Intracellular Behaviour of Legionella Non-pneumophila Strains within Three Amoeba Strains, Including Willaertia magna C2c Maky
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. L. Non-pneumophila Survival in an SCYEM Medium
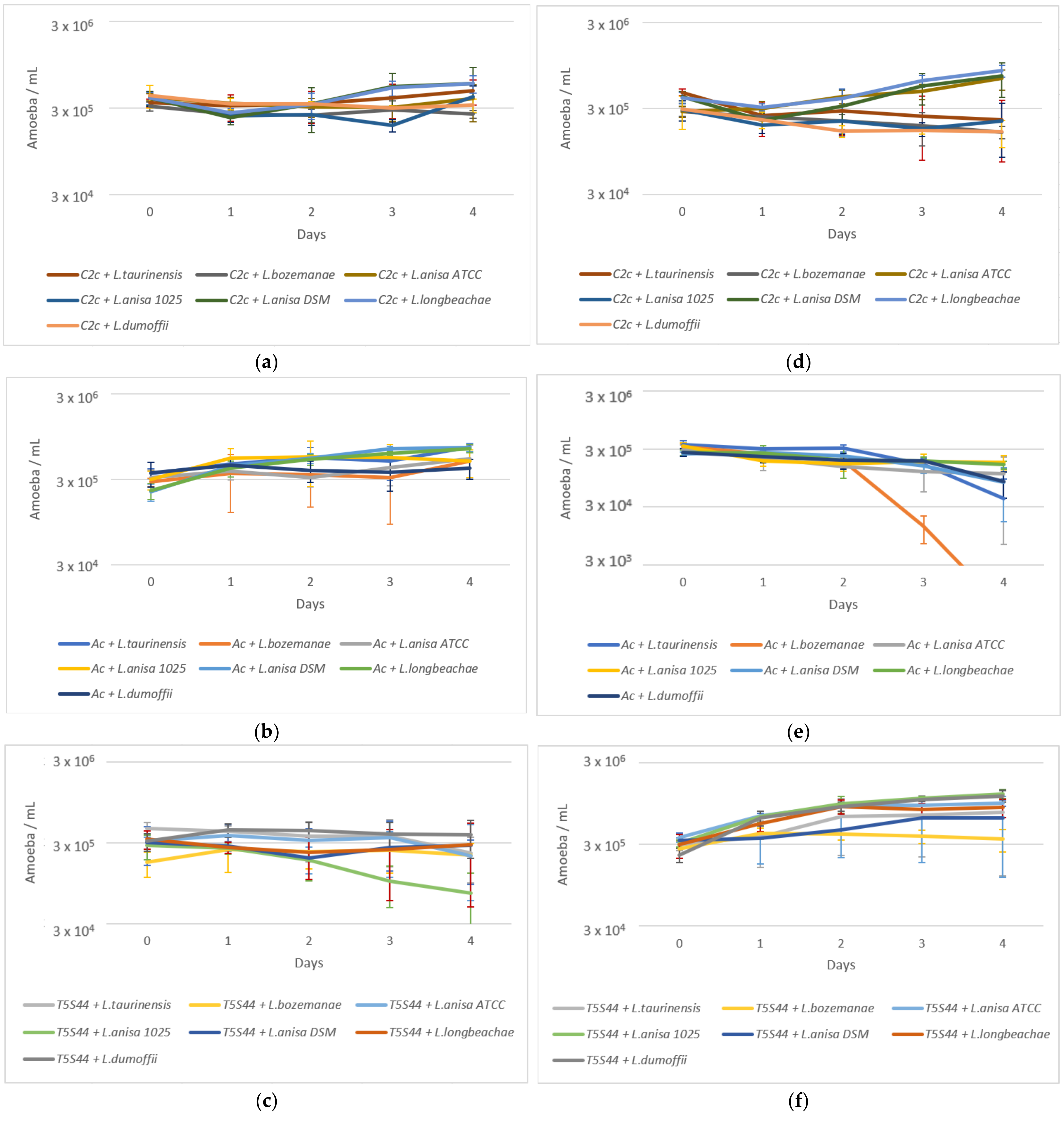
2.2. Amoeba Survival
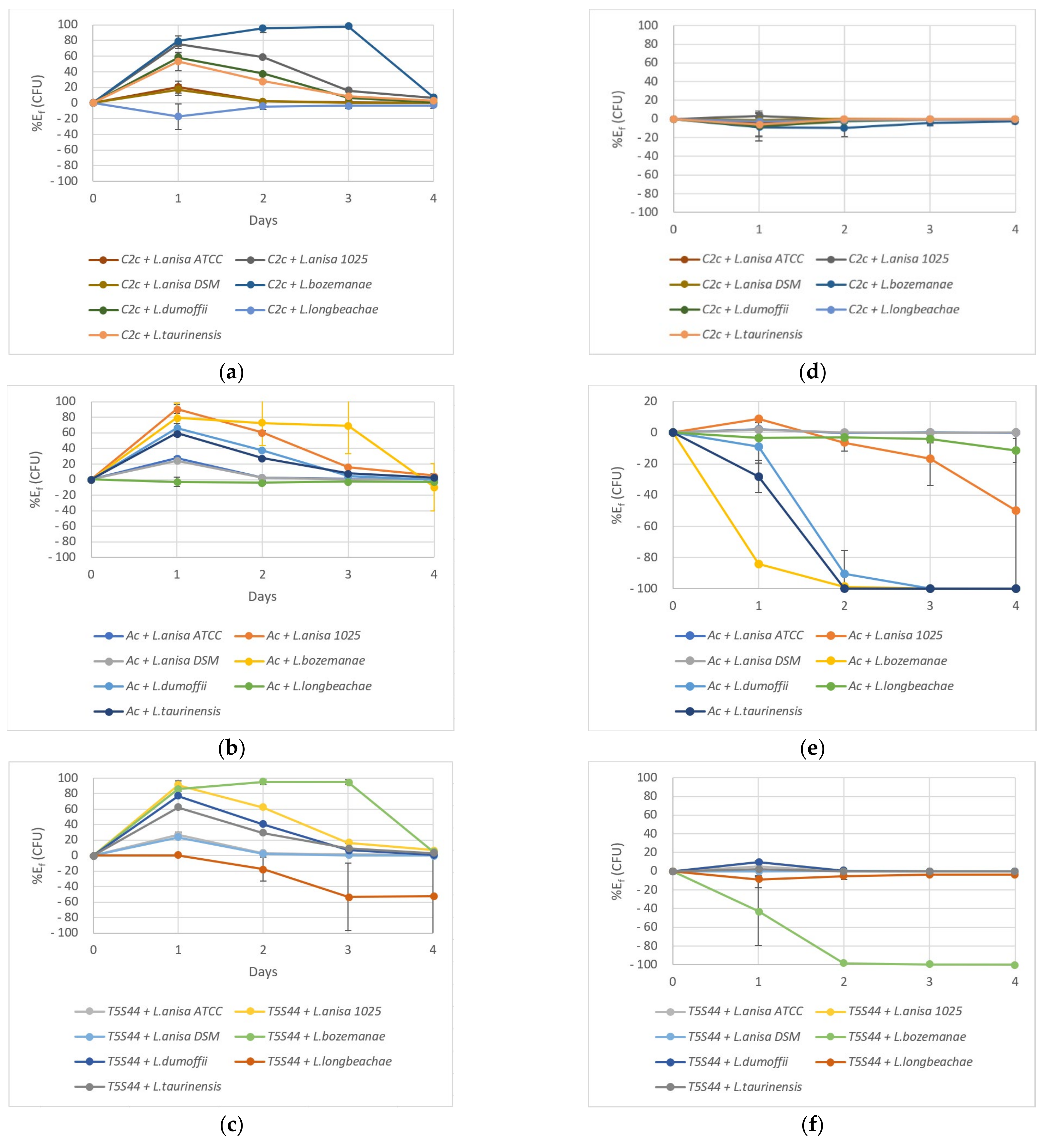
2.3. Coculture Experiments
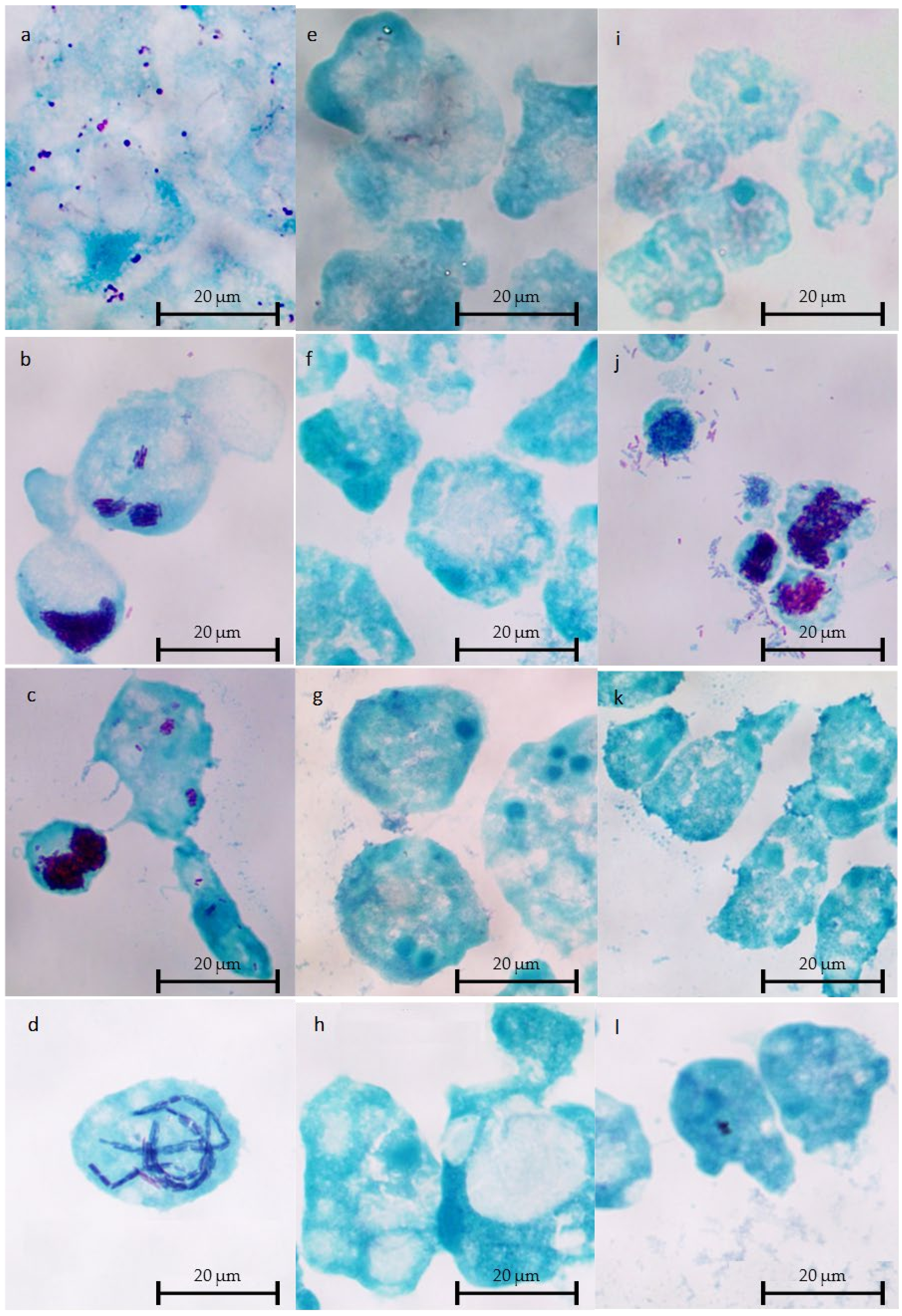
2.4. Microscopic Observations of Intracellular L. Non-pneumophila at 37 °C
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microbial Cultures
4.2. Bacteria and Amoeba Survival in SCYEM Medium (Controls)
4.3. Coculture Assays
4.4. Bacteria and Amoeba Quantifications in Coculture Assays from T0 to T96h
4.5. Microscopic Observations of Cocultures
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Vassiliadis, D.; Ong, S.Y.; Bennett-Wood, V.; Sugimoto, C.; Yamagishi, J.; Hartland, E.L.; Pasricha, S. Legionella Pneumophila Infection Rewires the Acanthamoeba Castellanii Transcriptome, Highlighting a Class of Sirtuin Genes. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, H.; Chintalapati, S.; Patel, P.; Halim, A.; Kithas, A.; Schmalzle, S.A. Legionella Longbeachae Pneumonia: Case Report and Review of Reported Cases in Non-Endemic Countries. IDCases 2021, 23, e01050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burillo, A.; Pedro-Botet, M.L.; Bouza, E. Microbiology and Epidemiology of Legionnaire’s Disease. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 31, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, H.J.; Ang, D.K.Y.; van Driel, I.R.; Hartland, E.L. Molecular Pathogenesis of Infections Caused by Legionella Pneumophila. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 274–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borella, P.; Guerrieri, E.; Marchesi, I.; Bondi, M.; Messi, P. Water Ecology of Legionella and Protozoan: Environmental and Public Health Perspectives. Biotechnol. Annu. Rev. 2005, 11, 355–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert-Weissenberger, C.; Cazalet, C.; Buchrieser, C. Legionella Pneumophila—A Human Pathogen That Co-Evolved with Fresh Water Protozoa. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2007, 64, 432–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Nour, M.; Duncan, C.; Low, D.E.; Guyard, C. Biofilms: The Stronghold of Legionella Pneumophila. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21660–21675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michel, R.; Just, H.M. Acanthamoebae, Naegleria and other free-living Amoebae in cooling and rinsing water of dental treatment units. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. Mikrobiol. Hyg. 1984, 179, 56–72. [Google Scholar]
- Barbaree, J.M.; Fields, B.S.; Feeley, J.C.; Gorman, G.W.; Martin, W.T. Isolation of Protozoa from Water Associated with a Legionellosis Outbreak and Demonstration of Intracellular Multiplication of Legionella Pneumophila. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1986, 51, 422–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Jonckheere, J.F. Ecology of Acanthamoeba. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1991, 13 (Suppl. 5), S385–S387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, V.; Bouchez, T.; Nicolas, V.; Robert, S.; Loret, J.F.; Lévi, Y. Amoebae in Domestic Water Systems: Resistance to Disinfection Treatments and Implication in Legionella Persistence. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 950–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, V.; Herrera-Rimann, K.; Blanc, D.S.; Greub, G. Biodiversity of Amoebae and Amoeba-Resisting Bacteria in a Hospital Water Network. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2428–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Jonckheere, J.F. Isolation and Molecular Identification of Free-Living Amoebae of the Genus Naegleria from Arctic and Sub-Antarctic Regions. Eur. J. Protistol. 2006, 42, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, V.; Loret, J.-F.; Jousset, M.; Greub, G. Biodiversity of Amoebae and Amoebae-Resisting Bacteria in a Drinking Water Treatment Plant. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2728–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockman, L.J.; Wright, C.J.; Visvesvara, G.S.; Fields, B.S.; Beach, M.J. Prevalence of Acanthamoeba Spp. and Other Free-Living Amoebae in Household Water, Ohio, USA—1990–1992. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowbotham, T.J. Preliminary Report on the Pathogenicity of Legionella Pneumophila for Freshwater and Soil Amoebae. J. Clin. Pathol. 1980, 33, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michel, R.; Müller, K.-D.; Amann, R.; Schmid, E.N. Legionella-like Slender Rods Multiplying within a Strain of Acanthamoeba Sp. Isolated from Drinking Water. Parasitol. Res. 1997, 84, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greub, G.; Raoult, D. Microorganisms Resistant to Free-Living Amoebae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abu Kwaik, Y.; Gao, L.-Y.; Stone, B.J.; Venkataraman, C.; Harb, O.S. Invasion of Protozoa by Legionella Pneumophila and Its Role in Bacterial Ecology and Pathogenesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3127–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berk, S.G.; Ting, R.S.; Turner, G.W.; Ashburn, R.J. Production of Respirable Vesicles Containing Live Legionella Pneumophila Cells by Two Acanthamoeba Spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowbotham, T.J. Current Views on the Relationships between Amoebae, Legionellae and Man. Isr. J. Med. Sci. 1986, 22, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bouyer, S.; Imbert, C.; Rodier, M.