Investigation of the Effect of Wall Thickness and Wall Height on Building Behaviour During an Earthquake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
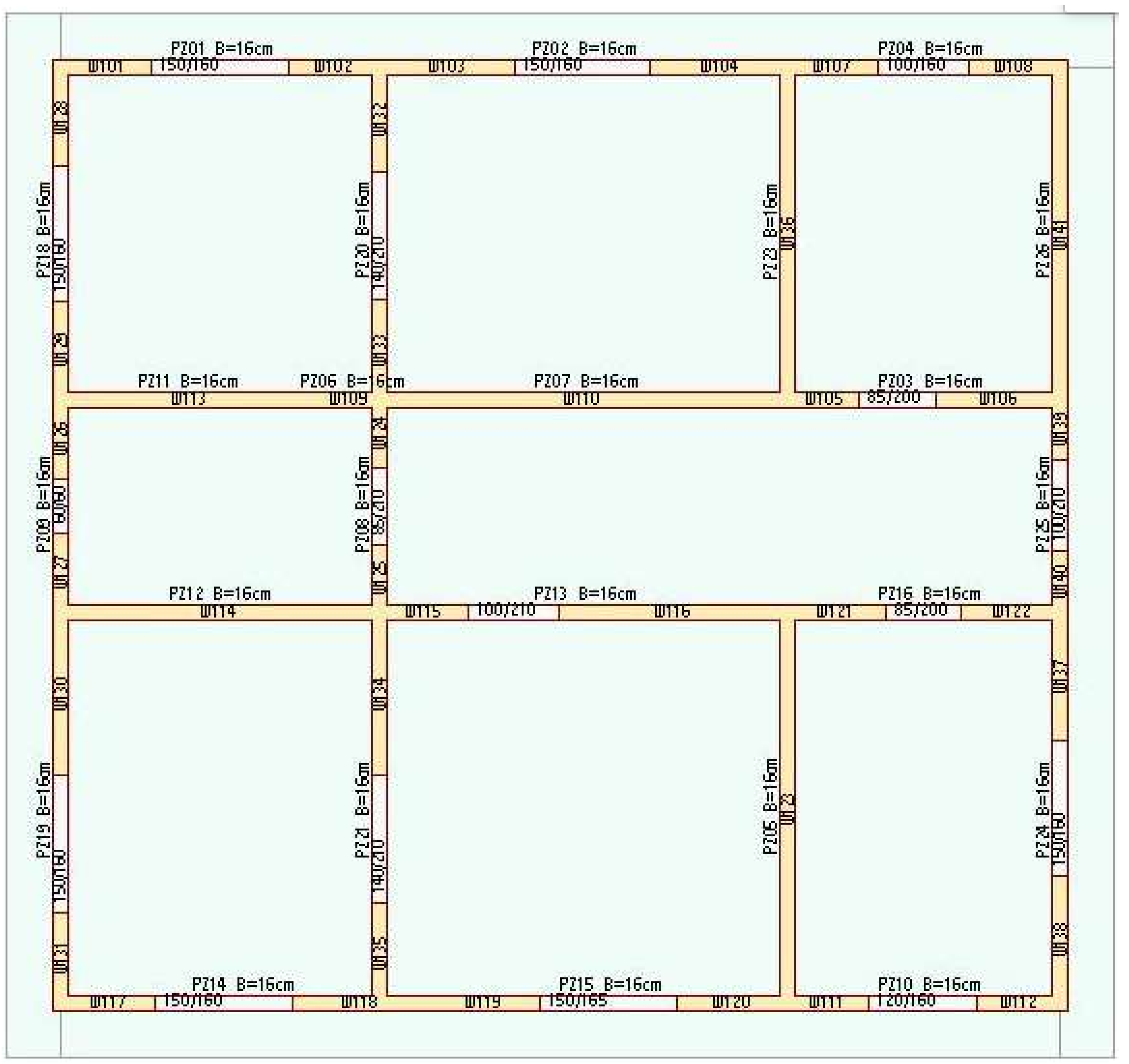
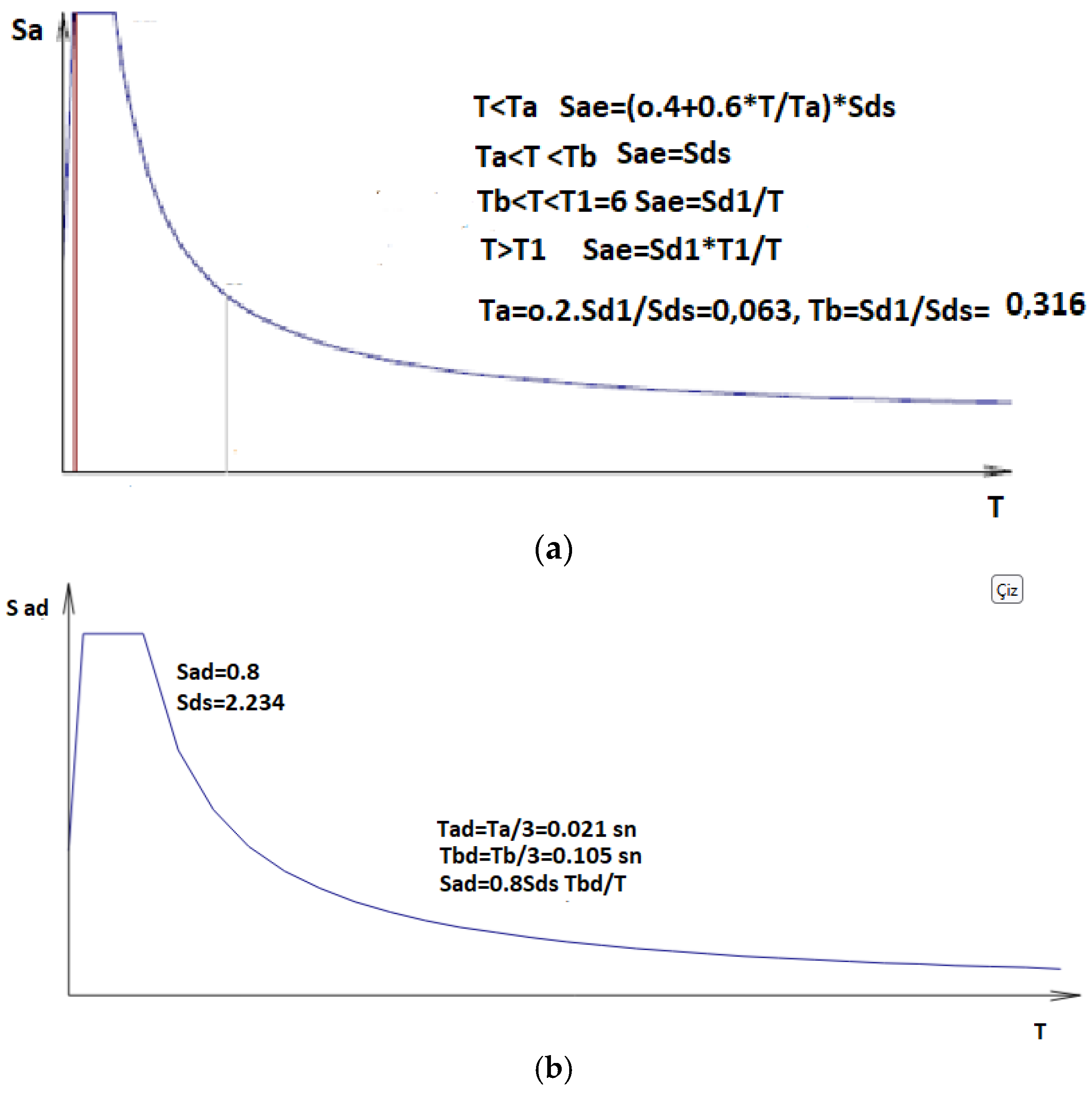
2.2. Numerical Modelling Processes
2.3. Method
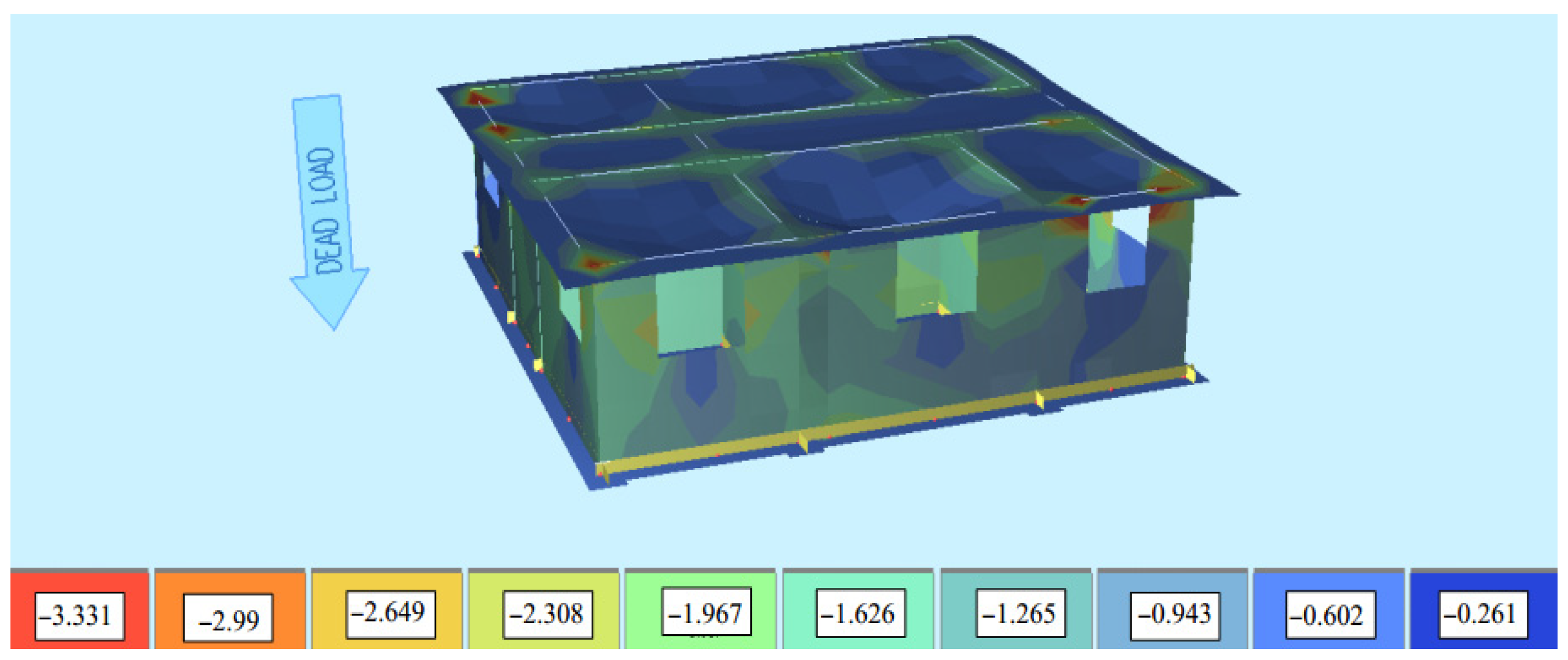
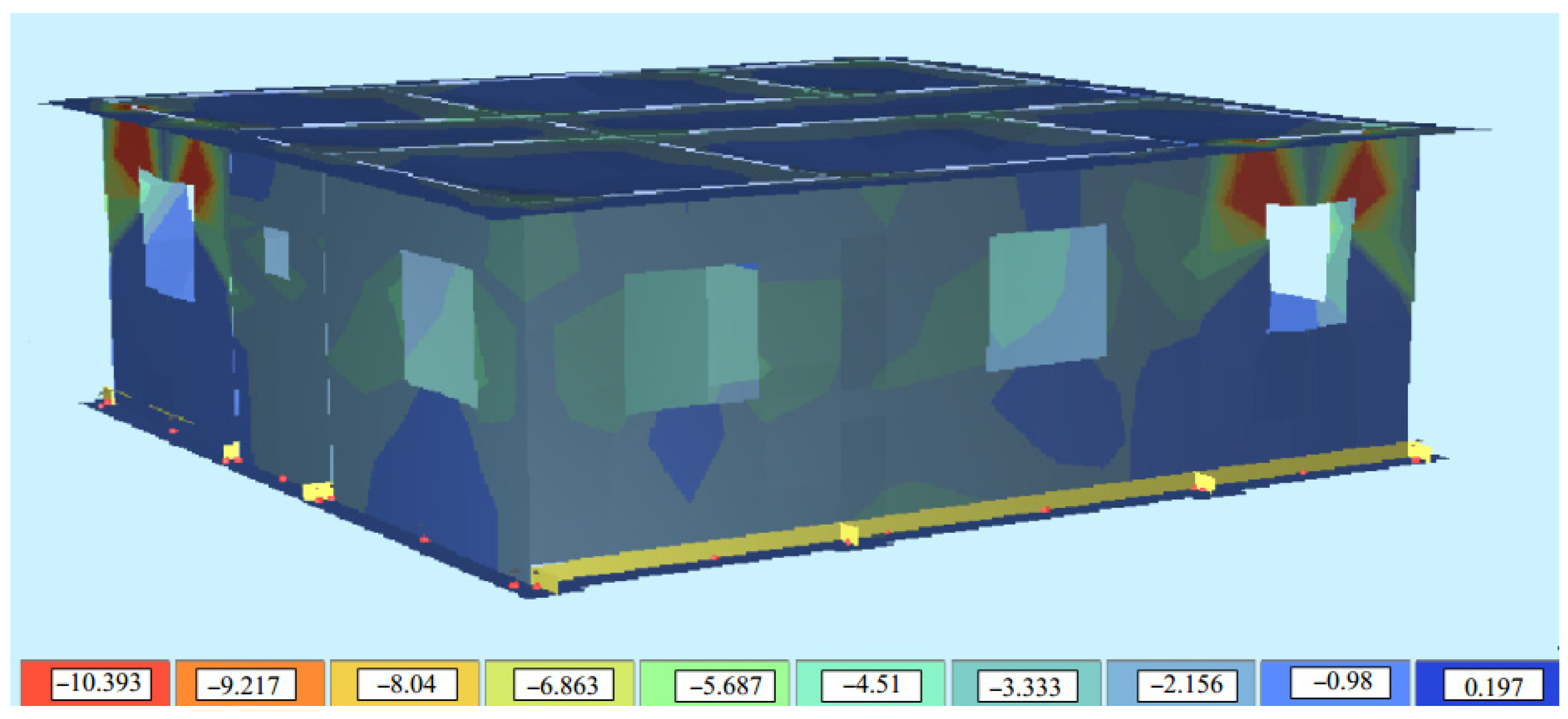
3. Analysis of Building Models Under the Effect of Earthquake
Analysis of the Effect of Wall Height on Masonry Structure Behaviour
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparative Examination of Building Parameters
4.2. Behaviour of Building Models Under Earthquake Effects
5. Statistical Analysis of Earthquake Parameters
5.1. Correlation Analysis
5.2. Prediction Models of the Earthquake Parameters
5.3. Paired Samples T-Test
6. Results and Recommendations
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bayır, S.İ.; Özgan, E. Yığma Yapılarda Duvar Boşluk Oranlarının Binanın Deprem Davranışına Etkisi. In Teori ve Uygulamada Mimarlık, Planlama ve Tasarım; Section 4; Duvar Yayınları, Aralık: İzmir, Türkiye, 2024; pp. 61–72. ISBN 978-625-5530-84-4. Available online: https://www.duvaryayinlari.com/Webkontrol/IcerikYonetimi/Dosyalar/teori-ve-uygulamada-mimarlik-planlama-ve-tasarim_icerik_g4340_wI1WFviV.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2025).
