Abstract
Ixodiphagus hookeri (Howard, 1907) (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae), a hyperparasitic wasp that parasitizes hard ticks, has been documented in various parts of Europe; however, data on its presence in southeastern regions has been lacking. This study provides the first molecular evidence of I. hookeri in ticks from the coastal areas of the Balkan Peninsula, specifically Croatia and Bulgaria. A total of 1043 questing ticks were collected between 2011 and 2013 across 15 locations. Molecular screening revealed I. hookeri DNA in Ixodes ricinus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Acari: Ixodidae) nymphs from inland Croatia (overall prevalence: 18.72%) and in Haemaphysalis concinna (Koch, 1844) (Acari: Ixodidae) nymphs and larvae from coastal Bulgaria (prevalence: 17.2%). All I. hookeri-positive samples were co-infected with Wolbachia spp. (Rickettsiales: Anaplasmataceae). This detection marks the southernmost record of I. hookeri in Central Europe, expanding its known range to the Balkan Peninsula and supporting its relevance as a potential natural enemy in integrated tick management strategies.
1. Introduction
Ticks (order Ixodida) are hematophagous ectoparasites of major medical and veterinary importance due to their role as vectors of numerous pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and protozoa [1]. The transmission of pathogens through tick bites leads to diseases that can affect multiple organ systems and present with symptoms ranging from mild flu-like illness to severe neurological, cardiac, or hematological complications. Tick-borne diseases (TBDs) such as Lyme borreliosis, tick-borne encephalitis, anaplasmosis, and babesiosis have been increasingly reported across Europe, driven in part by climatic and environmental changes, increased wildlife populations, and growing human mobility [2,3].
The Balkan Peninsula, with its complex topography, diverse habitats, and transitional climate zones, is particularly rich in tick species. At least 32 species across five genera, including Ixodes, Rhipicephalus, Dermacentor, Hyalomma, and Haemaphysalis, have been documented in this region, many of which are competent vectors of zoonotic pathogens [4,5,6]. Several bacterial pathogens have been detected in ticks across the Balkan region, including the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex—the widely distributed causative agent of Lyme borreliosis–as well as Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Rickettsia spp. (notably those from the spotted fever group), Coxiella burnetii, and Ehrlichia spp., all of which have been reported in ticks from Albania, Croatia, Serbia, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and other countries in the region [5,7]. The re-emergence of the spotted fever group has been documented, with clinical cases reported in countries such as Serbia, Bulgaria, and Croatia, highlighting their growing public health importance [5,7,8,9].
Protozoan pathogens such as Babesia spp. and Theileria spp. are also prevalent in the region, affecting domestic animals and humans. Viral pathogens, including tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) and Crimean–Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV), have been reported with increasing frequency [5]. The coastal regions along the Mediterranean and Black Seas represent key hotspots for human–vector interactions, especially during the summer months, when millions of tourists visit these areas [10,11]. This seasonal influx increases the risk of human exposure to infected ticks, underscoring the urgent need for effective and ecologically sustainable tick control strategies.
Among emerging biological control options, parasitoid wasps have received attention due to their species-specific life cycles and potential to reduce tick populations in natural settings. Ixodiphagus hookeri (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) is a cosmopolitan tick parasitoid known to parasitize both hard (Ixodidae) and soft (Argasidae) ticks [12,13,14]. The female wasp oviposits into developing tick stages, primarily nymphs, and its larvae develop internally, ultimately leading to the death of the tick host upon adult emergence (Figure 1) [14,15]. Due to this life cycle, I. hookeri has long been considered a promising candidate for the biological suppression of tick populations.

Figure 1.
Adult Ixodiphagus hookeri wasp that emerged from an Ixodes ricinus nymph. Image captured using a ZEISS Stemi 508 stereomicroscope (ZEISS, Oberkochen, Germany) with an Axiocam ERc 5s camera.
Despite its global distribution, the presence and ecological role of I. hookeri remain poorly studied in many parts of Europe, particularly in southeastern regions such as the Balkan Peninsula. While isolated reports of I. hookeri have emerged from central and western Europe, including Hungary, Germany, Poland, and Slovakia [13,16,17], data from the Mediterranean and Black Sea coastlines are absent. Environmental factors, tick host availability, and parasitism rates may influence the local distribution of this parasitoid, warranting region-specific investigation [14,17].
