Diversity of Hard Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) Fauna on Green Habitats of Urban Areas in Eastern Croatia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
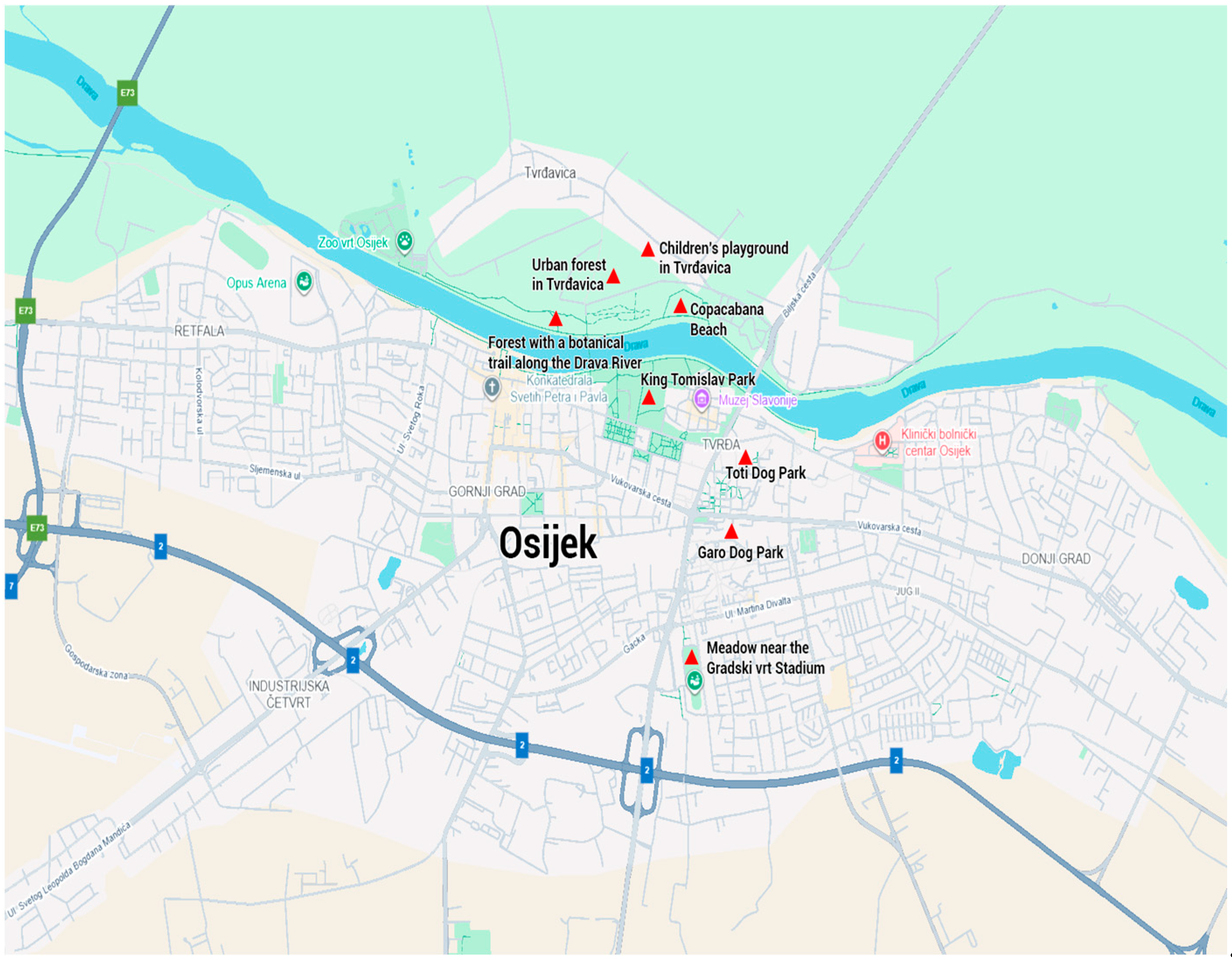
2.2. Sampling of Hard Ticks in Green Habitats of the City of Osijek