- Dolšek, M.; Fajfar, P. The effect of masonry infills on the seismic response of a four-storey reinforced concrete Frame a deterministic assessment. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 3186–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yön, B.; Onat, O. Failures of masonry dwelling triggered by East Anatolian Fault earthquakes in Turkey. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 133, 106126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachakis, G.; Vlachaki, E.; Lourenço, P.B. Learning from failure: Damage and failure of masonry structures, after the 2017 Lesvos earthquake (Greece). Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 117, 104803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatar, O.; Sözbilir, H.; Koçbulut, F.; Bozkurt, E.; Aksoy, E.; Eski, S.; Özmen, B.; Alan, H.; Metin, Y. Surface deformations of 24 January 2020 Sivrice (Elazığ)–Doğanyol (Malatya) earthquake (Mw = 6.8) along the Pütürge segment of the East Anatolian Fault Zone and its comparison with Turkey’s 100-year-surface ruptures. Mediterr. Geosci. Rev. 2020, 2, 385–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingham, J.; Griftith, M. Performance of unreinforced masonry buildings during the 2010 Darfield (Christchurch, NZ). Aut. J. Eng. 2010, 11, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augenti, N.; Parisi, F. Learning from construction failures due to the 2009 L’Aquila Italy earthquake. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. ASCE 2010, 24, 536–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahya, V.; Genç, A.F. Evaluation of earthquake-related damages on masonry structures due to the 6 February 2023 Kahramanmaraş-Türkiye earthquakes: A case study for Hatay Governorship Building 2024. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 156, 107855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işık, E.; Avcil, F. Structural damages in masonry buildings in Adıyaman during the Kahramanmaraş (Turkiye) earthquakes (Mw 7.7 and Mw 7.6) on 06 February 2023. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 151, 107405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, L.; Cattari, S.; da Porto, F.; Magenes, G.; Penna, A. Seismic behaviour of ordinary masonry buildings during the 2016 central Italy. Earthq. Bull Earthq. Eng. 2019, 17, 5583–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, H.; Shkodrani, N.; Hysenlliu, M.; Harirchian, E. Damage and performance evaluation of masonry buildings constructed in 1970s during the 2019 Albania earthquakes. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 131, 105824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariq, M.; Abbas, H.; Irtaza, H.; Qamaruddin, M. Influence of openings on seismic performance of masonry building walls. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, F.; Augenti, N. Uncertainty in Seismic Capacity of Masonry Buildings. Buildings 2012, 2, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassios, T.P. Seismic engineering of monuments. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2010, 8, 1231–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M. Earthquake response and damage patterns assessment of two historical masonry churches with bell tower. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 151, 107418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.; Milani, G. Seismic response and damage patterns of masonry churches: Seven case studies in Ferrara Italy. Eng. Struct. 2018, 177, 809–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghabeigi, P.; Farahmand-Tabar, S. Seismic vulnerability assessment and retrofitting of historic masonry building of Malek Timche in Tabriz Grand Bazaar. Eng. Struct. 2021, 240, 112418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krentowski, J.R.; Knyziak, P. Historical masonry buildings condition assessment by non-destructive and destructive testing. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 146, 107122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgun, T.; Ceylan, O.; Nasery, M.M.; Güler, O.; Sayin, B.; Uzdil, O.; Akcay, C. Seismic performance assessment and retrofitting proposal for a historic masonry school building (Bursa, Türkiye). Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e02087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meli, R.; Brzev, S.; Astroza, M.; Boen, T.; Crisafulli, F.; Dai, J.; Farsi, M.; Hart, T.; Mebarki, A.; Moghadam, A.S.; et al. Seismic Design Guide for Low-Rise Confined Masonry Buildings. In World Housing Encyclopedia; Publication WHE–2011–02; Earthquake Engineering Research Institute: Oakland, CA, USA, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- Brzev, S. Earthquake-Resistant Confined Masonry Construction, 1st ed.; National Information Center of Earthquake Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur: Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India, 2007; pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bourzam, A.; Ikemoto, T.; Miyajima, M. Lateral resistance of confined brick wall under cyclic quasi-static lateral loading. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Beijing, China, 12–17 October 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bourzam, A.; Goto, T.; Miyajima, M. Shear capacity prediction of confined masonry walls subjected to cyclic lateral loading. Doboku Gakkai Ronbunshuu A 2008, 64, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourzam, A.; Toshikazu, I.; Saiji, F.; Masakatsu, M. Influence of RC tie-columns due to dowel action on confined masonry panels subjected to in-plane cyclic loading. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2013, 5, 1924. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, K.; Kulkarni, S.M.; Subramaniam, S.; Murty, C.V.R.; Goswami, R.; Vijayanarayanan, A.R. Build A Safe House with Confined Masonry; Gujarat State Disaster Management Authority, Government of Gujarat: Gandhinagar, India, 2012.
- Tomaževič, M.; Klemenc, I. Seismic behaviour of confined masonry walls. Earth. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1997, 26, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfura, A.P.; Flores, P.J. Quindio, Colombia Earthquake, January 25, 1999: Reconnaissance Report; Technical Report MCEER-99-0017; Multidisciplinary Center for Earthquake Engineering Research, State University of New York at Buffalo: Buffalo, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Galvis, F.A.; Miranda, E.; Heresi, P.; Dávalos, H.; Ruiz-García, J. Overview of collapsed buildings in Mexico City after the 19 September 2017 (Mw7. 1) earthquake. Earthq. Spectra. 2020, 36, 83–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, B.; Singhal, V.; Kaushik, H.B. Sustainable housing using confined masonry buildings. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzev, S.; Astroza, M.; Moroni, O. Performance of Confined Masonry Buildings in the February 27, 2010 Chile Earthquake; Earthquake Engineering Research Institute: Oakland, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 1–177. [Google Scholar]
- Bilek, S.L.; Satake, K.; Sieh, K. Introduction to the Special Issue on the 2004 Sumatra–Andaman Earthquake and the Indian Ocean Tsunami. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 2007, 97, S1–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcocer, S.M.; Klingner, R.E. The Tecomán, México Earthquake, January 21, 2003: An EERI and SMIS Learning from Earthquakes Reconnaissance Report; Earthquake Engineering Research Institute: Oakland, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Meisl, C.S.; Safaie, S.; Elwood, K.J.; Gupta, R.; Kowsari, R. Housing Reconstruction in Northern Sumatra after the December 2004 Great Sumatra Earthquake and Tsunami. Earthq. Spectra. 2006, 22, 777–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boen, T. Sumatra Earthquake 26 Dec 2004; Earthquake Engineering Research Institute (EERI): Oakland, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Moroni, M.O.; Astroza, M.; Acevedo, C. Performance and Seismic Vulnerability of Masonry Housing Types Used in Chile. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2004, 18, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, B.H.; Alemi, F.; Ashtiany, G. Confined Brick Masonry Building with Concrete Tie-Columns and Beams; Iran, Report 27; World Housing Encyclopaedia, Earthquake Engineering Research Institute: Oakland, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- EERI. The Tehuacan, Mexico, Earthquake of June 15, 1999. In EERI Special Earthquake Report; Newsletter, Earthquake Engineering Research Institute: Oakland, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, M.; Bommer, J.J.; Pinho, R. Seismic Hazard Assessments, Seismic Design Codes, and Earthquake Engineering in El Salvador; The Geoglogical Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, J.I.; Villarreal, J.I.; Centeno, M.R.; Gonzalez, B.G.; Correa, J.J.G.; Acevedo, C.R.; Salazar, I.S. Tehuacan, Mexico, Earthquake of June 15, 1999. Seismol. Res. Lett. 1999, 70, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, A.E. Performance of Masonry Structures during Extreme Lateral Loading Events. In Masonry in the Americas; ACI Publication, SP 147-4; American Concrete Institute: Detroit, MI, USA, 1994; pp. 85–126. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Jian, Z. Functions of tied concrete columns in brick walls. In Proceedings of the Ninth World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Tokyo, Japan, 2–9 August 1988; Japan Association for Earthquake Disaster Prevention: Tokyo, Japan, 1989; Volume 6, pp. 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Borah, B.; Kaushik, H.B.; Singhal, V. Analysis and Design of Confined Masonry Structures: Review and Future Research Directions. Buildings 2023, 13, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.M.; El-Attar, A.G.; Elwaly, A. DIM for detecting Cracks in Masonry Piers with Different Crack Patterns. JES J. Eng. Sci. 2022, 50, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korswagen, P.A.; Longo, M.; Meulman, E.; Rots, J.G. Crack initiation and propagation in unreinforced masonry specimens subjected to repeated in-plane loading during light damage. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 17, 4651–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, M.; Bcattini, G.; Betti, M. Multilevel structural evaluation and rehabilitation design of an historic masonry fortress. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 63, 105379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhosis, V.; Dais, D.; Smyrou, E.; Bal, I.E.; Drougkas, A. Quantification of damage evolution in masonry walls subjected to induced seismicity. Eng. Struct. 2021, 243, 112529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Shahzada, K.; Genturk, B. Seismic Capacity Assessment of Unreinforced Concrete Block Masonry Buildings in Pakistan Before and After Retrofitting. J. Earthq. Eng 2015, 19, 357–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1998-1:2004; Eurocode 8: Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance–Part 1: General Rules, Seismic Actions and Rules for Buildings 2004. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2004.
