Evaluation of Ground Parameters Influenced by Pile Driving
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
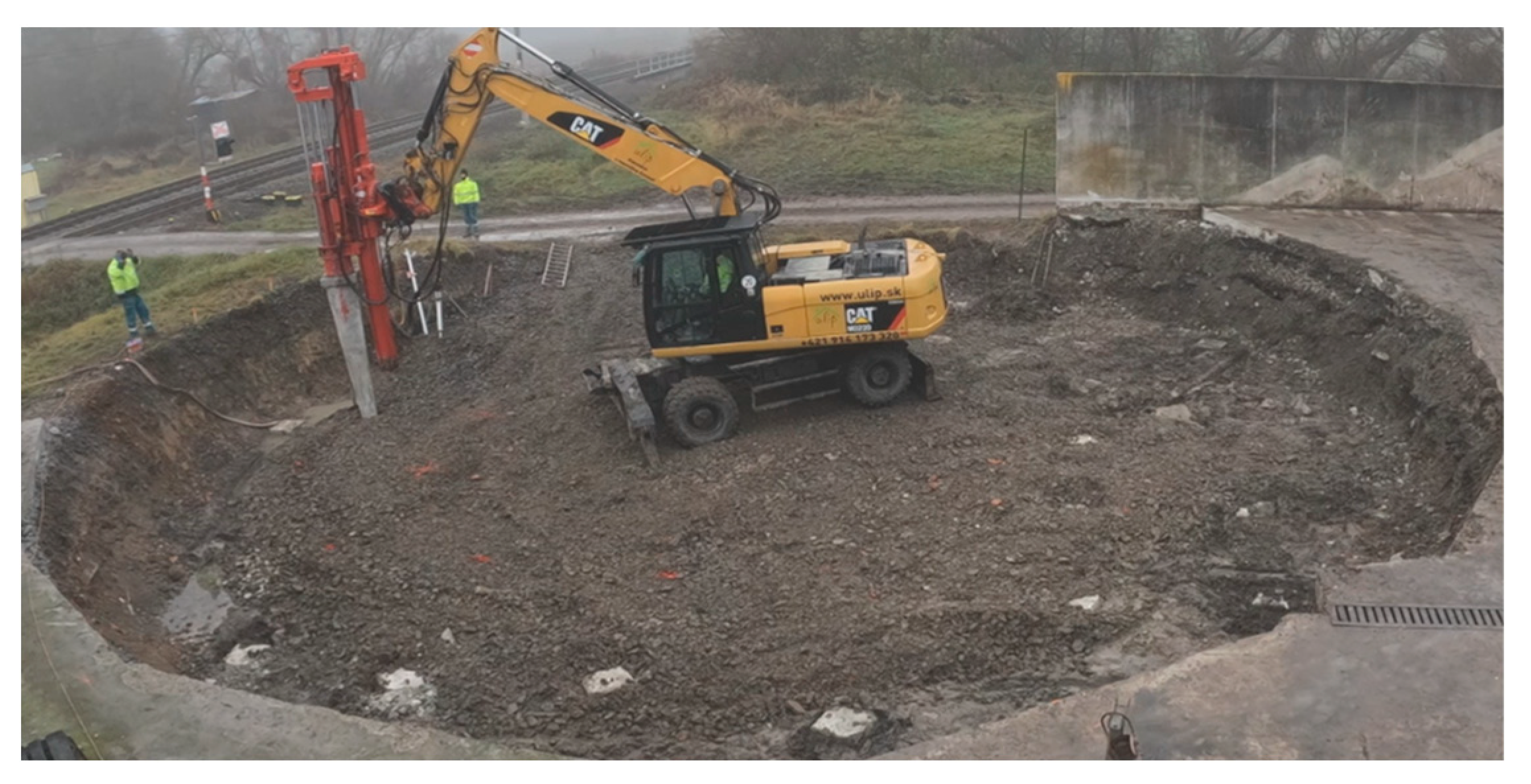
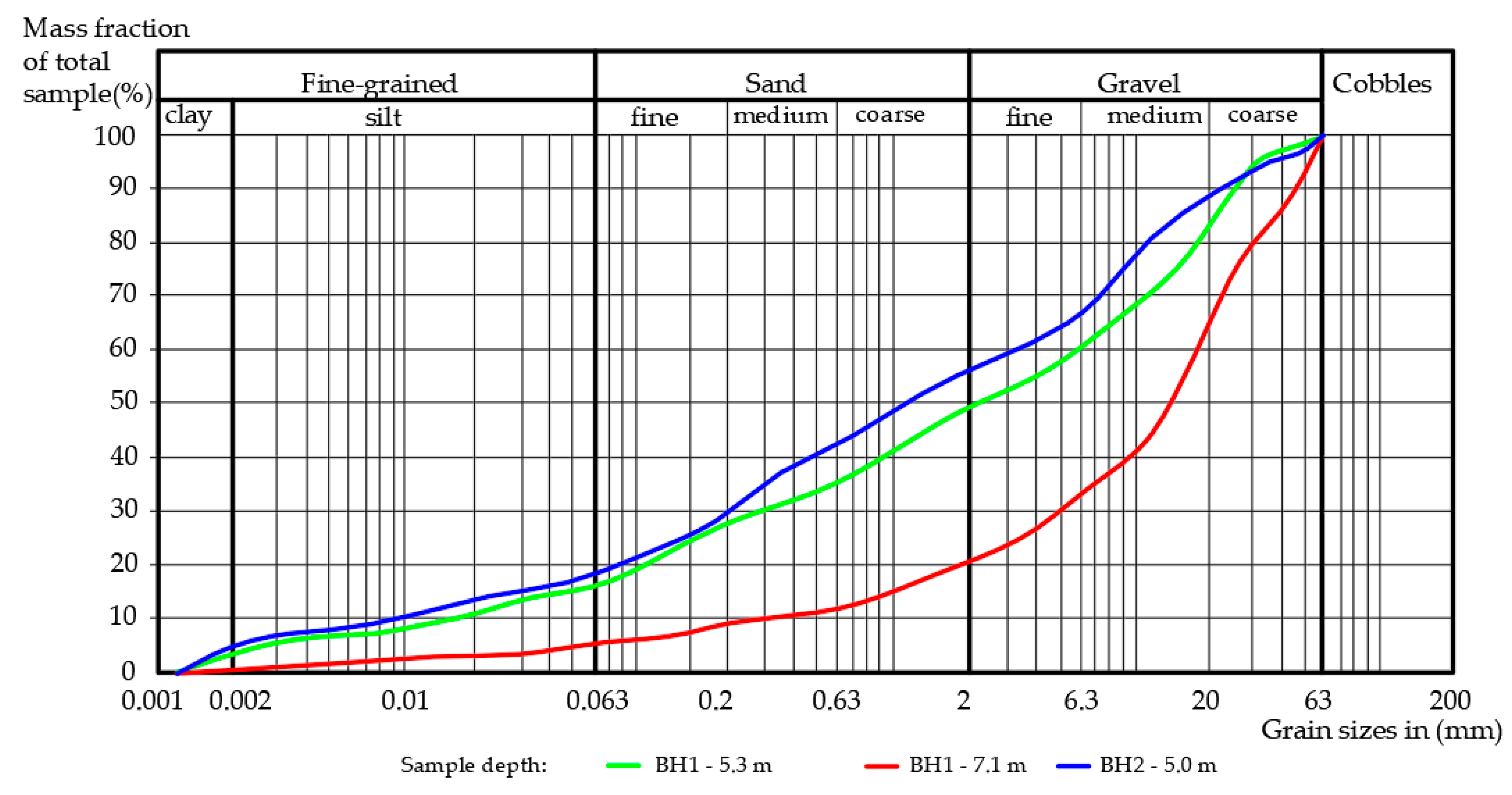
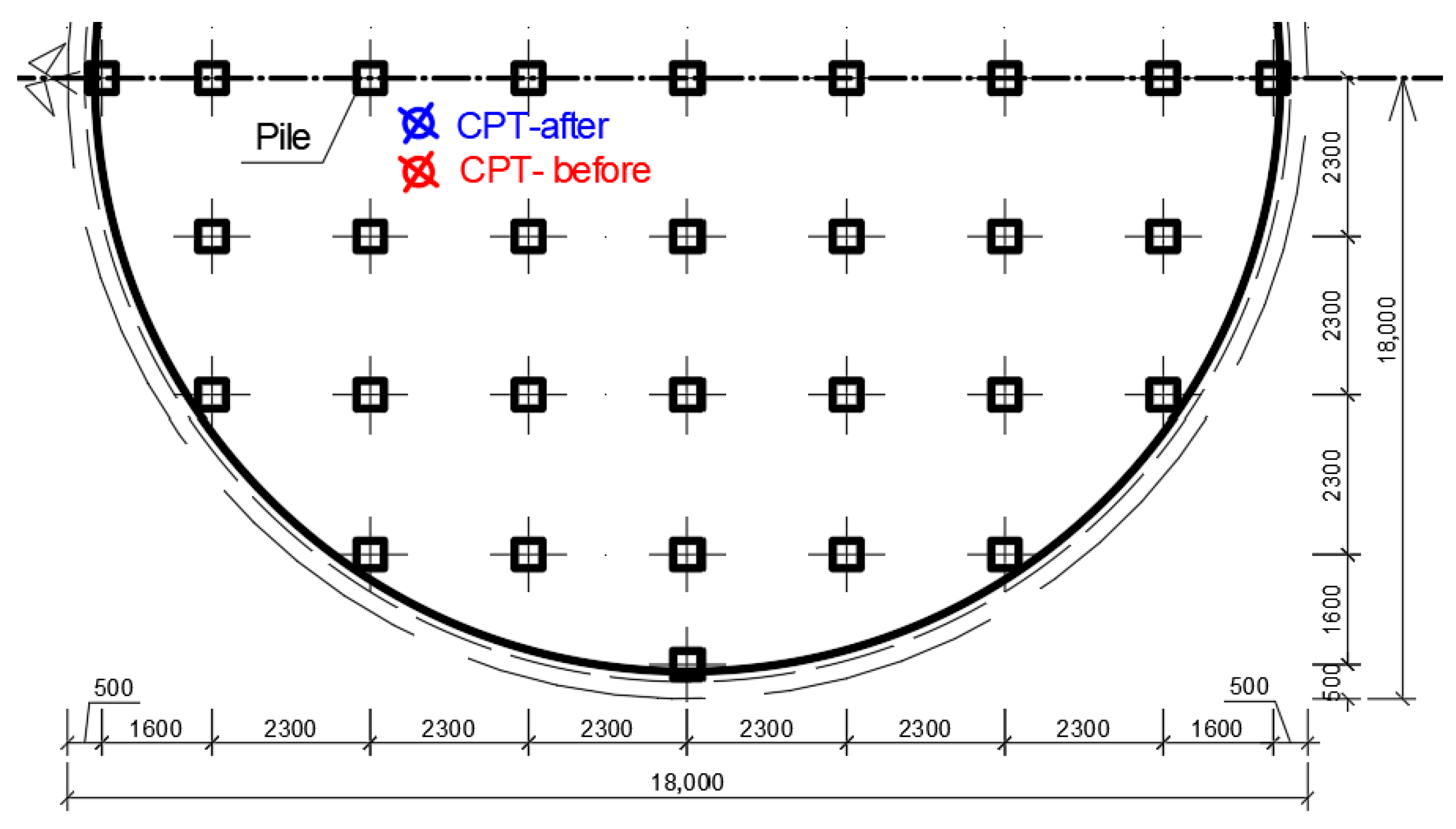
2.1. Testing Site
2.2. Deep Foundation Parameters
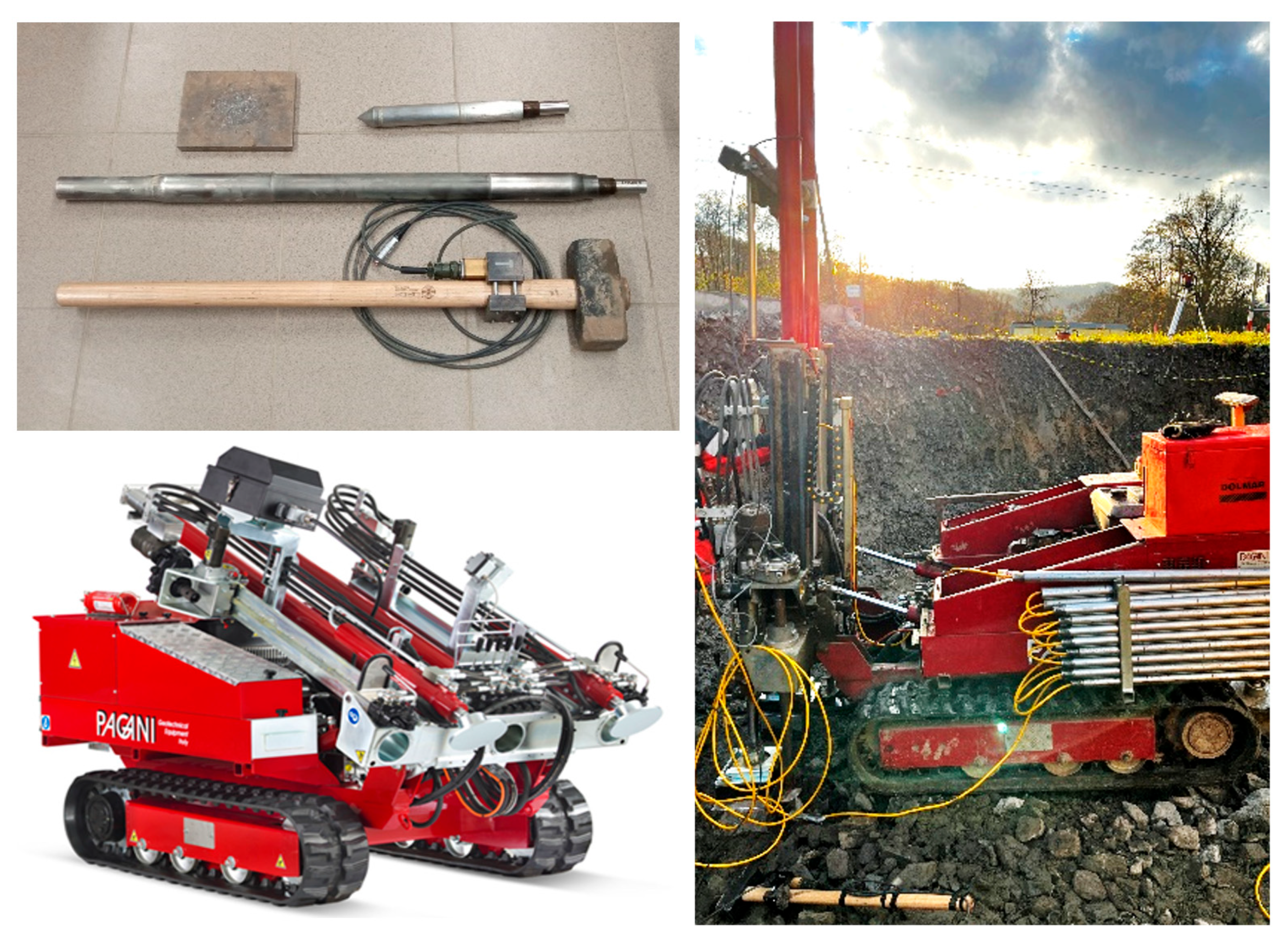
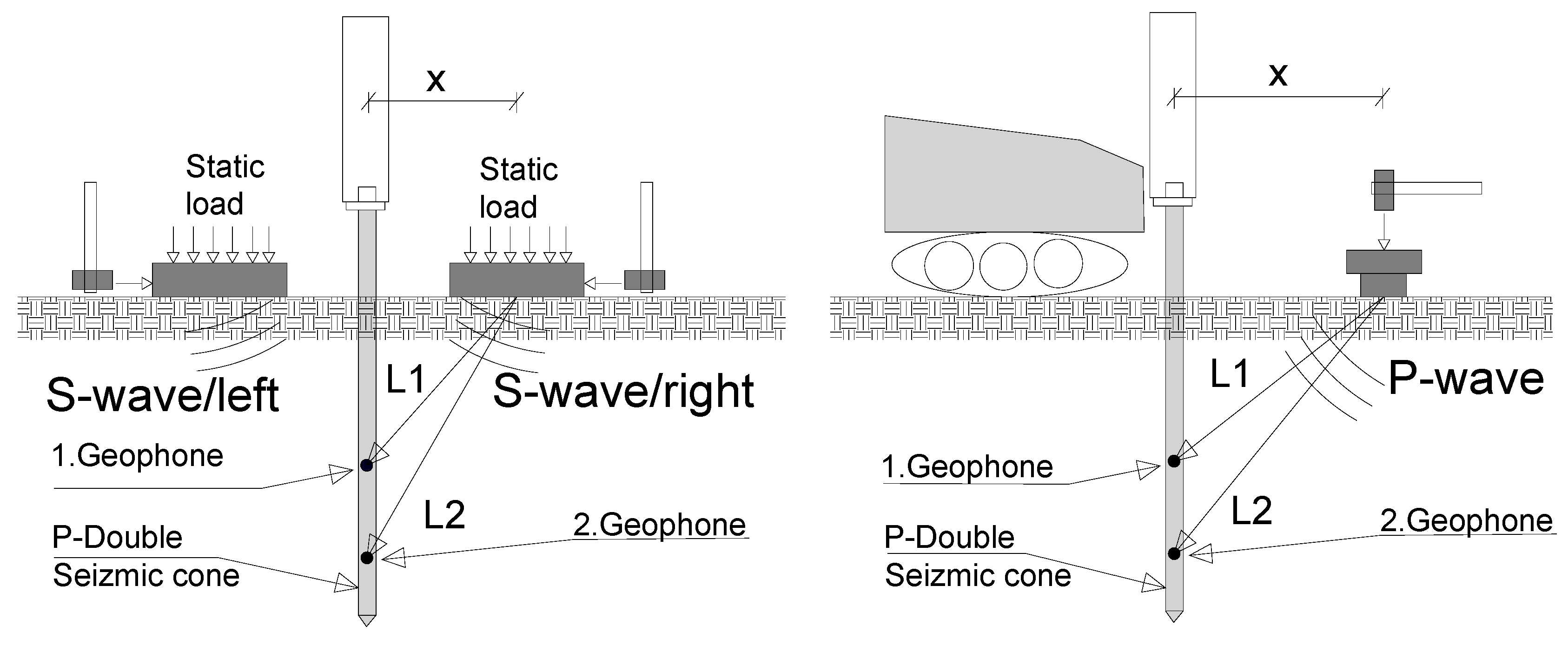
2.3. SCPTu Methodology
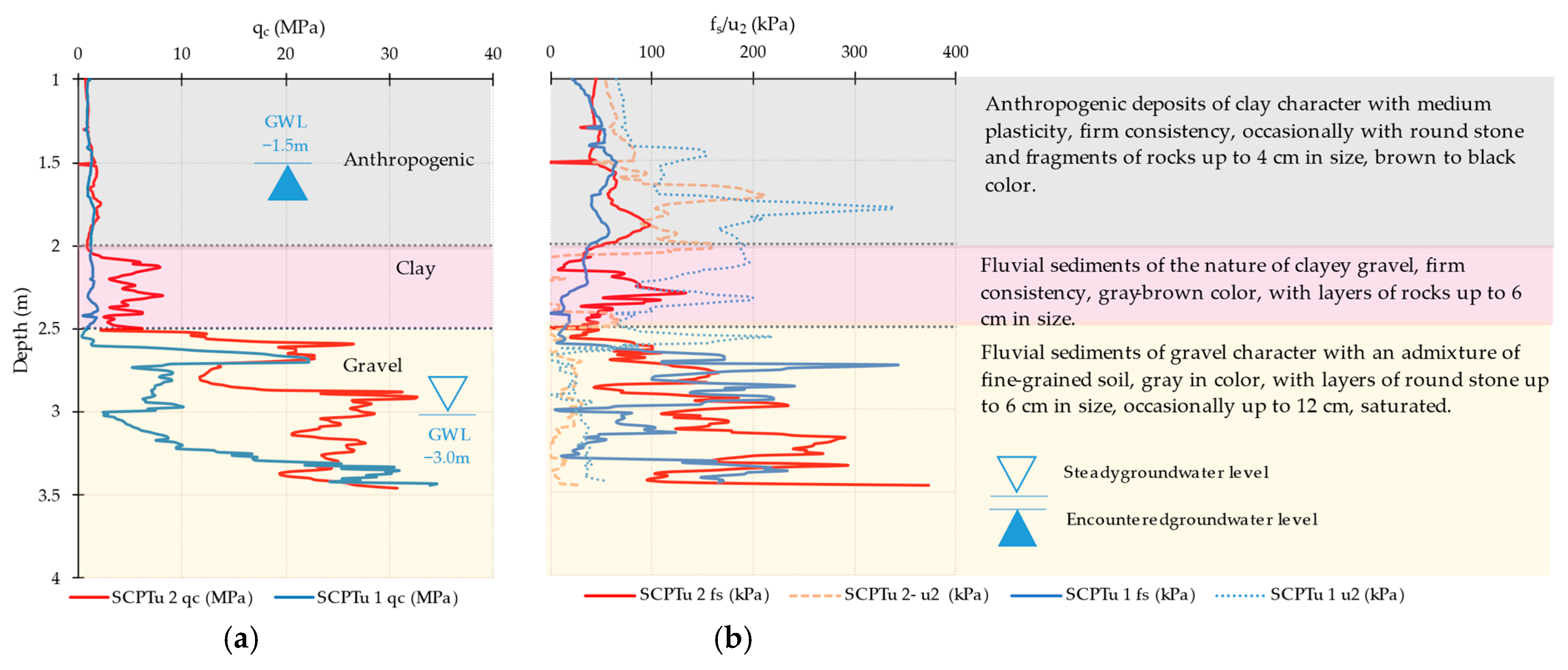
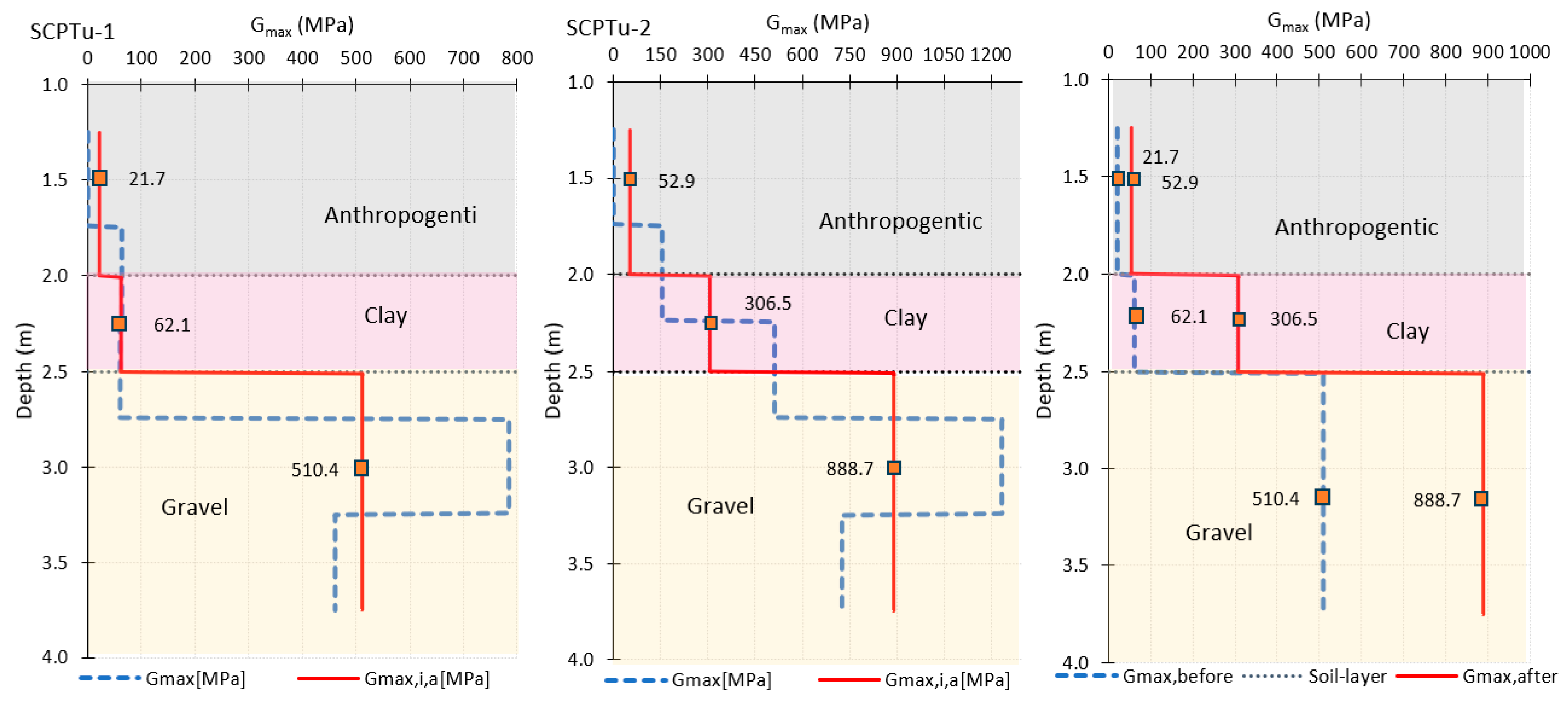
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Škvarka, J.; Bednárová, E.; Slávik, I. Analysis of Soil Susceptibility to Internal Suffusion in Selected Sites for Impoundment Objects. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 221, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzik, J.; Sitányiová, D.; Vondráčková, T.; Škoda, S. Hydrogeological Survey Data Analysis of Landslide Area by GIS Tools. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 15, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacho, J.; Súlovska, M.; Slavik, I. Analysis of the Shear Strength of a Soil-Geosynthetic Interface. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2023, 19, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putiška, R.; Marschalko, M.; Yilmaz, I.; Niemiec, D.; Cheng, X.; Dostal, I.; Kubáč, J. Surface Geophysical Methods Used to Verify the Karst Geological Structure in the Built-up Area: A Case Study of Specific Engineering-Geological Conditions. Acta Geol. Sin. 2021, 95, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovářík, K.; Mužík, J.; Sitányiová, D. A Fractional Step Local Boundary Integral Element Method for Unsteady Two-Dimensional Incompressible Flow. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2014, 44, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.; Mayne, P.W. Post Processing of Cone Penetration to Assess Seismic Ground Hazards, with Specific Application to the New Madrid Seismic Zone; MAE Center Report 07–09; Mid-America Earthquake Center: Urbana, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bulko, R.; Mužík, J.; Cigáň, F. Slope Stability Using Self-Drilling Anchor Rods. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2024, 20, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszyński, Z.; Rybak, J. Horizontal Displacement Control in Course of Lateral Loading of a Pile in a Slope. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 245, 032002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wistuba, M.; Malik, I.; Gorczyca, E.; Ślęzak, A. Establishing Regimes of Landslide Activity—Analysis of Landslide Triggers over the Previous Seven Decades (Western Carpathians, Poland). CATENA 2021, 196, 104888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujňaková, P.; Kraľovanec, J.; Perkowski, Z.; Bouchair, A. Verification of Precast Concrete Girder Bridge Under Static Load. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2022, 18, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ižvolt, L.; Dobeš, P.; Mečár, M. Diagnostics of the Deformation Resistance of the Track Bed in the Inter-Station Section Palárikovo-Nové Zámky-Track No. 1. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2023, 19, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozel, M.; Remek, Ľ.; Ďurínová, M.; Šedivý, Š.; Šrámek, J.; Danišovič, P.; Hostačná, V. Economic Impact Analysis of the Application of Different Pavement Performance Models on First-Class Roads with Selected Repair Technology. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, F.; Foti, S.; Hollender, F.; Bard, P.Y.; Cornou, C.; Cox, B.R.; Dechamp, A.; Ohrnberger, M.; Perron, V.; Sicilia, D.; et al. InterPACIFIC Project: Comparison of Invasive and Non-Invasive Methods for Seismic Site Characterization. Part II: Inter-Comparison between Surface-Wave and Borehole Methods. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2016, 82, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, F.; Foti, S.; Hollender, F.; Bard, P.Y.; Cornou, C.; Cox, B.R.; Ohrnberger, M.; Sicilia, D.; Asten, M.; Di Giulio, G.; et al. InterPACIFIC Project: Comparison of Invasive and Non-Invasive Methods for Seismic Site Characterization. Part I: Intra-Comparison of Surface Wave Methods. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2016, 82, 222–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, B.R.; Stolte, A.C.; Stokoe, K.H.; Wotherspoon, L.M. A Direct-Push Crosshole (DPCH) Test Method for the in Situ Evaluation of High-Resolution P- and S-Wave Velocities. Geotech. Test. J. 2019, 42, 1101–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agaiby, S. Advancements in the Interpretation of Seismic Piezocone Tests in Clays and Other Geomaterials. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Şahin, A. The Assessment of Seismic Liquefaction Triggering of Gravelly Soils. Master’s Thesis, School of Natural and Applied Sciences of Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Granskär, J. Evaluation of SCPT-Surveys as Method for Accessing Dynamic Modulus. Master’s Thesis, Department of Civil, Environmental and Natural Resources Engineering, University of Technology, Lulea, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jedrysiak, N.; Bagińska, I. Rozpoznanie Podłoża Gruntowego Sondą SCPTU. Górnictwo Geoinżynieria 2010, 33, 341–349. [Google Scholar]