Recent advances in molecular diagnostics, particularly the use of species-specific PCR and sequencing of mitochondrial markers such as COI and 16S rRNA, have significantly improved the detection of I. hookeri in field-collected ticks [13,17]. These tools have enabled more accurate assessments of host–parasite associations and have uncovered cryptic occurrences of I. hookeri in previously undocumented regions.
Given the ongoing public health threat posed by re-emerging TBDs in the Balkans, and the potential of I. hookeri as a biological control agent, this study was undertaken to address a knowledge gap more than a decade after the original sample collection.
In this study, we present the molecular evidence of I. hookeri parasitizing ticks collected from coastal ecosystems of the Mediterranean and Black Sea regions of Croatia and Bulgaria, within the Balkan Peninsula. This finding not only extends the known distribution range of I. hookeri into southeastern Europe but also contributes novel insights into its ecology and potential as a natural regulator of tick populations in regions of significant public health relevance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Geographically, Croatia encompasses a diverse western Balkan landscape that includes mountain ranges, a long Adriatic coastline, and lowland plains. The karstic limestone mountains form a distinct natural border between the continental interior and the Mediterranean littoral, influencing local climate and vegetation zones [18].
Bulgaria lies at the junction of the temperate and subtropical climate zones, with a highly heterogeneous topography. Elevations range from lowland areas around 200 m a.s.l. to the highest peak in the Balkans, Musala (2925 m a.s.l.). This variation defines five major climatic regions, contributing to significant biodiversity in flora and fauna, including tick populations [19].
2.2. Sampling Sites/Tick Collection
To assess the presence of I. hookeri in ticks from southern Europe, sampling was conducted at 15 model locations across the Balkan Peninsula—specifically, in Croatia (9 sites) and Bulgaria (6 sites). Tick sampling was performed in both inland and coastal zones, covering a range of climatic conditions, from Mediterranean along the coasts to more continental climates inland.
In Croatia, ticks were collected from a total of nine locations (Figure 2) between April and May 2011. These included one site in northern Croatia (Puščine/46°21.384′ N, 16°20.890′ E), four inland sites in the vicinity of Plitvice Lakes National Park (Mašvina/45°1.215′ N, 15°42.227′ E, Rakovica/44°59.775′ N, 15°39.328′ E, Stara Kršlja/45°00.027′ N, 15°40.074′ E, and Grabovac/44°58.279′ N, 15°38.416′ E), and four coastal sites along the Dalmatian coast (Makarska/43°17.122′ N, 17°01.751′ E, Tučepi/43°16.445′ N, 17°02.832′ E, Drvenik/43°09.539′ N, 17°14.428′ E, and Sirena/43°24.344′ N, 16°47.392′ E).
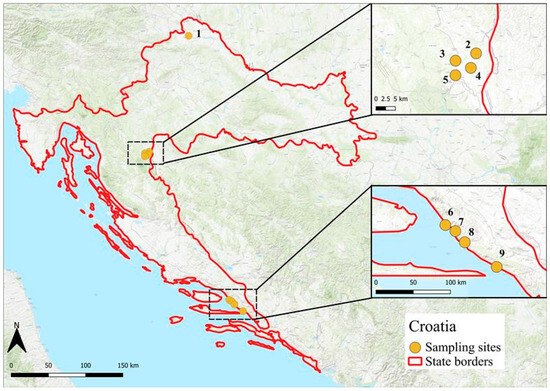
Figure 2.
Map of tick collection sites in Croatia (2011). Locations span inland (sites 1–5) and coastal (sites 6–9) zones (north → south: 1. Pušćine, 2. Mašvina, 3. Rakovica, 4. Stara Kršlja, 5. Grabovac, 6. Makarska, 7. Tučepi, 8. Sirena, and 9. Drvenik). The coordinates are listed in the Methods section.
In Bulgaria, tick sampling was performed from late May to early June 2013 at six locations (Figure 3). These included one site in the mountainous region near Rila National Park (Borovec/42°22.704′ N, 24°58.062′ E), three sites in the surroundings of Plovdiv (Plovdiv/42°08.512′ N, 24°47.096′ E, Glavatar/42°20.250′ N, 24°52.816′ E, and Drangovo/42°21.995′ N, 25°01.132′ E,), and two coastal sites on the Black Sea (Yasna Polyana/42°15.753′ N, 27°42.559′ E, and Primorsko/42°17.450′ N, 27°45.505′ E).
