Antimicrobial Resistant Staphylococcus spp., Escherichia coli, and Salmonella spp. in Food Handlers: A Global Review of Persistence, Transmission, and Mitigation Challenges
Abstract
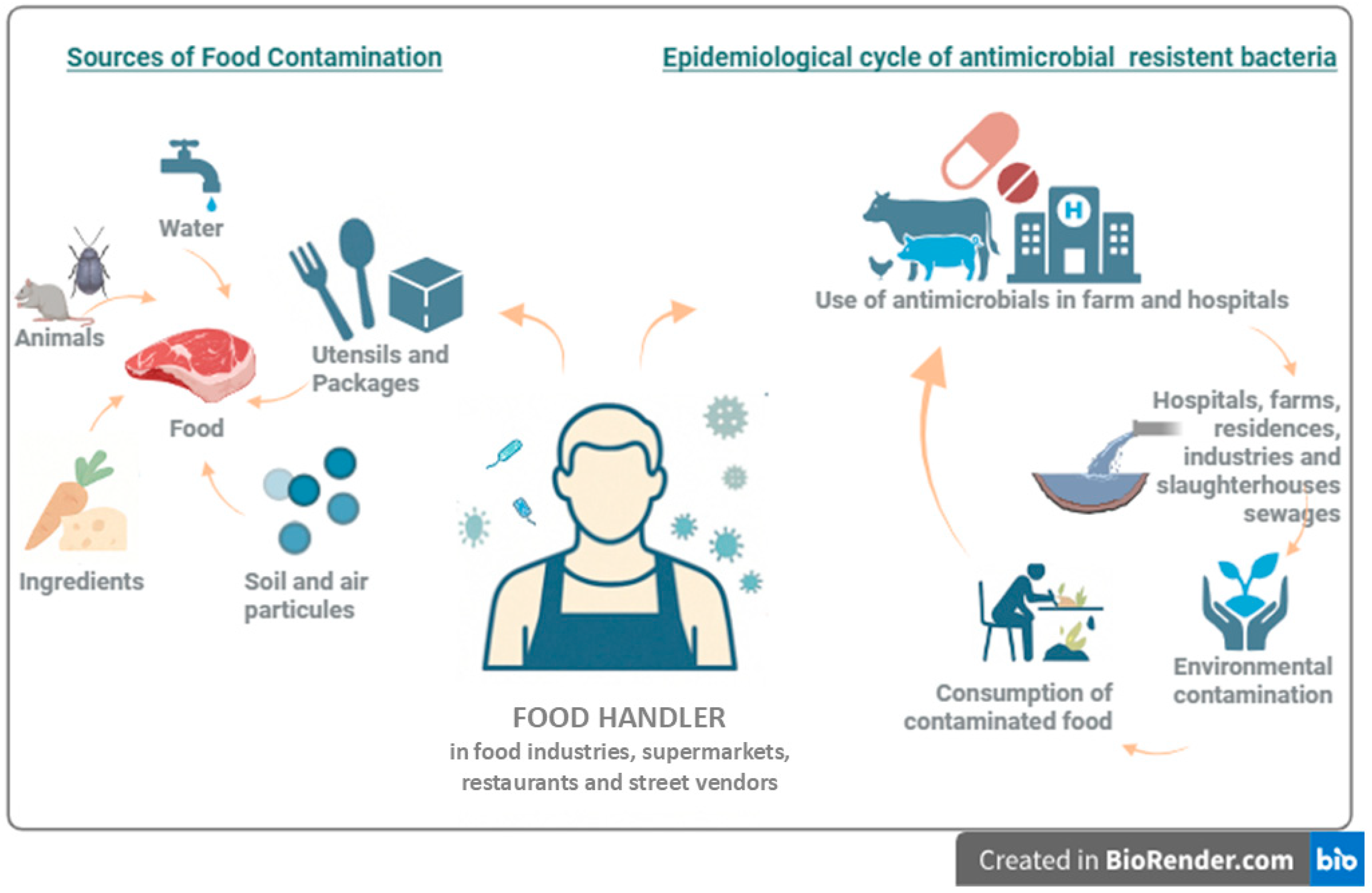
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Staphylococcus spp.
3.1. Overview of Staphylococcus Genus
3.2. Staphylococcus aureus as a Common Foodborne Pathogen
3.3. Colonization and Transmission Dynamics Related to Food Handlers
3.4. Antimicrobial Resistance in Staphylococcus spp. Isolated from Food Handlers
3.5. Outbreaks Linked to Antimicrobial Resistant S. aureus Isolated from a Food Handler
3.6. Prevention and Control Strategies
4. Escherichia coli
4.1. Overview of Escherichia coli
4.2. E. coli as a Common Foodborne Pathogen
4.3. Role of Food Handlers in E. coli Colonization and Transmission
4.4. Antimicrobial Resistance in E. coli Isolated from Food Handlers
4.5. Prevention and Control Strategies
5. Salmonella spp.
5.1. Overview of Salmonella spp.
5.2. Salmonella spp. as a Common Foodborne Pathogen
5.3. Role of Food Handlers in Salmonella spp. Colonization and Transmission
5.4. Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella spp. Isolated from Food Handlers
5.5. Outbreak Linked to Antimicrobial Resistant Salmonella spp. Isolated from a Food Handler
5.6. Prevention and Control Strategies
6. Comparative Analysis of Food Handler Associated Pathogens
7. Way Forward
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ho, C.S.; Wong, C.T.H.; Aung, T.T.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Mehta, J.S.; Rauz, S.; McNally, A.; Kintses, B.; Peacock, S.J.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Concise Update. Lancet Microbe 2025, 6, 100947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.W.K.; Millar, B.C.; Moore, J.E. Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 80, 11387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samtiya, M.; Matthews, K.R.; Dhewa, T.; Puniya, A.K. Antimicrobial Resistance in the Food Chain: Trends, Mechanisms, Pathways, and Possible Regulation Strategies. Foods 2022, 11, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulis, G.; Sayood, S.; Gandra, S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Current Status and Future Directions. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2021, 20, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghavi, M.; Vollset, S.E.; Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Gray, A.P.; Wool, E.E.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Mestrovic, T.; Smith, G.; Han, C.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis with Forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 18 April 2025).