- EN 1998-3:2005; Eurocode 8: Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance–Part 3: Assessment and Retrofitting of Buildings. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2005.
- IBC. Norme Tecniche per le Costruzioni (‘‘Italian Building Code’’); Ministerial Decree Dated of 17-01-2018; Ministero delle Infrastrutture Trasporti: Rome, Italy, 2018.
- TBDY 2018 Principles for the Design of Buildings Subject to Earthquake Effects, Türkiye 2018, 251. Available online: https://www.mevzuat.gov.tr/mevzuat?MevzuatNo=24468&MevzuatTur=7&MevzuatTertip=5 (accessed on 22 December 2025).
- STA4 CAD. Structural Analysis for Computer Aided Design; STA4 CAD: İstanbul, Türkiye, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- TS EN 772; Specification for Masonry. Turkish Standards Institute Turkish Standard: Ankara, Türkiye, 2005.
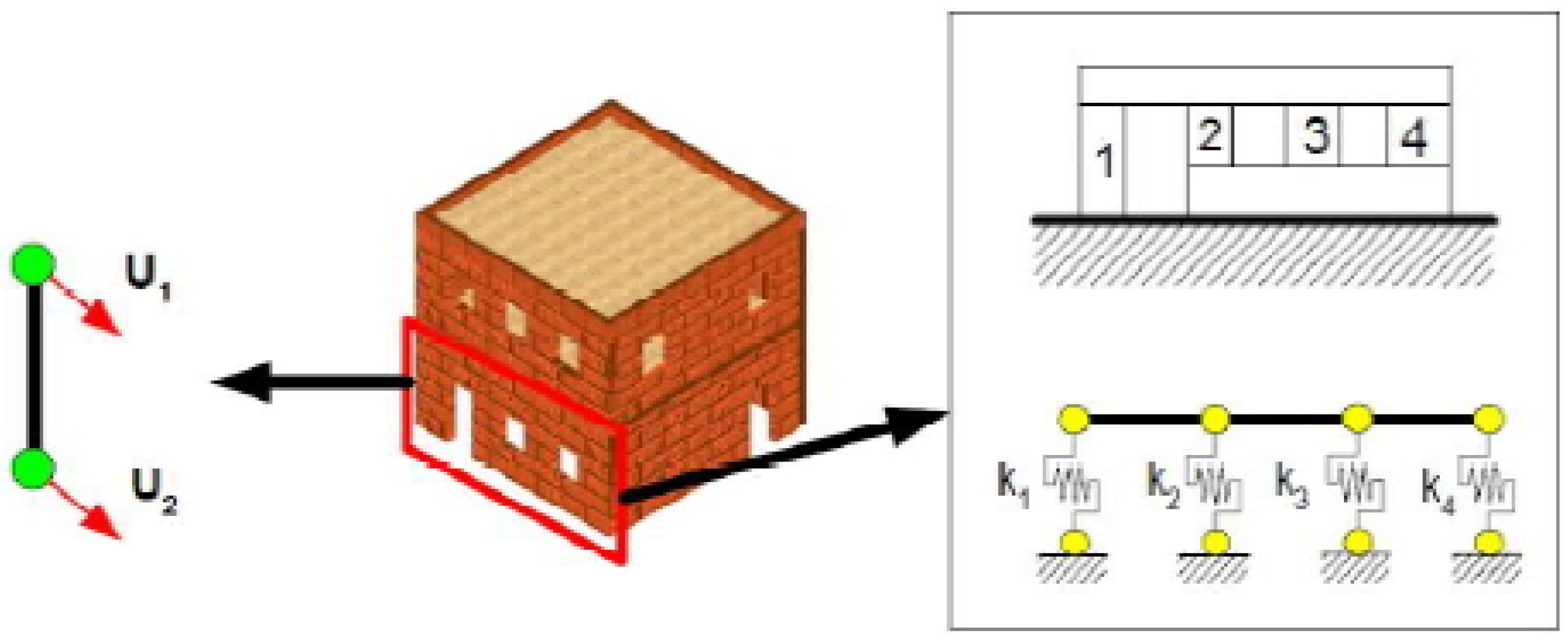
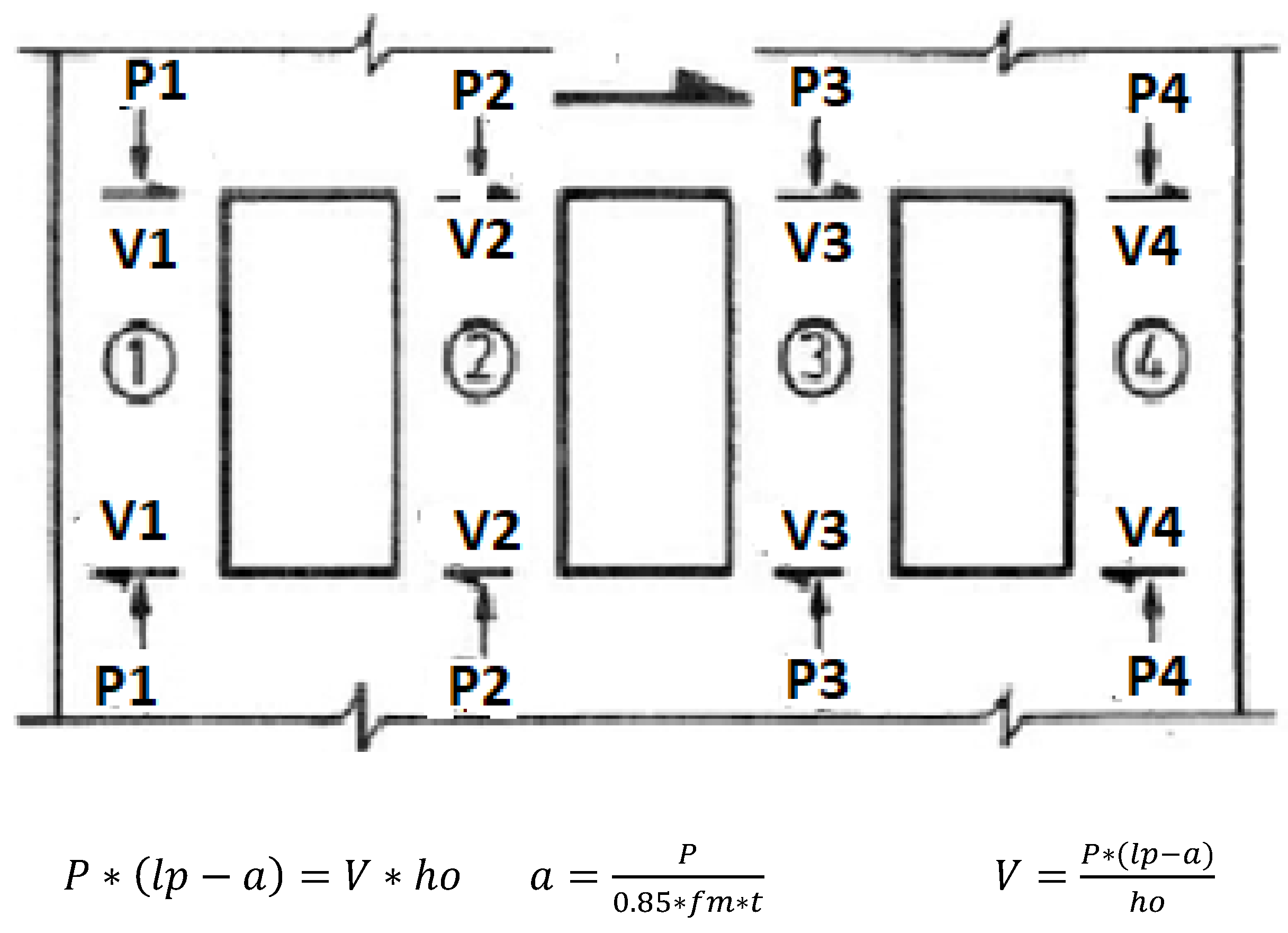
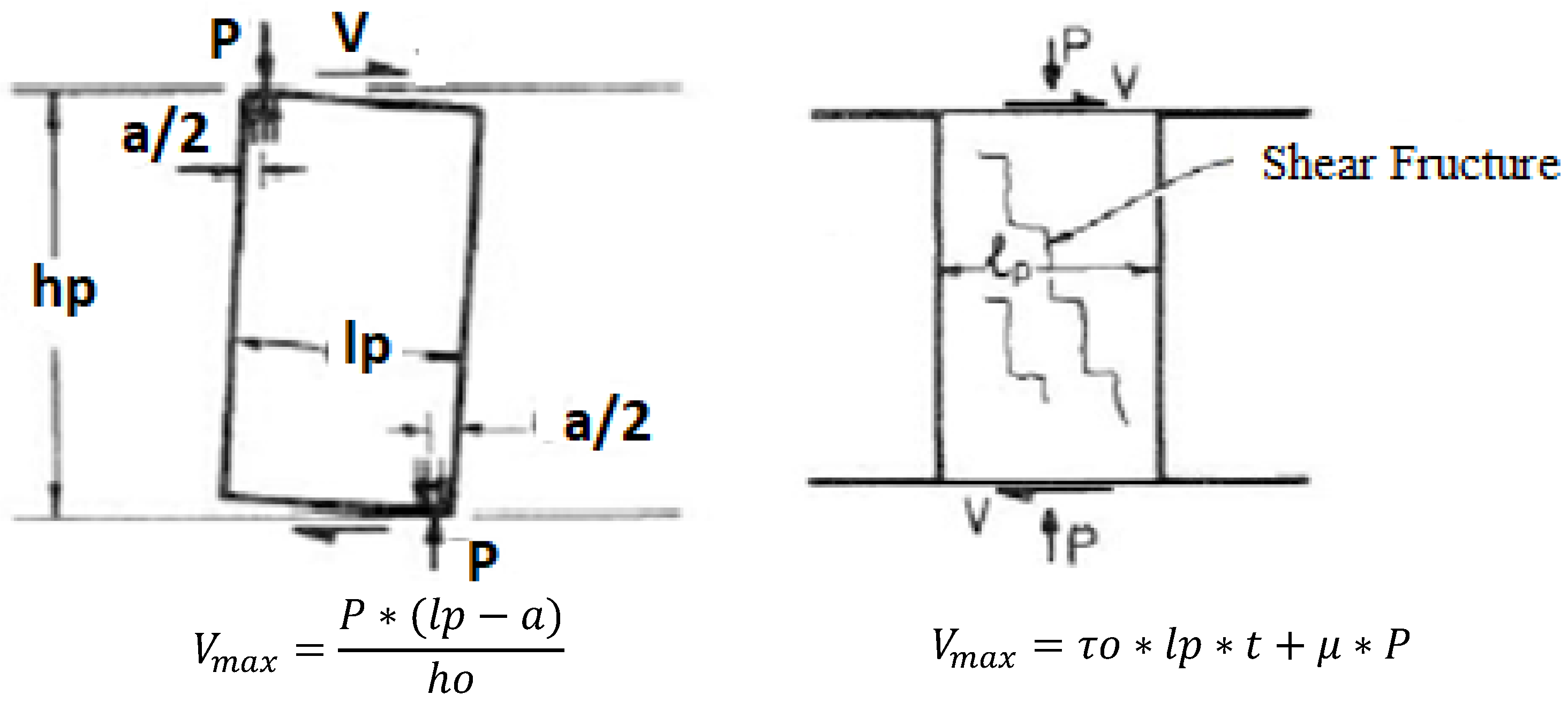
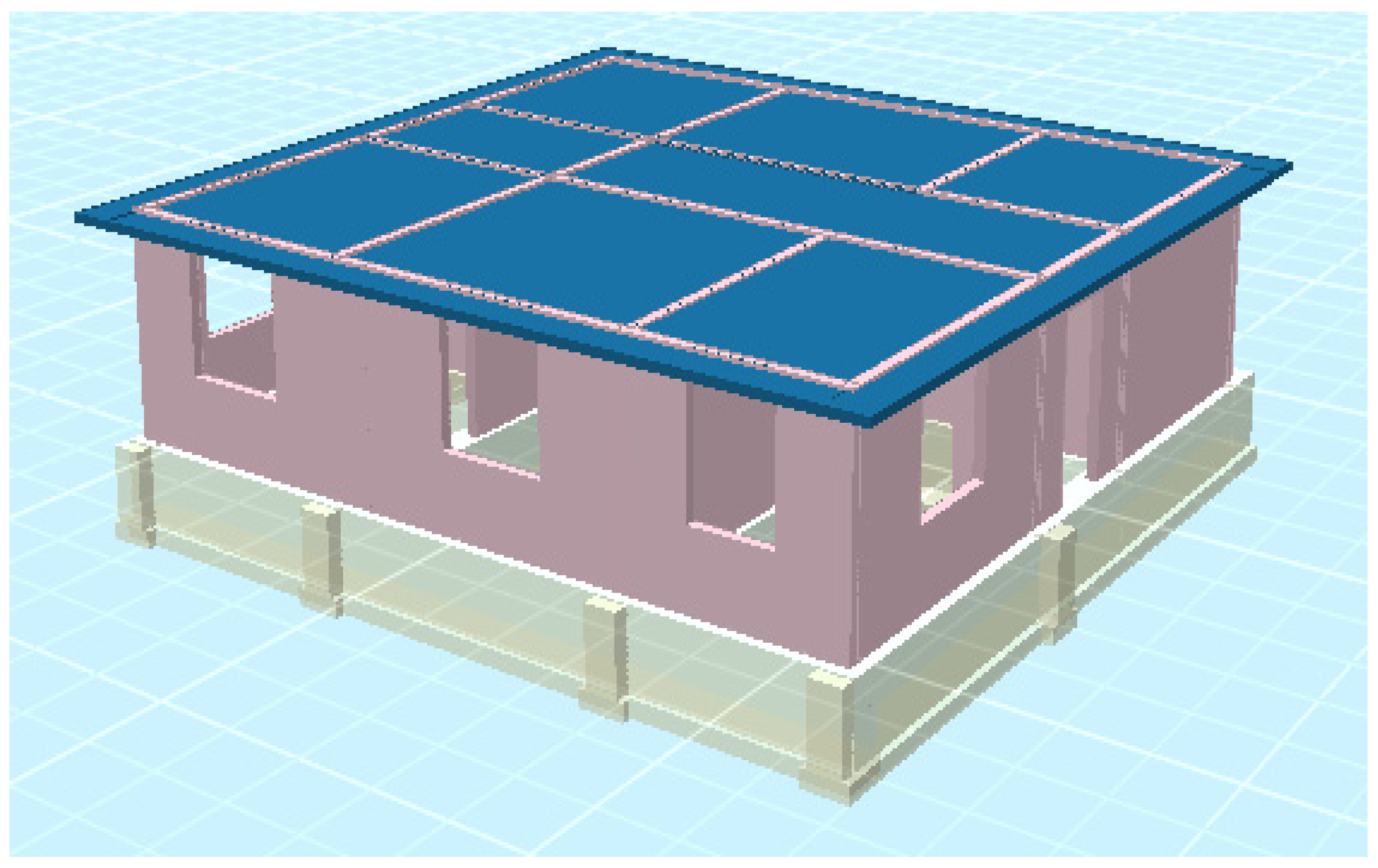
| Masonry Type | (tef) mm Effective Thickness of the Wall | (hef/tef) Max hef = Effective Height of the Wall |
|---|---|---|
| Unreinforced masonry, other masonry units | 240 | 12 |
| Modal | Floor Height (cm) | Wall Thickness (cm) | Wg (kN) | Wq (kN) | Hef/tef (12) | R Rx/Ry | D Dx/Dy | Wk (kN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWC 10 | 260 | 16 | 1083.35 | 26.07 | 16.25 > 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1159.94 |
| MWC 11 | 260 | 20 | 1201.92 | 26.07 | 13.00 > 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1283.12 |
| MWC 12 | 260 | 24 | 1282.92 | 26.07 | 10.83 < 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1389.03 |
| MWC 13 | 260 | 28 | 1431.00 | 26.07 | 9.28 < 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1507.60 |
| MWC 14 | 260 | 32 | 1549.57 | 26.07 | 8.13 < 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1626.26 |
| MWC 20 | 280 | 16 | 1132.09 | 26.07 | 17.25 > 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1208.68 |
| MWC 21 | 280 | 20 | 1261.44 | 26.07 | 14.00 > 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1341.57 |
| MWC 22 | 280 | 24 | 1385.50 | 26.07 | 11.67 < 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1462.19 |
| MWC 23 | 280 | 28 | 1512.20 | 26.07 | 10.00 < 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1588.89 |
| MWC 24 | 280 | 32 | 1638.91 | 26.07 | 8.75 < 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1715.60 |
| MWC 30 | 300 | 16 | 1172.69 | 26.07 | 18.75 > 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1249.38 |
| MWC 31 | 300 | 20 | 1315.68 | 26.07 | 15.00 > 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1392.37 |
| MWC 32 | 300 | 24 | 1458.66 | 26.07 | 12.50 > 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1535.25 |
| MWC 33 | 300 | 28 | 1593.50 | 26.07 | 10.71 < 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1670.09 |
| MWC 34 | 300 | 32 | 1736.49 | 26.07 | 9.37 < 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1813.08 |
| MWC 40 | 320 | 16 | 1221,43 | 26.07 | 20.00 > 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1298.12 |
| MWC 41 | 320 | 20 | 1372.56 | 26.07 | 16.00 > 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1449.15 |
| MWC 42 | 320 | 24 | 1523.68 | 26.07 | 13.33 > 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1600.27 |
| MWC 43 | 320 | 28 | 1668.82 | 26.07 | 11.42 < 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1751.39 |
| MWC 44 | 320 | 32 | 1825.83 | 26.07 | 10.00 < 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1902.52 |
| MWC 50 | 340 | 16 | 1270.17 | 26.07 | 21.25 > 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1346.87 |
