Research on Park Perception and Understanding Methods Based on Multimodal Text–Image Data and Bidirectional Attention Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
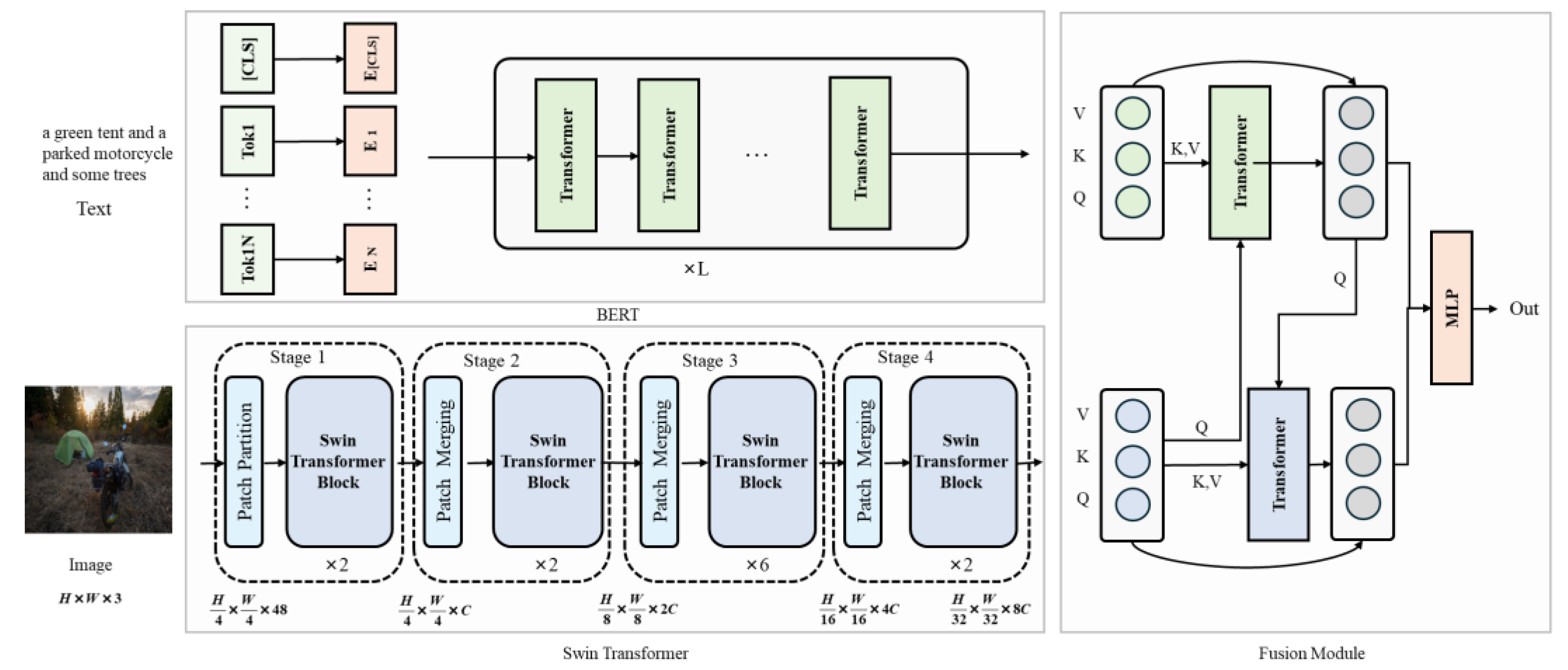
- The BERT model effectively captures semantic information in text using a bidirectional encoder, whereas the Swin Transformer efficiently extracts visual features from images through a local window self-attention mechanism. This study proposed a park perception and understanding method based on multimodal text–image data to effectively fuse text and image features and capture their interactions.
- To better integrate BERT and Swin Transformer features, a bidirectional cross-attention mechanism that enables mutual reinforcement of text and image information is introduced in order to enhance the accuracy and robustness of sentiment analysis.
