Abstract
Goats are key livestock animals and goat raising is an income-generating venture for smallholder farmers, supporting agricultural development in many parts of the world. However, goat production is often limited by various factors, such as tick-borne diseases. Goat piroplasmosis is a disease caused by apicomplexan parasites Babesia spp. and Theileria spp., while anaplasmosis is caused by bacterial Anaplasma spp. In the Philippines, the presence of Babesia, Theileria, and Anaplasma has not been reported in goats. In this study, DNA obtained from goats were molecularly screened for Babesia/Theileria and Anaplasma. Of 396, 77.02% (305/396) and 38.64% (153/396) were positive for piroplasma and Anaplasma using PCR assays targeting the 18S rRNA and 16S rRNA genes, respectively. Similarly, Babesia ovis was detected in six samples (1.52%). Representative Babesia/Theileria sequences shared 89.97–97.74% identity with each other and were most closely related to T. orientalis, T. annulata, and Theileria spp. Meanwhile, Anaplasma 16SrRNA sequences were related to A. odocoilei, A. platys, and A. phagocytophilum. This is the first molecular identification of B. ovis, Theileria spp., and Anaplasma spp. in goats from the Philippines.
1. Introduction
Babesiosis, theileriosis, and anaplasmosis are caused by tick-borne blood parasites of the genera Babesia, Theileria, and Anaplasma. These tick-borne diseases (TBDs) adversely affect livestock through direct and indirect losses in production. In small ruminants, the impact of TBDs has burdened farmers with losses linked to mortalities, less meat, milk, and wool produce, and increased costs for herd health management [1,2]. However, in endemic countries, TBDs are often overlooked despite being widespread in small ruminants, due to the lack of severe clinical manifestations during infection and strong tolerance through acquired natural immunity of infected hosts [3].
Several Babesia species can infect small ruminants, but the disease that develops varies between goats and sheep. Babesia ovis is fatal in sheep [4], while other species may have milder (B. motasi) [5] or low (B. crassa) [6] virulence. In goats, B. ovis causes subclinical infection [7,8], and B. motasi infects goats more frequently than sheep [5]. Additionally, some newly reported species have been identified in particular locations, namely Babesia sp. Xinjiang and B. motasi-like in China [9,10] and Babesia sp. in Turkey [11]. The clinical manifestations of babesiosis in small ruminants may include fever, anemia, jaundice, depression, and hemoglobinuria. In addition death may occur in severely affected animals [8]. Ticks of the genus Rhipicephalus, Hyalomma, and Haemaphysalis can transmit Babesia to small ruminants [12].
Theileriosis in small ruminants is caused by various species of Theileria, of which pathogenic species include T. lestoquardi, T. luwenshuni (Theileria sp. 1), and T. uilenbergi (Theileria sp. 2) [13]. Other Theileria species that can infect small ruminants are nonpathogenic [14], albeit considerably impact animal production [7]. The clinical disease in small ruminants may be accompanied by fever, lymph node swelling, icterus, hemorrhage, and diarrhea, while anemia, wasting, lack of appetite, and intermittent fever are observed during chronic infection [7]. Similar to babesiosis, infection in goats is less severe [5].
Anaplasma is the causative agent of anaplasmosis and is distributed globally, infecting a broad range of hosts. Small ruminants can get infected with several species, including A. marginale, A. ovis, A. phagocytophilum, and the newly discovered emerging pathogen A. capra [3,15,16]. Infected animals may experience fever, hemolytic anemia, loss of appetite, weight loss, and fatigue, which translate to reduced milk production in dairy small ruminants [3]. Biological vectors of Anaplasma are ixodid ticks, but mechanical vectors are also involved in the transmission, especially in places where the tick vectors are absent or rarely present [17].
Small ruminant production is an essential agro-socioeconomic activity that sustains agricultural development in many parts of the world by providing meat, milk, skin, and wool. Compared to other livestock, goat and sheep raising is attractive in rural households because of the relatively smaller resources and effort required to maintain them [18]. They can subsist on unpalatable low-quality fodder and browse and still be prolific, owing to the early sexual maturity, brief gestation duration, and short birth intervals [19]. In the Philippines, goat raising is a pillar of the mixed (crop–livestock) farming systems and provides supplemental income to smallholder farming families [20]. In 2021, there were 3.2 million heads of goats and the annual national production value was estimated at USD250 million [21]. Despite the huge contribution, goat production is suboptimal, and their full potential is not realized [18,22]. Several factors constrain caprine production in the Philippines, one of which is the high prevalence of parasites from genera Eimeria spp., Fasciola spp., Haemonchus spp., and Trichostrongylus spp. [20]. In contrast, the tick-borne parasites Babesia, Theileria, and Anaplasma have not been molecularly detected [23]. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to detect the molecular presence of these tick-borne pathogens in goats and determine the animal parameters associated with the detection.
2. Results
2.1. Sample Composition and Background Information
In this study, samples were collected from 396 randomly selected goats across six provinces in the Philippines (Figure 1), namely, Cavite (n = 42), Quezon (n = 20), Bohol (n = 35), Cebu (n = 74), Leyte (n = 26), and Davao del Sur (n = 199) (Table 1). The goat population was comprised of the following: 60% adult (n = 237) and 40% young (n = 159); 87% female (n = 344) and 13% male (n = 52); 56% purebred (n = 222), 22% crossbred (n = 87), 15.4% Philippine native (n = 61), and unknown breed 6.6% (n = 26). The goats were raised in backyards by smallholder farmers, except those from Cebu and Bohol, which were domesticated in semicommercial and stock farms, respectively. The backyard goats were tethered and/or freely grazed, while goats from semicommercial farms were reared in semi-intensive and intensive systems.
