Genetic Factors of Campylobacter jejuni Required for Its Interactions with Free-Living Amoeba
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Construction of Single Deletion Mutants
2.3. Complementation of the Selected Deletion Mutants
2.4. Internalization Assay
2.5. 24 h Intracellular Survival Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Selection of the Target Genes for the Study
3.2. Rationale and Optimization for the Modified Gentamicin Protection Assay
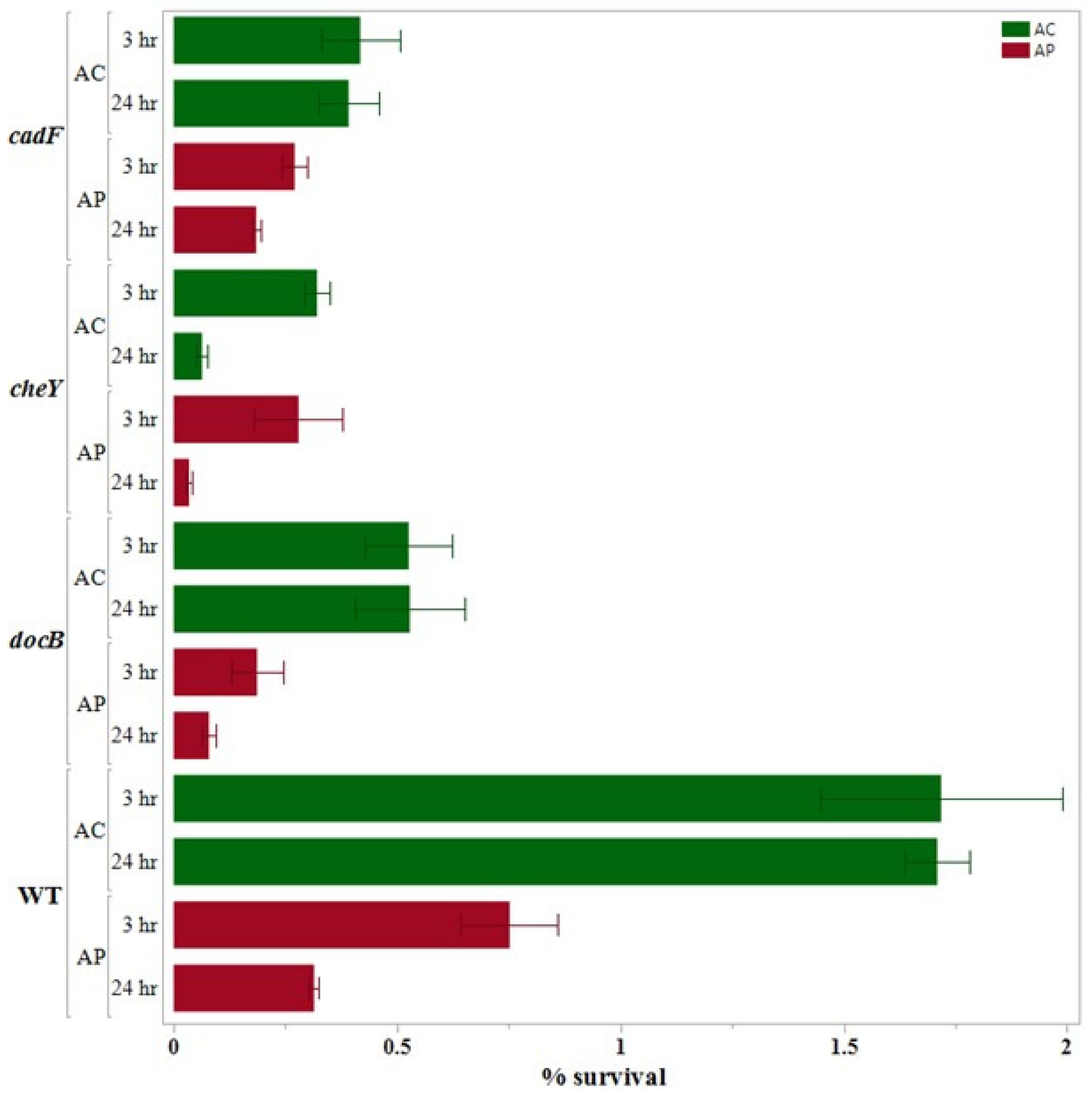
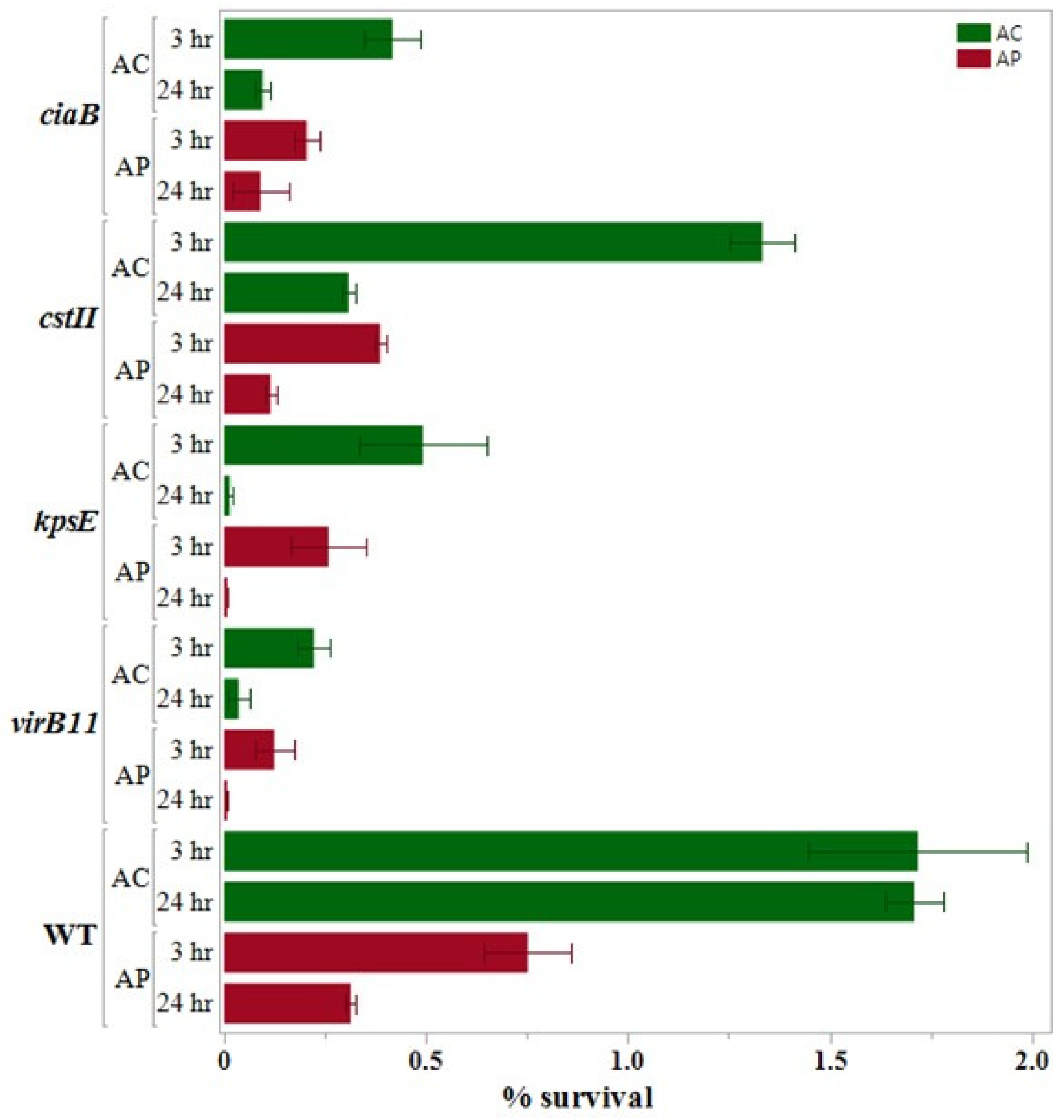
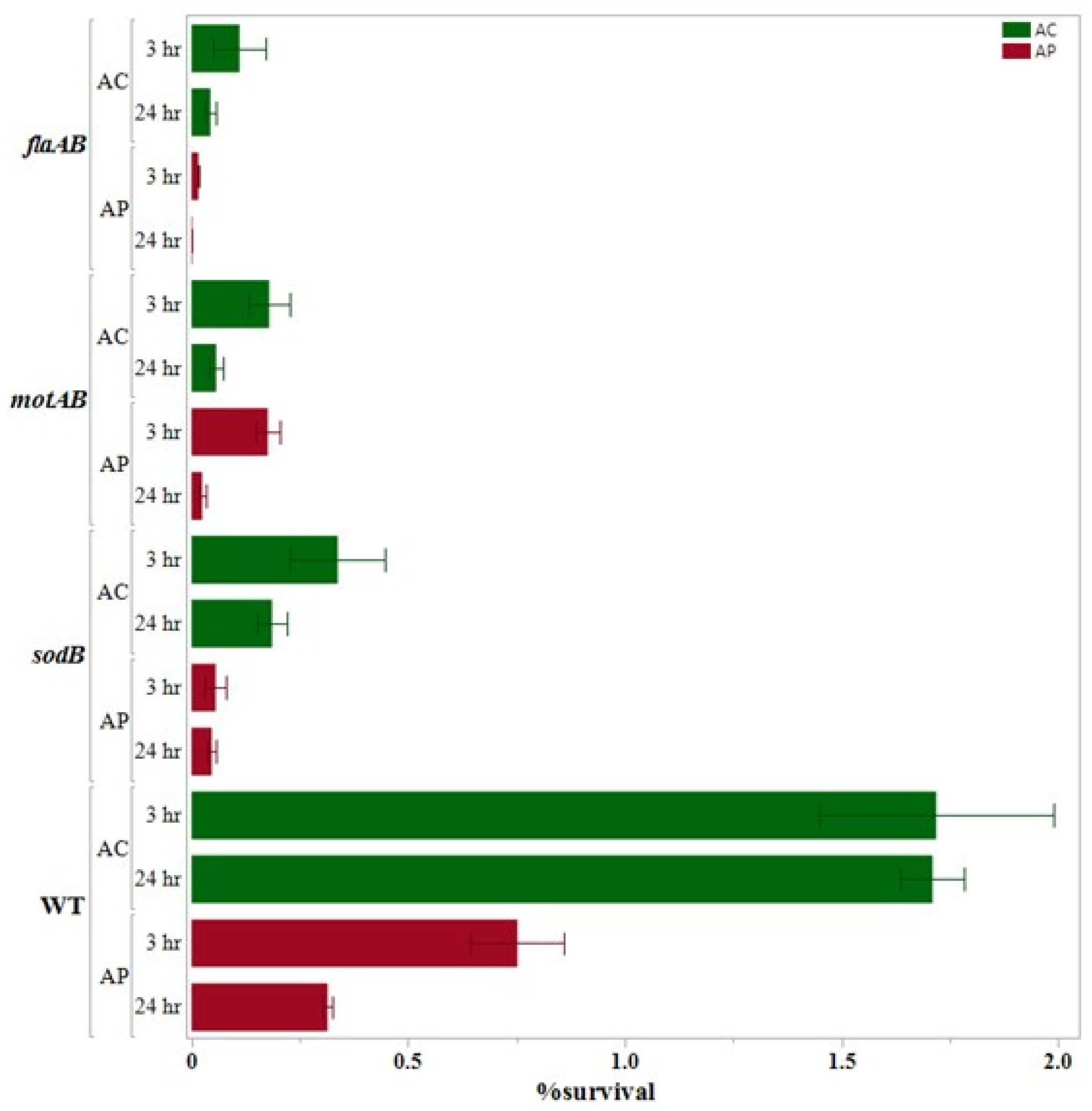
3.3. Internalization Assay
3.4. 24 h Survival Assay
3.5. Complementation Assay
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GBS | Guillain-Barrè syndrome |
| MFS | Miller Fisher syndrome |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharides |
| CDT | Cytolethal distending toxin |
| FLA | Free-living amoeba |
| GPA | Gentamicin protection assay |
| mGPA | modified gentamicin protection assay |
| LOG | Lipooligosaccharide |
| MH agar | Mueller-Hinton agar |
| PYG medium | Peptone-yeast extract-glucose medium |
| MOI | Multiplicity of infection |
| ROI | Rate of Internalization |
| ROIS | Rate of Intracellular Survival |
| MDR | Multidrug resistance |
References
- Ruiz-Palacios, G.M. The health burden of Campylobacter infection and the impact of antimicrobial resistance: Playing chicken. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheid, P. Relevance of free-living amoebae as hosts for phylogenetically diverse microorganisms. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 2407–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoni, K.; Papadopoulou, E.; Michailidou, E.; Kavaliotis, I. Campylobacter jejuni meningitis in a neonate: A rare case report. J. Neonatal-Perinat. Med. 2013, 6, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, D.J. Campylobacter virulence and survival factors. Food Microbiol. 2015, 48, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio, J.C.B.; Flores, V.I.D. Campylobacter jejuni from farm to fork: Campylobacteriosis and chicken meat. J. Curr. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 457–467. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, C.; De Klerk, M.; Endtz, H.; Jacobs, B.; Laman, J.; Van Der Meché, F.; Van Doorn, P. Guillain-Barré syndrome- and Miller Fisher syndrome-associated Campylobacter jejuni lipopolysaccharides induce anti-GM1 and anti-GQ1b antibodies in rabbits. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 2462–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajene, A.N.; Walker, C.L.F.; Black, R.E. Enteric pathogens and reactive arthritis: A systematic review of Campylobacter, Salmonella and Shigella-associated reactive arthritis. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2013, 31, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On, S.L.W. Taxonomy of Campylobacter, Arcobacter, Helicobacter and related bacteria: Current status, future prospects and immediate concerns. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 1S–15S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horrocks, S.M.; Anderson, R.C.; Nisbet, D.J.; Ricke, S.C. Incidence and ecology of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in animals. Anaerobe 2009, 15, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronowski, C.; James, C.E.; Winstanley, C. Role of environmental survival in transmission of Campylobacter jejuni. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 356, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, W.A.; Hess, C.; Hess, M. Re-thinking the chicken–Campylobacter jejuni interaction: A review. Avian Pathol. 2018, 47, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union One Health 2019 zoonoses report. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06406. [Google Scholar]
