A Study on the Mechanical Properties and Performance of Fibrous Rubberized Concrete
Abstract
1. Introduction
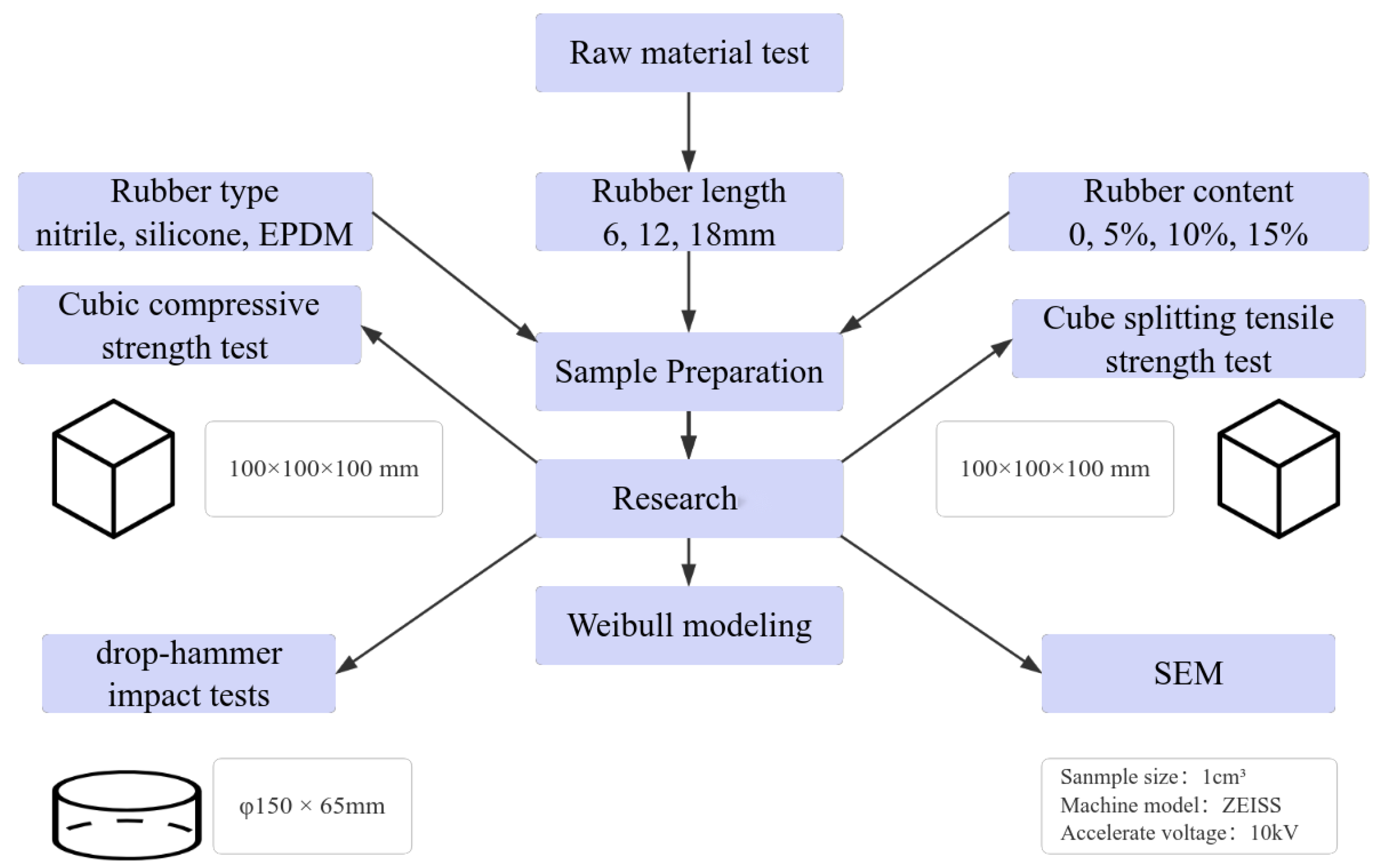
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Raw Materials
