Abstract
Geopolymers, achieved through geopolymerization of aluminosilicate-containing precursors, are environmentally friendly inorganic binders with excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and low carbon footprint. Beyond construction applications, geopolymers show great potential in environmental protection due to their ability to immobilize hazardous pollutants, adsorb ions and gases, and utilize industrial solid wastes. This review provides a state-of-the-art summary of recent advances in geopolymer applications in environmental fields, including (1) immobilization of hazardous wastes, (2) adsorption of hazardous ions and CO2, and (3) resource utilization of solid wastes through geopolymerization. The mechanisms underlying immobilization and adsorption are discussed, and research gaps and future directions will be highlighted to guide further development of geopolymer-based environmental materials or application of geopolymerization in solid waste utilization.
1. Introduction
Concrete, prepared from cement, sand, and stone, is one of the most widely used construction materials in the world. According to the latest IEA Global Energy Review 2025, global energy-related CO2 emissions reached 37.8 Gt in 2024, remaining at historically high levels despite a slight decline in industrial process emissions [1]. Among these, cement and clinker production—including both the calcination of CaCO3 and fuel combustion—accounts for approximately 5–8% of global anthropogenic CO2 emissions [2]. The direct emissions intensity of cement production has shown only a slow decline in recent years, and under the net-zero scenario, it must fall by over 3% annually to meet climate targets. Therefore, developing alternative low-carbon cementitious binders to mitigate the environmental impact of the construction industry attracts lots of attention [3,4,5].
Among these materials, geopolymers—emerging as a kind of green construction material—are prepared from two raw materials: solid precursors rich in silica and alumina (e.g., clay minerals, fly ash (FA), ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS), etc.) [6,7,8], and an activator solution, i.e., an alkali activator (e.g., NaOH and Na2SiO3 solution) [9] or an acid activator (e.g., H3PO4 solutions) [10,11]. The preparation process is just mixing these two raw materials, where raw materials undergo geopolymerization [12]. Depending on the type of activator, geopolymers can be categorized as alkali-activation and acid-activation geopolymer, with different microstructures and chemical compositions (Figure 1) [13,14]. The two activation routes yield geopolymers with distinct three-dimensional network structures and bonding configurations, which directly affect their mechanisms of immobilizing hazardous ions, adsorbing pollutants, and resisting chemical attack. From a sustainability perspective, activators such as NaOH and Na2SiO3 do contribute to some CO2 emissions during production, but several life-cycle analyses have shown that the total carbon footprint of geopolymers remains significantly lower than that of ordinary Portland cement (OPC) [14,15].
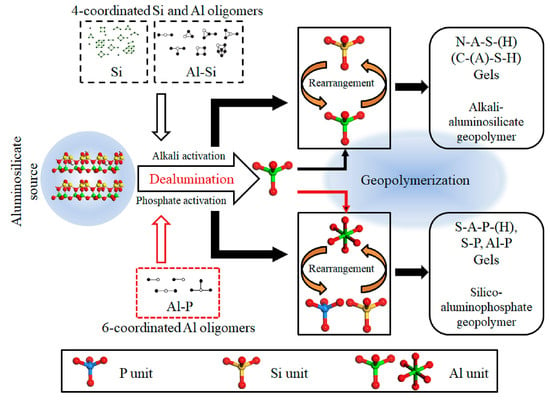
Figure 1.
Conceptual scheme for acid- and alkali-activation of an aluminosilicate source to form a geopolymer [16].
Alkali-activation geopolymers have been widely studied as construction and building materials. In fact, the invention of geopolymer is from the alkali activation of kaolinite by Prof. Davidovits [17]. Alkali-activation geopolymer is composed of randomly distributed [SiO4] and [AlO4] tetrahedra, interconnected by bridging oxygen to create a three-dimensional (3D) network structure, with alkali or alkaline earth metal ions occupying the interstitial spaces to balance the negative charges [18,19]. Van et al. [20] provided a brief summary of the geopolymerization process: under alkaline conditions, the aluminosilicate precursors dissolve, releasing aluminate and silicate monomers. These monomers then diffuse and polymerize to create a gel phase, during which water produced from condensation is expelled throughout the hardening process. Finally, the amorphous geopolymer with Si-O-Al structure is formed, which may be transformed into zeolites under certain conditions (Figure 2).