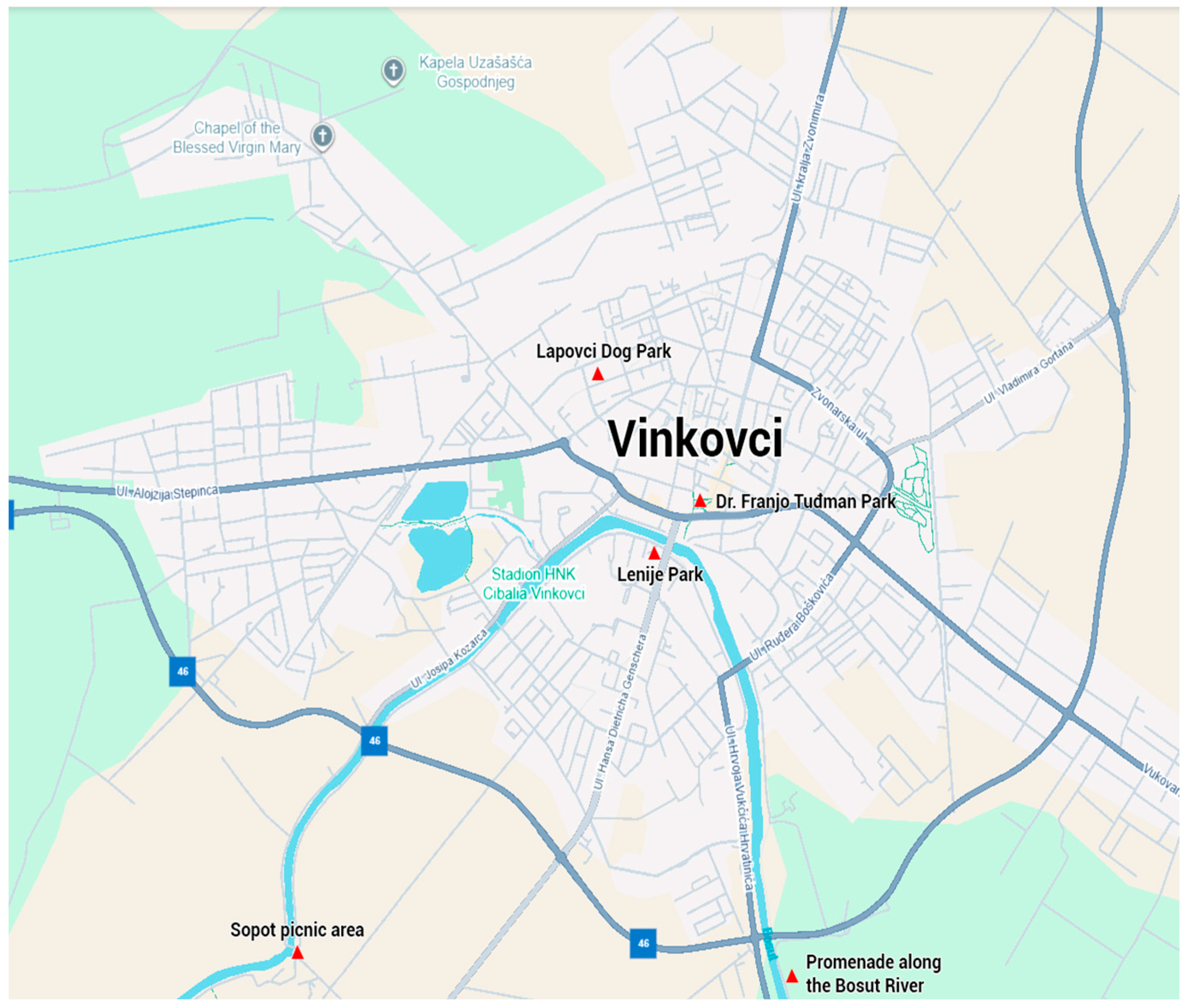
2.3. Sampling of Hard Ticks in Green Habitats of the City of Vinkovci
2.4. Sampling of Hard Ticks in Green Habitats of the City of Vukovar
2.5. Tick Collection, Identification, and Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Tick Diversity in Urban Areas of the Studied Cities