- Es-Soucratti, K.; Hammoumi, A.; Bouchrif, B.; Asmai, R.; En-Nassiri, H.; Karraouan, B. Occurrence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from poultry in Casablanca-Settat, Morocco. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2020, 9, 8692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, D.; Fearnley, C. Sources of Campylobacter colonization in broiler chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4343–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiley, H.; Van den Akker, B.; Giglio, S.; Bentham, R. The role of environmental reservoirs in human campylobacteriosis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 5886–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokajärvi, A.-M.; Pitkänen, T.; Siljanen, H.M.; Nakari, U.-M.; Torvinen, E.; Siitonen, A.; Miettinen, I.T. Occurrence of thermotolerant Campylobacter spp. and adenoviruses in Finnish bathing waters and purified sewage effluents. J. Water Health 2013, 11, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K. Campylobacters in water, sewage and the environment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 68S–79S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänninen, M.L.; Haajanen, H.; Pummi, T.; Wermundsen, K.; Katila, M.L.; Särkkinen, H.; Rautelin, H. Detection and typing of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli and analysis of indicator organisms in three waterborne outbreaks in Finland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, K.G.; Falkenhorst, G.; Emborg, H.-D.; Ceper, T.; Torpdahl, M.; Krogfelt, K.; Ethelberg, S.; Mølbak, K. Epidemiological and serological investigation of a waterborne Campylobacter jejuni outbreak in a Danish town. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revez, J.; Llarena, A.-K.; Schott, T.; Kuusi, M.; Hakkinen, M.; Kivistö, R.; Hänninen, M.-L.; Rossi, M. Genome analysis of Campylobacter jejuni strains isolated from a waterborne outbreak. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blaser, M.J.; Engberg, J. Clinical aspects of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli infections. In Campylobacter, 3rd ed.; Nachamkin, I., Szymanski, C.M., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 99–121. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, C.K.; Ethelberg, S.; van Pelt, W.; Tauxe, R.V. Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni infections in industrialized nations. In Campylobacter, 3rd ed.; Nachamkin, I., Szymanski, C.M., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 163–189. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, J. Current epidemiological issues in human campylobacteriosis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 85S–95S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitkänen, T. Review of Campylobacter spp. in drinking and environmental waters. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 95, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciolà, A.; Riso, R.; Avventuroso, E.; Visalli, G.; Delia, S.; Laganà, P. Campylobacter: From microbiology to prevention. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2017, 58, E79. [Google Scholar]