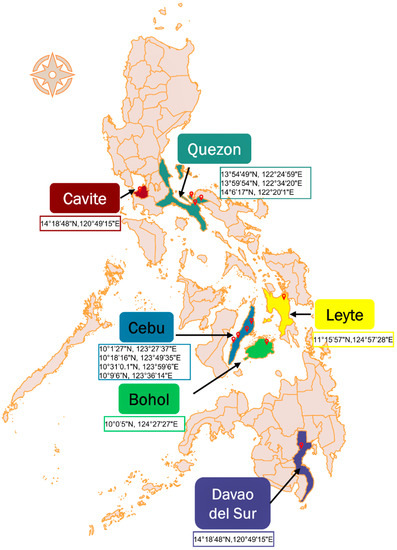
Figure 1.
The Philippine map showing the six provinces (colored) where samples were collected from, with pinned sampling sites and GPS coordinates. The map was generated using the QGIS software [24].

Table 1.
Molecular detection of Babesia/Theileria spp. and Anaplasma spp. based on sex, age-group, location, and breed of goats.
2.2. Detection of Pathogens and Its Association with Host Parameters
Using the nested PCR assay targeting the 18S rRNA V4 hypervariable region of Babesia/Theileria, piroplasma DNA was detected in 305 (77.02%) samples (Table 1). The highest detection rates were recorded from one year or older adult (191/237; 80.59%), female (273/344; 79.36%), and purebred (179/222; 80.63) goats. Notably, piroplasma were most frequently detected in samples from Davao del Sur (183/199; 91.96%). Statistical analysis indicated that sex (p = 0.007), breed (p = 0.027), and location (p < 0.001) were associated with testing positive for piroplasma (Table 1). On the other hand, 153/396 (38.64%) samples were positive for Anaplasma spp. (A. phagocytophilum). Anaplasma detection rates were higher in young (77/159; 48.43%), male (25/52; 48.08%), and purebred (101/222; 45.50%) goats, with those from Quezon (16/20; 80.00%) showing the highest positivity rate (Table 1). Significant factors associated with Anaplasma positivity were age-group (p = 0.001), location (p < 0.001), and breed (p = 0.026). In addition, six (6/396; 1.52%) samples from Leyte (n = 3) and Cavite (n = 3) showed amplicons corresponding to the target of the B. ovis PCR assay.
2.3. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of Representative Sequences
We sequenced representative samples that showed strong bands for piroplasma (n = 7), Anaplasma sp. (n = 14), and B. ovis (n = 1) to determine their sequence identities and to analyze their phylogenetic relationships with previously published sequences in the GenBank sequence database. The seven sequences (MW786647–MW786653) were confirmed as Theileria species and exhibited intersequence identities of 89.97–97.74%. As shown in Figure 2, three isolates (MW786649; MW786651; MW786653) were located in a subclade with other T. orientalis isolates from China, Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, and Malaysia. One Theileria sp. (MW786653) was most closely related to Theileria sp. Thung Song isolate from Thailand (99.30% identity) and formed a sister clade with the Chinese T. sinensis isolates, while MW786648 shared 99.53% identity with T. annulata isolates from India and Thailand (Figure 2). MW786650 was similar to cattle isolate of T. orientalis from Pakistan, whereas MW786652 was located in a branch solitarily (Figure 2). The Anaplasma sp. sequences (OP351259–OP351272) obtained in this study shared the following identities with each other: 99.68% (OP351261 and OP351271); 98.81–99.89% (OP351262, OP351263, OP351265–OP351270); 98.38% (OP351260 and OP351264), 98.48% (OP351259 and OP351267); 97.84% (OP351271 and OP351272). Based on the Anaplasma 16S rRNA phylogenetic tree, OP351260 and OP351264 clustered with A. phagocytophilum in Rhipicephalus microplus from Taiwan, Anaplasma sp. in cattle from Ethiopia, and Candidatus A. boleense in mosquitoes from China, while OP351262, OP351263, and OP351265–OP351270 grouped together and were related to A. odocoilei from the US (Figure 3). In addition, OP351261, OP351271, and OP351272 were phylogenetically related to various A. platys isolates. The B. ovis isolate from the current study (OP003548) was closely related and had 99.82% identity with sheep, goat, and horse B. ovis isolates from Turkey, Iran, Spain, and Portugal (Figure 4).
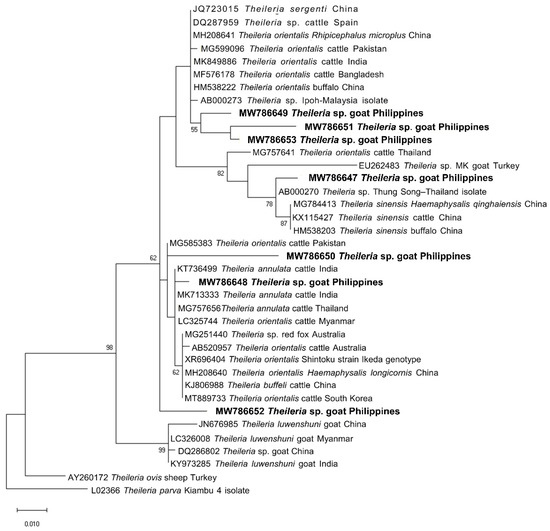
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of piroplasma sequences obtained in this study (MW786647–MW786653) based on the 18S rRNA gene. The maximum likelihood tree was constructed using the Tamura-3 model plus discrete gamma distribution (+G, parameter = 0.3348). The phylogeny test was performed using the bootstrap analysis with 1000 iterations. The sequences obtained from the current study are shown in bold. Theileria parva was designated the outgroup.
