Abstract
Here, 18S-rDNA sequences of Blastocystis sp., previously documented from symptomatic (cases) and asymptomatic (controls) carriers, were analyzed to determine their population structure, predict their secondary structure, and examine their interactions with ribosomal proteins (Bud23, RPS5, and RPS18). Phylogenetic and population differentiation analyses were performed using STRUCTURE software V2.3.4. Moreover, an analysis of the rRNA secondary structure and folding of each sequence was performed, and their probability of interaction with ribosomal proteins was determined. Phylogenetic and haplotype analyses sorted the sequences into genetic subtypes ST1, ST2, and ST3, while the population structure showed each cluster as a differentiated subpopulation, suggesting incipient speciation or cryptic species differentiation. Furthermore, the analysis of the secondary structure of rRNA exhibited specific arrangements for each subtype. In addition, the probability of interaction between 18S-rRNA sequences of Blastocystis from cases and controls with RPS5 and RPS18 was significant, matching the biological plausibility of the previously documented finding that control isolates had a lower generation time than isolates obtained from cases. These findings reinforce the hypothesis that ribosomal subtypes ST1–ST3 of Blastocystis represent evolutionarily distinct lineages with the potential to be recognized as future species. Furthermore, they underscore the functional relevance of 18S-rRNA sequences from clinical isolates of Blastocystis.
1. Introduction
Blastocystis sp. represents the most prevalent intestinal microeukaryote encountered in coproparasitological investigations worldwide. The prevalence of this organism exhibits significant geographic variation, with rates of 10–15% in developed nations compared to more than 50% in developing countries [1,2].
The pathogenicity of Blastocystis remains a subject of scientific debate. While numerous studies have established associations between Blastocystis colonization and various gastrointestinal and dermatological manifestations, other investigations suggest that it functions as a non-pathogenic commensal organism within the intestinal microbiota of asymptomatic individuals [3,4]. Furthermore, a remarkable characteristic of Blastocystis sp. is its extensive genetic diversity, with 44 distinct genetic subtypes (STs; ST1, ST2, ST3, … ST44) currently documented, all characterized through the analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA (18S) sequences [5].
On the other hand, ribosomes serve as essential sites of protein synthesis across most organisms, functioning as complex particles primarily composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. The eukaryotic ribosome consists of two distinct subunits (40S and 60S) that undergo an evolutionarily conserved assembly process. This process requires the precise arrangement of rRNA and more than 79 types of ribosomal proteins (RPs), coordinated by over 200 trans-acting biogenesis factors [6,7,8]. Within ribosomes, 18S-rRNA molecules form the structural core of the 40S subunit, folding into characteristic conformations, where small self-complementary regions create double helices and single-stranded hairpin structures. Research has demonstrated that specific regions of 18S-rRNA, through their secondary and tertiary configurations, facilitate the arrangement and assembly of various ribosomal proteins that constitute the ribosomal subunits [9]. Additionally, numerous investigations have utilized the secondary structures of ribosomal genes to validate or enhance phylogenetic reconstructions, highlighting their evolutionary significance [10,11]. Although 18S-rRNA is not commonly associated with pathogenicity, variation in its secondary structure can influence phenotype by tuning protein synthesis. Local shifts in 18S accessibility or conformation may alter prerRNA processing, small-subunit assembly, ribosomal protein recruitment, and translational efficiency, reshaping growth and environmental responses and, ultimately, traits linked to pathogenicity. Consistent with this view, temperature-dependent remodeling of the 18S structure and expression has been observed in Plasmodium, supporting a regulatory contribution of the rRNA structure to stage- and environment-specific phenotypes [12]. This mechanistic perspective leverages genomic evidence within an evolutionary framework, enabling phenotype-level explanations without relying on rigid virulence factor paradigms.
RPs are essential components that regulate protein synthesis and facilitate translation processes. However, numerous potential biological functions of these proteins remain unexplored [6]. Among the RPs most extensively investigated for their significant roles in diverse biological processes are Bud23, S5 (RPS5), and S18 (RPS18). It is important to note that Bud23, while not formally an RP, is a highly conserved methyltransferase that facilitates the critical processome-to-pre-40S transition during ribosome biogenesis [7,13].
The eukaryotic ribosomal protein RPS5 is located at the head of the 40S ribosomal subunit (5′ dominion) and belongs to a highly conserved ribosomal protein family. Beyond its fundamental role in translation, RPS5 exhibits significant extra-ribosomal functions. Research has demonstrated that RPS5 participates in cellular proliferation and apoptotic pathways [7,14] and contributes to hepatic pathophysiology [15].