| MWC 51 | 340 | 20 | 1429.44 | 26.07 | 17.00 > 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1506.03 |
| MWC 52 | 340 | 24 | 1596.74 | 26.07 | 14.17 > 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1673.43 |
| MWC 53 | 340 | 28 | 1756.00 | 26.07 | 12.14 > 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1832.59 |
| MWC 54 | 340 | 32 | 1923.31 | 26.07 | 10.62 < 12 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 2000.01 |
| Modal | Wall (cm) | Floor Height (cm) | X Direction | Y Direction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modal Analysis | Equivalent Earthquake Load (kN) | Earthquake Load (kN) | Modal Analysis (kN) | Equivalent Earthquake Load (kN) | Earthquake Load (kN) | |||
| MWC 10 | 16 | 260 | 792.32 | 1295.97 | 1166.42 | 792.29 | 1295.97 | 1166.42 |
| MWC 11 | 20 | 260 | 875.75 | 1428.46 | 1285.67 | 883.69 | 1428.46 | 1285.67 |
| MWC 12 | 24 | 260 | 965.09 | 1551.93 | 1396.69 | 965.09 | 1551.93 | 1396.69 |
| MWC 13 | 28 | 260 | 1049.92 | 1684.42 | 1515.94 | 1049.92 | 1684.42 | 1515.94 |
| MWC 14 | 32 | 260 | 1129.55 | 1816.91 | 1635.19 | 1129.55 | 1816.91 | 1635.19 |
| MWC 20 | 16 | 280 | 822.20 | 1350.40 | 1215.36 | 850.15 | 1350.40 | 1215.36 |
| MWC 21 | 20 | 280 | 920.35 | 1492.01 | 1342.85 | 945.18 | 1492.01 | 1342.45 |
| MWC 22 | 24 | 280 | 1012.84 | 1633.62 | 1470.24 | 1033.25 | 1633.62 | 1470.24 |
| MWC 23 | 28 | 280 | 1104.48 | 1775.13 | 1597.63 | 1119.25 | 1775.13 | 1597.63 |
| MWC 24 | 32 | 280 | 1193.52 | 1916.84 | 1725.12 | 1202.31 | 1916.84 | 1725.12 |
| MWC 30 | 16 | 300 | 881.51 | 1395.80 | 1256.25 | 877.61 | 1395.80 | 1256.25 |
| MWC 31 | 20 | 300 | 995.06 | 1555.56 | 1400.02 | 990.19 | 1555.56 | 1400.02 |
| MWC 32 | 24 | 300 | 1104.58 | 1715.31 | 1543.79 | 1098.75 | 1715.31 | 1543.79 |
| MWC 33 | 28 | 300 | 1208.30 | 1865.94 | 1679.32 | 1201.82 | 1865.94 | 1679.32 |
| MWC 34 | 32 | 300 | 1318.71 | 2025.69 | 1823.09 | 1311.56 | 2025.69 | 1823.09 |
| MWC 40 | 16 | 320 | 860.11 | 1450.33 | 1305.29 | 847.80 | 1450.33 | 1305.29 |
| MWC 41 | 20 | 320 | 981.90 | 1619.10 | 1457.19 | 965.28 | 1619.10 | 1457.19 |
| MWC 42 | 24 | 320 | 1088.17 | 1787.88 | 1609.10 | 1065.22 | 1787.88 | 1609.10 |
| MWC 43 | 28 | 320 | 1196.22 | 1956.75 | 1761.01 | 1167.99 | 1956.75 | 1761.01 |
| MWC 44 | 32 | 320 | 1320.49 | 2125.53 | 1913.01 | 1271.84 | 2125.53 | 1913.01 |
| MWC 50 | 16 | 340 | 858.24 | 1504.76 | 1354.32 | 845.74 | 1504.76 | 1354.32 |
| MWC 51 | 20 | 340 | 984.70 | 1682.65 | 1514.37 | 965.58 | 1682.65 | 1514.37 |
| MWC 52 | 24 | 340 | 1097.91 | 1869.57 | 1682.65 | 1072.18 | 1869.57 | 1682.65 |
| MWC 53 | 28 | 340 | 1207.62 | 2047.46 | 1842.80 | 1176.52 | 2047.46 | 1842.80 |
| MWC 54 | 32 | 340 | 1322.50 | 2234.48 | 2011.08 | 1286.16 | 2234.48 | 2011.08 |
| Modal | Wall Thickness (cm) | Floor Height (cm) | X Direction | Y Direction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ƩVr (kN) | ƩVe (kN) | ƩVe (Ve > Vr) | ƩVr (kN) | ƩVe (kN) | ƩVe (Ve > Vr) | Insufficient Breaking Capacity Rating | |||
| MWC 10 | 16 | 260 | 2034.81 | 1274.59 | 0.00 | 1772.38 | 1274.59 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 11 | 20 | 260 | 2395.90 | 1428.56 | 0.00 | 2147.49 | 1428.56 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 12 | 24 | 260 | 2847.80 | 1551.93 | 0.00 | 2555.85 | 1551.93 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 13 | 28 | 260 | 3300.19 | 1684.42 | 0.00 | 2964.89 | 1684.42 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 14 | 32 | 260 | 3752.28 | 1816.91 | 0.00 | 3373.74 | 1816.91 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 20 | 16 | 280 | 1993.63 | 