Iodobacter fluviatilis, a New Potential Opportunistic Pathogen Associated with Skin Lesions, First Report in Hypophthalmichthys nobilis in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Signs and Sample Collection
2.2. Bacterial Isolation and Characteristics
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of 16S RNA
2.4. Pathogenicity Assay
2.5. Drug Sensitivity Tests
3. Results
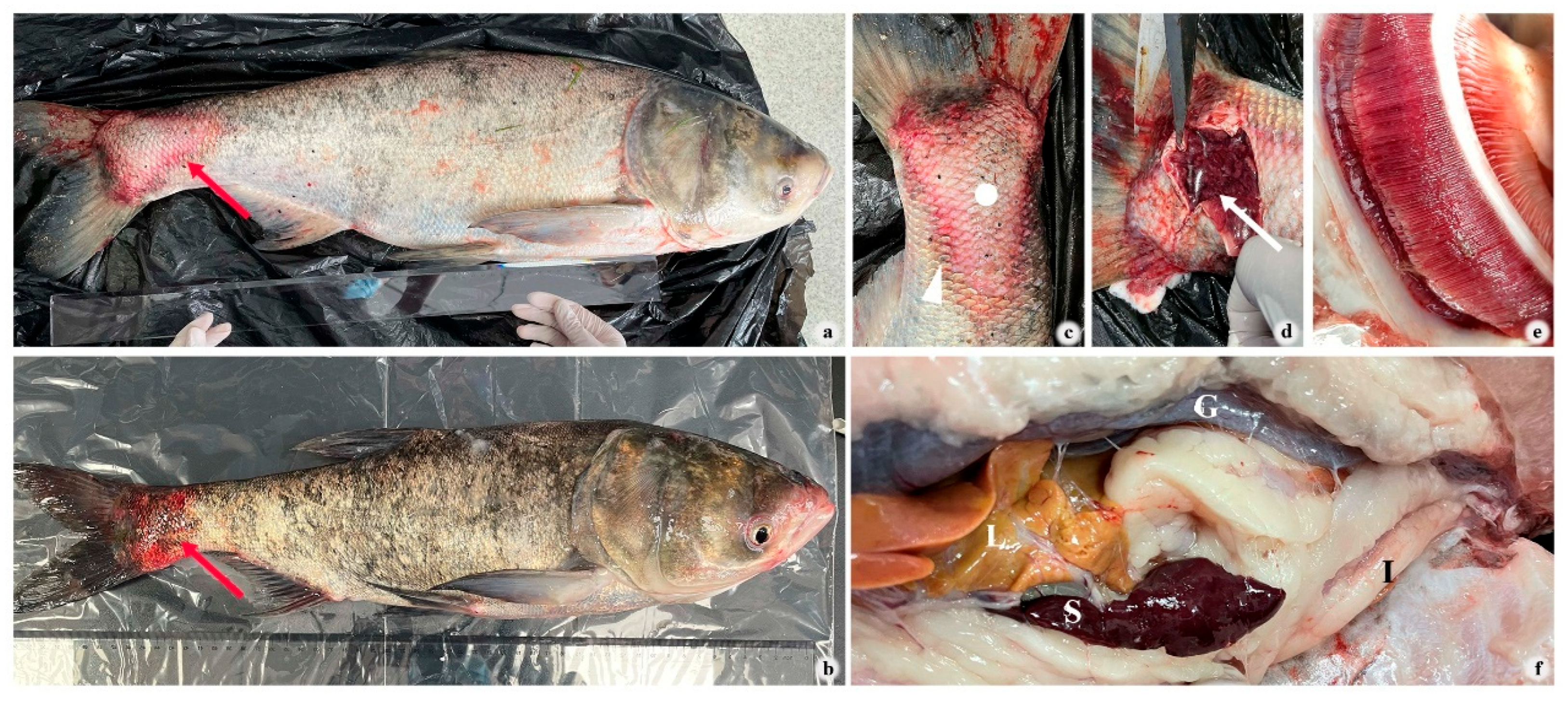
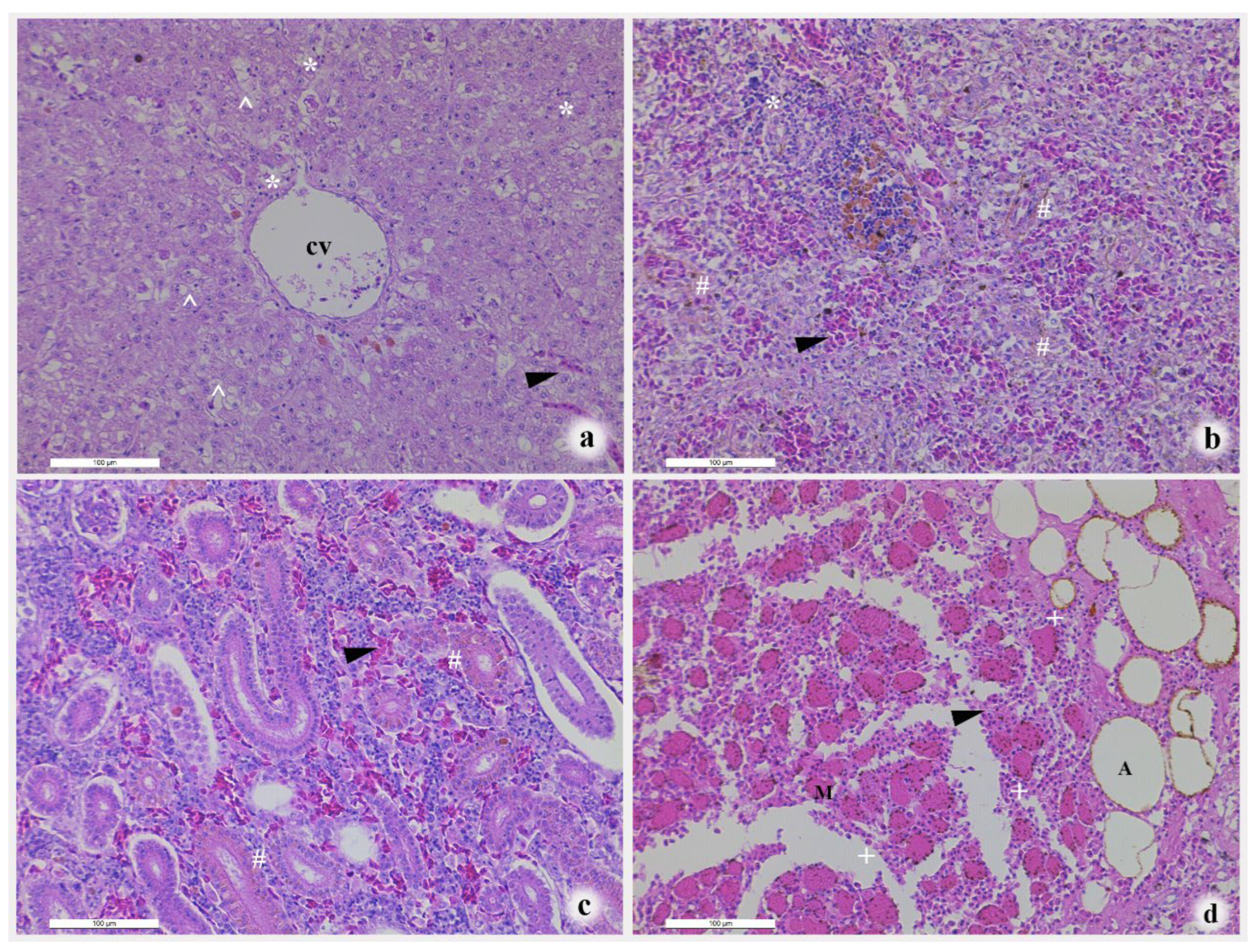
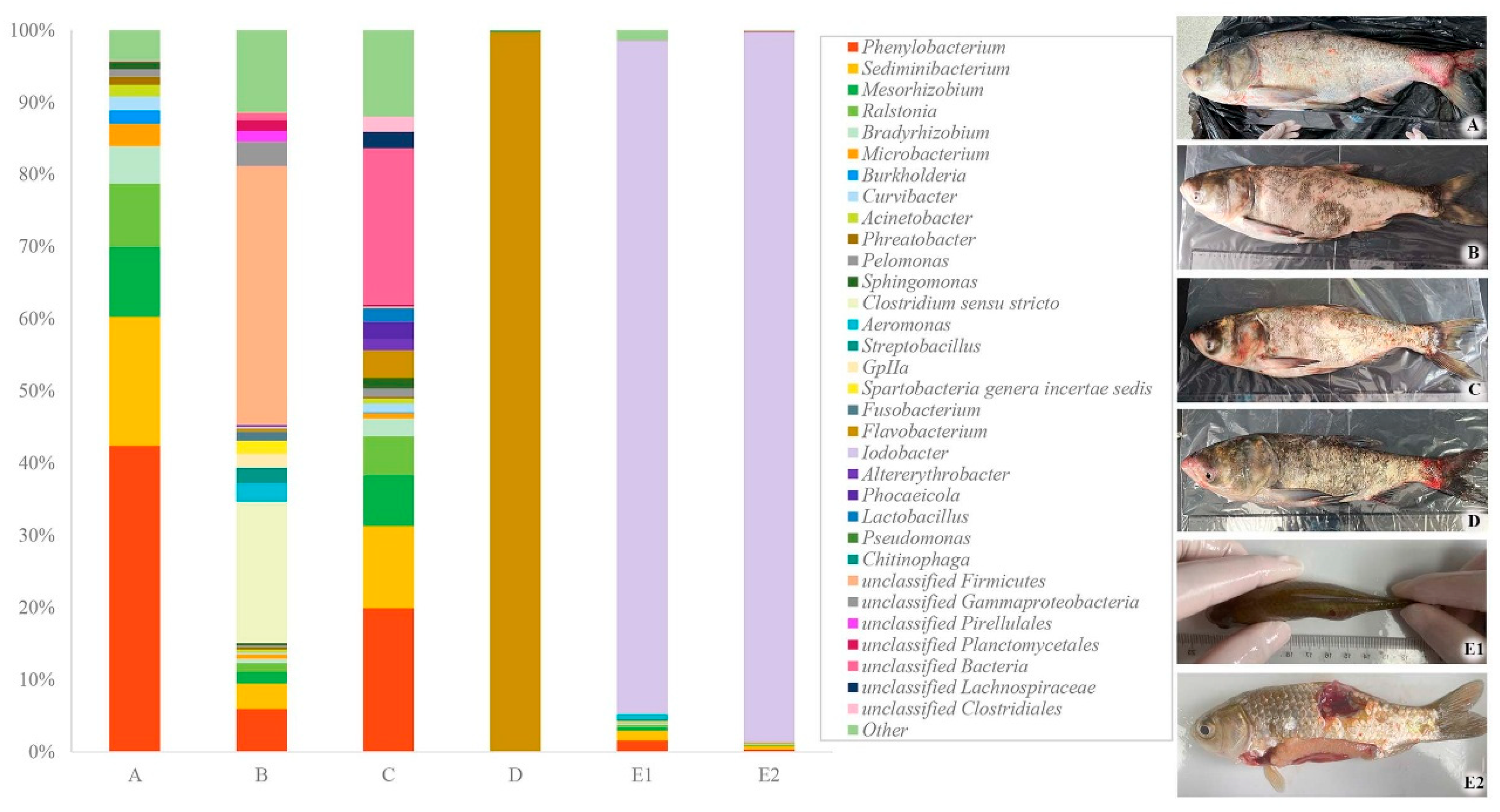
3.1. Clinical and Histopathological Changes
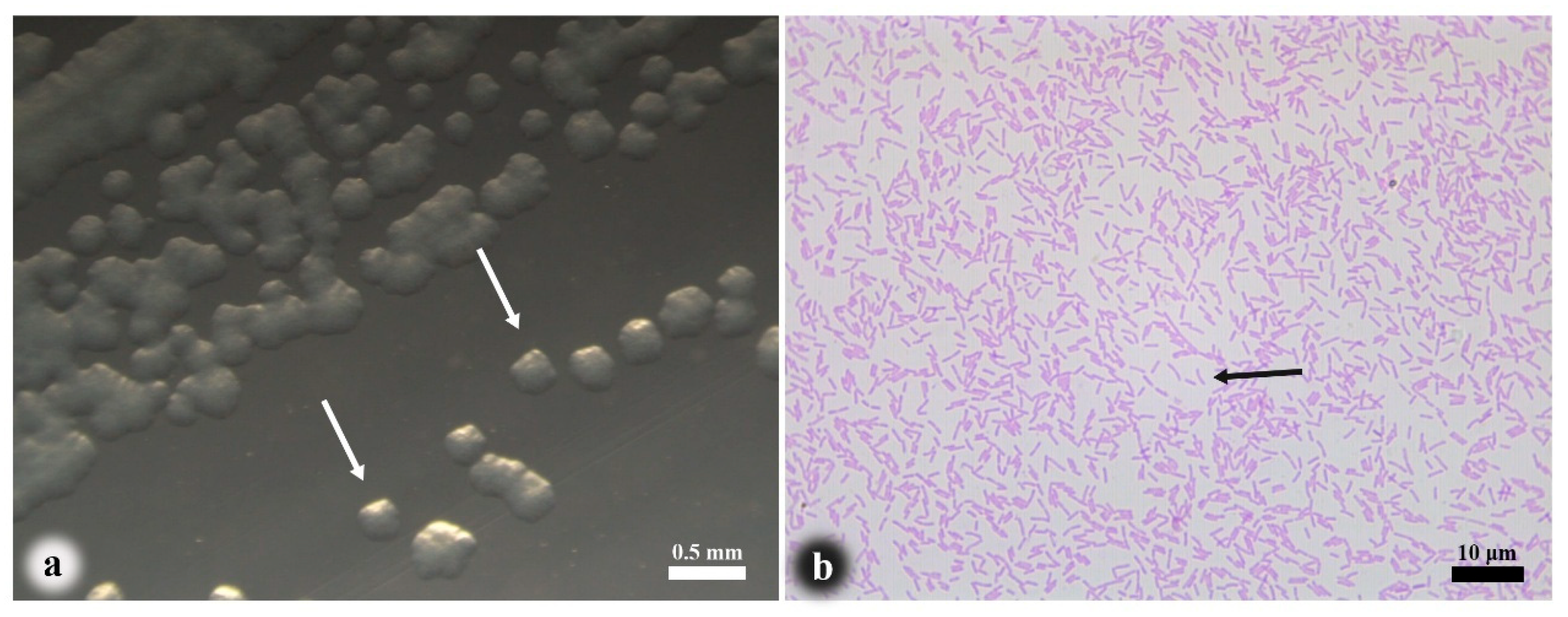
3.2. Pathogen Isolation and Morphological Observation
3.3. Biochemical Identification of Bacteria
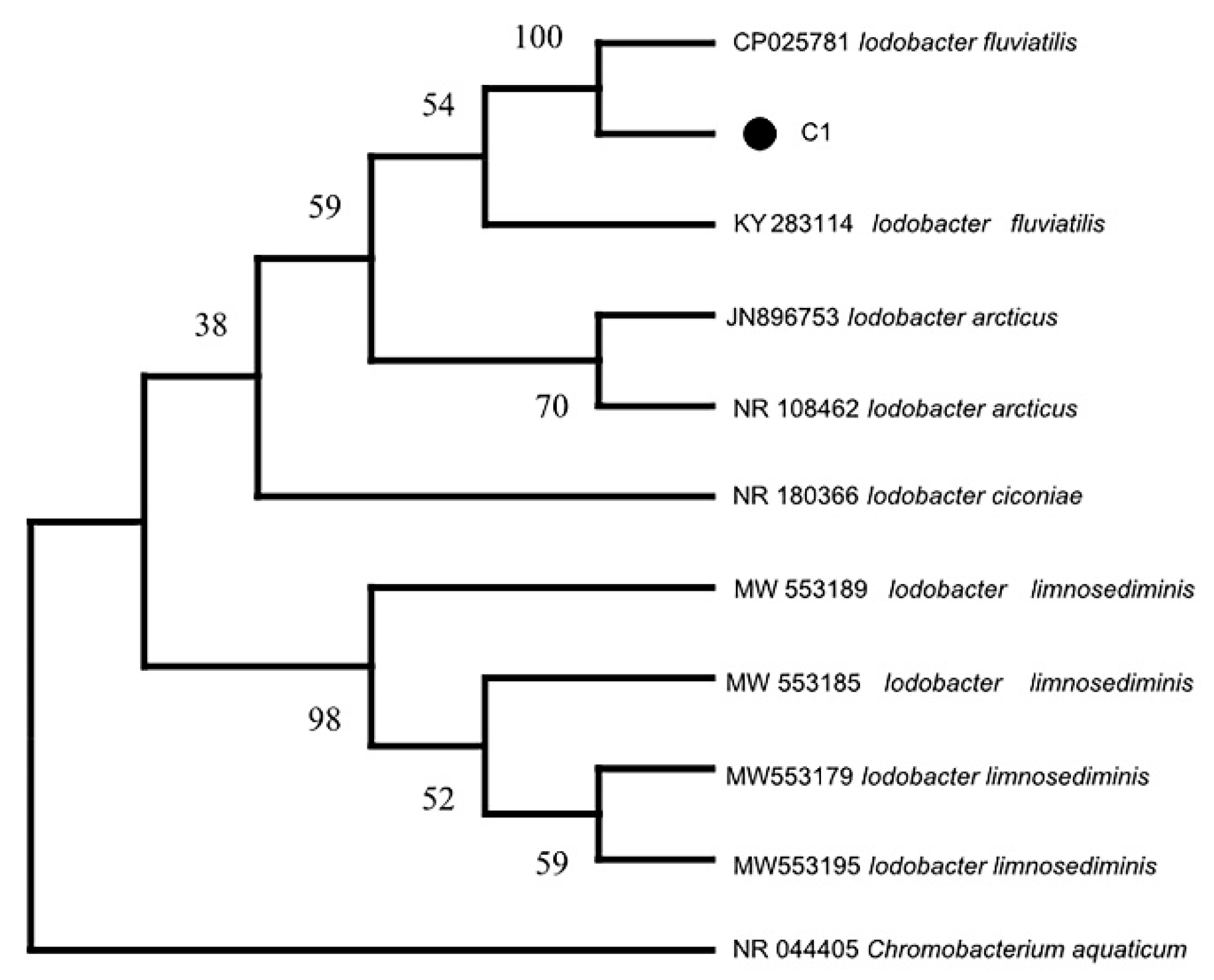
3.4. Bacterial 16S RNA Gene Sequence Analysis
3.5. Pathogenicity
3.6. Drug Sensitivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, D.; Wu, X. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2023; Available online: https://navi.cnki.net/knavi/yearbooks/YZYTN/detail?uniplatform=NZKPT (accessed on 11 May 2023). (In Chinese)
- Zhu, Y.J.; Li, X.M.; Yang, D.G. Food preference of paddlefish, Polyodon spathula (Walbaum, 1792), in polyculture with bighead carp Aristichthys nobilis (Richardson, 1845) in non-fed ponds. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2014, 30, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Zha, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Lu, H.; Yin, B. Eutrophication of Lake Waters in China: Cost, Causes, and Control. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Leavitt, P.R.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Anthropogenic eutrophication of shallow lakes: Is it occasional? Water Res. 2022, 221, 118728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Z.; Xie, P.; Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H. In situ study on the control of toxic Microcystis blooms using phytoplanktivorous fish in the subtropical Lake Taihu of China: A large fish pen experiment. Aquaculture 2007, 265, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ke, Z.; Xie, P.; Ni, L. Food Consumption by In Situ Pen-Cultured Planktivorous Fishes and Effects on an Algal Bloom in Lake Taihu, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2011, 24, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Xie, P.; Zhang, D.; Lei, H. In situ studies on the distribution patterns and dynamics of microcystins in a biomanipulation fish—Bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis). Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, Q.; Xie, P.; Tao, M.; Zhang, J.; Niu, Y.; Ma, Z. A non-classical biomanipulation experiment in Gonghu Bay of Lake Taihu: Control of Microcystis blooms using silver and bighead carp. Aquac. Res. 2015, 46, 2211–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, P.; Yao, W.J. Seasonal population dynamics of parasitic copepods, Sinergasilus spp. on farmed fish in China. Aquaculture 2000, 187, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.T.; Li, W.X.; Yao, W.J.; Nie, P. Mortalities induced by the copepod Sinergasilus polycolpus in farmed silver and bighead carp in a reservoir. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2002, 48, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakic, P.; Lenhardt, M.; Kolarevic, J. Sinergasilus polycolpus, a new copepod species in the ichthyoparasitofauna of Serbia and Montenegro. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2004, 58, 265–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, K.; Székely, C. Occurrence and pathology of Sinergasilus lieni (Copepoda: Ergasilidae), a parasite of the silver carp and bighead, in Hungarian ponds. Acta Vet. Hung. 2004, 52, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Ke, X.; Liu, L.; Lu, M.; Shi, C.; Liu, Z. Streptococcus agalactiae from tilapia (Oreochromis sp.) transmitted to a new host, bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis), in China. Aquac. Int. 2018, 26, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Cheng, H.; Li, W.; Li, M.; Zou, H.; Wang, G. Limnotrachelobdella hypophthalmichthysa n. sp. (Hirudinida: Piscicolidae) on Gills of Bighead Carp Hypophthalmichthys nobilis in China. Pathogens 2023, 12, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Ge, R.; Xiong, M. Studies on the “stigmatosis” of Sliver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) and Bighead Carp (Aristichthys nobilis). Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 1980, 11, 85–93. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Lu, J. Study on the hemolytic ascites disease of Hypophthalmichthys molitrix and Aristichthys nobilis. J. Zhanjiang Ocean Univ. 1997, 17, 17–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Fang, H.; Wang, X.; He, Z. Biological Characteristics and Phylogenetic Analysis of Aeromonas Caviae Isolated from Hypophthalmichthys molitrix and Aristichthys nobilis. Chin. Agr. Sci. Bull. 2006, 22, 455–459. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.; Ma, T.; Chen, L.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.; Peng, K.; Zhang, X.; Bao, C. Isolation, identification and virulence genes detection of Aeromonas veronii from Aristichthys nobilis. J. Anhui Agr. Univ. 2017, 44, 229–233. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, W. A preliminary study on the “putrid-skin” disease in Hypophthalmichthys molitrix and Aristichthys nobilis and Its prevention and cure. J. Fisheries China 1965, 2, 33–52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Yin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y. An outbreak of a new epizootic in Silver carp and Bighead carp—Yersinia-Ruckeri, a new pathogen of Silver Carp and Bighead Carp. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1991, 36, 620–622. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fang, P.; Ding, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, H. Isolation identification and phylogenetic analysis of Yersinia Ruckeri from Sliver Carp and Bighead Carp. J. Jiangsu Ocean Univ. (Nat. Sci. Edit.) 2017, 26, 84–87. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gu, Z.; Liu, Y. Morphological, histological and molecular characterization of three Myxobolus species (Cnidaria: Myxosporea) from silver carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix Valenciennes and bighead carp Hypophthalmichthys nobilis Richardson in China. Parasitol. Int. 2018, 67, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.; Shao, N.; Xi, B.; Xie, J. A Study on Bacterial Etiology and Histopathology Associated with Hemorrhagic Disease in American Shad Alosa sapidissima. Aquac. Res. 2024, 2024, 8869167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, C.R.; Lehman, D.C.; Manuselis, G. Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 978-0-323-08989-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K.; Battistuzzi, F.U. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivas, T.N.R.; Manasa, P.; Begum, Z.; Sunil, B.; Sailaja, B.; Singh, S.K.; Prasad, S.; Shivaji, S. Iodobacter arcticus sp, nov., a psychrotolerant bacterium isolated from meltwater stream sediment of an Arctic glacier. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 2800–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, N.A. Numerical Taxonomy of Violet-Pigmented, Gram-Negative Bacteria and Description of Iodobacter fluviatile gen. nov. comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1989, 39, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Kang, W.; Kim, P.S.; Lee, S.-Y.; Shin, N.-R.; Sung, H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Yun, J.-H.; Jeong, Y.-S.; Han, J.E.; et al. Iodobacter ciconiae sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from feces of oriental stork, Ciconia boyciana. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 2948–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, F.; Chang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Kan, W.; Xiao, M.; Shao, M.; Peng, F.; et al. Iodobacter limnosediminis sp, nov., isolated from Arctic lake sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 1464–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, N.A. Bergey’s Manual® of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; Brenner, D.J., Krieg, N.R., Staley, J.T., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.N.; Yadav, N.; Kour, D.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, K.; Kumar, A.; Rastegari, A.A.; Sachan, S.G.; Singh, B.; Chauhan, V.S.; et al. Bacterial community composition in lakes. In Freshwater Microbiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; p. 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkea-Aho, T.L.; Viljamaa-Dirks, S.; Heinikainen, S.; Kuronen, H.; Tiirola, M. Genetic diversity and phenotypic characterization of Iodobacter limnosediminis associated with skin lesions in freshwater fish. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 1711–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Allen-Austin, D. A Review-Bacterial pathogens of fish. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1985, 58, 483–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.A. Bacterial Fish Pathogens, 4th ed.; Austin, B., Austin, D.A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-Y.; Nakayama, K.; Murakami, Y.; Jung, S.-J.; Oh, M.-J.; Matsuoka, S.; Kawakami, H.; Kitamura, S.-I. Does heavy oil pollution induce bacterial diseases in Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 57, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgendy, M.Y.; Ali, S.E.; Abbas, W.T.; Algammal, A.M.; Abdelsalam, M. The role of marine pollution on the emergence of fish bacterial diseases. Chemosphere 2023, 344, 140366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, T.R.; Hunnicutt, D.W. Susceptibility of zebra fish Danio rerio to infection by Flavobacterium columnare and F. johnsoniae. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 76, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, Y.K.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Amal, M.N.A.; Mohamad, A.; Lee, J.Y.; Annas, S.; Al-saari, N. Effects of skin abrasion in immersion challenge with Vibrio harveyi in Asian seabass Lates calcarifer fingerlings. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2020, 137, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawisza, M.; Chadzinska, M.; Steinhagen, D.; Rakus, K.; Adamek, M. Gill disorders in fish: Lessons from poxvirus infections. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 16, 234–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemly, A.D. Winter Stress Syndrome: An Important Consideration for Hazard Assessment of Aquatic Pollutants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 1996, 34, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bly, J.E.; Quiniou, S.M.A.; Clem, L.W. Environmental effects on fish immune mechanisms. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1997, 90, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Ju, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Y. Micro-and nano-plastics induce kidney damage and suppression of innate immune function in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, P.; Cordero, H.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.Á.; Cuesta, A. In vitro immunotoxicological effects of heavy metals on European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) head-kidney leucocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 47, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutz, L.C.; Gil Barcellos, L.J.; Marteninghe, A.; Davi dos Santos, E.; Zanatta, R. Exposure to sublethal concentration of glyphosate or atrazine-based herbicides alters the phagocytic function and increases the susceptibility of silver catfish fingerlings (Rhamdia quelen) to Aeromonas hydrophila challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havixbeck, J.J.; Rieger, A.M.; Churchill, L.J.; Barreda, D.R. Neutrophils exert protection in early Aeromonas veronii infections through the clearance of both bacteria and dying macrophages. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 63, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, R.B.G.; Oliveira, W.F.d.; Correia, M.T.d.S.; Fontes, A.; Coelho, L.C.B.B. Aeromonas and Human Health Disorders: Clinical Approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 868890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardocci, G.; Navarro, C.; Cortes, P.P.; Imarai, M.; Montoya, M.; Valenzuela, B.; Jara, P.; Acuña-Castillo, C.; Fernandez, R. Neuroendocrine mechanisms for immune system regulation during stress in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gushgari-Doyle, S.; Lui, L.M.; Nielsen, T.N.; Wu, X.; Malana, R.G.; Hendrickson, A.J.; Carion, H.; Poole, F.L.; Adams, M.W.W.; Arkin, A.P.; et al. Genotype to ecotype in niche environments: Adaptation of Arthrobacter to carbon availability and environmental conditions. ISME Commun. 2022, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevrin, G.; Massier, S.; Chassaing, B.; Agus, A.; Delmas, J.; Denizot, J.; Denizot, J.; Billard, E.; Barnich, N. Adaptation of adherent-invasive E. coli to gut environment: Impact on flagellum expression and bacterial colonization ability. Gut Microbes 2018, 11, 364–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedel, G. Simple method to determine β-lactam resistance phenotypes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa using the disc agar diffusion test. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Idelevich, E.A.; Kriegeskorte, A.; Schleimer, N.; Peters, G.; von Eiff, C.; Becker, K. In Vitro Susceptibility of Clinical Staphylococcus aureus Small-Colony Variants to β-Lactam and Non-β-Lactam Antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02532-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindeldecker, D.; Moore, K.; Li, A.; Wozniak, D.J.; Anderson, M.; Dusane, D.H.; Stoodley, P. Novel Aminoglycoside-Tolerant Phoenix Colony Variants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00623-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lories, B.; Belpaire, T.E.R.; Yssel, A.; Ramon, H.; Steenackers, H.P. Agaric acid reduces Salmonella biofilm formation by inhibiting flagellar motility. Biofilm 2020, 2, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Xue, X.; Zhang, T.; Sun, H.; Xiong, S.; Lu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M. The phase variation between wrinkly and smooth colony phenotype affects the virulence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, T.; Leggat, W.; Huggett, M.J.; Ainsworth, T.D. Coral Disease Causes, Consequences, and Risk within Coral Restoration. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itabangi, H.; Sephton-Clark, P.C.S.; Tamayo, D.P.; Zhou, X.; Starling, G.P.; Mahamoud, Z.; Insua, I.; Probert, M.; Correia, J.; Moynihan, P.J.; et al. A bacterial endosymbiont of the fungus Rhizopus microsporus drives phagocyte evasion and opportunistic virulence. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 1115–1130.e1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.M.; Siddik, M.A.B.; Sørensen, M.; Brinchmann, M.F.; Thompson, K.D.; Francis, D.S.; Vatsos, I.N. Insect meal in aquafeeds: A sustainable path to enhanced mucosal immunity in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 150, 109625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characters | Strains/Isolates | Characters | Strains/Isolates | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | C1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Trehalose | + | + | + | N | N | + | Urea hydrolysis | − | − | N | N | − | N |
| Glucose | + | + | N | N | + | N | ONPG test | − | − | N | N | − | N |
| Maltose | + | + | + | + | + | + | Gluconate utilization | − | + | V | N | + | N |
| Mannitol | − | − | − | N | − | N | Citrate utilization | − | + | N | N | N | N |
| Sucrose | + | − | N | − | N | N | Malonate utilization | − | + | N | N | N | N |
| Arabinose | + | − | − | − | − | − | OF Test | F | N | F | N | N | F |
| Xylose | − | − | N | N | N | N | Growth in 6.5% NaCl | − | N | N | N | − | N |
| Raffinose | − | − | N | N | N | N | Nitrate reduced | + | + | N | N | + | + |
| Fructose | − | + | N | + | N | N | Phe deaminase | − | − | N | N | N | N |
| Galactose | − | − | − | N | N | N | Motility | + | N | N | N | N | N |
| Sorbose | − | − | N | N | N | N | H2S | − | − | N | N | N | N |
| Cellobiose | − | − | − | N | N | N | Gelatin hydrolysis | − | + | N | N | + | + |
| Melibiose | − | − | N | + | N | N | Catalase | + | N | N | N | + | N |
| Melizitose | − | − | N | N | N | N | Oxidase | + | + | N | N | + | N |
| Inulin | + | − | N | N | N | N | Voges–Proskauer test | − | − | N | N | N | N |
| Mannose | + | + | N | + | + | N | Methyl red test | + | − | N | N | N | N |
| Dulcitol | − | − | N | N | N | N | Orn decarboxylase | − | − | N | N | N | N |
| Inositol | − | − | − | N | N | − | Lys decarboxylase | − | − | N | N | N | N |
| Sorbitol | − | − | N | N | N | N | Arg decarboxylase | − | − | N | N | N | N |