Ribosomal protein RPS18 functions as a critical housekeeping component that specifically binds to 18S-rRNA, thereby stabilizing its structure and facilitating the assembly of the 40S subunit in eukaryotic cells. This protein plays an essential role in the binding of fMet-tRNA, which is crucial for translation initiation. Beyond its primary function in protein synthesis, RPS18 exhibits additional roles in various organisms, including modulation of bacterial growth patterns [16,17].
Previous research conducted on Blastocystis stool cultures compared isolates from patients experiencing gastrointestinal disorders (cases) with those from asymptomatic carriers (controls). This investigation revealed that isolates from symptomatic patients demonstrated significantly reduced growth rates and decreased nucleotide variability compared to those from asymptomatic individuals. Despite these physiological differences, Bayesian phylogenetic analysis successfully identified subtypes ST1, ST2, ST3, and ST7 across all isolates, but failed to establish distinct phylogenetic clusters that separated cases from controls [18].
The present study aims to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the population structure in conjunction with phylogenetic network assessment, while also predicting the secondary structure and folding patterns of 18S-rRNA in Blastocystis sp. isolates. Furthermore, we investigate potential interactions between these RNA structures and ribosomal proteins, utilizing previously documented sequence data obtained from both symptomatic and asymptomatic carriers to elucidate possible molecular mechanisms underlying pathogenicity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Data
For this study, we obtained 18S-rDNA sequence data from 96 Blastocystis sp. isolates (49 from symptomatic patients and 47 from asymptomatic carriers) previously documented by Vargas-Sanchez et al. [18]. Sequences were retrieved from GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, accessed on 3 February 2025) using accession numbers KP055659–KP055754, along with corresponding clinical metadata. These sequences map to the 5′ region of the complete 18S-rDNA gene, approximately positions 26 to 340.
2.2. Sequence Alignments
We implemented SSU-ALIGN v0.1.1 [19] in DNA mode with model guidance to align study sequences against a Blastocystis-specific consensus model derived from curated full-length references across all subtypes and sequences from animals not included in the subtype system [20]. Secondary structure support was estimated with RNAalifold v2.4.17 [21] using non-default settings (aln, color, dangles = 2) across five temperatures (37–41 °C), and covariance models were built with ssu-build [19], enforcing an 80% gap threshold (gapthresh 0.8) while disabling relative-entropy filtering (enone). To reduce spurious positions, we compared three masking schemes in ssu-mask [19]—strict (pf 0.95, pt 0.95), medium (pf 0.90, pt 0.92; key “med90”), and relaxed (pf 0.85, pt 0.90)—and retained the medium mask for downstream analyses due to its balance of coverage and structural consistency.
Study sequences were then aligned against this model, producing structurally consistent alignments that account for conservation at the sequence and structural levels, providing the foundation for subsequent analyses.
2.3. Phylogeny and Haplotype Network Analysis
A median-joining network analysis was carried out using NETWORK 4.6 software [22], and haplotype networks were depicted under default settings and assumptions. For all analyses, the following sequences of Blastocystis available in GenBank were used as controls of subtypes: ST1: HQ641595-6; ST2: HQ641602, HQ641654, and JX305874-5; ST3: JX305879, HQ641613, JX305880, JX305883, and HQ641611.
To compare the match between phylogenetic Blastocystis subtypes and the population analysis, a Bayesian inference was performed using Mr. Bayes 3.1.2 program [23] for 10 million generations with sampling trees every 100 generations. Inferences that reached the stationary phase were collected and used to build a consensus tree.
2.4. Population Structure Analysis
The STRUCTURE analysis with software V2.3.4 [24] was carried out to determine the most probable number of clusters across all Blastocystis samples with each ST. The value of K, representing the theoretical number of independent populations (considering two groups—cases and controls—and three STs), was established using the predetermined values of the software: correlated allele frequencies and admixture [25].
The algorithm starts with an initial random association of alleles into K clusters and was executed with 10 independent replicates for each value of K from 1 to 10 using a burn-in period of 10,000 and 100,000 repetitions after burn-in. The appropriate number of clusters was determined by calculating the delta K value [25]. A second run was performed using the delta K value assigned to the program (K = 2 or K = 3). These new analyses were conducted with a burn-in period of 20,000 and 100,000 Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) repetitions after burn-in [25].