2.2. Fibrous Rubber Concrete Sample Preparation
2.3. Test Methods
3. Results
3.1. Static Mechanical Property Analysis
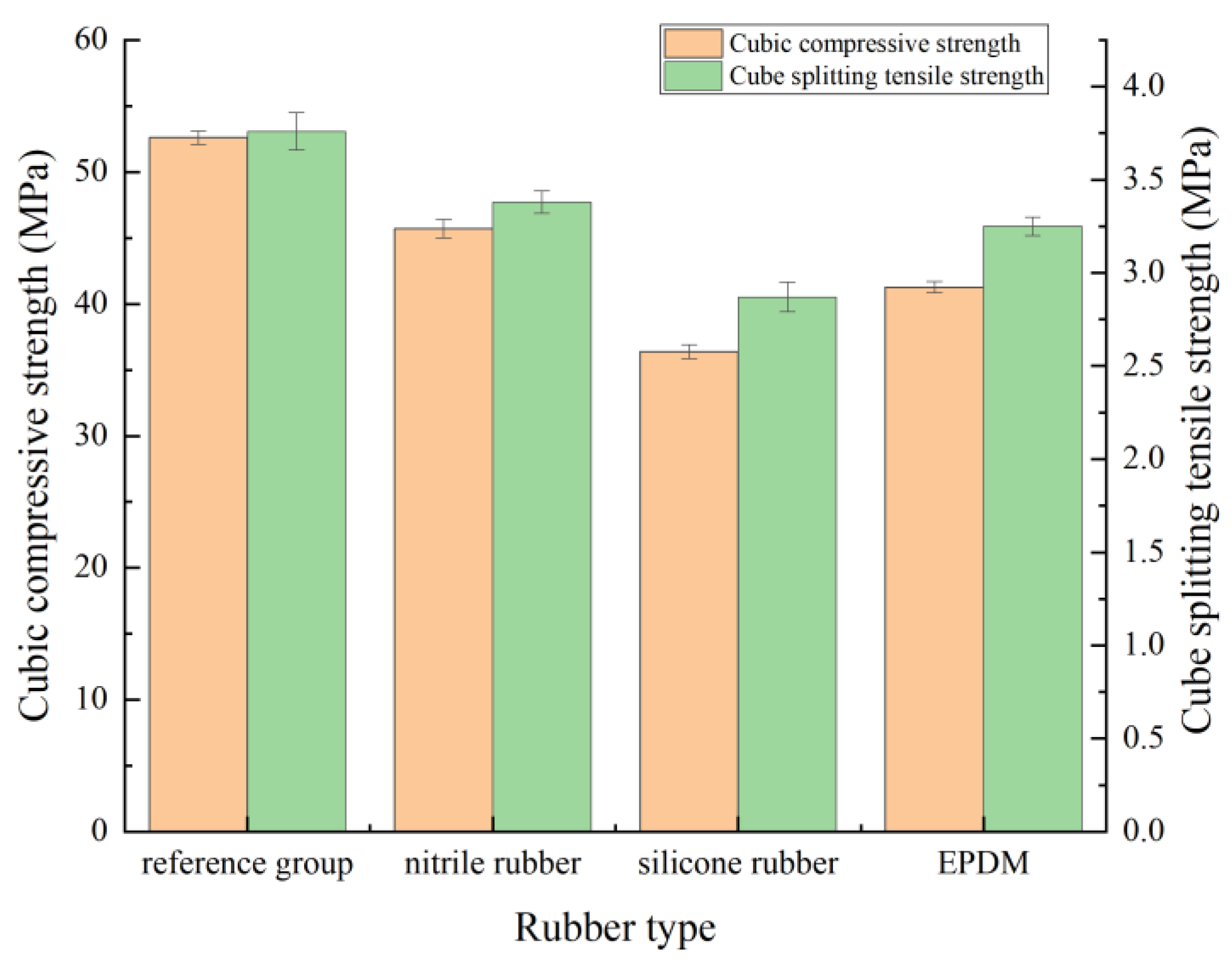
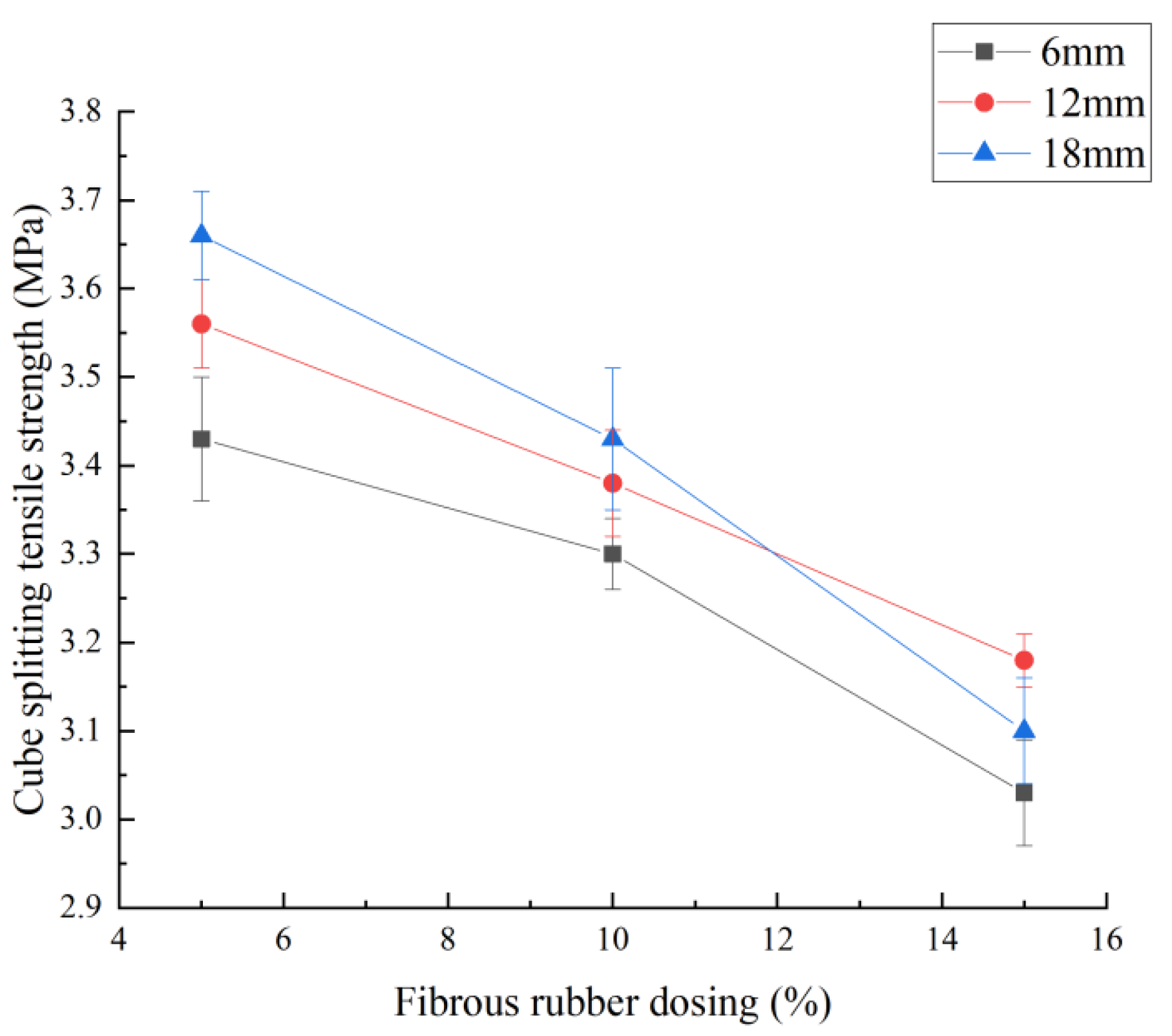
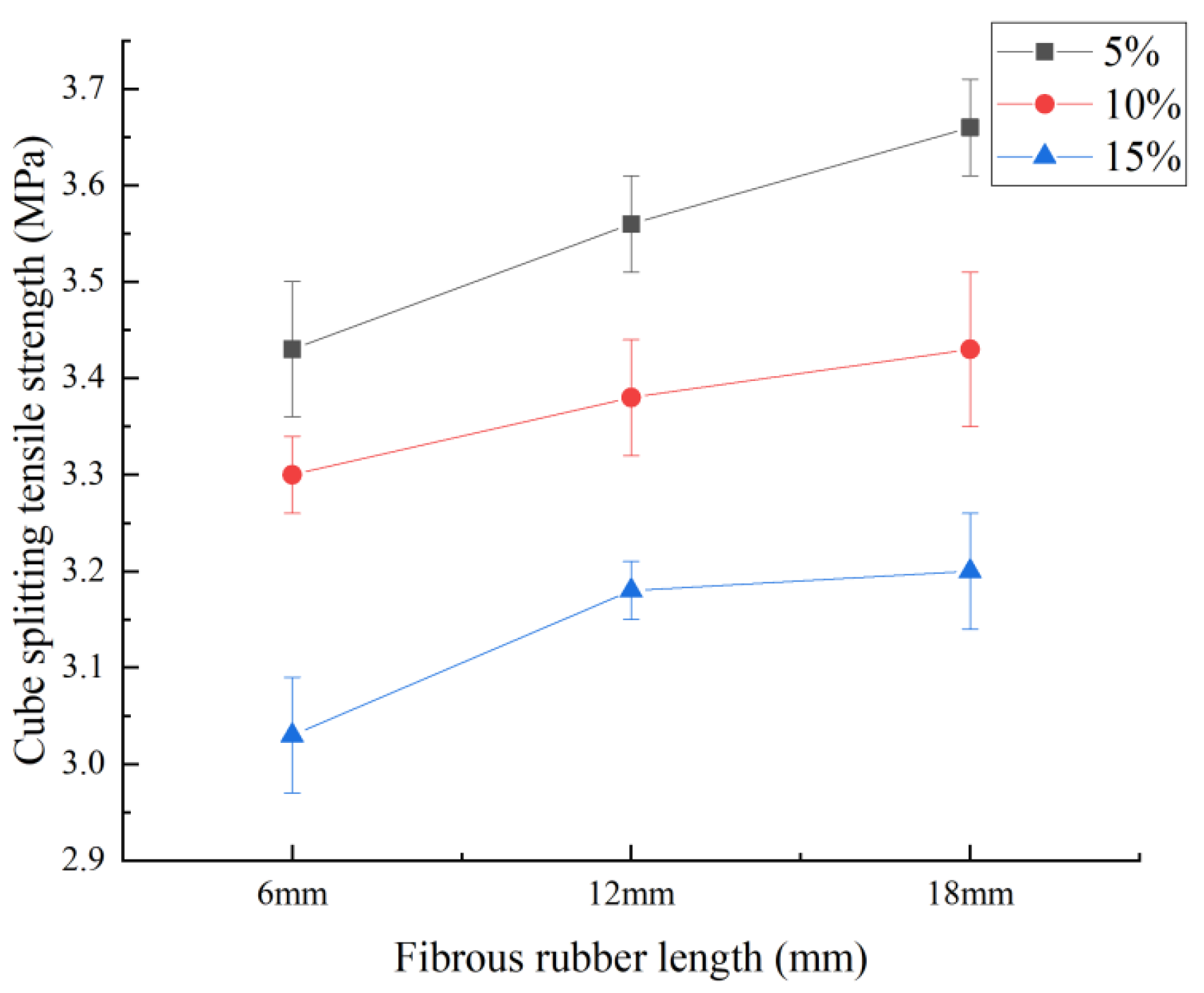
