Comprehensive Performance Evaluation of C Class Fly Ash Stability and Activity Index Based on Projection Pursuit Regression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Raw Materials and Test Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Test Methods
2.2.1. Soundness Test
2.2.2. Strength Activity Index Test
- R: 28-day compressive strength of the test mortar, MPa;
- R0: 28-day compressive strength of the reference mortar, MPa.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Soundness of Class C Fly Ash
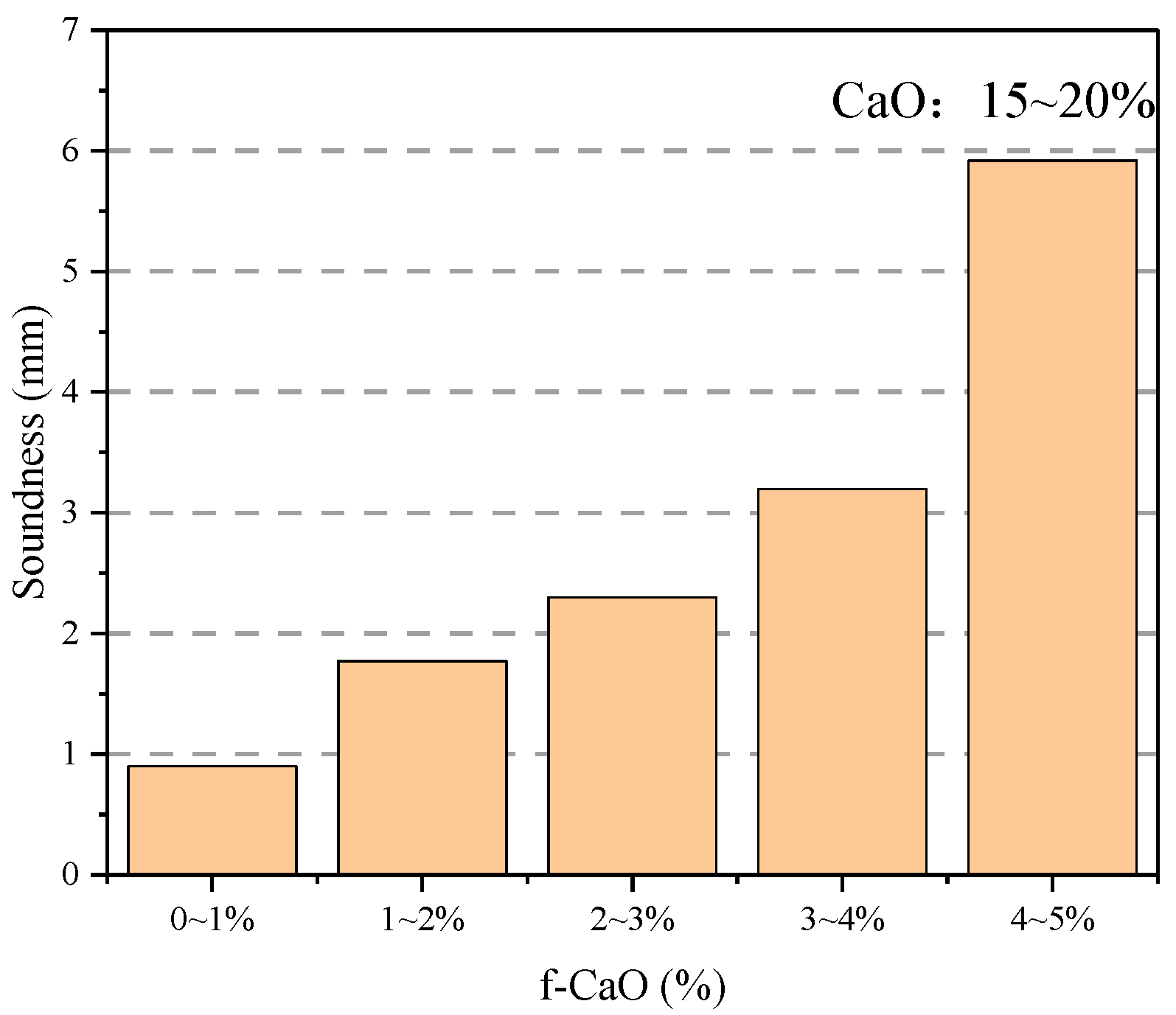
3.1.1. Effect of Free f-CaO Content in Class C Fly Ash on the Soundness of Specimens
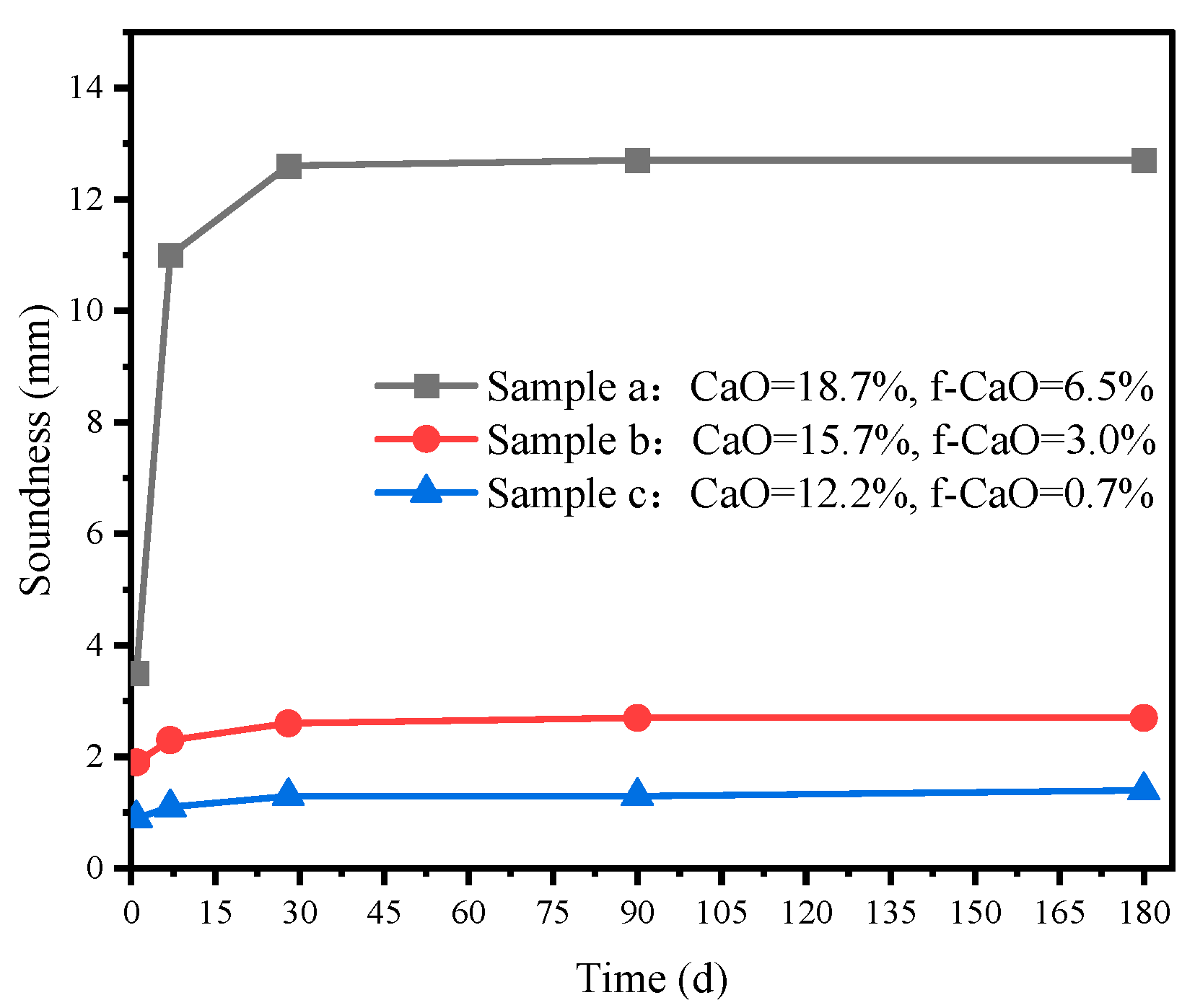
3.1.2. Effect of Curing Age on the Soundness of Specimens
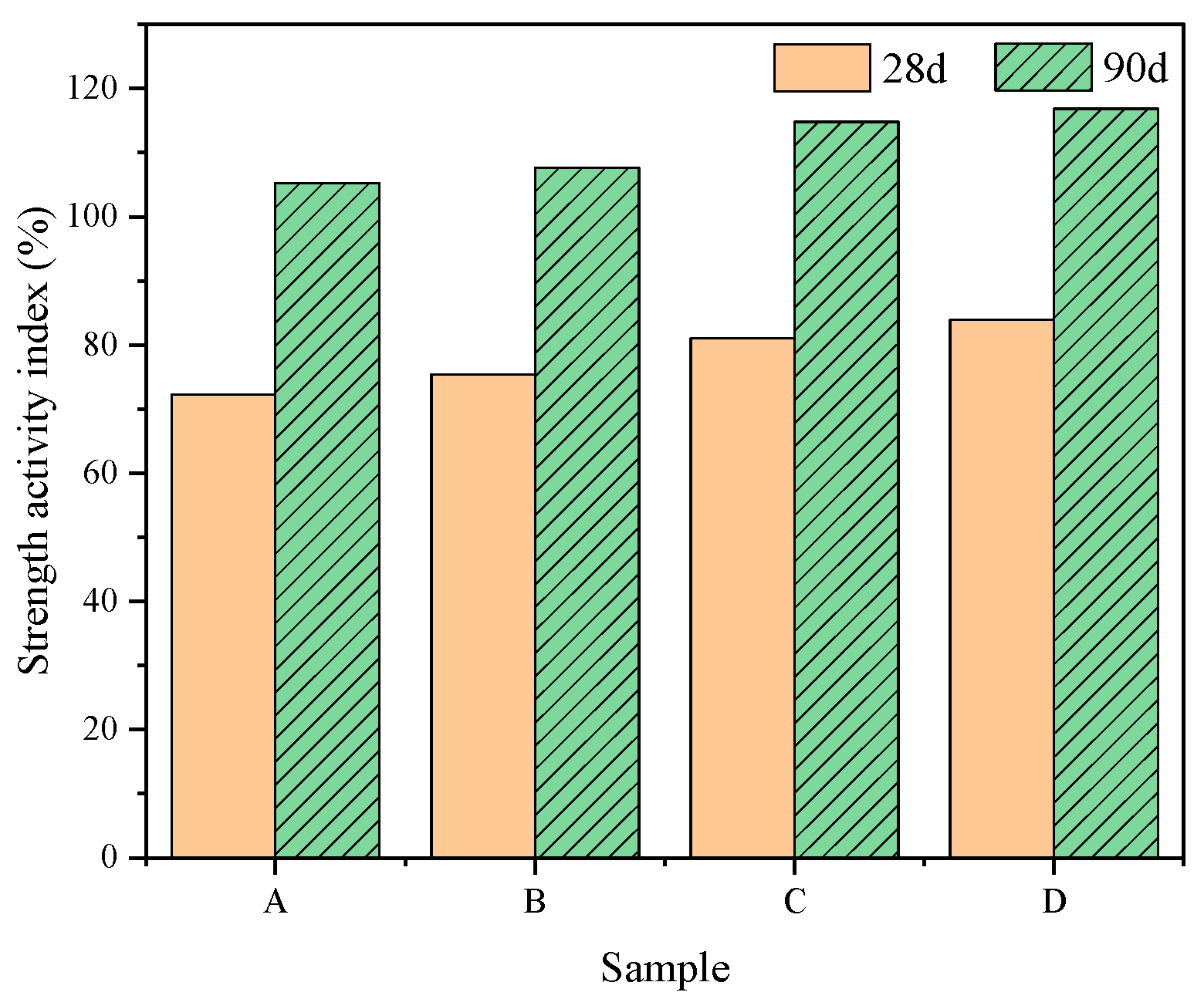
3.2. Strength Activity Index of Class C Fly Ash
4. PPR-Based Performance Optimization Model for Fly Ash
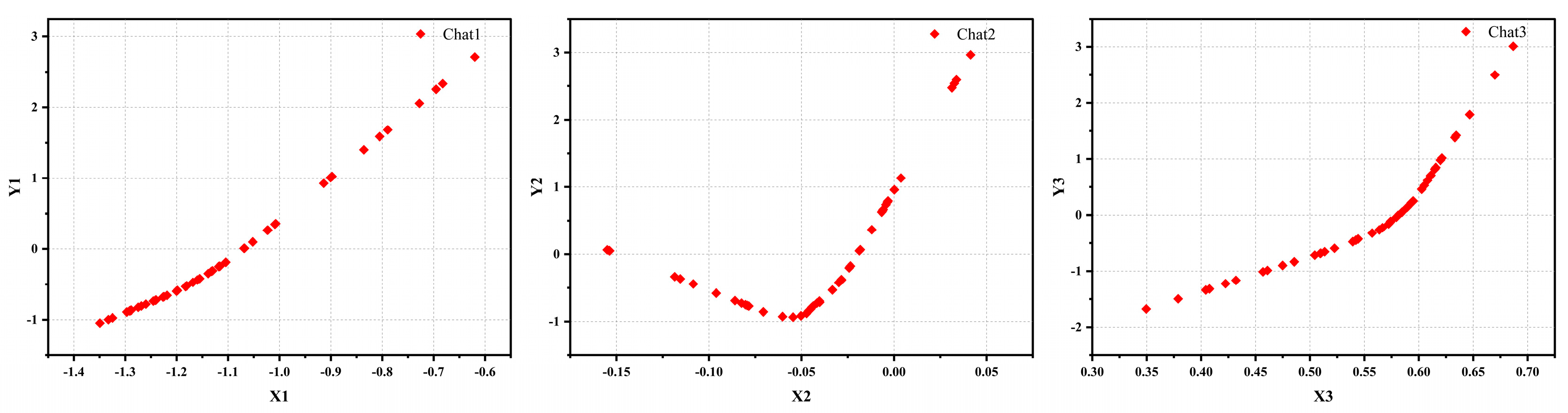