2.5. RNA Secondary Structure and Folding
The 18S sequences of Blastocystis sp. from cases and controls (320 bp) were transcribed into 18S-rRNAs. Then, these fragments were inserted into consensus alignments of whole 18S-rRNA of Blastocystis (positions 22 to 352 in the 5′ domain, according to Spahn et al. [26] and Granneman et al. [27]) for STs 1–3. The secondary structures and folding were predicted under the RNAfold web server [28], and the minimum free energy (ΔG) was estimated for stability comparison.
2.6. Prediction of RNA–Protein Interactions
The interaction between 18S-rRNA sequences of Blastocystis from cases and controls and Bud23, RPS5, and RPS18 was analyzed; sequences of these RPs from ST1 and ST4 genomes of Blastocystis available in GenBank (S18: OAO11934 and XP 014528798.1; S5: OAO14796) were downloaded. Then, analysis of RNA–protein interactions was performed online using RPISeq software V1.0 [27], contrasting the converted sequences of each 18S-rRNA from cases and controls with the sequences of Bud23, RPS5, and RPS18 to predict the probability of interaction between them using a Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithm.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Student’s t-test was used to compare means for ribosomal proteins RPS5, RPS18, and Bud23, and Levene’s test was used to assess homogeneity of variance. Mean differences and their respective 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were also analyzed. For the analysis of ST1, ST2, and ST3, proportions were tested using the X2 statistic, and compliance with the expected value assumption (e > 5) was verified. The analysis assumes a one-tailed hypothesis, with a significance level of p ≤ 0.05, with 95% CI. The analysis was performed using SPSS version 31 for iOS (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenies and Population Structure Analysis
Phylogenetic analysis revealed distinct clustering patterns for ST1, ST2, and ST3, with no discernible segregation between symptomatic cases and asymptomatic controls (Figure 1A). Consistent with these findings, STRUCTURE analysis generated a histogram clearly delineating three genetically distinct subpopulations corresponding to each ST (Figure 1C). In contrast, when the analysis was conducted under the assumption of two subpopulations (cases versus controls), no significant clustering pattern emerged (Figure 1B).
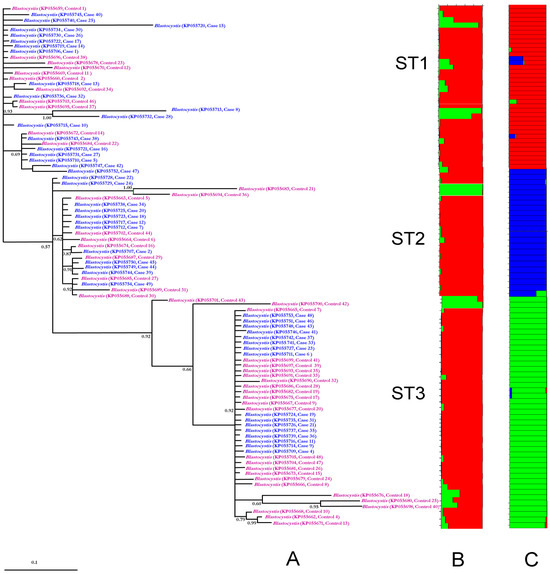
Figure 1.
In (A), phylogenetic inference based on 18S-rDNA sequences of Blastocystis sp. [18] is shown. The numbers at the nodes indicate Bayesian posterior probabilities. Figure 1 illustrates the genetic structure clusters (denoted by different colors) derived from the 18S-rDNA sequences of Blastocystis sp. These clusters were generated through Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulation, considering either two mayor subpopulations (cases and controls) in panel B or three subpopulations (ST1, ST2, and ST3) in panel C; where the colors means a defined subpopulation and each sample is represented by a vertical bar segmented into colored portions, indicating membership probability in either K = 2 or K = 3 clusters. The probabilities of group membership for the case–control analysis (B) ranged from 0.86 to 0.99 for K1 and from 0.91 to 0.99 for K2, while under the assumption of three subpopulations (C), probabilities ranged from 0.58 to 0.99 for K1, from 0.91 to 0.99 for K2, and 0.73–0.99 for K3.
The haplotype network analysis corroborated the phylogenetic findings, with sequences clustering into specific groups corresponding to each of the STs (Figure 2). While this analysis similarly failed to differentiate between case and control haplotypes, it revealed identical haplotypes shared between symptomatic and asymptomatic carriers across all subtypes.