- In addition, a method that enables an interpretability analysis of the model results is employed, focusing on the significance of key terms, which allowed us to identify key factors of the park environment that influence visitors’ emotional experience, for optimization and providing suggestions for park management.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overall Model Architecture
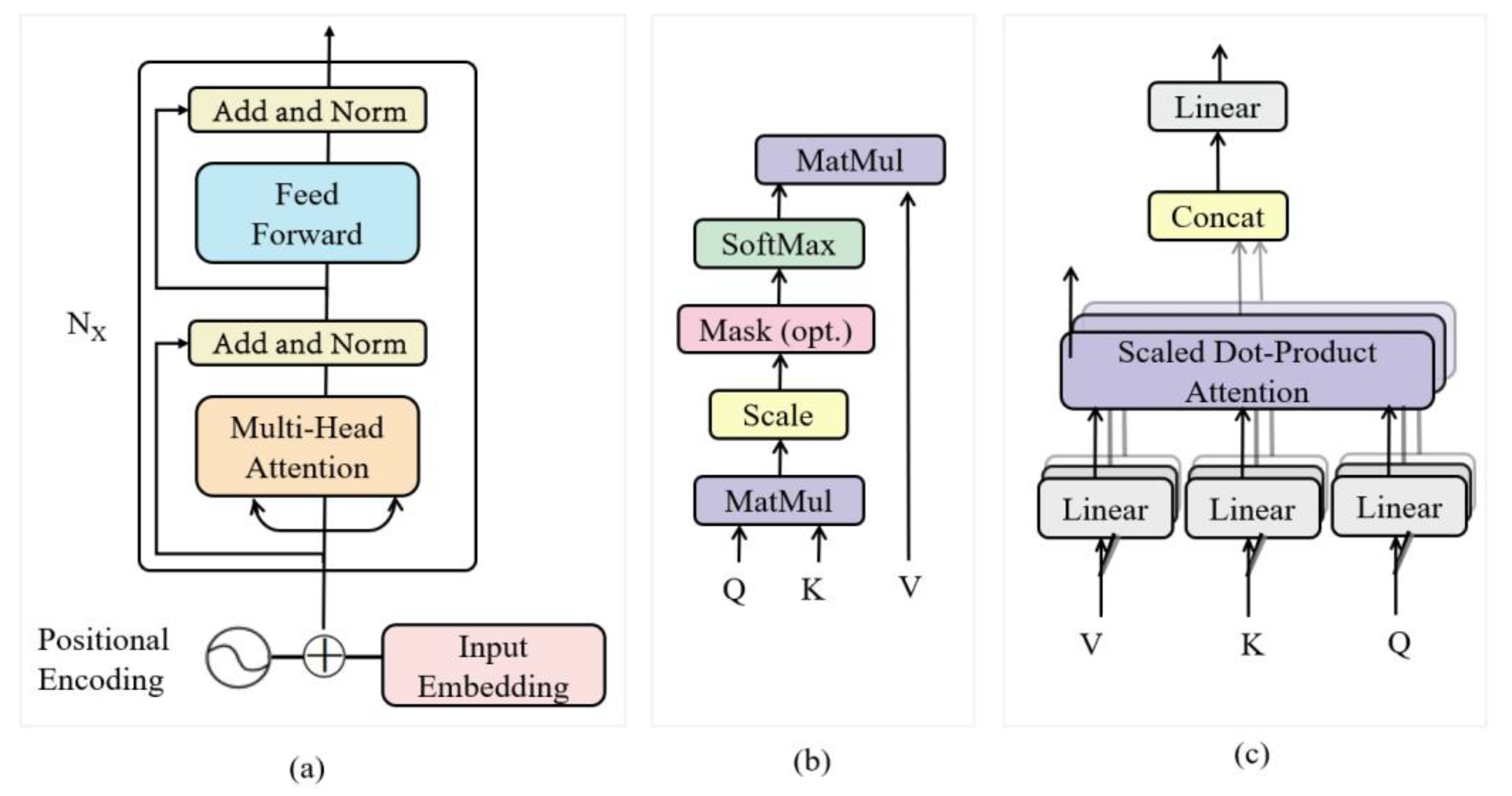
2.2. BERT-Based Text Feature Extraction Module
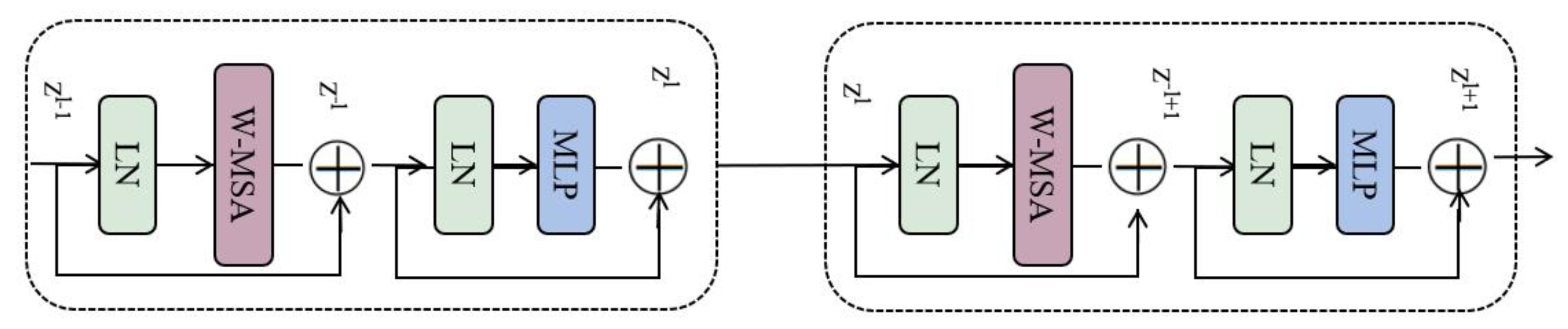
2.3. Swin Transformer-Based Image Perception Module
2.4. Bidirectional Cross-Attention Fusion Module
2.5. Data and Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
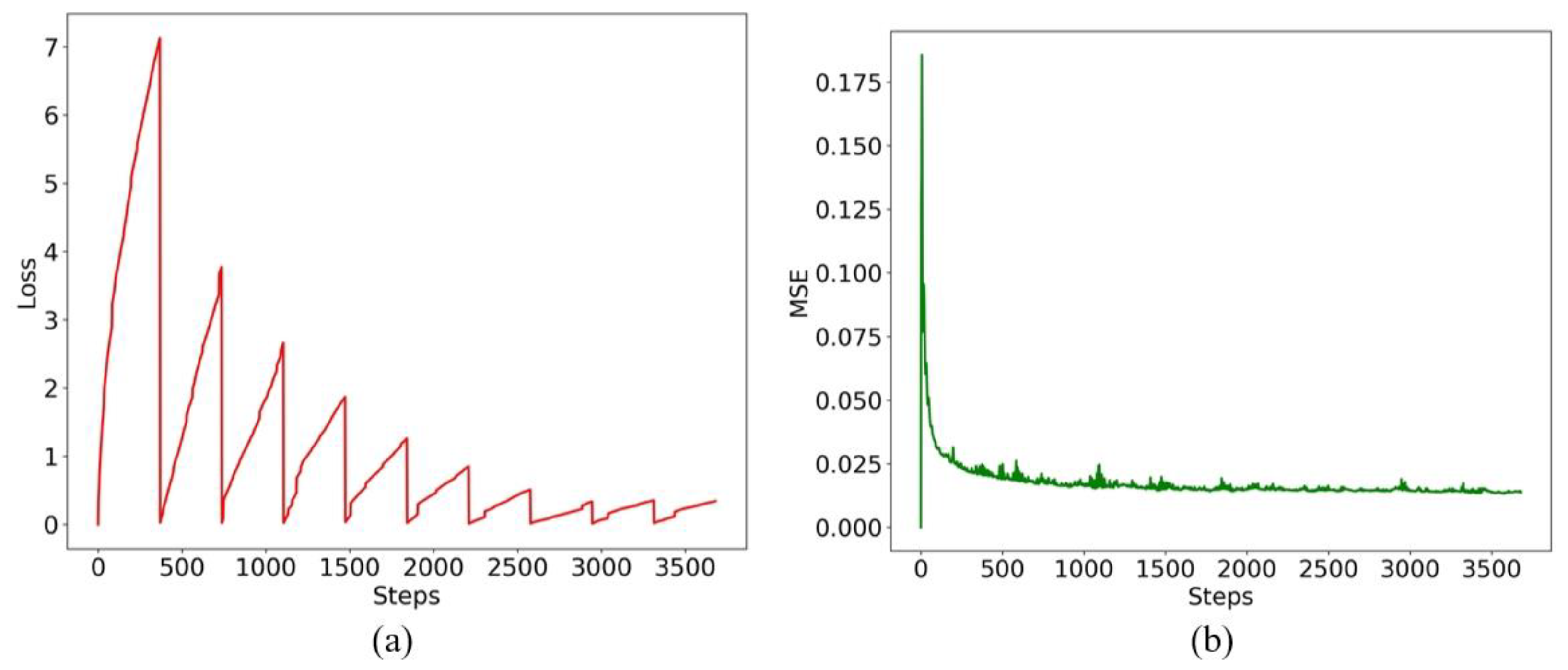
3.1. Experimental Results and Analysis