By using advanced technology, the microstructure of alkali-activation geopolymer becomes clearer. Zhang et al. [21] employed environmental scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to quantitatively trace the entire process of generation, development, and evolution of geopolymerization products in KOH-activated metakaolinite (MK)-based geopolymers. They found that in the early stages of hydration, MK particles are loosely packed, resulting in numerous large voids; as the curing time increases, a substantial amount of sponge-like species precipitate on the particle surfaces and expand outward; in later stages, the particles are densely enveloped by the gels, filling the voids and becoming dense. Walkley et al. [22] proposed a new structural model of hydrous alkali aluminosilicate (N-A-S-H) gel frameworks, where the charge-balancing, extra-framework Al species are observed in N-A-S-H gels by the application of 17O, 23Na, and 27Al triple-quantum magic-angle spinning solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy (Figure 3). In addition, the utilization of molecular dynamics simulations can provide an in-depth analysis of the molecular structure of geopolymers [23], and X-ray micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) can offer a 3D insight into the microstructure of geopolymers [24].
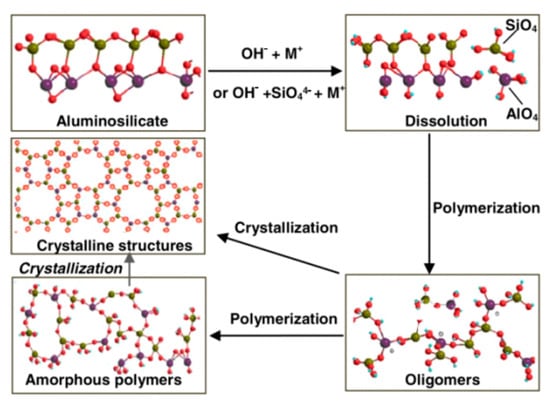
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the reaction mechanism of alkali-activated geopolymers [25].
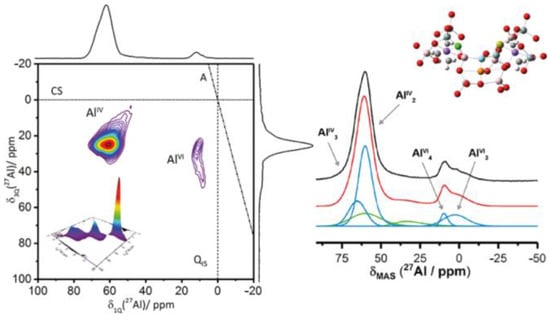
Figure 3.
New structure of alkali-activation geopolymers [22].
Compared with alkali-activation geopolymer, the studies on acid-activation geopolymer are much later and fewer. In 2002, researchers found that aluminosilicate precursors can also be activated by acid solution, forming an amorphous phase with a network structure of Al-O-P, Si-O-P and Si-O-Al [26]. Normally, MK is the most used precursor, and phosphoric acid solution is the most used acid activator [11,27,28,29]. In recent years, many solid wastes, like FA, mine tailing, etc., have been attempted to be used as precursors [30,31] and phosphate solution (e.g., AlH2PO4) as acid activators [32]. However, the geopolymerization mechanism of acid-activation geopolymers remains unclear due to the insufficient study on acid-based geopolymer. There are three main viewpoints of geopolymerization: (1) Deguang et al. [33] suggested that during the acid activation, the oligomeric P-O tetrahedra in phosphoric acid directly bonds with the reactive Al-O in MK, resulting in a Si-O-Al-O-P network structure (Figure 4); (2) Louati et al. [34,35] divided the acid-based geopolymerization into three steps: firstly, phosphoric acid disrupts the structure of MK, releasing free Al3+; secondly, the phosphate reacts with Al3+ to form AlPO4 and reacts with the de-aluminated kaolinite to generate Si-O-P structures; finally, Si-O-P condenses to form a 3D network structure; (3) Mathivet et al. [36] proposed that phosphoric acid reacts with MK to form Al-O-P and Al-O-Si network structures, along with the presence of amorphous silica gel. Recently, Cui et al. [37] found that the Al dissolved from MK reacts with phosphoric acid, while Si can be incorporated into Al-O-P in the form of amorphous silica to form Si-O-P-O-Al network.
