Wastewater Surveillance for Group A Streptococcus pyogenes in a Small City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Sample Collection and Site Selection
2.2. Sample Concentration and DNA/RNA Extraction
2.3. Microbial Quantification by dPCR
2.4. Particle Association Experiment
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Comparison with Google Trends Data
3. Results and Discussion
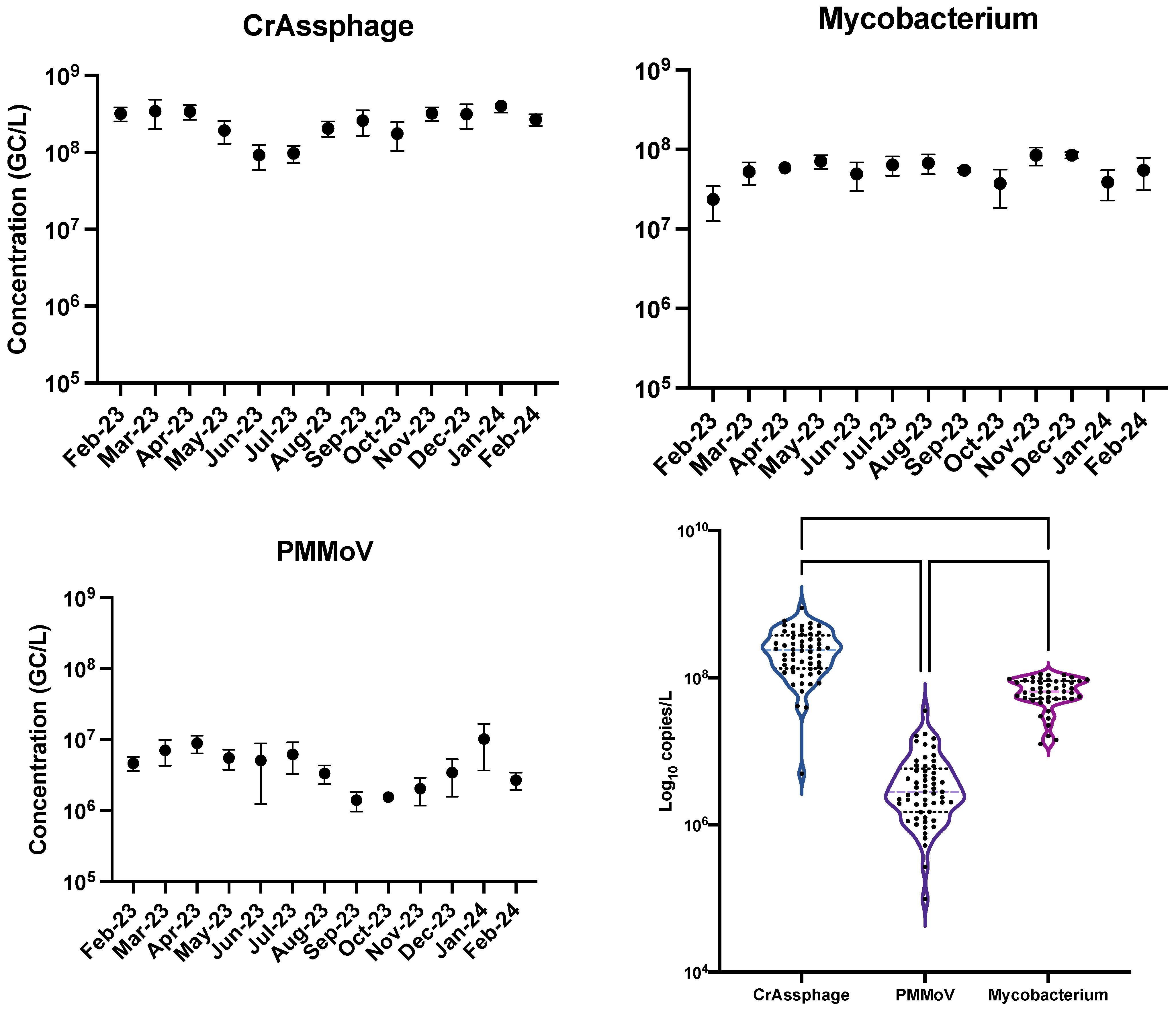
3.1. Comparison Between crAssphage and PMMoV
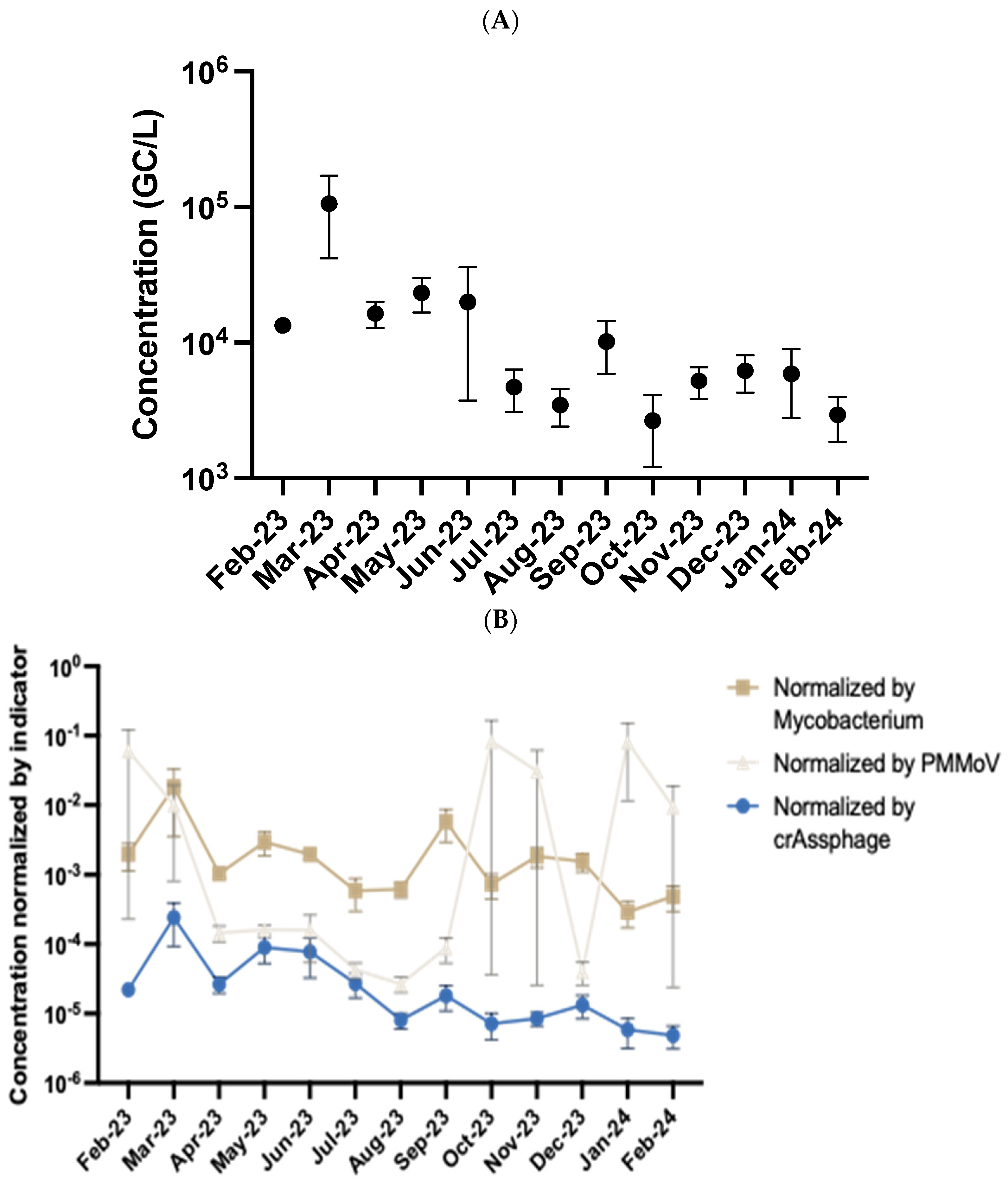
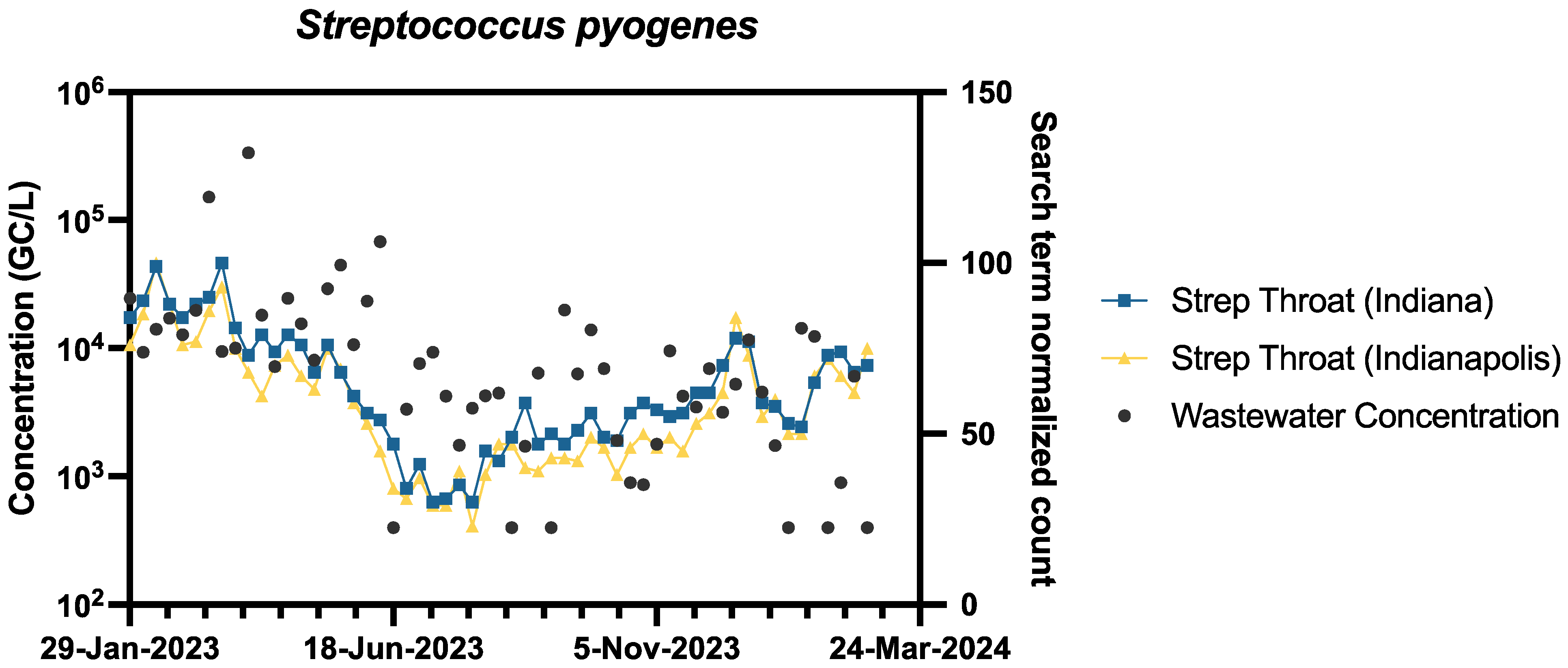
3.2. Temporal Detection of Streptococcus Pyogenes in Wastewater
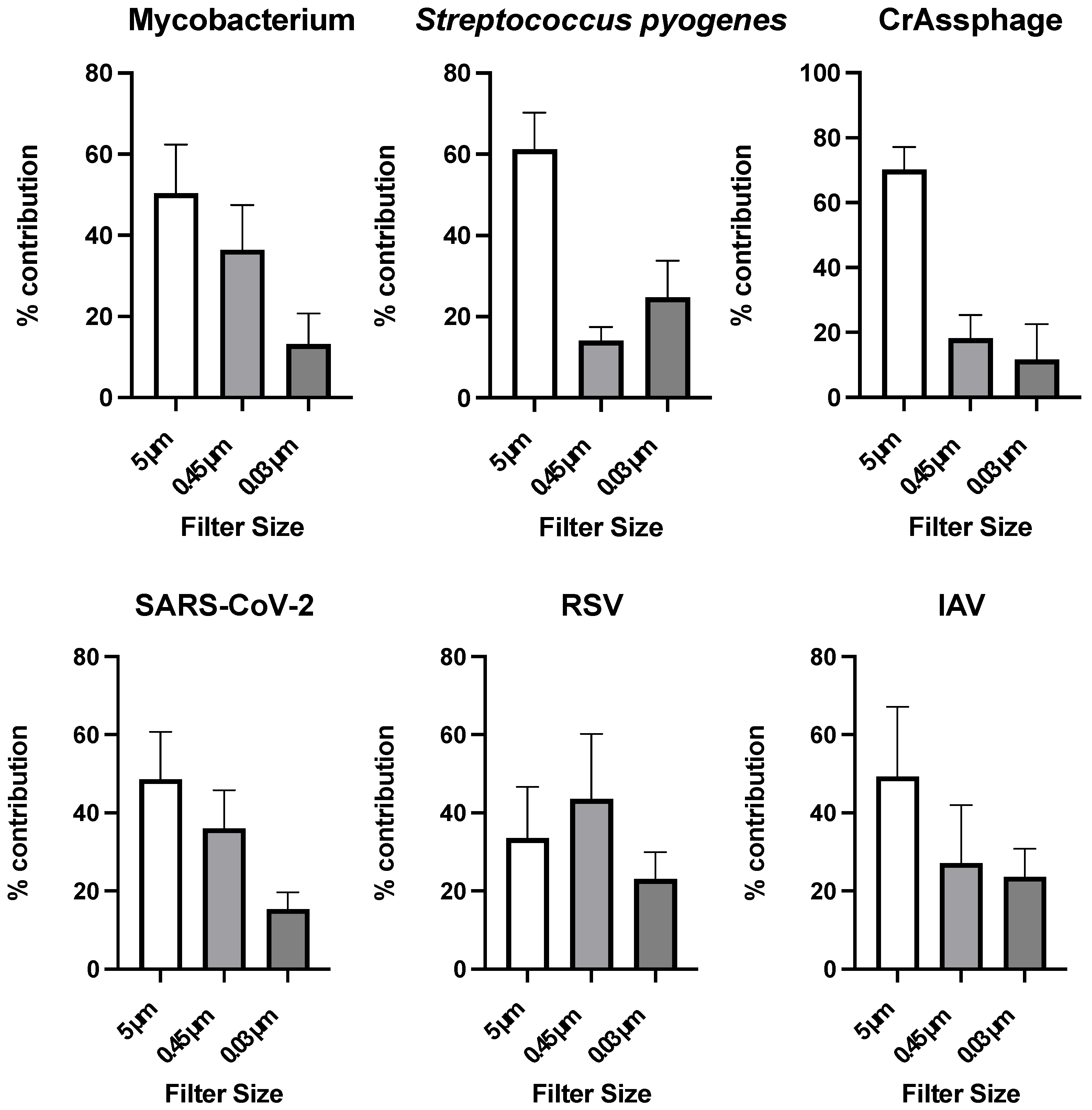
3.3. Particle Association of Microorganisms in Wastewater
3.4. Comparison of Pathogen Wastewater Levels to Publicly Available Data
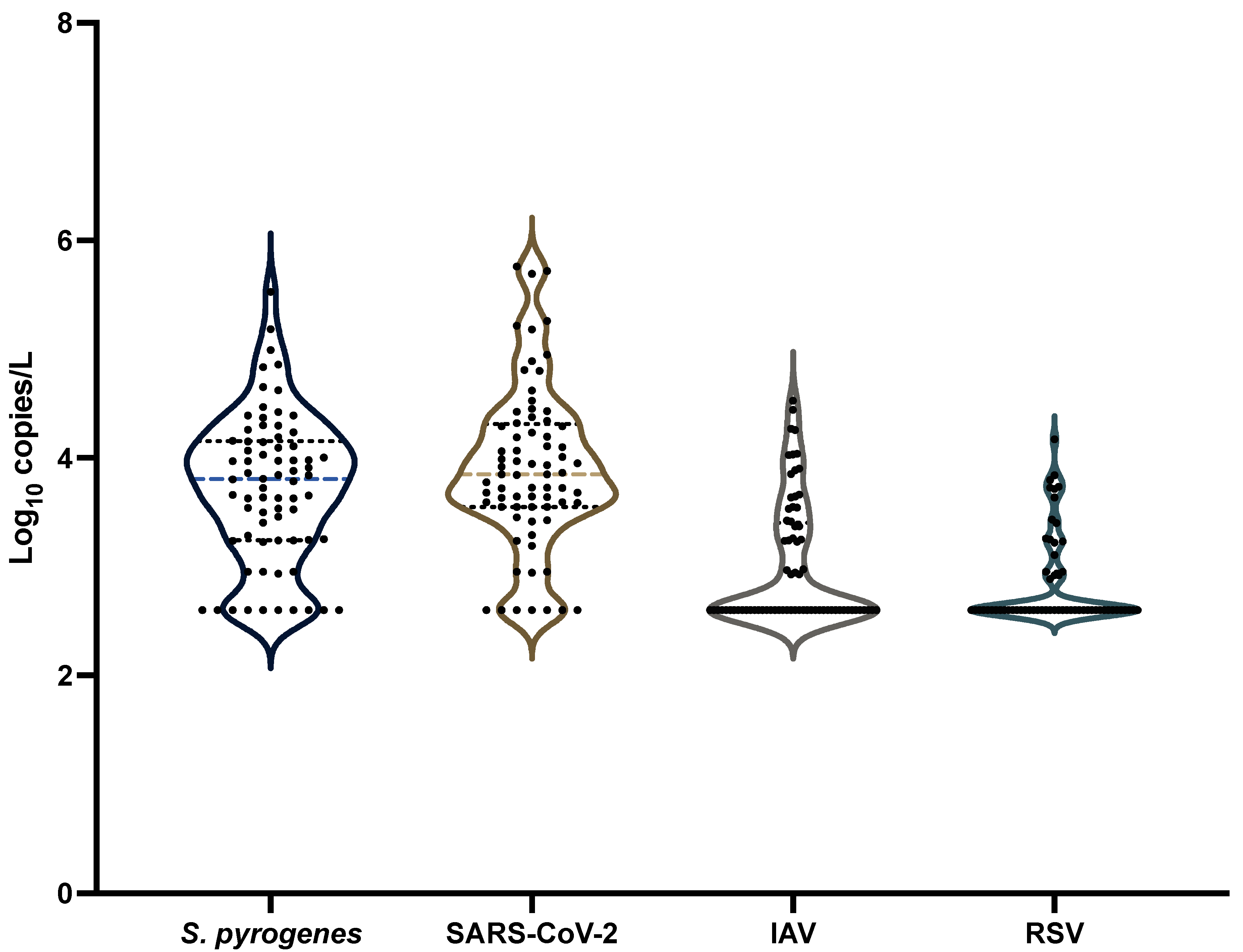
3.5. Comparison with Other Pathogens Commonly Tested in Wastewater
3.6. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kanwal, S.; Vaitla, P. Streptococcus Pyogenes. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Avire, N.J.; Whiley, H.; Ross, K. A Review of Streptococcus pyogenes: Public Health Risk Factors, Prevention and Control. Pathogens 2021, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Malla, B.; Haramoto, E. Group A Streptococcus pyogenes in wastewater: Applicability of wastewater-based epidemiology for monitoring the prevalence of GAS pharyngitis during the late COVID-19 pandemic phase. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 928, 172447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.J.; Brouwer, S.; Forde, B.M.; Worthing, K.A.; McIntyre, L.; Sundac, L.; Maloney, S.; Roberts, L.W.; Barnett, T.C.; Richter, J.; et al. Detection of Epidemic Scarlet Fever Group A Streptococcus in Australia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 1232–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, D.D.; Daw, J.; Xu, R.; Enkel, S.; Pickering, J.; McRae, T.; Engel, M.E.; Carapetis, J.; Wyber, R.; Bowen, A.C. Modes of transmission and attack rates of group A Streptococcal infection: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, K.G.; Shukla, R.; Mannell, M.; Graves, G.M.; Miller, A.C.; Vogel, J.; Malloy, K.; Deshpande, G.; Florea, G.; Shelton, K.; et al. Using Wastewater Surveillance to Monitor Gastrointestinal Pathogen Infections in the State of Oklahoma. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, M.B.; Keshaviah, A.; Bento, A.; Conroy-Ben, O.; Driver, E.M.; Ensor, K.B.; Halden, R.U.; Hopkins, L.P.; Kuhn, K.G.; Moe, C.L.; et al. Wastewater surveillance of pathogens can inform public health responses. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1992–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korfmacher, K.S.; Harris-Lovett, S.; Nelson, K.L. Campus Collaborations As a Model for Transforming SARS-CoV-2 Wastewater Surveillance Research into Public Health Action. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12770–12772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkins, M.D.; Lee, B.E.; Acosta, N.; Bautista, M.; Hubert, C.R.J.; Hrudey, S.E.; Frankowski, K.; Pang, X.L. Wastewater-based surveillance as a tool for public health action: SARS-CoV-2 and beyond. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 37, e0010322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClary-Gutierrez, J.S.; Mattioli, M.C.; Marcenac, P.; Silverman, A.I.; Boehm, A.B.; Bibby, K.; Balliet, M.; de Los Reyes, F.L., 3rd; Gerrity, D.; Griffith, J.F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Wastewater Surveillance for Public Health Action. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, D.H.; Wu, Y.H.; Wu, T.W.; Chang, S.C.; Shih, M.H. Infodemiology of Influenza-like Illness: Utilizing Google Trends’ Big Data for Epidemic Surveillance. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulli, A.; Zhang, Z.; Ruedaflores, M.; Sahly, J.; Angel, D.; Rohatgi, K.; Malik, W.; Hao, R.T.; Shepherd, J.; Peccia, J. Utilizing Internet Search Trends and Wastewater Surveillance to Identify Infectious Disease Outbreaks in Communities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 3401–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.A.; Garza, F.M.; Birch, O.N.; Greaves, J.C.J. Co-occurrence of adeno-associated virus 2 and human enteric adenovirus (group F) in wastewater after worldwide outbreaks of acute hepatitis of unknown etiology (AHUE). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 176806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomington, C.O. Blucher Poole Wastewater Treatment Plant. Available online: https://bloomington.in.gov/locations/blucher-poole-wastewater-treatment-plant (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Bloomington, C.O. Dillman Road Wastewater Treatment Plant. Available online: https://www.bloomington.in.gov/locations/dillman-road-wastewater-treatment-plant (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Greaves, J.; Stone, D.; Wu, Z.; Bibby, K. Persistence of emerging viral fecal indicators in large-scale freshwater mesocosms. Water Res. X 2020, 9, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Greaves, J.; Arp, L.; Stone, D.; Bibby, K. Comparative fate of CrAssphage with culturable and molecular fecal pollution indicators during activated sludge wastewater treatment. Environmental International 2020, 136, 105452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bivins, A.; Crank, K.; Greaves, J.; North, D.; Wu, Z.; Bibby, K. Cross-assembly phage and pepper mild mottle virus as viral water quality monitoring tools—Potential, research gaps, and way forward. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 16, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, J.; North, D.; Bibby, K. Particle association and size fraction of molecular viral fecal pollution indicators in wastewater. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2022, 8, 1814–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherchan, S.P.; Shahin, S.; Ward, L.M.; Tandukar, S.; Aw, T.G.; Schmitz, B.; Ahmed, W.; Kitajima, M. First detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater in North America: A study in Louisiana, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, A.B.; Hughes, B.; Duong, D.; Chan-Herur, V.; Buchman, A.; Wolfe, M.K.; White, B.J. Wastewater concentrations of human influenza, metapneumovirus, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial virus, rhinovirus, and seasonal coronavirus nucleic-acids during the COVID-19 pandemic: A surveillance study. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, E340–E348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, B.; Duong, D.; White, B.J.; Wigginton, K.R.; Chan, E.M.G.; Wolfe, M.K.; Boehm, A.B. Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) RNA in Wastewater Settled Solids Reflects RSV Clinical Positivity Rates. Environ. Sci. Techol. Let. 2022, 9, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, M.; Sassi, H.P.; Torrey, J.R. Pepper mild mottle virus as a water quality indicator. npj Clean. Water 2018, 1, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodani, M.; Yang, G.Y.; Conklin, L.M.; Travis, T.C.; Whitney, C.G.; Anderson, L.J.; Schrag, S.J.; Taylor, T.H.; Beall, B.W.; Breiman, R.F.; et al. Application of TaqMan Low-Density Arrays for Simultaneous Detection of Multiple Respiratory Pathogens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, M.; Takemura, Y.; Kawakami, S.; Yoochatchaval, W.; Tran, P.T.; Tomioka, N.; Ebie, Y.; Syutsubo, K. Quantitative detection and reduction of potentially pathogenic bacterial groups of Aeromonas, Arcobacter, Klebsiella pneumoniae species complex, and Mycobacterium in wastewater treatment facilities. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0291742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.K.; Le Guyader, F.S.; Le Saux, J.C.; Pommepuy, M.; Montgomery, M.A.; Elimelech, M. Norovirus Removal and Particle Association in a Waste Stabilization Pond. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9151–9157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder, M.L.; Middleton, F.; Larsen, D.A.; Du, Q.; Fenty, A.; Zeng, T.; Insaf, T.; Kilaru, P.; Collins, M.; Kmush, B.; et al. Co-quantification of crAssphage increases confidence in wastewater-based epidemiology for SARS-CoV-2 in low prevalence