1350.50 | 0.00 | 1775.03 | 1350.50 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 21 | 20 | 280 | 2398.25 | 1492.11 | 0.00 | 2145.53 | 1492.11 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 22 | 24 | 280 | 2851.72 | 1633.62 | 0.00 | 2554.67 | 1633.62 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 23 | 28 | 280 | 3304.60 | 1775.23 | 0.00 | 2963.62 | 1775.23 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 24 | 32 | 280 | 3757.09 | 1916.84 | 0.00 | 3372.36 | 1916.84 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 30 | 16 | 300 | 1997.35 | 1395.90 | 0.00 | 1801.71 | 1395.90 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 31 | 20 | 300 | 2467.00 | 1555.65 | 0.00 | 2223.01 | 1555.65 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 32 | 24 | 300 | 2935.96 | 1715.31 | 0.00 | 2645.78 | 1715.31 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 33 | 28 | 300 | 3403.35 | 1866.04 | 0.00 | 3067.18 | 1866.04 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 34 | 32 | 300 | 3872.22 | 2025.69 | 0.00 | 3489.85 | 2025.69 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 40 | 16 | 320 | 2008.73 | 1450.33 | 0.00 | 1780.13 | 1450.33 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 41 | 20 | 320 | 2429.54 | 1619.10 | 0.00 | 2171.03 | 1619.10 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 42 | 24 | 320 | 2890.36 | 1787.98 | 0.00 | 2586.64 | 1787.98 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 43 | 28 | 320 | 3350.50 | 1956.75 | 0.00 | 3002.16 | 1956.75 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 44 | 32 | 320 | 3810.34 | 2125.63 | 0.00 | 3417.48 | 2125.63 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 50 | 16 | 340 | 2034.42 | 1504.85 | 0.00 | 1805.92 | 1504.85 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 51 | 20 | 340 | 2454.06 | 1682.65 | 0.00 | 2196.63 | 1682.65 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 52 | 24 | 340 | 2918.31 | 1869.67 | 0.00 | 2615.67 | 1869.67 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 53 | 28 | 340 | 3380.50 | 2047.56 | 0.00 | 3033.34 | 2047.56 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| MWC 54 | 32 | 340 | 3843.58 | 2234.48 | 0.00 | 3451.80 | 2234.48 | 0.00 | Lim. Damage |
| Weight (kN) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wall Height (cm) | Wall 16 cm | Wall 20 cm | Wall 24 cm | Wall 28 cm | Wall 32 cm |
| 260 cm | 1159.95 | 1282.83 | 1389.04 | 1507.60 | 1626.26 |
| 280 cm | 1208.69 | 1341.57 | 1462.19 | 1588.90 | 1715.60 |
| 300 cm | 1249.39 | 1392.37 | 1535.26 | 1670.10 | 1813.08 |
| 320 cm | 1298.13 | 1449.15 | 1600.27 | 1751.40 | 1902.52 |
| 340 cm | 1346.87 | 1506.03 | 1673.43 | 1832.60 | 2000.00 |
| X and Y Direction Earthquake Load (kN) | |||||
| 260 cm | 1166.42 | 1285.67 | 1396.69 | 1515.94 | 1635.19 |
| 280 cm | 1215.36 | 1342.85 | 1470.24 | 1597.63 | 1725.12 |
| 300 cm | 1256.25 | 1400.02 | 1543.79 | 1679.32 | 1823.09 |
| 320 cm | 1305.29 | 1457.19 | 1609.10 | 1761.01 | 1913.01 |
| 340 cm | 1354.32 | 1514.37 | 1682.65 | 1842.80 | 2011.08 |
| The shear forces for X Direction (kN) | |||||
| 260 cm | 203.48 | 239.59 | 284.78 | 330.02 | 375.23 |
| 280 cm | 199.36 | 239.83 | 285.17 | 330.46 | 375.71 |
| 300 cm | 199.74 | 246.70 | 293.60 | 340.34 | 387.22 |
| 320 cm | 200.87 | 242.95 | 289.04 | 335.05 | 381.03 |
| 340 cm | 203.44 | 245.41 | 291.83 | 338.05 | 384.36 |
| The shear forces for Y Direction (kN) | |||||
| 260 cm | 177.24 | 214.75 | 255.58 | 296.49 | 337.37 |
| 280 cm | 177.50 | 214.55 | 255.47 | 296.36 | 337.24 |
| 300 cm | 180.17 | 222.30 | 264.58 | 306.72 | 348.98 |
| 320 cm | 178.01 | 217.10 | 258.66 | 300.22 | 341.75 |