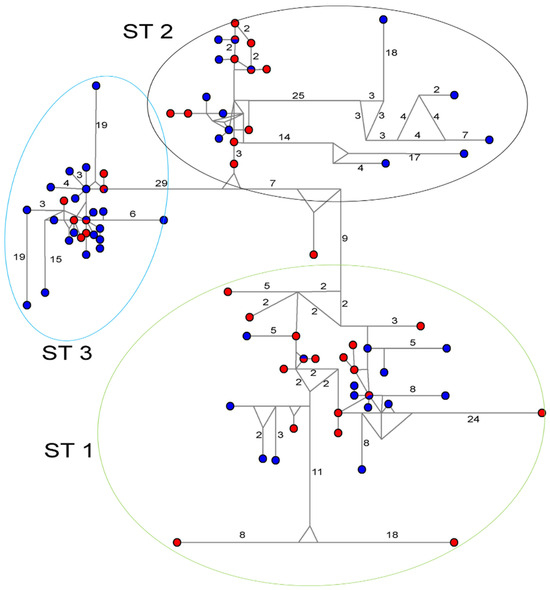
Figure 2.
Haplotype network tree generated using 18S-rDNA sequences of Blastocystis sp. [18]. Sizes of circles are proportional to haplotype frequencies, and the numbers in branches are mutational changes. Blue indicates the control samples, and red indicates the case samples.
3.2. 18S-rRNA Secondary Structure and Conformational Analysis
As illustrated in Figure 3, the secondary structure of 18S-rRNA exhibited similar architectural frameworks across all STs, characterized by a conserved scaffold with subtype-specific variations throughout the molecule. Each subtype displayed a primary helix framework that was consistent between cases and controls, though with distinctive substructural elements and loops, i.e., small double strands or loop projections derived from the main structure. Following the nomenclature established by Van de Peer et al. [29] and Wuyts et al. [30], individual helices and substructural loops were enumerated in a clockwise orientation from the 5′ to the 3′ terminus. This analysis identified 14 distinct substructures in ST1 and ST2, while ST3 exhibited 11 substructures (Figure 3). Notably, ST1 displayed conformational polymorphism in substructures 1 and 13, whereas ST2 and ST3 each presented four conformational variants. Importantly, no case-specific or control-specific substructural elements were identified in any of the subtypes.
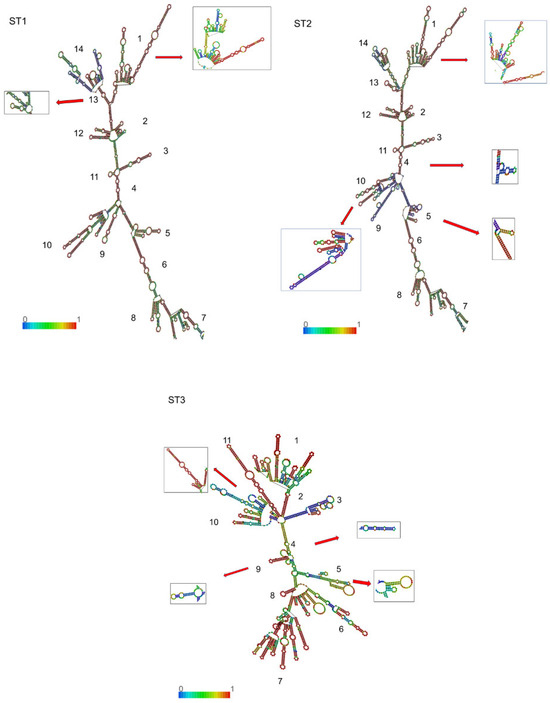
Figure 3.
Inferred secondary structures of 18S-rRNA for ST1, ST2, and ST3; the structures are colored by base-pairing probabilities. The numbers at the bases of the branches show the ordering of the substructural loops. The colored line at the base represents the base-pair probability. Polymorphic conformational substructures are shown in boxes. The ΔG values of the thermodynamic ensemble ranged from −587.42 to −1192.10 Kcal/mol for ST1, from −541.50 to −577.10 Kcal/mol for ST2, and from −556.72 to −553.45 Kcal/mol for ST3.
3.3. RNA–Protein Interaction Analysis
Based on the interaction probability data between ribosomal proteins (Bud23, RPS5, and RPS18) and 18S-rRNA sequences from Blastocystis isolates (Supplementary Materials, Table S1), we conducted comparative analyses between subtypes and between case and control groups. Table 1 summarizes these comparisons. All three ribosomal proteins demonstrated high interaction probabilities (mean > 0.91) with18S-rRNA, with Bud23 showing the highest values, followed by RPS18 and RPS5, respectively. The majority of the data points clustered between the lower quartile (Q1) and the median (Supplementary Materials, Figure S1). Notably, when comparing overall case versus control values, statistically significant differences were observed for RPS18 and RPS5 interactions; however, when stratified by subtype, no significant differences were detected between cases and controls within individual STs.