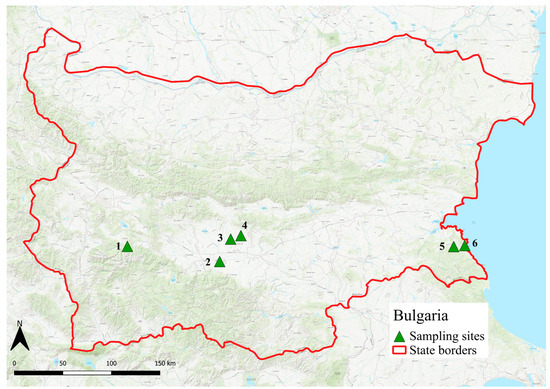
Figure 3.
Map of tick collection sites in Bulgaria (2013). The sites include inland regions and coastal Black Sea areas (west →east: 1. Borovec, 2. Plovdiv, 3. Glavatar, 4. Drangovo, 5. Yasna Polyana, 6. Primorsko).
Cartographic outputs were generated using QGIS LTR 3.42 Münster, utilizing the ESRI World Topographic Map as the base map.
Ticks were collected using the standard flagging method, where a 1 × 1 m white cotton cloth was mounted on a wooden pole and dragged across the vegetation [16]. At each sampling site, collections were conducted between 9:00 and 11:00 AM under similar weather conditions. After every 1–2 meters of flagging, the cloth was carefully inspected on both sides for attached ticks. Each field session lasted at least one hour per site.
All ticks were preserved in 70% ethanol and transported to the laboratory. Ticks were identified to species and developmental stage (and sex, where applicable) using morphological keys [20,21].
2.3. DNA Extractions and PCR Analyses
In 2024/2025, the genomic DNA was extracted from questing ticks collected in both Croatia (2011) and Bulgaria (2013) using the alkaline hydrolysis method described by Guy and Stanek [22]. All extracted DNA samples were stored at −20 °C until further processing. To ensure that no DNA degradation occurred despite long-term storage, a subset of randomly selected samples, collected more than a decade ago, was assessed using a NanoPhotometer™ UV/Vis Spectrophotometer (Implen GmbH, Munich, Germany). The high-quality DNA profiles confirmed the long-term stability of the samples, consistent with previous studies demonstrating the effectiveness of ethanol preservation and −20 °C storage for DNA integrity over extended periods [23]. Each DNA sample was initially screened for the presence of the parasitoid wasp by PCR, targeting two genetic markers: a region of the 28S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene and a fragment of the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 (cox1) gene, according to previously published protocols [13,24]. Following this, all samples were examined for the presence of the endosymbiotic bacterium Wolbachia spp., according to Zhou et al. [25].
PCR-positive amplicons corresponding to I. hookeri were purified using the NucleoSpin® Gel and PCR Cleanup Kit (Macherey-Nagel GmbH & Co., Düren, Germany). The purified products were subsequently subjected to Sanger sequencing in both directions, using the same primers as those employed in the PCR reactions. Sequencing was carried out by Eurofins Genomics (Ebersberg, Germany). Resulting sequences were compared to reference sequences using the NCBI BLAST tool (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 15 May 2025), and species identification was confirmed based on ≥99% similarity to known I. hookeri sequences in the GenBank database.
3. Results
A total of 606 ticks were collected in Croatia, comprising 525 I. ricinus (136 females, 170 males, and 219 nymphs) and 81 Rhipicephalus sanguineus (43 females and 38 males). All samples were molecularly screened for I. hookeri and Wolbachia spp. DNA. Ixodiphagus hookeri DNA was detected exclusively in the nymphs of I. ricinus, with an overall parasitism rate of 18.72% (Table 1). Positive detections were confined to four inland localities: Grabovac, Rakovica, Mašvina, and Stara Kršlja. The highest prevalence was observed in Grabovac, where 17.15% (35/204) of nymphs tested positive. In Rakovica, the prevalence was 3.7%, while a single positive specimen was recorded from both Mašvina and Stara Kršlja. All I. hookeri-positive samples also harbored Wolbachia spp., indicating a 100% co-occurrence of the endosymbiont with the parasitoid wasp.

Table 1.
Number of examined ticks and prevalence of I. hookeri and Wolbachia spp. in various tick species from the Balkan Peninsula.