| 340 cm | 180.59 | 219.66 | 261.57 | 303.33 | 345.18 |
| Parameters | Total Weight Ton | Earthquake Load (kN) | Shear Forces for x Direction (kN) | Shear Forces for y Direction (kN) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| For 260 cm Wall He/te | Pearson Correlation | −0.979 | −0.978 | −0.971 | −0.976 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.004 | |
| For 280 cm Wall He/te | Pearson Correlation | −0.983 | −0.983 | −0.979 | −0.979 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.004 | |
| For 300 cm Wall He/te | Pearson Correlation | −0.984 | −0.984 | −0.983 | −0.968 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.007 | |
| For 320 cm Wall He/te | Pearson Correlation | −0.979 | −0.979 | −0.976 | −0.977 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | |
| For 340 cm Wall He/te | Pearson Correlation | −0.979 | −0.979 | −0.976 | −0.977 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | |
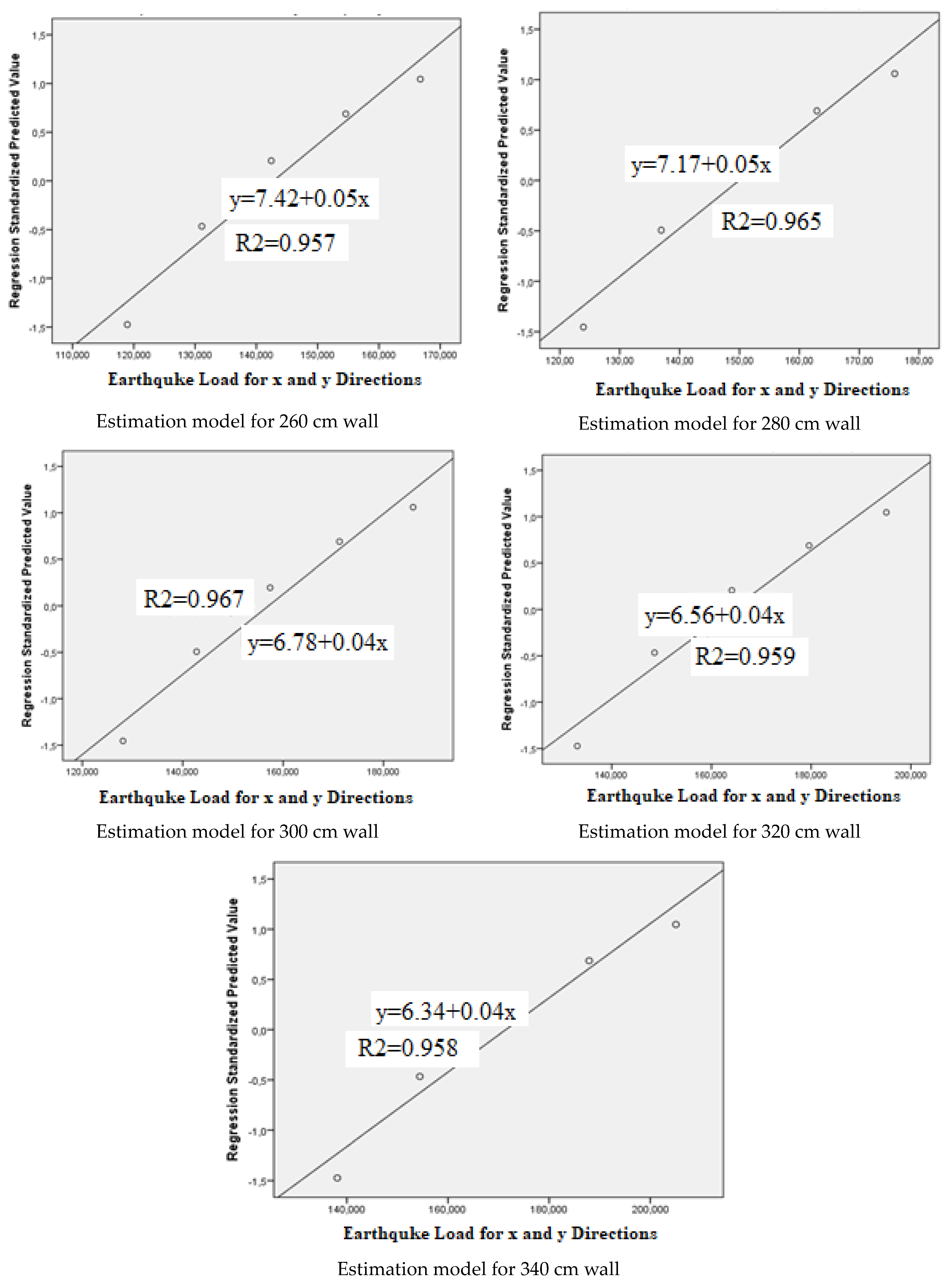
| Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the Estimate | Change Statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R Square Change | F Change | df1 | df2 | Sig. F Change | |||||
| 260 cm | 0.978 a | 0.957 | 0.943 | 4.50952 | 0.957 | 66.764 | 1 | 3 | 0.004 |
| 280 cm | 0.983 a | 0.965 | 0.954 | 4.40655 | 0.965 | 83.940 | 1 | 3 | 0.003 |
| 300 cm | 0.984 a | 0.967 | 0.957 | 4.748084 | 0.967 | 89,104 | 1 | 3 | 0.003 |
| 320 cm | 0.979 a | 0.959 | 0.945 | 5.718778 | 0.959 | 70.388 | 1 | 3 | 0.004 |
| 340 cm | 0.979 a | 0.958 | 0.944 | 6.28941 | 0.958 | 67.866 | 1 | 3 | 0.004 |
| ANOVA a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| 260 cm | Regression | 1357.706 | 1 | 1357.706 | 66.764 | 0.004 b |
| Residual | 61.007 | 3 | 20.336 | |||
| Total | 1418.713 | 4 | ||||
| 280 cm | Regression | 1629.27 | 1 | 1629.927 | 83.40 | 0.003 b |
| Residual | 58.253 | 3 | 19.418 | |||
| Total | 1688.180 | 4 | ||||
| 300 cm | Regression | 2008.797 | 1 | 2008.797 | 89.104 | 0.003 b |
| Residual | 67.633 | 3 | 22.544 | |||
| Total | 1688.180 | 4 | ||||
| 320 cm | Regression | 2302.00 | 1 | 2302.00 | 70.388 | 0.004 b |
| Residual | 98.113 | 3 | 32.704 | |||
| Total | 2400.114 | 4 | ||||
| 340 cm | Regression | 2684.551 | 1 | 2684.551 | 67.866 | 0.004 b |
| Residual | 118.670 | 3 | 39.557 | |||
| Total | 2803.221 | 4 | ||||
| Coefficients (a) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardised Coefficients | t | Sig. | 95% Confidence Interval for B | |||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| 260 cm | (Constant) | 208.489 | 8.293 | 25.140 | 0.000 | 182.097 | 234.882 | |
| He/te (x) | −5.717 | 0.700 | −0.978 | −8.171 | 0.004 | −7.943 | −3.490 | |
| Y = −5.717 × x + 208.489 (“Y” Earthquake load estimation model, “x” He/te rate) | ||||||||
| 280 cm | (Constant) | 223.603 | 8.280 | 27.006 | 0.000 | 197.253 | 249.953 | |
| He/te | −5.974 | 0.652 | −0.983 | −9.162 | 0.003 | −8.049 | −3.899 | |
| Y = −5.974 × x + 223.603 (“Y” Earthquake load estimation model, “x” He/te rate) | ||||||||
| 300 cm | (Constant) | 238.884 | 8.922 | 26.776 | 0.000 | 210.492 | 267.276 | |
| He/te | −6.632 | 0.703 | −0.984 | −9.440 | 0.003 | −8.867 | −4.396 | |
| Y = −5.994 × x + 238.603 (“Y” Earthquake load estimation model, “x” He/te rate) | ||||||||
| 320 cm | (Constant) | 249.626 | 10.512 | 23.748 | 0.000 | 216.173 | 283.078 | |
| He/te | −5.070 | 0.721 | −0.979 | −8.390 | 0.004 | −8.0383 | −3.752 | |
| Y = −5.070 × x + 249.626 (“Y” Earthquake load estimation model, “x” He/te rate) | ||||||||
| 340 cm | (Constant) | 263.804 | 11.562 | 22.817 | 0.000 | 227.009 | 300.599 | |
