Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization Assays as Customizable and Scalable Tools for Serological Surveillance and Immune Profiling
Abstract
1. Introduction
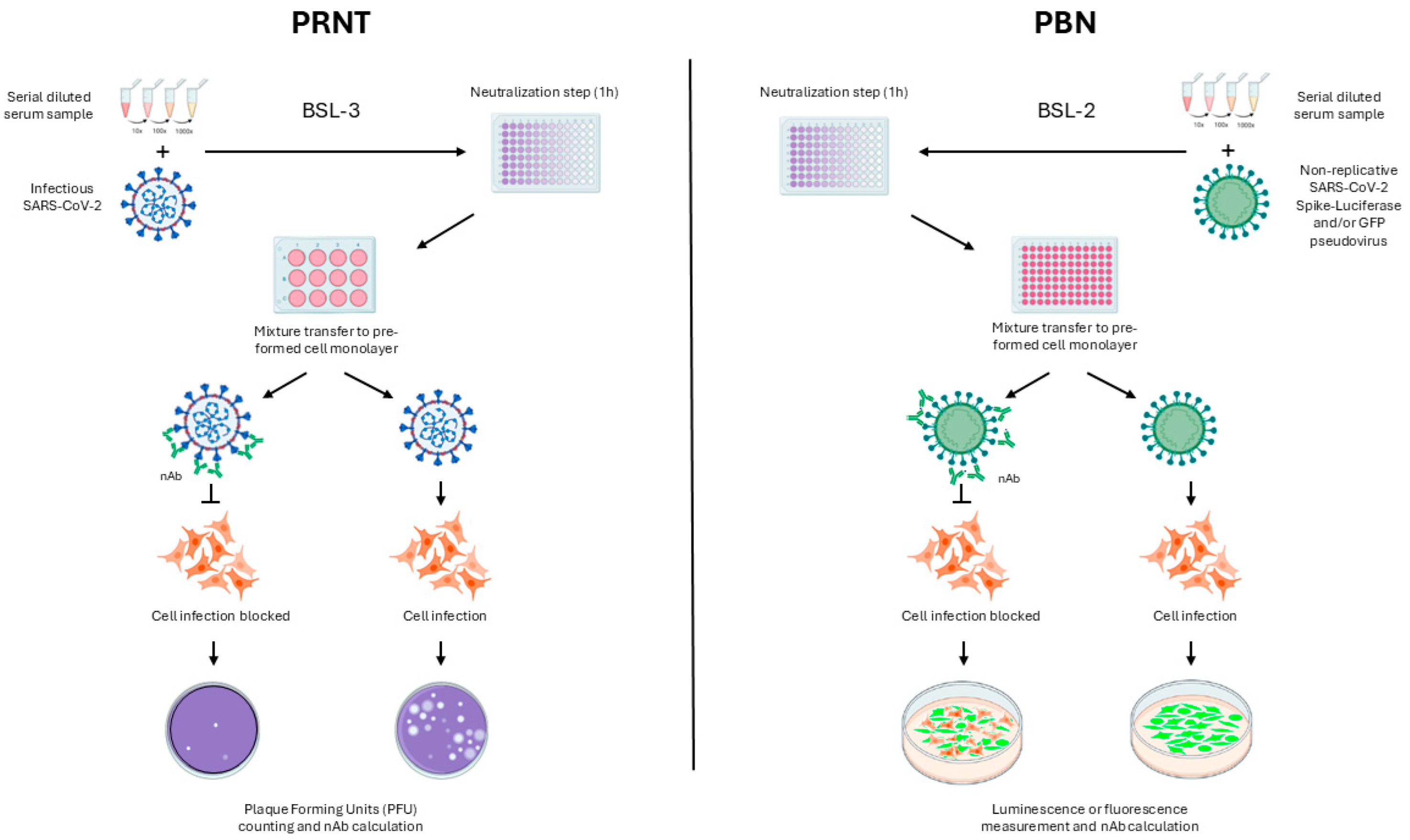
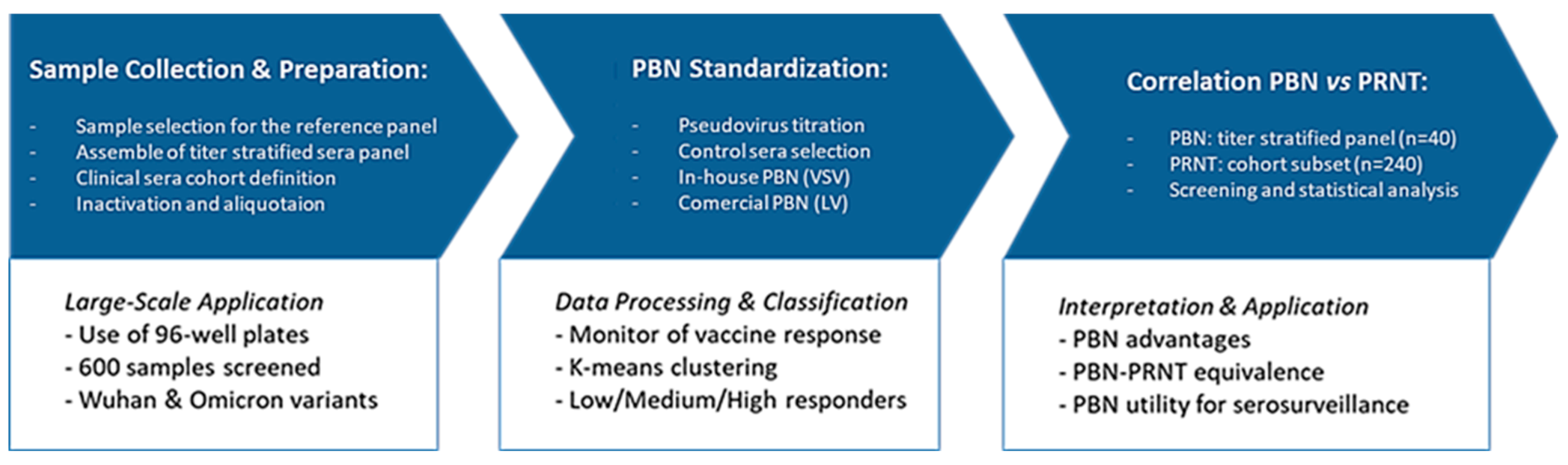
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lineages
2.2. Pseudotyped Viruses
2.3. Titer-Stratified Panel of Sera Samples
2.4. Control Sera Definition
2.5. PBN Protocol Definition
2.6. Comparison Between PBN Assays and PRNT
2.7. Screening of Clinical Cohort
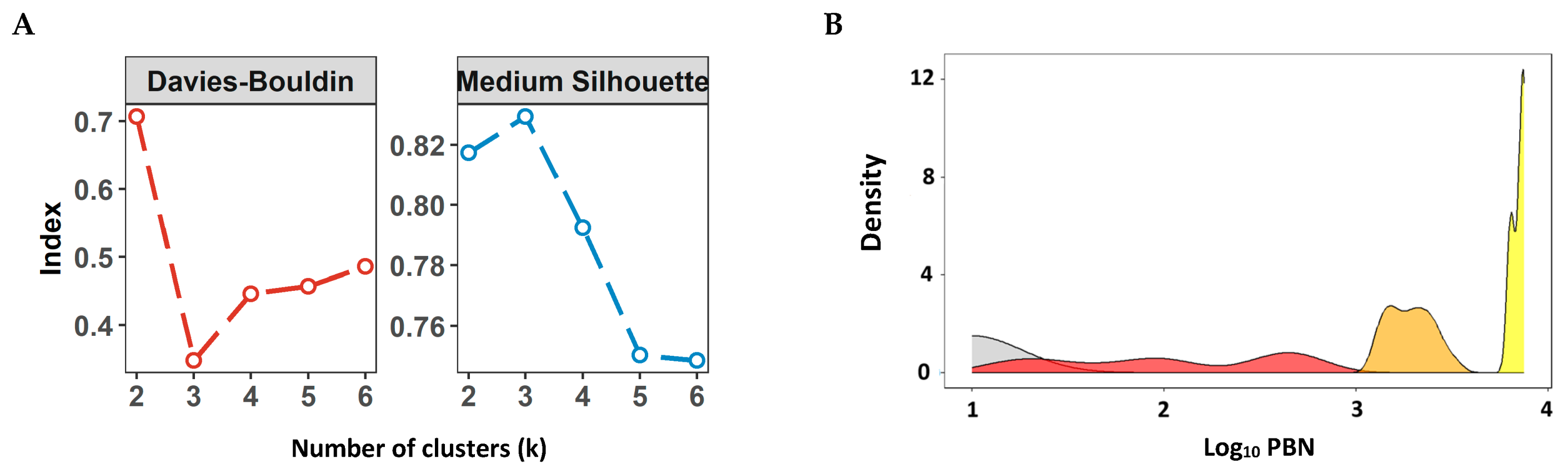
2.8. Defining Numeric Ranges for the nAb Titer Categories
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Standardization of Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization (PBN) Assays
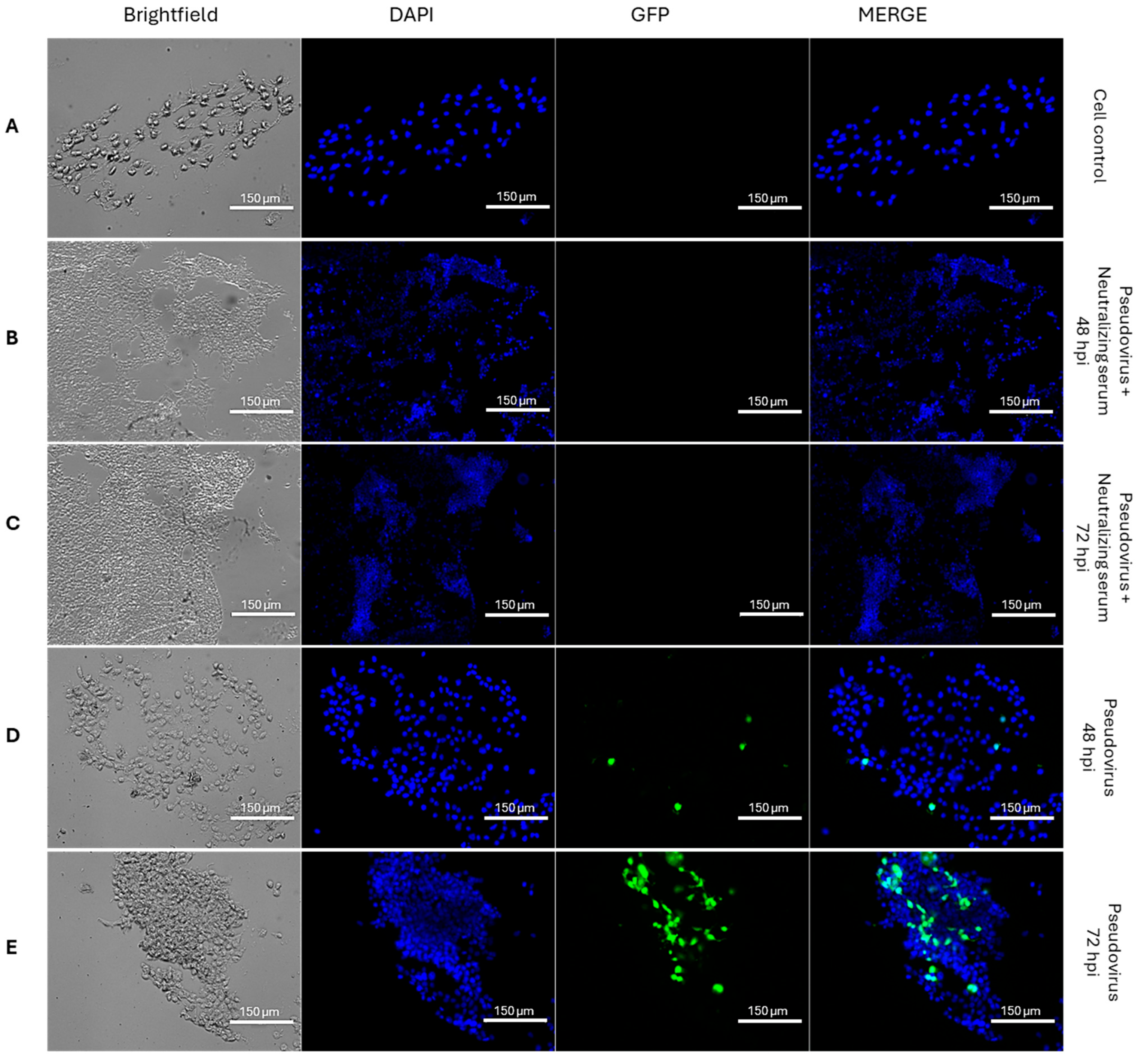
3.1.1. Entry of GFP-XBB-SARS-CoV-2 Pseudovirus into HEK293T-ACE2 Cells
3.1.2. Selection of Reference Sera for Quality Control of the Luc-SARS-CoV-2 Pseudovirus Assays
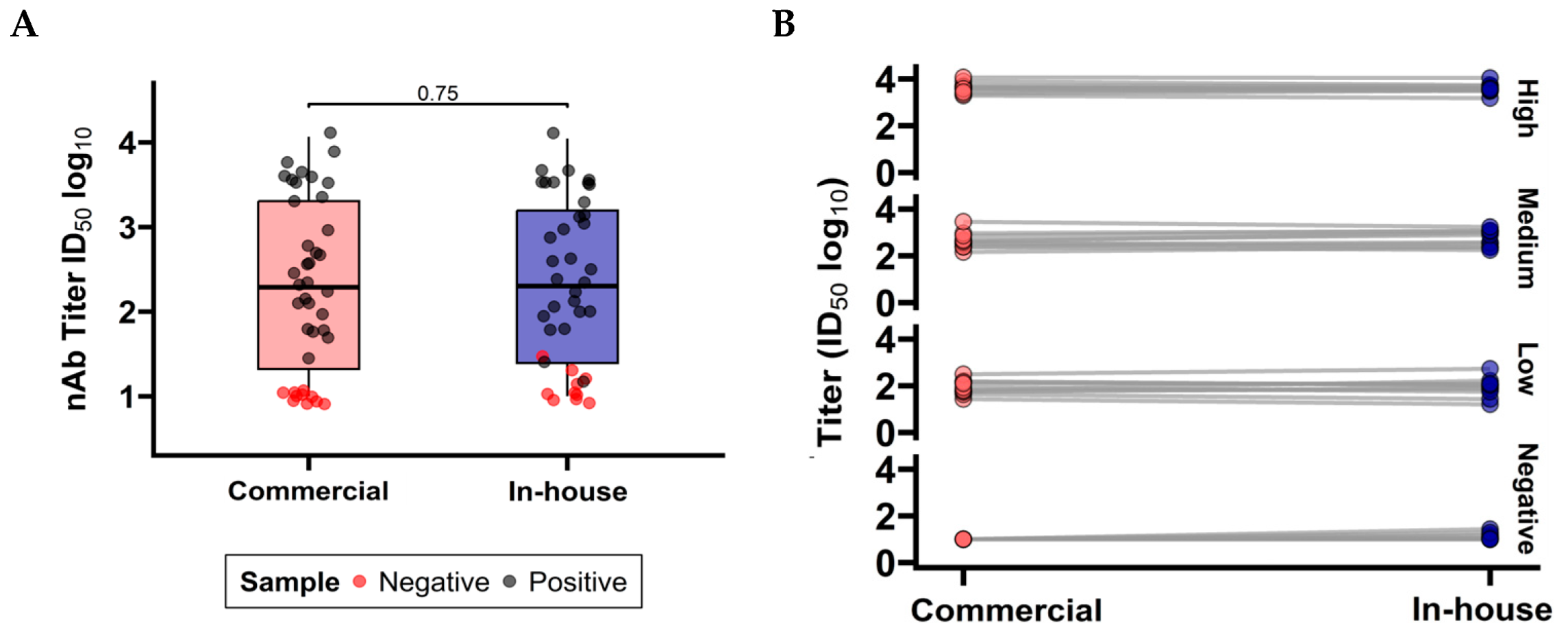
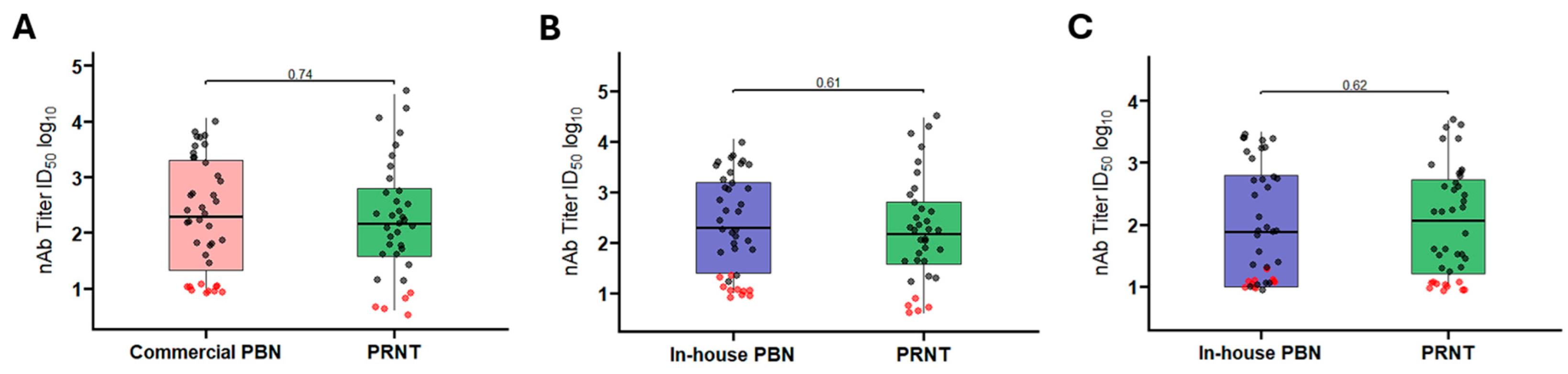
3.1.3. Comparison Between Commercial and In-House PBN Tests
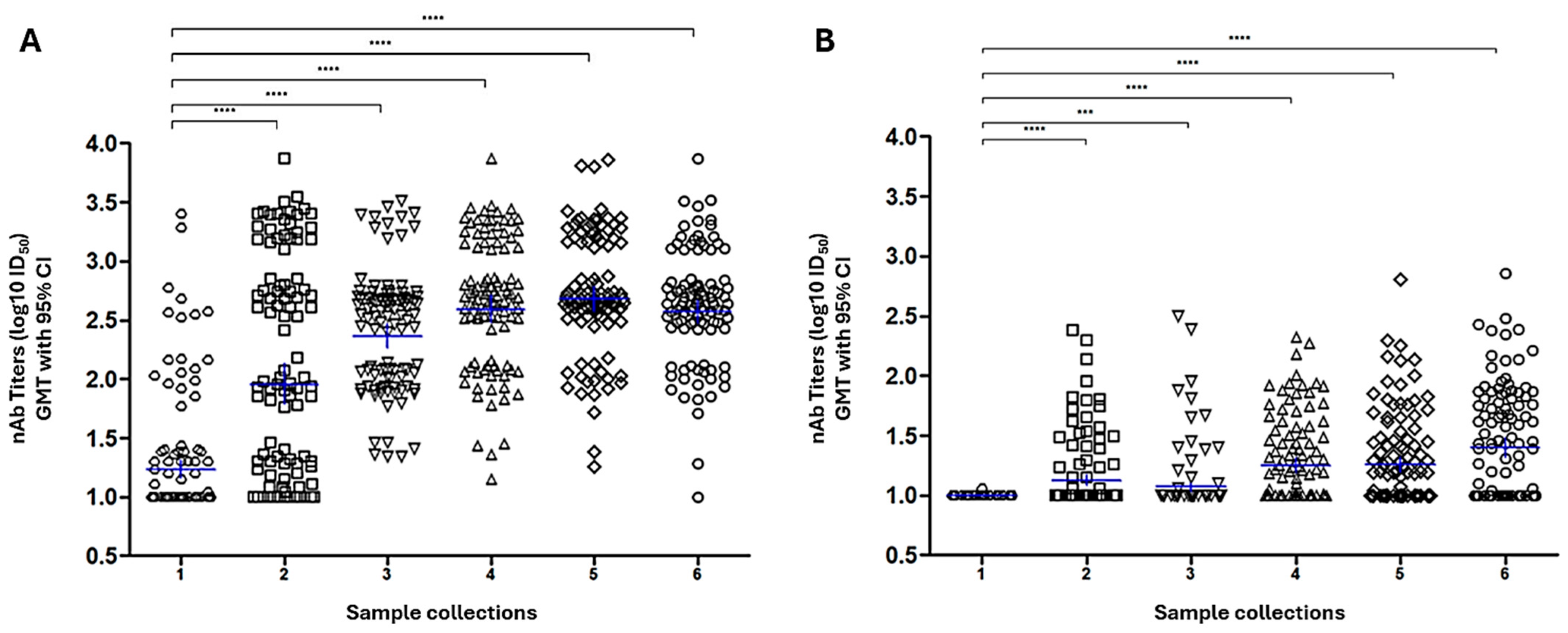
3.1.4. Screening of PRNT Titter-Stratified Panel by Standardized SARS-CoV-2 PBN Assays
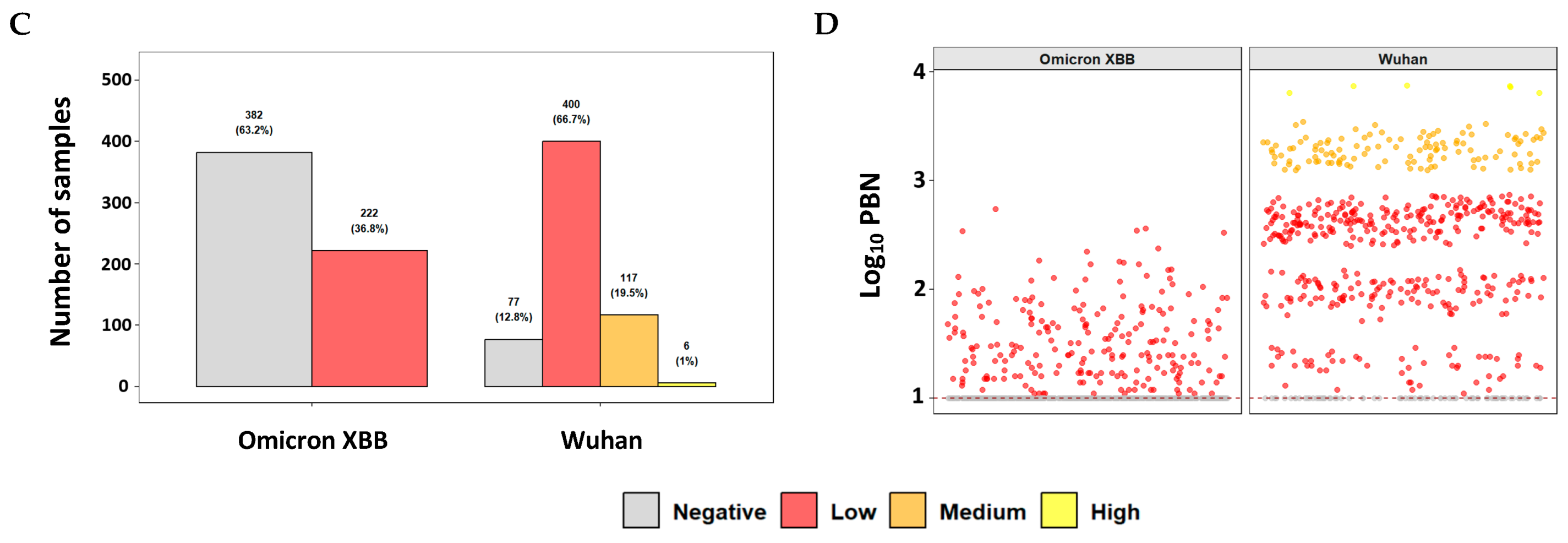
3.2. Evaluation of Neutralizing Antibody Responses in a Clinical Cohort Using the Commercial PBN Assays
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- COVID-19 Epidemiological Update–14 March 2025. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-epidemiological-update-edition-177 (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- Folegatti, P.M.; Ewer, K.J.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Becker, S.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Bellamy, D.; Bibi, S.; Bittaye, M.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: A preliminary report of a phase 1/2, single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-D.; Wang, J.-T.; Chao, T.-L.; Ieong, S.-M.; Tsai, Y.-M.; Kuo, P.-H.; Tsai, M.-J.; Chen, Y.-J.; Li, G.-C.; Ho, S.-Y.; et al. Evolution of neutralizing antibodies and cross-activity against different variants of SARS-CoV-2 in patients recovering from COVID-19. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2023, 122, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horbach, I.S.; de Souza Azevedo, A.; Schwarcz, W.D.; Alves, N.D.S.; de Moura Dias, B.; Setatino, B.P.; da Cruz Moura, L.; de Souza, A.F.; Denani, C.B.; da Silva, S.A.; et al. Plaque Reduction Neutralization Test (PRNT) Accuracy in Evaluating Humoral Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2. Diseases 2024, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhavachana, P.; Yuill, T.M.; Russell, P.K. Assay of arbovirus neutralizing antibody by micro methods. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1969, 63, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, W.W.S.I.; Alcena, D.C.; Rose, R.C.; Jin, X.; Schlesinger, J.J. An automated Dengue virus microneutralization plaque assay performed in human Fc{gamma} receptor-expressing CV-1 cells. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Haga, K.; Chen, Z.N.; Himeno, M.; Majima, R.; Moi, M.L. Utility of an In-Vitro Micro-Neutralizing Test in Comparison to a Plaque Reduction Neutralization Test for Dengue Virus, Japanese Encephalitis Virus, and Zika Virus Serology and Drug Screening. Pathogens 2023, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, N.; Tamura, M.; Hotta, S. Dengue virus plaque formation on microplate cultures and its application to virus neutralization (38564). Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1975, 148, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, M.; Camacho, L.A.B.; Yamamura, A.M.Y.; Miranda, E.H.; Cajaraville, A.C.R.A.; da Silva Freire, M. Evaluation of accuracy and reliability of the plaque reduction neutralization test (micro-PRNT) in detection of yellow fever virus antibodies. Biol. J. Int. Assoc. Biol. Stand. 2012, 40, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, S.R.; Brown, D.W.G.; Jin, L.; Samuel, D.; Andrews, N.; Brown, K.E. Development of a focus reduction neutralization test (FRNT) for detection of mumps virus neutralizing antibodies. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 163, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koishi, A.C.; Suzukawa, A.A.; Zanluca, C.; Camacho, D.E.; Comach, G.; Duarte Dos Santos, C.N. Development and evaluation of a novel high-throughput image-based fluorescent neutralization test for detection of Zika virus infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderheiden, A.; Edara, V.V.; Floyd, K.; Kauffman, R.C.; Mantus, G.; Anderson, E.; Rouphael, N.; Edupuganti, S.; Shi, P.