A Numerical Study on the Utilization of Small-Scale Model Testing for Slope Stability Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
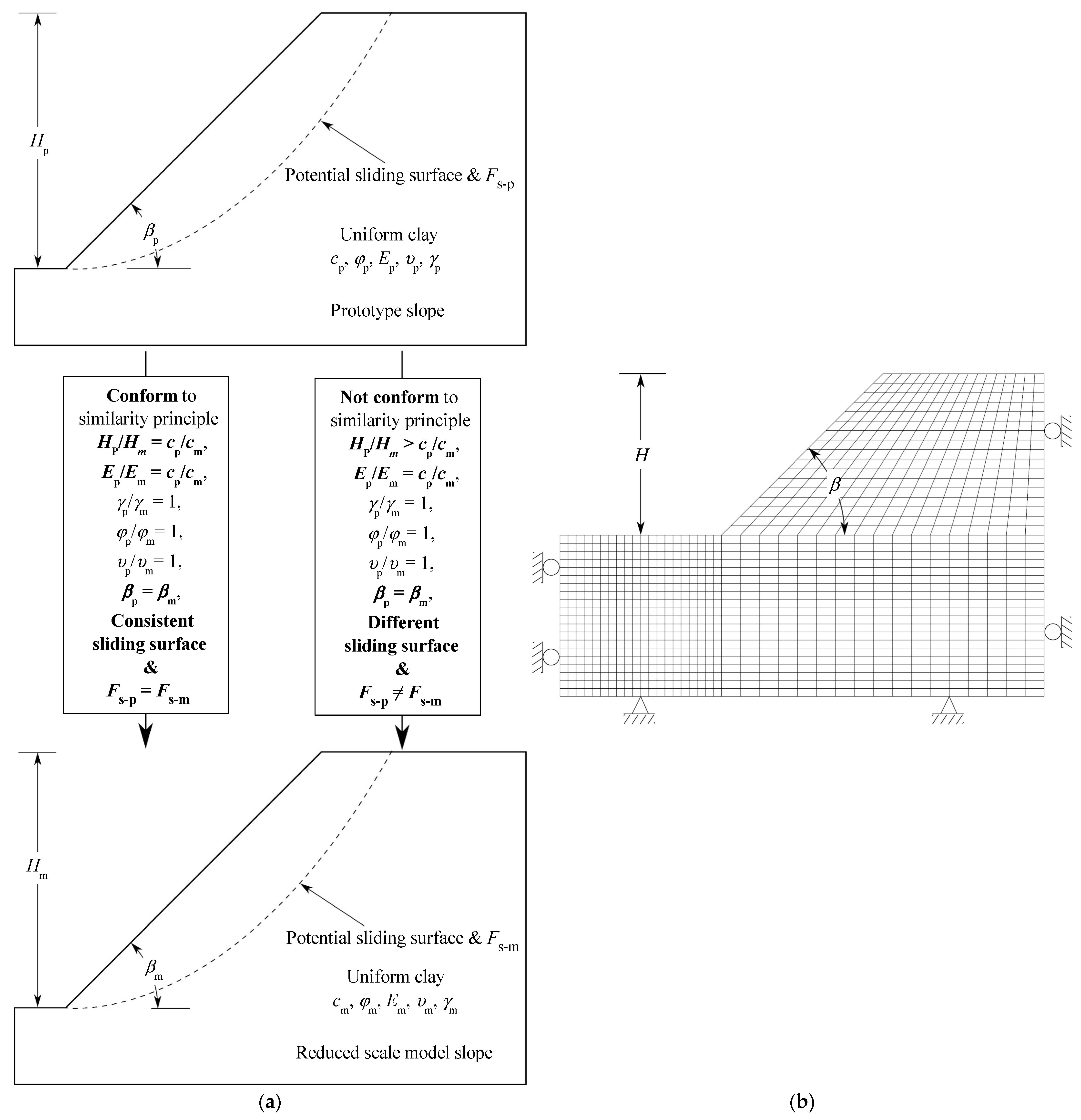
1.1. Reduced Scale Model Test
1.2. Previous Work
1.3. Objective of Present Study
2. Parametric Study Set Up
2.1. Finite Element Model
2.2. Material Model and Parameters
2.3. Conversion Coefficients
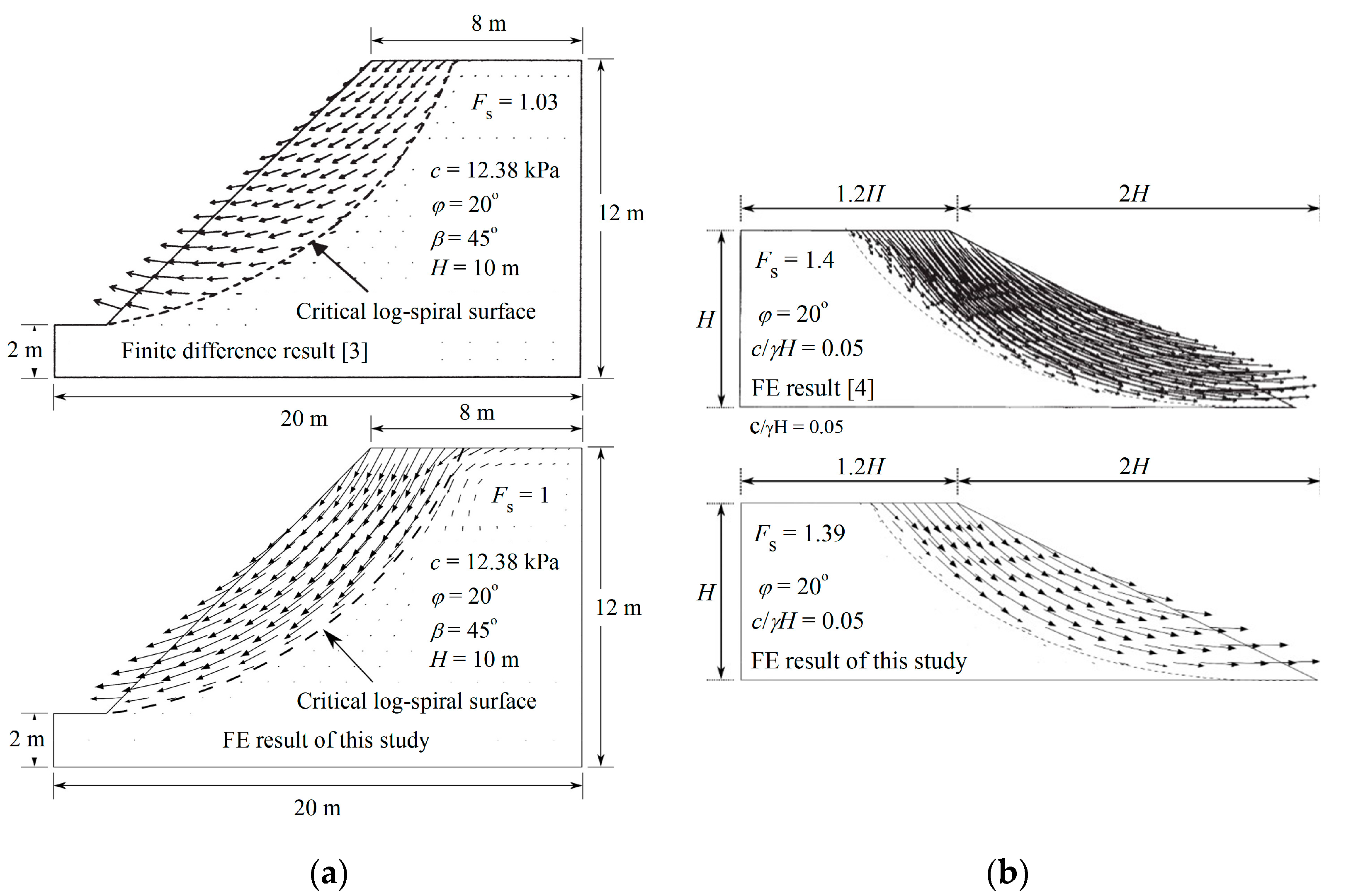
3. Validation of FE Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
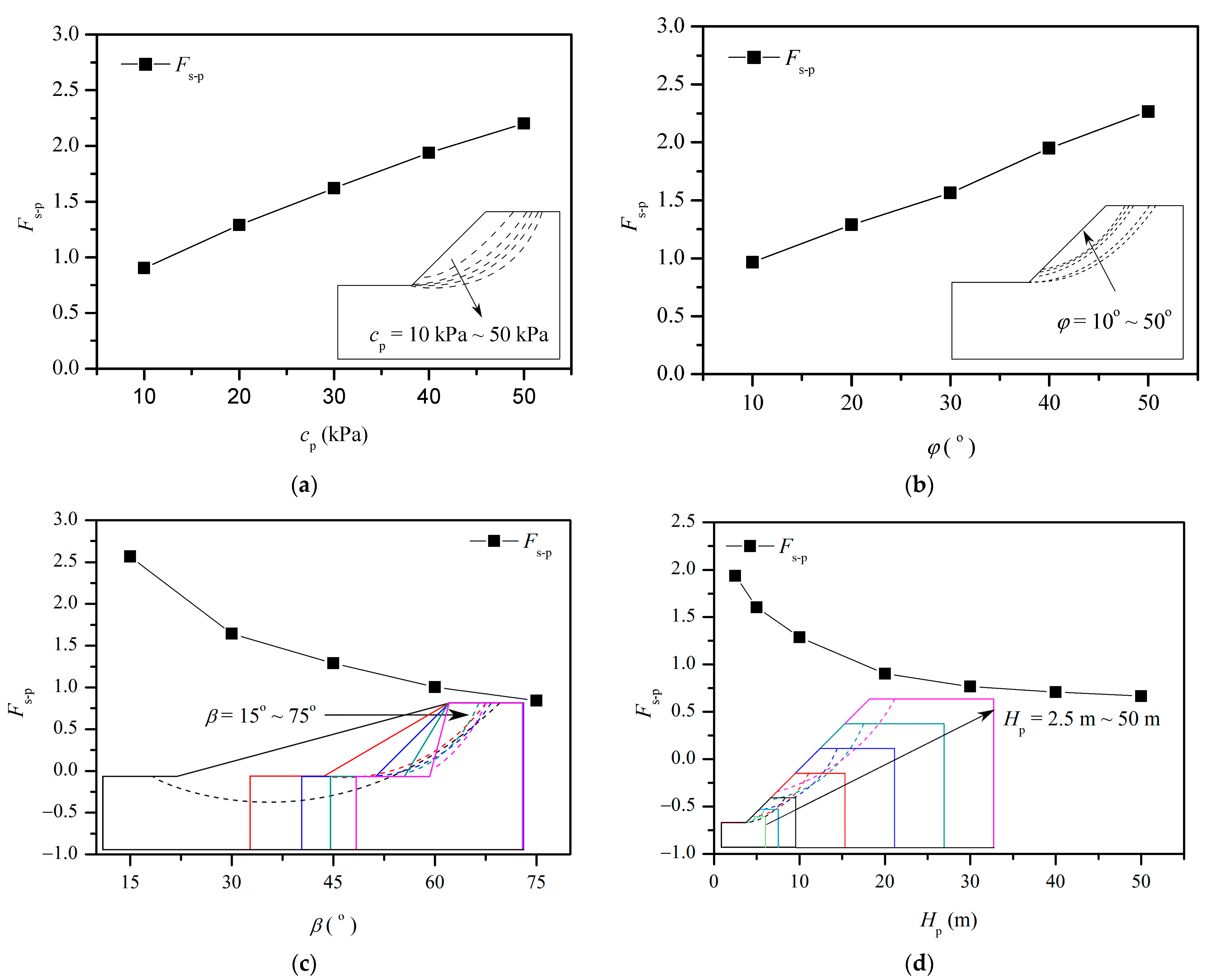
4.1. Effects of Four Influencing Factors on Prototype Slopes
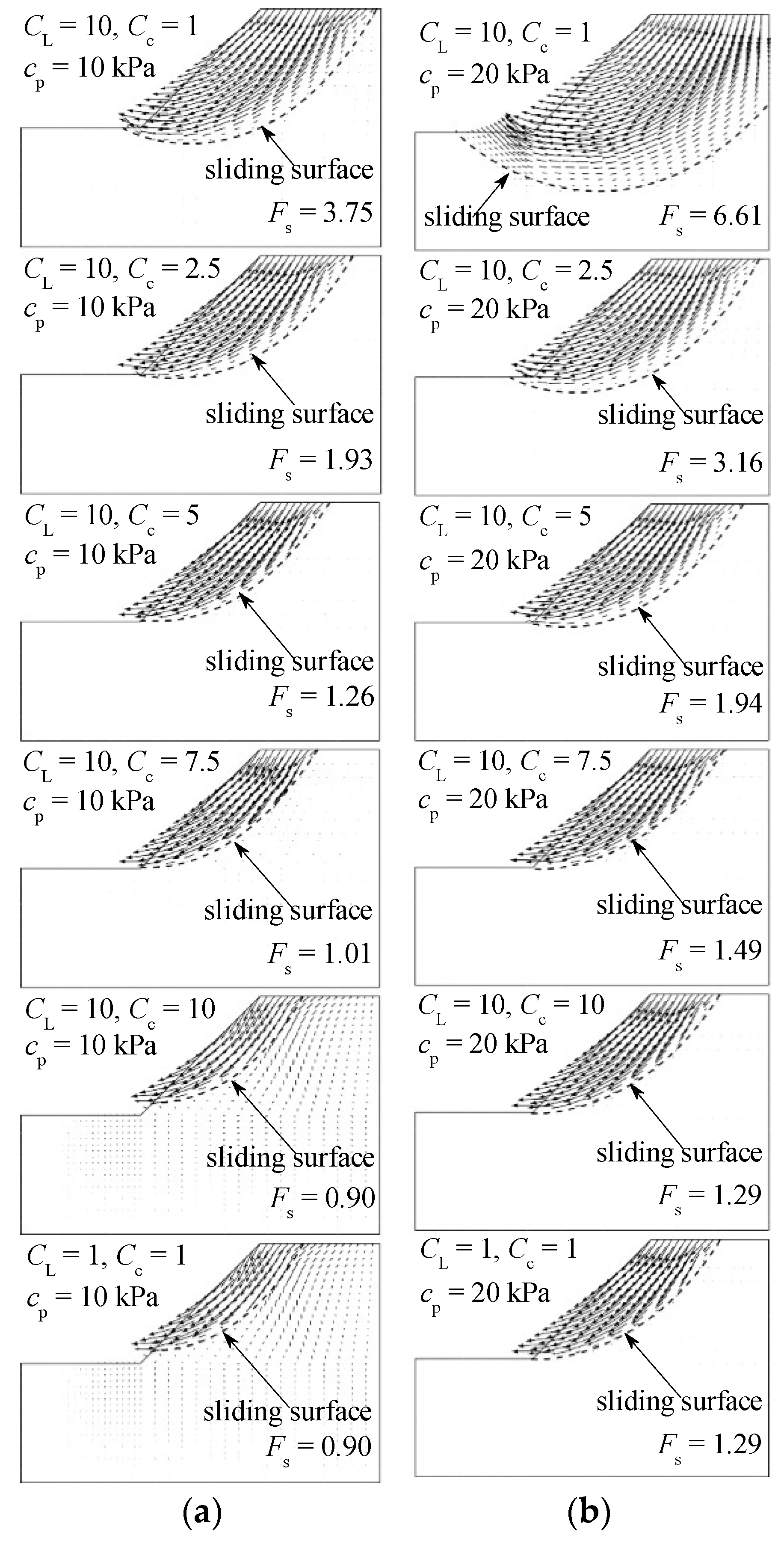
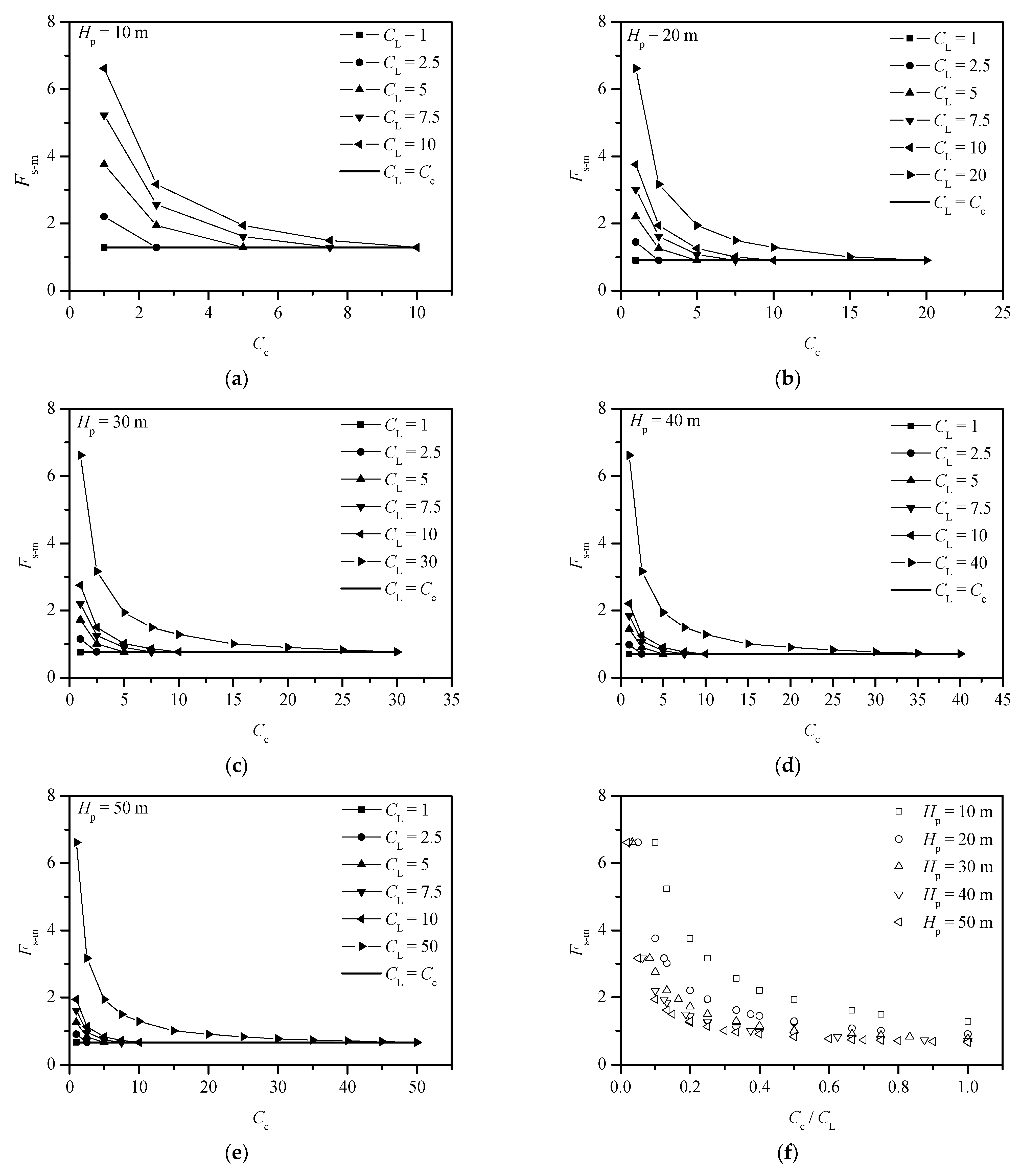
4.2. Parametric Study on Small-Scale Model Slopes
4.2.1. Effect of Model Scale with Varying Soil Cohesion
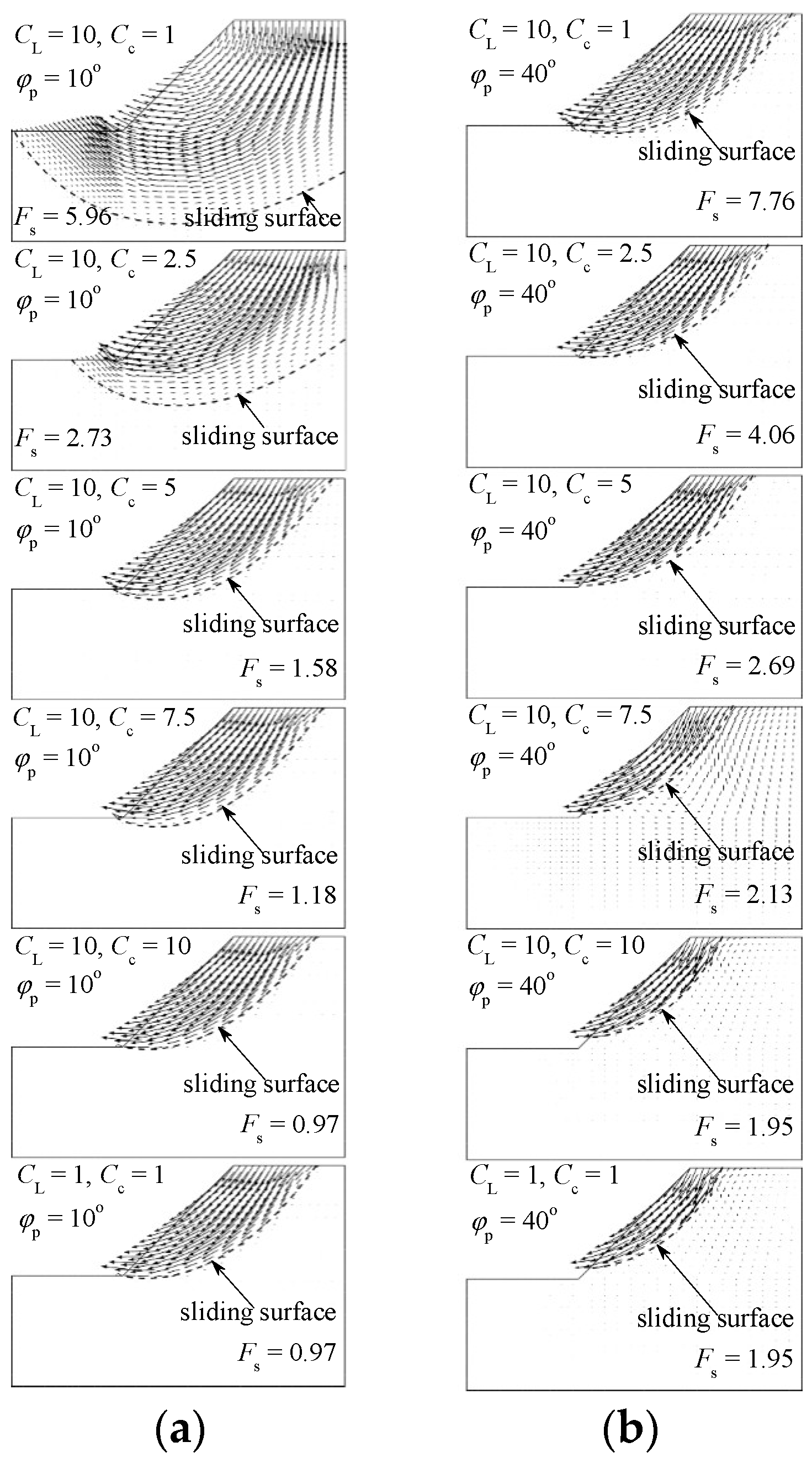
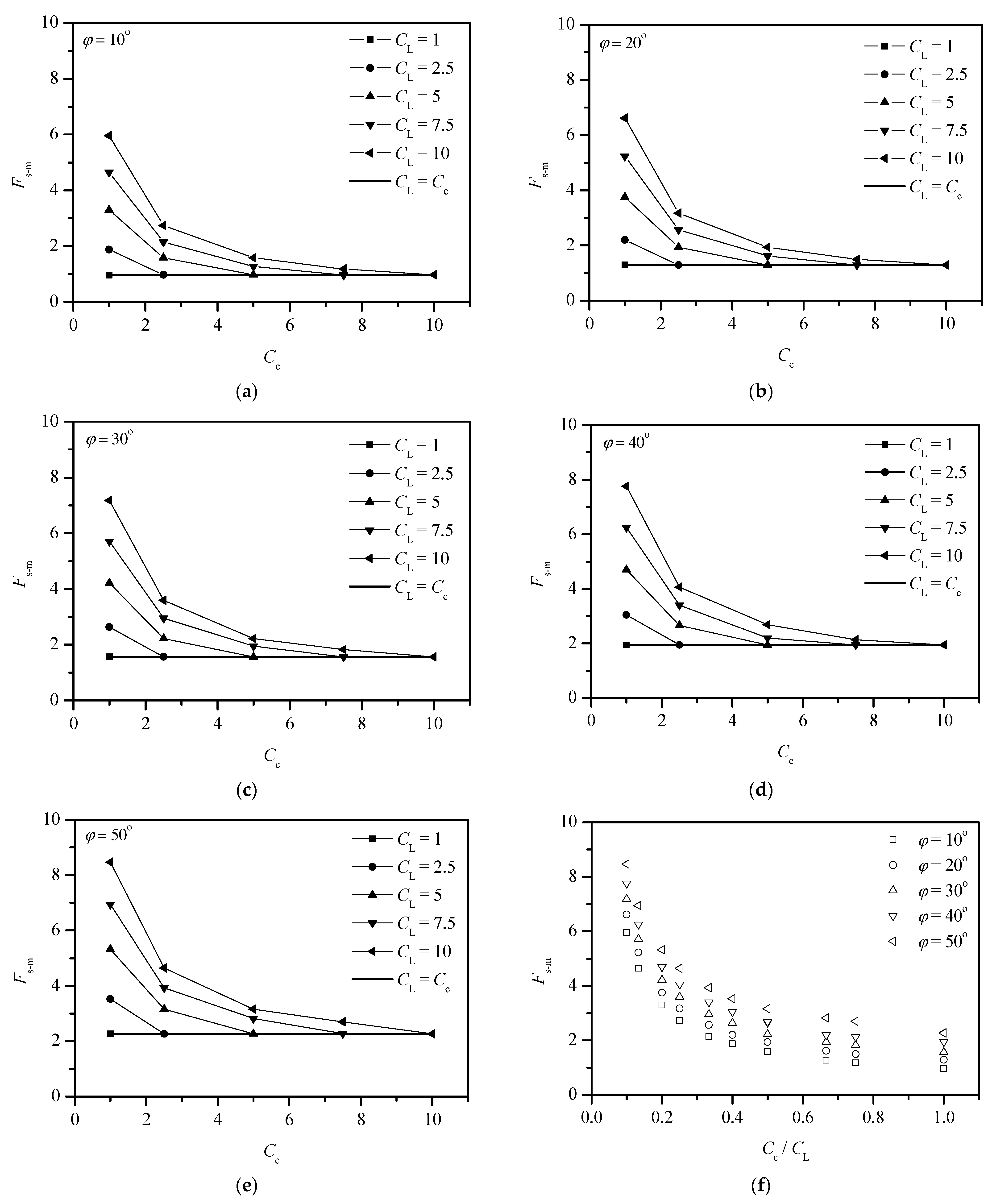
4.2.2. Effect of Model Scale with Varying Angle of Internal Friction
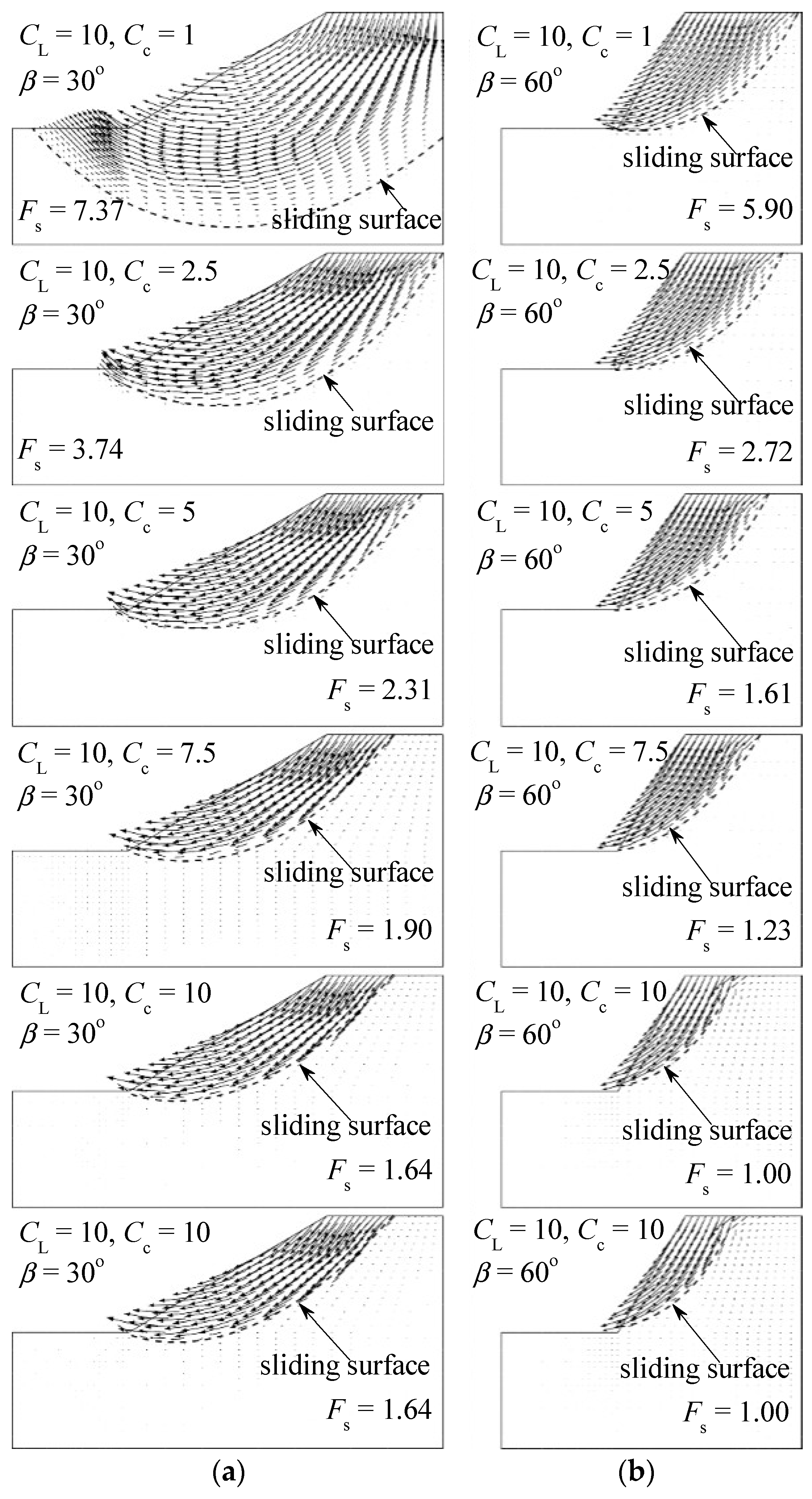
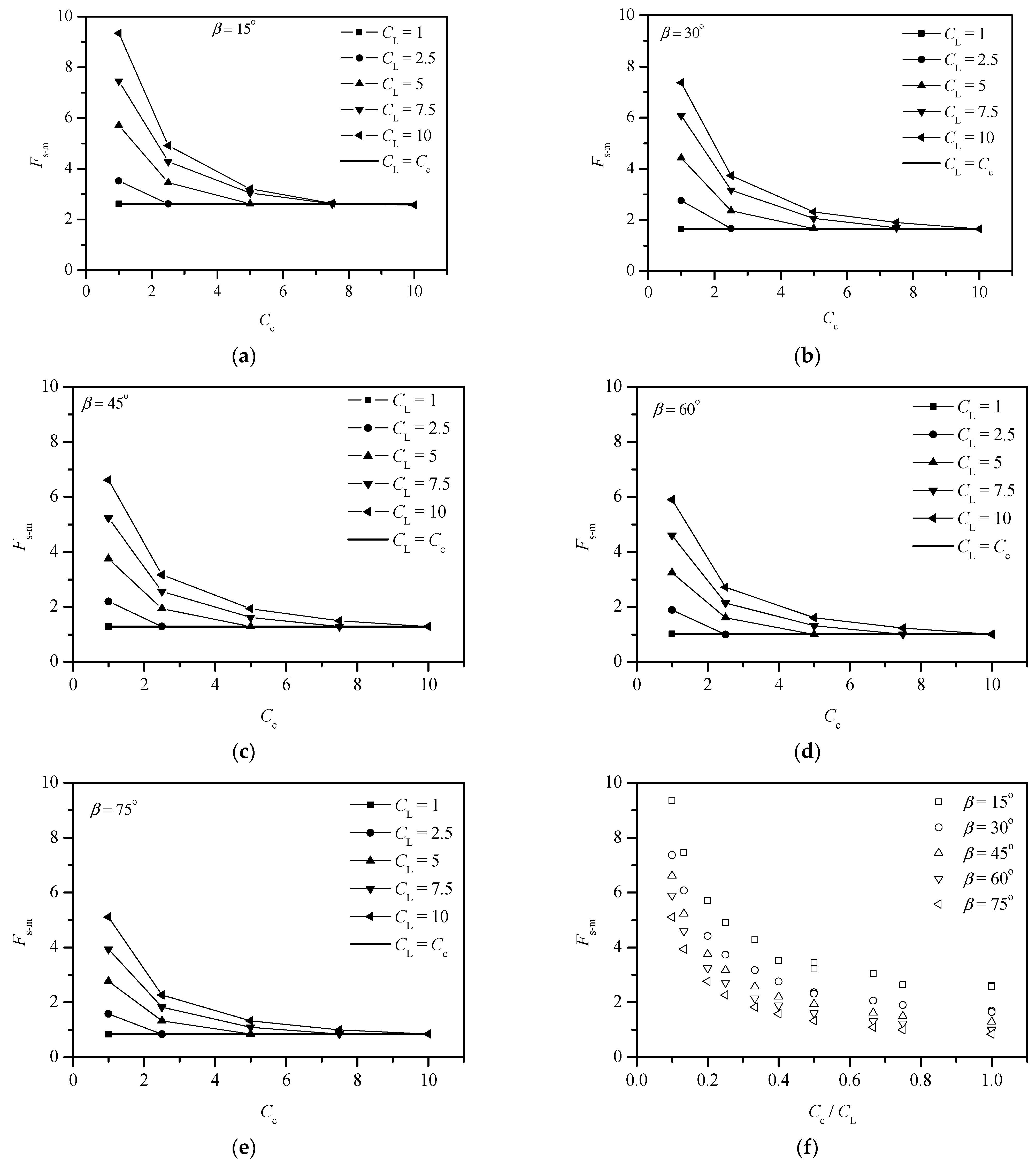
4.2.3. Effect of Model Scale with Varying Angle of Slope
4.2.4. Effect of Model Scale with Varying Slope Height
4.3. Failure Mechanism of Slope
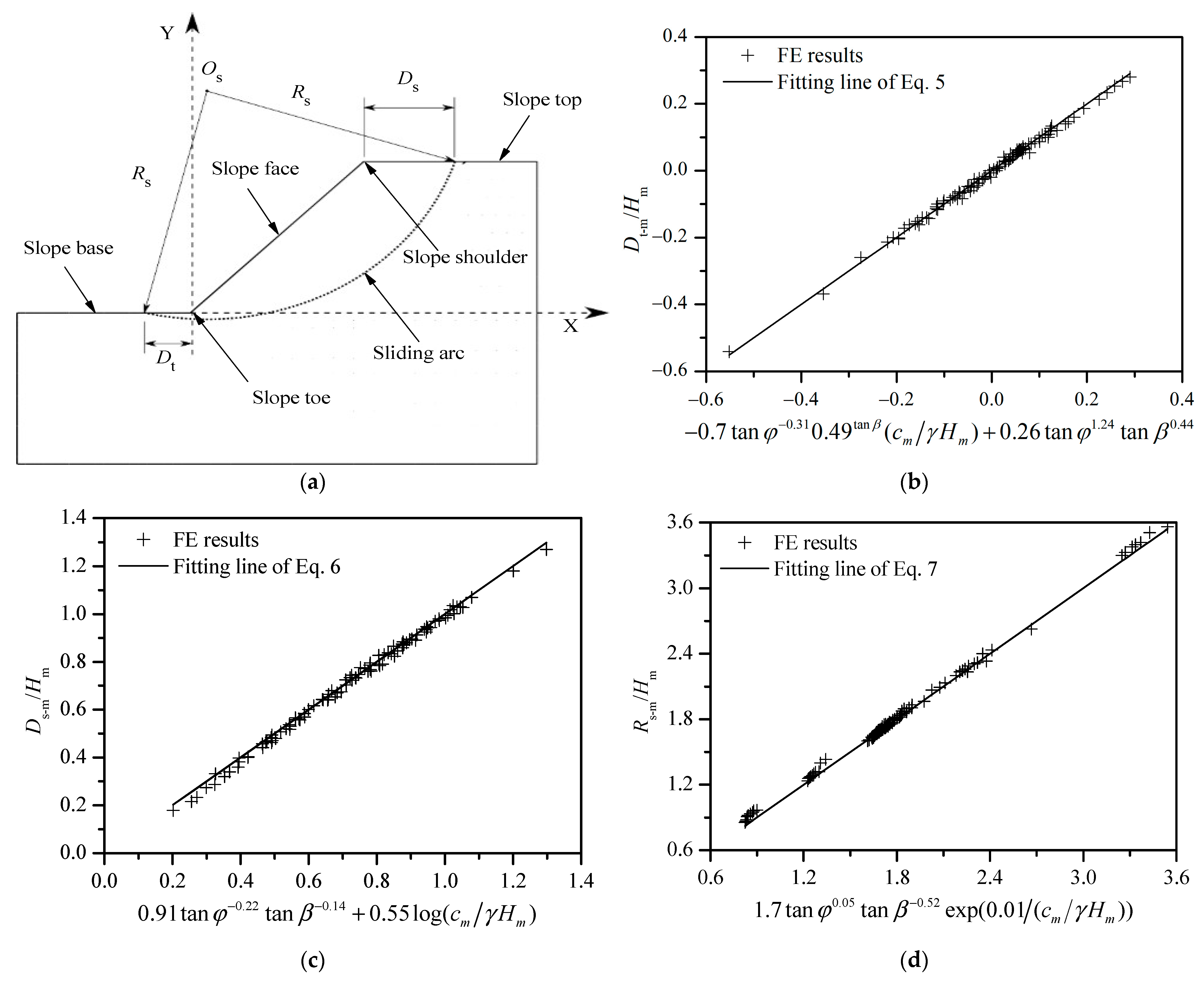
4.3.1. Position of the Slope’s Failure Surface
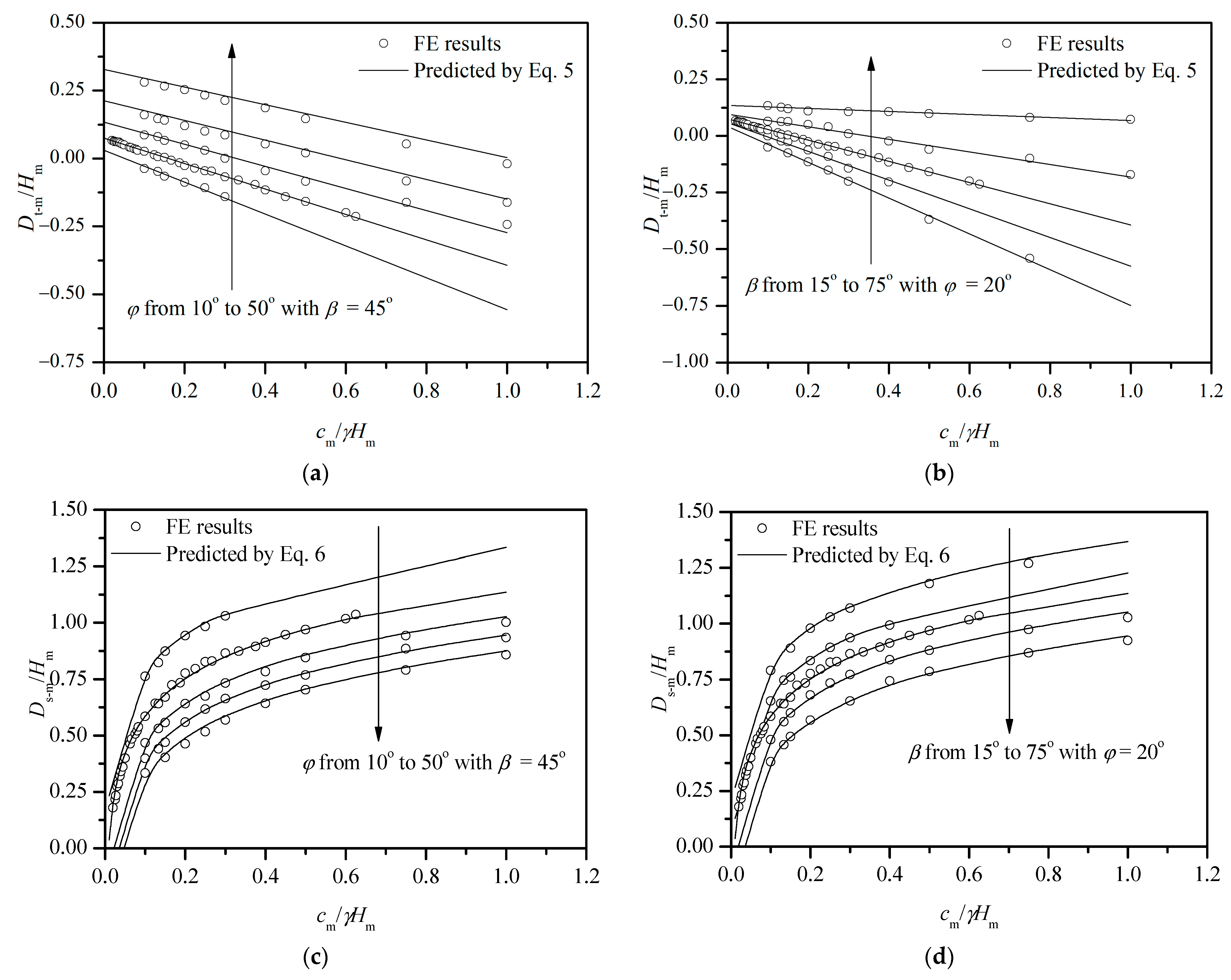
4.3.2. Prediction of the Slope Safety Factor in Model Testing
4.3.3. Predicting Prototype Slope Behavior