Table 1.
Probability of interaction determined by the Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithm between RP sequences (S18, S5, and Bud23) and 18S-rRNA of Blastocystis for cases and controls.
4. Discussion
Blastocystis STs are considered to be ribosomal linages [20], aligning with criteria established by Jacob et al. [31], which characterize ribosomal lineages as organisms with ≥80% of the 18S-rDNA gene sequenced, but lacking definitive morphological differentiation. These lineages may ultimately be reclassified as discrete, pending further morphological and molecular characterization. Our phylogenetic analyses and STRUCTURE histogram data provide robust support for the classification of ST1, ST2, and ST3 as distinct ribosomal lineages, offering compelling evidence for their status as cryptic species with genetically differentiated populations despite morphological homogeneity.
In human18S-rDNA, the copy number of ribosomal genes per cell demonstrates significant interpersonal variation, ranging from 67 to 412 copies (mean = 217) [32]. Comparatively, Blastocystis ST7 has been documented to contain 17 tandem copies [33], highlighting species-specific patterns of ribosomal gene organization.
The eukaryotic ribosomal RNA gene (rDNA) is structurally organized into multiple tandem-repeating units. These units of rDNA undergo coordinated evolution within species, resulting in homogenization of repetitive DNA sequences within a species while maintaining sequence divergence between species or higher taxonomic categories. This molecular evolutionary phenomenon is termed concerted evolution [34,35].
Concerted evolution provides a valuable framework for understanding cryptic speciation phenomena. For example, a phylogenetic investigation incorporating rRNA secondary structure analysis of eleven representative solefish specimens (family Soleidae) demonstrated that six species exhibited minimal variation, suggesting a concerted evolutionary pattern, while other samples suggested non-concerted evolutionary dynamics. Additionally, this analytical approach facilitated taxonomic clarification, resolving the previous misclassification of a genus [34].
In the present study, our analysis of the specific 18S-rRNA secondary structure arrangements for each subtype, coupled with the distinct subpopulation clustering observed in the STRUCTURE analysis, strongly suggests that concerted evolution drives the differentiation of Blastocystis subtypes. This evolutionary mechanism is consistent with the genomic organization of ribosomal genes in most eukaryotic organisms, where rDNA exists in tandem arrays and undergoes concerted evolution [34,36,37].
Our computational predictions of RNA–protein interactions revealed a hierarchical pattern of binding probabilities, with Bud23 demonstrating the highest interaction probability, followed by RPS18 and RPS5. Statistical analysis uncovered significant differences in RPS18 and RPS5 interaction probabilities between symptomatic and asymptomatic carriers in the overall sample. However, these differences were not observed when the interactions were stratified by subtype, suggesting subtype-specific interaction patterns. These findings align with the established functional roles of these ribosomal proteins. Bud23, as a highly conserved methyltransferase, functions during the early processome-to-pre-40S transition stage [7,13], making its interactions relatively resistant to 18S-rRNA sequence variations. Conversely, RPS18 and RPS5 directly bind to 18S-rRNA to stabilize its structure and facilitate 40S subunit assembly [16,17]. Consequently, sequence variations in 18S-rRNA more profoundly affect these later-stage interactions, potentially compromising assembly efficiency.
The bioenergetics of ribosome maturation represents a substantial cellular investment, with eukaryotic cells dedicating a majority of their metabolic energy to producing functional ribosomes [24]. The 5′ terminal region of 18S-rRNA exhibits considerable species-specific and cell type-specific variability [24]; nevertheless, its fundamental role in translation initiation and protein synthesis remains universally critical across eukaryotic lineages [6]. These functional constraints likely influence the evolutionary patterns observed in Blastocystis ribosomal RNA.
Previous research has documented that Blastocystis exhibits variable generation times (GT) in axenic culture, ranging from 8.5–19.4 h depending on strain, with a mean GT of 11.7 h across eight experimentally tested strains [38]. In an investigation conducted by Vargas-Sanchez et al. [18], fecal samples from symptomatic (cases) and asymptomatic (controls) Blastocystis carriers were cultured in two distinct media. This study revealed that isolates from symptomatic patients demonstrated significantly reduced growth rates compared to those from asymptomatic controls, suggesting enhanced protein synthesis efficiency in the control isolates. Furthermore, the controls exhibited greater nucleotide diversity relative to the case group. This observation aligns with established eukaryotic growth patterns, wherein hundreds of copies of transcriptional units are encoded during proliferative phases to accommodate increased ribosomal demand [39]. Consequently, greater sequence variation would be expected in samples displaying normal growth kinetics, such as those from the control group. These findings support the biological plausibility that subtle conformational alterations in ribosome assembly may substantially influence protein synthesis rates.