In Bulgaria, 437 ticks were collected, consisting of 280 I. ricinus (52 females, 23 males, and 205 nymphs), 123 Haemaphysalis concinna (1 female, 93 nymphs, and 29 larvae), and 34 female R. sanguineus. The presence of I. hookeri DNA was confirmed in the nymphs of H. concinna from the coastal site of Primorsko, with a prevalence of 17.2% (Table 1). In addition, I. hookeri DNA was detected in one of three larval pools of H. concinna from the same site. A single H. concinna nymph collected from Yasna Polyana, a nearby locality, also tested positive.
Nucleotide sequences of the cox1 and 28S rRNA genes of I. hookeri were obtained from positive I. ricinus and H. concinna specimens from the investigated sites in Croatia and Bulgaria. The obtained cox1 sequences were identical in the overlapping region. The 28S rRNA sequences were also identical with isolates from I. ricinus and/or H. concinna nymphs from Slovakia (e.g., PP084999-PP085004), as well as with the most frequent GP15 haplotype (MN956813) identified in four different tick species (H. concinna, R. microplus, I. persulcatus, and D. silvarum) in Russia and Western Africa by [24], except for one isolate (5BHCN/PP760461), obtained from H. concinna in Primorsko, Bulgaria, which was slightly different. Sequence alignment using the EMBOSS Needle Pairwise Alignment Tool revealed 97.8% similarity (520/527 nt) between the 5BHCN isolate and the remaining 28S rRNA sequences from both countries.
All the nucleotide sequences generated in this study were deposited in the GenBank database and are available under the following accession numbers:
I. hookeri 28S rRNA (Croatia): PP760504–PP760506; cox 1 (Croatia): PV707218-PV707224;
I. hookeri 28S rRNA (Bulgaria): PP760500, PP760461, PP760453, PP760446.
4. Discussion
In the Balkan Peninsula, at least 32 species of ixodid ticks have been documented across five genera, many of which are competent vectors of zoonotic pathogens [5]. Despite this considerable tick diversity and the associated public and veterinary health concerns, data on hyperparasitoids such as I. hookeri are limited in this region.
This study provides the first molecular evidence of I. hookeri in I. ricinus and H. concinna ticks from the coastal and inland regions of Croatia and Bulgaria. These findings represent the southernmost confirmed records of the wasps in Central Europe and mark the first documentation of this parasitoid in ticks from the Balkan Peninsula. Before this study, the southern limit of I. hookeri in Central Europe was established in Hungary [16], indicating a potential range expansion into the Balkans.
We detected I. hookeri in 18.72% of I. ricinus nymphs in Croatia, with the highest prevalence observed in Grabovac (17.15%). In Bulgaria, I. hookeri DNA was identified in 17.2% of H. concinna nymphs and in one larval pool from the Primorsko locality. These parasitism rates are at the upper end of those reported across Europe. Infestation rates in I. ricinus nymphs range from 3.2 to 12.5% in western France, from 19.6 to 20% in southwestern France, 8.2% in southern Italy, and from 0.4 to 2.3% in Finland [13,14]. The relatively high rates reported in this study suggest favorable ecological conditions for parasitoid persistence and reproduction in the studied Balkan habitats. All I. hookeri-positive ticks carried DNA of Wolbachia sp. The co-detection of Wolbachia spp. in all I. hookeri-positive samples supports previous findings that the endosymbiont is commonly associated with the parasitoid rather than the tick host [12]. While Wolbachia is not known to directly infect ticks, its presence may influence the biology of I. hookeri, including reproduction and host selection.
Consistent with previous research, I. hookeri was detected mostly in the nymphal stages of I. ricinus and H. concinna, and only rarely in larvae. However, parasitoids have been observed to overwinter in unfed or engorged larvae and are transferred transstadially to the nymphal stage in several tick species [9,23,24,25,26]. Occasional detections in larvae, such as those found in Bulgarian samples or reported in several other studies [8,13,20,21,22], may suggest earlier oviposition or less common parasitism strategies under certain environmental conditions.