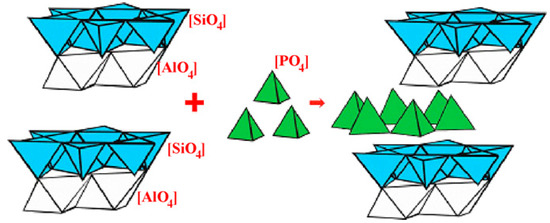
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the reaction mechanism of acid-activated geopolymers [37].
As mentioned above, benefiting from their 3D network structure, both alkali- and acid-activation geopolymers exhibit superior properties such as high mechanical strength [38,39], excellent corrosion resistance [40,41], and good fire resistance [42,43], indicating significant application prospects in construction materials, sealing materials, and high-temperature resistant materials. In addition, the energy consumption and CO2 emissions in manufacturing geopolymer are lower than ordinary Portland cement (OPC), which has made them promising alternative materials to OPC [44,45].
Not only the building materials, but also the application of geopolymer as environmental materials or the utilization of geopolymerization for environmental remediation has attracted lots of attention. For example, it is not only highly effective in immobilizing ions, but also in binding sludge particles during geopolymerization, allowing them to replace cement as new encapsulation materials for radioactive nuclear waste [46,47,48]. Moreover, geopolymers feature a zeolite-like structure that demonstrates adsorption properties for heavy metal ions, facilitating the purification of industrial wastewater [49]. More importantly, the utilization of some large amounts of solid wastes can yield high-performance geopolymers, which can further be used for adsorption or other environmental materials, contributing to the high value-added resource utilization of solid wastes [50].
Considering the huge potential of geopolymer in the environmental field, this paper reviews the state-of-the-art applications of geopolymerization technology or geopolymer in environmental remediation (e.g., solid waste utilization) or the obtained geopolymers as environmental materials, which is of practical significance for energy saving, CO2 emission reduction, resource utilization, and environmental protection. This review will provide references for further research and application of geopolymer-based materials in environment, energy, or chemical industry field.
This review focuses on three representative environmental applications of geopolymers: (i) immobilization/stabilization of heavy metals and radioactive wastes, (ii) adsorption of hazardous ions, organic dyes, and CO2, and (iii) resource utilization of solid wastes through geopolymerization. The objective is to summarize recent advances, elucidate underlying mechanisms, and highlight research gaps, rather than to provide an exhaustive survey of every environmental application. Publications were retrieved from major databases (Web of Science, Scopus, Google Scholar) mainly between 2000 and 2025 using combinations of keywords such as “geopolymer,” “alkali-activated,” “acid-activated,” “immobilization,” “adsorption,” “solid waste,” and “environmental remediation.” Priority was given to peer-reviewed articles that report mechanistic insights, long-term performance data, or novel approaches relevant to environmental protection.
2. Immobilization of Hazardous Pollutant Through Geopolymerization
The productive and social activities of humans have generated lots of waste. For instance, a variety of sludges are generated after wastewater treatment. These sludges are characterized by fine granules, low density, high moisture content, difficulty in dewatering, and a propensity for putrefaction and odor [51]. More importantly, these sludges contain large quantities of heavy metal ions, including Cu2+, Zn2+, Cr2+, and Pb2+, which will pose great risks to human health [52]. For example, numerous countries have established nuclear facilities as nuclear technology advances. However, safety issues such as nuclear leaks caused by natural disasters and the secure storage of nuclear materials remain [53]. Therefore, it will cause severe damage to geological and ecological environments if such hazardous wastes are not properly disposed of.