3.1.1. Influence of Rubber Fiber Type
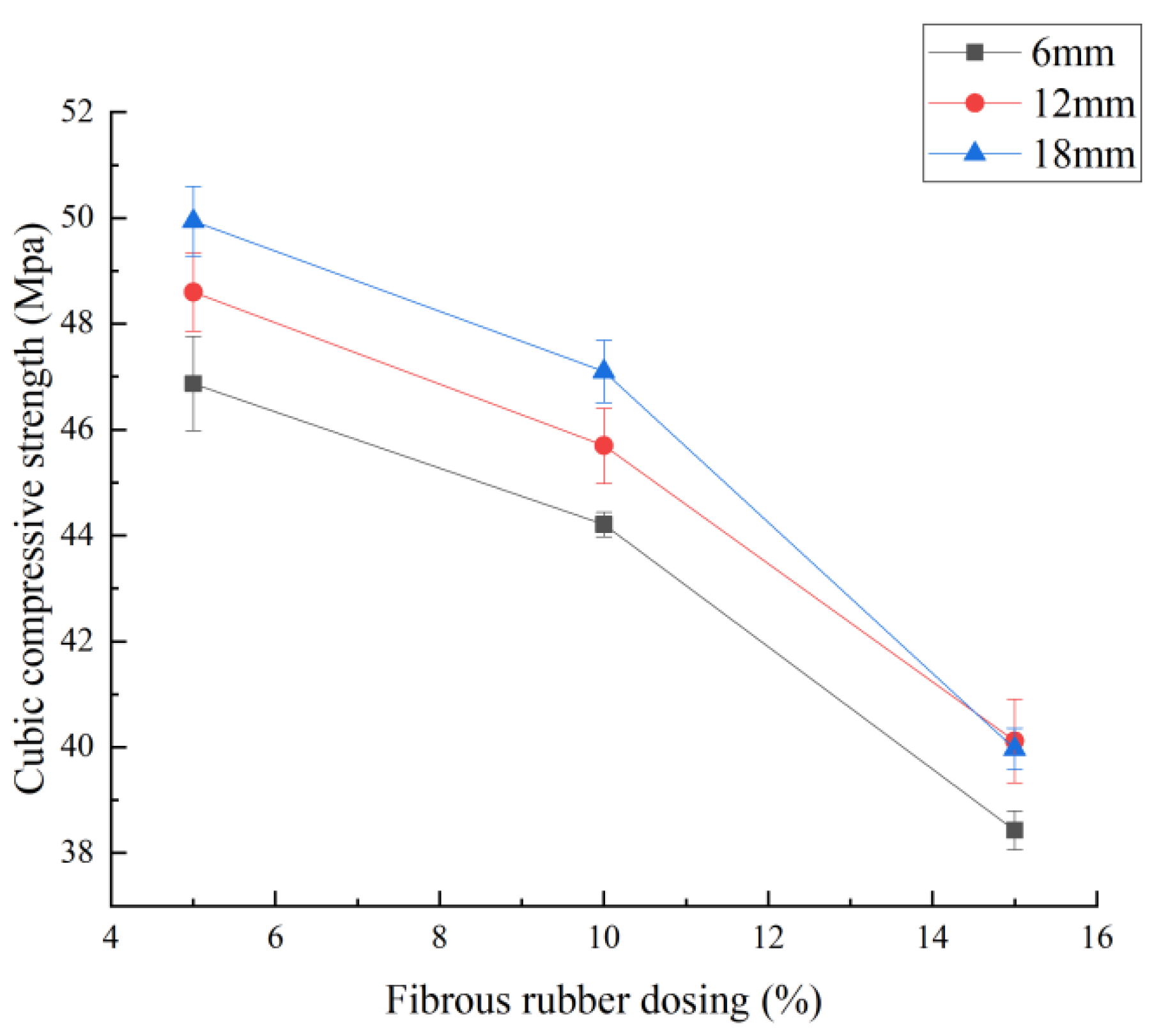
3.1.2. Synergistic Effect of Fibrous Rubber Doping and Length
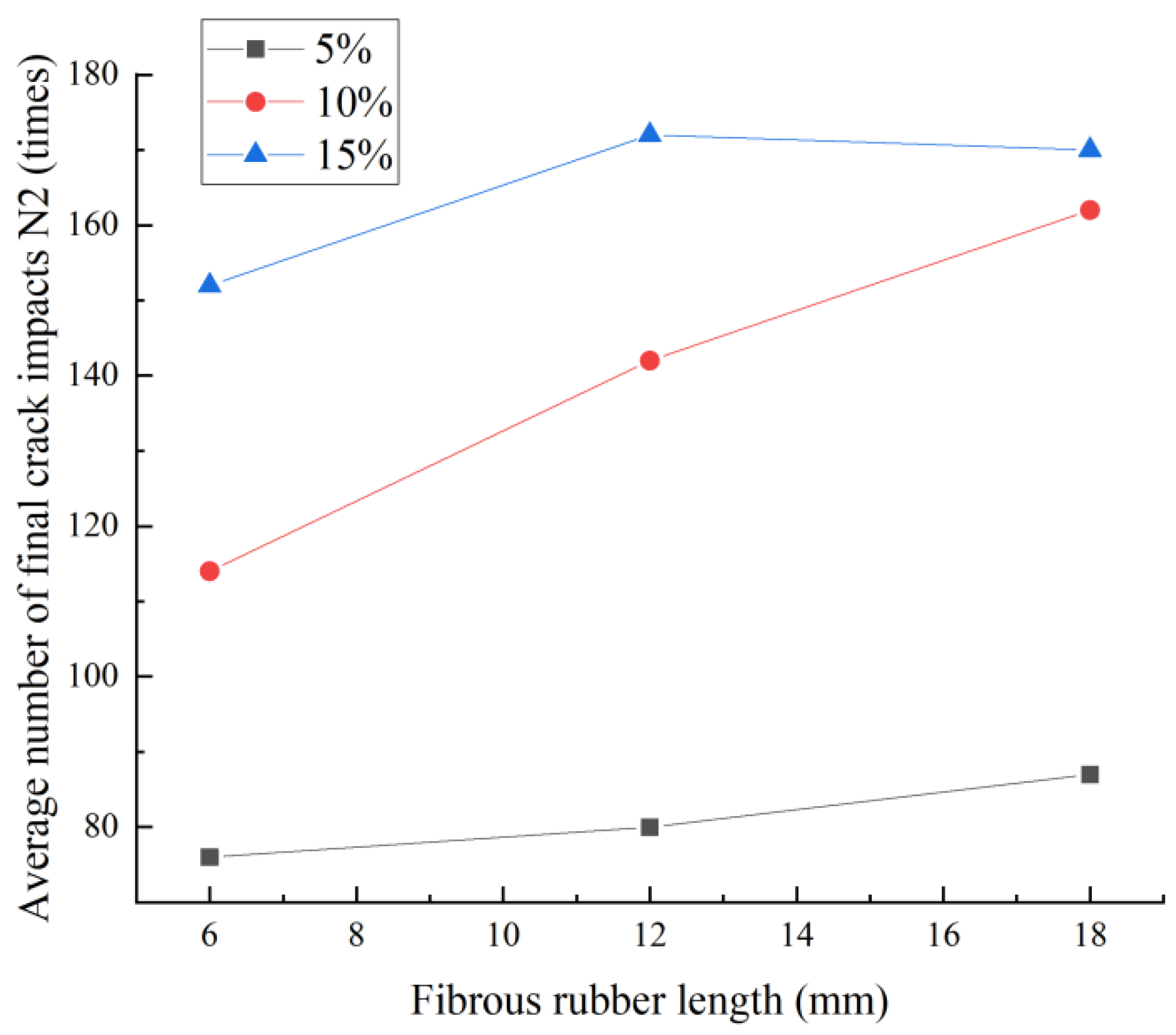
3.2. Impact Resistance