-Y.; Menachery, V.D.; et al. Development of a Rapid Focus Reduction Neutralization Test Assay for Measuring SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2020, 131, e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, M.C.; Bogardus, L.; Giacone, D.G.; Rubinstein, L.J.; Antonello, J.M.; Sun, D.; Daijogo, S.; Gurney, K.B. Virus Reduction Neutralization Test: A Single-Cell Imaging High-Throughput Virus Neutralization Assay for Dengue. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, V.S.L.; Ang, C.C.W.; Low, S.L.; Lee, P.X.; Setoh, Y.X.; Wong, J.C.C. Evaluation of three alternative methods to the plaque reduction neutralizing assay for measuring neutralizing antibodies to dengue virus serotype 2. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheck, M.K.; Lehmann, L.; Zaucha, M.; Schwarzlmueller, P.; Huber, K.; Pritsch, M.; Barba-Spaeth, G.; Thorn-Seshold, O.; Krug, A.B.; Endres, S.; et al. FluoRNT: A robust, efficient assay for the detection of neutralising antibodies against yellow fever virus 17D. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, P.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Z. Development of a Surrogate Neutralization Assay for Norovirus Vaccine Evaluation at the Cellular Level. Viruses 2018, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.W.; Chia, W.N.; Qin, X.; Liu, P.; Chen, M.I.-C.; Tiu, C.; Hu, Z.; Chen, V.C.-W.; Young, B.E.; Sia, W.R.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test based on antibody-mediated blockage of ACE2-spike protein-protein interaction. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekirov, I.; Petric, M.; Carruthers, E.; Lawrence, D.; Pidduck, T.; Kustra, J.; Laley, J.; Lee, M.-K.; Chahil, N.; Mak, A.; et al. Performance comparison of micro-neutralization assays based on surrogate SARS-CoV-2 and WT SARS-CoV-2 in assessing virus-neutralizing capacity of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. Access Microbiol. 