4.1. Projection Pursuit Regression (PPR) Method
4.2. Modeling Sample Conditions and Parameter Selection
4.2.1. Modeling Sample Conditions
4.2.2. Selection of Modeling Parameters
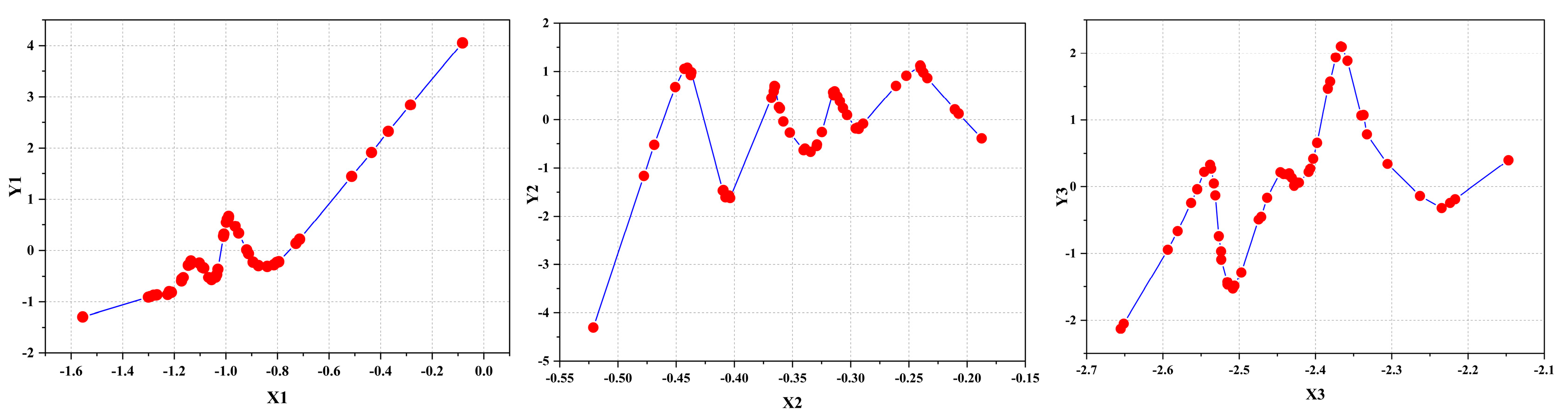
4.3. Model Data Analysis
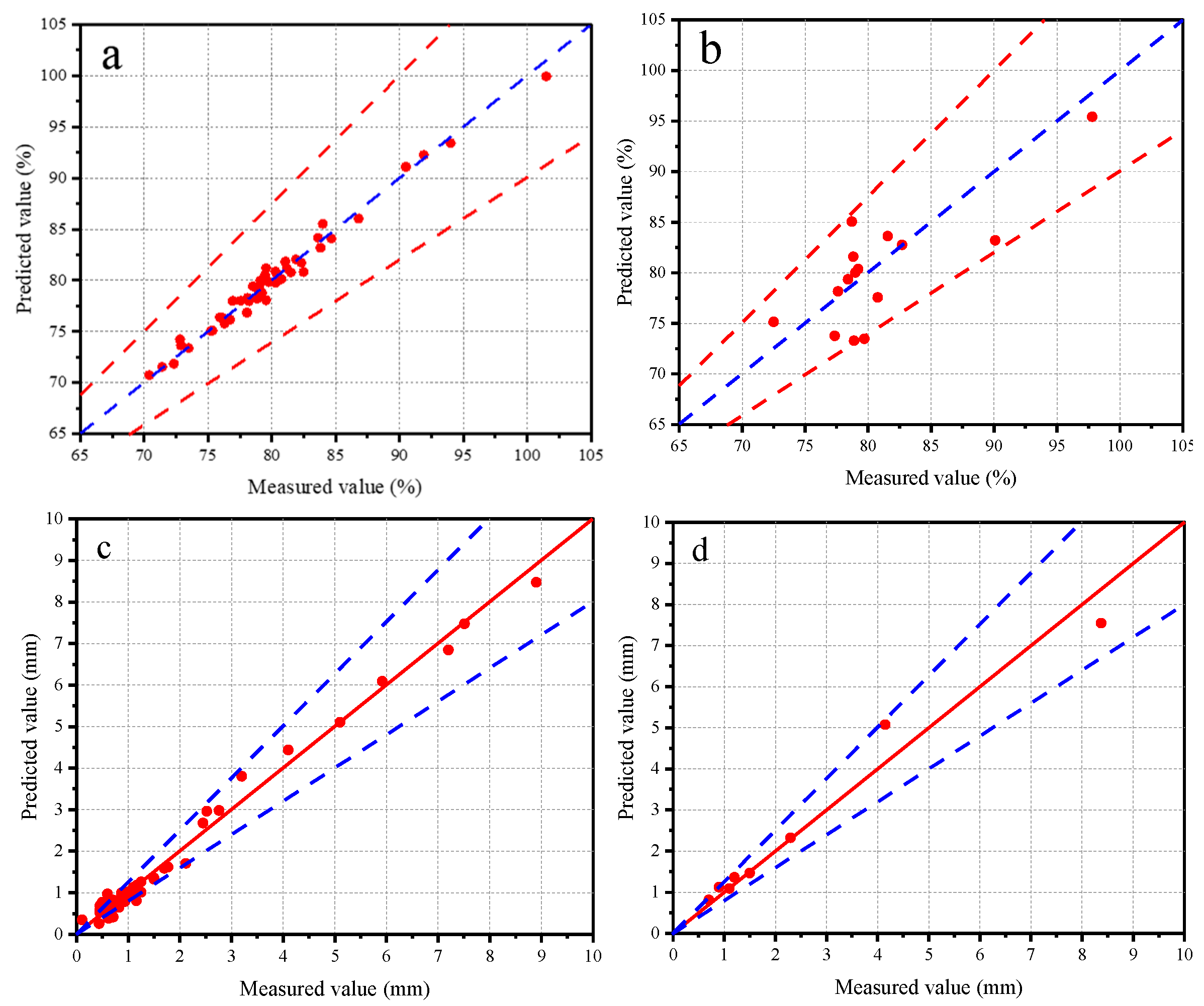
4.4. Model Accuracy Analysis
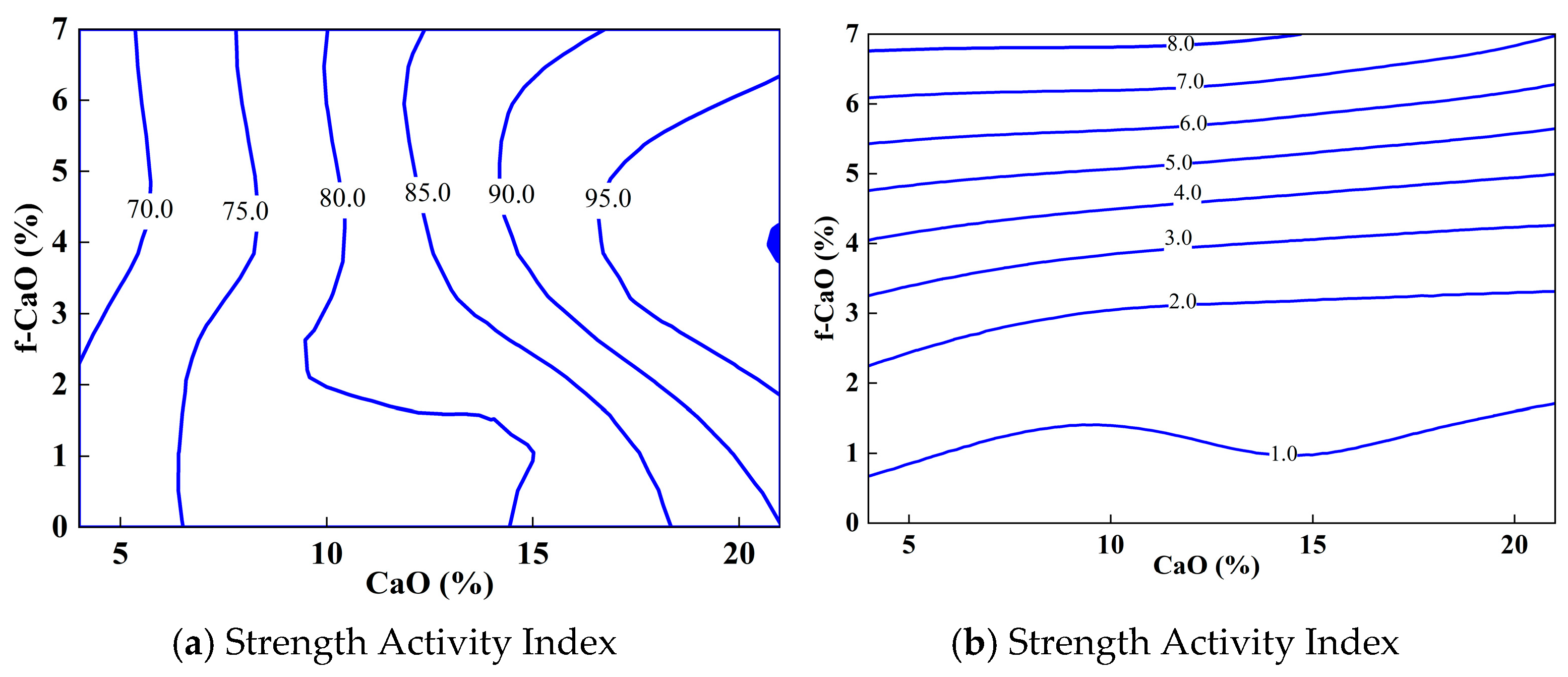
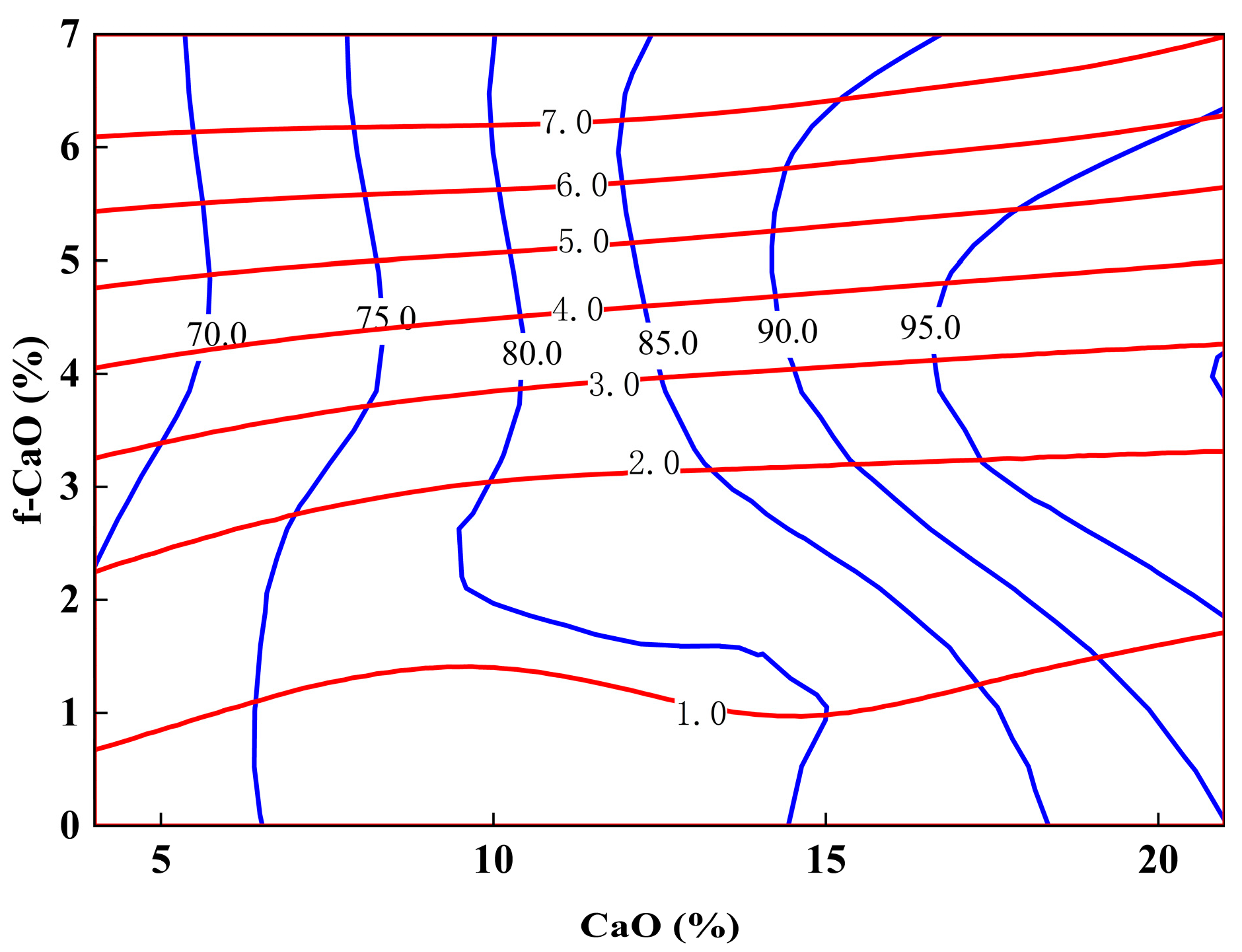
4.5. Simulation Calculation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- A prediction model for strength activity index and stability of Class C fly ash was developed using the PPR method. Experimental validation demonstrates the model’s high accuracy and stability, with relative errors between predicted and measured values within 10% and 20% for training and test samples, respectively. The qualification rates for strength activity index reached 100% and 93.8%, while stability achieved 78.3% and 75%. The model enables prediction of strength activity index and stability for Class C fly ash with varying CaO and f-CaO contents.
- (2)
- In practical engineering, both the stability and the strength activity index of Class C fly ash should be comprehensively considered. Research shows that stability requirements are met when f-CaO content does not exceed 4.82%. Under this condition, appropriately increasing CaO content can enhance the strength activity index, thereby improving concrete strength.