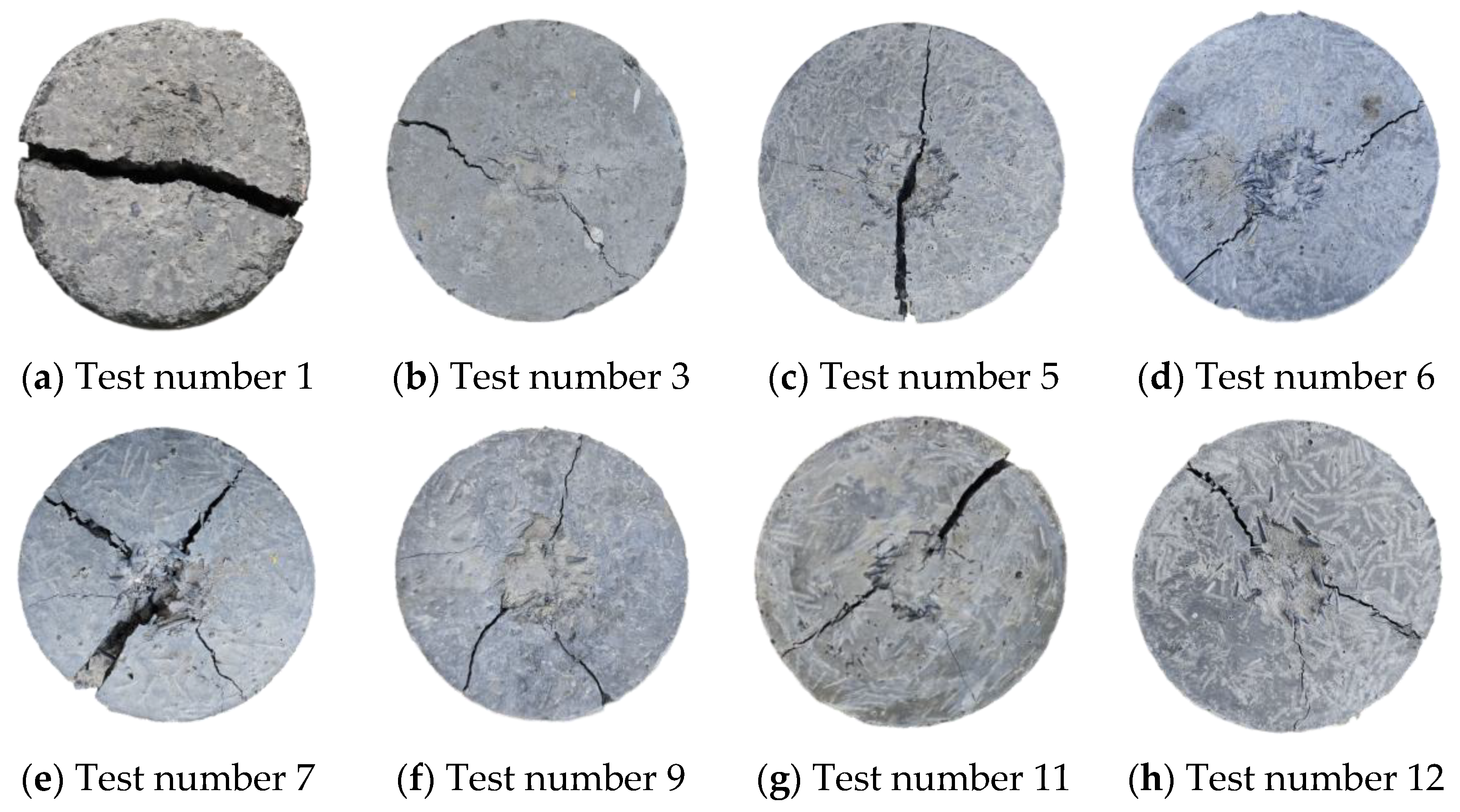
3.3. Macroscopic Enhancement of Fibrous Rubber
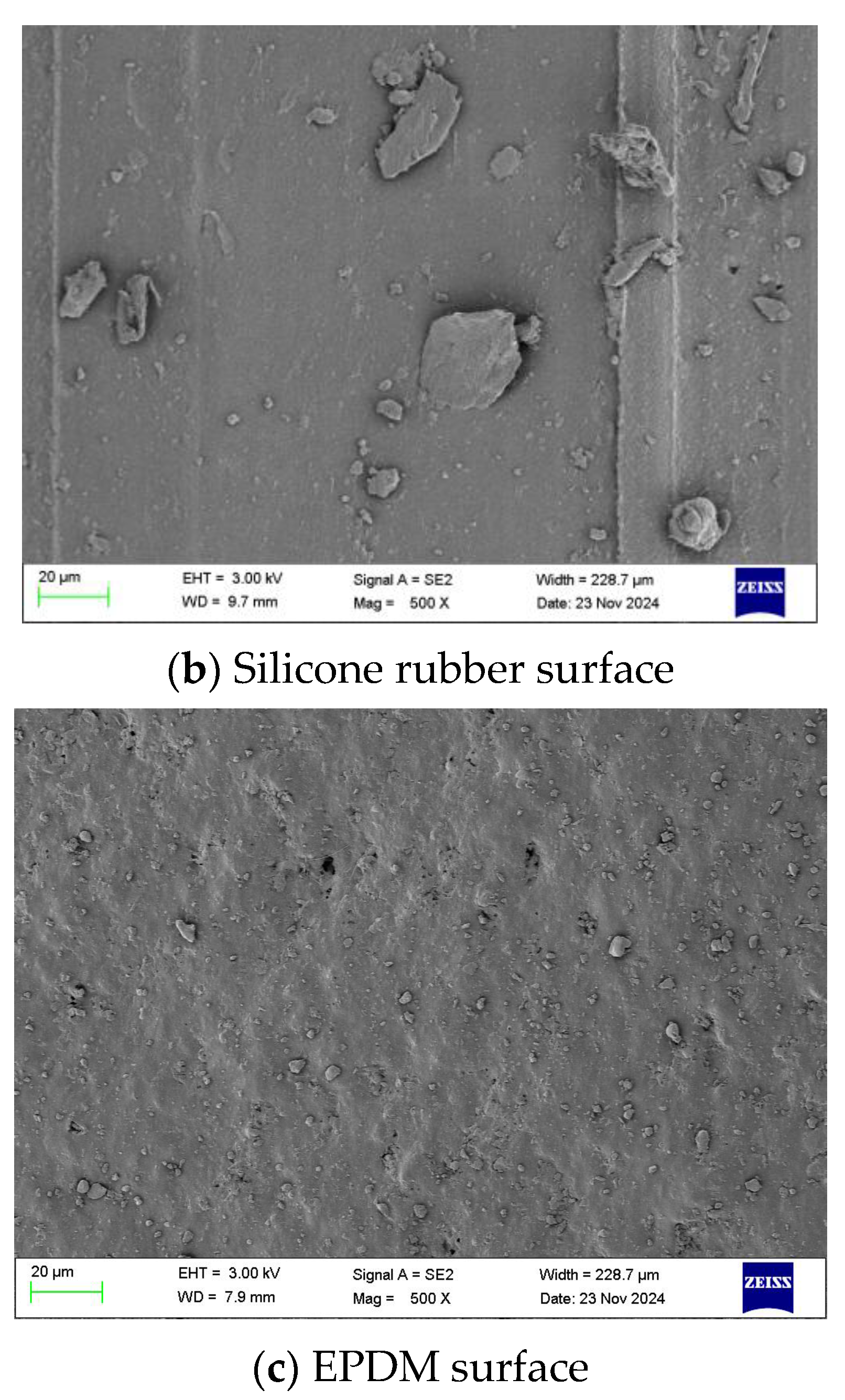
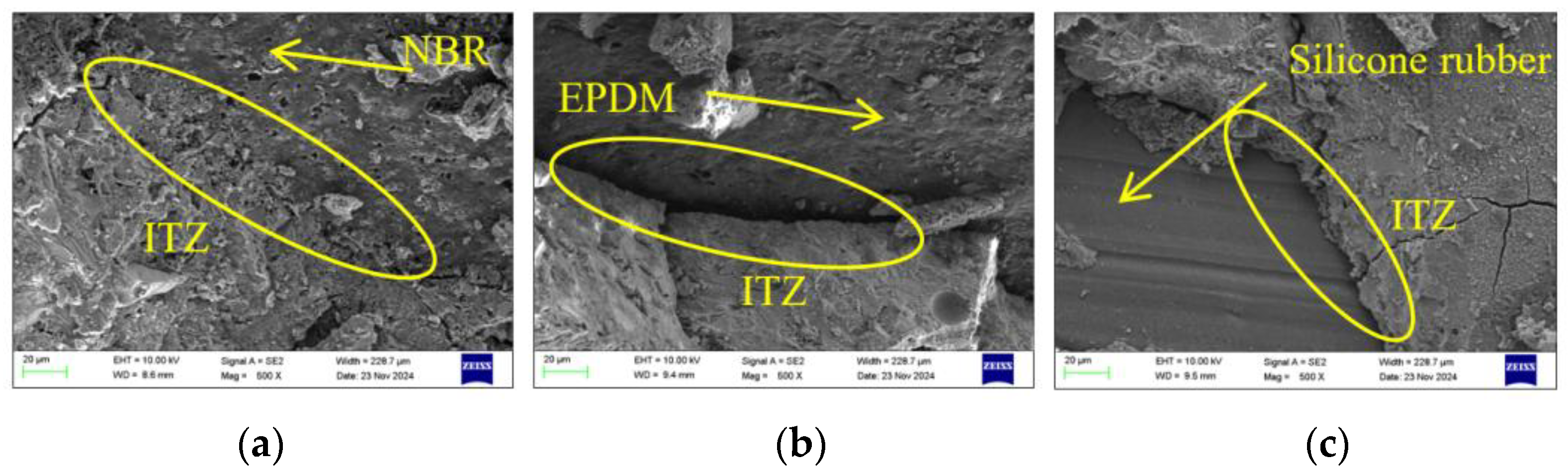
3.4. Impact Strengthening Mechanism and Microstructure