- Caniça, M.; Manageiro, V.; Abriouel, H.; Moran-Gilad, J.; Franz, C.M.A.P. Antibiotic Resistance in Foodborne Bacteria. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 84, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, P.; Aseem, A.; Banjara, S.K.; Veleri, S. The Role of Food Chain in Antimicrobial Resistance Spread and One Health Approach to Reduce Risks. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 391–393, 110148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founou, L.L.; Founou, R.C.; Essack, S.Y. Antimicrobial Resistance in the Farm-To-Plate Continuum: More than a Food Safety Issue. Future Sci. OA 2021, 7, FSO692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghnia, O.H.; Rotimi, V.O.; Al-Sweih, N.A. Preponderance of BlaKPC-Carrying Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales among Fecal Isolates from Community Food Handlers in Kuwait. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 737828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencardino, D.; Amagliani, G.; Brandi, G. Carriage of Staphylococcus aureus among Food Handlers: An Ongoing Challenge in Public Health. Food Control 2021, 130, 108362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, W.; Guo, C.; Xiong, H.; Chen, X.; Jiao, X.; Su, J.; Mao, L.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Q. Prevalence, Serotypes, and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles among Salmonella Isolated from Food Catering Workers in Nantong, China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltai, N.O.; Yassine, H.M.; Al Thani, A.A.; Abu Madi, M.A.; Ismail, A.; Ibrahim, E.; Alali, W.Q. Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates from Fecal Samples of Food Handlers in Qatar. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghnia, O.H.; Rotimi, V.O.; Al-Sweih, N.A. Monitoring Antibiotic Resistance Profiles of Faecal Isolates of Enterobacteriaceae and the Prevalence of Carbapenem-Resistant Isolates among Food Handlers in Kuwait. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 25, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, T.; Genetu, D.; Shenkute, D.; Shenkutie, T.T.; Amare, Y.E.; Yitayew, B. Foodborne Pathogens and Antimicrobial Resistance in Ethiopia: An Urgent Call for Action on “One Health”. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 5265–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, A.; Arshadi, M.; Khosrojerdi, M.A.; Abedinzadeh, M.; Ganjalishahi, M.; Maleki, A.; Heidary, M.; Khoshnood, S. The Resistance Mechanisms of Bacteria against Ciprofloxacin and New Approaches for Enhancing the Efficacy of This Antibiotic. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1025633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. The Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in the WHO African Region in 2019: A Cross-Country Systematic Analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2023, 12, e201–e216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, J.M. Finger Licking Good? An Observational Study of Hand Hygiene Practices of Fast Food Restaurant Employees and Consumers. Br. Food J. 2019, 121, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudeja, P.; Singh, A. Food handlers. In Food Safety in the 21st Century, 1st ed.; Dudeja, P., Gupta, R.K., Minhas, A.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 269–280. ISBN 9780128017739. [Google Scholar]
- Azanaw, J.; Engdaw, G.T.; Dejene, H.; Bogale, S.; Degu, S. Food Hygiene Knowledge, and Practices and Their Associated Factors of Street Food Vendors in Gondar City, Northwest Ethiopia, 2021: A Cross-Sectional Study. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu-Wu, J.W.F.; Guadamuz-Mayorga, C.; Oviedo-Cerdas, D.; Zamora, W.J. Antibiotic Resistance and Food Safety: Perspectives on New Technologies and Molecules for Microbial Control in the Food Industry. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, A.M.; Amano, A.; Abrahim, A.; Getahun, M.; Ababor, S.; Kumie, A. Food Hygiene Practices and Associated Factors among Food Handlers Working in Food Establishments in the Bole Sub City, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2020, 13, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, E.C.D. Food Workers as Cause of Enteric Illnesses, Personal Hygiene and Employee Health. In Encyclopedia of Food Safety, 2nd ed.; Smithers, G.W., Ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 372–386. ISBN 9780128225202. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X. Urban Street Foods in Shijiazhuang City, China: Current Status, Safety Practices and Risk Mitigating Strategies. Food Control 2014, 41, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnan, N.Z.N.; Basha, R.K.; Amin, N.A.M.; Ramli, S.H.M.; Tang, J.Y.H.; Aziz, N.A. Analysis of the Most Frequent Nonconformance Aspects Related to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) among Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in the Food Industry and Their Main Factors. Food Control 2022, 141, 109205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Ning, J.; Ahmed, S.; Huang, J.; Ullah, R.; An, B.; Hao, H.; Dai, M.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Selection and Dissemination of Antimicrobial Resistance in Agri-Food Production. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Ramos, C.; Monteiro, V.; Santos, J.; Fernandes, P. Virulence Potential and Antibiotic Susceptibility of S. aureus Strains Isolated from Food Handlers. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.; Ojha, A.K.; Dolma, K.G.; Majumdar, T.; Sarmah, P.; Hazarika, S.; Modi, D.; Gogoi, D.; Das, S.; Ramamurthy, T. Monitoring the Potential Dissemination of Antimicrobial Resistance in Foods, Environment, and Clinical Samples: A One Health Prospective. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlet, C.P.; Brown, M.M.; Horswill, A.R. Commensal Staphylococci Influence Staphylococcus aureus Skin Colonization and Disease. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laux, C.; Peschel, A.; Krismer, B. Staphylococcus aureus Colonization of the Human Nose and Interaction with Other Microbiome Members. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M. Staphylococcus aureus: A Major Pathogen of Food Poisoning. Nutr. Food Process. 2022, 5, 01–03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieza, M.Y.R.; Bonsaglia, E.C.R.; Rall, V.L.M.; Santos, M.V.d.; Silva, N.C.C. Staphylococcal Enterotoxins: Description and Importance in Food. Pathogens 2024, 13, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento Pereira, G.; da Silva Rosa, R.; Dias, A.A.; Santos, D.J.; Seribelli, A.A.; Pinheiro-Hubinger, L.; Eller, L.K.W.; de Carvalho, T.B.; Pereira, V.C. Characterization of the Virulence, Agr Typing and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Food Handlers in Brazil. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 26, 102698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, M.; San, T.; Aye, M.; Mya, S.; Maw, W.; Zan, K.; Htut, W.; Kawaguchiya, M.; Urushibara, N.; Kobayashi, N. Prevalence and Genetic Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus argenteus Isolates Harboring Panton-Valentine Leukocidin, Enterotoxins, and TSST-1 Genes from Food Handlers in Myanmar. Toxins 2017, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber, T.; Samir, M.; El-Mekkawy, R.M.; Ariny, E.; El-Sayed, S.R.; Enan, G.; Abdelatif, S.H.; Askora, A.; Merwad, A.M.A.; Tartor, Y.H. Methicillin- and Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Humans and Ready-To-Eat Meat: Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance and Biofilm Formation Ability. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 735494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, M.; Kerorsa, G.B.; Marami, L.M.; Kandi, V. Epidemiology, Pathogenicity, Animal Infections, Antibiotic Resistance, Public Health Significance, and Economic Impact of Staphylococcus aureus: A Comprehensive Review. Am. J. Public Health Res. 2020, 8, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léguillier, V.; Pinamonti, D.; Chang, C.