- Winiecka-Krusnell, J.; Wreiber, K.; von Euler, A.; Engstrand, L.; Linder, E. Free-living amoebae promote growth and survival of Helicobacter pylori. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greub, G.; Raoult, D. Microorganisms resistant to free-living amoebae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.M.; Ashbolt, N.J. Do free-living amoebae in treated drinking water systems present an emerging health risk? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayamajhee, B.; Subedi, D.; Peguda, H.K.; Willcox, M.D.; Henriquez, F.L.; Carnt, N. A systematic review of intracellular microorganisms within Acanthamoeba to understand potential impact for infection. Pathogens 2021, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayamajhee, B.; Willcox, M.D.; Henriquez, F.L.; Petsoglou, C.; Subedi, D.; Carnt, N. Acanthamoeba, an environmental phagocyte enhancing survival and transmission of human pathogens. Trends Parasitol. 2022, 38, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loret, J.-F.; Greub, G. Free-living amoebae: Biological by-passes in water treatment. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2010, 213, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheid, P. Viruses in close associations with free-living amoebae. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 3959–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matz, C.; Kjelleberg, S. Off the hook—How bacteria survive protozoan grazing. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, M. Legionella and Free-Living Amoebae Interactions: An Ecological Perspective of Drinking Water Safety and Controlling Legionellosis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltner, E.C.; Bermudez, L.E. Mycobacterium avium grown in Acanthamoeba castellanii is protected from the effects of antimicrobials. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1990–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, H.; Saeed, A.; Weintraub, A.; Nair, G.B.; Sandström, G. Vibrio cholerae O1 strains are facultative intracellular bacteria, able to survive and multiply symbiotically inside the aquatic free-living amoeba Acanthamoeba castellanii. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 60, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scola, B.L.; Raoult, D. Survival of Coxiella burnetii within free-living amoeba Acanthamoeba castellanii. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2001, 7, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofsson, J.; Axelsson-Olsson, D.; Brudin, L.; Olsen, B.; Ellström, P. Campylobacter jejuni actively invades the amoeba Acanthamoeba polyphaga and survives within non-digestive vacuoles. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A. Acanthamoeba: Biology and increasing importance in human health. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 564–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, R.; Khan, N.A. Biology and pathogenesis of Acanthamoeba. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, R.; Khan, N.A. War of the microbial worlds: Who is the beneficiary in Acanthamoeba–bacterial interactions? Exp. Parasitol. 2012, 130, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Queller, D.C.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Q.; He, Z.; He, Z.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Shu, L. The ecology and evolution of amoeba-bacterium interactions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e01866-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, T.S.; Vaccaro, L.; Magnet, A.; Izquierdo, F.; Ollero, D.; Martinez-Fernandez, C.; Mayo, L.; Moran, M.; Pozuelo, M.J.; Fenoy, S.; et al. Presence and interaction of free-living amoebae and amoeba-resisting bacteria in water from drinking water treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Mesonero, L.; Ferrús, M.A.; Moreno, Y. Determination of the bacterial microbiome of free-living amoebae isolated from wastewater by 16S rRNA amplicon-based sequencing. Environ. Res. 2020, 190, 109987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelsson-Olsson, D.; Waldenström, J.; Broman, T.; Olsen, B.; Holmberg, M. Protozoan Acanthamoeba polyphaga as a potential reservoir for Campylobacter jejuni. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, A.; Seddon, A.M.; Karlyshev, A.V. Campylobacter–Acanthamoeba interactions. Microbiology 2015, 161, 933–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelsson-Olsson, D.; Olofsson, J.; Svensson, L.; Griekspoor, P.; Waldenström, J.; Ellström, P.; Olsen, B. Amoebae and algae can prolong the survival of Campylobacter species in co-culture. Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 126, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson-Olsson, D.; Svensson, L.; Olofsson, J.; Salomon, P.; Waldenström, J.; Ellström, P.; Olsen, B. Increase in acid tolerance of Campylobacter jejuni through coincubation with amoebae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4194–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snelling, W.J.; Stern, N.J.; Lowery, C.J.; Moore, J.E.; Gibbons, E.; Baker, C.; Dooley, J.S. Colonization of broilers by Campylobacter jejuni internalized within Acanthamoeba castellanii. Arch. Microbiol. 2008, 189, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, T.-Y.; Gibson, K.E. Interactions between human norovirus surrogates and Acanthamoeba spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4005–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, P.K.; Negretti, N.M.; Turner, K.L.; Konkel, M.E. Molecular dissection of the Campylobacter jejuni CadF and FlpA virulence proteins in binding to host cell fibronectin. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, A.; Ketley, J. Pathogenesis of enteric Campylobacter infection. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 45S–56S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, D.; Van Deun, K.; Martel, A.; Van Immerseel, F.; Messens, W.; Heyndrickx, M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F. Colonization factors of Campylobacter jejuni in the chicken gut. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louwen, R.; Heikema, A.; van Belkum, A.; Ott, A.; Gilbert, M.; Ang, W.; Endtz, H.P.; Bergman, M.P.; Nieuwenhuis, E.E. The sialylated lipooligosaccharide outer core in Campylobacter jejuni is an important determinant for epithelial cell invasion. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 4431–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrixson, D.R.; DiRita, V.J. Identification of Campylobacter jejuni genes involved in commensal colonization of the chick gastrointestinal tract. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 52, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, C.L.; Christensen, J.E.; Pacheco, S.A.; Minnich, S.A.; Konkel, M.E. Campylobacter jejuni secretes proteins via the flagellar type III secretion system that contribute to host cell invasion and gastroenteritis. In Campylobacter; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 315–332. [Google Scholar]
- Bachtiar, B.M.; Coloe, P.J.; Fry, B.N. Knockout mutagenesis of the kpsE gene of Campylobacter jejuni 81116 and its involvement in bacterium–host interactions. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 49, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertins, S.; Allan, B.J.; Townsend, H.G.; Köster, W.; Potter, A.A. Role of motAB in adherence and internalization in polarized Caco-2 cells and in cecal colonization of Campylobacter jejuni. Avian Dis. 2012, 57, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chintoan-Uta, C.; Cassady-Cain, R.L.; Al-Haideri, H.; Watson, E.; Kelly, D.J.; Smith, D.G.; Sparks, N.H.; Kaiser, P.; Stevens, M.P. Superoxide dismutase SodB is a protective antigen against Campylobacter jejuni colonisation in chickens. Vaccine 2015, 33, 6206–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Novik, V.; Hofreuter, D.; Galán, J.E. Identification of Campylobacter jejuni genes involved in its interaction with epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 3540–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, J.C.; Guerry, P. Plasmids of Campylobacter jejuni 81-176. In Campylobacter: Molecular and Cellular Biology; Horizon Bioscience: Wymondham, UK, 2005; pp. 