2021, 3, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khromykh, A.A.; Varnavski, A.N.; Westaway, E.G. Encapsidation of the flavivirus kunjin replicon RNA by using a complementation system providing Kunjin virus structural proteins in trans. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 5967–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholle, F.; Girard, Y.A.; Zhao, Q.; Higgs, S.; Mason, P.W. trans-Packaged West Nile virus-like particles: Infectious properties in vitro and in infected mosquito vectors. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 11605–11614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.T.; Patkar, C.G.; Kuhn, R.J. Construction and applications of yellow fever virus replicons. Virology 2005, 331, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Kalkeri, R.; Zhu, M.; Cloney-Clark, S.; Haner, B.; Wang, M.; Osman, B.; Dent, D.; Feng, S.-L.; Longacre, Z.; et al. A Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Variants: A Rapid, Cost-Effective, BSL-2-Based High-Throughput Assay Useful for Vaccine Immunogenicity Evaluation. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizatdinova, S.N.; Ershova, A.E.; Astrakhantseva, I.V. Pseudotyped Viruses: A Useful Platform for Pre-Clinical Studies Conducted in a BSL-2 Laboratory Setting. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wen, X.; Li, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, M.; Zhang, L.; Lv, M.; Zhou, S.; Bai, S.; Zhao, W.; et al. Evaluation of Immunogenicity by Pseudovirus Neutralization Assays for SARS-CoV-2 Variants after Primary and Booster Immunization. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 117, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, A.; Dhama, N.; Gupta, R.D. Dengue virus neutralizing antibody: A review of targets, cross-reactivity, and antibody-dependent enhancement. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1200195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnell, G.W.; Ferrara, F.; Grehan, K.; Thompson, C.P.; Temperton, N.J. Pseudotype-based neutralization assays for influenza: A systematic analysis. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, F.; Del Rosario, J.M.M.; da Costa, K.A.S.; Kinsley, R.; Scott, S.; Fereidouni, S.; Thompson, C.; Kellam, P.; Gilbert, S.; Carnell, G.; et al. Development of Lentiviral Vectors Pseudotyped with Influenza B Hemagglutinins: Application in Vaccine Immunogenicity, mAb Potency, and Sero-Surveillance Studies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 661379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Duckers, H.J.; Sullivan, N.J.; Sanchez, A.; Nabel, E.G.; Nabel, G.J. Identification of the Ebola virus glycoprotein as the main viral determinant of vascular cell cytotoxicity and injury. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 886–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierson, T.C.; Sánchez, M.D.; Puffer, B.A.; Ahmed, A.A.; Geiss, B.J.; Valentine, L.E.; Altamura, L.A.; Diamond, M.S.; Doms, R.W. A rapid and quantitative assay for measuring antibody-mediated neutralization of West Nile virus infection. Virology 2006, 346, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhao, C.; Hao, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Nie, L.; Qin, H.; Wang, M.; et al. Establishment and validation of a pseudovirus neutralization assay for SARS-CoV-2. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahrsdörfer, B.; Groß, R.; Seidel, A.; Wettstein, L.; Ludwig, C.; Schwarz, T.; Körper, S.; Rojewski, M.; Lotfi, R.; Weinstock, C.; et al. Characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Potential of COVID-19-Convalescent Donors. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 2614–2622. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33980583/ (accessed on 6 August 2025). [CrossRef]
- D’Apice, L.; Trovato, M.; Gramigna, G.; Colavita, F.; Francalancia, M.; Matusali, G.; Meschi, S.; Lapa, D.; Bettini, A.; Mizzoni, K.; et al. Comparative analysis of the neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan-Hu-1 strain and variants of concern: Performance evaluation of a pseudovirus-based neutralization assay. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 981693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, A.J.; Satheshkumar, P.S.; Dietz, S.; Bull-Otterson, L.; Charles, M.; Edens, C.; Jones, J.M.; Bajema, K.L.; Clarke, K.E.N.; McDonald, L.C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Convalescent Sera Binding and Neutralizing Antibody Concentrations Compared with COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy Estimates against Symptomatic Infection. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0124722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, X.; Liu, Y.; Lei, X.; Li, P.; Mi, D.; Ren, L.; Guo, L.; Guo, R.; Chen, T.; Hu, J.; et al. Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, F.; Weisblum, Y.; Muecksch, F.; Hoffmann, H.-H.; Michailidis, E.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Mendoza, P.; Rutkowska, M.; Bednarski, E.; Gaebler, C.; et al. Measuring SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody activity using pseudotyped and chimeric viruses. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20201181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havranek, K.E.; Jimenez, A.R.; Acciani, M.D.; Lay Mendoza, M.F.; Reyes Ballista, J.M.; Diaz, D.A.; Brindley, M.A. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Alterations Enhance Pseudoparticle Titers and Replication-Competent VSV-SARS-CoV-2 Virus. Viruses 2020, 12, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.L.; Bouldin, D.W. A Cluster Separation Measure. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1979, PAMI-1, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekemeyong Awong, L.E.; Zielinska, T. Comparative Analysis of the Clustering Quality in Self-Organizing Maps for Human Posture Classification. Sensors 2023, 23, 7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SciSpace—Paper. Volume 1. University of California Press. 1967. Available online: https://scispace.com/papers/some-methods-for-classification-and-analysis-of-multivariate-4pswti19oz (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Fu, W.; Liang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Li, T.; Tong, J.; Liu, F.; Nie, J.; Lu, Q.; et al. Optimization and validation of a virus-like particle pseudotyped virus neutralization assay for SARS-CoV-2. MedComm 2024, 5, e615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenwick, C.; Croxatto, A.; Coste, A.T.; Pojer, F.; André, C.; Pellaton, C.; Farina, A.; Campos, J.; Hacker, D.; Lau, K.; et al. Changes in SARS-CoV-2 Spike versus Nucleoprotein Antibody Responses Impact the Estimates of Infections in Population-Based Seroprevalence Studies. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e01828-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samojlović, M.; Mesquita, J.R.; Santos-Silva, S.; Neptin, M.; Esbjörnsson, J. Investigating SARS-CoV-2 Neutralising Antibody Response in Sheep. Microorganisms 2024, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Devenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34002089/ (accessed on 7 August 2025). [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Phillips, D.J.; White, T.; Sayal, H.; Aley, P.K.; Bibi, S.; Dold, C.; Fuskova, M.; Gilbert, S.C.; Hirsch, I.; et al. Correlates of protection against symptomatic and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 2032–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromer, D.; Steain, M.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Khoury, D.S.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralising antibody titres as predictors of protection against SARS-CoV-2 variants and the impact of boosting: A meta-analysis. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, e52–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, P.B.; Montefiori, D.C.; McDermott, A.B.; Fong, Y.; Benkeser, D.; Deng, W.; Zhou, H.; Houchens, C.R.; Martins, K.; Jayashankar, L.; et al. Immune correlates analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial. Science 2022, 375, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanshylla, K.; Di Cristanziano, V.; Kleipass, F.; Dewald, F.; Schommers, P.; Gieselmann, L.; Gruell, H.; Schlotz, M.; Ercanoglu, M.S.; Stumpf, R.; et al. Kinetics and correlates of the neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 917–929.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Meng, X.; Wu, Q.; Lim, W.W.; Xin, Q.; Cowling, B.J.; Meng, W.; Yu, H.; Covasa, D.T. Assessment of neutralizing antibody response as a correlate of protection against symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections after administration of two doses of the CoronaVac inactivated COVID-19 vaccine: A phase III randomized controlled trial. J. Infect. 2024, 89, 106315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.; Reimerink, J.; Torriani, G.; Brouwer, F.; Godeke, G.-J.; Yerly, S.; Hoogerwerf, M.; Vuilleumier, N.; Kaiser, L.; Eckerle, I.; et al. Validation and clinical evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralisation test (sVNT). Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2394–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Tian, D.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, Y.; et al. Safe pseudovirus-based assay for neutralization antibodies against influenza A(H7N9) virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1685–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, W.-C.; Hwang, K.Y.; Kang, S.-J.; Kim, J.-O.; Song, M.J. Development of a neutralization assay based on the pseudotyped chikungunya virus of a Korean isolate. J. Microbiol. 2020, 58, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Denani, C.B.; Setatino, B.P.; Pereira, D.; Horbach, I.S.; Azevedo, A.S.; Coutinho, G.; Ferroco, C.L.; Xavier, J.; Leite, R.; Santos, E.; et al. Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization Assays as Customizable and Scalable Tools for Serological Surveillance and Immune Profiling. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111129
Denani CB, Setatino BP, Pereira D, Horbach IS, Azevedo AS, Coutinho G, Ferroco CL, Xavier J, Leite R, Santos E, et al. Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization Assays as Customizable and Scalable Tools for Serological Surveillance and Immune Profiling. Pathogens. 2025; 14(11):1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111129
Chicago/Turabian StyleDenani, Caio Bidueira, Bruno Pimenta Setatino, Denise Pereira, Ingrid Siciliano Horbach, Adriana Souza Azevedo, Gabriela Coutinho, Clara Lucy Ferroco, Janaína Xavier, Robson Leite, Ewerton Santos, and et al. 2025. "Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization Assays as Customizable and Scalable Tools for Serological Surveillance and Immune Profiling" Pathogens 14, no. 11: 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111129
APA StyleDenani, C. B., Setatino, B. P., Pereira, D., Horbach, I. S., Azevedo, A. S., Coutinho, G., Ferroco, C. L., Xavier, J., Leite, R., Santos, E., Maia, M. d. L., Schwarcz, W. D., & Sousa, I. P. (2025). Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization Assays as Customizable and Scalable Tools for Serological Surveillance and Immune Profiling. Pathogens, 14(11), 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111129