-M.; Gunjan; Mukherjee, R.; Himanshu; Cossetini, A.; Manzano, M.; Anba-Mondoloni, J.; Malet-Villemagne, J.; et al. A Review and Meta-Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus Prevalence in Foods. Microbe 2024, 4, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadariya, J.; Smith, T.C.; Thapaliya, D. Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcal Food-Borne Disease: An Ongoing Challenge in Public Health. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 827965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Riemann, M.; Juneja, V.K.; Mishra, A. Evaluating the Growth of Staphylococcus aureus during Slow Cooking of Beef and Turkey Formulations from 10 °C to 54.4 °C for an Extended Time. J. Food Prot. 2025, 88, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshebrawy, H.A.; Kasem, N.G.; Sallam, K.I. Methicillin- and Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Chicken Carcasses, Ready-To-Eat Chicken Meat Sandwiches, and Buffalo Milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2025, 427, 110968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Dou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, H.; Wen, K.; Yu, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. A Comprehensive Review on the Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins in Food Samples. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 23, e13264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Duan, N.; Gu, H.; Hao, L.; Ye, H.; Gong, W.; Wang, Z. A Review of the Methods for Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins. Toxins 2016, 8, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencardino, D.; Vitali, L.A. Staphylococcus aureus Carriage among Food Handlers in a Pasta Company: Pattern of Virulence and Resistance to Linezolid. Food Control 2019, 96, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, G. Staphylococcus aureus Infection: Pathogenesis and Antimicrobial Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-T.; Chen, E.-Z.; Yang, L.; Peng, C.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Chen, D.-Q. Emerging Resistance Mechanisms for 4 Types of Common Anti-MRSA Antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus: A Comprehensive Review. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 156, 104915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawani-Luwaj, E.; Tolulope, A.; Baratuaipre, I. Risk of Staphylococcus aureus Nasal Carriage among Food Handlers: Implications for Foodborne Illnesses. J. Food Saf. Hyg. 2024, 10, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, C.R.P.; de Aquino, N.S.M.; de Moraes Vieira, J.; Gonçalves, C.T.H.; Tondo, E.C. Assessing the Behavior of Food Handlers Wearing Face Masks and the Passage of Bacteria through Disposable Masks. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2025, 56, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.; Boost, M.V.; O’Donoghue, M.M. Tracking Sources of Staphylococcus aureus Hand Contamination in Food Handlers by Spa Typing. Am. J. Infect. Control 2015, 43, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahros, M.A.; Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Sallam, K.I. Multidrug-, Methicillin-, and Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Ready-To-Eat Meat Sandwiches: An Ongoing Food and Public Health Concern. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 346, 109165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galié, S.; García-Gutiérrez, C.; Miguélez, E.M.; Villar, C.J.; Lombó, F. Biofilms in the Food Industry: Health Aspects and Control Methods. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, M.T.; Getu, A.A. Assessment of Bacteriological Quality and Safety of Raw Meat at Slaughterhouse and Butchers’ Shop (Retail Outlets) in Assosa Town, Beneshangul Gumuz Regional State, Western Ethiopia. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argudín, M.A.; Mendoza, M.C.; González-Hevia, M.A.; Bances, M.; Guerra, B.; Rodicio, M.R. Genotypes, Exotoxin Gene Content, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus Strains Recovered from Foods and Food Handlers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 2930–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptistão, L.G.; Silva, N.C.C.; Bonsaglia, E.C.R.; Rossi, B.F.; Castilho, I.G.; Fernandes, A.; Rall, V.L.M. Presence of Immune Evasion Cluster and Molecular Typing of Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Food Handlers. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, A.; Santos, C.; Meireles, H.; Silva, J.; Teixeira, P. Food Handlers as Potential Sources of Dissemination of Virulent Strains of Staphylococcus aureus in the Community. J. Infect. Public Health 2016, 9, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adefrash, K.; Sharew, B.; Amare, W.; Shibabaw, A. Bacterial Foodborne Illness and Escherichia coli O157:H7 Strain Infection among Asymptomatic Food Handlers in Northeast Ethiopia: Implication for Hygienic Practices and Mass-Screening. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fooladvand, S.; Sarmadian, H.; Habibi, D.; van Belkum, A.; Ghaznavi-Rad, E. High Prevalence of Methicillin Resistant and Enterotoxin Gene-Positive Staphylococcus aureus among Nasally Colonized Food Handlers in Central Iran. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, W.-L.; Mahyudin, N.A.; Amin-Nordin, S.; Radu, S.; Abdul-Mutalib, N.A. Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus among Cooked Food and Food Handlers Associated with Their Occupational Information in Klang Valley, Malaysia. Food Control 2021, 124, 107872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touimi, G.B.; Bennani, L.; Berrada, S.; Moussa, B.; Bennani, B. Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance Profiles of Staphylococcus sp. Isolated from Food, Food Contact Surfaces and Food Handlers in a Moroccan Hospital Kitchen. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, A.A.; Amala, S.E.; Nwokah, E.G. Enterotoxin Production and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus Among Food Handlers in a Sub-Urban Setting in Rivers State, Nigeria. Eur. J. Pharm. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.L.; Lee, H.Y.; Mahyudin, N.A. Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Food Handler’s Hands. Food Control 2014, 44, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.S.; Costa, W.L.R.; Cerqueira, E.S.; Carvalho, J.S.; Oliveira, L.C.; Almeida, R.C.C. Food Handler-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Public Hospitals in Salvador, Brazil. Food Control 2014, 37, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Meng, J.; Lei, G.; Jia, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lv, H.; et al. Prevalence, Molecular Characterization, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Different Origins in Sichuan Province, China, 2007–2015. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.; Kamal-Dine, K.; El Omari, K.; Rafei, R.; Dabboussi, F.; Hamze, M. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus Methicillin-Sensitive and Methicillin-Resistant Nasal Carriage in Food Handlers in Lebanon: A Potential Source of Transmission of Virulent Strains in the Community. Access Microbiol. 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anowai, C.O.; Agarry, O.O.; Akin-Osanaiye, B.C. Antibiotic Susceptibility Profile of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Food Handlers in Abuja, Nigeria: A Review. World J. Res. Rev. 2019, 9, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; O’Donoghue, M.M.; Boost, M.V. Occupational Exposure to Raw Meat: A Newly-Recognized Risk Factor for Staphylococcus aureus Nasal Colonization amongst Food Handlers. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Sawant, S.; Karodia, N.; Rahman, A. Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm: Morphology, Genetics, Pathogenesis and Treatment Strategies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Sahore, S.; Kaur, P.; Rani, A.; Ray, P. Penetration Barrier Contributes to Bacterial Biofilm-Associated Resistance against Only Select Antibiotics, and Exhibits Genus-, Strain- and Antibiotic-Specific Differences. Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftw056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savini, F.; Romano, A.; Giacometti, F.; Indio, V.; Pitti, M.; Decastelli, L.; Devalle, P.L.; Rossella, S.; Miaglia, S.; Serraino, A. Investigation of a Staphylococcus aureus Sequence Type 72 Food Poisoning Outbreak Associated with Food-Handler Contamination in Italy. Zoonoses Public Health 2023, 70, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.F. An Outbreak of Community-Acquired Foodborne Illness Caused by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarpellon, M.N.; Gales, A.C.; Sasaki, A.L.; Selhorst, G.J.; Menegucci, T.C.; Cardoso, C.L.; Garcia, L.B.; Tognim, M.C.B. Survival of Vancomycin-Intermediate Staphylococcus aureus on Hospital Surfaces. J. Hosp. Infect. 2015, 90, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chieffi, D.; Fanelli, F.; Fusco, V. Antimicrobial and Biocide Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: Genomic Features, Decontamination Strategies, and the Role of S. aureus Complex-Related Species, with a Focus on Ready-To-Eat Food and Food-Contact Surfaces. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 1165871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Agarwal, J.K.; Kumar, A.; Ingole, K.V. Hand Contamination among Food Handlers: A Study on the Assessment of Food Handlers in Canteen of Various Hospitals in Solapur City, Maharashtra. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 15, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demisie, K.N.; Melese, D.M. Assessment of bacterial and parasitic contamination of fruits gathered from specific local markets in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1402898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, R.; Cheng, E.J.; Gan, P.; Oh, J.Q.; Aung, K.T. Microbiological Profiles of Disposable Gloves Used for Handling Ready-To-Eat Foods. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moges, M.; Rodland, E.K.; Legesse, T.; Argaw, A. Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Staphylococcus aureus and Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Street Foods in Selected Towns of Ethiopia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piewngam, P.; Otto, M. Staphylococcus aureus Colonisation and Strategies for Decolonisation. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, e606–e618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septimus, E. Decolonization to Prevent Healthcare-Associated Infections 2024 State-of-the-Art Review. Med. Res. Arch. 2024, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.; Almeida, M.; Gomes, J.J.F.; Henriques, A.R. Specific Personal Hygiene Procedures and Practices in Food Handlers—A Cross-Sectional Study in Butcher and Fishmonger Shops in Almada. Hygiene 2024, 4, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.H.; Nazir, K.H.M.N.H.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Kabir, A.; Sarker, S.A.; Siddique, M.P.; Ashour, H.M. Molecular Detection of Vancomycin and Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Food Processing Environments. One Health 2021, 13, 100276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavaraju, M.; Gunashree, B.S. Escherichia coli: An Overview of Main Characteristics. In Escherichia coli—Old and New Insights; Erjavec, M.S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023; ISBN 978-1-83969-870-5. [Google Scholar]
- Puvača, N.; de Llanos Frutos, R. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Humans and Pet Animals. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.-Y.I.; Habib, I. Pathogenic, E. coli in the Food Chain across the Arab Countries: A Descriptive Review. Foods 2023, 12, 3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakbin, B.; Brück, W.M.; Rossen, J.W.A. Virulence Factors of Enteric Pathogenic Escherichia coli: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, P.; Bandsode, V.; Singh, A.; Mendem, S.K.; Semmler, T.; Alam, M.; Ahmed, N. Genomic Insights into Virulence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Adaptation Acumen of Escherichia coli Isolated from an Urban Environment. MBio 2024, 15, e0354523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, L.; Brusa, V.; Rodríguez, R.; Signorini, M.; Oteiza, J.M.; Leotta, G.A. Escherichia coli in food products. In Escherichia coli in the Americas; Torres, A.G., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 173–203. ISBN 978-3-319-45092-6. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.A.; Hashem, H.R.; El-Mahallawy, H.S.; Abdelrahman, A.A.; Zaki, H.M.; Azab, M.M. Characterization of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli from Diarrhoeic Patients with Particular Reference to Production of Shiga-like Toxin. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 166, 105538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turunen, K.; Antikainen, J.; Lääveri, T.; Kirveskari, J.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; Kantele, A. Clinical Aspects of Heat-Labile and Heat-Stable Toxin-Producing Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: A Prospective Study among Finnish Travellers. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 38, 101855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mare, A.D.; Ciurea, C.N.; Man, A.; Tudor, B.; Moldovan, V.; Decean, L.; Toma, F. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, a Summary of the Literature. Gastroenterol. Insights 2021, 12, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.C.B.; Tanabe, R.H.S.; Vieira, M.A.; Cergole-Novella, M.C.; dos Santos, L.F.; Gomes, T.A.T.; Elias, W.P.; Hernandes, R.T. Analysis of the Virulence Profile and Phenotypic Features of Typical and Atypical Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (EAEC) Isolated from Diarrheal Patients in Brazil. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, G.; Dümen, E. Escherichia coli and food safety. In The Universe of Escherichia coli; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera-Sosa, L.; Ochoa, T.J. Escherichia coli diarrhea. In Hunter’s Tropical Medicine and Emerging Infectious Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 481–485. ISBN 978-0-323-55512-8. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Medina, M. Special Issue: Pathogenic Escherichia coli: Infections and Therapies. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonyar, L.A.; Smith, R.M.; Girón, J.A.; Zachos, N.C.; Ruiz-Perez, F.; Nataro, J.P. Aggregative Adherence Fimbriae II of Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli Are Required for Adherence and Barrier Disruption during Infection of Human Colonoids. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Wang, D.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, B.K.; Lin, S. Control Measurements of Escherichia coli Biofilm: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorić, O.; Pezo, L.; Šarić, L.; Kolarov, V.; Varga, A.; Čabarkapa, I.; Kocić-Tanackov, S. Comparison of the Efficiency of Selected Disinfectants against Planktonic and Biofilm Populations of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toushik, S.H.; Roy, A.; Alam, M.; Rahman, U.H.; Nath, N.K.; Nahar, S.; Matubber, B.; Uddin, M.J.; Roy, P.K. Pernicious Attitude of Microbial Biofilms in Agri-Farm Industries: Acquisitions and Challenges of Existing Antibiofilm Approaches. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xu, Y.; Guan, H.; Wang, D. Research Advances on the Contamination of Vegetables by Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli: Pathways, Processes and Interaction. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 64, 4833–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Suo, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Chen, S.; Ye, X.; Liu, D. Significance of Viable but Nonculturable Escherichia coli: Induction, Detection, and Control. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwar, A.; Aslam, B.; Rasool, M.H.; Bekhit, M.M.S.; Sasanya, J. A Health Threat from Farm to Fork: Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Co-Harboring BlaNDM-1 and Mcr-1 in Various Sources of the Food Supply Chain. Pathogens 2024, 13, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kintz, E.; Brainard, J.; Hooper, L.; Hunter, P. Transmission Pathways for Sporadic Shiga-Toxin Producing E. coli Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Aljuffali, I.A.; Fang, J.