Combined Effect of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Silica Fume on Mechanical, Physicochemical, and Thermal Properties of Concrete Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Samples
2.3. Testing and Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
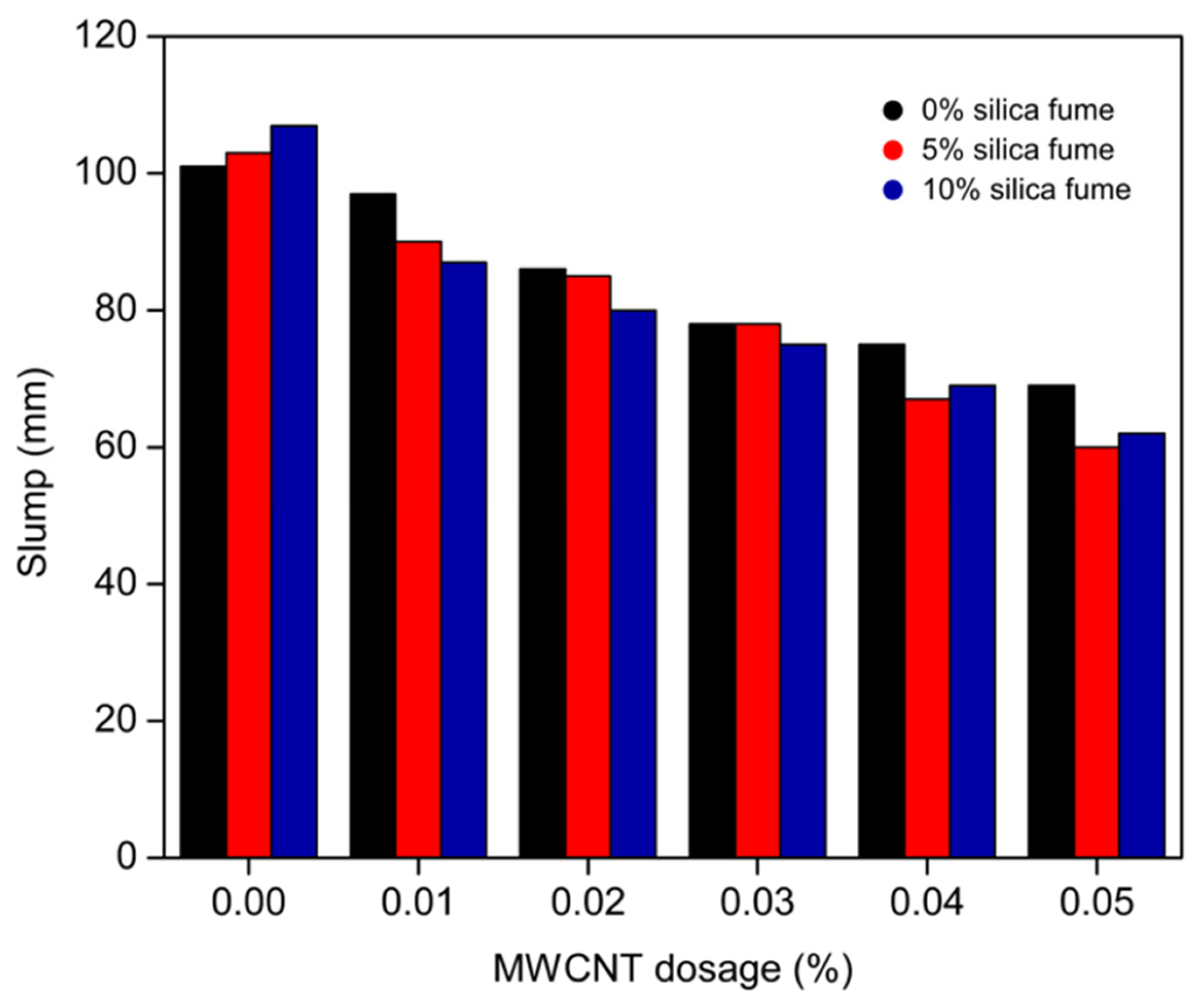
3.1. Workability of the Concrete Mixes
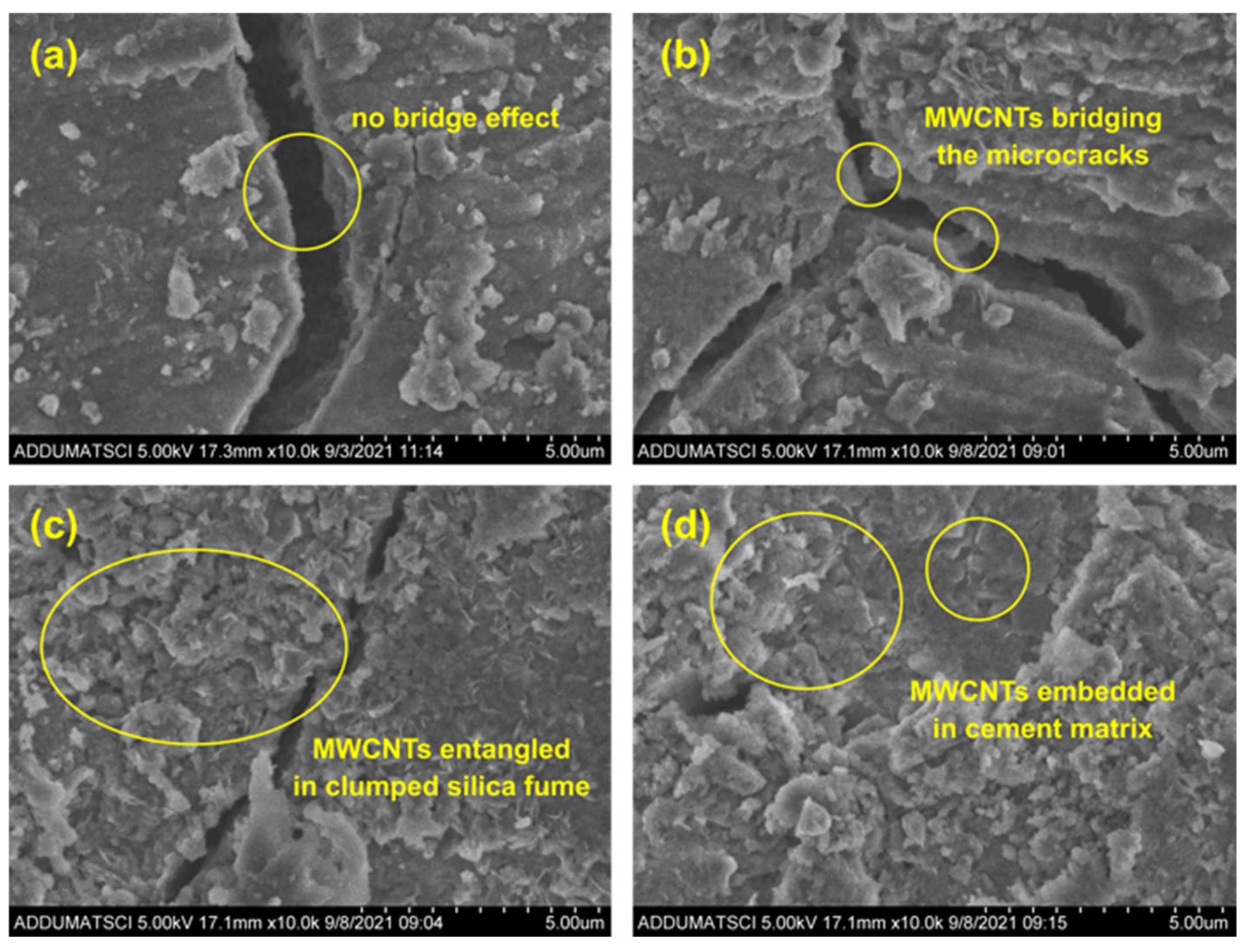
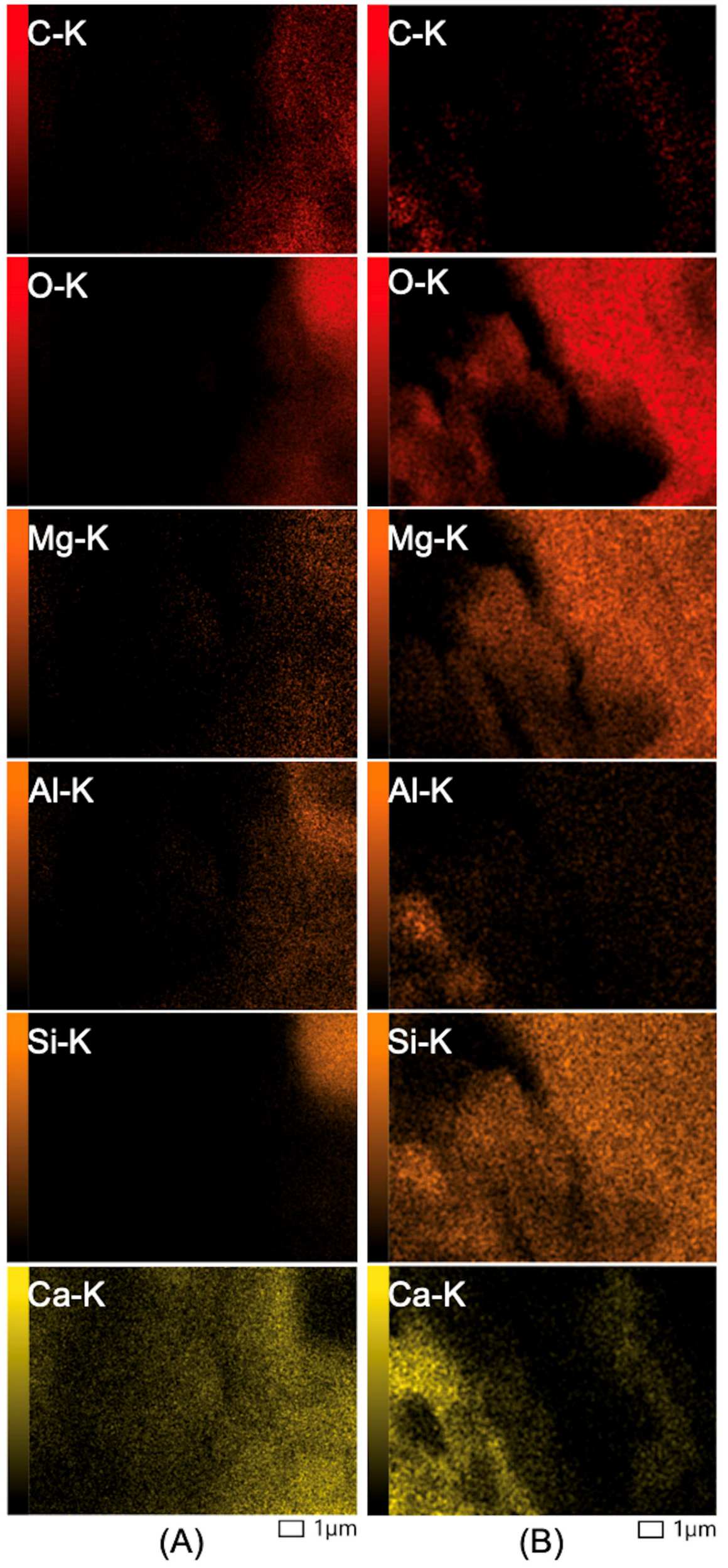
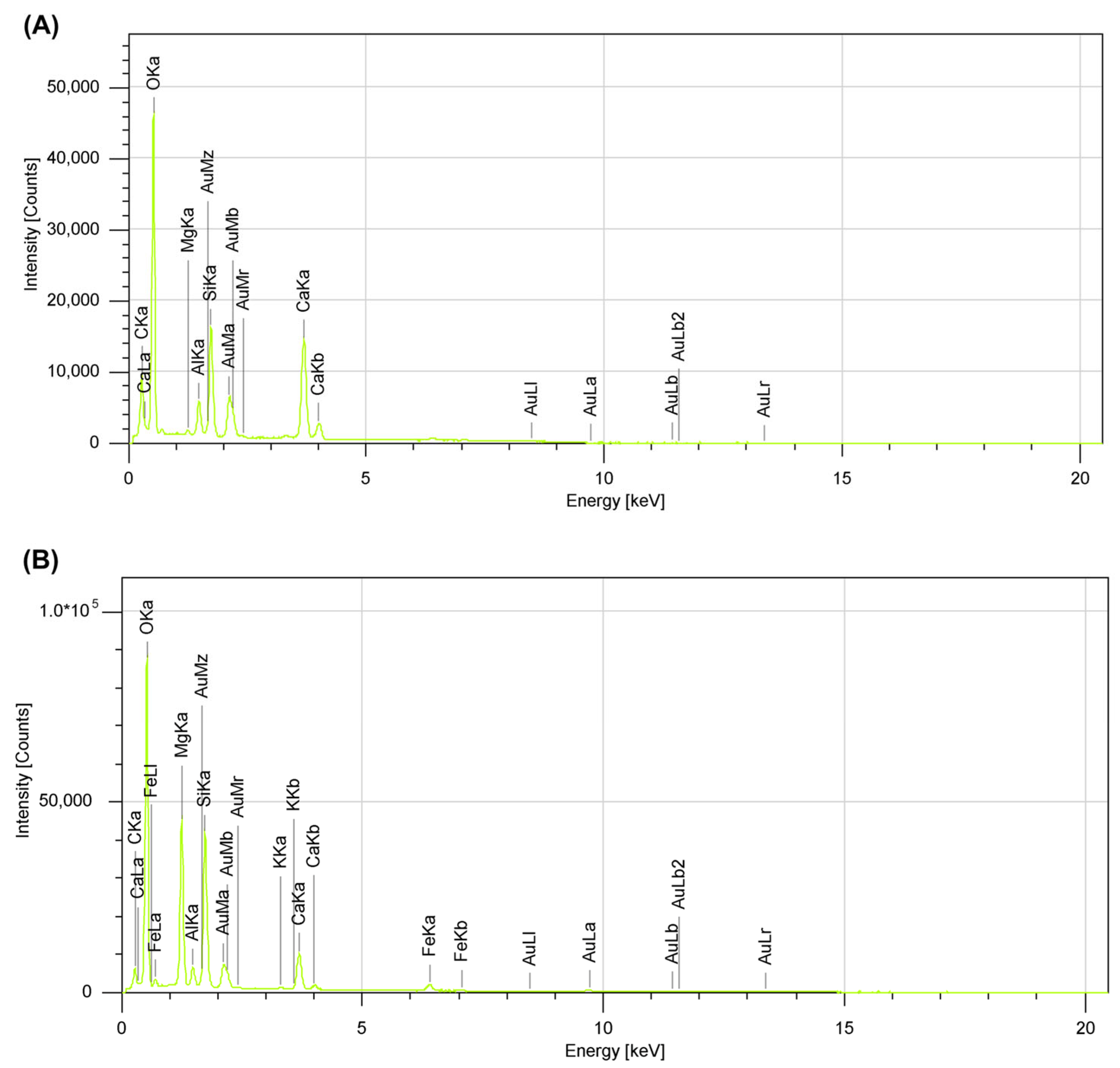
3.2. Microscopy and Morphological Characterization
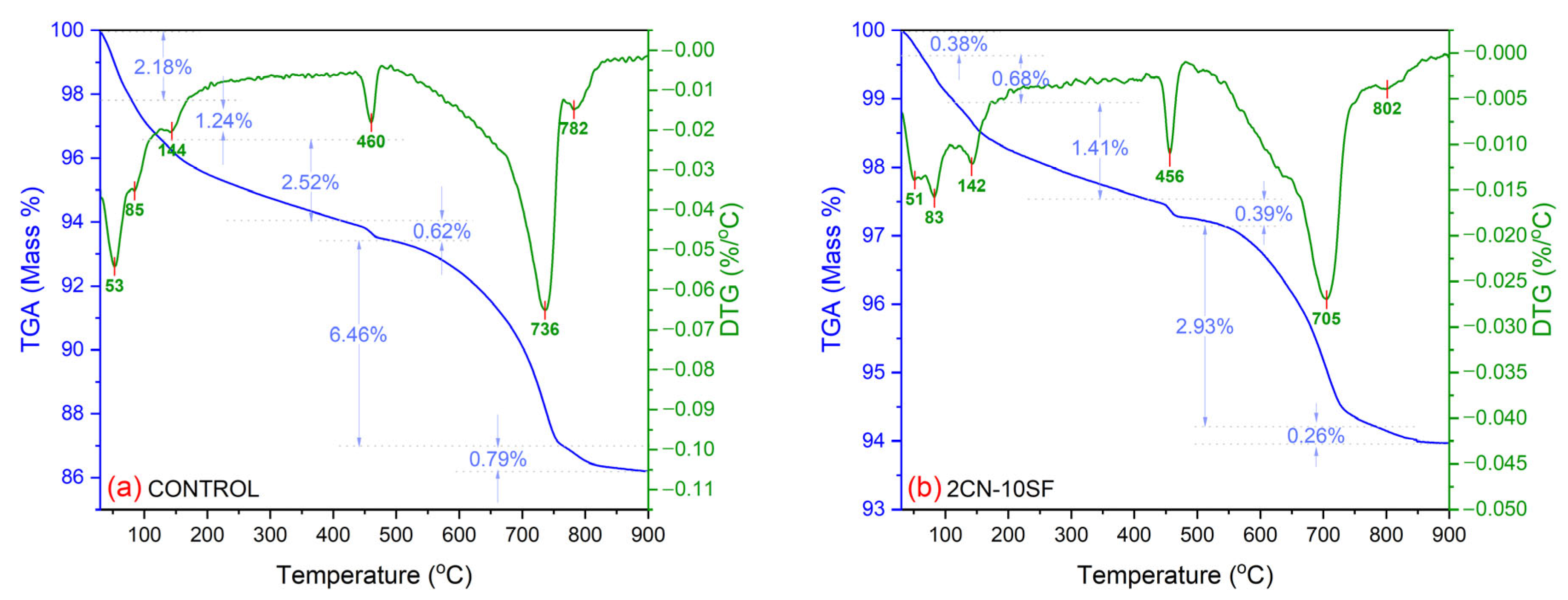
3.3. Thermal Analysis
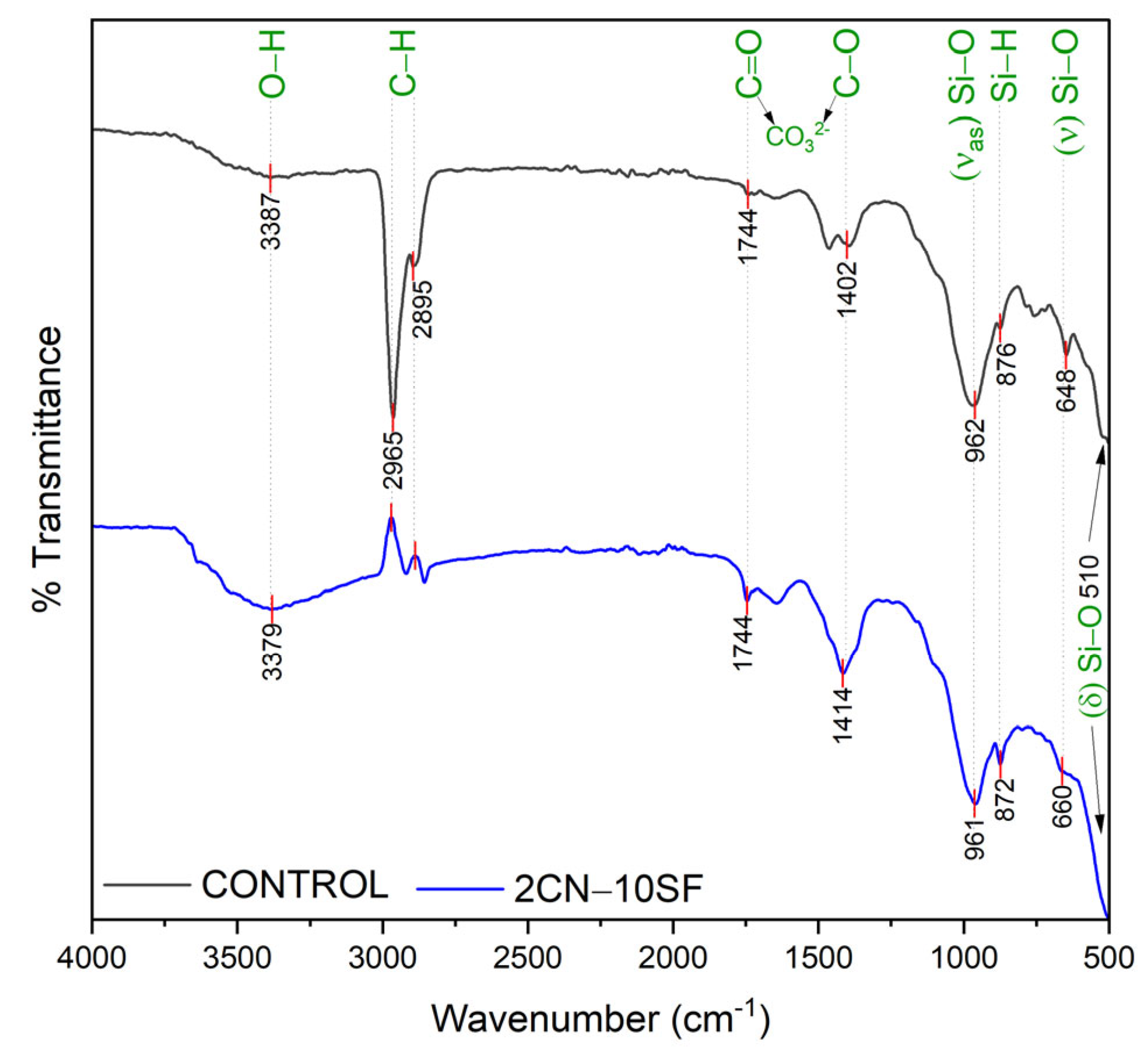
3.4. Chemical Structure Evaluation
3.5. Compressive Strength of the Concrete Mixes
3.6. Environmental Impacts
4. Conclusions
5. Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayanlere, S.; Ajamu, S.; Odeyemi, S.; Ajayi, O.; Kareem, M. Effects of water-cement ratio on bond strength of concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 86, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, T.; Ramaswamy, K.; Saraswathy, B. A review on the effects of chemical admixtures on alkali activated concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metaxa, Z.S.; Tolkou, A.K.; Efstathiou, S.; Rahdar, A.; Favvas, E.P.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. Nanomaterials in Cementitious Composites: An Update. Molecules 2021, 26, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramzi, S.; Hajiloo, H. The Effects of Supplementary Cementitious Materials (SCMs) on the Residual Mechanical Properties of Concrete after Exposure to High Temperatures—Review. Buildings 2022, 13, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Influence of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the multi-scale performance of internally cured concrete containing pre-wetted lightweight aggregate. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 58, 104986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Su, J.; Guo, J.; Hu, S. Influence of carbon nanotube on properties of concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Akono, A.-T. Influence of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the hydration products of ordinary Portland cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 137, 106197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Han, Y.; Zhang, T. Reinforcement of surface-modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes on cement-based composites. Adv. Cem. Res. 2014, 26, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allujami, H.M.; Abdulkareem, M.; Jassam, T.M.; Al-Mansob, R.A.; Ibrahim, A.; Ng, J.L.; Yam, H.C. Mechanical properties of concrete containing recycle concrete aggregates and multi-walled carbon nanotubes under static and dynamic stresses. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.W.; Sheehan, P.E.; Lieber, C.M. Nanobeam Mechanics: Elasticity, Strength, and Toughness of Nanorods and Nanotubes. Science 1997, 277, 1971–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.-F.; Lourie, O.; Dyer, M.J.; Moloni, K.; Kelly, T.F.; Ruoff, R.S. Strength and Breaking Mechanism of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Under Tensile Load. Science 2000, 287, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Metaxa, Z.S.; Shah, S.P. Highly dispersed carbon nanotube reinforced cement based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.S.; Alsayed, S.H.; Aqel, M. Hybrid effect of carbon nanotube and nano-clay on physico-mechanical properties of cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, C.R.; Marcuson, W.F.; Adiguzel, I. Will Supermolecules and Supercomputers Lead to Super Construction Materials? Civ. Eng. Mag. Arch. 2008, 78, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrekabi, S. Experimental investigation on the effect of ultrasonication on dispersion and mechanical performance of multi-wall carbon nanotube-cement mortar composites. Int. J. Civ. Environ. Struct. Constr. Archit. Eng. 2016, 10, 274–298. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Lai, P.; Li, Y.; Yu, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Effect of silica fume-enhanced carbon nanotube dispersion on the strength and damping properties of cement composites. Mater. Express 2020, 10, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kattan, I.M.; Khedr, M.H.; A Farghali, A.; Elsaeidy, M.; Soliman, F.N. Single and combined impact of silica fumes with Functionalized multi-walled carbon Nanotubes and nano silica on performance of cement mortars composites. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1046, p. 012024. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Li, Z. Effects of silica fume and steel fiber on the mechanical properties of high-strength concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 27, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aïtcin, P.-C. High-Performance Concrete, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-138-02943-7. [Google Scholar]
