Regional Social Sustainability of Public–Private Partnerships (PPPs): Effects Evaluation and Influencing Factors Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Social Sustainability of PPP
2.2. The Influencing Factors of PPP Development
3. Methodology
3.1. The Model for Evaluating PPPSE
3.2. Research Hypotheses of Influencing Factors
3.3. The Model and Variables for Exploring Influencing Factors
3.4. Data Set
4. Results
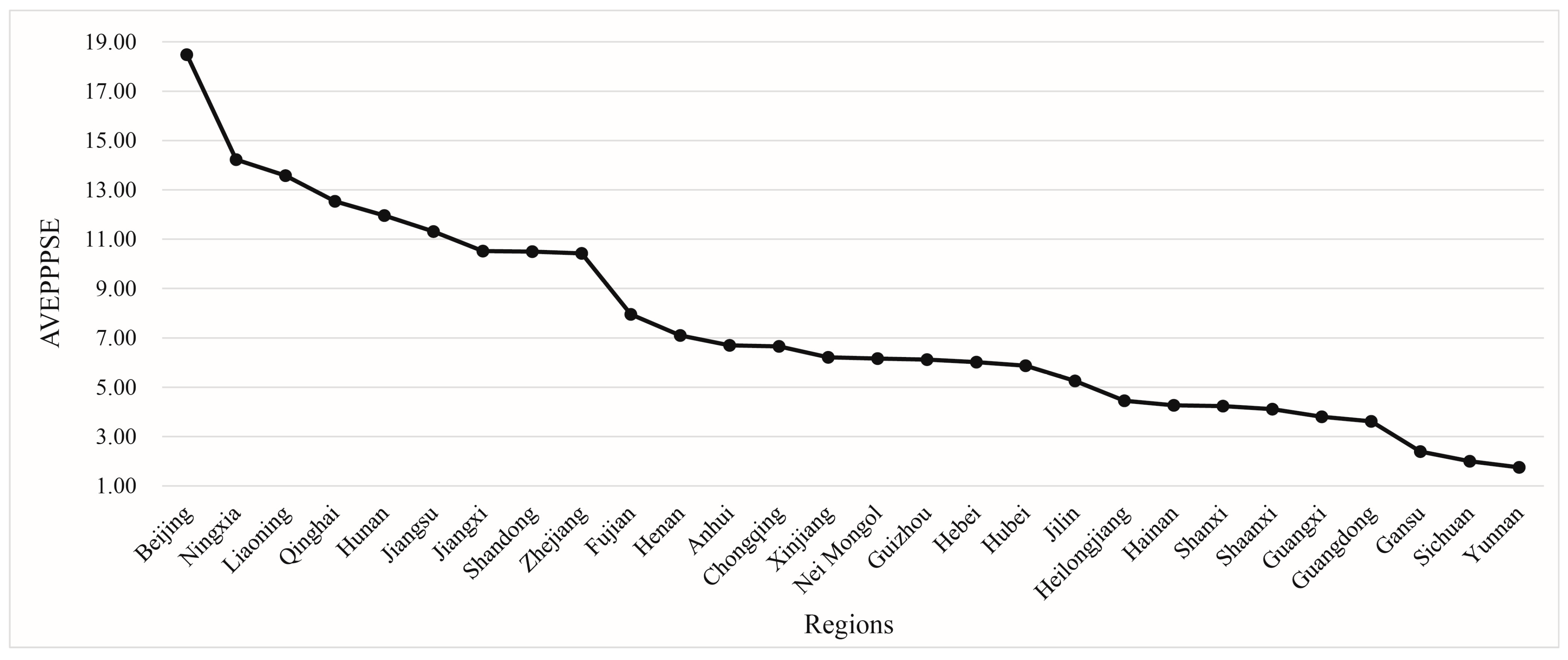
4.1. The Results of PPPSEs
4.2. The Results of Influencing Factors
5. Discussion
5.1. The PPPSEs and Influencing Factors
5.2. Practical Implications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Regions | PPPSE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
| Beijing | 22.63 | 18.77 | 18.57 | 16.23 | 16.21 |
| Ningxia | 9.66 | 20.18 | 13.82 | 13.82 | 13.64 |
| Liaoning | 13.19 | 13.95 | 14.17 | 13.28 | 13.30 |
| Qinghai | 12.37 | 12.97 | 12.46 | 12.45 | 12.45 |
| Hunan | 11.03 | 11.30 | 12.13 | 13.13 | 12.20 |
| Jiangsu | 10.01 | 10.26 | 11.21 | 12.81 | 12.27 |
| Jiangxi | 9.42 | 8.16 | 9.86 | 12.04 | 13.12 |
| Shandong | 10.64 | 11.70 | 10.31 | 9.95 | 9.91 |
| Zhejiang | 16.92 | 10.40 | 11.78 | 6.37 | 6.69 |
| Fujian | 7.30 | 7.97 | 8.16 | 8.20 | 8.16 |
| Henan | 7.95 | 7.33 | 6.67 | 6.84 | 6.69 |
| Anhui | 4.14 | 7.71 | 8.66 | 6.64 | 6.32 |
| Chongqing | 2.82 | 8.62 | 8.38 | 8.13 | 5.34 |
| Xinjiang | 10.47 | 5.82 | 6.44 | 4.43 | 3.91 |
| Nei Mongol | 7.94 | 5.90 | 6.72 | 5.15 | 5.07 |
| Guizhou | 7.82 | 6.81 | 5.29 | 5.63 | 5.06 |
| Hebei | 7.02 | 6.39 | 5.49 | 5.60 | 5.61 |
| Hubei | 4.17 | 6.19 | 6.53 | 6.27 | 6.22 |
| Jilin | 7.86 | 2.20 | 5.26 | 5.39 | 5.59 |
| Heilongjiang | 7.31 | 7.53 | 2.98 | 2.71 | 1.73 |
| Hainan | 6.07 | 3.83 | 3.82 | 3.82 | 3.82 |
| Shanxi | 17.78 | 1.04 | 1.07 | 0.64 | 0.65 |
| Shaanxi | 5.05 | 4.51 | 4.05 | 3.84 | 3.13 |
| Guangxi | 9.32 | 4.36 | 2.36 | 1.40 | 1.59 |
| Guangdong | 5.84 | 3.23 | 2.77 | 3.20 | 3.04 |
| Gansu | 5.05 | 1.35 | 1.48 | 1.80 | 2.28 |
| Sichuan | 5.16 | 3.84 | 0.42 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| Yunnan | 4.61 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 1.15 | 1.25 |
References
- Tariq, S.; Zhang, X. Critical Analysis of the Private Sector Roles in Water PPP Failures. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2021, 147, 04021015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado-Ballesteros, B.; Pena-Miguel, N. Analysing the link between corruption and PPPs in infrastructure projects: An empirical assessment in developing countries. J. Econ. Policy Reform 2022, 25, 136–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN. Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals (accessed on 16 May 2023).
- Besaiso, H.; Abualqumboz, M.; Cheng, X. Review of Studies on Sustainability of Public-Private Partnership Projects: A Bibliometric Analysis. Sustain. Dev. 2025, 33, 1551–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Duan, K.; Wu, G.; Zhang, R.; Feng, X. Comprehensive metrological and content analysis of the public-private partnerships (PPPs) research field: A new bibliometric journey. Scientometrics 2020, 127, 2145–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.A.; Tharun, D.; Laishram, B. Infrastructure development through PPPs in India: Criteria for sustainability assessment. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2016, 59, 708–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinz, A.; Roudyani, N.; Thaler, J. Public-private partnerships as instruments to achieve sustainability-related objectives: The state of the art and a research agenda. Public Manag. Rev. 2018, 20, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.; Shen, L.; Jiao, L.; Zuo, J.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Yan, H. Constraints to achieve infrastructure sustainability for mountainous townships in China. Habitat Int. 2018, 73, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizkorodov, E. Evaluating risk allocation and project impacts of sustainability-oriented water public-private partnerships in Southern California: A comparative case analysis. World Dev. 2021, 140, 105232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueskes, M.; Verhoest, K.; Block, T. Governing public-private partnerships for sustainability: An analysis of procurement and governance practices of PPP infrastructure projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 1184–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Cen, J.; Liu, B.; Qian, L.; Yuan, J. How Does Policy Implementation Affect the Sustainability of Public-Private Partnership Projects? A Stakeholder-Based Framework. Public Perform. Manag. Rev. 2022, 45, 1029–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ke, Y.; Sankaran, S. Achieving Social Sustainability in Public-Private Partnership Elderly Care Projects: A Chinese Case Study. Buildings 2025, 15, 3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, D.; Casady, C.B. The effects of contractual and relational governance on public-private partnership sustainability. Public Adm. 2024, 102, 1418–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourasia, A.S.; Dalei, N.N.; Jha, K. Evaluating public-private partnership role on the sustainability of airports in India. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 31, 3595–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, L.; Tan, Y.; Skibniewski, M.J. Evaluating the regional social sustainability contribution of public-private partnerships in China: The development of an indicator system. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 28, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppenjan, J.F.M.; Enserink, B. Public-Private Partnerships in Urban Infrastructures: Reconciling private sector participation and sustainability. Public Adm. Rev. 2009, 69, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, S.; Zhang, X. Socioeconomic, Macroeconomic, and Sociopolitical Issues in Water PPP Failures. J. Manag. Eng. 2021, 37, 04021047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Chen, B.; Wang, H.; Zhu, D. Public-private partnerships as a governance response to sustainable urbanization: Lessons from china. Habitat Int. 2020, 95, 102095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.P.C.; Lam, P.T.I.; Chan, D.W.M.; Cheung, E.; Ke, Y. Critical Success Factors for PPPs in Infrastructure Developments: Chinese perspective. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2010, 136, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, J.; Saz-Carranza, A. Determinants of public-private partnership policies. Public Manag. Rev. 2020, 22, 1171–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleta-Asin, J.; Munoz, F. Renewable energy public-private partnerships in developing countries: Determinants of private investment. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 29, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.J. Motivations, Obstacles, and Resources Determinants of Public-Private Partnership in State Toll Road Financing. Public Perform. Manag. Rev. 2014, 37, 679–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ma, M. Public-private partnership as a tool for sustainable development—what literatures say? Sustain. Dev. 2021, 29, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Liu, Y.; Hope, A.; Wang, J. Review of studies on the public private partnerships (PPP) for infrastructure projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2018, 36, 773–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel Diaz-Sarachaga, J.; Jato-Espino, D.; Alsulami, B.; Castro-Fresno, D. Evaluation of existing sustainable infrastructure rating systems for their application in developing countries. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 71, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yu, Y.; Osei-Kyei, R.; Chan, A.P.C.; Xu, J. Developing a project sustainability index for sustainable development in transnational public-private partnership projects. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 27, 1034–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Osei-Kyei, R.; Chan, A.P.C.; Chen, C.; Martek, I. Review of social responsibility factors for sustainable development in public-private partnerships. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 26, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthill, M. Strengthening the ‘Social’ in Sustainable Development: Developing a Conceptual Framework for Social Sustainability in a Rapid Urban Growth Region in Australia. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 18, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, N.; Bramley, G.; Power, S.; Brown, C. The Social Dimension of Sustainable Development: Defining urban social sustainability. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 19, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Su, L.; Kuinkel, M.S. Research status and trend of PPP in the US and China: Visual knowledge mapping analysis. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2023, 22, 3598–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, B.; Tiong, R.L.K. Official Tenure, Fiscal Capacity, and PPP Withdrawal of Local Governments: Evidence from china’s PPP project platform. Sustainability 2021, 13, 14012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Ke, Y.; Lin, J.; Yang, Z.; Cai, J. Spatio-temporal dynamics of public private partnership projects in China. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2016, 34, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Yang, Z.; Gao, H.; Tao, H.; Xu, M. Does PPP Matter to Sustainable Tourism Development? An Analysis of the Spatial Effect of the Tourism PPP Policy in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhao, J.Z. Explaining the adoption rate of public-private partnerships in Chinese provinces: A transaction cost perspective. Public Manag. Rev. 2021, 23, 590–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, J.; Moreira, A.C. The importance of non-financial determinants on public-private partnerships in Europe. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2015, 33, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Del Barrio Álvarez, D.; Yuan, J.; Kato, H. Determinants of the formation process in public-private partnership projects in developing countries: Evidence from China. Local Gov. Stud. 2023, 50, 521–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Qiang, W.; Liu, X. Exploring the geography of urban comprehensive development in mainland Chinese cities. Land Use Policy 2022, 115, 106004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission. Effectively Implement Public Private Partnerships in Traditional Infrastructure Sectors. Available online: https://new.tzxm.gov.cn/zckd/jdhy/202001/t20200109_1262183.shtml (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Li, J.; Xiong, W.; Casady, C.B.; Liu, B.; Wang, F. Advancing Urban Sustainability through Public-Private Partnerships: Case study of the gu’an new industry city in china. J. Manag. Eng. 2023, 39, 05022016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razin, E.; Hazan, A.; Elron, O. The rise and fall (?) of public-private partnerships in Israel’s local government. Local Gov. Stud. 2022, 48, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y. On the Development of Public-Private Partnerships in Transitional Economies: An explanatory framework. Public Adm. Rev. 2013, 73, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Chen, H.; Zhou, G.; Kong, F. Determinants of Public-Private Partnership Adoption in Solid Waste Management in Rural China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleta-Asin, J.; Munoz, F. How does risk transference to private partner impact on public-private partnerships’ success? Empirical evidence from developing economies. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2020, 72, 100869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, W.; Song, J. The moderating role of governance environment on the relationship between risk allocation and private investment in PPP markets: Evidence from developing countries. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2019, 37, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, D.; Zhu, D.; Quayson, M.; Hossin, M.A.; Omoruyi, O.; Bediako, A.K. A multicriteria decision framework for governance of PPP projects towards sustainable development. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2023, 87, 101580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouton, J.; Sanogo, W.; Djomgoue, N. Risk allocation in energy infrastructure PPPs projects in selected African countries: Does institutional quality, PPPs experience and income level make a difference? Econ. Change Restruct. 2023, 56, 537–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, E.; Zhang, Z.; He, S.; Jiang, X.; Skitmore, M. Why Are PPP Projects Stagnating in China? An Evolutionary Analysis of China’s PPP Policies. Buildings 2024, 14, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Finance of Shandong Province. Shandong PPP Governance Unit. Available online: http://czt.shandong.gov.cn/art/2017/9/18/art_10601_3430368.html (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Department of Finance of Henan Province. Hena PPP Governace Unit. Available online: https://czt.henan.gov.cn/2020/11-30/1911878.html (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Chan, D.W.M.; Sarvari, H.; Husein, A.A.J.A.; Awadh, K.M.; Golestanizadeh, M.; Cristofaro, M. Barriers to Attracting Private Sector Investment in Public Road Infrastructure Projects in the Developing Country of Iran. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, T. Effect of private capital in rival projects on public-private partnership adoption in China. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2023, 30, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhao, J.Z. The Rise of Public-Private Partnerships in China: An effective financing approach for infrastructure investment? Public Adm. Rev. 2019, 79, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayides, P.M.; Parola, F.; Lam, J.S.L. The effect of institutional factors on public-private partnership success in ports. Transp. Res. Part A Poilicy Pract. 2015, 71, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Zhong, N.; Wang, F.; Zhang, M.; Chen, B. Political opportunism and transaction costs in contractual choice of public-private partnerships. Public Adm. 2022, 100, 1125–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission; Ministry of Finance. Guiding Opinions on Standardizing the Implementation of a New Mechanism for Public Private Partnerships. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/2023/issue_10826/202311/content_6915818.html (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Wang, J. Focusing on the City Park PPP Project in Yuzhong. Available online: https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_24058410 (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Mu, R.; de Jong, M.; Koppenjan, J. The rise and fall of Public-Private Partnerships in China: A path-dependent approach. J. Transp. Geogr. 2011, 19, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. From State to Market: Private Participation in China’s Urban Infrastructure Sectors, 1992-2008. World Dev. 2014, 64, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y. The assisting hand’ or ‘the grabbing hand’: Experimental evidence from PPP investments in the implementation of official rotation systems. J. Chin. Gov. 2025, 10, 218–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopanska, A.; Asinski, R. Fiscal and political determinants of local government involvement in public-private partnership (PPP). Local Gov. Stud. 2019, 45, 957–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Cui, N.; Xue, S.; Du, Q. The impacts of whole life cycle project management on the sustainable development goals. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2025, early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Thuc, L.D.; Kim, S.Y. Critical Success Factors of Public-Private Partnership Infrastructure Projects from a Middle-Income Country: A Comparison with Countries in Asia. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2024, 150, 05024023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

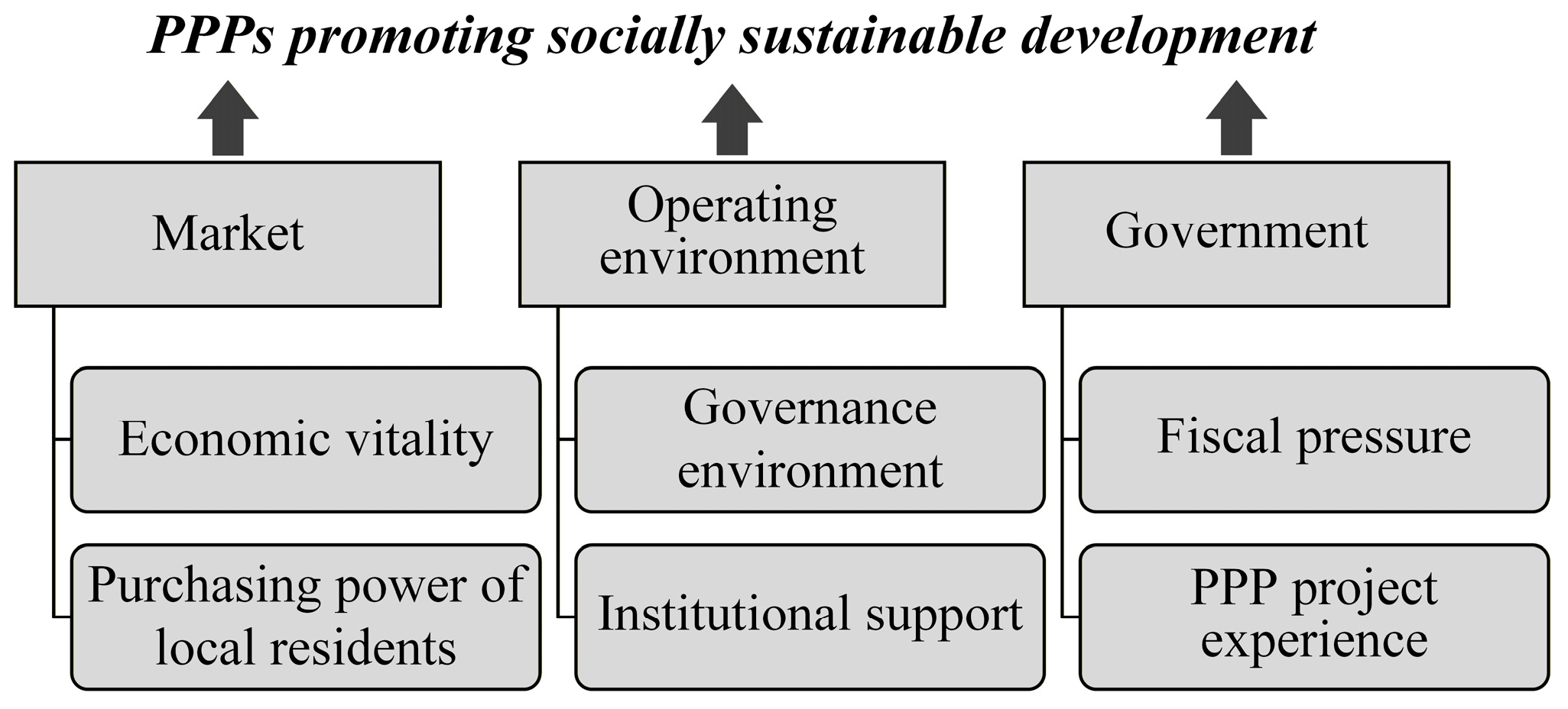
| Studies | Dependent Variables Reflecting PPP Development | Independent Variables Reflecting Influencing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Guo, alvarezA, Yuan, and Kato [36] | The number of PPP projects. | Local debt, availability of PPP policies, PPP funds. |
| Wang, Song, Zhang, and Tiong [31] | Local government’s PPP withdrawal. | Fiscal capacity, budget growth, local debt, land revenue growth, official tenure. |
| Tan and Zhao [34] | PPP adoption rate. | Government credibility, government capacity, legal environment, PPP funds. |
| Fleta-Asin and Munoz [21] | The degree of private involvement in PPPs in renewable energies. | Country size, voice, political stability, government effectiveness, regulatory quality, PPP funds. |
| Cheng, Yang, Gao, Tao, and Xu [33] | The number and investment of tourism PPP projects. | GDP, fiscal revenue, fiscal expenditure, investment in fixed assets, urbanization rate. |