Traditional binders, like OPC and limestone, have been utilized for solidification/stabilization of solid wastes with hazardous composition (e.g., heavy metal ions, radionuclides, etc.) in a long time. The hydration of cement can bind the particles and retain the hazardous compositions [54,55]. However, many problems have emerged over time: (1) Portland cement, silicate cement, and lime-based cement are incompatible with some waste materials, causing issues such as reduced strength. (2) Solidification products have poor durability [56]. For instance, high concentrations of organic matter in sludges can cause the degradation and decomposition of the solidification products, thereby accelerating the permeation of hazardous compositions [57].
Comparatively, the solidification/stabilization of hazardous pollutant using geopolymerization shows significant advantages in resource utilization, energy saving, emission reduction, and acid resistance. In 1993, the German company named B.P.S Engineering, which focused on nuclear waste treatment, was the first to use geopolymer materials for solidification/stabilization of nuclear waste. In 1999, Hermann et al. [58] demonstrated the successful small-scale treatment of radioactive solid waste using geopolymers. After that, increasingly related research has come out, from micro-mechanism to macro-properties. In this section, the application of alkali- and acid-activation geopolymers as immobilization materials and related mechanisms were reviewed.
2.1. Solidification/Stabilization of Heavy Metals
Heavy metals refer to metallic elements characterized by high density (≥4 g/cm3 or 5 times greater than water), which is toxic to humans even at low concentrations. Heavy metals can be found in the biosphere (rocks, soils, and water), originating from a variety of sources (mining, industrial effluents, sewage discharge, soil erosion, etc.) and many others. Due to the fact that heavy metals do not degrade, they will persist in the environment and accumulate in living organisms, and finally harm to human health [59].
Thus, there are many studies concerning the immobilization of different kinds of heavy metal ions using geopolymerization technology. Phair and Deventer [60] discovered that in an aqueous solution under alkaline conditions, Pb2+ and Cu2+ primarily occur as Pb(OH)2, Pb(OH)3−, Cu(OH)2, and Cu(OH)3−. However, the electrostatic repulsion prevents Pb(OH)3− and Cu(OH)3− from chemically bonding with the negatively charged geopolymer, resulting in Pb2+ and Cu2+ being primarily fixed in the geopolymer matrix through physical encapsulation. Wang et al. [61] used FA-based geopolymers to solidify different concentrations and types of heavy metal ions (1–3% Pb2+, Cd2+, Mn2+, and Cr3+). The results indicated that the solidification rate of heavy metal ions approaches 99.9%, with the solidification effectiveness following the order of Pb2+ > Cr3+ > Cd2+ > Mn2+. They pointed out that most ions are encapsulated in the geopolymer matrix, which has a dense structure that prevents leachate penetration, thereby inhibiting the leaching of heavy metals. Donatello et al. [62] used FA-based geopolymers to solidify HgCl2 (at a concentration of 5 g/kg), achieving a solidification ratio for Hg2+ of 98.8–99.6%. The precipitates of HgS, Hg2S, HgO, and HgSiO4 are physically encapsulated and solidified in the geopolymer matrix, while Cl− promotes the leaching of Hg2+. Jiang et al. [63] combined FA and red mud as precursors to prepare geopolymer for Pb2+ and Cu2+ immobilization. Through the chemical bonding of T (Si, Al)-O-M (Pb, Cu) and physical sealing (Figure 5), Pb2+ and Cu2+ can be solidified efficiently. Fernández-Pereira et al. [64] utilized aluminate geopolymers for Cd2+, Ni2+, or Pb2+ immobilization, showing that aluminate geopolymers are promising binders.
Figure 5.
Solidification mechanism of heavy metals using alkali-activated geopolymers [63].
In addition to ions, heavy metal-containing matters can also be immobilized by geopolymerization, mainly through physical encapsulation. Guo et al. [65] used FA-based geopolymers as solidifying agents to study the mechanisms of solidification for three lead-containing compounds (1–8% PbO, PbSO4, and PbS). The results indicated that for lead compounds that do not react with alkalis, solidification occurs primarily through physical encapsulation within the geopolymer. In contrast, for lead compounds that react with alkalis, they are incorporated into the geopolymer network during geopolymerization. In another study [66], they used FA-based geopolymers to solidify four chromium-containing compounds (Cr(NO3)3, Cr3O3, Cr, and CrO3). The results showed that both chemical bonding and physical encapsulation mechanisms are present in geopolymer solidification. In the case of Cr(NO3)3, chemical bonding is the primary mechanism for chromium solidification, whereas for Cr2O3, Cr, and CrO3, physical encapsulation serves as the predominant mechanism.