| He/te | −6.144 | 0.746 | −0.979 | −8.238 | 0.004 | −8.518 | −3.771 | |
| Y = −6.144 × x + 263.804 (“Y” Earthquake load estimation model, “x” He/te rate) | ||||||||
| Test Results for Weights | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wall Thicknesses cm | Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error Mean | 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference | t | df | Sig. (2-Tailed) | ||
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| Pair 1 | 16–20 cm | −14,457.40 | 1471.37 | 658.02 | −16,284.35 | −12,630.44 | −21.971 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Pair 2 | 16–24 cm | −28,494.60 | 3947.17 | 1765.22 | −33,395.65 | −23,593.54 | −16.142 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Pair 3 | 16–28 cm | −42,576.80 | 5637.21 | 2521.03 | −49,576.32 | −35,577.27 | −16.889 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Pair 4 | 16–32 cm | −56,989.80 | 7606.55 | 3401.75 | −66,434.58 | −47,545.01 | −16.753 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Test Results for Earthquake Loads | |||||||||
| Pair 1 | 16–20 cm | −14,325.80 | 1727.34 | 772.49 | −16,470.58 | −12,181.01 | −18.545 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Pair 2 | 16–24 cm | −28,651.80 | 3968.93 | 1774.96 | −33,579.88 | −23,723.71 | −16.142 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Pair 3 | 16–28 cm | −42,811.20 | 5668.54 | 2535.05 | −49,849.62 | −35,772.77 | −16.888 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Pair 4 | 16–32 cm | −57,304.00 | 7649.29 | 3420.86 | −66,801.85 | −47,806.14 | −16.751 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Test Results for Cutting Force in the X Direction | |||||||||
| Pair 1 | 16–20 cm | −4233.40 | 396.75 | 177.43 | −4726.03 | −3740.76 | −23.859 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Pair 2 | 16–24 cm | −8922.80 | 464.51 | 207.73 | −9499.57 | −8346.02 | −42.952 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Pair 3 | 16–28 cm | −13,603.20 | 525.67 | 235.09 | −14,255.91 | −12,950.48 | −57.864 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Pair 4 | 16–32 cm | −18,286.40 | 594.90 | 266.04 | −19,025.06 | −17,547.73 | −68.733 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Test Results for Cutting Force in the Y Direction | |||||||||
| Pair 1 | 16–20 cm | −3973.80 | 202.82 | 90.70 | −4225.63 | −3721.96 | −43.811 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Pair 2 | 16–24 cm | −8205.40 | 262.84 | 117.54 | −8531.76 | −7879.03 | −69.805 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Pair 3 | 16–28 cm | −12,432.20 | 317.02 | 141.77 | −12,825.83 | −12,038.56 | −87.689 | 4 | 0.000 |
| Pair 4 | 16–32 cm | −16,662.00 | 377.91 | 169.00 | −17,131.23 | −16,192.76 | −98.588 | 4 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Kap, T. Investigation of the Effect of Wall Thickness and Wall Height on Building Behaviour During an Earthquake. Buildings 2026, 16, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings16010127
Kap T. Investigation of the Effect of Wall Thickness and Wall Height on Building Behaviour During an Earthquake. Buildings. 2026; 16(1):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings16010127
Chicago/Turabian StyleKap, Tuncay. 2026. "Investigation of the Effect of Wall Thickness and Wall Height on Building Behaviour During an Earthquake" Buildings 16, no. 1: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings16010127
APA StyleKap, T. (2026). Investigation of the Effect of Wall Thickness and Wall Height on Building Behaviour During an Earthquake. Buildings, 16(1), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings16010127