Although I. hookeri is known to parasitize mainly immature stages of ticks, its DNA may also be detected in adults. The frequency of infestation in adult ticks may vary by region. In the study by Gaye et al. [13], parasitoid wasp DNA was detected in 3% (28/785) of the analyzed adult hard ticks across six species from western Africa (Côte d’Ivoire and Senegal) and far eastern Europe (Russia): Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, Ixodes persulcatus, Dermacentor silvarum, Haemaphysalis concinna, Amblyomma variegatum, and Haemaphysalis japonica. In contrast, Blažeková et al. [13] confirmed the presence of parasitoid DNA in only one adult Dermacentor reticulatus male. This was likely due to residual DNA from earlier developmental stages persisting through the tick’s metamorphosis, rather than indicating active parasitism in adulthood. Such sporadic detections should therefore be interpreted with caution, as they may not reflect a current biological interaction but rather a molecular trace of past infection. The ecological dynamics between I. hookeri, its tick hosts, and vertebrate reservoirs are complex and influenced by multiple biotic and abiotic factors. Recent studies suggest that the abundance of ungulates, particularly deer, plays a pivotal role in shaping the prevalence of I. hookeri in tick populations [26]. In a large-scale Dutch study, parasitism rates reached up to 16% and were positively correlated with deer density and deer-associated pathogens such as Anaplasma phagocytophilum, but not with rodent-associated Borrelia sp. [27]. These findings indicate that I. hookeri may indirectly influence the transmission dynamics of certain pathogens by modulating the structure and abundance of tick hosts.
While I. hookeri has been considered a potential biological control agent of ticks, its effectiveness remains debated. The parasitoid’s life cycle is tightly linked to that of its tick hosts and, indirectly, to vertebrate hosts such as deer. In regions with high deer populations, the density of ticks may remain high despite the presence of I. hookeri, limiting its potential impact on overall tick numbers [26,27]. Nevertheless, the relatively high parasitism rates observed in this study suggest their potential role in regulating natural tick populations in localized settings with suitable ecological conditions. It is essential to note, however, that the samples analyzed in this study were collected over a decade ago. Screening more recently collected tick specimens could provide insights into potential changes in parasitoid prevalence and distribution over time. To date, I. hookeri has been reported in several European countries, including the Czech Republic [28], Ukraine [29], France [12,30], Germany [31,32], the Netherlands [26,33], Finland [34], Italy [14], the United Kingdom, Slovakia [17,24,35,36,37,38], and Hungary [16]. Our findings extend the known distribution of the wasps in southeastern Europe.
5. Conclusions
The relatively high prevalence rates observed, particularly in nymphal stages of I. ricinus and H. concinna, suggest that local environmental conditions may support stable populations of I. hookeri. These findings not only broaden the known distribution of this tick parasitoid but also underscore the need to consider I. hookeri as a potentially valuable, yet underexplored, component of integrated tick management strategies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.V. and V.B.; methodology, V.B. and L.V.; software, V.B.; validation, V.B., D.Z. and M.S.; formal analysis, V.B.; investigation, K.M.Š.; resources, B.V.; data curation, B.V. and V.B.; writing—original draft preparation, B.V. and V.B.; writing—review and editing, B.V., D.Z. and M.S.; visualization, K.M.Š.; supervision, B.V.; project administration, B.V.; funding acquisition, B.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by projects VEGA 2/0051/24 and APVV SK-SRB-23-0046.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to Lukáš Ihnacik for preparing the cartographic materials presented in this study. We also acknowledge the valuable contributions of all colleagues involved in the collection of tick specimens, namely Branislav Peťko, Ladislav Mošanský, Martin Bona, Lucia Blaňarová, and Jasna Kraljik. We thank Daniel Barčák and Mikuláš Oros for the photos of parasites.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- de la Fuente, J.; Estrada-Pena, A.; Venzal, J.M.; Kocan, K.M.; Sonenshine, D.E. Overview: Ticks as Vectors of Pathogens That Cause Disease in Humans and Animals. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 6938–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlock, J.M.; Hansford, K.M.; Bormane, A.; Derdakova, M.; Estrada-Peña, A.; George, J.