- Niazi, F.S. Static Axial Pile Foundation Response Using Seismic Piezocone Data. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Randolph, M.F.; Wroth, C.P. A Simple Approach to Pile Design and the Evaluation of Pile Tests; ASTM Special Technical Publications: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1979; pp. 484–499. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Cai, G.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. Field Investigation of Maximum Dynamic Shear Modulus of Clay Deposit Using Seismic Piezocone. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 17, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, P.W.; Rix, G.J. Correlations Between Shear Wave Velocity and Cone Tip Resistance in Natural Clays. Soils Found. 1995, 35, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, C. Influence of Soil Plugging on Dynamic Soil Response During Simulated Pipe Pile Driving Model Test in Sands. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, T.; Mayne, P.W.; Cargill, E. Continuous-Interval Shear Wave Velocity Profiling by Auto-Source and Seismic Piezocone Tests. Can. Geotech. J. 2013, 50, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir Mohammad Hosseini, S.M.; Hajimohammadi, A.; Hajimohammadi, A. The Validity Assesment of Laboratory Shear Modolus Using In-Situ Seismic Piezocone Test Results. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2010, 8, 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Qi, X.; Chu, J. Site Characterization of Reclaimed Lands Based on Seismic Cone Penetration Test. Eng. Geol. 2021, 280, 105953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, Z. Statistical Characteristics of Soil Dynamics in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region and Their Impacts on Structural Seismic Analyses. Buildings 2025, 15, 3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizi, A.; Athanasopoulos-Zekkos, A.; Woods, R.D. Ground Vibration Measurements near Impact Pile Driving. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellenius, B. Increase of CPT Cone Resistance in Sand Due to Installation of Press-in Piles. DFI J. 2022, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarsch, K.R.; Fellenius, B.H. Engineering Assessment of Ground Vibrations Caused by Impact Pile Driving. Geotech. Eng. J. SEAGS AGSSEA 2015, 46, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Massarsch, K.R. Ground Vibrations Caused by Impact Pile Driving. In Environmental Vibrations: Prediction, Monitoring, Mitigation and Evaluation (ISEV 2005); CRC Press: London, UK, 2021; pp. 369–379. ISBN 978-1-00-320937-9. [Google Scholar]
- Bekbasarov, I.; Shanshabayev, N.; Atenov, Y. Impact-Driven Penetration of Multi-Strength Fiber Concrete Pyramid-Prismatic Piles. Buildings 2024, 14, 3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tol Van, A.F. Funderingstechnieken, Faculteit der Civiele Techniek Vakgroep Waterbouwkunde Sectie Geotechniek. 1994; pp. 24–42. Available online: https://repository.tudelft.nl/record/uuid:828b5167-0d9c-4ccb-b595-55a75d3f3c3c (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Duan, W.; Cai, G.; Yuan, J.; Liu, S. Evaluation of the Variation of Deformation Parameters Before and After Pile Driving Using SCPTU Data. In Proceedings of China-Europe Conference on Geotechnical Engineering; Wu, W., Yu, H.-S., Eds.; Springer Series in Geomechanics and Geoengineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 689–693. ISBN 978-3-319-97111-7. [Google Scholar]