In our current investigation, the probability of interaction between RPS18 and RPS5 and 18S-rRNA was significantly higher in the control sequences compared to the case sequences. This molecular distinction may elucidate the observed reduction in generation time, manifesting as accelerated growth in control isolates relative to those from symptomatic cases. The enhanced RNA–protein interaction efficiency could potentially facilitate more rapid ribosomal assembly and consequently expedite protein synthesis in asymptomatic carriers.
It is noteworthy that ribosomal proteins may exhibit functions beyond their canonical roles in protein synthesis. For instance, a comprehensive functional characterization of RPS18 from the cattle tick Rhipicephalus microplus demonstrated that recombinant RPS18 significantly inhibited the growth of both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria under in vitro conditions [16]. This finding suggests potential auxiliary functions of ribosomal proteins that may influence pathogen–host interactions in ways not directly related to translation efficiency.
While some studies have identified associations between symptomatic presentation and infection with specific Blastocystis subtypes [40,41], our findings do not support a direct correlation between virulence/pathogenicity and 18S-rRNA sequence composition. Although multiple studies have documented the release of factors that may induce inflammatory processes in the host [42,43,44], these pathogenic mechanisms have not been demonstrated to correlate with 18S-rRNA configuration or sequence variations.
Some limitations of the present study are as follows: First, complete 18S-rDNA sequencing was not performed, potentially underestimating the frequency of rRNA secondary structure folding polymorphisms. Second, pseudogene identification protocols were not implemented, introducing potential bias in the enumeration of substructure loops across STs. Third, there may be a potential sampling bias, because a small number of case and control samples were analyzed from a specific population.
5. Conclusions
Our findings reinforce the hypothesis that ribosomal subtypes ST1, ST2, and ST3 of Blastocystis represent evolutionarily distinct lineages with the potential to be recognized as future species. Furthermore, they underscore the functional relevance of 18S-rRNA sequences from clinical isolates of Blastocystis, suggesting the operation of concerted evolutionary processes in this organism. Furthermore, the differential interaction probabilities between Blastocystis 18S-rRNA secondary structures and ribosomal proteins RPS5 and RPS18 offer a mechanistic explanation for previously documented differences in generation times between isolates from symptomatic and asymptomatic carriers.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pathogens14101009/s1: Table S1: Values to predict the probability of interaction between the RPs (Bud23, RPS5, and RPS18) and the 18S-rRNA sequences of Blastocystis from each sample (case or control); Figure S1: Box plot.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.M.-H., G.V. and P.M.; methodology, F.M.-H., A.M., C.Z. and P.M.; software, F.M.-H., A.M. and C.J.-G.; validation, F.M.-H., A.M., C.Z., M.R.-V., C.J.-G., K.F.-M., A.T.-C., G.V. and P.M.; formal analysis, F.M.-H., A.M., C.Z., M.R.-V., C.J.-G., K.F.-M., A.T.-C., G.V. and P.M.; investigation, F.M.-H., A.M., C.Z., M.R.-V., K.F.-M., A.T.-C., G.V. and P.M.; resources, F.M.-H. and P.M.; data curation, F.M.-H. and P.M.; writing—original draft preparation, F.M.-H., A.M., C.Z., M.R.-V., C.J.-G., K.F.-M., A.T.-C., G.V. and P.M.; writing—review and editing, F.M.-H., A.M., C.Z., M.R.-V., C.J.-G., K.F.-M., A.T.-C., G.V. and P.M.; visualization F.M.-H., A.M., C.Z., M.R.-V., C.J.-G., K.F.-M., A.T.-C., G.V. and P.M.; supervision, F.M.-H., G.V. and P.M.; project administration, M.R.-V. and P.M.; funding acquisition, F.M.-H. and P.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Secretaría de Salud, Mexico, Hospital General “Dr. Manuel Gea Gonzalez”, Grant #E022.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Research Ethics and Research Committees of the Hospital General “Dr. Manuel Gea Gonzalez” approved the original study in which human fecal samples were recovered (approval number 12-87-2012, reference [18]).