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, C.R.; Khatiwara, A.; Ziprin, R.; Kwon, Y.M. Rapid construction of Campylobacter jejuni deletion mutants. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Alm, R.A.; Guerry, P. Construction of new Campylobacter cloning vectors and a new mutational cat cassette. Gene 1993, 130, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, A.H.M.; Wood, A.C.; Henderson, J.; Wooldridge, K.; Ketley, J.M. Genetic manipulation of enteric Campylobacter species. Methods Microbiol. 1998, 27, 407–419. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, R.; Burr, D.H.; Doig, P.; Trust, T.J.; Niu, H.; Guerry, P. Isolation of motile and non-motile insertional mutants of Campylobacter jejuni: The role of motility in adherence and invasion of eukaryotic cells. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 14, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zeng, X.; Haigh, R.D.; Ketley, J.M.; Lin, J. Identification and characterization of a new ferric enterobactin receptor, CfrB, in Campylobacter. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 4425–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, F.; Lin, J. Molecular, antigenic, and functional characteristics of ferric enterobactin receptor CfrA in Campylobacter jejuni. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 5437–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirks, B.P.; Quinlan, J.J. Development of a modified gentamicin protection assay to investigate the interaction between Campylobacter jejuni and Acanthamoeba castellanii ATCC 30010. Exp. Parasitol. 2014, 140, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strober, W. Trypan blue exclusion test of cell viability. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 1997, 21, A-3B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, A.J.; Gomes, K.X.; Cortines, J.R.; Peralta, J.M.; Peralta, R.H.S. Acanthamoeba spp. as a universal host for pathogenic microorganisms: One bridge from environment to host virulence. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 193, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadevall, A. Amoeba provide insight into the origin of virulence in pathogenic fungi. In Recent Advances on Model Hosts; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology (AEMB, Volume 710); Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thewes, S.; Soldati, T.; Eichinger, L. Amoebae as host models to study the interaction with pathogens. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenaar, T.M.; Blaser, M.J. Pathophysiology of Campylobacter jejuni infections of humans. Microbes Infect. 1999, 1, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasher, F.; Wren, B.W. Transient internalization of Campylobacter jejuni in amoebae enhances subsequent invasion of human cells. Microbiology 2022, 168, 001143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasher, F.; Wren, B.W. Flagellin O-linked glycans are required for the interactions between Campylobacter jejuni and Acanthamoeba castellanii. Microbiology 2023, 169, 001386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.; Ramesh, A.; Seddon, A.M.; Karlyshev, A.V. CmeABC multidrug efflux pump contributes to antibiotic resistance and promotes Campylobacter jejuni survival and multiplication in Acanthamoeba polyphaga. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01600-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balczun, C.; Scheid, P. Free-living amoebae as hosts for and vectors of intracellular microorganisms with public health significance. Viruses 2017, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamothe, J.; Thyssen, S.; Valvano, M.A. Burkholderia cepacia complex isolates survive intracellularly without replication within acidic vacuoles of Acanthamoeba polyphaga. Cell. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oloroso, M.J.W. Interactions Between Arcobacter butzleri and Free-Living Protozoa in the Context of Sewage & Wastewater Treatment. Master’s Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, M.; Wagner, M. Bacterial endosymbionts of free-living amoebae. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2004, 51, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matz, C.; Jürgens, K. High motility reduces grazing mortality of planktonic bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abukhalid, N.; Islam, S.; Ndzeidze, R.; Bermudez, L.E. Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis interactions with macrophage killing mechanisms. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Smith, D.M.; Adak, S.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Nagy, L.; Wolfgang, M.J.; O’Connor, T.J. Legionella pneumophila usurps host cell lipids for vacuole expansion and bacterial growth. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1011996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Elmose, J.; Call, D.R. Interactions between the environmental pathogen Listeria monocytogenes and a free-living protozoan (Acanthamoeba castellanii). Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, H.; Johansson, T.; Golovliov, I.; Sandström, G.; Forsman, M. Survival and growth of Francisella tularensis in Acanthamoeba castellanii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshua, G.P.; Guthrie-Irons, C.; Karlyshev, A.; Wren, B. Biofilm formation in Campylobacter jejuni. Microbiology 2006, 152, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalino, G.; Bozzo, G.; Dinardo, F.R.; D’Amico, F.; Dimuccio, M.M.; Camarda, A.; Ceci, E.; Romito, D.; Circella, E. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli from laying hens housed in different rearing systems. Animals 2022, 12, 2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snelling, W.; McKenna, J.; Lecky, D.; Dooley, J. Survival of Campylobacter jejuni in waterborne protozoa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5560–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandström, G.; Saeed, A.; Abd, H. Acanthamoeba-bacteria: A model to study host interaction with human pathogens. Curr. Drug Targets. 2011, 12, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofsson, J.; Griekspoor Berglund, P.; Olsen, B.; Ellström, P.; Axelsson-Olsson, D. The abundant free-living amoeba, Acanthamoeba polyphaga, increases the survival of Campylobacter jejuni in milk and orange juice. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2015, 5, 28675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Axelsson-Olsson, D.; Ellström, P.; Waldenström, J.; Haemig, P.D.; Brudin, L.; Olsen, B. Acanthamoeba-Campylobacter coculture as a novel method for enrichment of Campylobacter species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 6864–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Batlle, M.; Girbau, C.; Lopez-Arencibia, A.; Sifaoui, I.; Liendo, A.R.; Estrella, C.J.B.; Méndez, A.B.G.; Chiboub, O.; Hajaji, S.; Fernandez-Astorga, A. Variation in Campylobacter jejuni culturability in presence of Acanthamoeba castellanii Neff. Exp. Parasitol. 