- Stacul, S.; Fiera, F.; Perini, M.; Pagani, E.; Siviero, M.; Presti, D. On the Assessment of Compression and Shear Wave Velocities via Seismic Cone Penetration Test and Comparisons with Other Geophysical Tests at Different Sites. J. GeoEng. 2024, 19, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Presti, D.; Fiera, F.; Perini, M.; Pagani, E.; Siviero, M.; Stacul, S. Use of Seismic Piezocone for the Assessment of the Propagation Velocity of Body Waves. Riv. Ital. Geotec. 2024, 1281, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koreta, O.; Augustesen, A.; Krogh, L.; Lundvig, K.; Bøtker-Rasmussen, S. On the Accuracy and Precision of the Seismic Cone Penetration Test—A Field Test Study on the Seismic Source. In Cone Penetration Testing 2022; CRC Press: London, UK, 2022; pp. 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Wair, B.R.; DeJong, J.T.; Shantz, T. Guidelines for Estimation of Shear Wave Velocity Profiles; Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 1–95. [Google Scholar]
- Stolte, A.C.; Cox, B.R. Towards Consideration of Epistemic Uncertainty in Shear-Wave Velocity Measurements Obtained via Seismic Cone Penetration Testing (SCPT). Can. Geotech. J. 2020, 57, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, P.; Cargill, E.; Greig, J. The Cone Penetration Test: Better Information; ConeTec Group: Burnaby, BC, Canada, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Firouzianbandpey, S.; Nielsenl, B.N.; Andersen, L.V.; Ibsen, L.B. Geotechnical Site Assessment by Seismic Piezocone Test in North of Denmark. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Case Histories in Geotechnical Engineering, Chicago, IL, USA, 6–8 May 2013; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, P.; Cabal, K. Cone Penetration Testing Guide to, 7th ed.; Gregg Drilling LLC: Walnut Ave, CA, USA, 2023; pp. 1–165. [Google Scholar]
- Gottardi, G.; Tonni, L. Cone Penetration Testing 2022: Abstracts Volume, 1st ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2022; ISBN 978-1-00-332909-1. [Google Scholar]
- Holmsgaard, R.; Ibsen, L.B.; Nielsen, B.N. Interpretation of Seismic Cone Penetration Testing in Silty Soil. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 21, 4759–4779. [Google Scholar]
- Iliescu, A.; Geron, J. Seismic Cone Penetration Test. Experimental Results in Onshore Areas. Geol. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2012. Available online: https://projekter.aau.dk/projekter/files/63666390/Article1Experimental.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Miller, G.A.; Abuawad, T.Z.; Nevels, J. Demonstration of the Applicability of the New CPTU/SCPTU Correlations with Soil Parameter Evaluation; Sci. Report Federal Highway Administration, Department of Transportation Oklahoma: Oklahoma, OK, USA, 2022; pp. 1–184. [Google Scholar]
- Leetsaar, L.; Korkiala-Tanttu, L. Advantages of Using a Seismic Piezocone Penetration Test for Analysis of a Single Screw in Situ Displacement Pile in Silty Soils. Indian Geotech. J. 2025, 55, 802–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbák, M.; Chromčák, J.; Bačová, D.; Odrobiňák, J. Investigation of Actual In-Plane Geometric Imperfections of Steel Tied-Arch Bridges. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Layer | Anthropogenic | Clay | Gravel | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCPTu-1 | γt [kN/m3] | 17.1 | 16.7 | 18.7 |