4.4. Validation of Proposed Interpretation Procedure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, B.C.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.Y.; Cui, P.L.; Liu, Y.Y. Numerical Stability Analysis of Sloped Geosynthetic Encased Stone Column Composite Foundation under Embankment Based on Equivalent Method. Buildings 2024, 14, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, A.W. The use of the slip circle in the stability analysis of slopes. Geotechnique 1955, 5, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, E.M.; Roth, W.H.; Drescher, A. Slope stability analysis by strength reduction. Géotechnique 1999, 49, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D.V.; Lane, P.A. Slope stability analysis by finite elements. Geotechnique 1999, 49, 653–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Astaraki, F.; Imam, S.M.R.; Chalabii, J.; Movahedi Rad, M. Investigation of Shear Strength Reduction Method in Slope Stability of Reinforced Slopes by Anchor and Nail. Buildings 2024, 14, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Feng, X.; Rao, H.; Zheng, H. Treatment design of geological defects in dam foundation of Jinping I hydropower station. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2013, 5, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, B.; Dong, J.; Chen, J. Geomechanical model test on dam stability and application to Jinping High arch dam. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2015, 76, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, M.; Hu, Y.; Hossain, M.S. Behaviour of ball penetrometer in uniform single- and double-layer clays. Geotechnique 2013, 63, 682–694. [Google Scholar]
