Analyzing the Spatial-Temporal Patterns of Urban Heat Islands in Nanjing: The Role of Urbanization and Different Land Uses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
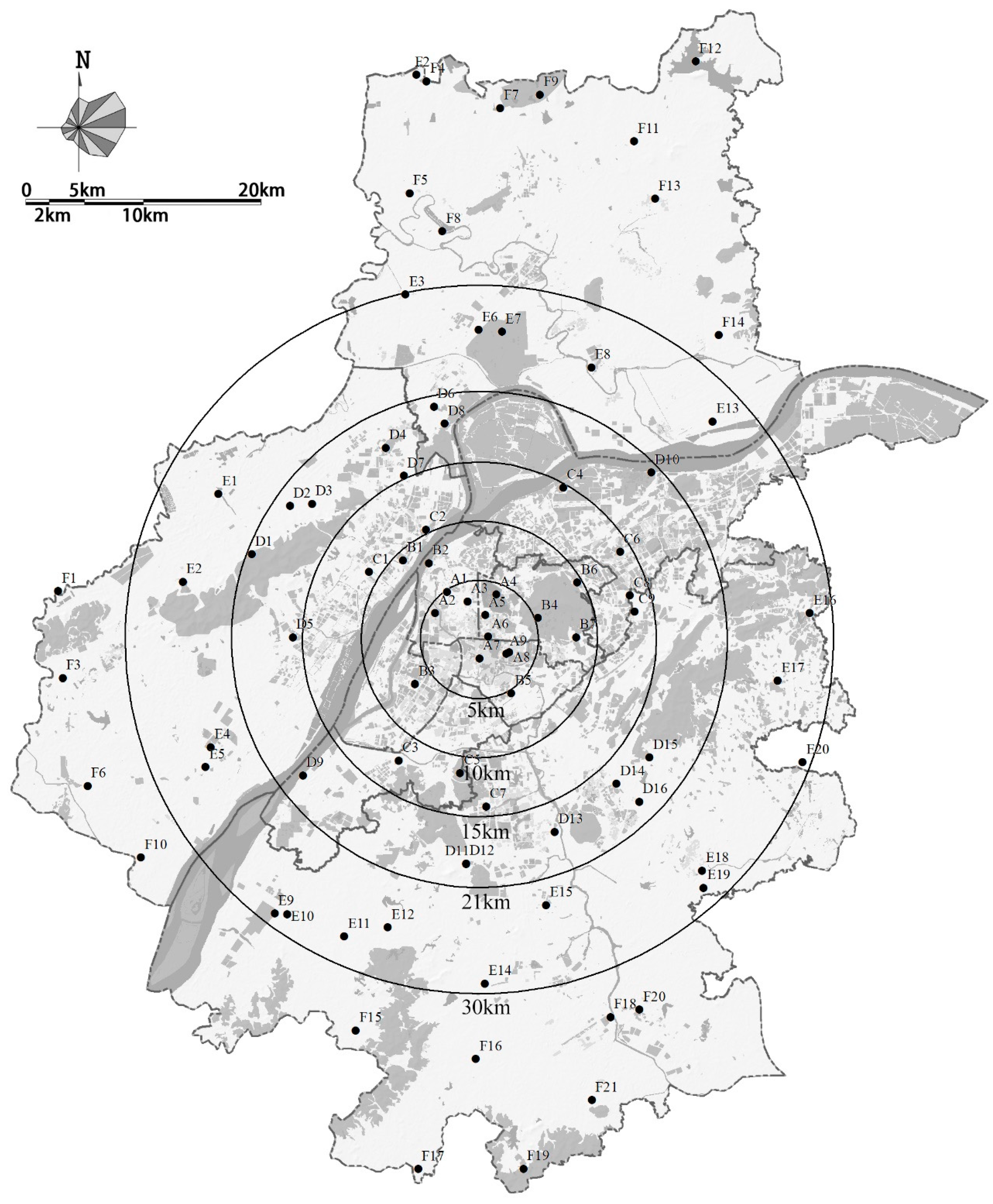
2.1. Annular Zone Division for UHI Analysis
2.2. Data Selection and Quality Control
2.3. Calculation of UHII and Selection of Representative Weather Stations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Temporal Distribution Characteristics of UHII
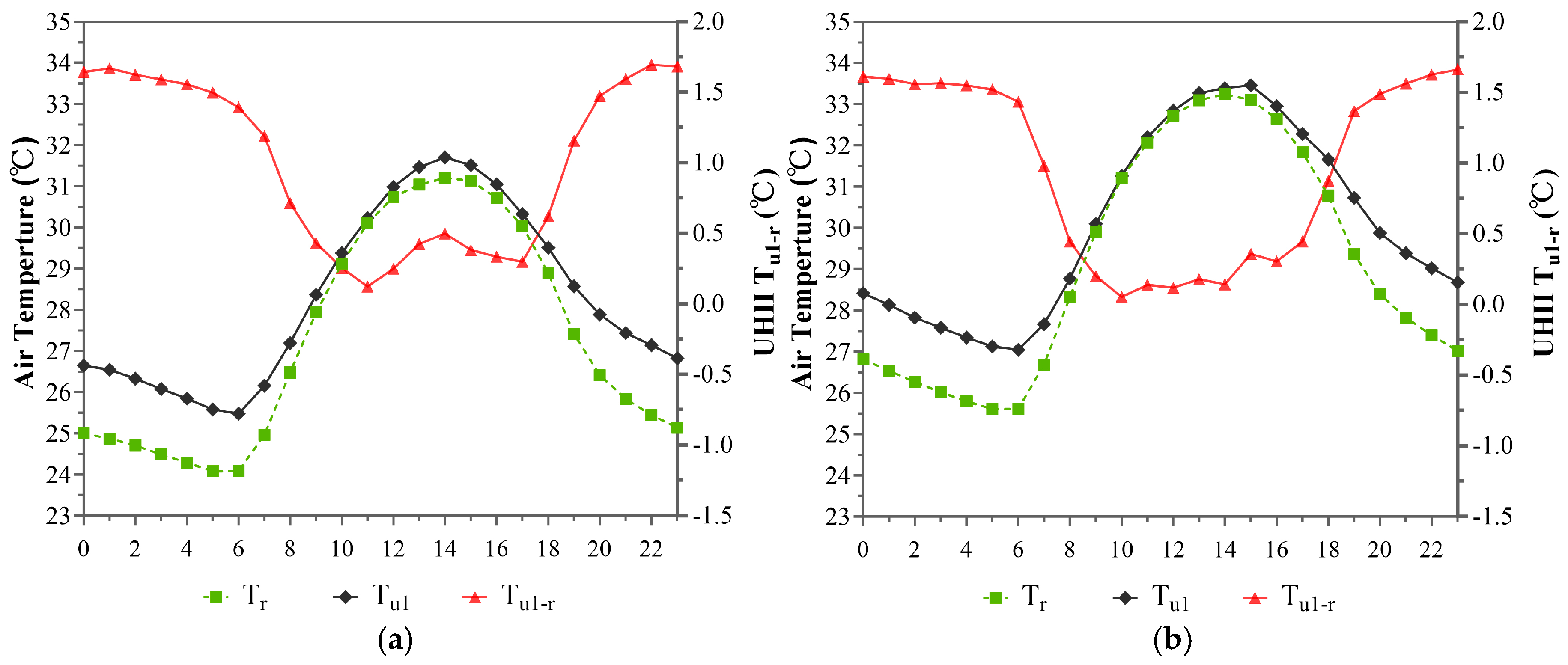
3.1.1. Temporal Distribution Characteristics of the UHI Effect Within the 1st Annular Zone (Within 5 km)
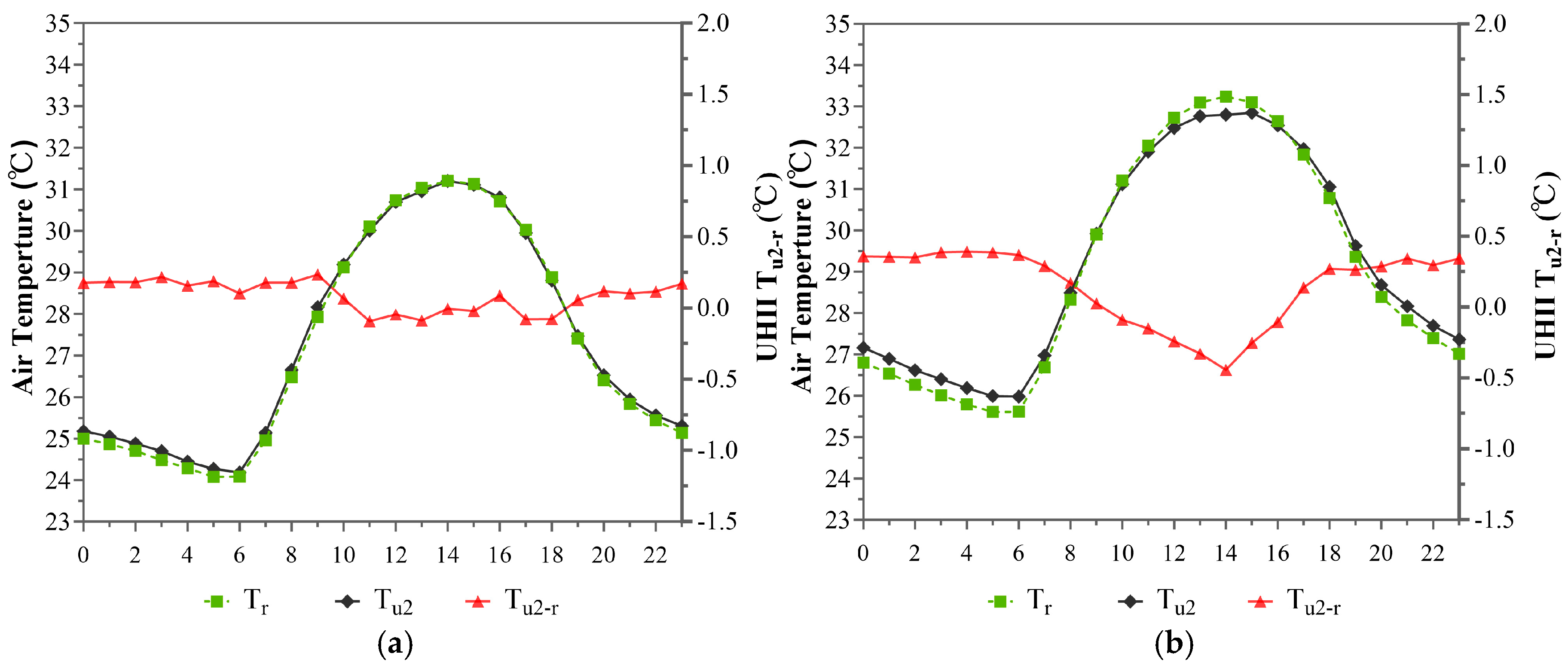
3.1.2. Temporal Distribution Characteristics of the UHI Effect Within the 2nd Annular Zone (5~10 km)
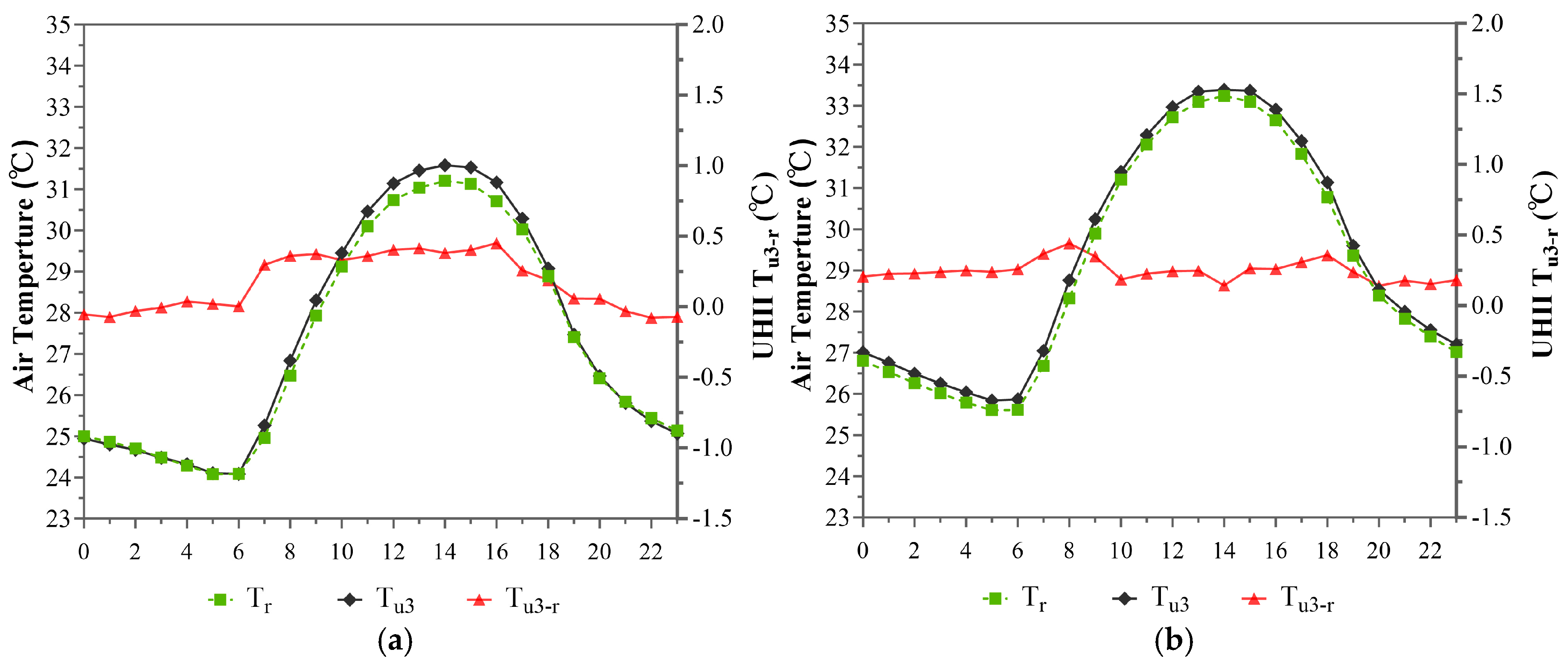
3.1.3. Temporal Distribution Characteristics of the UHI Effect Within the 3rd Annular Zone (10~15 km)
3.1.4. Temporal Distribution Characteristics of the UHI Effect Within the 4th Annular Zone (15~21 km)
3.1.5. Temporal Distribution Characteristics of the UHI Effect Within the 5th Annular Zone (21~30 km)
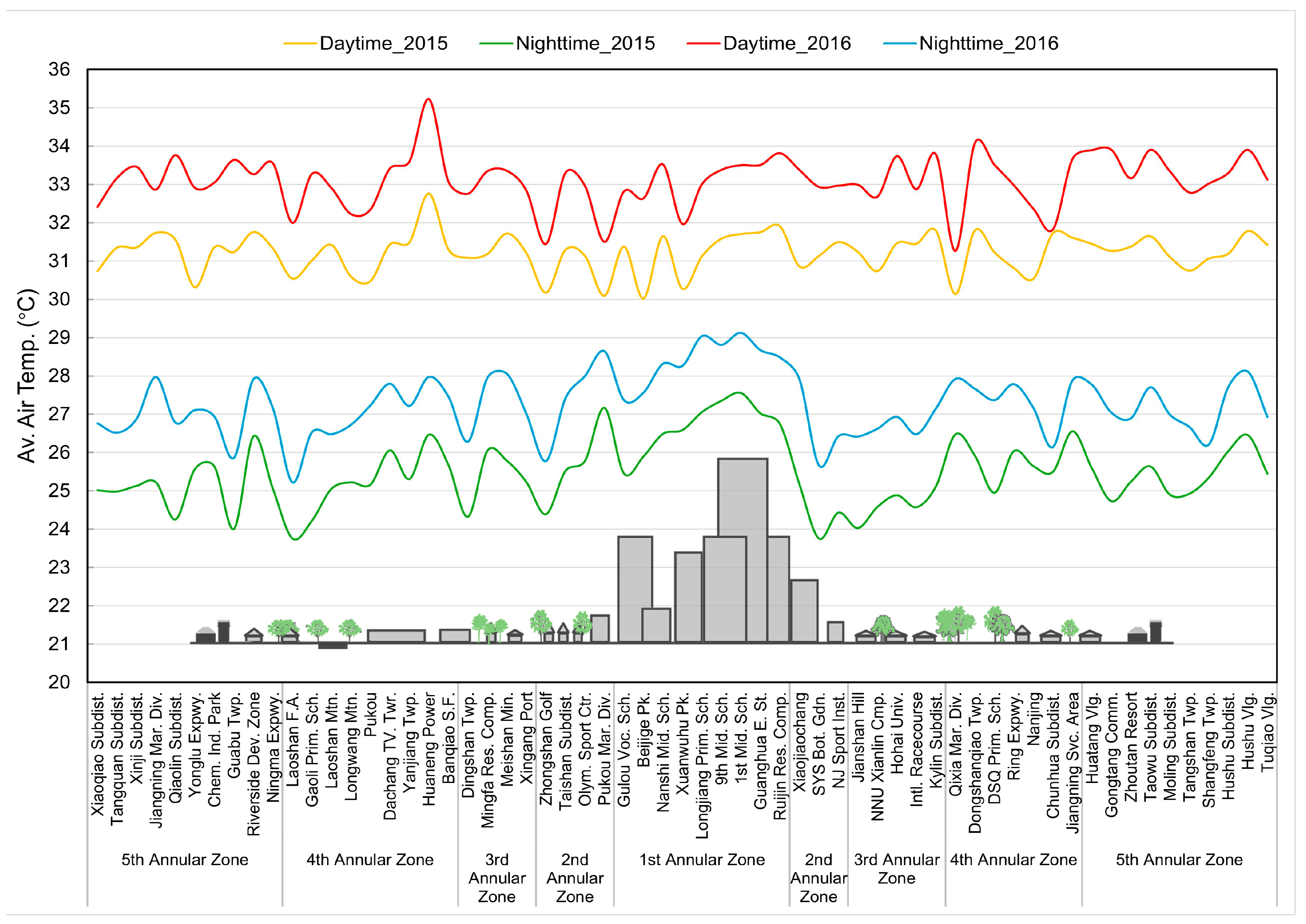
3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of UHII
3.2.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of the UHI Effect Within the 1st Annular Zone (Within 5 km)
3.2.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of the UHI Effect Within the 2nd Annular Zone (5~10 km)
3.2.3. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of the UHI Effect Within the 3rd Annular Zone (10~15 km)
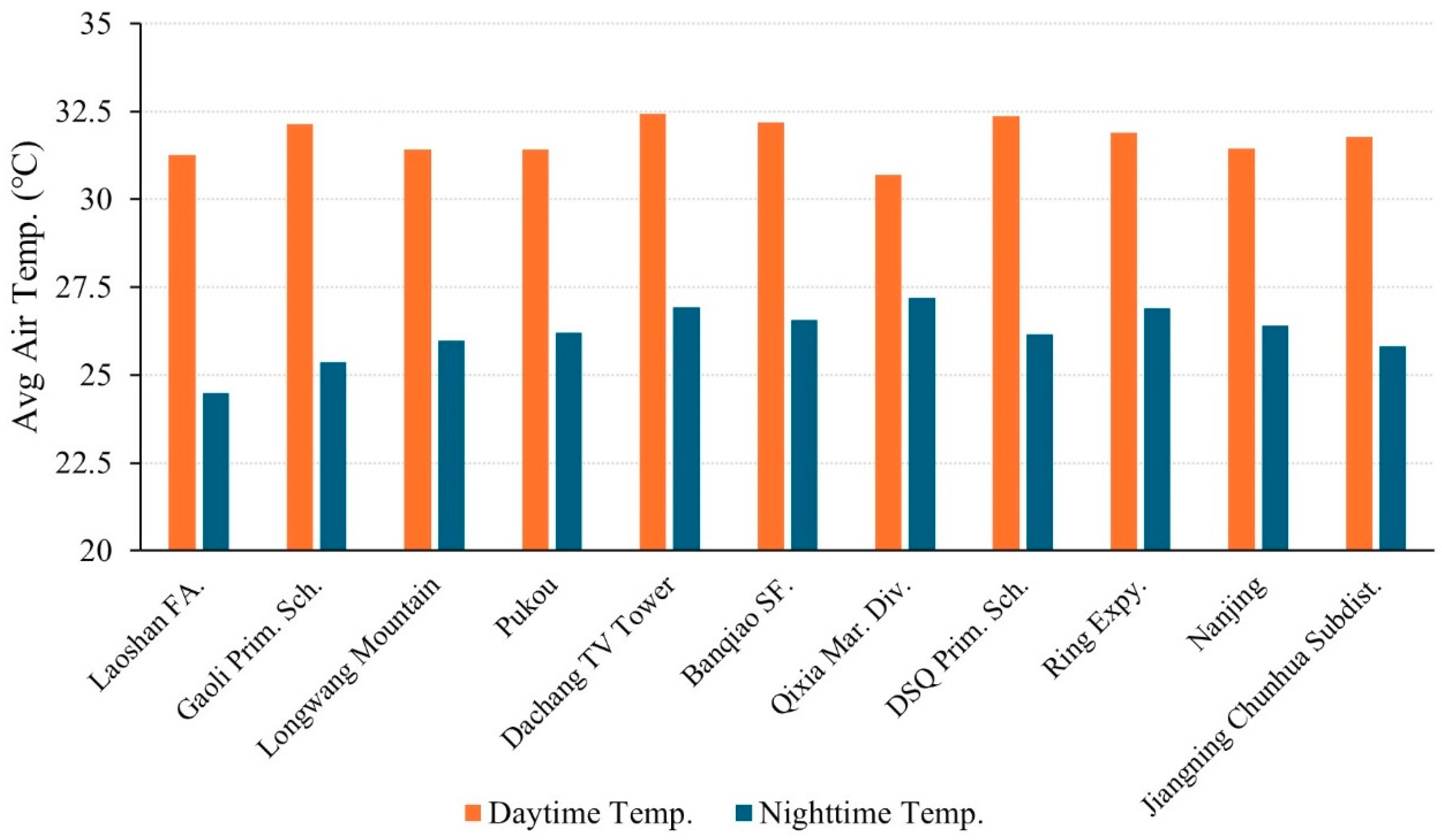
3.2.4. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of the UHI Effect Within the 4th Annular Zone (15~21 km)
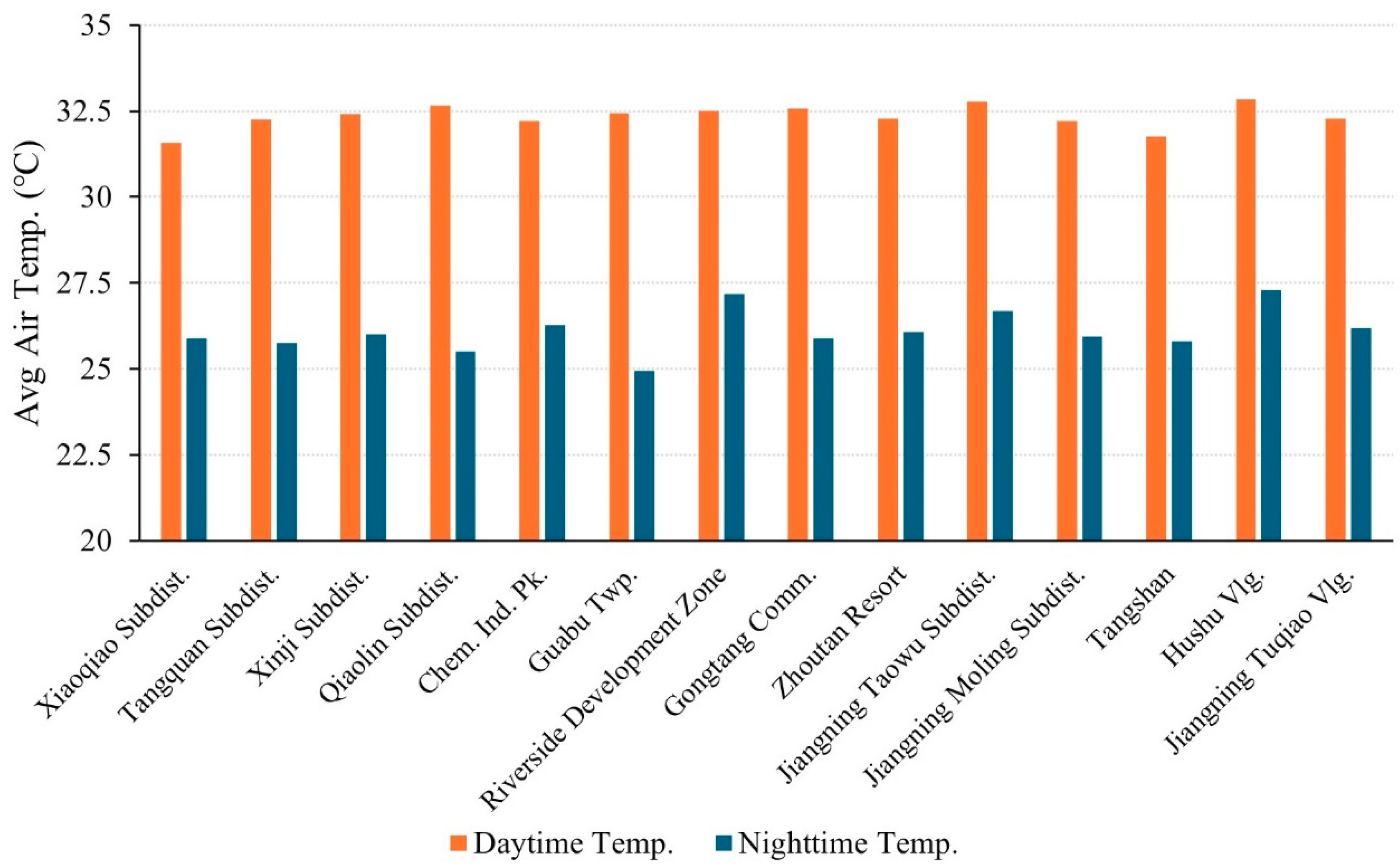
3.2.5. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of the UHI Effect Within the 5th Annular Zone (21~30 km)
4. Further Discussion
4.1. Temporal Distribution Characteristics of UHI
4.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of UHI
4.3. Boxplot Analysis of Average Temperature Variability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oke, T.R. City size and the urban heat island. Atmos. Environ. 1973, 7, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorahaki, S.; MollahassaniPour, M.; Rashidinejad, M.; Siano, P.; Shafie-khah, M. A flexibility-oriented model for a sustainable local multi-carrier energy community: A hybrid multi-objective probabilistic-IGDT optimization approach. Appl. Energy 2025, 377, 124678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, M.; Xiong, X.; Li, S. Impact of urban greenspace on the urban thermal environment: A case study of Shenzhen, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 112, 105591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tong, C. Spatiotemporal evolution of urban green space and its impact on the urban thermal environment based on remote sensing data: A case study of Fuzhou City, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 41, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Sun, S.; Song, C.; Li, J.; Xu, W.; Xu, Y. Understanding the spatiotemporal pattern of the urban heat island footprint in the context of urbanization, a case study in Beijing, China. Appl. Geogr. 2021, 133, 102496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kang, M.