An X-Domain Phosphoinositide Phospholipase C (PI-PLC-like) of Trypanosoma brucei Has a Surface Localization and Is Essential for Proliferation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.3. Cloning, Heterologous Expression, Purification of Recombinant TbPI-PLC-like, and Production of Antibodies
2.4. Enzymatic Assays
2.5. 3H-IP3 Binding Assay
2.6. Construct Design
2.7. Cell Transfections
2.8. Inositol Phosphate Extraction and Analysis of Phytic Acid (IP6) by LC-MS
2.9. Western Blot Analyses
2.10. RNA Interference
2.11. Immunofluorescence Assays
2.12. Yeast Two Hybrid Assays
2.13. In Vivo Studies
2.14. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
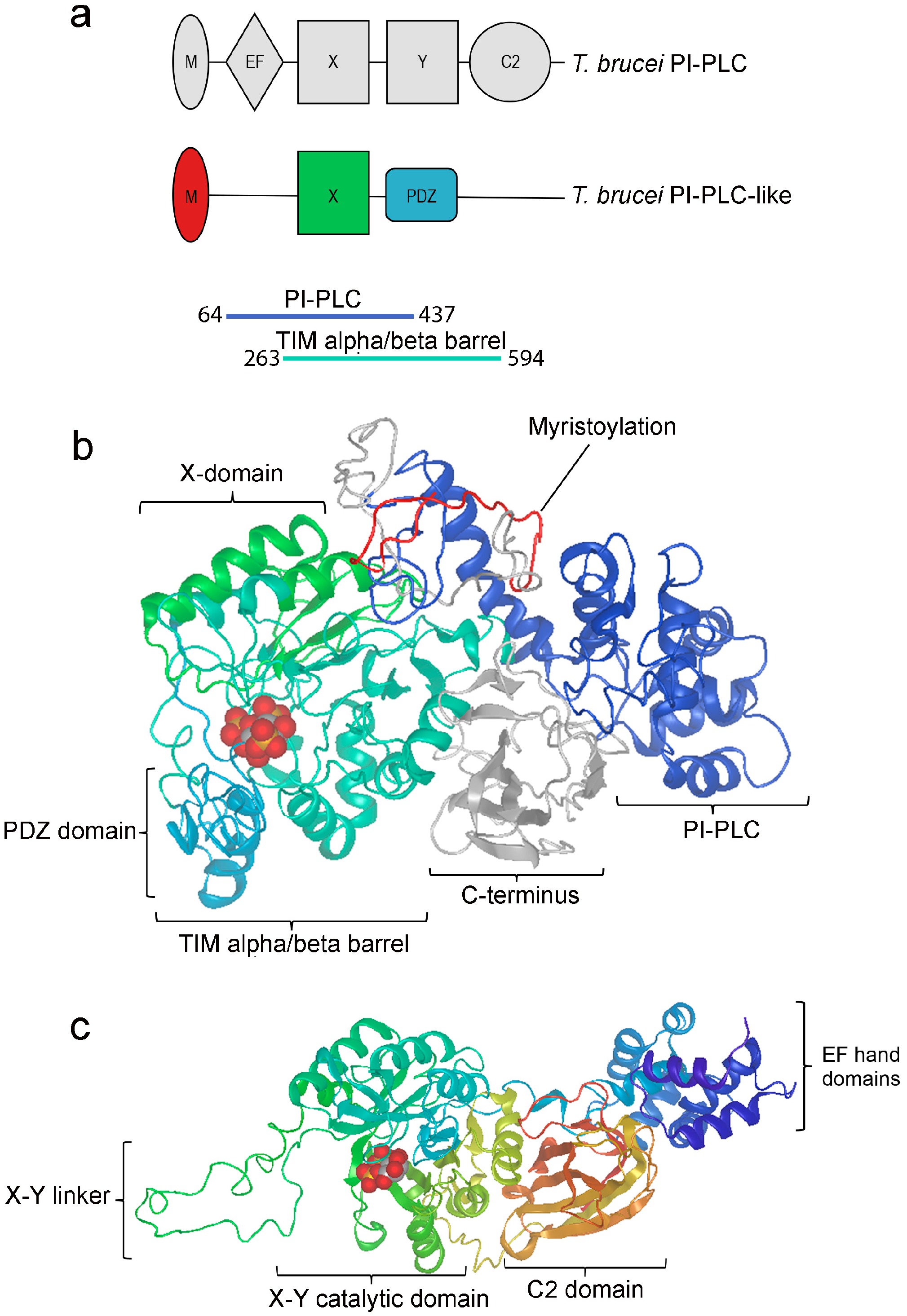
3.1. TbPI-PLC-like Sequence Analysis
3.2. Activity of Recombinant TbPI-PLC-like and Binding to IP3
3.3. TbPI-PLC-like Is Not Involved in the Synthesis of Inositol Polyphosphates
3.4. Subcellular Localization of TbPI-PLC-like
3.5. Interaction of TbPI-PLC-like with TbPI-PLC
3.6. Surface Localization of TbPI-PLC-like and TbPLC
3.7. Knockdown of TbPI-PLC-like Expression
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stevens, J.R.; Noyes, H.A.; Dover, G.A.; Gibson, W.C. The ancient and divergent origins of the human pathogenic trypanosomes, Trypanosoma brucei and T. cruzi. Parasitology 1999, 118 Pt 1, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufer, A.; Ellis, J.; Stark, D.; Barratt, J. The evolution of trypanosomatid taxonomy. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, D. Antigenic variation in African trypanosomes. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2014, 195, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, M.A.; Homans, S.W.; Dwek, R.A.; Rademacher, T.W. Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol moiety that anchors Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein to the membrane. Science 1988, 239, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakow, J.L.; Hereld, D.; Bangs, J.D.; Hart, G.W.; Englund, P.T. Identification of a glycolipid precursor of the Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 12147–12153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, D.; Berge, J.B.; de Almeida, M.L.C.; Bordier, C. Acetylcholinesterases from Musca domestica and Drosophila melanogaster brain are linked to membranes by a glycophospholipid anchor sensitive to an endogenous phospholipase. J. Neurochem. 1988, 50, 1158–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, M.L.C.; Turner, M.J. The membrane form of variant surface glycoproteins of Trypanosoma brucei. Nature 1983, 302, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorheis, H.P.; Bowles, D.J.; Smith, G.A. Characteristics of the release of the surface coat protein from bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma brucei. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 2300–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolin, S.; Hanocq-Quertier, J.; Paturiaux-Hanocq, F.; Nolan, D.; Salmon, D.; Webb, H.; Carrington, M.; Voorheis, P.; Pays, E. Simultaneous but independent activation of adenylate cyclase and glycosylphosphatidylinositol-phospholipase C under stress conditions in Trypanosoma brucei. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 10844–10852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, D.P.; Rolin, S.; Rodriguez, J.R.; Van Den Abbeele, J.; Pays, E. Slender and stumpy bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma brucei display a differential response to extracellular acidic and proteolytic stress. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, H.; Carnall, N.; Vanhamme, L.; Rolin, S.; Van Den Abbeele, J.; Welburn, S.; Pays, E.; Carrington, M. The GPI-phospholipase C of Trypanosoma brucei is nonessential but influences parasitemia in mice. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 139, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanrahan, O.; Webb, H.; O’Byrne, R.; Brabazon, E.; Treumann, A.; Sunter, J.D.; Carrington, M.; Voorheis, H.P. The glycosylphosphatidylinositol-PLC in Trypanosoma brucei forms a linear array on the exterior of the flagellar membrane before and after activation. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunter, J.; Webb, H.; Carrington, M. Determinants of GPI-PLC localisation to the flagellum and access to GPI-anchored substrates in trypanosomes. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King-Keller, S.; Moore, C.A.; Docampo, R.; Moreno, S.N. Ca2+ Regulation of Trypanosoma brucei Phosphoinositide Phospholipase C. Eukaryot. Cell 2015, 14, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Ulrich, P.N.; Storey, M.; Johnson, D.; Tischer, J.; Tovar, J.A.; Moreno, S.N.; Orlando, R.; Docampo, R. Proteomic analysis of the acidocalcisome, an organelle conserved from bacteria to human cells. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Bartlett, P.J.; Thomas, A.P.; Moreno, S.N.; Docampo, R. Acidocalcisomes of Trypanosoma brucei have an inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor that is required for growth and infectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmer, B.T.; Nakayasu, E.S.; Souther, C.; Choi, H.; Sobreira, T.J.; Epting, C.L.; Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Almeida, I.C.; Engman, D.M. Global analysis of protein palmitoylation in African trypanosomes. Eukaryot. Cell 2011, 10, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Fang, J.; Sant’Anna, C.; Li, Z.H.; Wellems, D.L.; Rohloff, P.; Docampo, R. Adaptor protein-3 (AP-3) complex mediates the biogenesis of acidocalcisomes and is essential for growth and virulence of Trypanosoma brucei. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 36619–36630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, I. New culture medium for maintenance of tsetse tissues and growth of trypanosomatids. J. Protozool. 1977, 24, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, E.; Leal, S.; Ochatt, C.; Cross, G.A. A tightly regulated inducible expression system for conditional gene knock-outs and dominant-negative genetics in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1999, 99, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirumi, H.; Hirumi, K. Continuous cultivation of Trypanosoma brucei blood stream forms in a medium containing a low concentration of serum protein without feeder cell layers. J. Parasitol. 1989, 75, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslett, M.; Aurrecoechea, C.; Berriman, M.; Brestelli, J.; Brunk, B.P.; Carrington, M.; Depledge, D.P.; Fischer, S.; Gajria, B.; Gao, X.; et al. TriTrypDB: A functional genomic resource for the Trypanosomatidae. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer-Stroh, S.; Eisenhaber, B.; Eisenhaber, F. N-terminal N-myristoylation of proteins: Prediction of substrate proteins from amino acid sequence. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 317, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bologna, G.; Yvon, C.; Duvaud, S.; Veuthey, A.L. N-Terminal myristoylation predictions by ensembles of neural networks. Proteomics 2004, 4, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.L.; Attwood, T.K.; Babbitt, P.C.; Blum, M.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Brown, S.D.; Chang, H.Y.; El-Gebali, S.; Fraser, M.I.; et al. InterPro in 2019: Improving coverage, classification and access to protein sequence annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D351–D360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega for making accurate alignments of many protein sequences. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Brunk, B.P.; Chen, F.; Gao, X.; Harb, O.S.; Iodice, J.B.; Shanmugam, D.; Roos, D.S.; Stoeckert, C.J., Jr. Using OrthoMCL to assign proteins to OrthoMCL-DB groups or to cluster proteomes into new ortholog groups. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2011, 35, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Posada, D.; Kozlov, A.M.; Stamatakis, A.; Morel, B.; Flouri, T. ModelTest-NG: A New and Scalable Tool for the Selection of DNA and Protein Evolutionary Models. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. MODELTEST: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, T.; Kashuba, C.; Docampo, R.; Moreno, S.N. A novel phosphatidylinositol-phospholipase C of Trypanosoma cruzi that is lipid modified and activated during trypomastigote to amastigote differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 6428–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Rossi, A.M.; Riley, A.M.; Rahman, T.; Potter, B.V.; Taylor, C.W. Binding of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and adenophostin A to the N-terminal region of the IP3 receptor: Thermodynamic analysis using fluorescence polarization with a novel IP3 receptor ligand. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 77, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, S.; Vadivelu, J.; Field, M.C. RNAit: An automated web-based tool for the selection of RNAi targets in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2003, 128, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaCount, D.J.; Barrett, B.; Donelson, J.E. Trypanosoma brucei FLA1 is required for flagellum attachment and cytokinesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 17580–17588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberholzer, M.; Morand, S.; Kunz, S.; Seebeck, T. A vector series for rapid PCR-mediated C-terminal in situ tagging of Trypanosoma brucei genes. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2006, 145, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantilla, B.S.; Kalesh, K.; Brown, N.W., Jr.; Fiedler, D.; Docampo, R. Affinity-based proteomics reveals novel targets of inositol pyrophosphate (5-IP7 )-dependent phosphorylation and binding in Trypanosoma cruzi replicative stages. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 115, 986–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gietz, R.D.; Schiestl, R.H. High-efficiency yeast transformation using the LiAc/SS carrier DNA/PEG method. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemercier, G.; Dutoya, S.; Luo, S.; Ruiz, F.A.; Rodrigues, C.O.; Baltz, T.; Docampo, R.; Bakalara, N. A vacuolar-type H+-pyrophosphatase governs maintenance of functional acidocalcisomes and growth of the insect and mammalian forms of Trypanosoma brucei. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 37369–37376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, W.J.; Lumsden, W.H. Trypanosoma brucei: A rapid “matching” method for estimating the host’s parasitemia. Exp. Parasitol. 1976, 40, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellatly, S.A.; Kalujnaia, S.; Cramb, G. Cloning, tissue distribution and sub-cellular localisation of phospholipase C X-domain containing protein (PLCXD) isoforms. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 424, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, C.D.; Saiardi, A.; Docampo, R. The inositol pyrophosphate synthesis pathway in Trypanosoma brucei is linked to polyphosphate synthesis in acidocalcisomes. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 106, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willert, E.K.; Phillips, M.A. Regulated expression of an essential allosteric activator of polyamine biosynthesis in African trypanosomes. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.; Jones, D.C.; Wyllie, S.; Fairlamb, A.H.; Phillips, M.A. Allosteric activation of trypanosomatid deoxyhypusine synthase by a catalytically dead paralog. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 15256–15267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paulo Martins, V.; Okura, M.; Maric, D.; Engman, D.M.; Vieira, M.; Docampo, R.; Moreno, S.N. Acylation-dependent export of Trypanosoma cruzi phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C to the outer surface of amastigotes. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 30906–30917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivarsson, Y. Plasticity of PDZ domains in ligand recognition and signaling. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2638–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzyniak, A.M.; Kashyap, R.; Zimmermann, P. Phosphoinositides and PDZ domain scaffolds. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 991, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, P.; Meerschaert, K.; Reekmans, G.; Leenaerts, I.; Small, J.V.; Vandekerckhove, J.; David, G.; Gettemans, J. PIP(2)-PDZ domain binding controls the association of syntenin with the plasma membrane. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortier, E.; Wuytens, G.; Leenaerts, I.; Hannes, F.; Heung, M.Y.; Degeest, G.; David, G.; Zimmermann, P. Nuclear speckles and nucleoli targeting by PIP2-PDZ domain interactions. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 2556–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krojer, T.; Garrido-Franco, M.; Huber, R.; Ehrmann, M.; Clausen, T. Crystal structure of DegP (HtrA) reveals a new protease-chaperone machine. Nature 2002, 416, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, K.; Inanobe, S.; Kanemaru, K.; Nakamura, Y. Phospholipase C is a key enzyme regulating intracellular calcium and modulating the phosphoinositide balance. Prog. Lipid Res. 2010, 49, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cestari, I.; Anupama, A.; Stuart, K. Inositol polyphosphate multikinase regulation of Trypanosoma brucei life stage development. Mol. Biol. Cell 2018, 29, 1137–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subota, I.; Julkowska, D.; Vincensini, L.; Reeg, N.; Buisson, J.; Blisnick, T.; Huet, D.; Perrot, S.; Santi-Rocca, J.; Duchateau, M.; et al. Proteomic analysis of intact flagella of procyclic Trypanosoma brucei cells identifies novel flagellar proteins with unique sub-localization and dynamics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 1769–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertommen, D.; Van Roy, J.; Szikora, J.P.; Rider, M.H.; Michels, P.A.; Opperdoes, F.R. Differential expression of glycosomal and mitochondrial proteins in the two major life-cycle stages of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2008, 158, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negrão, N.W.; Crowe, L.P.; Mantilla, B.S.; Baptista, R.P.; King-Keller, S.; Huang, G.; Docampo, R. An X-Domain Phosphoinositide Phospholipase C (PI-PLC-like) of Trypanosoma brucei Has a Surface Localization and Is Essential for Proliferation. Pathogens 2023, 12, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12030386
Negrão NW, Crowe LP, Mantilla BS, Baptista RP, King-Keller S, Huang G, Docampo R. An X-Domain Phosphoinositide Phospholipase C (PI-PLC-like) of Trypanosoma brucei Has a Surface Localization and Is Essential for Proliferation. Pathogens. 2023; 12(3):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12030386
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegrão, Núria W., Logan P. Crowe, Brian S. Mantilla, Rodrigo P. Baptista, Sharon King-Keller, Guozhong Huang, and Roberto Docampo. 2023. "An X-Domain Phosphoinositide Phospholipase C (PI-PLC-like) of Trypanosoma brucei Has a Surface Localization and Is Essential for Proliferation" Pathogens 12, no. 3: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12030386
APA StyleNegrão, N. W., Crowe, L. P., Mantilla, B. S., Baptista, R. P., King-Keller, S., Huang, G., & Docampo, R. (2023). An X-Domain Phosphoinositide Phospholipase C (PI-PLC-like) of Trypanosoma brucei Has a Surface Localization and Is Essential for Proliferation. Pathogens, 12(3), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12030386