- Sloan, S.W. Geotechnical stability analysis. Géotechnique 2013, 63, 531–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Wu, H.; Qiao, G.; Li, W.; Scaioni, M.; Feng, T.; Liu, S.; Chen, W.; Li, N.; Liu, C.; et al. Model test study on monitoring dynamic process of slope failure through spatial sensor network. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 3315–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Liu, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, R.; Wang, S. Cracking, stability and slope reinforcement analysis relating to the Jinping dam based on a geomechanical model test. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 4393–4410. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, H.I.; Wu, M.; Leshchinsky, D.; Leshchinsky, B. Centrifuge modeling of slope instability. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2009, 135, 758–767. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, C.; Kamchoom, V.; Leung, A.K. Centrifuge modelling of the effects of root geometry on transpiration-induced suction and stability of vegetated slopes. Landslides 2016, 13, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, A.N. Use of centrifugal model testing to assess slope stability. Can. Geotech. J. 1978, 15, 14–31. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, H.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z. Centrifugal Model Test of Multi-Level Slope under Combined Support of Pile-Anchor and Frame-Anchor. Buildings 2024, 14, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, M.; Chen, T.; Tsai, S. Modeling scale effects on consequent slope deformation by centrifuge model tests and the discrete elementmethod. Landslides 2017, 14, 981–993. [Google Scholar]