-Y.; Guan, Z.-R.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, A.-L.; Wu, W.-J.; Yang, H.-R. Assessing the role of urban green infrastructure in mitigating summertime Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect in metropolitan Shanghai, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 112, 105605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, R.; Guo, Y. How urban spatial characteristics impact surface urban heat island in subtropical high-density cities based on LCZs: A case study of Macau. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 112, 105587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anees, S.A.; Mehmood, K.; Raza, S.I.H.; Pfautsch, S.; Shah, M.; Jamjareegulgarn, P.; Shahzad, F.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Khan, W.R.; et al. Spatiotemporal analysis of surface Urban Heat Island intensity and the role of vegetation in six major Pakistani cities. Ecol. Inform. 2025, 85, 102986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamarkattel, U.; Lamichhane, B.R.; Gautam, S.; Niraj, K.C.; Sherchan, B.; Horanont, T. Analyzing Urban Heat Islands in Pokhara Metropolitan City-Nepal Through Remote Sensing Techniques. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2025, 37, 101479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Si, M.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Y.; Shang, G. The Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Forces of the Urban Heat Island in Shijiazhuang. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voogt, J.A.; Oke, T.R. Thermal remote sensing of urban climates. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dousset, B.; Gourmelon, F. Satellite multi-sensor data analysis of urban surface temperatures and landcover. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2003, 58, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Lu, D.; Schubring, J. Estimation of land surface temperature–vegetation abundance relationship for urban heat island studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottyán, Z.; Unger, J. A multiple linear statistical model for estimating the mean maximum urban heat island. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2003, 75, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, I. Urban nocturnal temperatures, street geometry and land use. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R.; Davis, C.W. Relation between satellite observed visible-near infrared emissions, population, economic activity and electric power consumption. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Sailor, D.J. Modeling the impacts of anthropogenic heating on the urban climate of Philadelphia: A comparison of implementations in two PBL schemes. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Lu, D.; Liang, B. Urban Surface Biophysical Descriptors and Land Surface Temperature Variations. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Weng, Q.; Ouyang, Z.; Li, W.; Schienke, E.W.; Zhang, Z. Land Surface Temperature Variation and Major Factors in Beijing, China. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2008, 74, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, W.M. Impact of Nanjing urban development on the boundary layer. Chin. J. Geophys. 