areas. Water Res. X 2021, 11, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabar, M.A.; Honda, R.; Haramoto, E. CrAssphage as an indicator of human-fecal contamination in water environment and virus reduction in wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, R.H.; Nagarkar, M.; Yeager, R.A.; Talley, D.; Chaney, A.C.; Rai, J.P.; Mukherjee, A.; Rai, S.N.; Bhatnagar, A.; Smith, T. Surveillance of RNase P, PMMoV, and CrAssphage in wastewater as indicators of human fecal concentration across urban sewer neighborhoods, Kentucky. FEMS Microbes 2022, 3, xtac003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davalos, A.F.; Garcia, P.K.; Montoya-Pachongo, C.; Rengifo, A.; Guerrero, D.; Diaz-Ordonez, L.; Diaz, G.; Ferro, B.E. Identification of Nontuberculous Mycobacteria in Drinking Water in Cali, Colombia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amha, Y.M.; Anwar, M.Z.; Kumaraswamy, R.; Henschel, A.; Ahmad, F. Mycobacteria in Municipal Wastewater Treatment and Reuse: Microbial Diversity for Screening the Occurrence of Clinically and Environmentally Relevant Species in Arid Regions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3048–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, N.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Future perspectives of wastewater-based epidemiology: Monitoring infectious disease spread and resistance to the community level. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiyebi, H.A.; Farah, J.A.; Ikert, H.; Srikanthan, N.; Hayat, S.; Bragg, L.M.; Qasim, A.; Payne, M.; Kaleis, L.; Paget, C.; et al. Assessment of seasonality and normalization techniques for wastewater-based surveillance in Ontario, Canada. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1186525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Denise, H.; Diggle, P.; Grimsley, J.; Holmes, C.; James, D.; Jersakova, R.; Mole, C.; Nicholson, G.; Smith, C.R.; et al. A spatio-temporal framework for modelling wastewater concentration during the COVID-19 pandemic. Environ. Int. 2023, 172, 107765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audi, A.; AlIbrahim, M.; Kaddoura, M.; Hijazi, G.; Yassine, H.M.; Zaraket, H. Seasonality of Respiratory Viral Infections: Will COVID-19 Follow Suit? Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 567184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, T.J.; Lee, J.; Shin, M.; Rhee, C.K. Seasonality of common respiratory viruses: Analysis of nationwide time-series data. Respirology 2024, 29, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, B.; Thapa, K. Indoor Staying During Winter Season Makes People More Susceptible to Flu. J. Nepal. Health Res. Counc. 2016, 14, 69–70. [Google Scholar]
- Fares, A. Factors Influencing the Seasonal Patterns of Infectious Diseases. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Philo, S.E.; De León, K.B.; Noble, R.T.; Zhou, N.A.; Alghafri, R.; Bar-Or, I.; Darling, A.; D’Souza, N.; Hachimi, O.; Kaya, D.; et al. Wastewater surveillance for bacterial targets: Current challenges and future goals. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2024, 90, e0142823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poopedi, E.; Singh, T.; Gomba, A. Potential Exposure to Respiratory and Enteric Bacterial Pathogens among Wastewater Treatment Plant Workers, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pica, N.; Bouvier, N.M. Environmental factors affecting the transmission of respiratory viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changruenngam, S.; Bicout, D.J.; Modchang, C. How the individual human mobility spatio-temporally shapes the disease transmission dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, S. Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996; p. xvii. 1273p. [Google Scholar]
- Bethencourt Mirabal, A.; Nguyen, A.D.; Ferrer, G. Lung Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infections. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Firquet, S.; Beaujard, S.; Lobert, P.E.; Sané, F.; Caloone, D.; Izard, D.; Hober, D. Survival of Enveloped and Non-Enveloped Viruses on Inanimate Surfaces. Microbes Environ. 2015, 30, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louten, J.; Reynolds, N. Essential Human Virology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Academic Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2016; p. xiii, 326p. [Google Scholar]