- (3)
- Based on the predictive model, fly ash selection criteria can be determined according to engineering requirements, providing robust data support for the application of Class C fly ash in hydraulic concrete and theoretical references for similar projects.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GB/T 1596-2017; Fly Ash Used for Cement and Concrete. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Wang, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhuang, S. The soundness of steel slag with different free CaO and MgO contents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cao, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J. Effect of Fe and Mn on the hydration activity of f-CaO in steel slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lv, T.; Han, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, B. Effects of fly ash on MgO-based shrinkage-compensating cement: Microstructure and properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 339, 127648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Ren, X.; Ye, J.; Cao, F.; Xu, C.; Zhai, M.; Zhang, W. Prediction of f-CaO content in cement clinker using a GRU-based deep learning model with masked-attention mechanism for incomplete DCS data. J. Sustain. Cem.-Based Mater. 2025, 14, 1413–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, C.; Bao, Y.; Lou, S.; Machingura, G.B.; Xiao, H.; Tian, P. SA-MSIFF: Soft sensing the cement f-CaO content with a self-adaptive multisource information fusion framework in clinker burning process. J. Process Control. 2024, 141, 103282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B. Study on the Volumetric Stability of High Calcium Fly Ash-Cement (Part 1). Fly Ash 2000, 4, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Uçurum, M.; Özdemir, A.; Teke, Ç. Optimization of surface modification parameters of fly ash with high calcium oxide (CaO) content to use as a filling material. Powder Technol. 2025, 451, 120463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H. Research on intrinsic characteristics and hydration properties of fly ash with high calcium oxide. J. Tongji Univ. 2003, 31, 1440–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H. Microstructure and hydration activity of calcium oxide. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 1994, 22, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W. Effect of temperature on the hydration characteristics of free lime. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Shi, H.; Fan, F. Research on the microstructure and hydration activity of f-CaO in some materials. J. Build. Mater. 1999, 2, 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Shi, S.; Feng, S.; Shen, B.; Zhang, J. Experimental Study on the Decomposition of f-CaO in High Calcium Fly Ash. Silic. Bull. 2009, 28, 1263–1266+1275. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Tan, C.Y.; Janasekaran, S.; Tai, V.C.; Wang, D.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Fan, Y. Multi-objective optimization of laser powder bed fusion parameters for SiC/Ti composites using a BP neural network and NSGA-II. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 39, 1466–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, H.; Rong, D.G.; Yunhua, L. Multi-objective Optimization for Axial Flow Fan Based on BP Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm. J. Chin. Soc. Mech. Eng. 2018, 39, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- Golafshani, E.M.; Pazouki, G. Predicting the compressive strength of self-compacting concrete containing fly ash using a hybrid artificial intelligence method. Comput. Concr. 2018, 22, 419–437. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Gong, J.; Tang, X.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, Z. Optimization Method of Comprehensive Properties of Low Heat Cement Cementitious System Based on Projection Pursuit Regression. J. Build. Mater. 2019, 22, 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Geng, X.; Yang, H.; Gao, P. Calculation Model for Moisture-Induced Deformation Based on PPR Unconditional Modeling. J. Wuhan Univ. 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Yang, W.; Liu, H.; Ma, J.; Wang, J. Stress-strain law fitting of sand and gravel based on PPR data modeling technology. Mater. Rev. 2023, 37, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, W.; Yang, H.; Liu, L.; He, J. Study of stress-strain relationship of hydraulic asphalt concrete at low to intermediate temperatures based on experimental data regression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 134059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 1346-2011; Test Methods for Water Requirement of Normal Consistency, Setting Time and Soundness of the Portland Cement. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- GB/T 17671-2021; Test Method of Cement Mortar Strength (ISO Method). China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Yang, Z.; He, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Lu, J. Optimization of asphalt concrete mix ratio based on PPR TOPSIS analysis. Adv. Water Resour. Hydropower Sci. Technol. 