2007, 50, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Orkomi, A.A.; Ameri, M. Investigating the intensity of urban heat island and the impacts of local climate using verified WRF data: A case study of Rasht, Northern Iran. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 106, 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xian, G.; Auch, R.; Gallo, K.; Zhou, Q. Urban Heat Island and Its Regional Impacts Using Remotely Sensed Thermal Data—A Review of Recent Developments and Methodology. Land 2021, 10, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhihong, J.; Limei, Y.; Fei, H. Numerical simulation of the impact of land cover change on Urban Heat Island effect in Nanjing. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering, Nanjing, China, 24–26 June 2011; pp. 4223–4226. [Google Scholar]
- Aquino-Martínez, L.P.; Ortega-Guerrero, B.; Quintanar, A.I.; Díaz-Esteban, Y. Synoptic patterns and heatwaves: Intensifying urban heat islands in the Mexico Basin. Urban Clim. 2025, 59, 102318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, A.; Hong, S.-H.; Park, K.; Baik, J.-J. Simulating urban heat islands and local winds in the Dhaka metropolitan area, Bangladesh. Urban Clim. 2025, 59, 102284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhong, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Unveiling the Role of Western Pacific Subtropical High in Urban Heat Islands Using Local Climate Zones Coupled WRF-BEP/BEM. Earth Syst. Environ. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Schubert, S.; Kropp, J.P.; Rybski, D. On the influence of density and morphology on the Urban Heat Island intensity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michau, Y.; Lemonsu, A.; Lucas-Picher, P.; Caillaud, C. Evaluation of the Urban Heat Island of 12 cities of France in a high-resolution regional climate model simulation. Urban Clim. 2023, 47, 101386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Najian, M.; Goudarzi, N. Towards Improving High Spatiotemporal Weather Forecast Accuracy with Data-Driven Modeling. In Proceedings of the ASME 2024 18th International Conference on Energy Sustainability collocated with the ASME 2024 Heat Transfer Summer Conference and the ASME 2024 Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting, Anaheim, CA, USA, 15–17 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Vitanova, L.L.; Kusaka, H. Study on the urban heat island in Sofia City: Numerical simulations with potential natural vegetation and present land use data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 40, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, P.A.; Haghighat, F. Approaches to study Urban Heat Island—Abilities and limitations. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 2192–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaroni, H.; Ben-Dor, E.; Bitan, A.; Potchter, O. Spatial distribution and microscale characteristics of the urban heat island in Tel-Aviv, Israel. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2000, 48, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, P.; Sengupta, R. Spatial bias in placement of citizen and conventional weather stations and their impact on urban climate research: A case study of the Urban Heat Island effect in Canada. Urban Clim. 2025, 59, 102280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zezzo, L.V.; Coltri, P.P.; Dubreuil, V.; Torres, G.A.L.; de Costa Trindade Amorim, M.C. Exploring the urban heat island phenomenon in a tropical medium-sized city: Insights for sustainable urban development. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, R.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Niu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Niu, Z. The influence of different data and method on estimating the surface urban heat island intensity. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-P.; Chen, Y.-C.; Matzarakis, A. Urban thermal stress climatic mapping: Combination of long-term climate data and thermal stress risk evaluation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 34, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Shui, T.; Chen, X.; Wu, Q. Analysis of local-scale urban heat island characteristics using an integrated method of mobile measurement and GIS-based spatial interpolation. Build. Environ. 2017, 117, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsin, P.K.; Knudby, A.; Krayenhoff, E.S.; Ho, H.C.; Brauer, M.; Henderson, S.B. Microscale mobile monitoring of urban air temperature. Urban Clim. 2016, 18, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Tan, X.; Chen, K.; Song, S.; Zhu, X.; Hou, D. Quantifying landscape-metrics impacts on urban green-spaces and water-bodies cooling effect: The study of Nanjing, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 55, 126838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Sailor, D.J.; Yang, X.; Xu, G.; Zhao, L. Are water bodies effective for urban heat mitigation? Evidence from field studies of urban lakes in two humid subtropical cities. Build. Environ. 2023, 245, 110860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Zhan, W.; Huang, F.; Voogt, J.; Bechtel, B.; Allen, M.; Peng, S.; Hong, F.; Liu, Y.; Du, P. Identification of typical diurnal patterns for clear-sky climatology of surface urban heat islands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkovich, N.B.; Larsen, L. A Bicycle-Based Field Measurement System for the Study of Thermal Exposure in Cuyahoga County, Ohio, USA. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Lee, K.; Cho, G.-H. Temporal and spatial variability of urban heat island by geographical location: A case study of Ulsan, Korea. Build. Environ. 2017, 126, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.I.; Gough, W.A.; Mohsin, T. Characterization of the urban heat island at Toronto: Revisiting the choice of rural sites using a measure of day-to-day variation. Urban Clim. 2018, 25, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, J.; Chapman, L.; Muller, C. Quantifying the Daytime and Night-Time Urban Heat Island in Birmingham, UK: A Comparison of Satellite Derived Land Surface Temperature and High Resolution Air Temperature Observations. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, R.; Cai, X.; Chapman, L.; Heaviside, C.; Thornes, J.E.; Muller, C.L.; Young, D.T.; Warren, E.L. Observations of urban heat island advection from a high-density monitoring network. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 2434–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, L.; Muller, C.L.; Grimmond, C.S.B.; Young, D.T.; Cai, X.-M. Toward a Standardized Metadata Protocol for Urban Meteorological Networks. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1161–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-M.; Xue, M.; Klein, P.M.; Illston, B.G.; Chen, S. Analysis of Urban Effects in Oklahoma City using a Dense Surface Observing Network. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 723–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Li, Z.; Fan, Z. Seasonal impacts of built environment and its interactions on urban park cooling effects in Nanjing, China. Build. Environ. 2023, 242, 110580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, M.; Lin, C.; Duan, X.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, L. Spatial distribution and driving force analysis of urban heat island effect based on raster data: A case study of the Nanjing metropolitan area, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Piao, Y.; Pan, C.; Lee, D.; Zhao, B. Using buffer analysis to determine urban park cooling intensity: Five estimation methods for Nanjing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 868, 161463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tan, S.; Liang, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, E. Predicting the impacts of urban development on urban thermal environment using machine learning algorithms in Nanjing, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 356, 120560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.D.; Xia, B.C.; Guo, L.; Li, N. Characteristics of multi-scale temporal-spatial distribution of urban heat island in Guangzhou. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2007, 18, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Estévez, J.; Gavilán, P.; Giráldez, J.V. Guidelines on validation procedures for meteorological data from automatic weather stations. J. Hydrol. 2011, 402, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquaotta, F.; Fratianni, S.; Aguilar, E.; Fortin, G. Influence of instrumentation on long temperature time series. Clim. Chang. 2019, 156, 385–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liubitskyi, V.V.; Shcherbatiuk, M.V.; Cherevychnyi, Y.O.; Shatkovskyi, A.P.; Zhuravlov, O.V. Assessment of the Accuracy of Meteorological Data Obtained from Virtual and Automatic Weather Stations for the Conditions of Ukrainian Polissya. Land Reclam. Water Manag. 2024, 2, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R.; East, C. The urban boundary layer in Montreal. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1971, 1, 411–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, H.; Zha, D.; Zhu, J. A fieldwork study on the diurnal changes of urban microclimate in four types of ground cover and urban heat island of Nanjing, China. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


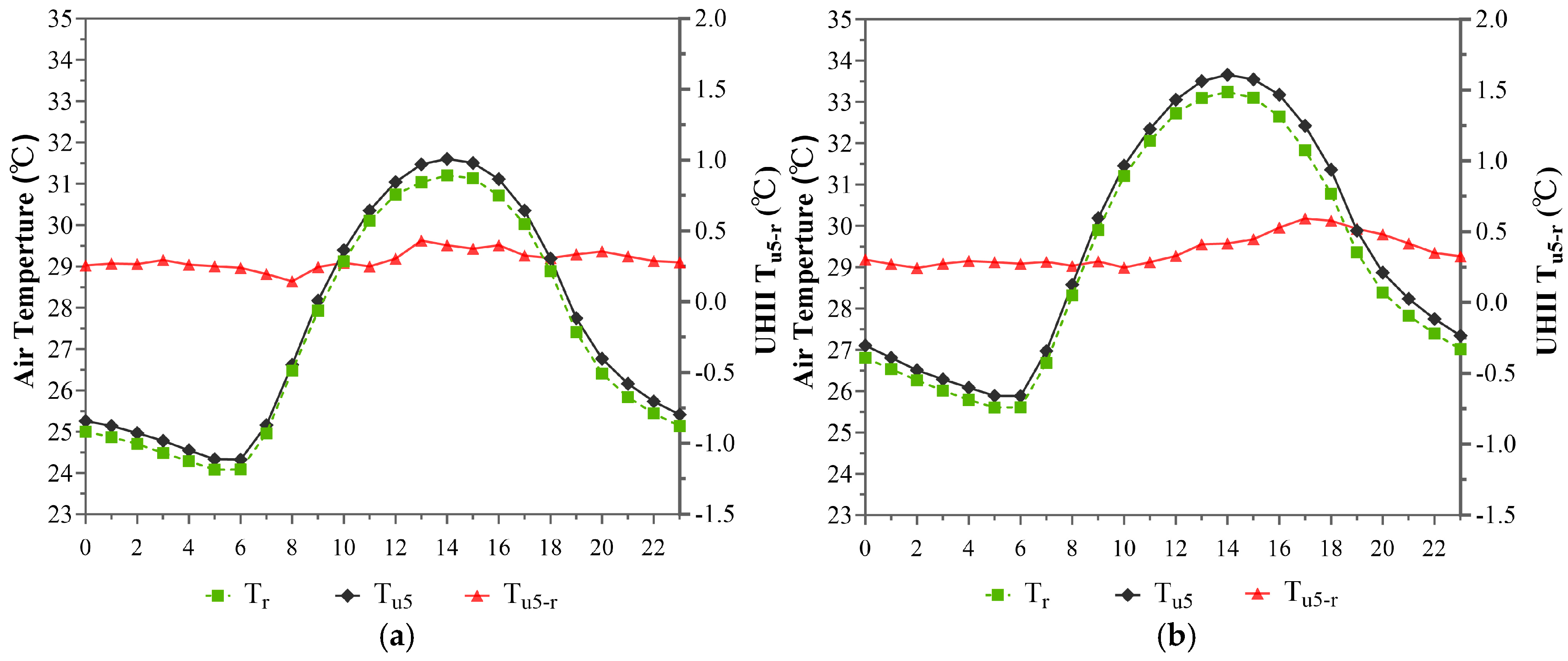
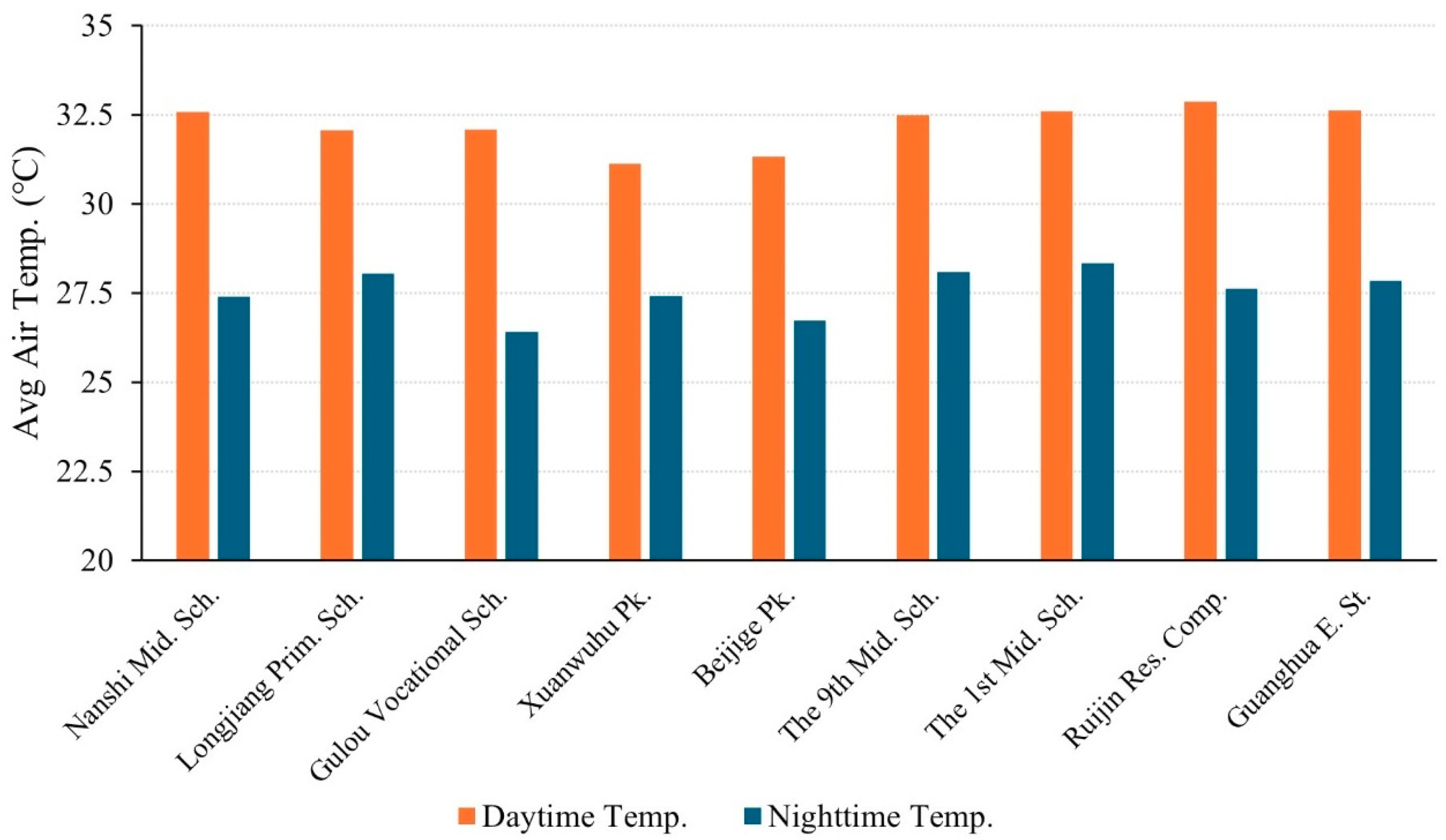
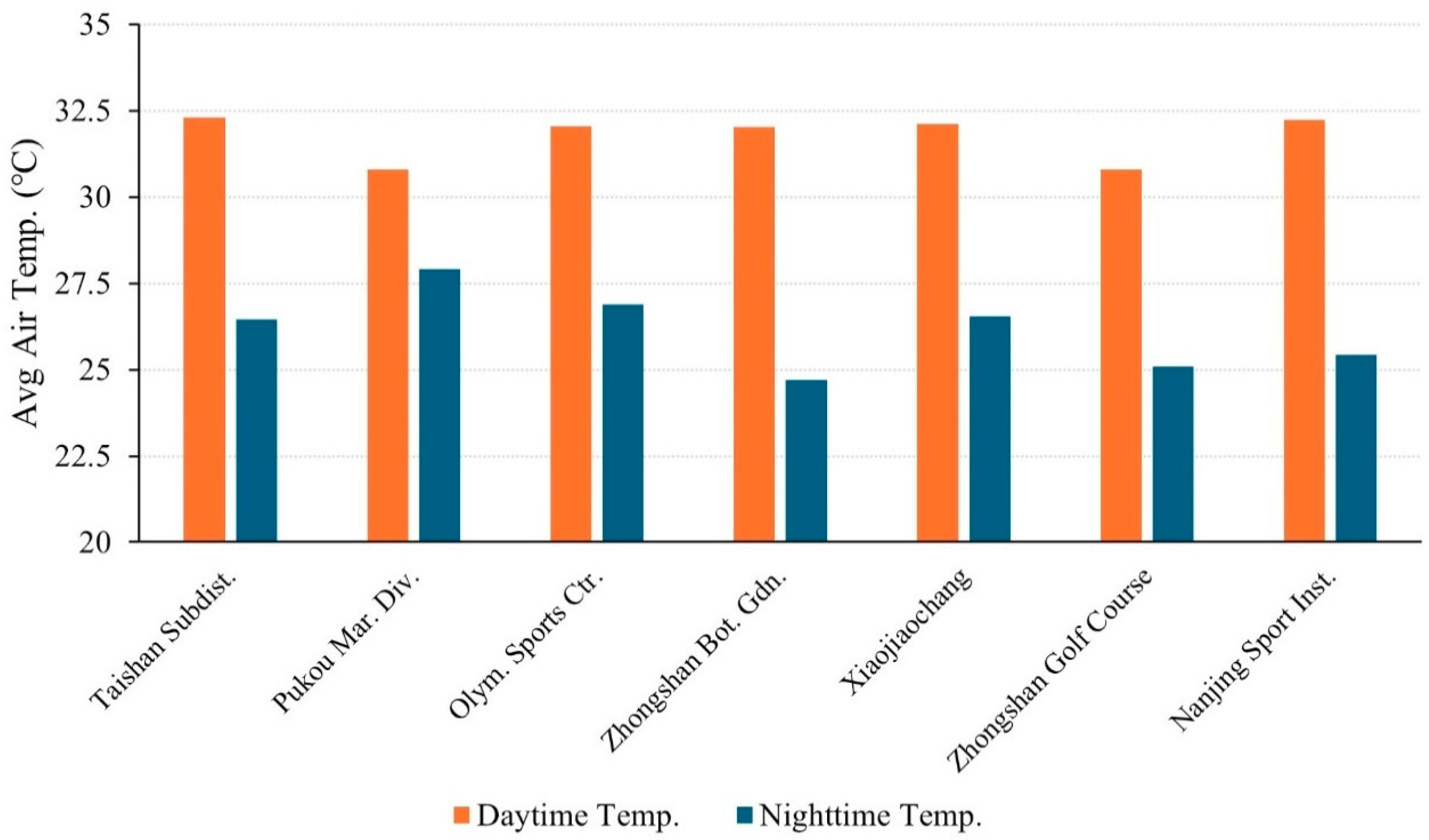
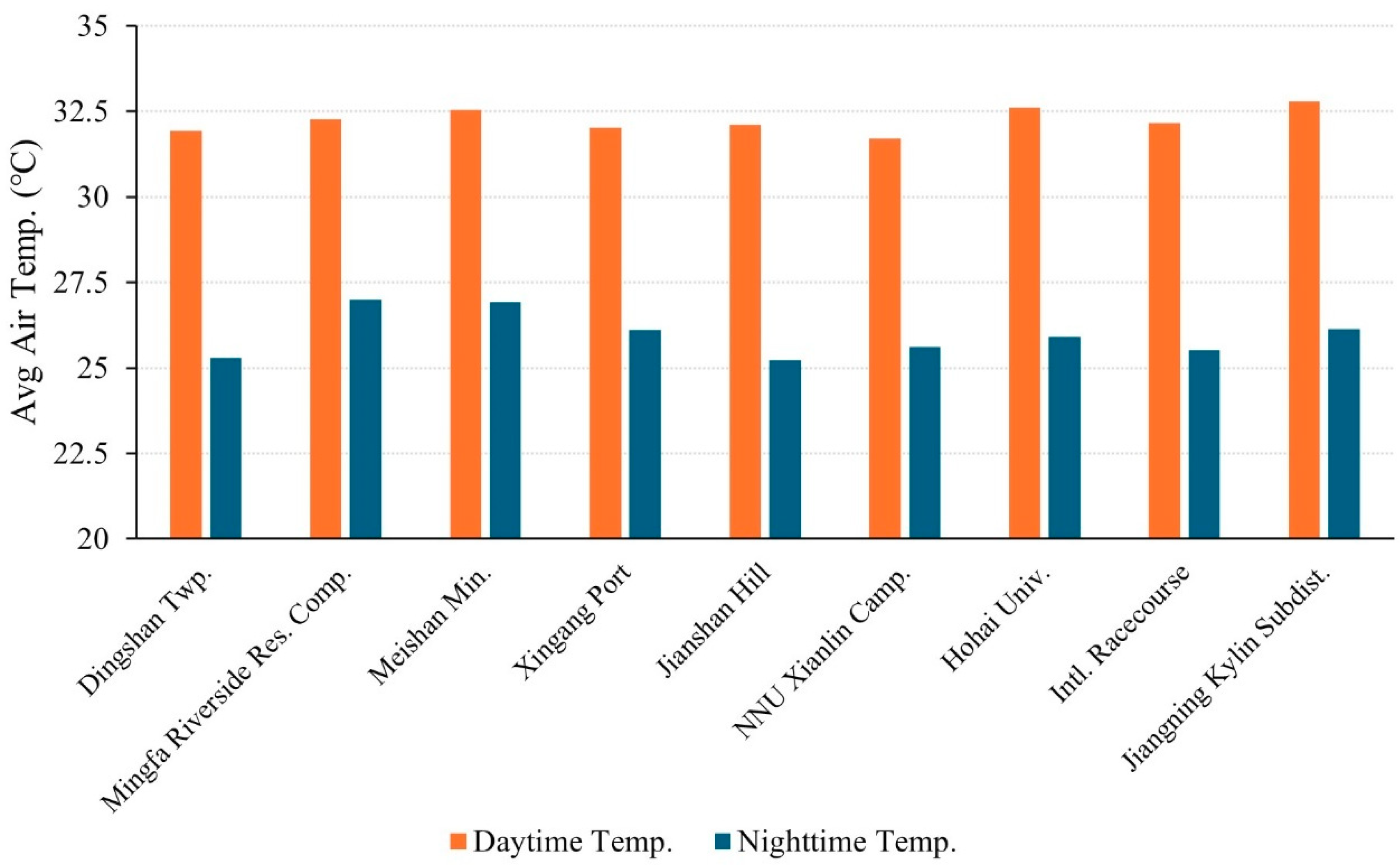

| Annular Zones | Built-Up Area Percentage | Names of the Selected AWSs | ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0~5 km | 94% | Nanshi Middle School | A01 |
| Longjiang Primary School | A02 | ||
| Gulou Vocational School | A03 | ||
| Xuanwuhu Park | A04 | ||
| Beijige Park | A05 | ||
| The 9th Middle School | A06 | ||
| The 1st Middle School | A07 | ||
| Ruijin Residential Complex | A08 | ||