- Republic. Portland Cement Technical Data Sheet. 2019. Available online: https://www.republiccement.com/_files/ugd/3c81d2_daf1f714fadf4731bfe5829809bda4bd.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- US Research Nanomaterials, Inc. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs). Available online: https://www.us-nano.com/nanotubes_graphene (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- U-Chem Industries, Inc. Superflow 3000 Polycarboxylate Base Accelerator Product Data Sheet/Specification Guide. Available online: https://mmuchem.com/admixtures/ (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- ASTM Standard C39/C39M; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021. [CrossRef]
- ASTM Standard C143/C143M; Standard Test Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Cement Concrete. Slump Test of Concrete, slump cone for Workability—Procedure, Apparatus. Civil Engineering Home for Civil Engineers. Available online: https://cementconcrete.org/concrete/concrete-slump-test/2171 (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- Zhang, W.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, F.; Wu, P.; Xu, G.; Gao, Y. Investigating the influence of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the mechanical and damping properties of ultra-high performance concrete. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2020, 27, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Jing, H.; Gao, Y.; Su, H.; Fang, H. Carbon nanomaterials enhanced cement-based composites: Advances and challenges. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogler, N.; Drabetzki, P.; Lindemann, M.; Kühne, H.-C. Description of the concrete carbonation process with adjusted depth-resolved thermogravimetric analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 6167–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nochaiya, T.; Sekine, Y.; Choopun, S.; Chaipanich, A. Microstructure, characterizations, functionality and compressive strength of cement-based materials using zinc oxide nanoparticles as an additive. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 630, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.S. Thermal Stability. In Clay-Containing Polymer Nanocomposites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozanikohan, G.; Abarghooei, M.N. The Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis for the clay mineralogy studies in a clastic reservoir. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2022, 12, 2093–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguer, R.; Lima, V.; Estolano, A.; Póvoas, Y.; Lima, N. The role of hydrogen bonds on the mechanical properties of cement-based mortars applied to concrete surfaces. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 115, 103848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqi, A.; Abbas, N.; Zahra, N.; Hussain, A.; Shabbir, S.Q. Effect of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) on the strength development of cementitious materials. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, J.; Li, Q. Mechanical properties and microstructure of multi-walled carbon nanotube-reinforced cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 76, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, R.; Mehta, A. Effect of carbon nanotubes on properties of cement mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, R. Utilization of silica fume in concrete: Review of hardened properties. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Constituent | OPC (Mass%) | Silica Fume (Mass%) |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 21.9 | 93.0 |
| Al2O3 | 4.9 | 0.4 |
| Fe2O3 | 3.7 | 0.5 |
| CaO | 62.3 | 0.7 |
| MgO | 2.0 | 0.5 |
| K2O | 0.5 | 0.8 |
| Na2O | 0.3 | – |
| SO3 | 2.2 | – |
| Loss on ignition (LOI) | 1.78 | 1.5 |
| Sum | 99.5 | 97.4 |
| Element | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| C | 97.58 |
| Al | 0.19 |
| Cl | 0.58 |
| Co | 1.01 |
| S | 0.24 |
| Mn | 0.33 |
| O | 0.13 |
| Property | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Purity | >95% (carbon nanotubes) >97% (carbon content) |
| Outside diameter | <7 nm |
| Inside diameter | 2–5 nm |
| Length | 10–30 µm |
| SSA | >500 m2/g |
| Color | black |
| Ash | <1.5 wt.% |
| Electrical conductivity | >100 s/cm |
| Tap density | 0.27 g/cm3 |
| True density | ~2.1 g/cm3 |
| Property | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Visual appearance | Pale brown viscous liquid |
| Density (23 °C) | 1.12 ± 0.2 kg/L |
| pH (23 °C) | 9.0 ± 0.5 |
| Solid content (%) | No crystallization |
| Stability (0 °C, 24 h) | ≤0.10 |
| Na2SO4 (%) Na2O + 0.658 K2O (%) | ≤4.0 |
| Mixture | Sample | Cement | Sand | Gravel | Water | Superplasticizer | MWCNT | Silica Fume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CONTROL | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.000 | 0.0000 | 0.00 |
| 2 | 1CN-0SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0001 | 0.00 |
| 3 | 2CN-0SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0002 | 0.00 |