-H.; Héchard, Y. Long-Term Survival of Legionella Pneumophila Associated with Acanthamoeba Castellanii Vesicles. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1341–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, B.S. The Molecular Ecology of Legionellae. Trends Microbiol. 1996, 4, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilvington, S.; Price, J. Survival of Legionella Pneumophila within Cysts of Acanthamoeba Polyphaga Following Chlorine Exposure. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1990, 68, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuy, M.; Binet, M.; Bouteleux, C.; Herbelin, P.; Soreau, S.; Héchard, Y. Permissiveness of Freshly Isolated Environmental Strains of Amoebae for Growth of Legionella Pneumophila. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.G.; Katayama, H.; Ohgaki, S. Effect of Intracellular Resuscitation of Legionella Pneumophila in Acanthamoeba Polyphage Cells on the Antimicrobial Properties of Silver and Copper. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7434–7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, J.D.; Falkow, S.; Tompkins, L.S. Growth of Legionella Pneumophila in Acanthamoeba Castellanii Enhances Invasion. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 3254–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nora, T.; Lomma, M.; Gomez-Valero, L.; Buchrieser, C. Molecular Mimicry: An Important Virulence Strategy Employed by Legionella Pneumophila to Subvert Host Functions. Future Microbiol. 2009, 4, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameri, R.M.; Bodennec, J.; Bezin, L.; Demanèche, S. Mitigation of Expression of Virulence Genes in Legionella Pneumophila Internalized in the Free-Living Amoeba Willaertia Magna C2c Maky. Pathogens 2020, 9, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, R.; Bodennec, J.; Mameri, M.O.; Pernin, P. Free-Living Freshwater Amoebae Differ in Their Susceptibility to the Pathogenic Bacterium Legionella Pneumophila. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 290, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dey, R.; Mameri, M.R.; Trajkovic-Bodennec, S.; Bodennec, J.; Pernin, P. Impact of Inter-Amoebic Phagocytosis on the L. Pneumophila Growth. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2020, 367, fnaa147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasni, I.; Jarry, A.; Quelard, B.; Carlino, A.; Eberst, J.-B.; Abbe, O.; Demanèche, S. Intracellular Behaviour of Three Legionella Pneumophila Strains within Three Amoeba Strains, Including Willaertia Magna C2c Maky. Pathogens 2020, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Legionnaires’ Disease—Annual Epidemiological Report for 2019. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/legionnaires-disease-annual-epidemiological-report-2019 (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- Collier, S.A.; Deng, L.; Adam, E.A.; Benedict, K.M.; Beshearse, E.M.; Blackstock, A.J.; Bruce, B.B.; Derado, G.; Edens, C.; Fullerton, K.E.; et al. Estimate of Burden and Direct Healthcare Cost of Infectious Waterborne Disease in the United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. CDC 2021, 27, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, J.; Huh, J.Y.; Ito, Y.; Kobuchi, T.; Kusukawa, K.; Hayashi, H. Can We Truly Rely on the Urinary Antigen Test for the Diagnosis? Legionella Case Report. J. Gen. Fam. Med. 2017, 18, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jarraud, S.; Lina, G. Legionella_Rapport Activité 2019_FINAL.Pdf—CNR Sites Web (10-01-2020 08:26). Available online: https://clarolineconnect.univ-lyon1.fr/resource/open/file/5322646 (accessed on 11 August 2021).