| Guanghua East Street | A09 | ||
| 5~10 km | 84% | Taishan Subdistrict | B01 |
| Pukou Maritime Division | B02 | ||
| Olympic Sports Centre | B03 | ||
| Zhongshan Botanical Garden | B04 | ||
| Xiaojiaochang | B05 | ||
| Zhongshan Golf Course | B06 | ||
| Nanjing Sport Institute | B07 | ||
| 10~15 km | 65% | Dingshan Township | C01 |
| Mingfa Riverside Residential Complex | C02 | ||
| Meishan Mining | C03 | ||
| Xingang Port | C04 | ||
| Jianshan Hill | C05 | ||
| Nanjing Normal University Xianlin Campus | C06 | ||
| Hohai University | C07 | ||
| International Racecourse | C08 | ||
| Jiangning Kylin Subdistrict | C09 | ||
| 15~21 km | 41% | Laoshan Forestry Area | D01 |
| Gaoli Primary School | D02 | ||
| Laoshan Mountain | D03 | ||
| Longwang Mountain | D04 | ||
| Pukou | D05 | ||
| Dachang TV Tower | D06 | ||
| Yanjiang Township | D07 | ||
| Huaneng Power Plant | D08 | ||
| Banqiao Steam Ferry | D09 | ||
| Qixia Maritime Division | D10 | ||
| Dongshanqiao Township | D11 | ||
| Dongshanqiao Primary School | D12 | ||
| Ring Expressway | D13 | ||
| Nanjing | D14 | ||
| Jiangning Chunhua Subdistrict | D15 | ||
| Jiangning Service Area | D16 | ||
| 21~30 km | 22% | Xiaoqiao Subdistrict | E01 |
| Tangquan Subdistrict | E02 | ||
| Xinji Subdistrict | E03 | ||
| Jiangning Maritime Division | E04 | ||
| Qiaolin Subdistrict | E05 | ||
| Yong-Liu Expressway | E06 | ||
| Chemical Industry Park | E07 | ||
| Guabu Township | E08 | ||
| Riverside Development Zone | E09 | ||
| Ning-Ma Expressway | E10 | ||
| Lulang Huatang Village | E11 | ||
| Gongtang Community | E12 | ||
| Zhoutan Resort | E13 | ||
| Jiangning Taowu Subdistrict | E14 | ||
| Jiangning Moling Subdistrict | E15 | ||
| Tangshan | E16 | ||
| Shangfeng Township | E17 | ||
| Jiangning Hushu Subdistrict | E18 | ||
| Hushu Village | E19 | ||
| Jiangning Tuqiao Village | E20 | ||
| >30 km | 20% | Ninghe North Slope | F01 |
| Ning-Lian Expressway | F02 | ||
| Xingdian Township | F03 | ||
| Liuhe Service Area | F04 | ||
| Chengqiao Subdistrict | F05 | ||
| Shiqiao Community | F06 | ||
| Pingshan Post Office | F07 | ||
| North of Chu River Bridge | F08 | ||
| Pingshan Forest Farm | F09 | ||
| Wujiang Community | F10 | ||
| Babai Township | F11 | ||
| Jinniu Lake Scenic Area | F12 | ||
| Xinhuang Township | F13 | ||
| Donggou Township | F14 | ||
| Damiao Village | F15 | ||
| Hengxi Vegetable Institute | F16 | ||
| Jiangning Little Danyang | F17 | ||
| Airport Expressway | F18 | ||
| Hengshan Forest Farm | F19 | ||
| Zhetang | F20 | ||
| Jiangning Tongshan Subdistrict | F21 |
| Annular Zones | Names of the Selected AWSs | Land Use | Zone Level | Avg. Greenery Coverage | Avg. Sky View Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~5 km | Nanshi Middle School | Educational | Sub-central | 60% | 0.6~0.7 |
| Longjiang Primary School | Educational | Sub-central | 40% | 0.6~0.7 | |
| Gulou Vocational School | Educational | Central | 38% | 0.4~0.5 | |
| Xuanwuhu Park | Green space | Central | 75% | 0.9~1 | |
| Beijige Park | Green space | Central | 75% | 0.9~1 | |
| The 9th Middle School | Educational | Central | 15% | 0.5~0.6 | |
| The 1st Middle School | Educational | Central | 15% | 0.4~0.5 | |
| Ruijin Residential Complex | Residential | Sub-central | 10% | 0.5~0.6 | |
| Guanghua East Street | Residential | Sub-central | 10% | 0.5~0.6 | |