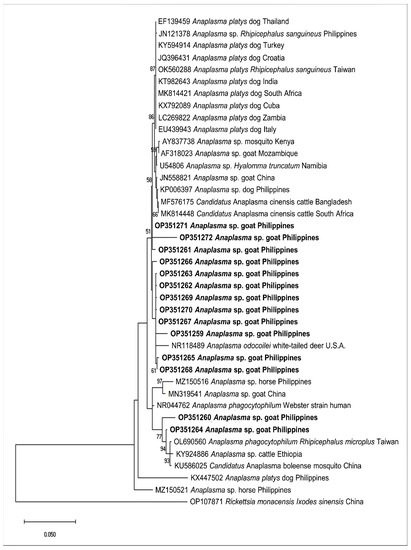
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of Anaplasma spp. sequences obtained in this study (OP351259–OP351272) based on the 16S rRNA gene. The maximum likelihood tree was constructed using the Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano model plus discrete gamma distribution (+G, parameter = 0.3915). The phylogeny test was performed using the bootstrap analysis with 1000 iterations. The sequences obtained from the current study are shown in bold. Rickettsia monacensis was designated the outgroup.
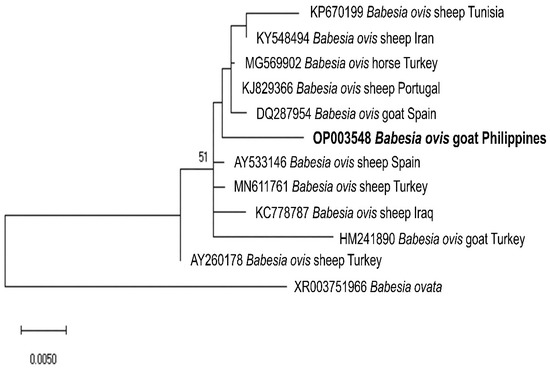
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic analysis of the B. ovis sequence obtained in this study (OP003548) based on the ssu rRNA gene. The maximum likelihood tree was constructed using the Jukes–Cantor model with uniform rates among sites. The phylogeny test was performed using the bootstrap analysis with 1000 iterations. The sequence obtained from the current study is shown in bold. Babesia ovata was designated the outgroup.
3. Discussion
Herein, we present the first molecular identification of Babesia, Theileria, and Anaplasma in goats from the Philippines. A high detection rate of piroplasma DNA was recorded in goats (77.02%), which was higher than caprine Babesia and Theileria rates recorded in Pakistan (5–40.80%) [25,26], Turkey (21.40%) [27], Italy (11.70%) [3], China (11.90–34.70%) [28,29], Ethiopia (1.90%) [30], and Tunisia (4.70%) [31], while comparable to that from Malawi (72.70%) [32]. The detection rate (38.64%) of Anaplasma spp. in the current study was higher than what was observed in goats from Bangladesh (15.75%) [33], Thailand (13.50%) [34], Pakistan (7.80%) [35], and South Korea (7.62%) [36], but lower than in goats from China (58.50%) [37]. The relatively high detection rates may be due to several factors related to the climate, environment, host susceptibility, vector population density, and management production systems [3,27,38]. In addition, B. ovis was detected in 1.52% of the goat samples and was present in two provinces (Leyte and Cavite). The current non-detection of B. ovis in Cebu goats agrees with the results of a previous molecular investigation where Babesia was not detected in caprine blood samples [23].
Significant association between host parameters, including sex, age-group, breed, and location, and pathogen detection was noted in the present study. Piroplasma positivity in female goats was significantly higher than in male ones, while studies on small ruminants in Ethiopia [30], Turkey [39], and Tunisia [40] found goat sex to be negligible. On the other hand, Anaplasma spp. detection in young goats was significantly higher than in adults, which is parallel to the findings in Pakistan goats [35]. Moreover, detection of Anaplasma spp. and Babesia/Theileria were significantly associated with goat breed, wherein a higher number of purebred or exotic goats tested positive compared to upgraded and native goats. Earlier surveys observed a similar trend, where the indigenous goat breeds were described to have higher resistance to piroplasma [40,41] and Anaplasma [42]. Information available on goat breed resistance to TBDs is scarce, but one possible explanation may be the greater susceptibility of exotic goat breeds to tick bites compared to local breeds [43]. Piroplasma and Anaplasma detection rates significantly differed among the location of the goats. The same was observed in goat herds from China [29], Tunisia [40], and Oman [44]. Location-specific factors in this study, such as management practices and macroclimatic conditions that affect tick proliferation, may be attributed to the different sampling sites characterized by diverse topography, terrain, microclimate, and fauna.
Sequencing and phylogenetic analysis confirmed that the representative Theileria sp. sequences obtained in this study were most closely related to T. orientalis, T. annulata, and Theileria sp. Thung Song isolate. Four Theileria isolates in the present study (MW786649; MW786651; MW786653) were similar to T. orientalis isolates from other locations. Members of the T. orientalis complex have been reported in cattle from the Philippines in previous studies [45,46,47]. More notably, we obtained an isolate highly similar to T. annulata. T. annulata is a species that can infect goats and causes a potentially fatal disease in cattle [48]. However, it should be confirmed whether the infected goats can be inapparent carriers of various T. orientalis genotypes and T. annulata and if they are able to spread the pathogens to bovids, as in sheep [48,49,50]. Theileria sp. Thung Song is an isolate from dairy cattle in Thailand and was genotypically divergent from other benign T. orientalis types (T. buffeli and T. sergenti) [51,52]. Its detection in goats in the current study may indicate host shifting of this parasite. We also obtained an isolate phylogenetically distinct from other analyzed sequences (MW786652; 98.75% identity with Theileria sequences in GenBank), which may be a new Theileria sp., although more studies are needed to verify this claim. On the other hand, T. luwenshuni, which is a common species in goats reported from nearby Southeast Asian countries, namely, Thailand [34,53,54,55], Myanmar [56], and Vietnam [50,57,58], was not confirmed in the obtained sequences.