- Fumagalli, E. Statical and Geomechanical Models, 1st ed.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1973; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Mcnearny, R.L.; Abel Jr, J.F. Large-scale two-dimensional block caving model tests. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1993, 30, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Liu, D.; Wu, J.; Cheng, S.; Shen, H.; Xu, K.; Huang, X. Model test study on landslide under rainfall and reservoir water fluctuation. Yanshilixue Yu Gongcheng Xuebao 2005, 24, 2476–2483. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Kulatilake, P.; Peng, J.; Che, W.; Li, Y.; Meng, Z. In-flight excavation of a loess slope in a centrifuge model test. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2016, 34, 1577–1591. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Lin, M. Initiation and displacement of landslide induced by earthquake—A study of shaking table model slope test. Eng. Geol. 2011, 122, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Kumsar, H.; Aydan, Ö.; Ulusay, R. Dynamic and Static Stability Assessment of Rock Slopes Against Wedge Failures. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2000, 33, 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, G.W.; Zhan, T.L.T.; Chen, Y.M.; Fredlund, D.G. Performance of a large-scale slope model subjected to rising and lowering water levels. Eng. Geol. 2009, 106, 92–103. [Google Scholar]
- Moriwaki, H.; Inokuchi, T.; Hattanji, T.; Sassa, K.; Ochiai, H.; Wang, G. Failure processes in a full-scale landslide experiment using a rainfall simulator. Landslides 2004, 1, 277–288. [Google Scholar]
- Saghaee, G.; Mousa, A.A.; Meguid, M.A. Plausible failure mechanisms of wildlife-damaged earth levees: Insights from centrifuge modeling and numerical analysis. Can. Geotech. J. 2017, 54, 1496–1508. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.H.; Zornberg, J.G.; Liu, C.N.; Lin, H.D. Stress distribution and development within geosynthetic-reinforced soil slopes. Geosynth. Int. 2012, 19, 62–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Zhong, H.; Yang, K.; Yang, X.; Cai, C.; Xiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, B. A Study on the Factors Influencing High Backfill Slope Reinforced with Anti-Slide Piles under Static Load Based on Numerical Simulation. Buildings 2024, 14, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.K.; Kamchoom, V.; Ng, C. Influences of root-induced soil suction and root geometry on slope stability: A centrifuge study. Can. Geotech. J. 2016, 54, 291–303. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, I.M.; Hobbs, R. Finite element analysis of centrifuged and built-up slopes. Geotechnique 1974, 24, 531–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simulia, D.C.S. Abaqus 6.11 Analysis User’s Manual; Dassault Systemes, Providence: Johnston, RI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Tham, L.G.; Liu, D. On two definitions of the factor of safety commonly used in the finite element slope stability analysis. Comput. Geotech. 