Analysis of Fibrous Rubber Concrete
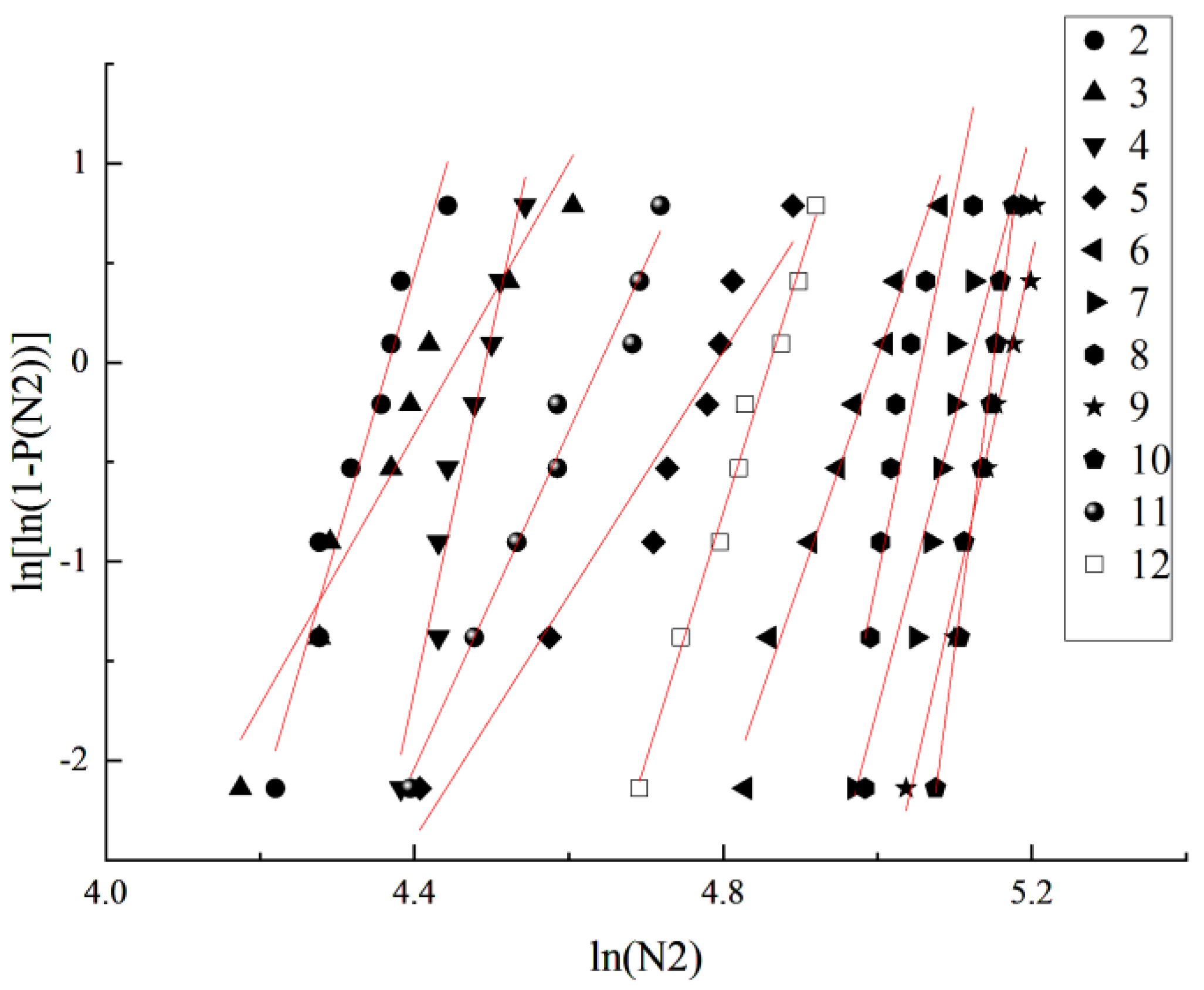
3.5. Impact Life Reliability Analysis of Fibrous Rubberized Concrete
3.5.1. The Weibull Distribution Model
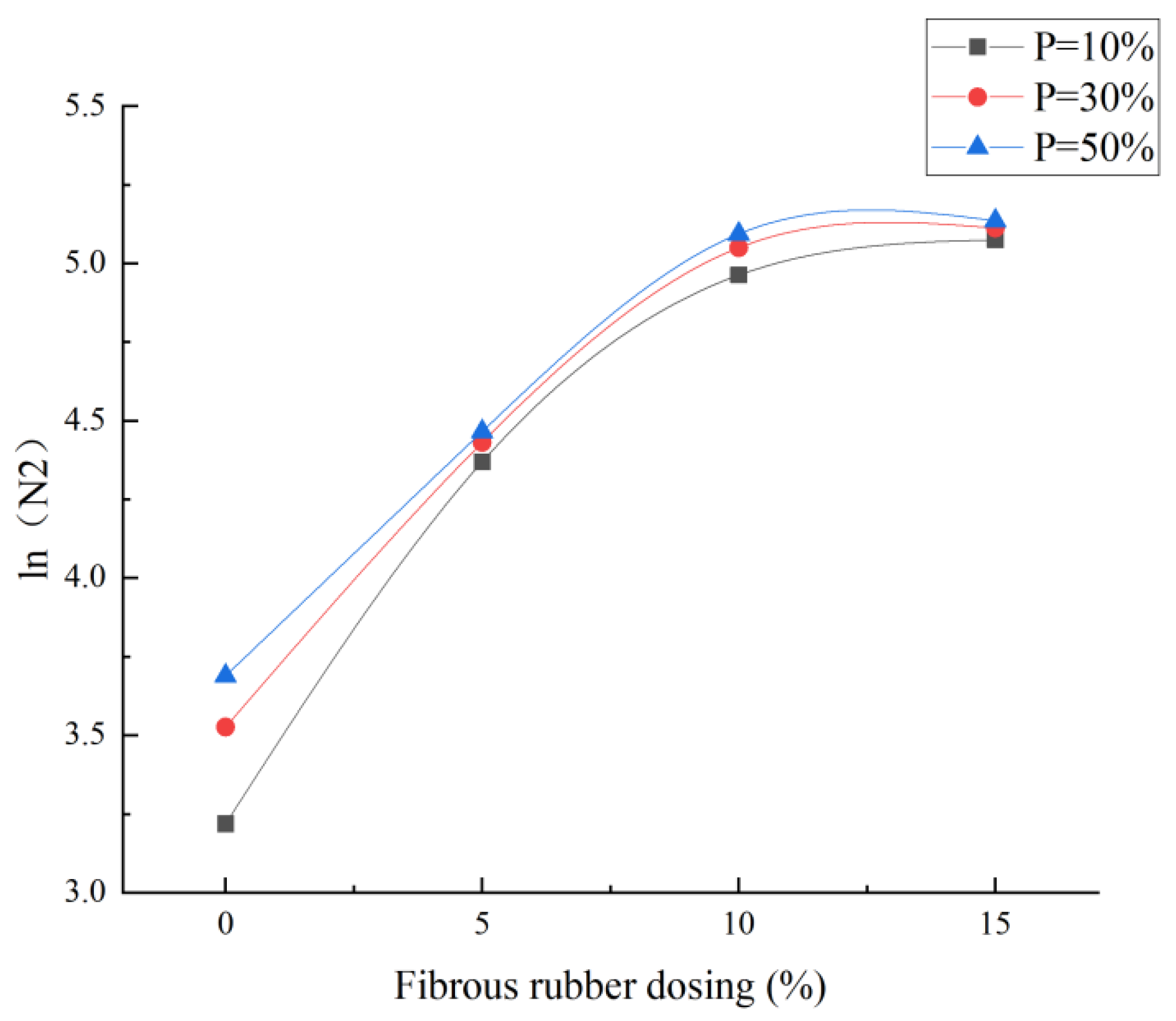