| 4 | 3CN-0SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0003 | 0.00 |
| 5 | 4CN-0SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0004 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 5CN-0SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0005 | 0.00 |
| 7 | 0CN-5SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0000 | 0.05 |
| 8 | 1CN-5SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0001 | 0.05 |
| 9 | 2CN-5SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0002 | 0.05 |
| 10 | 3CN-5SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0003 | 0.05 |
| 11 | 4CN-5SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0004 | 0.05 |
| 12 | 5CN-5SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0005 | 0.05 |
| 13 | 0CN-10SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0000 | 0.10 |
| 14 | 1CN-10SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0001 | 0.10 |
| 15 | 2CN-10SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0002 | 0.10 |
| 16 | 3CN-10SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0003 | 0.10 |
| 17 | 4CN-10SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0004 | 0.10 |
| 18 | 5CN-10SF | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.0005 | 0.10 |
| Element | Line | CONTROL | 2CN-10SF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (%) | Atomic (%) | Weight (%) | Atomic (%) | ||
| C | K | 7.80 | 13.57 | 7.08 | 11.48 |
| O | K | 45.38 | 59.30 | 48.65 | 59.23 |
| Si | K | 8.54 | 6.36 | 15.04 | 10.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cea, E.J.C.; Omisol, C.J.M.; Tuble, K.A.Q.; Bongabong, A.G.; Aguinid, B.J.M.; Asequia, D.M.A.; Erjeno, D.J.D.; Ahalajal, M.A.N.; Maravillas, F.P.; Cavero, A.I.; et al. Combined Effect of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Silica Fume on Mechanical, Physicochemical, and Thermal Properties of Concrete Composites. Buildings 2025, 15, 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071087
Cea EJC, Omisol CJM, Tuble KAQ, Bongabong AG, Aguinid BJM, Asequia DMA, Erjeno DJD, Ahalajal MAN, Maravillas FP, Cavero AI, et al. Combined Effect of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Silica Fume on Mechanical, Physicochemical, and Thermal Properties of Concrete Composites. Buildings. 2025; 15(7):1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071087
Chicago/Turabian StyleCea, Evalyn Joy C., Christine Joy M. Omisol, Kent Andrew Q. Tuble, Ariel G. Bongabong, Blessy Joy M. Aguinid, Dan Michael A. Asequia, Daisy Jane D. Erjeno, Mary Ann N. Ahalajal, Felrose P. Maravillas, Applegen I. Cavero, and et al. 2025. "Combined Effect of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Silica Fume on Mechanical, Physicochemical, and Thermal Properties of Concrete Composites" Buildings 15, no. 7: 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071087
APA StyleCea, E. J. C., Omisol, C. J. M., Tuble, K. A. Q., Bongabong, A. G., Aguinid, B. J. M., Asequia, D. M. A., Erjeno, D. J. D., Ahalajal, M. A. N., Maravillas, F. P., Cavero, A. I., Dumancas, G. G., Malaluan, R. M., & Lubguban, A. A. (2025). Combined Effect of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Silica Fume on Mechanical, Physicochemical, and Thermal Properties of Concrete Composites. Buildings, 15(7), 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071087