| Salicin | − | − | N | N | N | N | Arg dihydrolase | − | N | − | + | − | − |
| Esculin hydrolysis | − | − | − | N | N | − | Indole | − | − | N | N | − | − |
| Bile esculin test | − | N | N | N | N | N | |||||||
| Antibiotic | Disk Potency | Inhibition Zone Diameter (mm) | Result | Antibiotic | Disk Potency | Inhibition Zone Diameter (mm) | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEN | 10 U | 24 | S | MI | 30 µg | 23 | S |
| OX | 10 µg | 6 | R | E | 15 µg | 15 | I |
| AMP | 10 µg | 27 | S | AZI | 15 µg | 18 | I |
| PIP | 100 µg | 30 | S | NOR | 10 µg | 21 | S |
| CN | 30 µg | 21 | S | CIP | 5 µg | 24 | S |
| CZ | 30 µg | 35 | S | MY | 2 µg | 6 | R |
| CXM | 30 µg | 28 | S | VAN | 30 µg | 6 | R |
| CAZ | 30 µg | 24 | S | PB | 300 IU | 11 | R |
| CTR | 30 µg | 25 | S | SXT | 25 µg | 12 | R |
| CPZ | 75 µg | 25 | S | C | 30 µg | 27 | S |
| AMK | 30 µg | 22 | S | CC | 2 µg | 6 | R |
| GEN | 10 µg | 18 | I | LEV | 5 µg | 21 | S |
| KAN | 30 µg | 20 | S | IPM | 10 µg | 35 | S |
| S | 10 µg | 14 | R | DO | 30 µg | 21 | S |
| TET | 30 µg | 22 | S | FFC | 30 µg | 31 | S |
| ENR | 10 µg | 26 | S | N | 30 µg | 24 | S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, K.; Shen, N.; Qin, T.; Lu, L.; Xu, D.; Xi, B.; Xie, J. Iodobacter fluviatilis, a New Potential Opportunistic Pathogen Associated with Skin Lesions, First Report in Hypophthalmichthys nobilis in China. Pathogens 2025, 14, 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100978
Chen K, Shen N, Qin T, Lu L, Xu D, Xi B, Xie J. Iodobacter fluviatilis, a New Potential Opportunistic Pathogen Associated with Skin Lesions, First Report in Hypophthalmichthys nobilis in China. Pathogens. 2025; 14(10):978. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100978
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Kai, Nannan Shen, Ting Qin, Liushen Lu, Dongpo Xu, Bingwen Xi, and Jun Xie. 2025. "Iodobacter fluviatilis, a New Potential Opportunistic Pathogen Associated with Skin Lesions, First Report in Hypophthalmichthys nobilis in China" Pathogens 14, no. 10: 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100978
APA StyleChen, K., Shen, N., Qin, T., Lu, L., Xu, D., Xi, B., & Xie, J. (2025). Iodobacter fluviatilis, a New Potential Opportunistic Pathogen Associated with Skin Lesions, First Report in Hypophthalmichthys nobilis in China. Pathogens, 14(10), 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100978