Notably, compared to cation, the solidification of anion using geopolymer appears to less efficient. Al-Mashqbeh et al. [67] attempted to solidify three anions (Cr2O72−, MnO4−, Fe(CN)63−) using MK-based geopolymers. As the concentration of anions increases from 0.2% to 1.5%, the leaching rate rises from 10% to 20%. The Si/Al ratio significantly influences the solidification effectiveness. This suggests that although geopolymers can encapsulate highly soluble anions, their fixation ability is somewhat constrained. Ji et al. [68] immobilized heavy metal cations (Cd2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+) and anions (AsO43− and Cr2O72−) using GGBFS-based geopolymer and found that the immobilization effect of cations are much higher than that of anions because the former has charge neutralization effect. Meanwhile, crystalline phase was formed after adding anions. Wang et al. [69] also compared the immobilization effect of heavy metal cations (Pb2+ and Zn2+) and anions (AsO43− and Cr2O72−) by geopolymer. The results show that heavy metal ions are distributed in geopolymer matrix evenly (Figure 6), and the incorporation of Pb2+, Zn2+, and AsO2− induced significant changes in the Si chemical environment. They also found that Pb2+ and AsO2− can be solidified in the form of Si−O−Pb/Al−O−Pb and Si−O−As covalent bonds, where Zn2+ mainly facilitates ion exchange with Na+, and Cr2O72− is partially immobilized through physical encapsulation, without being incorporated into the geopolymer structure.
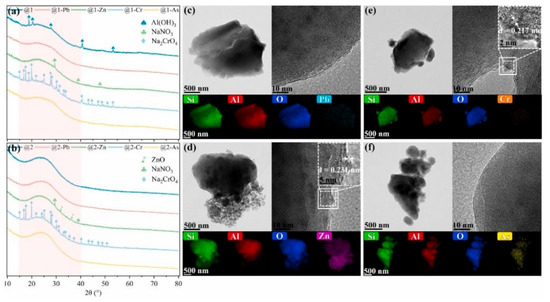
Figure 6.
Solidification of heavy metal ions using alkali-activation geopolymers. (a,b) XRD patterns of geopolymer with different conditions; (c–f) TEM and EDX mapping of geopolymers with different conditions and selected area [69].
Although laboratory studies consistently report near-complete immobilization of heavy metals, successful field application requires consideration of additional practical factors. Cost is a key issue, as the alkali activators used for geopolymerization are generally more expensive than OPC, which may limit adoption in large-scale waste treatment unless optimized mix designs are developed. Social acceptance is another challenge, since substituting Portland cement in waste management could disrupt existing industry practices. Most importantly, the long-term stability of immobilized contaminants must be ensured. Future research should therefore include pilot-scale demonstrations and long-term leaching tests to validate the excellent laboratory performance under real environmental conditions.