2006, 33, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.F.; Ren, J. A two-grid search scheme for large-scale 3-D finite element analyses of slope stability. Comput. Geotech. 2014, 62, 203–215. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, T.; San, K. Finite Element Slope Stability Analysis by Shear Strength Reduction Technique. Soils Found. 2008, 32, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugai, K. A method of calculation of total safety factor of slope by elasto-plastic FEM. Soils Found. 2008, 29, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, H. Scale Issues and Interpretation of Ball Penetration in Stratified Deposits in Centrifuge Testing. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J.M. State of the Art: Limit Equilibrium and Finite-Element Analysis of Slopes. J. Geotech. Eng. 1996, 123, 577–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-F. Limit Analysis and Soil Plasticity; Elsevier Scientific Pub. Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.M.; Lansivaara, T.; Wei, W.B. Two-dimensional slope stability analysis by limit equilibrium and strength reduction methods. Comput. Geotech. 2007, 34, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.F.; Zhang, F.; Lei, G.H.; Li, D.Y. An extended limit analysis of three-dimensional slope stability. Géotechnique 2013, 63, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


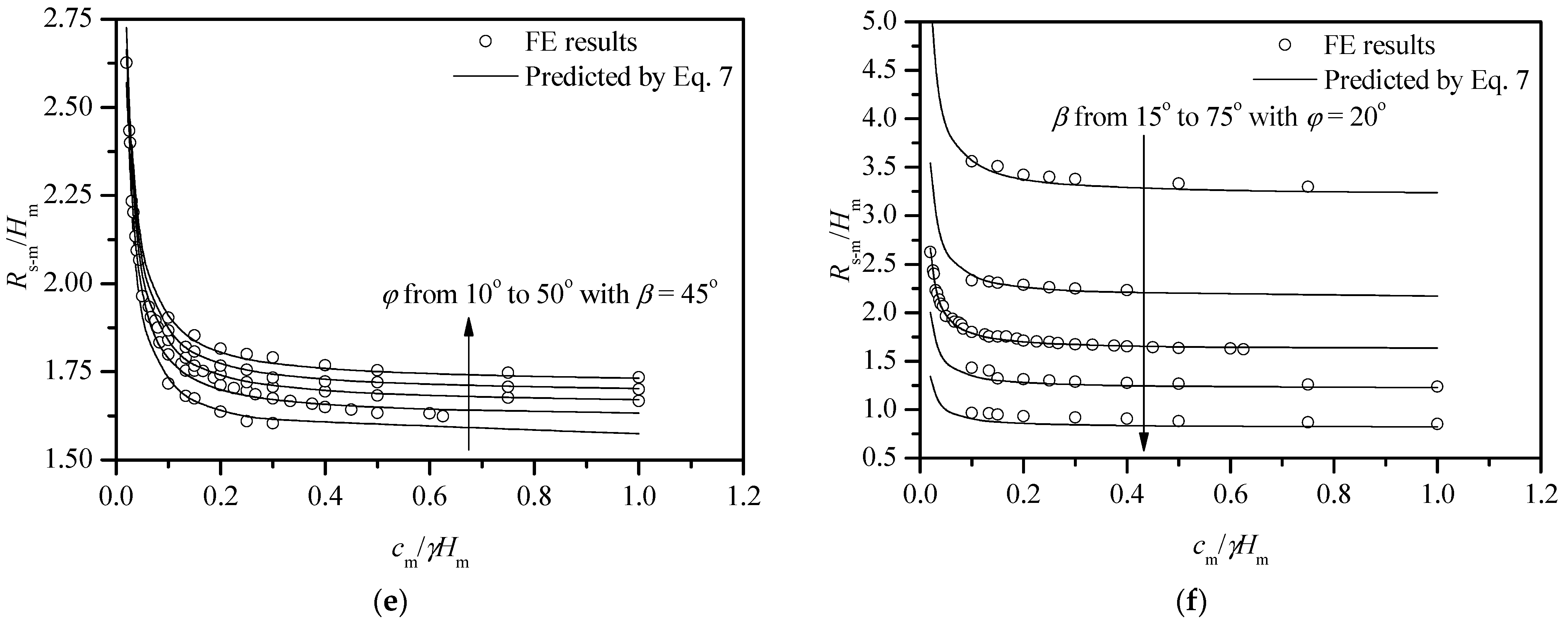
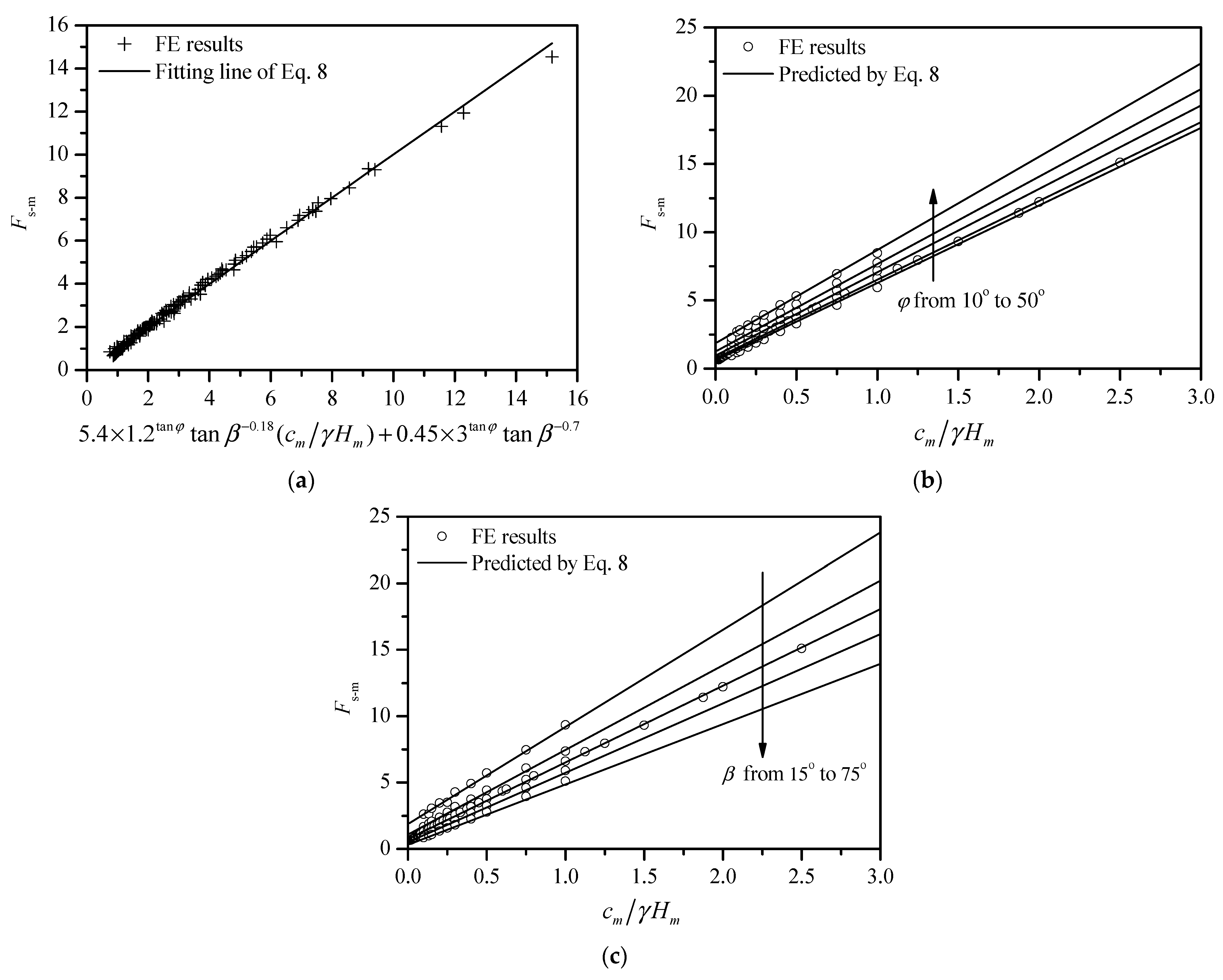