- Amemura-Maekawa, J.; Kura, F.; Chida, K.; Ohya, H.; Kanatani, J.; Isobe, J.; Tanaka, S.; Nakajima, H.; Hiratsuka, T.; Yoshino, S.; et al. Legionella Pneumophila and Other Legionella Species Isolated from Legionellosis Patients in Japan between 2008 and 2016. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00721-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brenner, D.J.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Gorman, G.W.; Weaver, R.E.; Feeley, J.C.; Cordes, L.G.; Wilkinson, H.W.; Patton, C.; Thomason, B.M.; Sasseville, K.R.L. Legionella Bozemanii Sp. Nov. AndLegionella Dumoffii Sp. Nov.: Classification of Two Additional Species OfLegionella Associated with Human Pneumonia. Curr. Microbiol. 1980, 4, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, S.T.; Slow, S.; Scott-Thomas, A.; Murdoch, D.R. Legionellosis Caused by Non-Legionella Pneumophila Species, with a Focus on Legionella Longbeachae. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordes, L.G.; Wilkinson, H.W.; Gorman, G.W.; Fikes, B.J.; Fraser, D.W. Atypical Legionella-like Organisms: Fastidious Water-Associated Bacteria Pathogenic for Man. Lancet Lond. Engl. 1979, 2, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.; Smith, J.; Burton, J.; Evelyn, R.; Harper, B.; Huckell, V.; Jones, E. Legionella Longbeachae Pneumonia Diagnosed by Bronchial Brushing. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1982, 127, 223–224. [Google Scholar]
- Vaccaro, L.; Izquierdo, F.; Magnet, A.; Hurtado, C.; Salinas, M.A.; Gomes, T.S.; Angulo, S.; Salso, S.; Pelaez, J.; Tejeda, M.I.; et al. First Case of Legionnaire’s Disease Caused by Legionella Anisa in Spain and the Limitations on the Diagnosis of Legionella Non-Pneumophila Infections. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, V.L.; Plouffe, J.F.; Pastoris, M.C.; Stout, J.E.; Schousboe, M.; Widmer, A.; Summersgill, J.; File, T.; Heath, C.M.; Paterson, D.L.; et al. Distribution of Legionella Species and Serogroups Isolated by Culture in Patients with Sporadic Community-Acquired Legionellosis: An International Collaborative Survey. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steege, L.; Moore, G. The Presence and Prevalence of Legionella Spp in Collected Rainwater and Its Aerosolisation during Common Gardening Activities. Perspect. Public Health 2018, 138, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, M.; Salaris, S.; Pascale, M.R.; Girolamini, L.; Cristino, S. Occurrence of Legionella Spp. in Man-Made Water Sources: Isolates Distribution and Phylogenetic Characterization in the Emilia-Romagna Region. Pathogens 2021, 10, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priest, P.C.; Slow, S.; Chambers, S.T.; Cameron, C.M.; Balm, M.N.; Beale, M.W.; Blackmore, T.K.; Burns, A.D.; Drinković, D.; Elvy, J.A.; et al. The Burden of Legionnaires’ Disease in New Zealand (LegiNZ): A National Surveillance Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, T.S.; Gjiknuri, J.; Magnet, A.; Vaccaro, L.; Ollero, D.; Izquierdo, F.; Fenoy, S.; Hurtado, C.; Del Águila, C. The Influence of Acanthamoeba-Legionella Interaction in the Virulence of Two Different Legionella Species. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salinas, M.B.; Fenoy, S.; Magnet, A.; Vaccaro, L.; Gomes, T.D.; Hurtado, C.; Ollero, D.; Valdivieso, E.; Del Águila, C.; Pozuelo, M.J.; et al. Are Pathogenic Legionella Non-Pneumophila a Common Bacteria in Water Distribution Networks? Water Res. 2021, 196, 117013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Head, B.M.; Graham, C.I.; MacMartin, T.; Keynan, Y.; Brassinga, A.K.C. Development of a Fluorescent Tool for Studying Legionella Bozemanae Intracellular Infection. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, G.W.; Feeley, J.C.; Steigerwalt, A.; Edelstein, P.H.; Moss, C.W.; Brenner, D.J. Legionella Anisa: A New Species of Legionella Isolated from Potable Waters and a Cooling Tower. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- La Scola, B.; Mezi, L.; Weiller, P.J.; Raoult, D. Isolation of Legionella Anisa Using an Amoebic Coculture Procedure. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 365–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagnier, I.; Croce, O.; Robert, C.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Genome Sequence of Legionella Anisa, Isolated from a Respiratory Sample, Using an Amoebal Coculture Procedure. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fenstersheib, M.D.; Miller, M.; Diggins, C.; Liska, S.; Detwiler, L.; Werner, S.B.; Lindquist, D.; Thacker, W.L.; Benson, R.F. Outbreak of Pontiac Fever Due to Legionella Anisa. Lancet 1990, 336, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindall, B.J. Taking a Closer Look at the Valid Publication and Authorship of Legionella Bozemanae Brenner et al. 1980, Fluoribacter Bozemanae Garrity et al. 1980, Legionella Pittsburghensis Pasculle et al. 1980, Legionella Micdadei Hébert et al. 1980 and Tatlockia Micdadei (Hébert et al. 1980) Garrity et al. 1980. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinney, R.M.; Porschen, R.K.; Edelstein, P.H.; Bissett, M.L.; Harris, P.P.; Bondell, S.P.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Weaver, R.E.; Ein, M.E.; Lindquist, D.S.; et al. Legionella Longbeachae Species Nova, Another Etiologic Agent of Human Pneumonia. Ann. Intern. Med. 1981, 94, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiley, H.; Bentham, R. Legionella Longbeachae and Legionellosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornley, C.N.; Harte, D.J.; Weir, R.P.; Allen, L.J.; Knightbridge, K.J.; Wood, P.R.T. Legionella Longbeachae Detected in an Industrial Cooling Tower Linked to a Legionellosis Outbreak, New Zealand, 2015; Possible Waterborne Transmission? Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 2382–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumeister, B.; Schöniger, S.; Faigle, M.; Eichner, M.; Dietz, K. Multiplication of Different Legionella Species in Mono Mac 6 Cells and in Acanthamoeba Castellanii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo Presti, F.; Riffard, S.; Meugnier, H.; Reyrolle, M.; Lasne, Y.; Grimont, P.A.; Grimont, F.; Vandenesch, F.; Etienne, J.; Fleurette, J.; et al. Legionella Taurinensis Sp. Nov., a New Species Antigenically Similar to Legionella Spiritensis. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49 Pt 2, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzin, L.; Gioannini, P. Legionella Taurinensis, a New Species of Legionella Isolated in Turin, Italy. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50 Pt 2, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlan, D.; Coupat-Goutaland, B.; Risler, A.; Reyrolle, M.; Souchon, M.; Briolay, J.; Jarraud, S.; Doublet, P.; Pélandakis, M. Micriamoeba Tesseris Nov. Gen. Nov. Sp.: A New Taxon of Free-Living Small-Sized Amoebae Non-Permissive to Virulent Legionellae. Protist 2012, 163, 888–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornier, F.; Zas, E.; Potheret, D.; Laaberki, M.-H.; Coupat-Goutaland, B.; Charpentier, X. Environmental Free-Living Amoebae Can Predate on Diverse Antibiotic-Resistant Human Pathogens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, AEM0074721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, D.F. Staining Rickettsiae in Yolk-Sac Cultures. Stain Technol. 1964, 39, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greer, P.W.; Chandler, F.W.; Hicklin, M.D. Rapid Demonstration of Legionella Pneumophila in Unembedded Tissue. An Adaptation of the Giménez Stain. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1980, 73, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Bacterial Name | Origin |
|---|---|
| L. anisa ATCC | ATCC 35291 |
| L. anisa 1025 | Clinical isolate |
| L. anisa DSM | DSM 17627/ATCC 35292 |
| L. bozemanae | DSM 16523/ATCC 33217 |
| L. dumoffii | DSM 17625/ATCC 33279 |
| L.longbeachae | DSM 10572/ATCC 33462 |
| L. taurinensis | DSM 21897/ATCC 700508 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Croze, A.; Carlino, A.; Quélard, B.; Saha, A.; Convert, T.; Eberst, J.-B.; Demanèche, S. Intracellular Behaviour of Legionella Non-pneumophila Strains within Three Amoeba Strains, Including Willaertia magna C2c Maky. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101350
Croze A, Carlino A, Quélard B, Saha A, Convert T, Eberst J-B, Demanèche S. Intracellular Behaviour of Legionella Non-pneumophila Strains within Three Amoeba Strains, Including Willaertia magna C2c Maky. Pathogens. 2021; 10(10):1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101350
Chicago/Turabian StyleCroze, Aurélien, Antoine Carlino, Benjamin Quélard, Adeline Saha, Tiphaine Convert, Jean-Baptiste Eberst, and Sandrine Demanèche. 2021. "Intracellular Behaviour of Legionella Non-pneumophila Strains within Three Amoeba Strains, Including Willaertia magna C2c Maky" Pathogens 10, no. 10: 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101350
APA StyleCroze, A., Carlino, A., Quélard, B., Saha, A., Convert, T., Eberst, J.-B., & Demanèche, S. (2021). Intracellular Behaviour of Legionella Non-pneumophila Strains within Three Amoeba Strains, Including Willaertia magna C2c Maky. Pathogens, 10(10), 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101350