-C.; Golovljova, I.; Jaenson, T.G.T.; Jensen, J.-K.; Jensen, P.M.; et al. Driving Forces for Changes in Geographical Distribution of Ixodes ricinus Ticks in Europe. Parasit. Vectors 2013, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzoli, A.; Silaghi, C.; Obiegala, A.; Rudolf, I.; Hubálek, Z.; Földvári, G.; Plantard, O.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Bonnet, S.; Špitalská, E.; et al. Ixodes ricinus and Its Transmitted Pathogens in Urban and Peri-Urban Areas in Europe: New Hazards and Relevance for Public Health. Front. Public. Health 2014, 2, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efstratiou, A.; Karanis, G.; Karanis, P. Tick-Borne Pathogens and Diseases in Greece. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapo, N.; Zuber Bogdanović, I.; Gagović, E.; Žekić, M.; Veinović, G.; Sukara, R.; Mihaljica, D.; Adžić, B.; Kadriaj, P.; Cvetkovikj, A.; et al. Ixodid Ticks and Zoonotic Tick-Borne Pathogens of the Western Balkans. Parasites Vectors 2024, 17, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoxha, I.; Dervović, J.; Ruivo, M.; Wijnveld, M.; Obwaller, A.G.; Jäger, B.; Weiler, M.; Walochnik, J.; Kniha, E.; Alić, A. Molecular Typing of Tick-Borne Pathogens in Ixodids of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defaye, B.; Moutailler, S.; Pasqualini, V.; Quilichini, Y. Distribution of Tick-Borne Pathogens in Domestic Animals and Their Ticks in the Countries of the Mediterranean Basin between 2000 and 2021: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banović, P.; Díaz-Sánchez, A.A.; Foucault-Simonin, A.; Mateos-Hernandez, L.; Wu-Chuang, A.; Galon, C.; Simin, V.; Mijatović, D.; Bogdan, I.; Corona-González, B.; et al. Emerging Tick-Borne Spotted Fever Group Rickettsioses in the Balkans. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2023, 107, 105400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakimovski, D.; Mateska, S.; Dimitrova, E.; Bosilkovski, M.; Mijatović, D.; Simin, V.; Bogdan, I.; Grujić, J.; Budakov-Obradović, Z.; Meletis, E.; et al. Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus and Borrelia burgdorferi Seroprevalence in Balkan Tick-Infested Individuals: A Two-Centre Study. Pathogens 2023, 12, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapusta, A.; Wiluś, R. Geography of Tourism in Croatia. In The Geography of Tourism of Central and Eastern European Countries, 2nd ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 109–147. [Google Scholar]
- Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Krcmar, S.; Bogdanic, M.; Tomljenovic, M.; Barbic, L.; Roncevic, D.; Sabadi, D.; Vucelja, M.; Santini, M.; Hunjak, B.; et al. An Overview of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Epidemiology in Endemic Regions of Continental Croatia, 2017–2023. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plantard, O.; Bouju-Albert, A.; Malard, M.-A.; Hermouet, A.; Capron, G.; Verheyden, H. Detection of Wolbachia in the Tick Ixodes ricinus Is Due to the Presence of the Hymenoptera Endoparasitoid Ixodiphagus hookeri. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buczek, A.; Buczek, W.; Bartosik, K.; Kulisz, J.; Stanko, M. Ixodiphagus hookeri Wasps (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) in Two Sympatric Tick Species Ixodes ricinus and Haemaphysalis concinna (Ixodida: Ixodidae) in the Slovak Karst (Slovakia): Ecological and Biological Considerations. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, R.A.N.; de Macedo, L.O.; Bezerra-Santos, M.A.; de Carvalho, G.A.; Verocai, G.G.; Otranto, D. The Role of Parasitoid Wasps, Ixodiphagus Spp. (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae), in Tick Control. Pathogens 2023, 12, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasu, K.; Nakamura, S. Life History of the Tick Parasitoid Ixodiphagus hookeri (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) in Kenya. Biol. Control 2008, 46, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.G.; Farkas, R.; Gyurkovszky, M.; Krikó, E.; Solymosi, N. First Detection of Ixodiphagus hookeri (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) in Ixodes ricinus Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) from Multiple Locations in Hungary. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blažeková, V.; Stanko, M.; Sprong, H.; Kohl, R.; Zubriková, D.; Vargová, L.; Bona, M.; Miklisová, D.; Víchová, B. Ixodiphagus hookeri (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) and Tick-Borne Pathogens in Ticks with Sympatric Occurrence (and Different Activities) in the Slovak Karst National Park (Slovakia), Central Europe. Pathogens 2024, 13, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognar, A. Croatia—The Land and Natural Features. GeoJournal 1996, 38, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, S. Geographic Location and Contemporary State Borders of Bulgaria. Espaço Econ. Rev. Bras. Geogr. Econômica 2015, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippova, N.A. Ixodid Ticks of the Subfamily Ixodina. Fauna USSR 1977, 4, 396. [Google Scholar]