Informed Consent Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, although this research does not involve human subjects, human material, human tissues, or human data. During the original study, in which human fecal samples were recovered, written informed consent was obtained from each participant.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| 18S-rDNA | 18S ribosomal DNA |
| 18S-rRNA | 18S ribosomal RNA |
| rRNA | Ribosomal RNA |
| ST | Subtype |
| RP | Ribosomal protein |
References
- Tan, K.S. New insights on classification, identification, and clinical relevance of Blastocystis spp. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 639–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, H.I.; Ju, J.W.; Lee, M.R. Molecular Prevalence of Blastocystis sp. from Patients with Diarrhea in the Republic of Korea. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olyaiee, A.; Sadeghi, A.; Yadegar, A.; Mirsamadi, E.S.; Mirjalali, H. Gut Microbiota Shifting in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: The Mysterious Role of Blastocystis sp. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 890127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Tan, K.S.W.; Clark, C.G. Blastocystis. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 315–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santin, M.; Figueiredo, A.; Molokin, A.; George, N.S.; Köster, P.C.; Dashti, A.; González-Barrio, D.; Carmena, D.; Maloney, J.G. Division of Blastocystis ST10 into three new subtypes: ST42–ST44. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2024, 71, e12998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Chao, W.; Zhong, S.; Ren, A.J. Eukaryotic Ribosomal Protein S5 of the 40S Subunit: Structure and Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.J.; Johnson, A.W. Release of the ribosome biogenesis factor Bud23 from small subunit precursors in yeast. RNA 2022, 28, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, M.L.; Woodson, S.A. A roadmap for rRNA folding and assembly during transcription. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 46, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Cerca, S.; Pöll, G.; Gleizes, P.E.; Tschochner, H.; Milkereit, P. Roles of eukaryotic ribosomal proteins in maturation and transport of pre-18S rRNA and ribosome function. Mol. Cell 2005, 20, 2632–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, J.J.; McKenna, C.H.; Yoder, M.J.; Gutell, R.R.; Johnston, J.S.; Kathirithamby, J.; Cognato, A.I. Assessing the odd secondary structural properties of nuclear small subunit ribosomal RNA sequences (18S) of the twisted-wing parasites (Insecta: Strepsiptera). Insect Mol. Biol. 2005, 14, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.; Förster, F.; Müller, T.; Dandekar, T.; Schultz, J.; Wolf, M. Including RNA secondary structures improves accuracy and robustness in reconstruction of phylogenetic trees. Biol. Direct 2010, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, Q.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, M.; Chen, B.; Huang, J.; Ma, C.; Wang, X. RNA Secondary Structurome Revealed Distinct Thermoregulation in Plasmodium falciparum. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 9, 766532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, J.J.; Sardana, R.; Elmir, E.W.; Johnson, A.W. Bud23 promotes the final disassembly of the small subunit processome in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1009215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matragkou, C.N.; Papachristou, E.T.; Tezias, S.S.; Tsiftsoglou, A.S.; Choli-Papadopoulou, T.; Vizirianakis, I.S. The potential role of ribosomal protein S5 on cell cycle arrest and initiation of murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 104, 1477–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.H.; Hu, H.G.; Tian, Y.; Wang, S.Z.; Li, J.; Li, J.Z.; Deng, X.; Qian, H.; Qiu, L.; Hu, Z.L.; et al. Bioactive compound reveals a novel function for ribosomal protein S5 in hepatic stellate cell activation and hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology 2014, 60, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, G.C.A.; Silva, F.A.A.; Torquato, R.J.S.; Silva Vaz, I.; Parizi, L.F.; Tanaka, A.S. Evaluation of the biological function of ribosomal protein S18 from cattle tick Rhipicephalus microplus. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2024, 15, 102333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malygin, A.A.; Karpova, G.G. Structural motifs of the bacterial ribosomal proteins S20, S18 and S16 that contact rRNA present in the eukaryotic ribosomal proteins S25, S26 and S27A, respectively. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 2089–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vargas-Sanchez, G.B.; Romero-Valdovinos, M.; Ramirez-Guerrero, C.; Vargas-Hernandez, I.; Ramirez-Miranda, M.E.; Martinez-Ocaña, J.; Valadez, A.; Ximenez, C.; Lopez-Escamilla, E.; Hernandez-Campos, M.E.; et al. Blastocystis Isolates from Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome and from Asymptomatic Carriers Exhibit Similar Parasitological Loads, but Significantly Different Generation Times and Genetic Variability across Multiple Subtypes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrocki, E.P. Structural RNA Homology Search and Alignment Using Covariance Models. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Medicine, Washington University in Saint Louis, St. Louis, MO, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Clark, C.G. Pre-empting Pandora’s Box: Blastocystis Subtypes Revisited. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.R.; Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Neuböck, R.; Hofacker, I.L. The Vienna RNA website. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W70–W74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelt, H.J.; Forster, P.; Röhl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquis, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software structure: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spahn, C.M.; Beckmann, R.; Eswar, N.; Penczek, P.A.; Sali, A.; Blobel, G.; Frank, J. Structure of the 80S ribosome from Saccharomyces cerevisiae—tRNA-ribosome and subunit-subunit interactions. Cell 2001, 107, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granneman, S.; Petfalski, E.; Swiatkowska, A.; Tollervey, D. Cracking pre-40S ribosomal subunit structure by systematic analyses of RNA-protein cross-linking. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 2026–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muppirala, U.K.; Honavar, V.G.; Dobbs, D. Predicting RNA-Protein Interactions Using Only Sequence Information. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Peer, Y.; De Rijk, P.; Wuyts, J.; Winkelmans, T.; De Wachter, R. The European small subunit ribosomal RNA database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuyts, J.; De Rijk, P.; Van de Peer, Y.; Winkelmans, T.; De Wachter, R. The European Large Subunit Ribosomal RNA Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, A.S.; Busby, E.J.; Levy, A.D.; Komm, N.; Clark, C.G. Expanding the Entamoeba Universe: New Hosts Yield Novel Ribosomal Lineages. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2016, 63, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, E.; Kalmárová, M.; Koberna, K.; Zemanová, Z.; Malínský, J.; Masata, M.; Cvacková, Z.; Michalová, K.; Raska, I. NORs and their transcription competence during the cell cycle. Folia Biol. 2006, 52, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, P.; Meloni, D.; Nourrisson, C.; Wawrzyniak, I.; Viscogliosi, E.; Livrelli, V.; Delbac, F. Molecular subtyping of Blastocystis spp. using a new rDNA marker from the mitochondria-like organelle genome. Parasitology 2014, 141, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D. Concerted evolution: Molecular mechanism and biological implications. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 64, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Shi, W.; Yang, M.; Kong, X. Characterization of 18S-ITS1-5.8S rDNA in eleven species in Soleidae: Implications for phylogenetic analysis. Hydrobiologia 2018, 819, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coen, E.; Strachan, T.; Dover, G. Dynamics of concerted evolution of ribosomal DNA and histone gene families in the melanogaster species subgroup of Drosophila. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 158, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlötterer, C.; Tautz, D. Chromosomal homogeneity of Drosophila ribosomal DNA arrays suggests intrachromosomal exchanges drive concerted evolution. Curr. Biol. 1994, 4, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierdt, C.H.; Swan, J.C. Generation time and growth rate of the human intestinal parasite Blastocystis hominis. J. Protozool. 1981, 28, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eickbush, T.H.; Eickbush, D.G. Finely orchestrated movements: Evolution of the ribosomal RNA genes. Genetics 2007, 175, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelberg, C.; Stensvold, C.R.; Monecke, S.; Ditzen, A.; Stopsack, K.; Heinrich-Gräfe, U.; Pöhlmann, C. Blastocystis sp. subtype 2 detection during recurrence of gastrointestinal and urticarial symptoms. Parasitol. Int. 2010, 59, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.C.; Suresh, K.G.; Smith, H.V. Phenotypic and genotypic characterisation of Blastocystis hominis isolates implicates subtype 3 as a subtype with pathogenic potential. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 104, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Arenas, N.R.; Villalobos, G.; Vargas-Sanchez, G.B.; Avalos-Galarza, C.A.; Marquez-Valdelamar, L.M.; Ramirez-Miranda, M.E.; Olivo-Diaz, A.; Romero-Valdovinos, M.; Martinez-Hernandez, F.; Maravilla, P. Is the genetic variability of Cathepsin B important in the pathogenesis of Blastocystis spp.? Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3935–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wawrzyniak, I.; Poirier, P.; Viscogliosi, E.; Dionigia, M.; Texier, C.; Delbac, F.; Alaoui, H.E. Blastocystis, an unrecognized parasite: An overview of pathogenesis and diagnosis. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2013, 1, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourrisson, C.; Wawrzyniak, I.; Cian, A.; Livrelli, V.; Viscogliosi, E.; Delbac, F.; Poirier, P. Blastocystis secreted cysteine proteases: A legumain-activated cathepsin B increases paracellular permeability of intestinal Caco-2 cell monolayers. Parasitology 2016, 143, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).