| Mota and Moreira [35] | The investment of PPP projects. | Budget, market conditions, economic environment, legal system, political environment, PPP experience. |
| Research Hypotheses | Independent Variables | Related Literature | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Market | RH1: Economic vitality. | GDP growth rate. | GDPR | Panayides et al. [53] |
| RH2: Purchasing power of local residents. | Per capita disposable income. | PINC | Wang and Zhao [22] | |
| Operating environment | RH3: PPP governance unit. | Coded 1 if the region has established a PPP governance unit, 0 otherwise. | PPPUNIT | Tan and Zhao [34] |
| RH4: PPP funds. | Coded 1 if the region has established a provincial-level PPP fund, 0 otherwise. | PPPFUND | Guo, alvarezA, Yuan and Kato [36] | |
| Government | RH5: Fiscal pressure. | The ratio of fiscal expenditure to revenue. | FISRAT | Pan, Chen, Zhou and Kong [42] |
| RH6: PPP project experience. | Total investment of previous PPP projects. | PPPHIST | Wang, Liu, Xiong and Song [44] | |
| RH# | Independent Variables | Expected Sign | Coef (t) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | |||
| RH1 | GDPR | + | −3.621 (−0.881) | −3.496 (−0.837) | 0.800 (0.194) | 0.430 (0.104) | |||
| RH2 | PINC | 1.304 *** (5.393) | 1.282 *** (5.251) | 2.148 *** (5.039) | 2.202 *** (4.944) | ||||
| RH3 | PPPUNIT | −0.180 (−1.216) | −0.141 (−1.042) | −0.187 (−1.336) | −0.090 (−0.685) | ||||
| RH4 | PPPFUND | −0.167 (−1.072) | −0.053 (−0.370) | −0.073 (−0.474) | 0.128 (0.875) | ||||
| RH5 | FISRAT | −0.696 *** (−3.539) | 0.697 ** (2.112) | −0.702 *** (−3.566) | 0.727 ** (2.133) | ||||
| RH6 | PPPHIST | −0.336 *** (−3.575) | −0.156 * (−1.667) | −0.325 *** (−3.352) | −0.171 * (−1.809) | ||||
| RH# | Independent Variables | Coef (t) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 7 | Model R1 | Model R2 | ||
| RH1 | GDPR | 0.430 (0.104) | 0.744 (0.539) | 0.693 (0.187) |
| RH2 | PINC | 2.202 *** (4.944) | 0.867 *** (5.837) | 2.018 *** (5.063) |
| RH3 | PPPUNIT | −0.090 (−0.685) | −0.017 (−0.382) | −0.145 (−1.238) |
| RH4 | PPPFUND | 0.128 (0.875) | 0.051 (1.052) | 0.135 (1.031) |
| RH5 | FISRAT | 0.727 ** (2.133) | 0.314 *** (2.765) | 0.658 ** (2.156) |
| RH6 | PPPHIST | −0.171 * (−1.809) | −0.053 * (−1.682) | −0.143 * (−1.681) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Yuan, J.; Zheng, S.; Tan, Y.; Skibniewski, M.J. Regional Social Sustainability of Public–Private Partnerships (PPPs): Effects Evaluation and Influencing Factors Analysis. Buildings 2025, 15, 4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15244529
Zhang L, Yuan J, Zheng S, Tan Y, Skibniewski MJ. Regional Social Sustainability of Public–Private Partnerships (PPPs): Effects Evaluation and Influencing Factors Analysis. Buildings. 2025; 15(24):4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15244529
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lei, Jingfeng Yuan, Saina Zheng, Yongtao Tan, and Mirosław J. Skibniewski. 2025. "Regional Social Sustainability of Public–Private Partnerships (PPPs): Effects Evaluation and Influencing Factors Analysis" Buildings 15, no. 24: 4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15244529
APA StyleZhang, L., Yuan, J., Zheng, S., Tan, Y., & Skibniewski, M. J. (2025). Regional Social Sustainability of Public–Private Partnerships (PPPs): Effects Evaluation and Influencing Factors Analysis. Buildings, 15(24), 4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15244529








