Secreted MbovP0145 Promotes IL-8 Expression through Its Interactive β-Actin and MAPK Activation and Contributes to Neutrophil Migration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Silico Analyses
2.2. Cultivation of Bacterial Strains and Cell Lines
2.3. Cloning, Expression, and Purification of a Recombinant MbovP0145 Protein
2.4. Construction of Strain Complementary to M. bovis ΔMbov_0145
2.4.1. In Trans Complementation of M. bovis T6.93 via a Plasmid Carrying the Gene Mbov_0145
2.4.2. Western Blot Analysis of MbovP0145 Expression in M. bovis Strains
2.5. EBL Cells Either Infected with M. bovis or Treated with rMbovP0145
2.6. Analysis of IL-8 mRNA Expression with Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. GST Pull-Down Assay to Identify Interactive Protein of MbovP0145
2.8. Immunoprecipitation Assay on Interaction between β-Actin and MbovP0145
2.9. Colocation Analysis with Confocal Laser Fluorescence Microscopy
2.10. Knockdown Assay of β-Actin with siRNA Interference
2.11. Inhibition of Actin Polymerization by Cytochalasin D
2.12. Analysis of the Molecules Critical to Signaling Pathways
2.13. Neutrophil Chemotaxis Assay
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
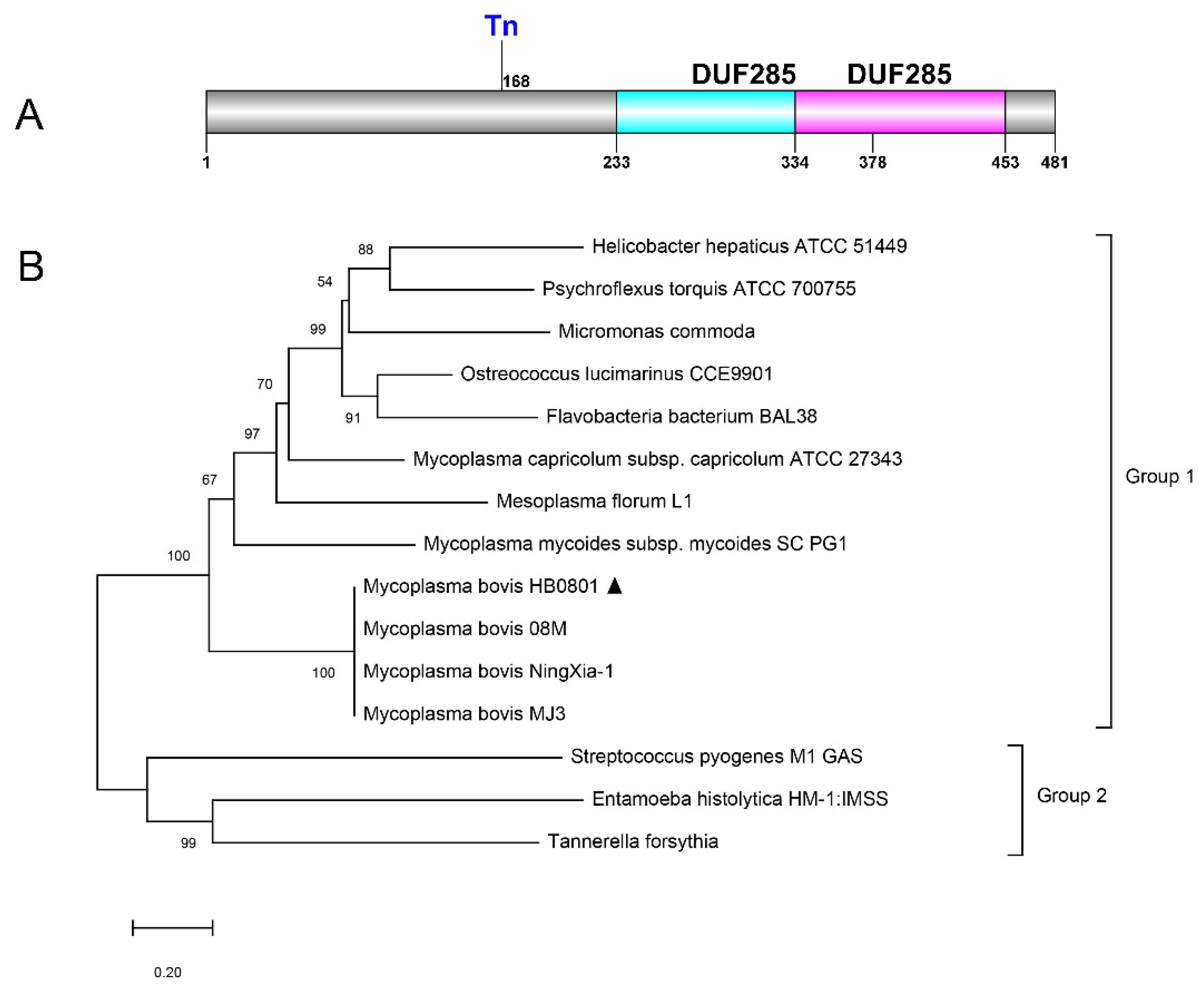
3.1. Bioinformatic Prediction of Genomic Features for the Mbov_0145 Gene
3.2. MbovP0145 Specifically Induced IL-8 Expression in EBL Cells
3.3. MbovP0145 Induction of IL-8 Expression Is Regulated by the MAPK Pathway
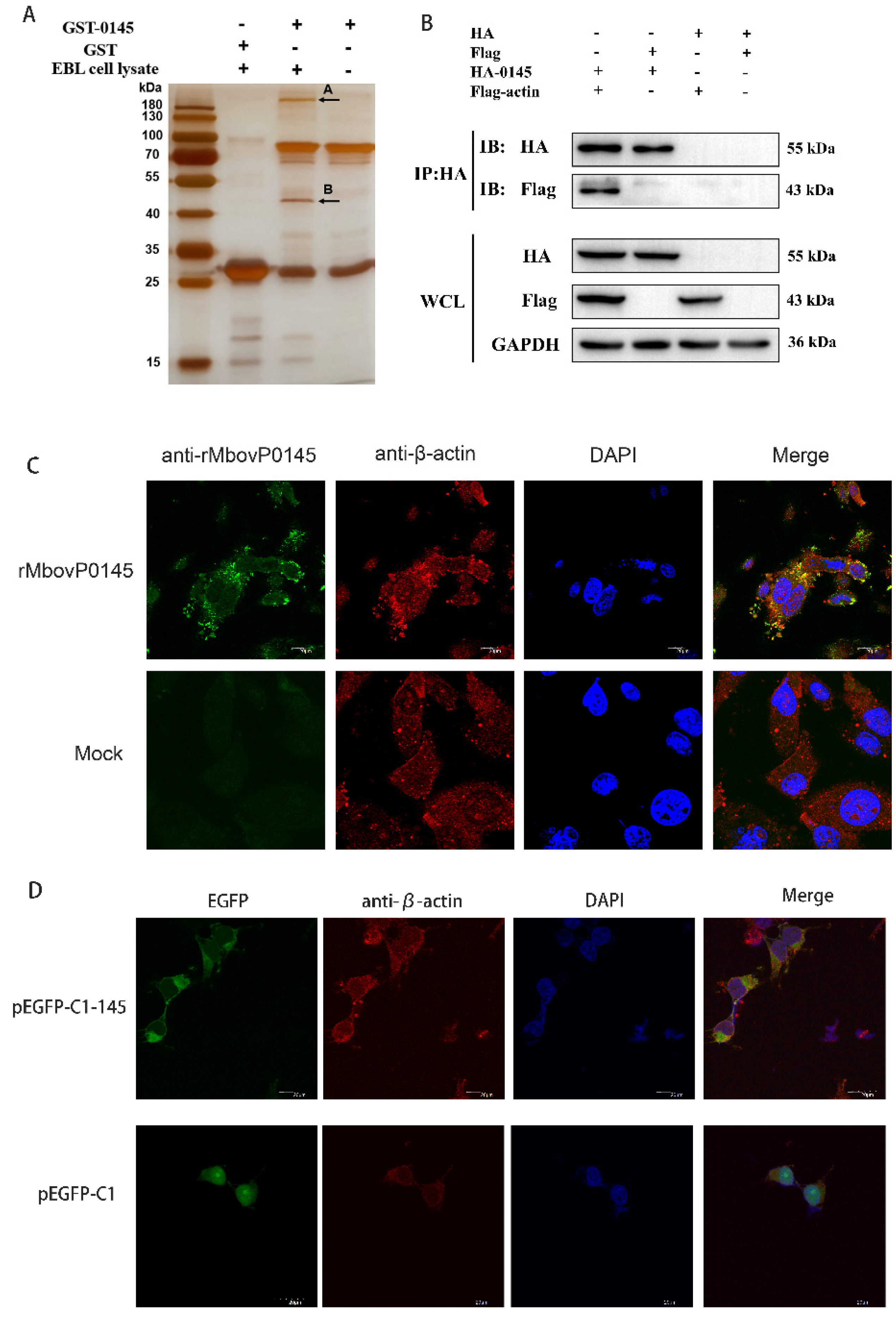
3.4. Preliminarily Identification of MbovP0145 Interactive Proteins
3.5. Confirmation of β-Actin as the Interactive Protein of MbovP0145
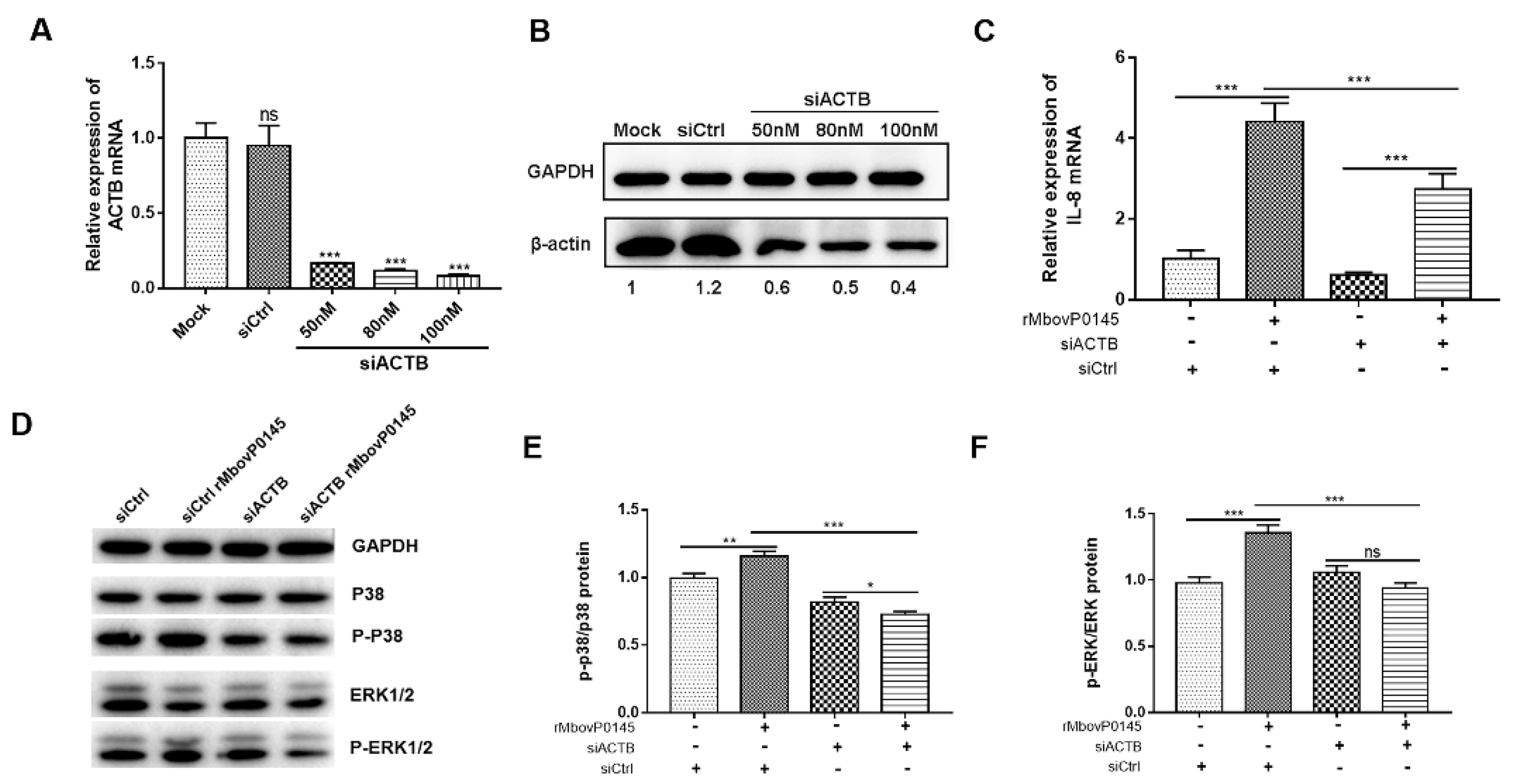
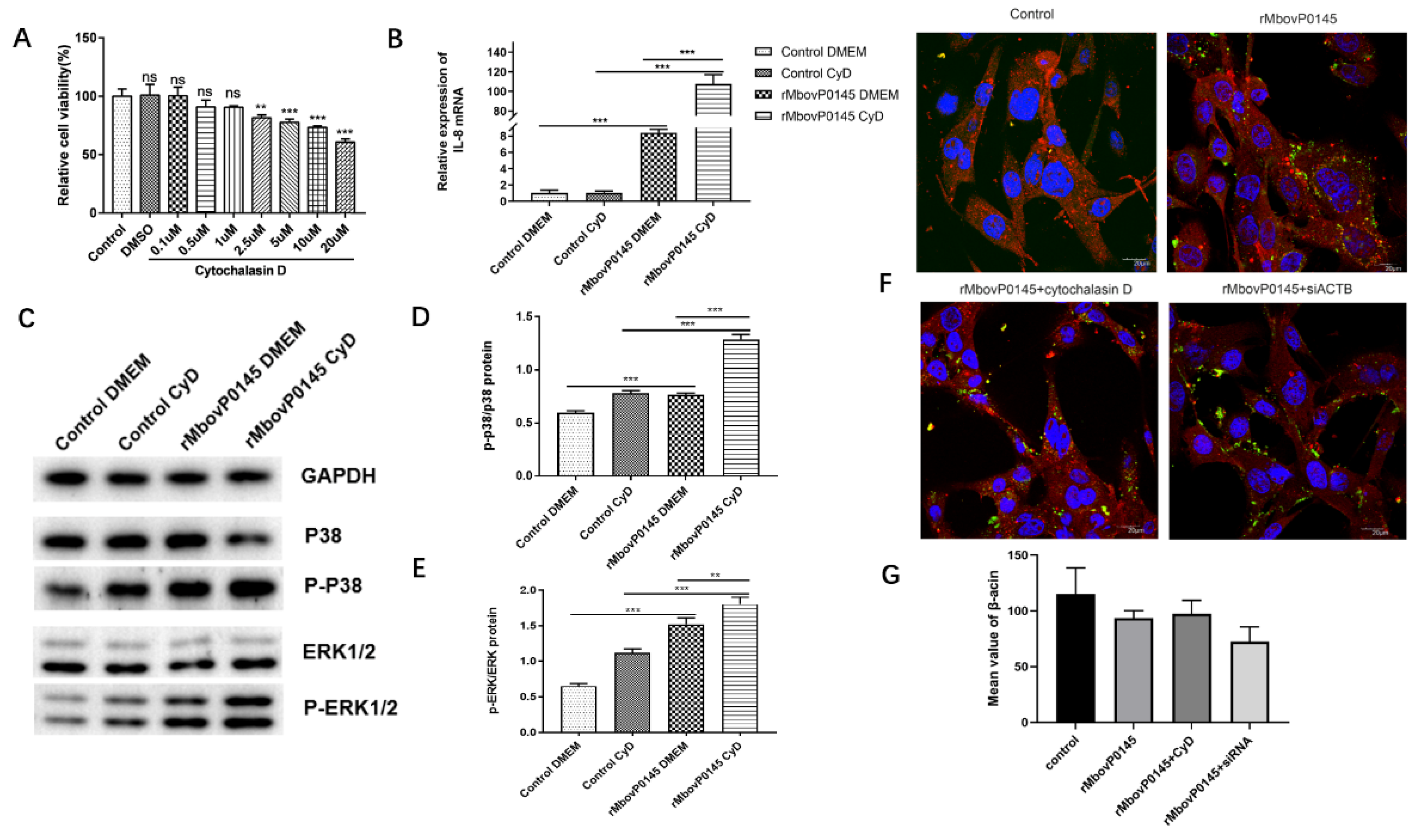
3.6. IL-8 Expression Induced by MbovP0145 Depends on Its Interactive β-Actin
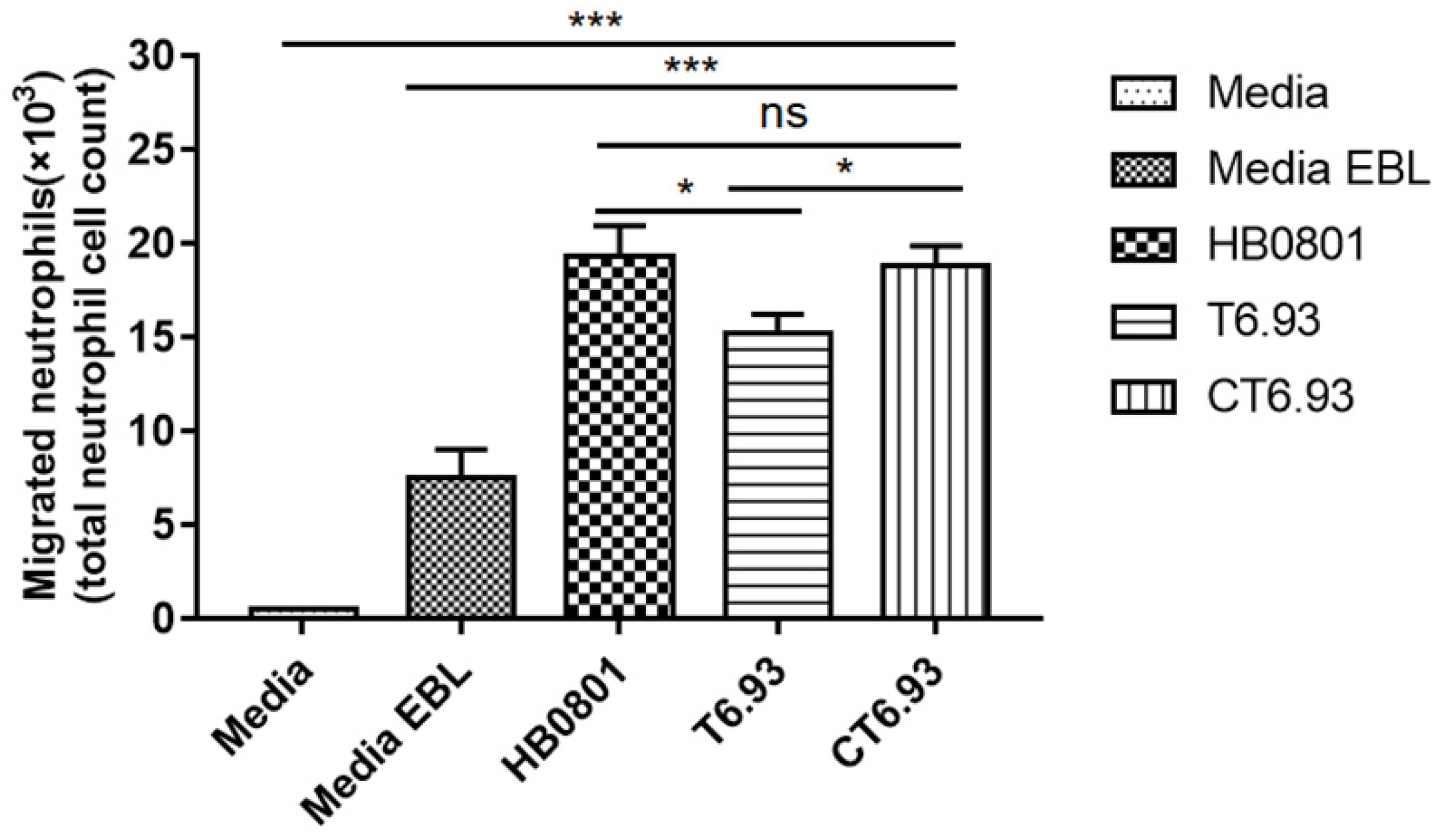
3.7. MbovP0145 Induces Neutrophil Migration by Regulating the Production of IL-8
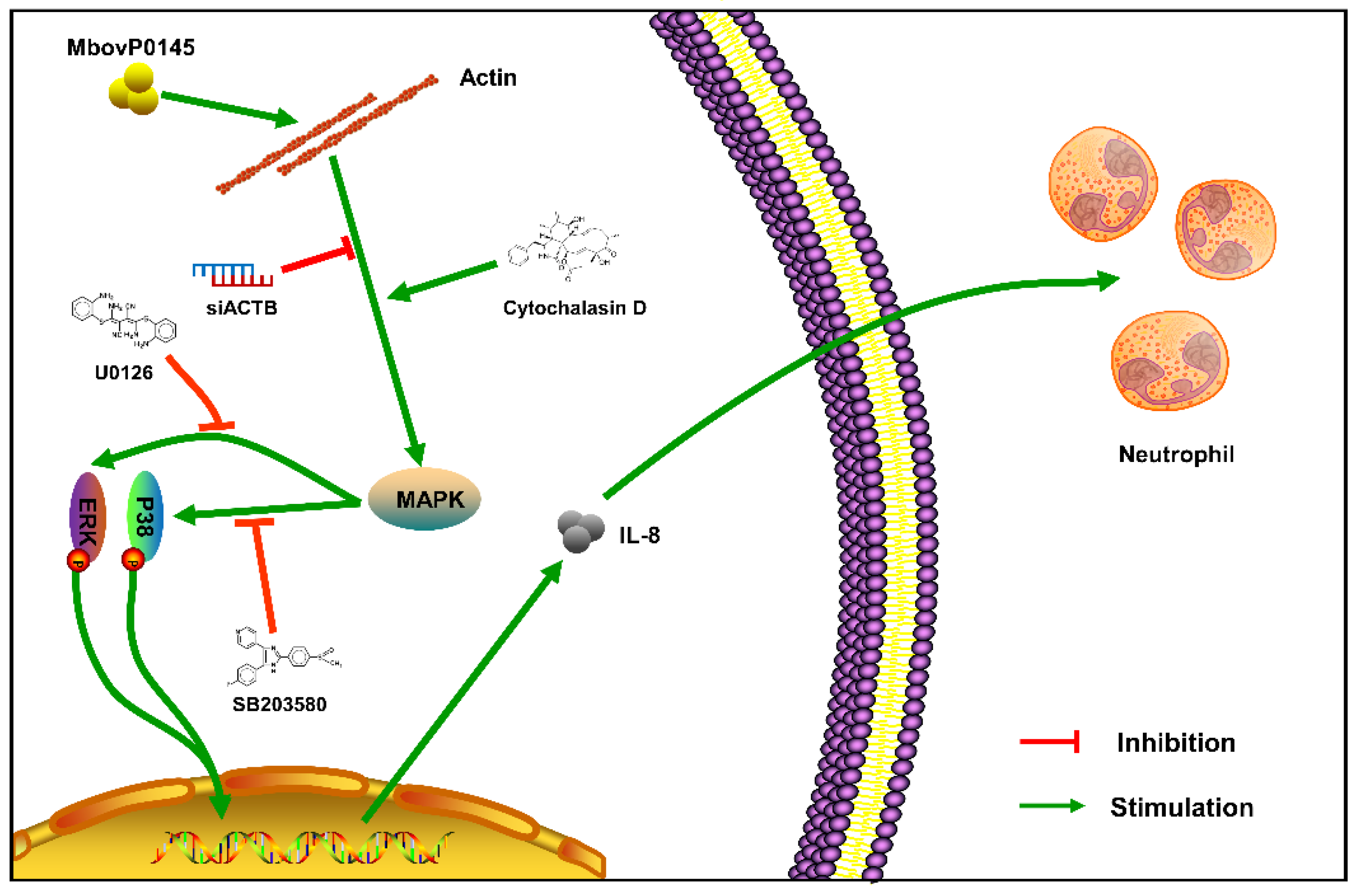