- Siuda, K. Kleszcze Polski (Acari: Ixodida): Systematyka i Rozmieszczenie; Polskie Towarzystwo Parazytologiczne: Warsaw, Poland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Guy, E.C.; Stanek, G. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in Patients with Lyme Disease by the Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Clin. Pathol. 1991, 44, 610–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Z.T. A Hands-on Overview of Tissue Preservation Methods for Molecular Genetic Analyses. Org. Divers. Evol. 2010, 10, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaye, M.; Amanzougaghene, N.; Laidoudi, Y.; Niang, E.H.A.; Sekeyová, Z.; Laroche, M.; Bérenger, J.-M.; Raoult, D.; Kazimírová, M.; Fenollar, F.; et al. Hymenopteran Parasitoids of Hard Ticks in Western Africa and the Russian Far East. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Rousset, F.; O’Neil, S. Phylogeny and PCR-Based Classification of Wolbachia Strains Using Wsp Gene Sequences. Proc. Biol. Sci. 1998, 265, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollet, T.; Sprong, H.; Lejal, E.; Krawczyk, A.I.; Moutailler, S.; Cosson, J.-F.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Estrada-Peña, A. The Scale Affects Our View on the Identification and Distribution of Microbial Communities in Ticks. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, A.I.; Bakker, J.W.; Koenraadt, C.J.M.; Fonville, M.; Takumi, K.; Sprong, H.; Demir, S. Tripartite Interactions among Ixodiphagus hookeri, Ixodes ricinus and Deer: Differential Interference with Transmission Cycles of Tick-Borne Pathogens. Pathogens 2020, 9, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouček, Z.; Černỳ, V. Cizopasník Klístat, Chalcidka Hunterellus hookeri How. v CSR. Folia Zool. Entomol. 1954, 3, 109–111. [Google Scholar]
- Klyushkina, E.A. A Parasite of the Ixodid Ticks, Hunterellus hookeri How. in the Crimea. Zool. Zh 1958, 37, 1561–1563. [Google Scholar]
- Doby, J.M.; Van Laere, G. Hunterellus Hookeri Howard, 1907, Hymenoptère Chalcididae Parasite de La Tique Ixodes ricinus Dans l’ouest et Le Centre de La France. Bull. Société Française Parasitol. 1993, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Collatz, J.; Fuhrmann, A.; Selzer, P.; Oehme, R.M.; Hartelt, K.; Kimmig, P.; Meiners, T.; Mackenstedt, U.; Steidle, J.L.M. Being a Parasitoid of Parasites: Host Finding in the Tick Wasp Ixodiphagus hookeri by Odours from Mammal. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2010, 134, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collatz, J.; Selzer, P.; Fuhrmann, A.; Oehme, R.M.; Mackenstedt, U.; Kahl, O.; Steidle, J.L.M. A Hidden Beneficial: Biology of the Tick-Wasp Ixodiphagus hookeri in Germany. J. Appl. Entomol. 2011, 135, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijsse-Klasen, E.; Braks, M.; Scholte, E.-J.; Sprong, H. Parasites of Vectors–Ixodiphagus hookeri and Its Wolbachia Symbionts in Ticks in The Netherlands. Parasit. Vectors 2011, 4, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sormunen, J.J.; Sippola, E.; Kaunisto, K.M.; Vesterinen, E.J.; Sääksjärvi, I.E. First evidence of Ixodiphagus hookeri (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) parasitization in Finnish castor bean ticks (Ixodes ricinus). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 79, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slovak, M. Finding of the Endoparasitoid Ixodiphagus hookeri (Hymenoptera, Encyrtidae) in Haemaphysalis concinna Ticks in Slovakia. Biologia 2003, 58, 890. [Google Scholar]
- Bohacsova, M.; Mediannikov, O.; Kazimirova, M.; Raoult, D.; Sekeyova, Z. Arsenophonus nasoniae and Rickettsiae Infection of Ixodes ricinus Due to Parasitic Wasp Ixodiphagus hookeri. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samish, M.; Rehacek, J. Pathogens and Predators of Ticks and Their Potential in Biological Control. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1999, 44, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehácek, J.; Kocianová, E. Attempt to Infect Hunterellus hookeri Howard (Hymenoptera, Encyrtidae), an Endoparasite of Ticks, with Coxiella burnetti. Acta Virol. 1992, 36, 492. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).