-Y. Current Pathogenic Escherichia coli Foodborne Outbreak Cases and Therapy Development. Arch. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamandane, A.; Malfeito-Ferreira, M.; Brito, L. The Socioeconomic Factors of Street Food Vending in Developing Countries and Its Implications for Public Health: A Systematic Review. Foods 2023, 12, 3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhanu, L.; Mereta, S.T.; Gume, B.; Kassa, T.; Berihun, G.; Dadi, L.S.; Suleman, S.; Tegegne, D.; Getaneh, A.; Bedru, H. Effect of Microbial Quality of Washing Water on Hand Hygiene Status of Food Handlers in Jimma Town: Implication for Food Hygiene and Safety. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2021, 14, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkemngong, C.; Teska, P. Biofilms, Mobile Genetic Elements and the Persistence of Pathogens on Environmental Surfaces in Healthcare and Food Processing Environments. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1405428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanna, D.; Eryando, T.; Kusuma, A. The Relationship Between Knowledge and Behaviour of Food Handlers to Escherichia coli Contamination in Serving Foods in a Campus. World Appl. Sci. J. 2015, 33, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Rosales, A.P.; Linnemann, A.R.; Luning, P.A. Food Safety Knowledge, Self-Reported Hygiene Practices, and Street Food Vendors’ Perceptions of Current Hygiene Facilities and Services—An Ecuadorean Case. Food Control 2023, 144, 109377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Soares, K.; Ribeiro, C.; Esteves, A. Evaluation of the Effects of Food Safety Training on the Microbiological Load Present in Equipment, Surfaces, Utensils, and Food Manipulator’s Hands in Restaurants. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woh, P.Y.; Thong, K.L.; Behnke, J.M.; Lewis, J.W.; Zain, S.N.M. Characterization of Nontyphoidal Salmonella Isolates from Asymptomatic Migrant Food Handlers in Peninsular Malaysia. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, H.; Kanamori, H.; Kudo, H.; Kuroki, Y.; Higashi, S.; Oka, K.; Takahashi, M.; Yoshida, M.; Oshima, K.; Aoyagi, T.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli from Patients and Asymptomatic Food Handlers in Japan. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diercke, M.; Kirchner, M.; Claussen, K.; Mayr, E.; Strotmann, I.; Frangenberg, J.; Schiffmann, A.; Bettge-Weller, G.; Arvand, M.; Uphoff, H. Transmission of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O104:H4 at a Family Party Possibly due to Contamination by a Food Handler, Germany 2011. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abey, S.L.; Teka, M.; Bitew, A.B.; Molla, W.; Ejo, M.; Dagnaw, G.G.; Adugna, T.; Nigatu, S.; Mengistu, B.A.; Kinde, M.Z.; et al. Detection and antibiogram profile of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli isolated from two abattoir settings in northwest Ethiopia: A one health perspective. One Health Outlook 2024, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzitey, F.; Huda, N.; Shariff, A.H.M. Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Escherichia coli from Raw Meats, Ready-to-Eat Meats, and Their Related Samples in One Health Context. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovdey, R.; Sargeant, J.M.; Fisman, D.N.; Greer, A.L. Examining the Role of Person-To-Person Transmission during a Verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli Outbreak in Ontario, Canada. BMC Res. Notes 2022, 15, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amare, A.; Eshetie, S.; Kasew, D.; Moges, F. High Prevalence of Fecal Carriage of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase and Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae among Food Handlers at the University of Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Eifert, J.D.; Etaka, C.A.; Strawn, L.K. Recovery and Survival of Aerosolized Escherichia coli and Enterococcus Faecium on Food-Grade Rubber, HDPE Plastic, Stainless Steel, and Waxed Cardboard. J. Food Saf. 2024, 44, e70002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diriba, K.; Awulachew, E.; Tekele, L.; Ashuro, Z. Fecal Carriage Rate of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella Pneumoniae among Apparently Health Food Handlers in Dilla University Student Cafeteria. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3791–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanneh, B.; Kebbeh, A.; Jallow, H.S.; Camara, Y.; Mwamakamba, L.W.; Ceesay, I.F.; Barrow, E.; Sowe, F.O.; Sambou, S.M.; Baldeh, I.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Faecal Carriage of Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase Producing Enterobacteriaceae among Food Handlers in Lower Basic Schools in West Coast Region of the Gambia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suswati, E.; Supangat; Indreswari, L.; U’alifa, F.N.; Nabila, F.; Hertian, I.G.P. Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolated from Jember Hospital Food Handler in Indonesia. Bali Med. J. 2023, 12, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Cui, S.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Lin, L.; Hu, C.; Jin, S.; Ye, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, Y. Characterization Of Escherichia coli Isolates from Healthy Food Handlers in Hospital. Microb. Drug Resist. 2011, 17, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghita, B.T.; Bennani, L.; Berrada, S.; Benboubker, M.; Bennani, B. Molecular Serotyping and Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Escherichia coli Isolated in Hospital Catering Service in Morocco. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 5961521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, A.O.; Kenya, E.U.; Mbithi, J.J.N.; Ng’ayo, M.O. Pathogenic Escherichia coli and Food Handlers in Luxury Hotels in Nairobi, Kenya. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2009, 7, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallem, N.; Hammami, A.; Mnif, B. Trends in Human Intestinal Carriage of ESBL- and Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales among Food Handlers in Tunisia: Emergence of C1-M27-ST131 Subclades, BlaOXA-48 and BlaNDM. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 2142–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasugba, O.; Gardner, A.; Mitchell, B.G.; Mnatzaganian, G. Ciprofloxacin Resistance in Community- and Hospital-Acquired Escherichia coli Urinary Tract Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicar, E.K.; Alo, D.B.; Koyiri, V.C.; Opare-Asamoah, K.; Obeng-Bempong, M.; Mensah, G.I. Carriage of Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria and Associated Factors among Food Handlers in Tamale Metropolis, Ghana: Implications for Food Safety. Microbiol. Insights 2023, 16, 11786361221150695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrollahian, S.; Graham, J.P.; Halaji, M. A Review of the Mechanisms That Confer Antibiotic Resistance in Pathotypes of E. coli. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1387497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurittu, P.; Khakipoor, B.; Aarnio, M.; Nykäsenoja, S.; Brouwer, M.; Myllyniemi, A.-L.; Vatunen, E.; Heikinheimo, A. Plasmid-Borne and Chromosomal ESBL/AmpC Genes in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Global Food Products. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 592291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, N.; Hashiguchi, T.C.O.; Cecchini, M. Food safety policies and their effectiveness to prevent foodborne diseases in catering establishments: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Onofre, N.; Soler, C.; Merino-Torres, J.F.; Soriano, J.M. “Five Keys to Safer Food” and COVID-19. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, A.; Van Doren, J.M. An Agent-Based Model for Pathogen Persistence and Cross-Contamination Dynamics in a Food Facility. Risk Anal. 2018, 39, 992–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.; Fu, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, T.; Li, Y. Mechanisms of Action of Luteolin against Single- and Dual-Species of Escherichia coli and Enterobacter Cloacae and Its Antibiofilm Activities. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 193, 1397–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Castillo, A.G.; González-Rivas, F.; Rodríguez-Jerez, J.J. Bactericidal Efficacy of Hydrogen Peroxide-Based Disinfectants against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria on Stainless Steel Surfaces. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2351–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cota, A.S.; de Freitas, R.S.G.; Lefèvre, F.; Stedefeldt, E. Food handlers’ lack of knowledge, and misunderstanding of safe food temperatures: An analysis using the theory of social representations. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, P.; Checinska Sielaff, A.; Rasco, B.; Smith, S. Efficacy of Food Safety Training in Commercial Food Service. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, J.; Khalil, T.; Khalil, M.; Shakeel, N.; Shukat, R.; Aleem, M.T.; Shaukat, I.; Shaukat, A.; Asrar, R.; Sharafat, H. Impact of Food-Borne Diseases in Association to One Health Concept and Efforts of their Prevention. In One Health Triad; Khan, A., Abbas, R.Z., Aguilar-Marcelino, L., Saeed, N.M., Younus, M., Eds.; Unique Scientific Publishers: Faisalabad, Pakistan, 2023; Volume 1, pp. 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madjdian, D.S.; van Asseldonk, M.; Ilboudo, G.; Dione, M.; Ouedraogo, A.-A.; Roesel, K.; Grace, D.; Talsma, E.F.; Knight-Jones, T.J.D.; de Vet, E. Training and tool supply to enhance food safety behaviors among ready-to-eat chicken vendors in informal markets in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso: A randomized-controlled trial. Food Control 2024, 163, 110510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, A.; Anis, S.H.; Mushfiq, D.M. A Cross-Sectional Study on Food Safety Knowledge, Practices, and Associated Factors among Meat Handlers in Kandahar City, Afghanistan. J. Consum. Prot. Food Saf. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehuwa, O.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Jaiswal, S. Salmonella, Food Safety and Food Handling Practices. Foods 2021, 10, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naushad, S.; Ogunremi, D.; Huang, H. Salmonella: A Brief Review. In Salmonella—Perspectives for Low-Cost Prevention, Control and Treatment; Huang, H., Naushad, S., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023; pp. 1–22. ISBN 978-1-83962-474-2. [Google Scholar]
- Teklemariam, A.D.; Al-Hindi, R.R.; Albiheyri, R.S.; Alharbi, M.G.; Alghamdi, M.A.; Filimban, A.A.R.; Al Mutiri, A.S.; Al-Alyani, A.M.; Alseghayer, M.S.; Almaneea, A.M.; et al. Human Salmonellosis: A Continuous Global Threat in the Farm-to-Fork Food Safety Continuum. Foods 2023, 12, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Qazi, I.H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, G.; Han, H. Salmonella Virulence and Immune Escape. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, A.M.P.; Ferrari, R.G.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Virulence Factors in Salmonella Typhimurium: The Sagacity of a Bacterium. Curr. Microbiol. 2019, 76, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, M.J. Salmonella Bloodstream Infections. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, B.M.; Melo-Gonzalez, F.; Salazar, G.A.; Porto, B.N.; Riedel, C.A.; Kalergis, A.M.; Bueno, S.M. New Insights on the Early Interaction between Typhoid and Non-Typhoid Salmonella Serovars and the Host Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 647044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, G.L.; Papa, M.I. Salmonella spp. Infection—A Continuous Threat Worldwide. GERMS 2021, 11, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikmeier, D.; Medus, C.; Smith, K. Incubation Period for Outbreak-Associated, Non-Typhoidal Salmonellosis Cases, Minnesota, 2000–2015. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierer, J. Invasive Non-Typhoidal Salmonella (INTS) Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.; Mylona, E.; Frankel, G. Typhoidal Salmonella: Distinctive Virulence Factors and Pathogenesis. Cell. Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Mor, O. Persistent Infection and Long-Term Carriage of Typhoidal and Nontyphoidal Salmonellae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 32, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Als, D.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Arora, P.; Gaffey, M.F.; Campisi, S.; Velummailum, R.; Zareef, F.; Bhutta, Z.A. Global Trends in Typhoidal Salmonellosis: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99 (Suppl. S3), 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M. The Global Burden of NontyphoidalSalmonellaGastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. Mechanisms for the Invasion and Dissemination of Salmonella. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 2022, 2655801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Li, R.; Xiao, X.; Wu, H. Global Transcriptomic Acid Tolerance Response in Salmonella Enteritidis. LWT 2018, 92, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, G.; Xia, P.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, C.; Meng, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhu, G. Fimbriae and Related Receptors for Salmonella Enteritidis. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 126, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.; Zhang, P.; Piao, R.; Wang, Y. Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 (SPI-1) and Its Complex Regulatory Network. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Liang, Z.; He, S.; Chin, F.W.L.; Huang, D.; Hong, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, D. Salmonella Dry Surface Biofilm: Morphology, Single-Cell Landscape, and Sanitization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e0162324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.; Lambert, P.A.; Stedman, Y.; Hilton, A.C. Combined Effect of Temperature and Relative Humidity on the Survival of Salmonella Isolates on Stainless Steel Coupons. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormsby, M.J.; White, H.L.; Metcalf, R.; Oliver, D.M.; Feasey, N.A.; Quilliam, R.S. Enduring Pathogenicity of African Strains of Salmonella on Plastics and Glass in Simulated Peri-Urban Environmental Waste Piles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Peng, H.; Liu, J.; Nguyen, T.H.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Shen, C. Occurrence and Quantification of Culturable and Viable but Non-Culturable (VBNC) Pathogens in Biofilm on Different Pipes from a Metropolitan Drinking Water Distribution System. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, D.F.; Lincopan, N.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Landgraf, M. Current Insights on High Priority Antibiotic-Resistant Salmonella enterica in Food and Foodstuffs: A Review. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 26, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Youn, S.; Jeong, O.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Jeong, J.; Kwon, Y.; Kang, M. Sequential Transmission of Salmonella in the Slaughtering Process of Chicken in Korea. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Rasschaert, G.; Zutter, L.D.; Mattheus, W.; Reu, K.D. Identification of the Source for Salmonella Contamination of Carcasses in a Large Pig Slaughterhouse. Pathogens 2021, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Yoon, Y.; Yoon, J.-W.; Oh, S.-W.; Lee, S.; Lee, H. Salmonella Risk Assessment in Poultry Meat from Farm to Consumer in Korea. Foods 2023, 12, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, B. Fresh Vegetables and Fruit as a Source of Salmonella Bacteria. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2022, 30, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, G.; Mitiku, H.; Teklemariam, Z.; Marami, D. Salmonella and Shigella among Asymptomatic Street Food Vendors in the Dire Dawa City, Eastern Ethiopia: Prevalence, Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern, and Associated Factors. Environ. Health Insights 2019, 13, 117863021985358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumalo, A.; Gambura, E.; Dodicho, T.; Ahmed, K.S.; Balcha, T.; Beshir, B.; Abraham, M. Prevalence of Intestinal Parasites and Salmonella Typhi among Food Handlers Working in Catering Establishments of Public Institutes Found in Dawuro Zone, South-Western Ethiopia. J. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Tanjia, N.; Mitra, A.K.; Hossain, A.; Jasika, M.T.; Susi, S.S.; Hossain, S.J. Inadequate food safety knowledge and hygiene practices among street food vendors in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh-Van, B.; Vuong-Thao, V.; Huynh-Thi-Thanh, T.; Dang-Xuan, S.; Huynh-Van, T.; Tran-To, L.; Nguyen-Thi-Thao, N.; Huynh-Bach, C.; Nguyen-Viet, H. Factors Associated with Food Safety Compliance among Street Food Vendors in Can Tho City, Vietnam: Implications for Intervention Activity Design and Implementation. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mama, M.; Alemu, G. Prevalence, Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns and Associated Risk Factors of Shigella and Salmonella among Food Handlers in Arba Minch University, South Ethiopia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donachie, A.; Melillo, T.; Bubba, L.; Hartman, H.; Borg, M.-L. National outbreak of Salmonella Give linked to a local food manufacturer in Malta, October 2016. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengist, A.; Mengistu, G.; Reta, A. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Salmonella and Shigella among Food Handlers in Catering Establishments at Debre Markos University, Northwest Ethiopia. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 75, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, D.T.; Braga, A.R.C.; de Camargo Passos, E.; Stedefeldt, E.; de Rosso, V.V. The Existence of Optimistic Bias about Foodborne Disease by Food Handlers and Its Association with Training Participation and Food Safety Performance. Food Res. Int. 2015, 75, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, F.B.; Wada, F.W.; Anjulo, A.A.; Koyra, H.C.; Tufa, E.G. Burden of Intestinal Pathogens and Associated Factors among Asymptomatic Food Handlers in South Ethiopia: Emphasis on Salmonellosis. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getie, M.; Abebe, W.; Tessema, B. Prevalence of Enteric Bacteria and Their Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns among Food Handlers in Gondar Town, Northwest Ethiopia. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garedew-Kifelew, L.; Wondafrash, N.; Feleke, A. Identification of Drug-Resistant Salmonella from Food Handlers at the University of Gondar, Ethiopia. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diriba, K.; Awulachew, E.; Ashuro, Z. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern of Salmonella, Shigella, and Intestinal Parasites and Associated Factor among Food Handlers in Dilla University Student Cafeteria, Dilla, Ethiopia. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legese, H.; Kahsay, T.; Gebrewahd, A.; Berhe, B.; Fseha, B.; Tadesse, S.; Gebremariam, G.; Negash, H.; Mardu, F.; Tesfay, K. Prevalence, Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern, and Associated Factors of Salmonella and Shigella among Food Handlers in Adigrat University Student’s Cafeteria, Northern Ethiopia, 2018. Trop. Dis. Travel Med. Vaccines 2020, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marami, D.; Hailu, K.; Tolera, M. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Salmonella and Shigella Species among Asymptomatic Food Handlers Working in Haramaya University Cafeterias, Eastern Ethiopia. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesigat, T.; Jemal, M.; Birhan, W. Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Salmonella, Shigella, and Intestinal Parasites among Food Handlers in Motta Town, North West Ethiopia. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 6425946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amare, A.; Eshetie, S.; Kasew, D.; Amare, A.; Abebe, W.; Moges, F. Prevalence of Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., and Intestinal Parasites among Food Handlers Working in University of Gondar Student’s Cafeteria, Northwest Ethiopia. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1370338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, Y.; Kakizawa, H.; Baba, Y.; Ito, T.; Haremaki, Y.; Yonemichi, M.; Ikeda, T.; Kuroda, M.; Ohya, K.; Hara-Kudo, Y.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella Isolated from Food Workers and Chicken Products in Japan. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemura, H.; Sakatsume, E.; Sekizuka, T.; Yokoyama, H.; Hamada, K.; Etoh, Y.; Carle, Y.; Mizumoto, S.; Hirai, S.; Matsui, M.; et al. Food Workers as a Reservoir of Extended-Spectrum-Cephalosporin-Resistant Salmonella Strains in Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00072-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, T.R.; Bibi, S.; Mustufa, M.A.; Ayaz, S.M.; Khan, A. High Prevalence of Typhoidal Salmonella enterica Serovars Excreting Food Handlers in Karachi-Pakistan: A Probable Factor for Regional Typhoid Endemicity. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2015, 33, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohata, N.; Noda, M.; Ohta, K.; Hatta, M.; Nakayama, T. Prevalence of Streptomycin and Tetracycline Resistance and Increased Transmissible Third-Generation Cephalosporin Resistance in Salmonella enterica Isolates Derived from Food Handlers in Japan from 2006 to 2021. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2024, 135, lxae236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Tang, Y.; Li, Q.; Jiao, X. A Multidrug-Resistant Monophasic Salmonella Typhimurium Co-Harboring Mcr-1, FosA3, BlaCTX-M-14 in a Transferable IncHI2 Plasmid from a Healthy Catering Worker in China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3569–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Xiong, H.; Lu, J.; Luo, F.; Liu, C.; Zhou, H.; Tong, W.; Xia, Z.; Liu, D. Epidemiological and Whole Genome Sequencing Analysis of Restaurant Salmonella Enteritidis Outbreak Associated with an Infected Food Handler in Jiangxi Province, China, 2023. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2024, 21, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Relaño, Á.; Díaz, A.V.; Lorenzo, B.H.; Gómez-Gascón, L.; Rodríguez, M.Á.M.; Jiménez, E.C.; Rodríguez, F.P.; Márquez, R.J.A. Salmonella and Salmonellosis: An Update on Public Health Implications and Control Strategies. Animals 2023, 13, 3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Fu, S.; Guo, H.; Hu, M.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Jiao, X. Application and Challenge of Bacteriophage in the Food Protection. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 380, 109872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtiss, R. Vaccines to Control Salmonella in Poultry. Avian Dis. 2023, 67, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Hu, X.; Du, X.; Lv, C.; Yuk, H. Biofilm Formation in Food Processing Plants and Novel Control Strategies to Combat Resistant Biofilms: The Case of Salmonella spp. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 32, 1703–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Bryan, C.A.; Ricke, S.C.; Marcy, J.A. Public Health Impact of Salmonella spp. On Raw Poultry: Current Concepts and Future Prospects in the United States. Food Control 2022, 132, 108539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, A.B.; Adesola, R.O.; Idris, I.; Scott, G.Y.; Alfa, S.; Ajibade, F.A. Combatting Extensively Drug-Resistant Salmonella: A Global Perspective on Outbreaks, Impacts, and Control Strategies. Pathog. Glob. Health 2024, 118, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, B. Salmonellosis: An Overview of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Innovative Approaches to Mitigate the Antimicrobial Resistant Infections. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desalegn, S.; Abaya, G.; G’Yesus, T.; Admasu, D.; Mussema, A. Prevalence of Intestinal Parasites, Salmonella, Shigella and Antimicrobial Resistance of Bacterial Isolates among Food Handlers in Wachemo University Students’ Food Service Facility, Southcentral Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study. IJID Reg. 2025, 15, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, E.C.D. Personal Hygiene and Health. In Food Safety Management, 1st ed.; Lelieveld, H., Motarjemi, Y., Eds.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 769–789. ISBN 9780123815057. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, R.T.; Pedrosa, G.T.S.; Franco, A.J.S.; Grilo, M.M.S.; de Lucena, F.A.; Barão, C.E.; Jung, J.; Schaffner, D.W.; Magnani, M. Transfer, survival and photoinactivation of Salmonella enterica on fresh produce and gloves. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2025, 431, 111089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemeda, B.A.; Dione, M.; Ilboudo, G.; Assefa, A.; Lallogo, V.; Grace, D.; Knight-Jones, T.J.D. Food safety and hygiene knowledge, attitudes and practices in street restaurants selling chicken in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1448127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuglo, L.S.; Agordoh, P.D.; Tekpor, D.; Pan, Z.; Agbanyo, G.; Chu, M. Food Safety Knowledge, Attitude, and Hygiene Practices of Street-Cooked Food Handlers in North Dayi District, Ghana. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2021, 26, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abey, S.L.; Gedefaw, M.; Molla, W.; Dagnaw, G.G.; Mengistu, B.A.; Kinde, M.Z.; Nigatu, S.; Jemberu, W.T.; Adugna, T.; Berju, A.; et al. Molecular Detection and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Salmonella Isolated from Humans, Animals, Abattoir Equipment and Environment. Appl. Food Res. 2024, 4, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Country | Location of Collection | Isolates from Food Handler (%) | Sample | Antimicrobial Factors | Resistance Genes | MDR (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethiopia | Multiple | 181/384 (47.1%) | Hand | Not analyzed | Not analyzed | 96/181 (53.0%) | [56] |
| Iran | Not informed | 224/1113 (20.1%) | Nasal | 37 MRSA | Not analyzed | Not analyzed | [57] |
| Brazil | Pilot kitchen | 74/82 (90.2%) | Underside of nails and nasal | 7 MRSA | 7 mecA | Not informed | [34] |
| Myanmar | Hotel and Restaurant | 144/563 (25.6%) | Hands and Nasal | Not analyzed | Not analyzed | 2/144 (1.4%) | [35] |
| Egypt | Not informed | 12/40 (30.0%) | Hand | 12 MRSA 3 VRSA | 12 mecA 3 vanA 2 vanB | 12/12 (100.0%) | [36] |
| Malaysia | Not informed | 95/100 (95.0%) | Hand | Not analyzed | Not analyzed | 2/95 (2.1%) | [58] |
| Italy | Pasta company | 7/28 (25.0%) | Hand and nasal | Not analyzed | 22 blaZ 9 msrA 1 linA 1 fusB | 5/28 (18.0%) | [44] |
| Morrocco | Hospital | 55/70 (78.6%) | Hand and nasal | Not analyzed | 13 mecA | 51/51 (100.0%) | [59] |
| Nigeria | Street food handlers | 101/360 (28.1%) | Hand and nasal | 22 MRSA | Not analyzed | 96/101 (95.0%) | [60] |
| Malaysia | School | 179/1020 (17.5%) | Hand | Not analyzed | Not analyzed | 1/148 (0.7%) | [61] |
| Brazil | Hospital | 111/280 (39.6%) | Hand and nasal | 40 MRSA | Not analyzed | Not informed | [62] |
| China | Not informed | 231/1927 (12.0%) | Hand | 17 MRSA | 17 mecA | 17/231 (7.4%) | [63] |
| Lebanon | Not informed | 38/160 (23.8%) | Nasal | 5 MRSA | Not analyzed | Not informed | [64] |
| Nigeria | Roadside food handlers | 28/180 (15.6%) | Hand and Nasal | Not analyzed | Not analyzed | 10/28 (35.7%) | [65] |
| Hong Kong | Catering establishments | 99/434 (22.8%) | Nasal | 5 MRSA | 5 mecA | Not informed | [66] |
| Country | Location of Collection | Positive Isolates from Food Handler (%) | Sample Type | Antimicrobial Mechanisms | Resistance Genes | MDR (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethiopia | Multiple | 95/384 (24.7%) | Hand and Fecal | Not analyzed | Not analyzed | 56/95 (59.0%) | [56] |
| Ethiopia | University cafeterias (Including Hospital) | 245/290 (84.5%) | Fecal | 43 ESBL 4 Carbapenemase | Not analyzed | 104/245 (42.4%) | [115] |
| Ethiopia | University cafeterias | 119/220 (54.1%) | Fecal | 29 ESBL | Not analyzed | 27/119 (22.7%) | [117] |
| Qatar | Migrant food handlers during mandatory medical screening | 78/456 (17.1%) | Fecal | 7 ESBL | Not analyzed | 21/78 (27.0%) | [14] |
| Kuwait | Commercial eateries and Healthcare settings | 425/681 (62.4%) | Fecal | 80 ESBL | Not analyzed | 130/425 (30.6%) | [15] |
| Gambia | Schools | 8 ESBL producing E. coli/565 * | Fecal | 8 ESBL 4 AmpC 1 Carbapenemase | Not analyzed | 8/8 (100.0%) | [118] |
| Indonesia | Hospitals | 24/58 (41.4%) | Hand and Nasal | Not analyzed | Not analyzed | 20/24 (83.3%) | [119] |
| Malaysia | Schools | 28/1020 (2.8%) | Hands | Not analyzed | Not analyzed | 4/28 (14.3%) | [61] |
| China | Military hospital | 92/103 (89.3%) | Fecal | 7 ESBL 46 intI1 2 qepA1 1 qnrS1 1 qnrB6 | 5 blaCTX-M14 1 blaCTX-M79 1 blaCTX-M-106 | 47/92 (51.1%) | [120] |
| Morroco | Hospital | 18/40 (45.0%) | Hands | ESBL not detected 16 metallo-β-lactamase | Not analyzed | 16/18 (88.9%) | [121] |
| Kenya | Hotels | 39/885 (4.4%) | Fecal | Not analyzed | Not analyzed | 16/39 (40.2%) | [122] |
| Tunisia | Not mentioned | 378 ESBL producing E. coli/2135 * | Fecal | 378 ESBL | 219 blaCTX-M-15 70 blaCTX-M-1 52 blaCTX-M-27 23 blaCTX-M-14 10 blaSHV-12 3 blaSHV-2a 1 blaCTX-M-3 | Not informed | [123] |
| Country | Location of Collection | Isolates from Food Handler (%) | Sample | Antimicrobial Factors | Resistance Genes | MDR (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethiopia * | Multiple | 161/3140 (5.1%) | Fecal and Hand | Not analyzed | Not analyzed | 88/161 (54.7%) | [56,165,173,174,175,176,177,178,179,180] |
| China | Catering industry | 193/214,542 (0.09%) | Fecal | Not analyzed | Not analyzed | 85/116 (73.4%) | [13] |
| Japan | Cooks and servers in restaurants and food factory workers | 583/740,635 (0.079%) | Fecal | Not analyzed | 5 blaCMY-2 2 blaCTX-M-15 1 blaLAT-3 3 blaCTX-M-55 1 blaTEM-52B 1 blaLAP-2 1 blaTEM-1 | 110/273 (40.3%) | [181] |
| Japan | Cooks and servers in restaurants and food factory workers | 164/145,220 (0.113%) | Fecal | 4 ESBL and 3 AmpC-lactamase | 1 blaCTX-M-14 3 blaCTX-M-15 3 blaCMY-2 | Not informed | [182] |
| Malaysia | Food establishments | 9/317 (2.8%) | Fecal | Not analyzed | Not analyzed | 7/9 (77.8%) | [109] |
| Pakistan | Food street vendors | 19/209 (9.1%) | Fecal | Not analyzed | Not analyzed | 1/19 (5.3%) | [183] |
| Japan | Not mentioned | 19 602/27,848,713 (0.07%) | Fecal | 3/400 ** ESBL 7/400 ** AmpC | 7 blaCMY-2 1blaTEM 1 blaSHV | Not informed | [184] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viana, G.G.F.; Cardozo, M.V.; Pereira, J.G.; Rossi, G.A.M. Antimicrobial Resistant Staphylococcus spp., Escherichia coli, and Salmonella spp. in Food Handlers: A Global Review of Persistence, Transmission, and Mitigation Challenges. Pathogens 2025, 14, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050496
Viana GGF, Cardozo MV, Pereira JG, Rossi GAM. Antimicrobial Resistant Staphylococcus spp., Escherichia coli, and Salmonella spp. in Food Handlers: A Global Review of Persistence, Transmission, and Mitigation Challenges. Pathogens. 2025; 14(5):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050496
Chicago/Turabian StyleViana, Gustavo Guimarães Fernandes, Marita Vedovelli Cardozo, Juliano Gonçalves Pereira, and Gabriel Augusto Marques Rossi. 2025. "Antimicrobial Resistant Staphylococcus spp., Escherichia coli, and Salmonella spp. in Food Handlers: A Global Review of Persistence, Transmission, and Mitigation Challenges" Pathogens 14, no. 5: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050496
APA StyleViana, G. G. F., Cardozo, M. V., Pereira, J. G., & Rossi, G. A. M. (2025). Antimicrobial Resistant Staphylococcus spp., Escherichia coli, and Salmonella spp. in Food Handlers: A Global Review of Persistence, Transmission, and Mitigation Challenges. Pathogens, 14(5), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050496