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Citti, C.; Blanchard, A. Mycoplasmas and their host: Emerging and re-emerging minimal pathogens. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitcher, D.G.; Nicholas, R.A.J. Mycoplasma host specificity: Fact or fiction? Vet. J. 2005, 170, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burki, S.; Frey, J.; Pilo, P. Virulence, persistence and dissemination of Mycoplasma bovis. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 179, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, H.H.; Helmboldt, C.F.; Plastridge, W.N.; Stula, E.F. Bovine mastitis caused by a Mycoplasma species. Cornell Vet. 1962, 52, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perez-Casal, J. Pathogenesis and Virulence of Mycoplasma bovis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2020, 36, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, P.; Wu, W.; Peng, C. MBOVPG45_0375 Encodes an IgG-Binding Protein and MBOVPG45_0376 Encodes an IgG-Cleaving Protein in Mycoplasma bovis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 644224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Hao, H.; Zhao, P.; Ji, W.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Chu, Y. Differential Immunoreactivity to Bovine Convalescent Serum Between Mycoplasma bovis Biofilms and Planktonic Cells Revealed by Comparative Immunoproteomic Analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Baranowski, E.; Dong, Y.; Li, X.; Hao, Z.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, H.; Lu, D.; Rasheed, M.; Chen, Y.; et al. An emerging role for cyclic dinucleotide phosphodiesterase and nanoRNase activities in Mycoplasma bovis: Securing survival in cell culture. PLoS Pathog 2020, 16, e1008661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirigotaki, A.; De Geyter, J.; Sostaric, N.; Economou, A.; Karamanou, S. Protein export through the bacterial Sec pathway. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Schieck, E.; Hu, C.; Chen, H.; Guo, A. Novel Secreted Protein of Mycoplasma bovis MbovP280 Induces Macrophage Apoptosis Through CRYAB. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 619362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, G.; Guo, Y.; Menghwar, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Guo, A. Mycoplasma bovis MBOV_RS02825 Encodes a Secretory Nuclease Associated with Cytotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, G.; Lu, D.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zubair, M.; Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Comparative Secretome Analyses of Mycoplasma bovis Virulent and Attenuated Strains Revealed MbovP0145 as a Promising Diagnostic Biomarker. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, A.; Plaze, A.; Berthon, P.; Thibeaux, R.; Guillen, N.; Labruyere, E. In Entamoeba histolytica, a BspA family protein is required for chemotaxis toward tumour necrosis factor. Microb. Cell 2015, 2, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Gong, R.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Pei, J.; Hu, Z.; Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Liu, T.; Chen, Y.; et al. Preliminary Diagnosis of Cattle infections Mycoplasma bovis Pneumonia. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2008, 27, 572. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Dong, Y.; Baranowski, E.; Li, X.; Zhao, G.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Chen, H.; et al. Mbov_0503 Encodes a Novel Cytoadhesin that Facilitates Mycoplasma bovis Interaction with Tight Junctions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Guo, A.; Cui, P.; Chen, Y.; Mustafa, R.; Ba, X.; Hu, C.; Bai, Z.; Chen, X.; Shi, L.; et al. Comparative geno-plasticity analysis of Mycoplasma bovis HB0801 (Chinese isolate). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Han, L.; Xie, C.; Li, W.; Lin, L.; Pan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Jin, M.; Zhang, A. Identification of extracellular Actin as a ligand for triggering receptor expressed on myeloid Cells-1 signaling. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.A.; Faisal, M.; Chao, J.; Liu, K.; Chen, X.; Zhao, G.; Menghwar, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Rasheed, M.A.; et al. Immunoproteomic identification of MbovP579, a promising diagnostic biomarker for serological detection of Mycoplasma bovis infection. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 39376–39395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.P.; Xue, B.Y.; Li, L.L.; Nan, Y.C.; Zhang, L.; Li, K.K.; Zhao, Q.; Hiscox, J.A.; Stewart, J.P.; Wu, C.Y.; et al. Direct Interaction Between CD163 N-Terminal Domain and MYH9 C-Terminal Domain Contributes to Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Internalization by Permissive Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Furze, R.C.; Birrell, M.A.; Rankin, S.M.; Hume, A.N.; Seabra, M.C. A role for Rab27 in neutrophil chemotaxis and lung recruitment. BMC Cell. Biol. 2014, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilo, P.; Martig, S.; Frey, J.; Vilei, E.M. Antigenic and genetic characterisation of lipoprotein lppC from Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides SC. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Sojar, H.T.; Glurich, I.; Honma, K.; Kuramitsu, H.K.; Genco, R.J. Cloning, expression, and sequencing of a cell surface antigen containing a leucine-rich repeat motif from Bacteroides forsythus ATCC 43037. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 5703–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikegami, A.; Honma, K.; Sharma, A.; Kuramitsu, H.K. Multiple functions of the leucine-rich repeat protein LrrA of Treponema denticola. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 4619–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Onishi, S.; Honma, K.; Liang, S.; Stathopouiou, P.; Kinane, D.; Hajishengallis, G.; Sharma, A. Toll-like receptor 2-mediated interleukin-8 expression in gingival epithelial cells by the Tannerella forsythia leucine-rich repeat protein BspA. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Inagaki, S.; Honma, K.; Sfintescu, C.; Baker, P.J.; Evans, R.T. Tannerella forsythia-induced alveolar bone loss in mice involves leucine-rich-repeat BspA protein. J. Dent. Res. 2005, 84, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbinden, C.; Pilo, P.; Frey, J.; Bruckmaier, R.M.; Wellnitz, O. The immune response of bovine mammary epithelial cells to live or heat-inactivated Mycoplasma bovis. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 179, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, K.; Gondaira, S.; Okamoto, M.; Nebu, T.; Koiwa, M.; Ohtsuka, H.; Murai, K.; Matsuda, K.; Fujiki, J.; Iwano, H.; et al. Effect of Mycoplasma bovis on expression of inflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases mRNA in bovine synovial cells. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2019, 216, 109920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondaira, S.; Nishi, K.; Fujiki, J.; Iwano, H.; Watanabe, R.; Eguchi, A.; Hirano, Y.; Higuchi, H.; Nagahata, H. Innate immune response in bovine neutrophils stimulated with Mycoplasma bovis. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.E.; Kim, K.W.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, K.E.; Sohn, M.H. Modulation of IL-8 Boosted by Mycoplasma pneumoniae lysate in Human Airway Epithelial Cells. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmura, K.; Bai, X.Y.; Nakamura, M.; Kandasamy, P.; McGibney, M.; Kuronuma, K.; Mitsuzawa, H.; Voelker, D.R.; Chan, E.D. Induction of IL-8 by Mycoplasma pneumoniae membrane in BEAS-2B cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung C 2008, 295, L220–L230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojcius, D.M.; Hardy, R.D.; Coalson, J.J.; Peters, J.; Chaparro, A.; Techasaensiri, C.; Cantwell, A.M.; Kannan, T.R.; Baseman, J.B.; Dube, P.H. Analysis of Pulmonary Inflammation and Function in the Mouse and Baboon after Exposure to Mycoplasma pneumoniae CARDS Toxin. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shao, X.; Dou, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Hao, C.; Fan, M.; Ji, W.; Yan, Y. Role of the Mycoplasma pneumoniae/Interleukin-8/Neutrophil Axis in the Pathogenesis of Pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pease, J.E.; Sabroe, I. The role of interleukin-8 and its receptors in inflammatory lung disease: Implications for therapy. Am. J. Respir. Med. 2002, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaida, N. Pathophysiological roles of interleukin-8/CXCL8 in pulmonary diseases. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung C 2003, 284, L566–L577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugina, V.B.; Shagieva, G.S.; Shakhov, A.S.; Alieva, I.B. The Cytoplasmic Actins in the Regulation of Endothelial Cell Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winder, S.J.; Ayscough, K.R. Actin-binding proteins. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantaloni, D.; Le Clainche, C.; Carlier, M.F. Mechanism of actin-based motility. Science 2001, 292, 1502–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, B.B.A.; Madhkoor, R.; Schleicher, I.; Uphoff, C.C.; Turnbull, L.; Whitchurch, C.B.; Rohde, M.; Padula, M.P.; Djordjevic, S.P. Extracellular Actin Is a Receptor for Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, A.; Freitas, J.; Keles, F.; Snoek, M.; van Marle, J.; Jansen, H.M.; Lutter, R. Cytoskeletal architecture differentially controls post-transcriptional processing of IL-6 and IL-8 mRNA in airway epithelial-like cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kustermans, G.; El Mjiyad, N.; Horion, J.; Jacobs, N.; Piette, J.; Legrand-Poels, S. Actin cytoskeleton differentially modulates NF-kappaB-mediated IL-8 expression in myelomonocytic cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 