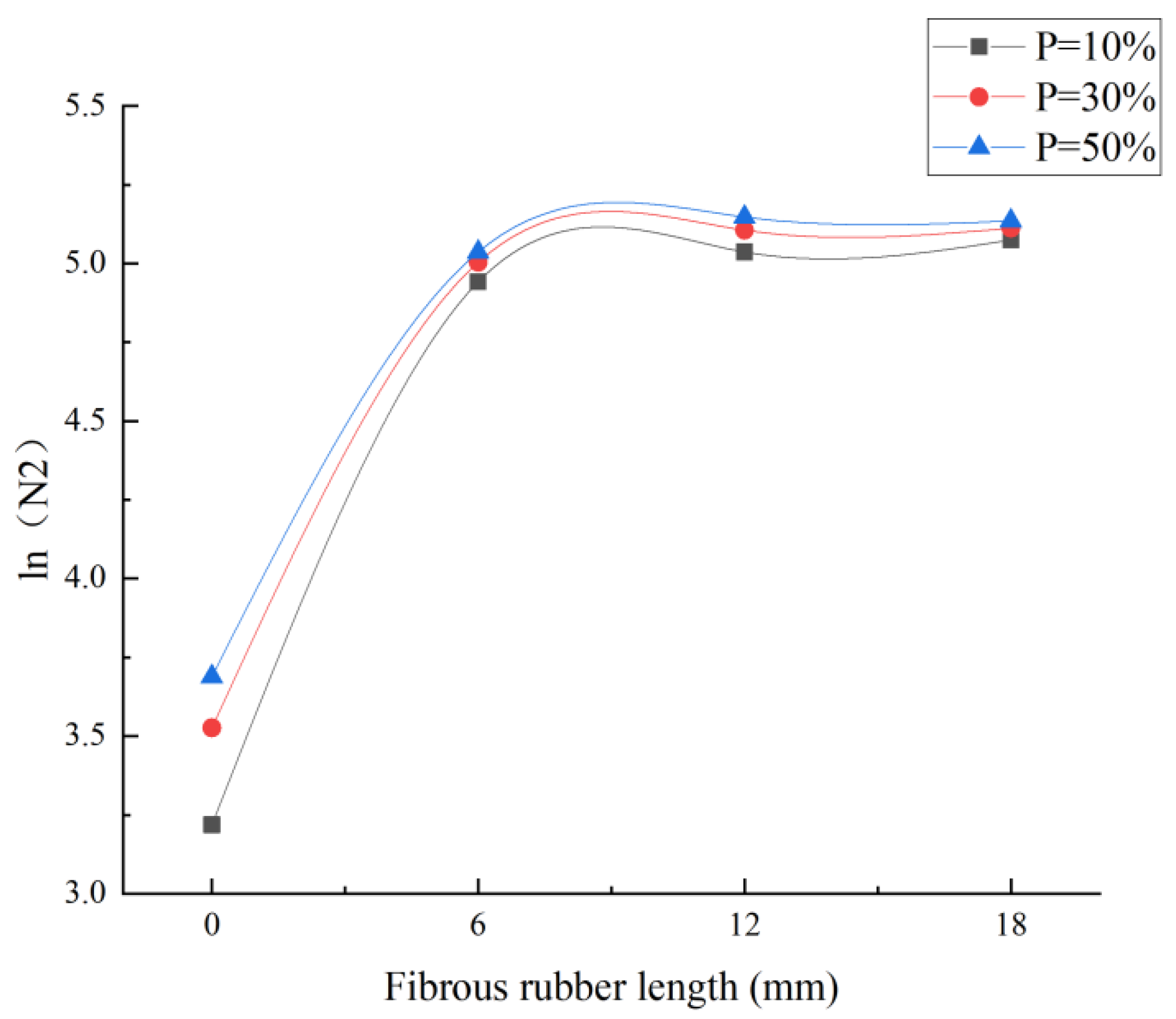
3.5.2. Number of Impacts with Different Failure Probabilities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Correlation between Static Strength and Rubber Type
- 2.