- Chahal, C.; van den Akker, B.; Young, F.; Franco, C.; Blackbeard, J.; Monis, P. Pathogen and Particle Associations in Wastewater: Significance and Implications for Treatment and Disinfection Processes. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 97, 63–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hejkal, T.W.; Wellings, F.M.; Lewis, A.L.; Larock, P.A. Distribution of Viruses Associated with Particles in Waste-Water. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1981, 41, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.Y.; Brighton, K.; Chen, J.H.; Shuai, D.M.; Aw, T.G. Quantification of Particle-Associated Viruses in Secondary Treated Wastewater Effluent. Food Environ. Virol. 2025, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Pinto, B.; Anto, A.; Czarlewski, W.; Anto, J.M.; Fonseca, J.A.; Bousquet, J. Assessment of the Impact of Media Coverage on COVID-19-Related Google Trends Data: Infodemiology Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e19611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, T.S.; Wu, A.W.; Sharma, D.; Illing, E.A.; Rubel, K.; Ting, J.Y.; Snot Force, A. Correlations of Online Search Engine Trends With Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Incidence: Infodemiology Study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020, 6, e19702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lang, J.C.; Chen, Y.H. Assessment of using Google Trends for real-time monitoring of infectious disease outbreaks: A measles case study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.W.; Guerra, A.; Wittke, F.; Lang, J.C.; Bakker, K.; Lee, A.W.; Finelli, L.; Chen, Y.H. Real-Time Monitoring of Infectious Disease Outbreaks with a Combination of Google Trends Search Results and the Moving Epidemic Method: A Respiratory Syncytial Virus Case Study. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gier, B.; Vlaminckx, B.J.M.; Woudt, S.H.S.; van Sorge, N.M.; van Asten, L. Associations between common respiratory viruses and invasive group A streptococcal infection: A time-series analysis. Influenza Other Resp. 2019, 13, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, S.R.D.; Wolf, J.M.; Pille, A.; Freese, L.; Petek, H.; Rocha, B.D.; Giannini, G.L.T.; Bristot, G.; Andreis, T.F.; de Oliveira, F.H.; et al. Temporal trends in respiratory pathogens following the COVID-19 pandemic and climate variables: A unicentric retrospective evaluation of 24 pathogens in a temperate subtropical region. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, S.; Rivera-Hernandez, T.; Curren, B.F.; Harbison-Price, N.; De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Jespersen, M.G.; Davies, M.R.; Walker, M.J. Pathogenesis, epidemiology and control of Group A Streptococcus pyogenes infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 619, Corrected in: Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, B.; Birch, O.N.; Greaves, J.C. Monitoring Multiple Sexually Transmitted Pathogens Through Wastewater Surveillance. Pathogens 2025, 14, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Birch, O.N.; Garza, F.M.; Greaves, J.C. Wastewater Surveillance for Group A Streptococcus pyogenes in a Small City. Pathogens 2025, 14, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070658
Birch ON, Garza FM, Greaves JC. Wastewater Surveillance for Group A Streptococcus pyogenes in a Small City. Pathogens. 2025; 14(7):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070658
Chicago/Turabian StyleBirch, Olivia N., Frankie M. Garza, and Justin C. Greaves. 2025. "Wastewater Surveillance for Group A Streptococcus pyogenes in a Small City" Pathogens 14, no. 7: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070658
APA StyleBirch, O. N., Garza, F. M., & Greaves, J. C. (2025). Wastewater Surveillance for Group A Streptococcus pyogenes in a Small City. Pathogens, 14(7), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070658