In this study, Anaplasma isolates (OP351259–OP351272) closely related to A. odocoilei, A. phagocytophilum, and A. platys were confirmed in goats from the Philippines. A. odocoilei is a species causing chronic Anaplasma infection in white-tailed deer discovered in the US [59]. A. odocoilei does not cause severe clinical disease in experimentally infected white-tailed deer, and natural infections have only been detected from North America and South America [60,61,62]. Additionally, we obtained isolates (OP351261 and OP351271) highly similar to A. platys (99.10% and 99.46% identity with other A. platys isolates, respectively) and OP351272, a potential novel A. platys-like isolate (97.30% highest identity with GenBank A. platys isolates). A novel A. platys-like species that can be vertically transmitted to the goat’s offspring has been identified in China recently [63]. Furthermore, a previous study indicated that a couple of novel A. phagocytophilum-like and A. ovis-like variants are circulating in Philippine horses [64]. Thus, the isolates obtained from the current study warrant further probing on their genetic characteristics and clinical impact of the infections they inflict on goats.
Despite the high rate of positivity, clinical signs associated with TBDs were not observed. This may indicate the endemicity of these pathogens in goats in the Philippines. Likewise, this may correspond to persistent infections, a characteristic of natural infections in places where the disease is presumed endemic [7]. While B. ovis causes acute and severe disease in sheep, natural infection with B. ovis in goats is rarely clinical [8]. This was evident in the positive goats in the current study. In the case of Theileria- and Anaplasma-positive goats, the impact of subclinical infections should not be ignored because the pathogenicity of different species and genotypes vary depending on the host [15,65].
Some aspects were outside the scope of this study. For instance, few samples were subjected to sequencing analysis and species confirmation was performed by partial amplification of one fragment from one gene. Therefore, additional studies based on species-specific detection should be conducted to elucidate the species diversity of Babesia, Theileria, and Anaplasma in goats from the Philippines. In this study, the tick vectors were not determined. Since tethering and freely grazing systems are the more common production system in the Philippines [20], there are more opportunities for the ticks to feed on the host as goats are exposed to vegetation where questing ticks are abundant. The most likely vector of piroplasmas and Anaplasma is the ubiquitous R. microplus ticks, which was found infesting goats in Bulacan province [66]. The tick species R. microplus and Haemaphysalis bispinosa infesting goats from neighboring countries Thailand [34,67] and Malaysia [68] were also confirmed to be carrying T. luwenshuni. Similarly, R. sanguineus sensu lato (s.l.) ticks, the vector of canine A. platys in the Philippines [69,70], may also be implicated as the vector of A. platys-like variants detected in the present study. The three-host tick R. sanguineus s.l. commonly infests dogs, its main host, but humans and other animals may also be incidentally infested [71]. A majority of goats in this study were raised in backyards and regularly interacted with companion animals (dog and cats), which may have possibly exposed goats to the former’s tick vectors. Moreover, the possibility of other transmission means, particularly, the role of mechanical transmission by insect vectors other than ticks, such as blood-sucking arthropods Tabanus, Stomoxys, and mosquitoes [17], should be further investigated.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statements
Field sampling and animal handling protocols were conducted in accordance with the Philippine Animal Welfare Act (Republic Act 10631) and the guidelines set by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of the Philippines Cebu and Cavite State University. Experimental procedures and methodologies related to this study were permitted by Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine, Obihiro, Hokkaido, Japan (permits 20–128 and 1723–4). The farmers and owners of the animals were oriented regarding the purpose of the study and provided verbal consent prior to the start of the sample collection.
4.2. Sample Collection and Sampling Sites
In this study, 396 whole-blood samples from randomly chosen goats were collected. The goats were randomly chosen irrespective of sex, age, and breed from March 2017 to March 2020. Sampling was done in backyards and farms selected by convenience in the provinces of Cavite (n = 42), Quezon (n = 20), Bohol (n = 35), Cebu (n = 74), Leyte (n = 26), and Davao del Sur (n = 199), Philippines. The specific sampling sites and their GPS coordinates are shown in Figure 1. Approximately 2 mL of blood was collected via venipuncture of the jugular vein of the goats into sterile EDTA tubes and kept cool until processing in the laboratory.
4.3. Genomic DNA Isolation
Genomic DNA was extracted using the QIAamp® DNA Blood Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. About 200 μL of whole blood was used for the DNA extraction using the column-based blood kit. The DNA samples were transported to the National Research Center for Protozoan Diseases, Obihiro, Hokkaido, Japan and stored at −30 °C until use. Quality and the estimated concentration of the extracted DNA samples were checked using the NanoDrop™ 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) prior to screening the samples.
4.4. PCR Assays for Pathogen Detection
The PCR conditions performed in this study are referred to in Table 2. The samples were processed using a nested PCR assay targeting the hypervariable V4 region of the 18S rRNA gene of piroplasma [72,73] and 16S rRNA of Anaplasma spp. (A. phagocytophilum) [74]. In addition, a single specific primer set amplifying the B. ovis 18S rRNA gene was also used [75]. For the nested PCR assays, both first and final reactions were run to a final volume of 10 µL consisting of 1× ThermoPol® buffer (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA), 2 mM of dNTP mix (New England Biolabs) 2 µM of forward and reverse primers, 0.25 U of Taq DNA polymerase (New England Biolabs), and 2 µL of genomic DNA sample for the first assay or 1 µL of the PCR product for the nested assay. For the screening of B. ovis, the conventional assay was performed similarly to the aforementioned setup, except for the final concentration of primers (5 µM). The company-provided thermocycling conditions were followed, with the annealing temperature for each assay listed in Table 2. Positive (DNA samples confirmed positive for Theileria sp., B. ovis, and Anaplasma sp. [76]) and negative controls (UltraPure™ DNase/RNase-Free distilled water; Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) were run alongside the samples in each assay. Visualization of amplicons after exposure to UV light was done after electrophoresis of PCR products in 1.5% agarose gel and staining with ethidium bromide solution.