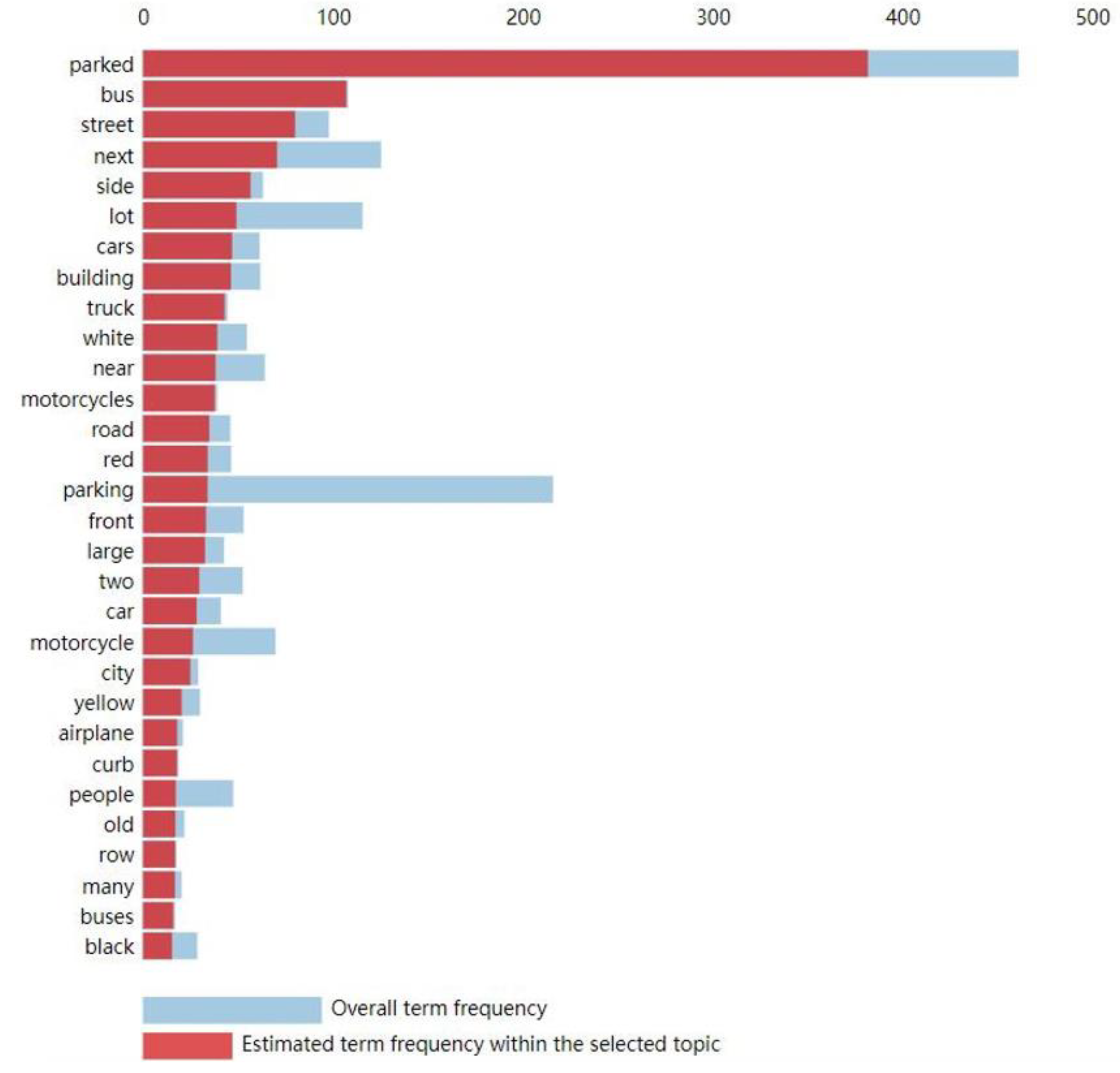
3.2. Theme Word Analysis
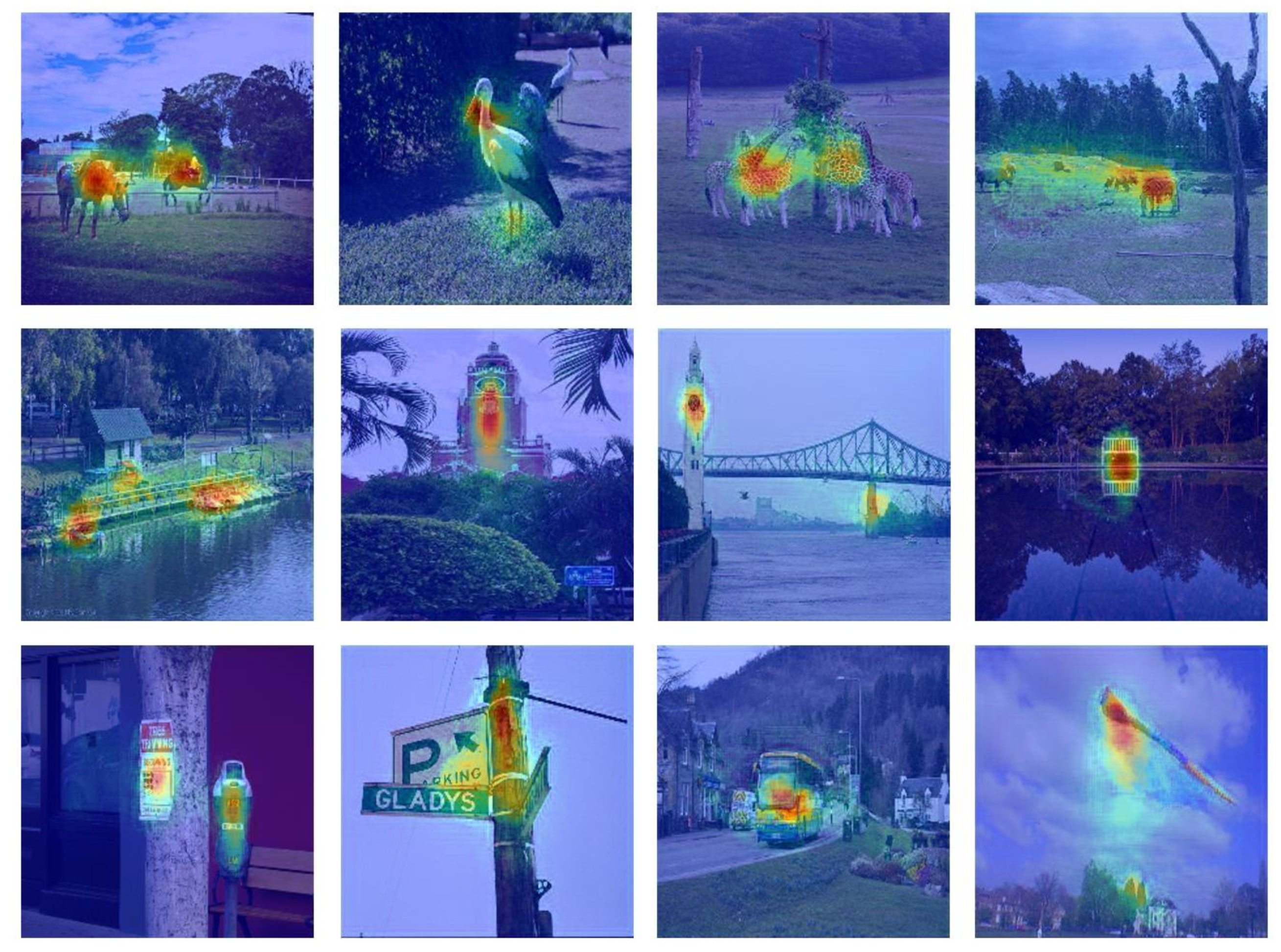
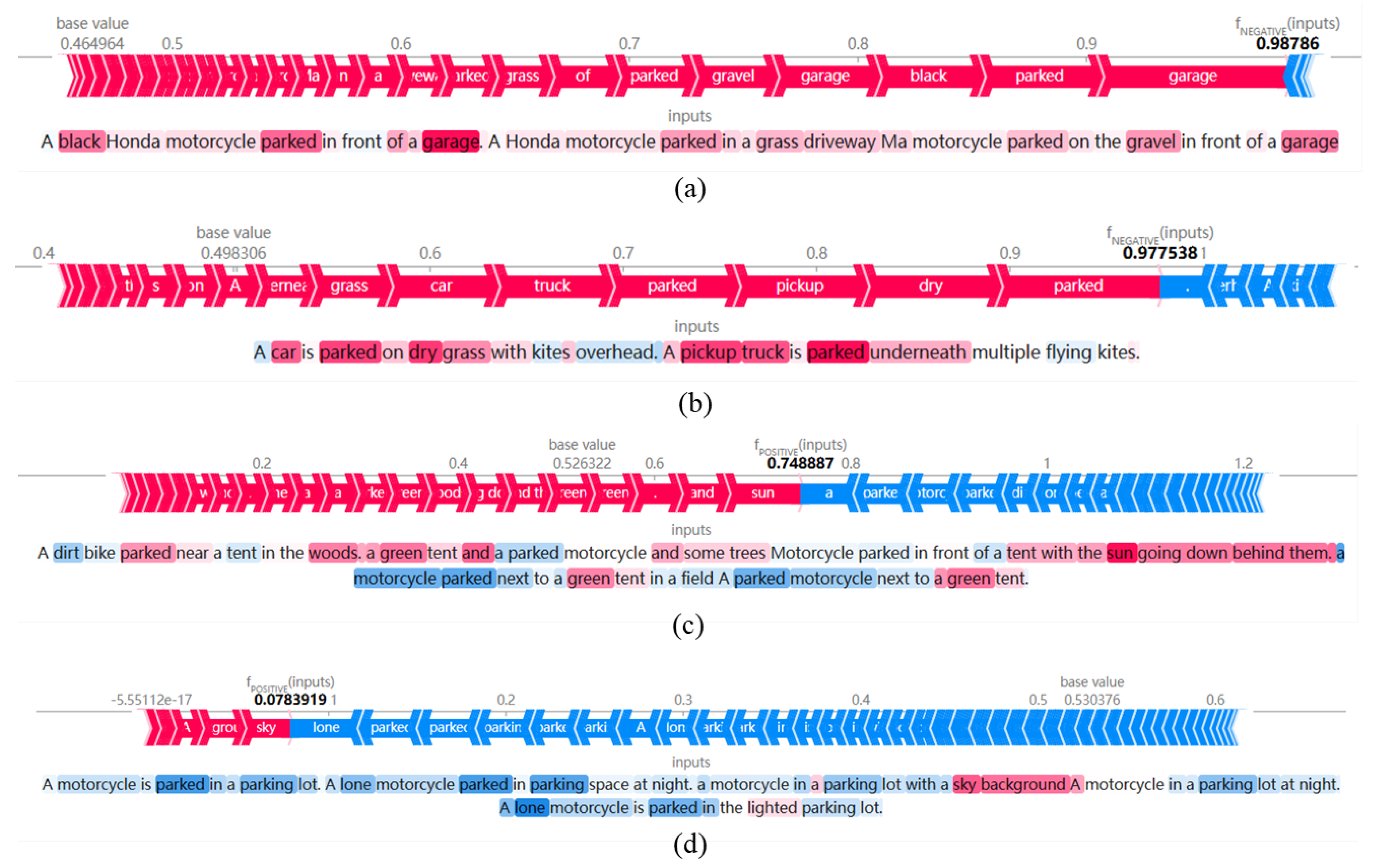
3.3. Saliency Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Methodological Contributions
4.2. Theoretical Reflections Based on Phenomenological and Neuroscientific Perspectives
4.3. Key Factors Influencing Visitors’ Emotional Experiences
4.4. Practical Applications of the Model
4.5. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
- The combination of BERT-based text feature extraction and Swin Transformer-based image feature extraction, along with the bidirectional cross-attention mechanism, enables the model to capture the deep interaction between text and images, thereby improving the accuracy of emotional tendency prediction.