2023, 43, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; He, J.; Yang, W.; Lu, J. Calculation model of deviational stress of hydraul ic asphalt concrete based on PPR assumption-free modeling. J. Wuhan Univ. 2024, 57, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Zheng, R.; Qin, C.; Chen, R.; Cao, G. Prediction of thermal conductivity of concrete under variable temperatures in cold regions using projection pursuit regression. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2022, 203, 103642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Jiang, C.; Tang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, L. Optimization of mixture proportions in ternary low-heat Portland cement-based cementitious systems with mortar blends based on projection pursuit regression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Bai, Y.; Chen, X.; Tian, Z.; Ning, Y. Evaluation and prediction on abrasion resistance of hydraulic concrete after exposure to different freeze-thaw cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 316, 126055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Gong, J.; Xie, G. Modeling Hydration Kinetics of the Portland-Cement-Based Cementitious Systems with Mortar Blends by Non-Assumptive Projection Pursuit Regression. Thermochim. Acta 2021, 705, 179035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Weng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ji, X.; Liu, J. Calculation of f-CaO Hydration Ratio in Steel Slag Based on Mathematical Model of Hydration Expansion of Steel Slag–Cement Cementitious Materials. JOM 2023, 75, 5243–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Q.; Fang, K. Optimization of f-MgO/f-CaO phase in ladle furnace slag by air rapidly cooling. Mater. Lett. 2020, 280, 128528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusra, I. Thermodynamic Simulation of Fly Ash’s Influence on the Phase Composition of Cement Paste Hydration Products. Ph.D. Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, D. Research on Data Augmentation and Soft Measurement Model for Free Calcium in Cement Clinker Based on Generative Adversarial Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
| Qualification | Density (g/cm3) | Specific Surface Area (m2/kg) | Setting Time (min) | Rupture Strength (MPa) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Set | Final Set | 7 d | 28 d | 7 d | 28 d | |||
| low heat Portland cement | 3.20 | 315 | 157 | 227 | 3.5 | 7.8 | 14.4 | 44.4 |
| Chemical and Composition | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | SO3 | C3S | C2S | C3A | C4AF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| low heat Portland cement | 59.67 | 22.77 | 4.07 | 5.29 | 2.20 | 28.6 | 43.8 | 1.8 | 16.1 |
| Sample | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | K2O | Na2O | SO3 | f-CaO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 56.67 | 23.19 | 6.07 | 2.32 | 4.04 | 2.67 | 1.50 | 0.42 | 0.01 |
| S2 | 49.10 | 17.74 | 7.24 | 4.56 | 11.20 | 2.02 | 3.79 | 0.62 | 0.82 |
| S3 | 43.75 | 15.77 | 8.13 | 5.64 | 12.24 | 1.67 | 3.94 | 2.69 | 0.66 |
| S4 | 44.29 | 15.99 | 8.31 | 4.74 | 11.60 | 2.09 | 3.75 | 2.33 | 0.62 |
| S5 | 42.79 | 15.64 | 8.77 | 4.95 | 12.71 | 2.05 | 3.74 | 2.57 | 0.98 |
| S6 | 41.06 | 16.89 | 8.80 | 5.07 | 14.92 | 2.08 | 3.58 | 2.59 | 1.46 |
| S7 | 42.95 | 16.44 | 9.20 | 4.53 | 11.79 | 2.11 | 3.50 | 2.43 | 1.57 |
| S8 | 43.90 | 17.14 | 8.80 | 4.60 | 12.88 | 2.00 | 4.02 | 2.05 | 0.87 |
| S9 | 38.16 | 14.93 | 10.38 | 6.64 | 13.27 | 1.66 | 5.04 | 2.67 | 0.89 |
| S10 | 44.72 | 16.89 | 6.98 | 5.97 | 14.44 | 1.78 | 3.41 | 1.10 | 0.75 |
| S11 | 42.22 | 16.29 | 8.00 | 6.12 | 15.70 | 1.67 | 3.23 | 1.36 | 1.16 |
| S12 | 52.30 | 18.52 | 9.65 | 3.13 | 7.30 | 1.83 | 2.67 | 0.78 | 0.55 |
| S13 | 46.05 | 17.25 | 8.25 | 4.85 | 14.64 | 1.97 | 2.72 | 1.12 | 1.10 |
| S14 | 46.68 | 17.55 | 8.21 | 4.51 | 13.50 | 1.86 | 3.15 | 0.65 | 0.74 |
| S15 | 47.92 | 17.51 | 7.60 | 4.52 | 12.40 | 1.87 | 3.25 | 0.58 | 0.49 |
| S16 | 46.57 | 16.79 | 9.08 | 4.03 | 11.21 | 2.13 | 3.06 | 1.89 | 1.18 |
| S17 | 41.08 | 15.66 | 8.80 | 4.81 | 11.50 | 1.88 | 3.62 | 2.99 | 1.10 |
| S18 | 41.34 | 16.08 | 9.08 | 4.70 | 12.50 | 1.90 | 3.39 | 3.04 | 0.90 |
| S19 | 40.95 | 15.99 | 10.21 | 4.68 | 11.90 | 1.80 | 3.30 | 2.43 | 1.03 |
| S20 | 39.67 | 15.19 | 7.87 | 5.20 | 14.58 | 1.82 | 3.80 | 3.57 | 1.64 |
| S21 | 39.47 | 15.23 | 7.64 | 5.35 | 14.66 | 1.84 | 3.79 | 3.68 | 1.57 |
| S22 | 51.75 | 17.38 | 4.64 | 4.25 | 12.16 | 1.34 | 3.31 | 0.65 | 0.69 |
| S23 | 52.87 | 17.61 | 4.46 | 4.19 | 8.14 | 1.92 | 4.13 | 0.28 | 0.30 |
| S24 | 52.48 | 17.19 | 6.73 | 3.72 | 10.50 | 2.82 | 3.20 | 1.07 | 0.10 |
| S25 | 51.80 | 17.04 | 6.42 | 4.02 | 9.74 | 2.70 | 3.45 | 1.22 | 0.25 |
| S26 | 49.34 | 16.80 | 6.73 | 4.47 | 10.25 | 2.64 | 3.61 | 1.55 | 0.21 |
| S27 | 49.67 | 16.45 | 6.13 | 4.48 | 11.23 | 2.52 | 3.98 | 1.70 | 0.49 |
| S28 | 40.13 | 16.84 | 7.93 | 5.51 | 16.19 | 1.36 | 3.65 | 1.65 | 1.39 |
| S29 | 48.67 | 16.07 | 6.73 | 4.42 | 9.84 | 2.60 | 3.79 | 1.77 | 0.19 |
| S30 | 44.53 | 13.99 | 4.83 | 5.19 | 13.43 | 1.72 | 5.29 | 2.94 | 0.59 |
| S31 | 41.87 | 15.95 | 9.41 | 4.63 | 11.74 | 1.95 | 2.95 | 2.68 | 0.23 |
| S32 | 50.49 | 21.37 | 7.76 | 3.18 | 11.26 | 1.62 | 2.74 | 0.62 | 0.51 |