2017, 183, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.H.; Shotts, E.B.; Wooley, R.E.; Porter, K.G. Survival of coliforms and bacterial pathogens within protozoa during chlorination. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 3023–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasher, F.; Lehri, B.; Stabler, R.A.; Wren, B.W. Acanthamoeba castellanii as a model for unveiling Campylobacter jejuni host-pathogen dynamics. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baré, J.; Sabbe, K.; Huws, S.; Vercauteren, D.; Braeckmans, K.; Van Gremberghe, I.; Favoreel, H.; Houf, K. Influence of temperature, oxygen and bacterial strain identity on the association of Campylobacter jejuni with Acanthamoeba castellanii. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 74, 371–381. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, X.T.; Qvortrup, K.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D.; Creuzenet, C. Effect of environmental stress factors on the uptake and survival of Campylobacter jejuni in Acanthamoeba castellanii. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, X.T.; Winding, A.; Qvortrup, K.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D.; Creuzenet, C. Survival of Campylobacter jejuni in co-culture with Acanthamoeba castellanii: Role of amoeba-mediated depletion of dissolved oxygen. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 2034–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadevall, A. Evolution of intracellular pathogens. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 62, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, R.O.; Galán, J.E. Campylobacter jejuni survives within epithelial cells by avoiding delivery to lysosomes. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habyarimana, F.; Al-Khodor, S.; Kalia, A.; Graham, J.E.; Price, C.T.; Garcia, M.T.; Kwaik, Y.A. Role for the Ankyrin eukaryotic-like genes of Legionella pneumophila in parasitism of protozoan hosts and human macrophages. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1460–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ó Cróinín, T.; Backert, S. Host epithelial cell invasion by Campylobacter jejuni: Trigger or zipper mechanism? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derengowski, L.S.; Paes, H.C.; Albuquerque, P.; Tavares, A.H.F.; Fernandes, L.; Silva-Pereira, I.; Casadevall, A. The transcriptional response of Cryptococcus neoformans to ingestion by Acanthamoeba castellanii and macrophages provides insights into the evolutionary adaptation to the mammalian host. Eukaryot. Cell 2013, 12, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmi, A.; Watson, E.; Sandu, P.; Gundogdu, O.; Mills, D.C.; Inglis, N.F.; Manson, E.; Imrie, L.; Bajaj-Elliott, M.; Wren, B.W. Campylobacter jejuni outer membrane vesicles play an important role in bacterial interactions with human intestinal epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 4089–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoll, P.; Rolando, M.; Gomez-Valero, L.; Buchrieser, C. From amoeba to macrophages: Exploring the molecular mechanisms of Legionella pneumophila infection in both hosts. In Molecular Mechanisms in Legionella Pathogenesis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Molmeret, M.; Horn, M.; Wagner, M.; Santic, M.; Kwaik, Y.A. Amoebae as training grounds for intracellular bacterial pathogens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardas, M.; Khan, N.A.; Alsam, S. Staphylococcus aureus exhibit similarities in their interactions with Acanthamoeba and ThP1 macrophage-like cells. Exp. Parasitol. 