4.2. Rhipicephalus sanguineus s.l.
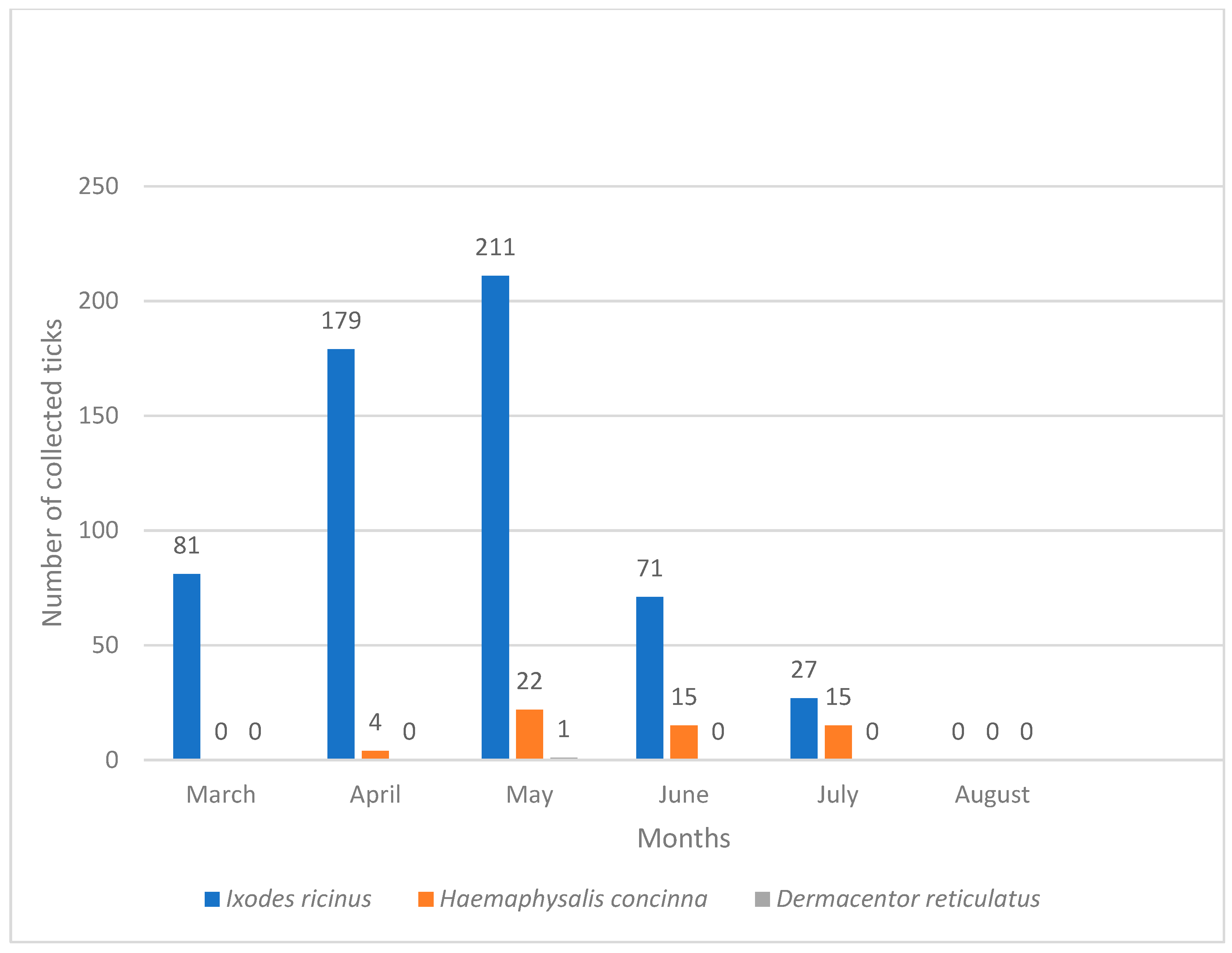
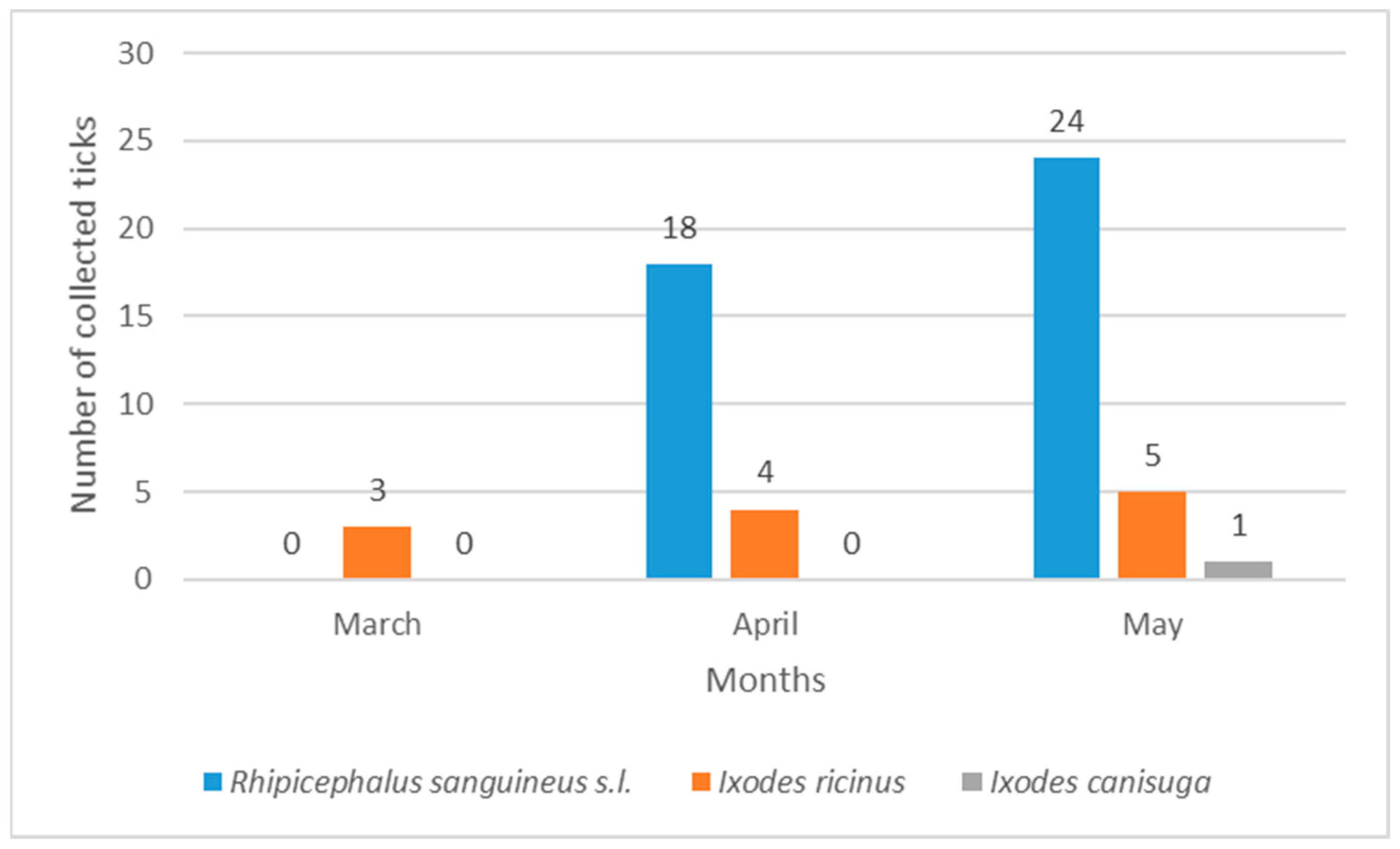
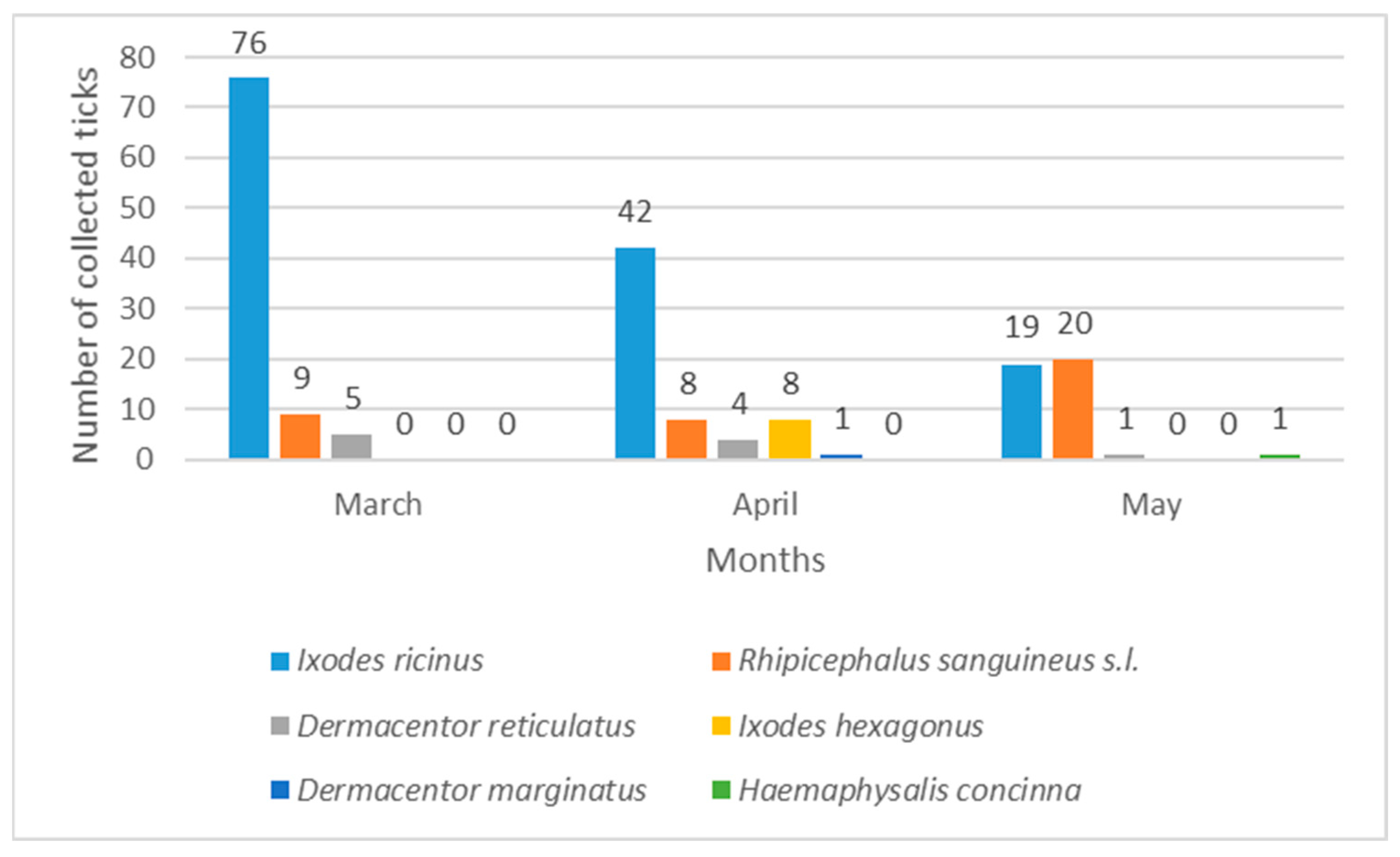
4.3. Seasonal Dynamics of Hard Ticks
4.4. Vector Role
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Otranto, D. Best Practices for Preventing Vector-Borne Diseases in Dogs and Humans. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, P.; Raoult, D. Ticks and Tickborne Bacterial Diseases in Humans: An Emerging Infectious Threat. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 897–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Venzal, J.M.; Kocan, K.M.; Sonenshine, D.E. Overview: Ticks as Vectors of Pathogens That Cause Disease in Humans and Animals. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 6938–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sándor, A.D.; Domsa, C.; Péter, Á.; Hornok, S. Ixodid ticks of Western Palearctic bats: Ecology, host-parasite relationships, geographic distribution and zoonotic importance. Front. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1517704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gortázar, C.; Ruiz-Fons, J.F.; Höfle, U. Infections Shared with Wildlife: An Updated Perspective. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2016, 62, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongejan, F.; Uilenberg, G. The Global Importance of Ticks. Parasitology 2004, 129, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzoli, A.; Silaghi, C.; Obiegala, A.; Rudolf, I.; Hubalek, Z.; Földvári, G.; Plantard, O.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Bonnet, S.; Špitalská, E.; et al. Ixodes ricinus and its transmitted pathogens in urban and peri-urban areas in Europe: New hazards and relevance for public health. Front. Public Health 2014, 2, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, J.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Rafael, M.; Almazán, C.; Bermúdez, S.; Abdelbaset, A.E.; Kasaija, P.D.; Kabi, F.; Akande, A.F.; Ajagbe, D.O.; et al. Perception of Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases Worldwide. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Peña, A. Climate, Niche, Ticks, and Models: What They Are and How We Should Interpret Them. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 103, S87–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, E.; Tälleklint, L.; Polfeldt, T. Impact of Climatic Change on the Northern Latitude Limit and Population Density of the Disease-Transmitting European Tick Ixodes ricinus. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindgren, E.; Gustafson, R. Tick-Borne Encephalitis in Sweden and Climate Change. Lancet 2001, 358, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, F.D.; Ballantyne, R.; Morgan, E.R.; Wall, R. Prevalence, Distribution and Risk Associated with Tick Infestation of Dogs in Great Britain. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2011, 25, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.E.L.; Cote, M.; Le Naour, E.; Bonnet, S.I. Environmental Factors Influencing Tick Densities over Seven Years in a French Suburban Forest. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Földvári, G.; Široký, P.; Szekeres, S.; Majoros, G.; Sprong, H. Dermacentor reticulatus: A Vector on the Rise. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiewra, D.; Czulowska, A. Evidence for an Increased Distribution Range of Dermacentor reticulatus in South-West Poland. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2013, 59, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciebiera, O.; Grochowalska, R.; Łopińska, A.; Zdunjak, P.; Strzala, T.; Jerzak, L. Ticks and spirochetes of the genus Borrelia in urban areas of Central-Western Poland. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2024, 93, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansford, K.M.; Wheeler, B.W.; Tschirren, B. Questing Ixodes ricinus ticks and Borrelia spp. In urban green space across Europe: A review. Zoonoses Public Health 2022, 69, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uspensky, I. Tick pests and vectors (Acari: Ixodoidea) in European towns: Introduction, persisten ce and management. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansford, K.M.; Gillingham, E.L.; Vaux, A.G.C.; Cull, B.; McGinely, L.; Catton, M.; Wheeler, B.W.; Tschirren, B.; Medlock, J.M. Impact of green space connectivity on urban tick presence density and Borrelia infected ticks in different habitats and seasons in three cities in Southern England. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2023, 14, 102103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzén, T.; Choudhury, F.; Hammer, M.; Petersson, M.; Dinnéte, P. Tick-public health risks in urban green spaces. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 10131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vencliková, K.; Betášová, L.; Šikutová, S.; Jedličková, P.; Hubálek, Z.; Rudolf, I. Human pathogenic borreliae in Ixodes ricinus ticks in natural and urban ecosystem (Czech Republic). Acta Parasitol. 2014, 59, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalec, M.; Szewczyk, T.; Welc-Faleciak, R.; Sinski, E.; Karbowiak, G.; Bajer, A. Ticks and the city-are there any differences between city parks and natural forests in terms of tick abundance and prevalence of spirochaetes? Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, D.; Springer, A.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Strube, C. Two-year monitoring of tick abundance and influencing factors in an urban area (city of Hanover, Germany). Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubel, F.; Dautel, H.; Nijhof, A.M.; Kahl, O. Ticks in the metropolitan area of Berlin, Germany. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 102029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weżyk, D.; Dwuznik-Szarek, D.; Kowalec, M.; Biela, S.; Biernacki, K.; Macion, A.; Mencwel, Z.; Safarzynska, N.; Sajnok, L.; Slomka, W.; et al. Are you ready for the tick season? Spring dynamic of tick diversity and density in urban and suburban areas. Parasites Vectors 2025, 18, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucelja, M.; Bjedov, L.; Boljfetić, M.; Klobučar, A.; Krčmar, S.; Borak, S.; Modrić, M.; Juričić, K.; Peleš, V.; Margaletić, J.; et al. Monitoring of Hard Ticks at Urban Recreational Sites in the City of Zagreb from 2016 to 2018. Infektoloski Glas. 2019, 39, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranjek, N.; Teni, M.; Galić, A.; Prskalo, M.; Uranjek, S. Elaborat Zaštite Okoliša-Crpljenje Podzemne Vode, Klisa, Grad Osijek, Osječko-Baranjska Županija, 1st ed.; Promo eko d.o.o.: Osijek, Hrvatska, 2023; pp. 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Njegač, D. Eastern Croatia. In The Big Atlas of Croatia, 1st ed.; Borovac, I., Ed.; Mozaik knjiga: Zagreb, Croatia, 2002; pp. 255–271. [Google Scholar]
- Hillyard, P. Ticks of North-west Europe. In Synopses of the British Fauna (New Series); Kermack, D.M., Barnes, R.S.K., Crothers, J.H., Eds.; The Linnean Society of London and The Estuarine and Coastal Sciences Association: Shrewsbury, UK, 1996; pp. 1–178. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Bouattour, A.; Camicas, J.-L.; Walker, A. Ticks of Domestic Animals in the Mediterranean Region. A Guide to Identification of Species, 1st ed.; University of Zaragoza: Zaragoza, Spain, 2004; pp. 1–130. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Mihalca, A.D.; Petney, T.N. Ticks of Europe and North Africa: A Guide to Species Identification, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–403. [Google Scholar]
- Hornok, S.; Sándor, A.D.; Beck, R.; Farkas, R.; Beati, L.; Kontschán, J.; Takács, N.; Földvári, G.; Silaghi, C.; Meyer-Kayser, E.; et al. Contributions to the Phylogeny of Ixodes (Pholeoixodes) canisuga, I. (Ph.) kaiseri, I. (Ph.) hexagonus and a simple pictorial key for the identification of their females. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šošić, I. Applied Statistics, 2nd ed.; Školska knjiga Zagreb: Zagreb, Croatia, 2006; pp. 1–781. [Google Scholar]
- Krčmar, S. Diversity, Ecology, and Seasonality of Hard Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in Eastern Croatia. J. Vector Ecol. 2019, 44, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, J.; Bučanović, T.; Krčmar, S. Hard tick fauna (Acari: Ixodidae) in different types of habitats in the city of Osijek (Eastern Croatia). Nat. Croat. 2020, 29, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, O.; Gray, S.J. The biology of Ixodes ricinus with emphasis on its ecology. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2023, 14, 102114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heylen, D.; Lasters, R.; Adriaensen, F.; Fonville, M.; Sprong, H.; Matthysen, E. Ticks and tick-borne diseases in the city: Role of landscape connectivity and green space characteristics in a metropolitan area. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorn, S.; Pfister, K.; Reulen, H.; Mahling, M.; Silaghi, C. Occurrence of Babesia spp., Rickettsia spp. and Bartonella spp. In Ixodes ricinus in Bavarian public parks, Germany. Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krčmar, S. Hard Ticks (Acari, Ixodidae) of Croatia. ZooKeys 2012, 234, 19–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobec, M.; Golubic, D.; Punda-Polic, V.; Kaeppeli, F.; Sievers, M. Rickettsia helvetica in Dermacentor reticulatus Ticks. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milutinović, M.; Radulović, Ž.; Tomanović, S.; Tomanović, Ž. Seasonal distribution of Borreliae in Ixodes ricinus ticks in the Belgrade region, Serbia. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2006, 58, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sormunen, J.J.; Kulha, N.; Klemola, T.; Mäkelä, S.; Vesilahti, E.M.; Vesterinen, E.J. Enhanced threat of tick-borne infections within cities? Assessing public health risks due to ticks in urban green spaces in Helsinki, Finland. Zoon. Pub Health 2020, 67, 822–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medlock, J.M.; Hansford, K.M.; Bormane, A.; Derdakova, M.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Claude George, J.; Golovljova, I.; Jaenson, T.G.T.; Jensen, J.K.; Jensen, P.M.; et al. Driving forces for changes in geographical distribution of Ixodes ricinus ticks in Europe. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skuballa, J.; Petney, T.; Pfäffle, M.; Oehme, R.; Hartlet, K.; Fingerle, V.; Kimmig, P.; Taraschewski, H. Occurrence of different Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato genospecies including B. afzelli, B. bavariensis and B. spielmanii in hedgehogs (Erinaceus spp.) in Europe. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F. Biology and Ecology of the Brown Dog Tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Parasites Vectors 2010, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornok, S.; Kováts, D.; Horváth, G.; Kontschán, J.; Farkas, R. Checklist of the hard tick (Acari: Ixodidae) fauna of Hungary with emphasis on host-associations and the emergence of Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2020, 80, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.S.; Dautel, H.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Kahl, O.; Lindgren, E. Effects of Climate Change on Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases in Europe. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2009, 2009, 593232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilibić-Čavlek, T.; Krčmar, S.; Bogdanić, M.; Tomljenović, M.; Barbić, L.; Rončević, D.; Sabadi, D.; Vucelja, M.; Santini, M.; Hunjak, B.; et al. An Overview of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Epidemiology in Endemic Regions of Continental Croatia, 2017–2023. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Földvári, G.; Farkas, R. Ixodid tick species attaching to dogs in Hungary. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 129, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubel, F.; Brugger, K.; Walter, M.; Vogelgesang, J.R.; Didyk, Y.M.; Fu, S.; Kahl, O. Geographical distribution, climate adaptation and vector competence of the Eurasian hard tick Haemaphysalis concinna. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz Louly, C.C.; Nogueira Fonseca, I.; Ferreira de Oliviera, V.; Fontgalland Coelho Linhares, G.; Borges de Menezes, L.; Ferreira Borges, L.M. Seasonal dynamics of Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Acari: Ixodidae) in dogs from a police unit in Goiânia, Goiás, Brazil. Ciência Rural 2007, 37, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubel, F.; Brugger, K.; Pfeffer, M.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Didyk, Y.M.; Leverenz, S.; Dautel, H.; Kahl, O. Geographical distribution of Dermacentor marginatus and Dermacentor reticulatus in Europe. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak, K.; Sielawa, H.; Dziekoňska-Rynko, J.; Kubiak, D.; Rydzewska, M.; Dzika, E. Dermacentor reticulatus ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) distribution in north-eastern Poland: An endemic area of tick-borne diseases. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 75, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krčmar, S.; Klobučar, A.; Vucelja, M.; Boljfetić, M.; Kučinić, M.; Madić, J.; Cvek, M.; Bruvo Mađarić, B. DNA barcoding of hard ticks (Ixodidae), notes on distribution of vector species and new faunal record for Croatia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 101920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilibić-Čavlek, T.; Janev-Holcer, N.; Bogdanic, M.; Ferenc, T.; Ferenc, M.V.; Krcmar, S.; Savić, V.; Stevanović, V.; Ilić, M.; Barbić, L. Current status of Vector-Borne Diseases in Croatia: Challenges and Future Prospects. Life 2023, 13, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.; Kahl, O.; Zintl, A. Pathogens transmitted by Ixodes ricinus. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2024, 15, 102402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Tick Species/City | Osijek | Vinkovci | Vukovar | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ixodes ricinus | 569 | 137 | 12 | 718 | 82.06 |
| Rhipicephalus sanguineus s.l | - | 37 | 42 | 79 | 9.03 |
| Haemaphysalis concinna | 56 | 1 | - | 57 | 6.51 |