- Fiber Length–Dosage Synergy
- 3.
- Enhanced Impact Resistance Mechanisms
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diaferio, M.; Varona, F.B. Concrete Structures: Latest Advances and Prospects for a Sustainable Future. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, F.; Wang, Y. Application Status and Research Direction of Waste Tire Recycling Technology in China. Recycl. Resour. Circ. Econ. 2021, 14, 27–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bu, C.; Zhu, D.; Liu, L.; Lu, X.; Sun, Y.; Yu, L.; OuYang, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, F. Research progress on rubber concrete properties: A review. J. Rubber Res. 2022, 25, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Ding, J.; Deng, H.; Mosallam, A.S. Mechanical properties, durability, and structural applications of rubber concrete: A state-of-the-art-review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshazly, F.A.; Mustafa, S.A.; Fawzy, H.M. Rubberized concrete properties and its structural engineering applications—An overview. Egypt. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2020, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Fan, L.; Han, Y.; Li, H.; Han, X.; Hao, Q. Damage Study of Rubberized Concrete under Impact Loading. J. Vib. Shock 2019, 38, 73–80. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Murugan, R.B.; Natarajan, C. Investigation on the use of waste tyre crumb rubber in concrete paving blocks. Comput. Concr. 2017, 20, 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, T. Effects of compaction method and rubber content on the properties of concrete paving blocks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najim, K.B.; Hall, M.R. Mechanical and dynamic properties of self-compacting crumb rubber modified concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 27, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, B.; Shui, Z. Experimental study on the performance and microstructure of rubberized lightweight aggregate concrete. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2012, 28, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Guo, X.; Feng, L.; Song, D.; Ji, W. Frost resistance of modified rubberized concrete. People’s Yellow River 2017, 39, 113–116. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K. Study on Impact Resistance and Abrasion Resistance of Basalt Fiber Rubberized Concrete. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi, China, 2022. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, T.; Sharma, R.K.; Chaudhary, S. Impact resistance of concrete containing waste rubber fiber and silica fume. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 83, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Yuan, Q.; Feng, L.; Wang, W.; Zhao, F. Study on impact resistance of rubberized concrete. People’s Yellow River 2018, 40, 107–109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Topcu, I.B.; Avcular, N. Collision behaviours of rubberized concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 38, 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Impact Energy Dissipation of High-Content Rubberized Concrete. Master’s Thesis, Anhui University of Science and Technology, Huainan, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.K.; Hassan, A.; Lachemi, M. Effect of fiber type on impact and abrasion resistance of engineered cementitious composite. ACI Mater. J. 2018, 115, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Cao, P.; Sun, J.; Zhao, Y. Analysis and micro-characterization of compressive strength of basalt fiber reinforced concrete. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2018, 37, 111–120. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Youssf, O.; Mills, J.E.; Hassanli, R. Assessment of the mechanical performance of crumb rubber concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Gao, P.; Li, F.; Ma, A.; Yu, Z. Experimental study on mechanical properties of rubberized concrete with different replacement rates. J. Build. Mater. 2020, 23, 85–92. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- SL/T 325-2020; Hydraulic Concrete Test Procedure. Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- CECS 13:2009; Standard Test Methods for Fiber Concrete. Beijing China Planning Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Wen, Y.; Liu, P. Study on impact resistance of rubberized concrete. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 37, 792–799. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, H. Experimental study and statistical analysis on impact resistance of steel fiber lightweight aggregate concrete. J. Dalian Univ. Technol. 2010, 50, 557–563. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Weibull, W. A statistical distribution function of wide applicability. J. Appl. Mech. 1951, 18, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, S.; Li, Q. Experimental study on bending fatigue life of ultra-high toughness cementitious composites under constant-amplitude fatigue loading. J. Build. Struct. 2012, 33, 119–127. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Oh, B.H. Fatigue life distribution of concrete forvarious stress levels. ACI Mater. J. 1991, 88, 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, T.; Kiani, B.; Shekarchi, M.; Safari, A. Statistical and experimental analysis on the behavior of fiber reinforced concretes subjected to drop weight test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 37, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkadir, I. Nanomaterials in Rubberised Concrete: A Brief Review of Latest Research Trends. Adv. Offshore Struct. Eng. J. 2024, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, R.; Zhao, Y. Mechanical properties test of steel fiber reinforced concrete and its application in pavement construction technology. Sci. Innov. 2025, 230–232. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.S.; Wu, J.C.; Hwang, S.; Sheu, B.C. Assessment of statistical variations in impact resistance of high-strength concrete and high-strength steel fiber-reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraja, M.C.; Nagaraj, T.S.; Basavaraja, S.B. Reproportioning of steel fibre reinforced concrete mixes and their impact resistance. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Density | Specific Surface Area | Standard Consistency Water Consumption | Setting Time (min) | Compression Strength (MPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g/cm3) | (m2/kg) | (%) | Initial setting | Final setting | 3 d | 28 d | 3 d | 28 d |