2012, 132, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khodor, S.; Kalachikov, S.; Morozova, I.; Price, C.T.; Kwaik, Y.A. The PmrA/PmrB two-component system of Legionella pneumophila is a global regulator required for intracellular replication within macrophages and protozoa. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-H.; Charpentier, X.; Torres-Urquidy, O.; McEvoy, M.M.; Rensing, C. The metal efflux island of Legionella pneumophila is not required for survival in macrophages and amoebas. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 301, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.T.; Hanford, H.E.; Al-Quadan, T.; Santic, M.; Shin, C.J.; Da’as, M.S.; Abu Kwaik, Y. Amoebae as training grounds for microbial pathogens. mBio 2024, 15, e00827-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansfield, L.S.; Schauer, D.B.; Fox, J.G. Animal models of Campylobacter jejuni infections. In Campylobacter; Nachamkin, I., Szymanski, C.M., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 367–379. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, R.O.; Galán, J.E. Interaction of Campylobacter jejuni with host cells. In Campylobacter; Nachamkin, I., Szymanski, C.M., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N.A. Acanthamoeba: Biology and Pathogenesis; British Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Anacarso, I.; Guerrieri, E.; Bondi, M.; de Niederhäusern, S.; Iseppi, R.; Sabia, C.; Messi, P. Influence of Legionella pneumophila and other water bacteria on the survival and growth of Acanthamoeba polyphaga. Arch. Microbiol. 2010, 192, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, C.M.; Clyne, M.; Bourke, B. Campylobacter jejuni adhere to and invade chicken intestinal epithelial cells in vitro. Microbiology 2007, 153, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasher, F.; Lehri, B.; Horney, M.F.; Stabler, R.A.; Wren, B.W. Survival of Campylobacter jejuni 11168H in Acanthamoeba castellanii provides mechanistic insight into host–pathogen interactions. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Sahin, O.; Michel, L.O.; Zhang, Q. Critical role of multidrug efflux pump CmeABC in bile resistance and in vivo colonization of Campylobacter jejuni. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 4250–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Quadan, T.; Price, C.T.; Kwaik, Y.A. Exploitation of evolutionarily conserved amoeba and mammalian processes by Legionella. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, W.; Gross, R. Intracellular survival strategies of mutualistic and parasitic prokaryotes. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harb, O.S.; Gao, L.Y.; Kwaik, Y.A. From protozoa to mammalian cells: A new paradigm in the life cycle of intracellular bacterial pathogens. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 2, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samarth, D.P.; Abbasi, A.Z.; Kwon, Y.M. Genetic Factors of Campylobacter jejuni Required for Its Interactions with Free-Living Amoeba. Pathogens 2025, 14, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060546
Samarth DP, Abbasi AZ, Kwon YM. Genetic Factors of Campylobacter jejuni Required for Its Interactions with Free-Living Amoeba. Pathogens. 2025; 14(6):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060546
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamarth, Deepti Pranay, Asim Z. Abbasi, and Young Min Kwon. 2025. "Genetic Factors of Campylobacter jejuni Required for Its Interactions with Free-Living Amoeba" Pathogens 14, no. 6: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060546
APA StyleSamarth, D. P., Abbasi, A. Z., & Kwon, Y. M. (2025). Genetic Factors of Campylobacter jejuni Required for Its Interactions with Free-Living Amoeba. Pathogens, 14(6), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060546