| SCPTu-2 | γt [kN/m3] | 17.6 | 17.7 | 19.1 |
| Depth Interval [m] | Gmax [MPa] Before Piling | Gmax [MPa] After Piling | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gmax1 | 1.25–1.75 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Gmax2 | 1.75–2.25 | 73.2 | 187.5 |
| Gmax3 | 2.25–2.75 | 68.0 | 665.4 |
| Gmax4 | 2.75–3.25 | 989.4 | 1535.7 |
| Gmax5 | 3.25–3.75 | 554.4 | 875.5 |
| Depth Interval [m] | Gmax [MPa] Before Piling | Gmax [MPa] After Piling | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gmax1 | 0.00–2.00 | 21.8 | 52.9 |
| Gmax2 | 2.00–2.50 | 62.1 | 306.5 |
| Gmax3 | 3.00–3.75 | 510.4 | 888.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gago, F.; Mihálik, J.; Vlček, J.; Drusa, M.; Nguyen, G.; Michałek, J. Evaluation of Ground Parameters Influenced by Pile Driving. Buildings 2025, 15, 4127. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15224127
Gago F, Mihálik J, Vlček J, Drusa M, Nguyen G, Michałek J. Evaluation of Ground Parameters Influenced by Pile Driving. Buildings. 2025; 15(22):4127. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15224127
Chicago/Turabian StyleGago, Filip, Ján Mihálik, Jozef Vlček, Marian Drusa, Giang Nguyen, and Jarosław Michałek. 2025. "Evaluation of Ground Parameters Influenced by Pile Driving" Buildings 15, no. 22: 4127. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15224127
APA StyleGago, F., Mihálik, J., Vlček, J., Drusa, M., Nguyen, G., & Michałek, J. (2025). Evaluation of Ground Parameters Influenced by Pile Driving. Buildings, 15(22), 4127. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15224127