Table 2.
List of PCR primers and conditions used in the study.
4.5. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
Amplicons were purified using NucleoSpin® Gel and PCR Clean-up kit (Macherey Nagel, Düren, Germany). Then, the purified amplicons were cloned by ligation into pGEM®-T Easy Vector (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA) and transformation in Escherichia coli DH5α strain calcium-competent cells. After overnight incubation of positive transformants, high-density bacterial cultures were lysed and plasmids were purified using NucleoSpin Plasmid QuickPure Kit (Macherey Nagel). Purified plasmids were sequenced by the Sanger sequencing method using BigDye™ Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) and ABI Prism 3100 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems).
Forward and reverse reads were manually trimmed and overlapped to assemble the sequences. Shared identities between presently obtained and previously deposited sequences were determined by NCBI BLASTn search, while the identity matrix generated from EMBL Clustal Omega multiple sequence alignment [77] determined the intersequence percentage identities. After nucleotide alignment by Clustal W and determination of the best DNA model, the maximum likelihood trees were constructed by phylogeny testing using the bootstrap method with 1000 replications. All analyses related to phylogeny were conducted using the Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) X software [78]. The sequences obtained from this study were banked in the NCBI GenBank with accession numbers MW786647–MW786653 for Theileria sp. 18S rRNA (372–426 bp), OP003548 for B. ovis 18S rRNA (552 bp), and OP351259–OP351272 for Anaplasma sp. 16S rRNA (923–925 bp).
4.6. Statistical Analyses
Association between Babesia/Theileria sp. and Anaplasma sp. positivity (dependent variable) and animal parameters (categorical independent variables), namely, sex, age group, breed, and location, was evaluated. Background data of animal samples were available for all except for the breeds of goats from Leyte; thus, we excluded them in the analysis for the breed variable. Fisher’s exact test was used to calculate the exact p values, whereas if not applicable, Pearson’s chi-square test was employed to calculate the approximate p values. A p value of <0.05 was considered significant. All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad software, San Diego, CA, USA).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.M.G. and X.X.; methodology, E.M.G., R.H.Y., A.M.M., G.R.E., M.T.R.M., M.D.V., A.G., R.J.F., M.R.C., K.J.L., M.A.T., B.B., S.J. and I.Z.; formal analysis, E.M.G.; investigation, E.M.G. and R.H.Y.; visualization, E.M.G.; validation, X.X. and R.H.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, E.M.G.; writing—review and editing, R.H.Y., A.M.M., A.Y. and X.X.; funding acquisition, A.M.M., R.H.Y., A.Y. and X.X.; supervision, X.X.; project administration, X.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The primary author (E.M.G.) is a grantee of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Research Fellowship for Young Scientists, Japan (20J20134). This research was funded by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan through a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (18H02336) and the JSPS Core-to-Core program, and by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries of Japan through a grant from the Strategic International Collaborative Research Project (JPJ008837). The study was also partially funded by the Philippine Commission on Higher Education (Institutional Development and Innovation Grants) and by Cavite State University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Field sampling and animal handling protocols were conducted in accordance with the Philippine Animal Welfare Act (Republic Act 10631) and the guidelines set by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of the Philippines Cebu and Cavite State University. Experimental procedures and methodologies related to this study were permitted by Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine, Obihiro, Hokkaido, Japan (permits 20–128 and 1723–4). The farmers and owners of the animals were oriented regarding the purpose of the study and provided verbal consent prior to the start of the sample collection.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the Philippine Carabao Center—Ubay Stock Farm for the assistance in blood collection of goats in Bohol. The authors also thank the local government unit offices, farmers, students, and livestock technicians for their assistance and cooperation in the sample collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, writing of the manuscript, or decision to publish the results.
References
- Hurtado, O.J.B.; Giraldo-Ríos, C. Economic and health impact of the ticks in production animals. In Ticks and Tick-Borne Pathogens; Abubakar, M.K., Perera, P., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-78985-765-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgic, H.B.; Bakırcı, S.; Kose, O.; Unlu, A.H.; Hacılarlıoglu, S.; Eren, H.; Weir, W.; Karagenc, T. Prevalence of tick-borne haemoparasites in small ruminants in Turkey and diagnostic sensitivity of single-PCR and RLB. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torina, A.; Caracappa, S. Tick-borne diseases in sheep and goats: Clinical and diagnostic aspects. Small Rumin. Res. 2012, 106, S6–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi-Fesharki, R. Tick-borne diseases of sheep and goats and their related vectors in Iran. Parassitologia 1997, 39, 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.C.; Sherman, D.M. Goat Medicine; Wiley—Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-119-94952-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hasherni-Fesharki, R.; Uilenberg, G. Babesia crassa n. sp. (Sporozoa, Babesiidae) of domestic sheep in Iran. Vet. Q. 1981, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuen, S. Haemoparasites—Challenging and wasting infections in small ruminants: A review. Animals 2020, 10, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeruham, I.; Hadani, A.; Galker, F. Some epizootiological and clinical aspects of ovine babesiosis caused by Babesia ovis—A review. Vet. Parasitol. 