1214–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Wu, S.; Ji, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Yue, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, W. The influence of actin depolymerization induced by Cytochalasin D and mechanical stretch on interleukin-8 expression and JNK phosphorylation levels in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, Z.H.; Deitch, E.A.; Davidson, M.T.; Szabo, C.; Vizi, E.S.; Hasko, G. Disruption of the actin cytoskeleton results in nuclear factor-kappa B activation and inflammatory mediator production in cultured human intestinal epithelial cells (vol 200, pg 71, 2004). J. Cell. Physiol. 2004, 200, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xythalis, D.; Frewin, M.B.; Gudewicz, P.W. Inhibition of IL-8-mediated MAPK activation in human neutrophils by beta(1) integrin ligands. Inflammation 2002, 26, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Manzanares, M.; Choi, C.K.; Horwitz, A.R. Integrins in cell migration--the actin connection. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J. Myosin Heavy Chain 9: Oncogene or Tumor Suppressor Gene? Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Names | Primer Sequences (5′→3′) 1 |
|---|---|
| IL-8-F | GAAGAGAGCTGAGAAGCAAGATCC |
| IL-8-R | ACCCACACAGAACATGAGGC |
| GAPDH-F | TGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTGAAC |
| GAPDH-R | ATGGCGACGATGTCCACTTT |
| pOH/P-0145-F1 | ATTTGCGGCCGCACGGGGCTAAAGAAGCTGATAT (NotI) |
| pOH/P-0145-R1 | TAGCAAAAAGCATAATTATTTATATCCTTTTCTT |
| pOH/P-0145-F2 | TAAATAATTATGCTTTTTGCTAGTTCACTTCCTTT |
| pOH/P-0145-R2 | AATTGCGGCCGCTTATTTAGATACTTGCCTAAAA (NotI) |
| GST-0145-F | TTCCAGGGGCCCCTGGGATCCATGCTGTTTGCCTCAAGCCTG (BamHI) |
| GST-0145-R | GTCACGATGCGGCCGCTCGAGTTATTTGCTAACCTGACGAAAATTCG (XhoI) |
| HA-0145-F | GTTCCAGATTACGCTGAATTCATGCTGTTTGCCTCAAGCCTG (EcoRI) |
| HA-0145-R | ATTAAGATCTGCTAGCTCGAGTTATTTGCTAACCTGACGAAAATTCG (XhoI) |
| Flag-actin-F | AAGCTTGCGGCCGCGAATTCAATGGATGATGATATTGCTGCGC (EcoRI) |