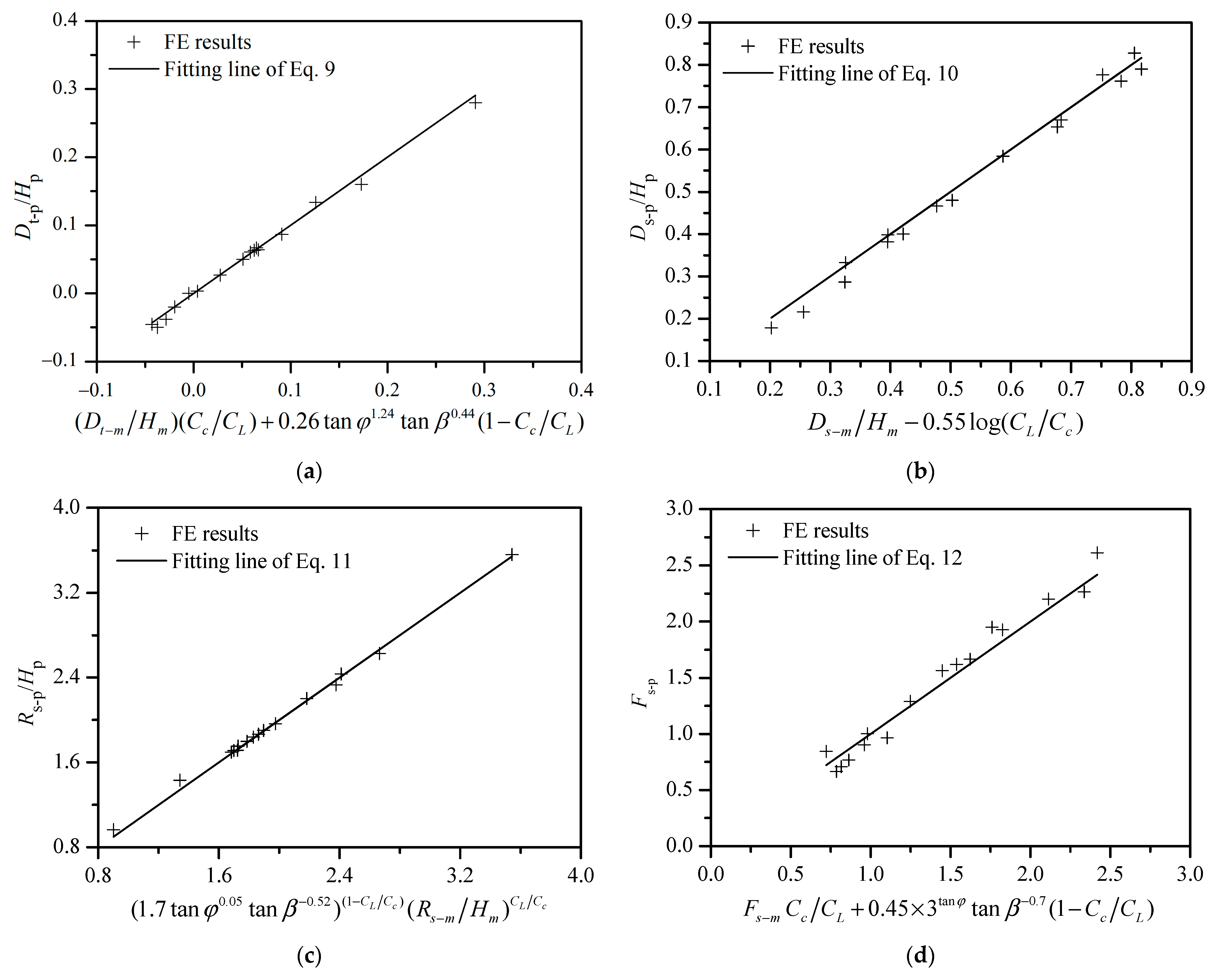

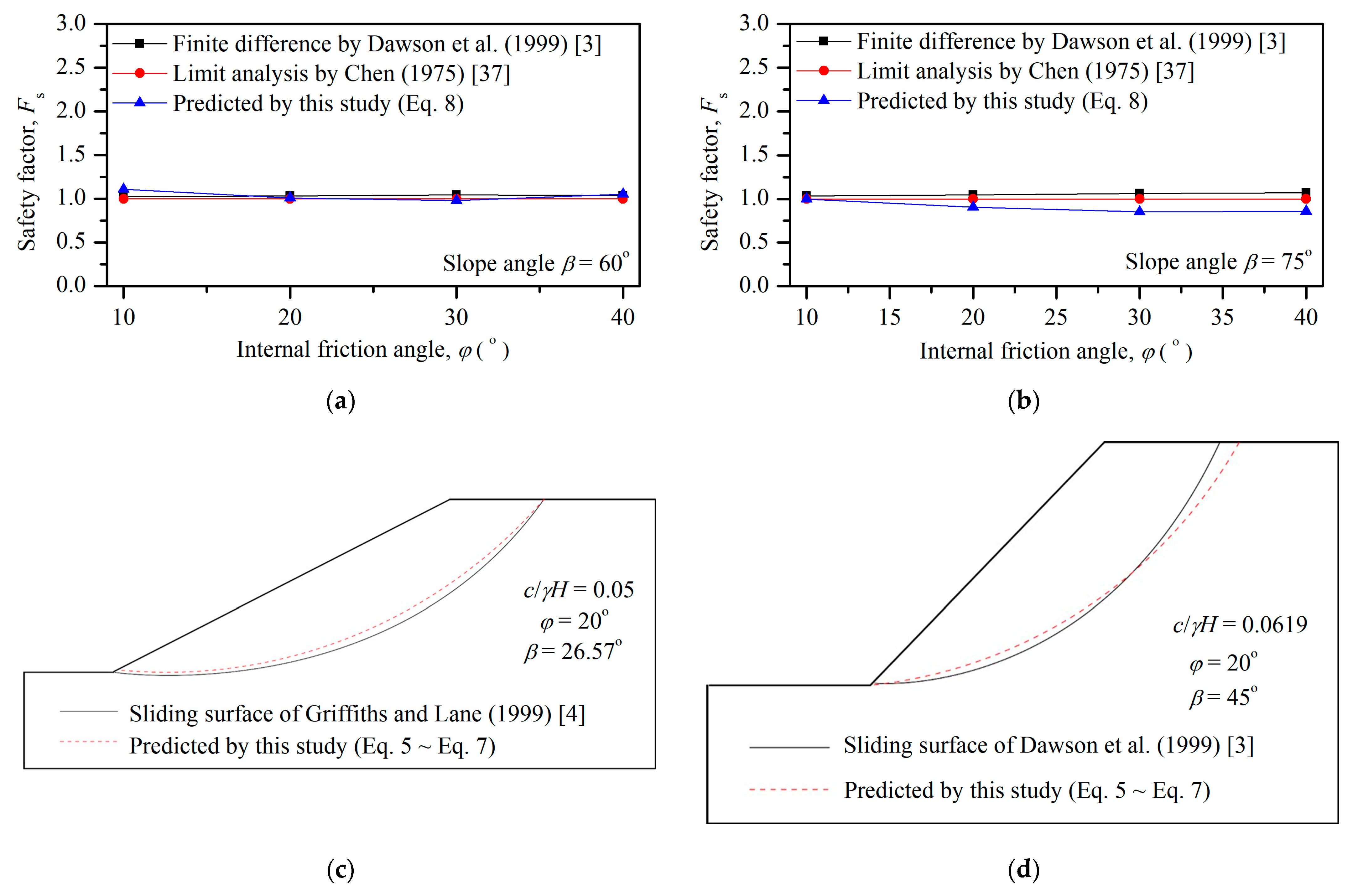
| Conversion Coefficients | Notation | Expression ** | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geometry conversion coefficient | CL | Lp/Lm | n |
| Unit weight conversion coefficient | Cγ | γp/γm | 1 |
| Poisson’s ratio conversion coefficient | Cυ | υp/υm | 1 |
| Stress conversion coefficient | Cσ | σp/σm | n |
| Modulus conversion coefficient | CE | Ep/Em | n |
| Internal friction angle conversion coefficient | Cφ | φp/φm | 1 |
| Analysis | cp (kPa) | φ (°) | β (°) | Hp (m) | CL | Cc | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group I | 12.38 | 20 | 45 | 10 | 1 | 1 | Validation against Dawson et al. (1999) [3] |
| Group II | 10 | 20 | 26.57 | 10 | 1 | 1 | Validation against Griffiths and Lane (1999) [4] |
| Group III | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 | 20 | 45 | 10 | 1 | 1 | Investigation of the effect of cp, φ, β, and Hp on the stability of the prototype slope |
| 20 | 10, 30, 40, 50 | 45 | 10 | ||||
| 20 | 20 | 15, 30, 60, 75 | 10 | ||||
| 20 | 20 | 45 | 2.5, 5, 20, 30, 40, 50 | ||||
| Group IV | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 | 20 | 45 | 10 | 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10 | 1, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10 | Investigation of the effect of cp on the stability of the model slope |
| Group V | 20 | 10, 30, 40, 50 | 45 | 10 | 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10 | 1, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10 | Investigation of the effect of φ on the stability of the model slope |
| Group VI | 20 | 20 | 15, 30, 60, 75 | 10 | 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10 | 1, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10 | Investigation of the effect of β on the stability of the model slope |
| Group VII | 20 | 20 | 45 | 20, 30, 40, 50 | 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 | 1, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 | Investigation of the effect of Hp on the stability of the model slope |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Fu, G.; Zhou, M.; Chen, J. A Numerical Study on the Utilization of Small-Scale Model Testing for Slope Stability Analysis. Buildings 2025, 15, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071015
Wang M, Wang X, Fu G, Zhou M, Chen J. A Numerical Study on the Utilization of Small-Scale Model Testing for Slope Stability Analysis. Buildings. 2025; 15(7):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071015
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Minghua, Xiaoliang Wang, Guoqiang Fu, Mi Zhou, and Jian Chen. 2025. "A Numerical Study on the Utilization of Small-Scale Model Testing for Slope Stability Analysis" Buildings 15, no. 7: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071015
APA StyleWang, M., Wang, X., Fu, G., Zhou, M., & Chen, J. (2025). A Numerical Study on the Utilization of Small-Scale Model Testing for Slope Stability Analysis. Buildings, 15(7), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071015