1998, 74, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.H.; Yin, H.; Guan, G.Q.; Schnittger, L.; Liu, Z.J.; Ma, M.L.; Dang, Z.S.; Liu, J.L.; Ren, Q.Y.; Bai, Q.; et al. At least two genetically distinct large Babesia species infective to sheep and goats in China. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 147, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Luo, J.; Guan, G.; Liu, Z.; Ma, M.; Liu, A.; Gao, J.; Ren, Q.; Li, Y.; Qiu, J.; et al. Differentiation of two ovine Babesia based on the ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequences. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 121, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozubek, S.; Aktas, M. Molecular evidence of a new Babesia sp. in goats. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 233, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedhoff, K.T. Tick-borne diseases of sheep and goats caused by Babesia, Theileria or Anaplasma spp. Parassitologia 1997, 39, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, J.S.; Luo, J.; Schnittger, L.; Seitzer, U.; Jongejan, F.; Yin, H. Phylogenetic position of small-ruminant infecting piroplasms. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1081, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, J.; Yin, H.; Bakheit, M.; Liu, Z.; Mehlhorn, H.; Seitzer, U. Small ruminant theileriosis. In Progress in Parasitology; Mehlhorn, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 135–153. ISBN 978-3-642-21395-3. [Google Scholar]
- Woldehiwet, Z. The natural history of Anaplasma phagocytophilum. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 167, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Lu, C.; Yan, Y.; Shi, K.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, C.; Wang, R.; Zhang, L.; Jian, F.; Ning, C. The first detection of Anaplasma capra, an emerging zoonotic Anaplasma sp., in erythrocytes. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocan, K.M.; de la Fuente, J.; Blouin, E.F.; Coetzee, J.F.; Ewing, S.A. The natural history of Anaplasma marginale. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 167, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollott, G.; Wilson, R.T. Sheep and Goats for Diverse Products and Profits; FAO diversification booklet; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009; ISBN 978-92-5-106137-4. [Google Scholar]
- Dar, W.; Faylon, P. Small ruminant development in the Philippines. In Sustainable Parasite Control in Small Ruminants; Watson Ferguson & Co.: Brisbane, Australia, 1996; pp. 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- The 2003 Goat Farming Committee. The Philippines Recommends for Goat Farming; Philippine Council for Agriculture, Forestry and Natural Resources Research and Development, Department of Science and Technology: Los Banos, Philippines, 2004; ISBN 978-971-20-0522-0. [Google Scholar]
- Philippine Statistics Authority. Goat Situation Report: January–December 2021; Philippine Statistics Authority: Quezon City, Philippines, 2022. Available online: https://psa.gov.ph/ (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- Terrili, C.E. Trends in Sheep and Goat Production over the Past 20 Years. In Small Ruminant Production in the Developing Countries; FAO Animal Production and Health Paper; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1986; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ybañez, A.P.; Arrabis, O.V.; Alvarez, D.J.M.; Galon, E.M.S.; Jayag, R.M.P.; Delan, E.S.; Ybañez, R.H.D.; Xuan, X. Evaluation on the presence of Anaplasma, Ehrlichia, and Babesia spp. in goats (Capra hircus) in Cebu, the Philippines. Vet. World 2019, 12, 774–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QGIS Development Team. QGIS Geographic Information System 2019. Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project. Available online: https://www.qgis.org (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- Iqbal, F.; Khattak, R.; Ozubek, S.; Khattak, M.; Rasul, A.; Aktas, M. Application of the reverse line blot assay for the molecular detection of Theileria and Babesia sp. in sheep and goat blood samples from Pakistan. Iran J. Parasitol. 2013, 8, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nasreen; Khan, A.; Niaz, S.; Hassan shah, M.; Khan, A.; Ahmed, H.; Khattak, I.; Zeb, J.; Naeem, H.; Hassan, M.A.; et al. Molecular detection of small ruminant piroplasmosis and first report of Theileria luwenshuni (Apicomplexa: Theileridae) in small ruminants of Pakistan. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 212, 107872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozubek, S.; Aktas, M. Molecular and parasitological survey of ovine piroplasmosis, including the first report of Theileria annulata (Apicomplexa: Theileridae) in sheep and goats from Turkey. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Mukhtar, M.U.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X. Molecular detection and identification of tick-borne bacteria and protozoans in goats and wild siberian roe deer (Capreolus pygargus) from Heilongjiang province, northeastern China. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, J.-H.; Upadhyay, A.; Zhao, J.-G.; Huang, L.-Y.; Liao, C.-H.; Han, Q. Identification of Theileria spp. and investigation of hematological profiles of their infections in goats in Hainan island, China. Parasite 2022, 29, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrekidan, H.; Hailu, A.; Kassahun, A.; Rohoušová, I.; Maia, C.; Talmi-Frank, D.; Warburg, A.; Baneth, G. Theileria infection in domestic ruminants in northern Ethiopia. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 200, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M’ghirbi, Y.; Ros-García, A.; Iribar, P.; Rhaim, A.; Hurtado, A.; Bouattour, A. A molecular study of tick-borne haemoprotozoan parasites (Theileria and Babesia) in small ruminants in northern Tunisia. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 198, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatanga, E.; Kainga, H.; Maganga, E.; Hayashida, K.; Katakura, K.; Sugimoto, C.; Nonaka, N.; Nakao, R. Molecular identification and genetic characterization of tick-borne pathogens in sheep and goats at two farms in the central and southern regions of Malawi. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Faruque, M.d.R.; Rahman, M.d.M.; Chowdhury, M.Y.E. Epidemiology and molecular detection of Anaplasma spp. in goats from Chattogram district, Bangladesh. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, A.; Kaewlamun, W.; Narapakdeesakul, D.; Poofery, J.; Kaewthamasorn, M. Molecular detection and characterization of tick-borne parasites in goats and ticks from Thailand. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 101938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaz, S.; Rahman, Z.U.; Ali, I.; Cossío-Bayúgar, R.; Amaro-Estrada, I.; Alanazi, A.D.; Khattak, I.; Zeb, J.; Nasreen, N.; Khan, A. Molecular prevalence, characterization and associated risk factors of Anaplasma spp. and Theileria spp. in small ruminants in northern Pakistan. Parasite 2021, 28, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, E.A.; Han, S.-W.; Cho, Y.-K.; Choi, K.-S.; Chae, J.-S. Co-infection with Anaplasma species and novel genetic variants detected in cattle and goats in the Republic of Korea. Pathogens 2021, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fu, M.; Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Song, J.; Zhao, G. Molecular characterization of Anaplasma spp. among dairy, cashmere, and meat goats in Shaanxi Province, northwestern China. Animals 2022, 12, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, C.; Manfredi, M.T. Tick species infesting ruminants in Italy: Ecological and bio-climatic factors affecting the different regional distribution. Parassitologia 1999, 41 (Suppl. S1), 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Cao, S.; Sevinc, F.; Sevinc, M.; Ceylan, O.; Ekici, S.; Jirapattharasate, C.; Moumouni, P.F.A.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; et al. Molecular detection and genetic characterization of Babesia, Theileria and Anaplasma amongst apparently healthy sheep and goats in the central region of Turkey. Ticks Tick-borne Dis. 2017, 8, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rjeibi, M.R.; Gharbi, M.; Mhadhbi, M.; Mabrouk, W.; Ayari, B.; Nasfi, I.; Jedidi, M.; Sassi, L.; Rekik, M.; Darghouth, M.A. Prevalence of piroplasms in small ruminants in north-west Tunisia and the first genetic characterisation of Babesia ovis in Africa. Parasite 2014, 21, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.d.F.; Rudra, P.G.; Singha, S.; Das, T.; Gebrekidan, H.; Uddin, M.B.; Chowdhury, M.Y.E. Molecular epidemiology and characterization of Theileria in goats. Protist 2021, 172, 125804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, M.B.; Belkahia, H.; Alberti, A.; Zobba, R.; Bousrih, M.; Yahiaoui, M.; Daaloul-Jedidi, M.; Mamlouk, A.; Gharbi, M.; Messadi, L. Molecular survey of Anaplasma species in small ruminants reveals the presence of novel strains closely related to A. phagocytophilum in Tunisia. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwalback, M.; Greyling, J.; David, M. The efficacy of a 10% aqueous neem (Azadirachta indica) seed extract for tick control in Small East African and Toggenburg female goat kids in Tanzania. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 33, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fahdi, A.; Alqamashoui, B.; Al-Hamidhi, S.; Kose, O.; Tageldin, M.H.; Bobade, P.; Johnson, E.H.; Hussain, A.-R.; Karagenc, T.; Tait, A.; et al. Molecular surveillance of Theileria parasites of livestock in Oman. Ticks Tick-borne Dis. 2017, 8, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, I.C.B.; Capuno, L.X.B.; Collera, P.D.L.P.; Cabralda, A.P.D.; De Ramos, K.A.S.; Bernardo, J.M.G.; Divina, B.P.; Masatani, T.; Tanaka, T.; Galay, R.L. Molecular detection and characterization of Babesia and Theileria in cattle and water buffaloes from southern Luzon, Philippines. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochirkhuu, N.; Konnai, S.; Mingala, C.N.; Okagawa, T.; Villanueva, M.; Pilapil, F.M.I.R.; Murata, S.; Ohashi, K. Molecular Epidemiological survey and genetic analysis of vector-borne infections of cattle in Luzon island, the Philippines. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 212, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotindos, L.; Lazaro, J.; Villanueva, M.; Mingala, C. Molecular detection and characterization of Theileria species in the Philippines. Acta Parasitol. 2014, 59, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.G.D.; Ilhan, T.; Kirvar, E.; Thomas, M.; Wilkie, G.; Leemans, I.; Hooshmand-Rad, P. Theileria lestoquardi and T. annulata in cattle, sheep, and goats: In vitro and in vivo Studies. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 849, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, K.E.; Gedye, K.; Hickson, R.; Wang, B.; Carvalho, L.; Zhao, Y.; Pomroy, W.E. The role of sheep (Ovis aries) in maintaining Theileria orientalis Ikeda type infection. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 291, 109391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khukhuu, A.; Lan, D.T.B.; Long, P.T.; Ueno, A.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; de Macedo, A.C.C.; Matsumoto, K.; Inokuma, H.; Kawazu, S.-I.; et al. Molecular epidemiological survey of Theileria orientalis in Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2011, 73, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chansiri, K.; Sarataphan, N. Molecular phylogenetic study of Theileria sp. (Thung Song) based on the thymidylate synthetase gene. Parasitol. Res. 2002, 88, S33–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chansiri, K.; Kawazu, S.; Kamio, T.; Terada, Y.; Fujisaki, K.; Philippe, H.; Sarataphan, N. Molecular phylogenetic studies on Theileria parasites based on small subunit ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Vet. Parasitol. 1999, 83, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewhom, P.; Thitasarn, W. The prevalence of Theileria spp. of goat in Watthana Nakhon District, Sa Kaeo province. J. Mahanakorn Vet. Med. 2017, 12, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, H.L.C.; Nugraheni, Y.R.; Tiawsirisup, S.; Saiwichai, T.; Thiptara, A.; Kaewthamasorn, M. Development of a novel multiplex PCR assay for the detection and differentiation of Plasmodium caprae from Theileria luwenshuni and Babesia spp. in goats. Acta Trop. 2021, 220, 105957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udonsom, R.; Mahittikorn, A.; Jirapattharasate, C. Molecular detection and genetic diversity of tick-borne pathogens in goats from the southern part of Thailand. Pathogens 2022, 11, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawm, S.; Kakisaka, K.; Thu, M.J.; Chel, H.M.; Oo, Y.M.N.; Soe, N.C.; Win, S.Y.; Htun, L.L.; Win, M.M.; Suzuki, H.; et al. First molecular detection of Theileria luwenshuni from goats in Myanmar. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3361–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, T.; Lan, D.T.B.; Long, P.T.; Yoshinari, T.; Tattiyapong, M.; Guswanto, A.; Okubo, K.; Igarashi, I.; Inoue, N.; Xuan, X.; et al. PCR detection and genetic diversity of bovine hemoprotozoan parasites in Vietnam. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, T.; Tuvshintulga, B.; Kothalawala, H.; Silva, S.S.P.; Lan, D.T.B.; Long, P.T.; Ybañez, A.P.; Ybañez, R.H.D.; Benitez, D.F.; Tayebwa, D.S.; et al. Host range and geographical distribution of Babesia sp. Mymensingh. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, C.M.; Howerth, E.W.; Mead, D.G.; Dugan, V.G.; Luttrell, M.P.; Sahora, A.I.; Munderloh, U.G.; Davidson, W.R.; Yabsley, M.J. Anaplasma odocoilei sp. nov. (Family Anaplasmataceae) from white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2013, 4, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabsley, M.J.; Davidson, W.R.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Varela, A.S.; Swift, P.K.; Devos, J.C.; Dubay, S.A. Evidence of tick-borne organisms in mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) from the western United States. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2005, 5, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojeda-Chi, M.M.; Rodriguez-Vivas, R.I.; Esteve-Gasent, M.D.; Pérez de León, A.; Modarelli, J.J.; Villegas-Perez, S. Molecular detection of rickettsial tick-borne agents in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus yucatanensis), Mazama deer (Mazama temama), and the ticks they host in Yucatan, Mexico. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, M.M.; Argibay, H.D.; Minatel, L.; Guillemi, E.C.; Berra, Y.; Schapira, A.; Di Nucci, D.; Marcos, A.; Lois, F.; Falzone, M.; et al. A participatory surveillance of marsh deer (Blastocerus dichotomus) morbidity and mortality in Argentina: First results. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.-W.; Jiang, B.-G.; Liu, H.-B.; Wei, R.; Jiang, R.-R.; Cui, X.-M.; Li, L.-F.; Yuan, T.-T.; et al. Anaplasma platys-like infection in goats, Beijing, China. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galon, E.M.; Macalanda, A.M.; Garcia, M.M.; Ibasco, C.J.; Garvida, A.; Ji, S.; Zafar, I.; Hasegawa, Y.; Liu, M.; Ybañez, R.H.; et al. Molecular identification of selected tick-borne protozoan and bacterial pathogens in thoroughbred racehorses in Cavite, Philippines. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, T.; Hayashida, K.; Sugimoto, C.; Yokoyama, N. Evolution and genetic diversity of Theileria. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 27, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, P.H.; Claveria, F. Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus ticks (Family Ixodidae) in goats raised in a small private farm in San Jose del Monte, Bulacan, central Luzon, Philippines. Philipp. J. Sci. 2017, 146, 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Hirunkanokpun, S.; Ahantarig, A.; Baimai, V.; Pramual, P.; Rakthong, P.; Trinachartvanit, W. Spotted fever group Rickettsia, Anaplasma and Coxiella-like endosymbiont in Haemaphysalis ticks from mammals in Thailand. Vet. Res. Commun. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, F.S.; Khoo, J.J.; Akhavanrezeai, M.; Loong, S.K.; Khor, C.S.; AbuBakar, S. Detection of Theileria luwenshuni (Piroplasmida: Theileriidae) from ticks infesting goats in Peninsular Malaysia. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 24, 1971–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ybañez, A.P.; Perez, Z.O.; Gabotero, S.R.; Yandug, R.T.; Kotaro, M.; Inokuma, H. First molecular detection of Ehrlichia canis and Anaplasma platys in ticks from dogs in Cebu, Philippines. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galay, R.L.; Manalo, A.A.L.; Dolores, S.L.D.; Aguilar, I.P.M.; Sandalo, K.A.C.; Cruz, K.B.; Divina, B.P.; Andoh, M.; Masatani, T.; Tanaka, T. Molecular detection of tick-borne pathogens in canine population and Rhipicephalus sanguineus (sensu lato) ticks from southern Metro Manila and Laguna, Philippines. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas-Torres, F. Biology and ecology of the brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Parasites Vectors 2010, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbels, J.M.; de Vos, A.P.; van der Weide, M.; Viseras, J.; Schouls, L.M.; de Vries, E.; Jongejan, F. Simultaneous detection of bovine Theileria and Babesia species by reverse line blot hybridization. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georges, K.; Loria, G.R.; Riili, S.; Greco, A.; Caracappa, S.; Jongejan, F.; Sparagano, O. Detection of haemoparasites in cattle by reverse line blot hybridisation with a note on the distribution of ticks in Sicily. Vet. Parasitol. 2001, 99, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlough, J.E.; Madigan, J.E.; DeRock, E.; Bigornia, L. Nested polymerase chain reaction for detection of Ehrlichia equi genomic DNA in horses and ticks (Ixodes pacificus). Vet. Parasitol. 1996, 63, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktaş, M.; Altay, K.; Dumanlı, N. Development of a polymerase chain reaction method for diagnosis of Babesia ovis infection in sheep and goats. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 133, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumwebaze, M.A.; Byamukama, B.; Tayebwa, D.S.; Byaruhanga, J.; Angwe, M.K.; Galon, E.M.; Liu, M.; Lee, S.-H.; Ringo, A.E.; Adjou Moumouni, P.F.; et al. First molecular detection of Babesia ovis, Theileria spp., Anaplasma spp., and Ehrlichia ruminantium in goats from western Uganda. Pathogens 2020, 9, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Basutkar, P.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Potter, S.C.; Finn, R.D.; et al. The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W636–W641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).