| 5~10 km | Taishan Subdistrict | Industrial | Suburban | 20% | 0.7~0.8 |
| Pukou Maritime Division | Water bodies | Suburban | 0 | 0.9~1 | |
| Olympic Sports Centre | Recreational | Sub-central | 50% | 0.6~0.7 | |
| Zhongshan Botanical Garden | Green space | Sub-central | 85% | 0.9~1 | |
| Xiaojiaochang | Residential | Sub-central | 5% | 0.5~0.6 | |
| Zhongshan Golf Course | Green space | Sub-central | 75% | 0.9~1 | |
| Nanjing Sport Institute | Educational | Sub-central | 60% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| 10~15 km | Dingshan Township | Farm and forestry | Suburban | 15% | 0.5~0.6 |
| Mingfa Riverside Residential Complex | Residential | Subcentral | 40% | 0.5~0.6 | |
| Meishan Mining | Industrial | Suburban | 15% | 0.8~0.9 | |
| Xingang Port | Industrial | Suburban | 15% | 0.8~0.9 | |
| Jianshan Hill | Forestry | Suburban | 90% | 0.9~1 | |
| NJ Normal University Xianlin Campus | Educational | Suburban | 70% | 0.6~0.7 | |
| Hohai University | Educational | Sub-central | 50% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| International Racecourse | Recreational | Suburban | 45% | 0.9~1 | |
| Jiangning Kylin Subdistrict | Residential | Suburban | 50% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| 15~21 km | Laoshan Forestry Area | Forestry | Rural | 90% | 0.9~1 |
| Gaoli Primary School | Educational | Rural | 50% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| Laoshan Mountain | Forestry | Rural | 90% | 0.6~0.7 | |
| Longwang Mountain | Industrial | Suburban | 85% | 0.9~1 | |
| Pukou | Residential | Suburban | 40% | 0.5~0.6 | |
| Dachang TV Tower | Industrial | Suburban | 50% | 0.8~0.9 | |
| Yanjiang Township | Industrial | Suburban | 20% | 0.6~0.7 | |
| Huaneng Power Plant | Industrial | Rural | 10% | 0.8~0.9 | |
| Banqiao Steam Ferry | Industrial | Rural | 40% | 0.9~1 | |
| Qixia Maritime Division | Water bodies | Suburban | 30% | 0.9~1 | |
| Dongshanqiao Township | Residential | Rural | 40% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| Dongshanqiao Primary School | Residential | Rural | 40% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| Ring Expressway | Industrial | Rural | 45% | 0.8~0.9 | |
| Nanjing | Transportation | Suburban | 40% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| Jiangning Chunhua Subdistrict | Industrial | Rural | 25% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| Jiangning Service Area | Transportation | Suburban | 30% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| 21~30 km | Xiaoqiao Subdistrict | Farm and forestry | Rural | 85% | 0.9~1 |
| Tangquan Subdistrict | Commercial | Rural | 15% | 0.6~0.7 | |
| Xinji Subdistrict | Residential | Rural | 50% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| Jiangning Maritime Division | Industrial | Suburban | 75% | 0.9~1 | |
| Qiaolin Subdistrict | Farm and forestry | Rural | 85% | 0.8~0.9 | |
| Yong-Liu Expressway | Industrial | Rural | 20% | 0.8~0.9 | |
| Chemical Industry Park | Industrial | Rural | 5% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| Guabu Township | Farm and forestry | Rural | 80% | 0.9~1 | |
| Riverside Development Zone | Industrail | Suburban | 30% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| Ning-Ma Expressway | Farm | Rural | 85% | 0.9~1 | |