| S33 | 47.25 | 20.07 | 7.41 | 3.34 | 8.67 | 1.56 | 1.81 | 2.32 | 0.34 |
| S34 | 41.78 | 16.94 | 8.81 | 5.65 | 15.82 | 1.24 | 3.88 | 1.84 | 0.72 |
| S35 | 30.8 | 16.04 | 17.93 | 4.03 | 21.24 | 1.32 | 0.53 | 3.53 | 2.43 |
| S36 | 49.02 | 17.34 | 9.11 | 3.25 | 13.38 | 1.72 | 2.50 | 0.73 | 6.41 |
| S37 | 51.65 | 18.28 | 9.54 | 3.16 | 9.08 | 1.80 | 2.63 | 0.77 | 1.72 |
| S38 | 50.99 | 18.04 | 9.43 | 3.18 | 10.15 | 1.78 | 2.60 | 0.76 | 2.89 |
| S39 | 50.33 | 17.81 | 9.32 | 3.20 | 11.23 | 1.76 | 2.57 | 0.75 | 4.06 |
| S40 | 37.66 | 15.77 | 7.50 | 5.47 | 21.32 | 1.28 | 3.41 | 1.55 | 7.19 |
| S41 | 39.63 | 16.62 | 7.84 | 5.50 | 17.47 | 1.34 | 3.60 | 1.63 | 2.55 |
| S42 | 38.64 | 16.19 | 7.67 | 5.48 | 19.40 | 1.31 | 3.50 | 1.59 | 4.87 |
| S43 | 38.15 | 15.98 | 7.58 | 5.48 | 20.36 | 1.30 | 3.46 | 1.57 | 6.03 |
| S44 | 56.67 | 23.19 | 6.07 | 2.32 | 5.09 | 2.67 | 1.50 | 0.42 | 0.01 |
| S45 | 53.10 | 21.70 | 5.76 | 2.49 | 10.67 | 2.51 | 1.41 | 0.40 | 5.90 |
| S46 | 55.95 | 22.90 | 6.01 | 2.35 | 6.21 | 2.64 | 1.48 | 0.41 | 1.18 |
| S47 | 45.74 | 18.15 | 9.25 | 4.64 | 11.18 | 1.55 | 3.97 | 0.74 | 0.72 |
| S48 | 55.24 | 22.60 | 5.95 | 2.39 | 7.32 | 2.61 | 1.47 | 0.41 | 2.36 |
| S49 | 54.52 | 22.30 | 5.88 | 2.42 | 8.44 | 2.58 | 1.45 | 0.41 | 3.54 |
| S50 | 53.81 | 22.00 | 5.82 | 2.46 | 9.55 | 2.54 | 1.43 | 0.40 | 4.72 |
| S51 | 51.10 | 17.16 | 4.60 | 4.26 | 14.73 | 1.33 | 3.27 | 0.64 | 1.86 |
| S52 | 50.45 | 16.94 | 4.56 | 4.27 | 15.74 | 1.31 | 3.22 | 0.64 | 3.03 |
| S53 | 49.80 | 16.71 | 4.52 | 4.28 | 16.74 | 1.30 | 3.18 | 0.63 | 4.20 |
| S54 | 49.15 | 16.49 | 4.47 | 4.29 | 17.74 | 1.29 | 3.14 | 0.62 | 5.37 |
| S55 | 45.6 | 17.52 | 7.05 | 4.86 | 13.01 | 1.50 | 3.66 | 1.10 | 0.44 |
| S56 | 42.62 | 17.29 | 8.34 | 5.60 | 15.20 | 1.35 | 3.88 | 1.73 | 1.16 |
| S57 | 49.16 | 17.69 | 7.26 | 4.62 | 12.6 | 2.01 | 3.82 | 0.68 | 0.67 |
| S58 | 45.58 | 16.78 | 7.86 | 5.30 | 12.16 | 1.83 | 2.70 | 0.78 | 1.12 |
| S59 | 51.54 | 17.23 | 4.96 | 4.58 | 10.37 | 2.08 | 3.75 | 0.37 | 0.41 |
| S60 | 54.54 | 18.15 | 6.17 | 3.95 | 8.04 | 2.70 | 2.91 | 0.33 | 0.28 |
| S61 | 54.74 | 18.32 | 5.05 | 3.84 | 10.62 | 2.30 | 3.48 | 0.49 | 0.14 |
| S62 | 38.83 | 16.21 | 10.50 | 5.95 | 14.67 | 1.15 | 4.48 | 1.78 | 1.70 |
| S63 | 49.68 | 17.57 | 9.22 | 3.23 | 12.31 | 1.74 | 2.53 | 0.74 | 5.24 |
| S64 | 39.14 | 16.41 | 7.76 | 5.49 | 18.43 | 1.33 | 3.55 | 1.61 | 3.71 |
| S65 | 48.50 | 16.27 | 4.43 | 4.30 | 18.74 | 1.27 | 3.10 | 0.62 | 6.54 |
| f-CaO/% | CaO/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–5 | 5–10 | 10–15 | 15–20 | |
| 0–2 | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| 2–4 | △ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| 4–6 | △ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| 6–8 | △ | △ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Serial Number | Span | (%) | Modeling Pass Rate (%) | Inspection Pass Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.9 | 10 | 98 | 81.3 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 10 | 100 | 87.5 |
| 3 | 0.1 | 5 | 100 | 75 |
| 4 | 0.1 | 10 | 100 | 93.8 |
| 5 | 0.1 | 15 | 100 | 93.8 |
| Serial Number | Span | (%) | Modeling Pass Rate (%) | Inspection Pass Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.9 | 20 | 34.6 | 37.5 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 20 | 50.0 | 50.0 |
| 3 | 0.1 | 15 | 72.1 | 70.0 |
| 4 | 0.1 | 20 | 78.3 | 75.0 |
| 5 | 0.1 | 25 | 79.1 | 90.0 |
| Span | M | Mu | P | N | Q |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 3 | 3 | 14 | 65 | 1 |
| Oxide | CaO | SiO2 | MgO | Fe2O3 | Na2O | P2O5 | BaO | Al2O3 | f-CaO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impact weight | 1 | 0.796 | 0.620 | 0.533 | 0.521 | 0.500 | 0.467 | 0.440 | 0.290 |
| Oxide | f-CaO | SO3 | CaO | SrO | MgO | SiO2 | K2O | TiO2 | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impact weight | 1 | 0.807 | 0.669 | 0.604 | 0.557 | 0.486 | 0.370 | 0.363 | <0.363 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, X.; Gong, M.; Chen, M.; Gong, J.; Jia, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y. Comprehensive Performance Evaluation of C Class Fly Ash Stability and Activity Index Based on Projection Pursuit Regression. Buildings 2025, 15, 4344. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15234344
Kong X, Gong M, Chen M, Gong J, Jia L, Yang L, Wang Y. Comprehensive Performance Evaluation of C Class Fly Ash Stability and Activity Index Based on Projection Pursuit Regression. Buildings. 2025; 15(23):4344. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15234344
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Xiangzhi, Miaomiao Gong, Mingshan Chen, Jingwei Gong, Liting Jia, Liqun Yang, and Yiyi Wang. 2025. "Comprehensive Performance Evaluation of C Class Fly Ash Stability and Activity Index Based on Projection Pursuit Regression" Buildings 15, no. 23: 4344. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15234344
APA StyleKong, X., Gong, M., Chen, M., Gong, J., Jia, L., Yang, L., & Wang, Y. (2025). Comprehensive Performance Evaluation of C Class Fly Ash Stability and Activity Index Based on Projection Pursuit Regression. Buildings, 15(23), 4344. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15234344