- Compared with traditional methods such as ResNet, RNN, and LSTM, our method excels in several evaluation metrics, including MSE, MAE, RMSE, and R2. This confirms the advantages of the model in handling complex sentiment analysis tasks.
- The theme word analysis conducted using the SHAP method identified key factors, such as “water”, “green”, and “sky”, that significantly impact visitors’ emotional experiences. These findings not only contribute to a deeper understanding of the emotional drivers of visitors but also provide park managers with concrete directions for enhancing the park environment.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| FFN | Feed-Forward Neural Network |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| RMSE | Root Mean Squared Error |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| SHAP | SHapley Additive exPlanations |
References
- Kong, L.; Liu, Z.; Pan, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wu, J. How Do Different Types and Landscape Attributes of Urban Parks Affect Visitors’ Positive Emotions? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 226, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabisch, N.; Kraemer, R.; Masztalerz, O.; Hemmerling, J.; Püffel, C.; Haase, D. Impact of Summer Heat on Urban Park Visitation, Perceived Health and Ecosystem Service Appreciation. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 60, 127058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedla, D.; Halecki, W. The Value of River Valleys for Restoring Landscape Features and the Continuity of Urban Ecosystem Functions—A Review. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, F. Research on Environmental Behavior of Urban Parks in the North of China during Cold Weather—Nankai Park as a Case Study. Buildings 2024, 14, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Yan, Z.; Lan, S. Relationships between Green Space Perceptions, Green Space Use, and the Multidimensional Health of Older People: A Case Study of Fuzhou, China. Buildings 2024, 14, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerholm, N.; Eilola, S.; Arki, V. Outdoor Recreation and Nature’s Contribution to Well-Being in a Pandemic Situation—Case Turku, Finland. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 64, 127257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, X. Reexamine the Value of Urban Pocket Parks under the Impact of the COVID-19. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 64, 127294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhakka, R. University Students’ Participation in Outdoor Recreation and the Perceived Well-Being Effects of Nature. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour. 2021, 36, 100425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Hauer, R.J.; Sun, Y.; Meng, L.; Guo, P. Emotional Perceptions of People Exposed to Green and Blue Spaces in Forest Parks of Cities at Rapid Urbanization Regions of East China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2022, 78, 127772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wei, W.; Zhao, B. Effects of Urban Parks on Residents’ Expressed Happiness before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 212, 104118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kang, J. Natural Sounds Can Encourage Social Interactions in Urban Parks. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2023, 239, 104870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Gan, X.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, J. How Do Landscape Patterns in Urban Parks Affect Multiple Cultural Ecosystem Services Perceived by Residents? Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himschoot, E.A.; Crump, M.C.; Buckley, S.; Cai, C.; Lawson, S.; White, J.; Beeco, A.; Taff, B.D.; Newman, P. Feelings of Safety for Visitors Recreating Outdoors at Night in Different Artificial Lighting Conditions. J. Environ. Psychol. 2024, 97, 102374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhao, M.; Li, Y.; Tang, T.; Meng, Z.; Ding, Y. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Environmental Interpretation in National Parks Based on Visitors’ Spatiotemporal Behavior and Emotional Experience: A Case Study of Pudacuo National Park, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, M.; Wang, Y.; Xue, J. Which Factors Influence Public Perceptions of Urban Attractions?—A Comparative Study. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, S.; Van De Voorde, T. Which Environmental Features Contribute to Positive and Negative Perceptions of Urban Parks? A Cross-Cultural Comparison Using Online Reviews and Natural Language Processing Methods. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 218, 104307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Yun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, T.; Mu, Z. Usage Behavior and Health Benefit Perception of Youth in Urban Parks: A Case Study from Qingdao, China. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 923671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subiza-Pérez, M.; Hauru, K.; Korpela, K.; Haapala, A.; Lehvävirta, S. Perceived Environmental Aesthetic Qualities Scale (PEAQS)—A Self-Report Tool for the Evaluation of Green-Blue Spaces. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 43, 126383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, E.; Timperio, A.; Loh, V.H.Y.; Deforche, B.; Veitch, J. Critical Factors Influencing Adolescents’ Active and Social Park Use: A Qualitative Study Using Walk-along Interviews. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 58, 126948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.I.; Lim, S.; Kim, M.-L.; Joo, J. The Relationship between Perceived Restorativeness and Place Attachment for Hikers at Jeju Gotjawal Provincial Park in South Korea: The Moderating Effect of Environmental Sensitivity. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1201112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, B.K.L.; Jim, C.Y. Contributions of Human and Environmental Factors to Concerns of Personal Safety and Crime in Urban Parks. Secur. J. 2022, 35, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitra, B.; Jain, M.; Chundelli, F.A. Understanding the Soundscape Environment of an Urban Park through Landscape Elements. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.L.; Mowen, A.J.; Webster, N. Development and Validation of a Scale Measuring Public Perceptions of Racial Environmental Justice in Parks. J. Leis. Res. 2024, 55, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Abdul Aziz, F.; Song, M.; Zhang, H.; Ujang, N.; Xiao, Y.; Cheng, Z. Evaluating Visitor Usage and Safety Perception Experiences in National Forest Parks. Land 2024, 13, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkoltsiou, A.; Paraskevopoulou, A. Landscape Character Assessment, Perception Surveys of Stakeholders and SWOT Analysis: A Holistic Approach to Historical Public Park Management. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour. 2021, 35, 100418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosal, A.S.; Geijzendorffer, I.R.; Václavík, T.; Poulin, B.; Ziv, G. Using Social Media, Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing to Map Multiple Recreational Beneficiaries. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 38, 100958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hu, X.; Song, Z.; Yuan, X. Identifying the Integrated Visual Characteristics of Greenway Landscape: A Focus on Human Perception. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 99, 104937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, Y. Public Emotions and Visual Perception of the East Coast Park in Singapore: A Deep Learning Method Using Social Media Data. Urban For. Urban Green. 2024, 94, 128285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Huang, H.; Lin, G.; Lu, Y. Exploring Temporal and Spatial Patterns and Nonlinear Driving Mechanism of Park Perceptions: A Multi-Source Big Data Study. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 119, 106083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Sun, R.; Li, J.; Li, W. Urban Landscape and Climate Affect Residents’ Sentiments Based on Big Data. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 152, 102902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Miao, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhu, Z.; Qureshi, S.; Chang, Q. Revealing the Differences of Urban Parks’ Services to Human Wellbeing Based upon Social Media Data. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 63, 127233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fu, J.; Gao, J.; Zhou, R.; Wang, K.; Zhou, K. Effects of the Spatial Patterns of Urban Parks on Public Satisfaction: Evidence from Shanghai, China. Landsc. Ecol. 2023, 38, 1265–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Z.; Cheng, K.; Jian, Y.; Wang, Z. Comparison and Applicability Study of Analysis Methods for Social Media Text Data: Taking Perception of Urban Parks in Beijing as an Example. Landsc. Archit. Front. 2023, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, S.; Liu, S.; Zheng, T.; Van De Voorde, T. Are Social Media Data and Survey Data Consistent in Measuring Park Visitation, Park Satisfaction, and Their Influencing Factors? A Case Study in Shanghai. Urban For. Urban Green. 2023, 81, 127869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanahuati-Ceballos, M.; Valdivia, L.J. Detection of Depressive Comments on Social Media Using RNN, LSTM, and Random Forest: Comparison and Optimization. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2024, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhao, T.; Cao, L.; Biljecki, F. Water View Imagery: Perception and Evaluation of Urban Waterscapes Worldwide. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, T.; Zhang, S. Using Flickr Data to Understand Image of Urban Public Spaces with a Deep Learning Model: A Case Study of the Haihe River in Tianjin. IJGI 2022, 11, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, C. Discovering the Tourists’ Behaviors and Perceptions in a Tourism Destination by Analyzing Photos’ Visual Content with a Computer Deep Learning Model: The Case of Beijing. Tour. Manag. 2019, 75, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Mendes, C.; Ribeiro, J.; Ribeiro, R.; Miragaia, R.; Rodrigues, N.; Costa, N.; Pereira, A. Systematic Review of Emotion Detection with Computer Vision and Deep Learning. Sensors 2024, 24, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutia, T.; Baruah, N. A Review on Emotion Detection by Using Deep Learning Techniques. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, U.; Razzak, I.; Musial, K.; Imran, M. Transformer Based Deep Intelligent Contextual Embedding for Twitter Sentiment Analysis. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 113, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hittawe, M.M.; Harrou, F.; Sun, Y.; Knio, O. Stacked Transformer Models for Enhanced Wind Speed Prediction in the Red Sea. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Beijing, China, 18–20 August 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filali, H.; Riffi, J.; Boulealam, C.; Mahraz, M.A.; Tairi, H. Multimodal Emotional Classification Based on Meaningful Learning. BDCC 2022, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Liang, C. Emotion Recognition Using Multimodal Deep Learning in Multiple Psychophysiological Signals and Video. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cyber. 2020, 11, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, A.; Adhvaryu, K.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Hussain, A. Multimodal Sentiment Analysis: A Systematic Review of History, Datasets, Multimodal Fusion Methods, Applications, Challenges and Future Directions. Inf. Fusion. 2023, 91, 424–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Leng, Q.; Zhao, X. Deep Learning-Based Multimodal Emotion Recognition from Audio, Visual, and Text Modalities: A Systematic Review of Recent Advancements and Future Prospects. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Wen, Z.; Liang, B.; Yang, M.; Qin, B.; Xu, R. Image-to-Text Conversion and Aspect-Oriented Filtration for Multimodal Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2024, 15, 1264–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, T.; Guo, C.; Feng, X.; Chen, Y.; Song, J. A Comprehensive Survey on Deep Learning Multi-Modal Fusion: Methods, Technologies and Applications. CMC 2024, 80, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Association for Computational Linguistics North American Chapter Conference: Human Language Technologies (NAACL HLT 2019), Minneapolis, Minnesota, 2–7 June 2019; Volume 1, pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer Using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 9992–10002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, Y.; Fu, Y. Image-Text Embedding Learning via Visual and Textual Semantic Reasoning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stateczny, A.; Praveena, H.D.; Krishnappa, R.H.; Chythanya, K.R.; Babysarojam, B.B. Optimized Deep Learning Model for Flood Detection Using Satellite Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, G.; Liu, J. Long-Term Perceptual Soundscape Modeling of Urban Parks: A Case Study of Three Urban Parks in Vancouver, Canada. Landsc. Archit. 2022, 29, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Zhan, K.; Chen, Z.; Hong, X.-C. Research on Landscape Perception of Urban Parks Based on User-Generated Data. Buildings 2024, 14, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Liu, M.; Yin, L.; Yin, Z.; Liu, X.; Zheng, W. The Multi-Modal Fusion in Visual Question Answering: A Review of Attention Mechanisms. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewicka, M. Place Attachment: How Far Have We Come in the Last 40 Years? J. Environ. Psychol. 2011, 31, 207–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, C.M.; Bai, S.; Privitera, A.J.; Chen, S.-H.A. Brain Imaging Studies of Multisensory Integration in Emotion Perception: A Scoping Review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2025, 172, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.; Kross, E. Sensory Emotion Regulation. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2023, 27, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Georgiadis, T.; Cremonini, L.; Marini, S.; Toselli, S. The Perceptions and Attitudes of Residents Towards Urban Green Spaces in Emilia-Romagna (Italy)—A Case Study. Land 2024, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Yan, Y.; Lu, H.; Pan, Q.; Zhu, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Rong, Y.; Zhan, Y. Visitors’ Perception Based on Five Physical Senses on Ecosystem Services of Urban Parks from the Perspective of Landsenses Ecology. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2020, 27, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, J.W.A.; Evans, K.L. An Experimental Test of the Impact of Avian Diversity on Attentional Benefits and Enjoyment of People Experiencing Urban Green-space. People Nat. 2022, 4, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, S. Urban Ecological Risk Assessment Management Platform. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2018, 25, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhao, J. A Framework Designation for the Assessment of Urban Ecological Risks. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2018, 25, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Konijnendijk Van Den Bosch, C.C.; Lin, C.; Liu, F.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Q.; Dong, J. Effects of Personality, Health and Mood on Satisfaction and Quality Perception of Urban Mountain Parks. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 63, 127210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Guo, R.; Guo, F.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z. Pocket Parks-a Systematic Literature Review. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 083003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tang, L.R.; Kim, E. More than Words: Do Emotional Content and Linguistic Style Matching Matter on Restaurant Review Helpfulness? Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 77, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-L.; Chung, W.-Y. Sentiment-Based Masked Language Modeling for Improving Sentence-Level Valence–Arousal Prediction. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 16353–16369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | MSE | MAE | RMSE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet | 0.0352 | 0.1578 | 0.2216 | 0.7992 |
| RNN | 0.0278 | 0.1325 | 0.1764 | 0.8174 |
| LSTM | 0.0199 | 0.1163 | 0.1345 | 0.9424 |
| Our method | 0.0109 | 0.0781 | 0.1044 | 0.9819 |
| Method | Satisfaction Rate of Manual Assessment of Prediction Results |
|---|---|
| ResNet | 0.74 |
| RNN | 0.82 |
| LSTM | 0.86 |
| Our method | 0.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, K.; Lin, X.; Xia, T.; Bai, R. Research on Park Perception and Understanding Methods Based on Multimodal Text–Image Data and Bidirectional Attention Mechanism. Buildings 2025, 15, 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091552
Chen K, Lin X, Xia T, Bai R. Research on Park Perception and Understanding Methods Based on Multimodal Text–Image Data and Bidirectional Attention Mechanism. Buildings. 2025; 15(9):1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091552
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Kangen, Xiuhong Lin, Tao Xia, and Rushan Bai. 2025. "Research on Park Perception and Understanding Methods Based on Multimodal Text–Image Data and Bidirectional Attention Mechanism" Buildings 15, no. 9: 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091552
APA StyleChen, K., Lin, X., Xia, T., & Bai, R. (2025). Research on Park Perception and Understanding Methods Based on Multimodal Text–Image Data and Bidirectional Attention Mechanism. Buildings, 15(9), 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091552