| Dermacentor reticulatus | 1 | 10 | - | 11 | 1.26 |
| Ixodes hexagonus | - | 8 | - | 8 | 0.91 |
| Dermacentor marginatus | - | 1 | - | 1 | 0.11 |
| Ixodes canisuga | - | - | 1 | 1 | 0.11 |
| Total | 626 | 194 | 55 | 875 | 99.99 |
| Green Habitats/Tick Species | I. ricinus | H. concinna | D. reticulatus | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban forest in Tvrđavica | 410 | 55 | - | 465 | 74.28 |
| Children’s playground in Tvrđavica | 93 | 1 | - | 94 | 15.01 |
| Copacabana beach | 62 | - | - | 62 | 9.90 |
| Forest with a botanical trail along the Drava River | - | - | 1 | 1 | 0.16 |
| King Tomislav Park | - | - | - | - | - |
| Meadow near the stadium Gradski vrt | 1 | - | - | 1 | 0.16 |
| Garo dog park | 3 | - | - | 3 | 0.48 |
| Toti dog park | - | - | - | - | - |
| Total | 569 | 56 | 1 | 626 | 99.99 |
| Green Habitats/Tick Species | I. ricinus | I. canisuga | R. sanguineus s.l. | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adica Forest Park | 3 | - | - | 3 | 5.45 |
| Forest near the Memorial Cemetery (MCVHW) | 9 | 1 | - | 10 | 18.18 |
| Mazda Park | - | - | 42 | 42 | 76.36 |
| Total | 12 | 1 | 42 | 55 | 99.99 |
| Green Habitats/Tick Species | I. ricinus | R. sanguineus s.l. | D. reticulatus | I. hexagonus | D. marginatus | H. concinna | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dr. Franjo Tuđman park | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | 1.54 |
| Park Lenije | 34 | 6 | - | - | - | - | 40 | 20.62 |
| Dog park Lapovci | 25 | 5 | - | - | - | - | 30 | 15.46 |
| Promenade along the Bosut River | 36 | 10 | 4 | 4 | 1 | - | 55 | 28.35 |
| Sopot picnic area | 39 | 16 | 6 | 4 | - | 1 | 66 | 34.02 |
| Total | 137 | 37 | 10 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 194 | 99.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krčmar, S.; Matak, P.; Krčmar, L.; Nikolić, K. Diversity of Hard Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) Fauna on Green Habitats of Urban Areas in Eastern Croatia. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101010
Krčmar S, Matak P, Krčmar L, Nikolić K. Diversity of Hard Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) Fauna on Green Habitats of Urban Areas in Eastern Croatia. Pathogens. 2025; 14(10):1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101010
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrčmar, Stjepan, Petra Matak, Lora Krčmar, and Kristina Nikolić. 2025. "Diversity of Hard Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) Fauna on Green Habitats of Urban Areas in Eastern Croatia" Pathogens 14, no. 10: 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101010
APA StyleKrčmar, S., Matak, P., Krčmar, L., & Nikolić, K. (2025). Diversity of Hard Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) Fauna on Green Habitats of Urban Areas in Eastern Croatia. Pathogens, 14(10), 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101010