| 3.13 | 366 | 26.7 | 184 | 237 | 25.7 | 51.5 | 5.6 | 8.6 |
| Element Content | C | O | Ca | Zn | S | Na | Cl | K | Si | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | 66.44 | 17.27 | 6.04 | 0.67 | 0.93 | 0.12 | 3.92 | 0.03 | 4.41 | 0.17 |
| Element Content | C | O | Ca | Zn | S | Na | Cl | K | Si | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | 47.21 | 27.69 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 24.25 | 0.15 |
| Element Content | C | O | Ca | Zn | S | Na | Cl | K | Si | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | 78.16 | 12.45 | 4.74 | 0.84 | 1.55 | 0.73 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 1.11 | 0.16 |
| Test Number | Cement (kg·m−3) | Water (kg·m−3) | Sand (kg·m−3) | Stone (kg·m−3) | Rubber Length (mm) | Rubber Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 475 | 190 | 677.5 | 1016 | — | — |
| 2 | 475 | 190 | 643.6 | 1016 | 6 | 5 |
| 3 | 475 | 190 | 643.6 | 1016 | 12 | 5 |
| 4 | 475 | 190 | 643.6 | 1016 | 18 | 5 |
| 5 | 475 | 190 | 609.8 | 1016 | 6 | 10 |
| 6 | 475 | 190 | 609.8 | 1016 | 12 | 10 |
| 7 | 475 | 190 | 609.8 | 1016 | 18 | 10 |
| 8 | 475 | 190 | 575.9 | 1016 | 6 | 15 |
| 9 | 475 | 190 | 575.9 | 1016 | 12 | 15 |
| 10 | 475 | 190 | 575.9 | 1016 | 18 | 15 |
| 11 | 475 | 190 | 609.8 | 1016 | 12 | 10 |
| 12 | 475 | 190 | 609.8 | 1016 | 12 | 10 |
| Test Number | Rubber Length (mm) | Rubber Doping (%) | Cubic Compressive Strength (MPa) | Relative Value (%) | Cubic Splitting Tensile Strength (MPa) | Relative Value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | — | — | 52.6 | 100 | 3.76 | 100 |
| 2 | 6 | 5 | 46.87 | 89.11 | 3.43 | 91.22 |
| 3 | 12 | 5 | 48.6 | 92.4 | 3.56 | 94.68 |
| 4 | 18 | 5 | 49.94 | 94.94 | 3.66 | 97.34 |
| 5 | 6 | 10 | 44.21 | 84.05 | 3.3 | 87.77 |
| 6 | 12 | 10 | 45.7 | 86.88 | 3.38 | 89.89 |
| 7 | 18 | 10 | 47.1 | 89.54 | 3.43 | 91.22 |
| 8 | 6 | 15 | 38.43 | 73.06 | 3.03 | 80.59 |
| 9 | 12 | 15 | 40.12 | 76.27 | 3.18 | 84.57 |
| 10 | 18 | 15 | 39.97 | 75.99 | 3.1 | 82.45 |
| 11 | 12 | 10 | 36.37 | 69.14 | 2.87 | 76.33 |
| 12 | 12 | 10 | 41.28 | 78.48 | 3.25 | 86.44 |
| Test Number | Number of Impacts | Number of Impacts of a Single Sample in Each Group of Specimens | Average | Impact Work (J) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||||
| 1 | N1 | 31 | 26 | 40 | 34 | 46 | 50 | 33 | 54 | 39 | 775 |
| N2 | 32 | 27 | 40 | 35 | 47 | 51 | 35 | 55 | 40 | 795 | |
| 2 | N1 | 65 | 67 | 60 | 73 | 68 | 75 | 72 | 77 | 70 | 1391 |
| N2 | 72 | 72 | 68 | 79 | 75 | 80 | 78 | 85 | 76 | 1510 | |
| 3 | N1 | 78 | 88 | 62 | 67 | 73 | 69 | 93 | 75 | 75 | 1490 |
| N2 | 83 | 92 | 65 | 73 | 79 | 72 | 100 | 81 | 80 | 1589 | |
| 4 | N1 | 77 | 79 | 82 | 85 | 83 | 73 | 80 | 86 | 81 | 1609 |
| N2 | 84 | 84 | 88 | 91 | 90 | 80 | 85 | 94 | 87 | 1728 | |
| 5 | N1 | 93 | 111 | 77 | 127 | 107 | 116 | 118 | 115 | 110 | 2185 |
| N2 | 97 | 113 | 82 | 133 | 111 | 121 | 123 | 119 | 114 | 2265 | |
| 6 | N1 | 119 | 123 | 138 | 154 | 134 | 145 | 142 | 128 | 135 | 2682 |
| N2 | 125 | 129 | 144 | 161 | 141 | 152 | 150 | 136 | 142 | 2821 | |
| 7 | N1 | 159 | 155 | 172 | 151 | 147 | 134 | 152 | 154 | 153 | 3039 |
| N2 | 168 | 164 | 180 | 159 | 156 | 144 | 161 | 164 | 162 | 3218 | |
| 8 | N1 | 142 | 150 | 146 | 153 | 160 | 141 | 140 | 144 | 146 | 2900 |
| N2 | 149 | 155 | 152 | 158 | 168 | 147 | 146 | 151 | 152 | 3020 | |
| 9 | N1 | 159 | 173 | 147 | 165 | 162 | 169 | 156 | 174 | 164 | 3258 |
| N2 | 166 | 181 | 154 | 173 | 171 | 177 | 164 | 182 | 172 | 3417 | |
| 10 | N1 | 158 | 170 | 153 | 166 | 167 | 159 | 165 | 163 | 163 | 3238 |
| N2 | 165 | 177 | 160 | 174 | 173 | 166 | 170 | 172 | 170 | 3377 | |
| 11 | N1 | 76 | 107 | 103 | 82 | 91 | 102 | 87 | 93 | 93 | 1847 |
| N2 | 81 | 112 | 109 | 88 | 98 | 108 | 93 | 98 | 99 | 1967 | |
| 12 | N1 | 102 | 113 | 109 | 119 | 124 | 129 | 117 | 126 | 118 | 2344 |
| N2 | 109 | 121 | 115 | 125 | 131 | 137 | 124 | 134 | 125 | 2483 | |
| Test Number | α | β | R2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | N2 | N1 | N2 | N1 | N2 | |
| 1 | 3.712 | 3.846 | 14.003 | 14.596 | 0.96 | 0.957 |
| 2 | 11.617 | 13.252 | 49.744 | 57.868 | 0.987 | 0.959 |
| 3 | 6.855 | 6.813 | 30.08 | 30.334 | 0.934 | 0.948 |
| 4 | 17.783 | 17.979 | 78.527 | 80.753 | 0.993 | 0.954 |
| 5 | 5.781 | 6.107 | 27.492 | 29.259 | 0.919 | 0.944 |
| 6 | 10.978 | 11.21 | 54.329 | 56.022 | 0.975 | 0.979 |
| 7 | 13.05 | 14.576 | 66.105 | 74.615 | 0.905 | 0.922 |
| 8 | 19.16 | 18.993 | 96.085 | 96.042 | 0.84 | 0.808 |
| 9 | 16.938 | 17.09 | 86.754 | 88.33 | 0.988 | 0.983 |
| 10 | 27.73 | 28.934 | 141.654 | 149.007 | 0.984 | 0.984 |
| 11 | 8.042 | 8.46 | 36.854 | 39.261 | 0.982 | 0.976 |
| 12 | 12.201 | 12.431 | 58.593 | 60.422 | 0.995 | 0.99 |
| Test Number | 10% | 30% | 50% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | N2 | N1 | N2 | N1 | N2 | |
| 1 | 24 | 25 | 33 | 34 | 39 | 40 |
| 2 | 60 | 66 | 66 | 73 | 70 | 77 |
| 3 | 58 | 62 | 69 | 74 | 76 | 81 |
| 4 | 73 | 79 | 78 | 84 | 81 | 87 |
| 5 | 79 | 83 | 97 | 102 | 109 | 113 |
| 6 | 115 | 121 | 128 | 135 | 136 | 143 |
| 7 | 133 | 143 | 146 | 156 | 154 | 163 |
| 8 | 134 | 140 | 143 | 149 | 148 | 154 |
| 9 | 147 | 154 | 158 | 165 | 164 | 172 |
| 10 | 153 | 160 | 159 | 166 | 163 | 170 |
| 11 | 74 | 79 | 86 | 92 | 93 | 99 |
| 12 | 101 | 108 | 112 | 119 | 118 | 125 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, C. A Study on the Mechanical Properties and Performance of Fibrous Rubberized Concrete. Buildings 2025, 15, 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081245
Li Z, Li S, Jiang C. A Study on the Mechanical Properties and Performance of Fibrous Rubberized Concrete. Buildings. 2025; 15(8):1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081245
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhantao, Shuangxi Li, and Chunmeng Jiang. 2025. "A Study on the Mechanical Properties and Performance of Fibrous Rubberized Concrete" Buildings 15, no. 8: 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081245
APA StyleLi, Z., Li, S., & Jiang, C. (2025). A Study on the Mechanical Properties and Performance of Fibrous Rubberized Concrete. Buildings, 15(8), 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081245