| Flag-actin-R | CAGGGATGCCACCCGGGATCCCTAGAAGCATTTGCGGTGGAC (BamHI) |
| EGFP-0145 F | AGTCCGGACTCAGATCTCGAGATATGCTGTTTGCCTCAAGCCTG (XhoI) |
| EGFP-0145 R | TTATCTAGATCCGGTGGATCCTTATTTGCTAACCTGACGAAAATTCG (BamHI) |
| Band | Protein Name | Accession No.a | Unique Peptide Count b | Percentage Coverage c | MW (KDa) d | PI e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Myosin heavy chain 9 | F1MQ37 | 92 | 35.62% | 227,201.32 | 5.49 |
| B | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | P60712 | 10 | 24.00% | 41,736.29 | 5.29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Anwar Khan, F.; Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Yang, L.; Chen, H.; Guo, A. Secreted MbovP0145 Promotes IL-8 Expression through Its Interactive β-Actin and MAPK Activation and Contributes to Neutrophil Migration. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121628
Lu D, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Zhao G, Anwar Khan F, Chen Y, Hu C, Yang L, Chen H, Guo A. Secreted MbovP0145 Promotes IL-8 Expression through Its Interactive β-Actin and MAPK Activation and Contributes to Neutrophil Migration. Pathogens. 2021; 10(12):1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121628
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Doukun, Hui Zhang, Yiqiu Zhang, Gang Zhao, Farhan Anwar Khan, Yingyu Chen, Changmin Hu, Liguo Yang, Huanchun Chen, and Aizhen Guo. 2021. "Secreted MbovP0145 Promotes IL-8 Expression through Its Interactive β-Actin and MAPK Activation and Contributes to Neutrophil Migration" Pathogens 10, no. 12: 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121628
APA StyleLu, D., Zhang, H., Zhang, Y., Zhao, G., Anwar Khan, F., Chen, Y., Hu, C., Yang, L., Chen, H., & Guo, A. (2021). Secreted MbovP0145 Promotes IL-8 Expression through Its Interactive β-Actin and MAPK Activation and Contributes to Neutrophil Migration. Pathogens, 10(12), 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121628







