a Receptor for Several Group 1 Coronaviruses, Identifies Key Determinants of Viral Host Range. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohdatsu, T.; Izumiya, Y.; Yokoyama, Y.; Kida, K.; Koyama, H. Differences in Virus Receptor for Type I and Type II Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus. Arch. Virol. 1998, 143, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dye, C.; Temperton, N.; Siddell, S.G. Type I Feline Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotien Fails to Recognize Aminopeptidase N as a Functional Receptor on Feline Cell Lines. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, A.D.; Ousterout, D.G.; Whittaker, G.R. Feline Lectin Activity Is Critical for the Cellular Entry of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7917–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Flensburg, C.; Bilardi, R.A.; Majewski, I.J. Uridine-Cytidine Kinase 2 Potentiates the Mutagenic Influence of the Antiviral β-d-N4-Hydroxycytidine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 12031–12042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Satoh, K.; Doki, T. Possible Antiviral Activity of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid in Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus (Feline Coronavirus) Infection. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 647189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doki, T.; Takahashi, K.; Hasegawa, N.; Takano, T. In Vitro Antiviral Effects of GS-441524 and Itraconazole Combination against Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 144, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doki, T.; Shimada, J.; Tokunaga, M.; To, K.; Orino, K.; Takano, T. Protoporphyrin IX-Dependent Antiviral Effects of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid against Feline Coronavirus Type II. Viruses 2024, 16, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gut, M.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Huder, J.B.; Pedersen, N.C.; Lutz, H. One-Tube Fluorogenic Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction for the Quantitation of Feline Coronaviruses. J. Virol. Methods 1999, 77, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doki, T.; Toda, M.; Hasegawa, N.; Hohdatsu, T.; Takano, T. Therapeutic Effect of an Anti-Human-TNF-Alpha Antibody and Itraconazole on Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, T.; Hohdatsu, T. Serological Diagnosis of Feline Coronavirus Infection by Immunochromatographic Test. Coronaviruses Methods Protoc. 2015, 1282, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, U.M.; Hasan, M.M.; Havranek, B.; Islam, S.M. SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2024, 11, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.X.; Zhou, S.T.; Yang, Z.B.; Wang, Z. Molnupiravir Inhibits Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection In Vitro. Viruses 2023, 15, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Virus Strains | IC50 (μM, 95%CI) |
|---|---|
| FCoV-1 KU-2 | 17.8 a (15.9–19.6) |
| FCoV-2 79-1146 | 20.9 a (18.1–23.6) |
| CCoV-2 1-71 | 6.1 b (5.4–6.8) |
| TGEV TO163 | 6.6 b (6.1–7.2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doki, T.; Shinohara, K.; To, K.; Takano, T. Molnupiravir Inhibits Replication of Multiple Alphacoronavirus suis Strains in Feline Cells. Pathogens 2025, 14, 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080787
Doki T, Shinohara K, To K, Takano T. Molnupiravir Inhibits Replication of Multiple Alphacoronavirus suis Strains in Feline Cells. Pathogens. 2025; 14(8):787. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080787
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoki, Tomoyoshi, Kazuki Shinohara, Kaito To, and Tomomi Takano. 2025. "Molnupiravir Inhibits Replication of Multiple Alphacoronavirus suis Strains in Feline Cells" Pathogens 14, no. 8: 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080787
APA StyleDoki, T., Shinohara, K., To, K., & Takano, T. (2025). Molnupiravir Inhibits Replication of Multiple Alphacoronavirus suis Strains in Feline Cells. Pathogens, 14(8), 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080787