| Lulang Huatang Village | Farm | Rural | 80% | 0.9~1 | |
| Gongtang Community | Farm | Rural | 90% | 0.9~1 | |
| Zhoutan Resort | Wetland | Rural | 95% | 0.9~1 | |
| Jiangning Taowu Subdistrict | Residential | Rural | 50% | 0.6~0.7 | |
| Jiangning Moling Subdistrict | Industrial | Suburban | 15% | 0.6~0.7 | |
| Tangshan | Farm and forestry | Rural | 80% | 0.9~1 | |
| Shangfeng Township | Farm and forestry | Rural | 80% | 0.8~0.9 | |
| Jiangning Hushu Subdistrict | Industrial | Rural | 25% | 0.8~0.9 | |
| Hushu Village | Residential | Suburban | 50% | 0.5~0.6 | |
| Jiangning Tuqiao Village | Residential | Rural | 80% | 0.8~0.9 | |
| >30 km | Ninghe North Slope | Farm | Rural | 90% | 0.9~1 |
| Ning-Lian Expressway | Farm and forestry | Rural | 90% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| Xingdian Township | Residential | Rural | 60% | 0.5~0.6 | |
| Liuhe Service Area | Transportation | Rural | 30% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| Chengqiao Subdistrict | Residential | Rural | 50% | 0.6~0.7 | |
| Shiqiao Community | Residential | Rural | 30% | 0.5~0.6 | |
| Pingshan Post Office | Residential | Rural | 70% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| North of Chu River Bridge | Wetland | Rural | 90% | 0.9~1 | |
| Pingshan Forest Farm | Forestry | Rural | 95% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| Wujiang Community | Residential | Suburban | 30% | 0.4~0.5 | |
| Babai Township | Residential | Rural | 60% | 0.5~0.6 | |
| Jinniu Lake Scenic Area | Wetland | Rural | 90% | 0.9~1 | |
| Xinhuang Township | Residential | Rural | 60% | 0.5~0.6 | |
| Donggou Township | Residential | Rural | 65% | 0.6~0.7 | |
| Damiao Village | Residential | Rural | 80% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| Hengxi Vegetable Institute | Residential | Rural | 70% | 0.6~0.7 | |
| Jiangning Little Danyang | Residential | Suburban | 40% | 0.5~0.6 | |
| Airport Expressway | Transportation | Rural | 70% | 0.8~0.9 | |
| Hengshan Forest Farm | Forestry | Rural | 90% | 0.7~0.8 | |
| Zhetang | Residential | Rural | 60% | 0.6~0.7 | |
| Jiangning Tongshan Subdistrict | Residential | Suburban | 40% | 0.5~0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, J.-Y.; Lao, H.; Mei, C.; Chen, Y.; He, Y.; Liao, K. Analyzing the Spatial-Temporal Patterns of Urban Heat Islands in Nanjing: The Role of Urbanization and Different Land Uses. Buildings 2025, 15, 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081289
Deng J-Y, Lao H, Mei C, Chen Y, He Y, Liao K. Analyzing the Spatial-Temporal Patterns of Urban Heat Islands in Nanjing: The Role of Urbanization and Different Land Uses. Buildings. 2025; 15(8):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081289
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Ji-Yu, Hua Lao, Chenyang Mei, Yizhen Chen, Yueyang He, and Kaihuai Liao. 2025. "Analyzing the Spatial-Temporal Patterns of Urban Heat Islands in Nanjing: The Role of Urbanization and Different Land Uses" Buildings 15, no. 8: 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081289
APA StyleDeng, J.-Y., Lao, H., Mei, C., Chen, Y., He, Y., & Liao, K. (2025). Analyzing the Spatial-Temporal Patterns of Urban Heat Islands in Nanjing: The Role of Urbanization and Different Land Uses. Buildings, 15(8), 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081289