2.2. Solidification/Stabilization of Radioactive Nuclear Waste
Apart from heavy metal ions, geopolymers were originally employed for the solidification of radioactive nuclear waste, which show better effect than cement [70,71]. However, in lab-scale research, isotopes are used instead of radioisotopes for safety considerations. It should be noted that laboratory studies typically use non-radioactive isotopes to replace radioactive isotopes for safety reasons, since their ionic radii, charge, and chemical behavior are essentially identical, except for radioactivity. Generally, 133Cs and 87Sr are the two most used isotopes for simulating 137Cs and 90Sr, respectively, in geopolymer immobilization. He et al. [72] prepared MK-based geopolymer by adding 133Cs(OH)2, followed by high-temperature calcination. The resulting ceramic exhibited a low leaching rate for 133Cs+ (2.51 × 10−4 g·m−2·d−1), indicating the significant potential of geopolymer ceramics for Cs solidification. Deng et al. [73] prepared FA-based geopolymer adding 2% 133CsNO3, and the γ-rays test results indicate that γ-ray irradiation has a minimal impact on the microstructure of the geopolymer but increases the porosity of the geopolymer and consequently the leaching rate of 133Cs+. Tavor et al. [74] assessed the immobilization performance of FA-based geopolymers for 133Cs+ solidification and found that 133Cs+ will increase the porosity of geopolymer. However, 133Cs+ will not destroy the geopolymers’ chemical structure and can be immobilized efficiently (Figure 7). Blackford et al. [75] employed transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and NMR testing to investigate the solidification of 5% 133Cs+ and 87Sr2+ in MK-based geopolymers. The study results indicated that 133Cs+ was incorporated into the amorphous phase of the geopolymer at the nanoscale, while 87Sr2+ preferentially formed SrCO3 rather than being incorporated into the geopolymer gel.
Figure 7.
Solidification and related mechanism of Cs+ using geopolymers [76].
With the increase in radioactive nuclear wastes, many other radionuclide ions have also been researched for solidification. Niu et al. [77] prepared phosphoric acid-activated MK-based geopolymers for radionuclide anion (K2SeO3, K2SeO4, KI, and KIO3) immobilization. Compared to alkali-activation geopolymer, acid-activation geopolymers can solidify anions through electrostatic attraction because they possess a positively charged surface (Figure 8), and the matrix structure of geopolymers remains unchanged, which shows much better effect in radionuclide anion immobilization [47]. Iqbal et al. [78] explored MK-based geopolymer for immobilizing co-hosting cationic and anionic radionuclides. They concluded that Cs+ was retained by charge balance with [AlO4]-, Eu3+ was likely solidified by complexation and sorption mechanisms, while MoO42- reacted during geopolymerization to form Na2MoO4·2H2O and then was likely retained through encapsulation. 60Co is also a kind of radioactive waste in the nuclear industry. Yu et al. [79] used geopolymer to immobilize Co2+. The results indicate that Mn-slag-based geopolymer shows better solidification effect on Co2+ than MK-based geopolymer. This is because the oxidation reaction of Co2+ during geopolymerization of Mn-slag effectively enhanced its immobilization.
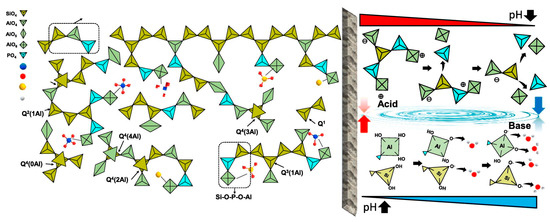
Figure 8.
Solidification mechanism of anions using acid-activation geopolymers [77].
In addition to solutions, geopolymers can also applied to solidify/stabilize radioactive liquid organic waste, achieving a promising effect [80,81].
2.3. Solidification/Stabilization Mechanism
The mechanisms of solidification/stabilization during solidification can mainly be divided into two categories: (1) physical encapsulation and (2) chemical bonding [82]. These two actions occur simultaneously during geopolymerization. Generally, alkali-activation geopolymers can effectively reduce the migration rate of cations but are less effective for oxyanions. This is in contrary to acid-activation geopolymers.
Physical encapsulation generally occurs at the micrometer scale. In the alkali-based geopolymerization, precursors firstly dissolve Si and Al under the influence of an alkaline solution, forming oligomers such as [SiO(OH)3]−, [SiO2(OH)2]2−, [SiO3(OH)]3−, and [Al(OH)4], which then condense to form a binder and ultimately generate an amorphous 3D network structure (Figure 9). During this reaction, the coating effect of the oligomer gel can encapsulate ions (or related precipitates) within the matrix structure of the geopolymer [83]. Additionally, the ions can be effectively immobilized if the dimensions of the zeolite-like cage structure are compatible. At the same time, geopolymers can act as physical barriers, which prevent leaching hazardous components by inhibiting its contact with leaching media [84].
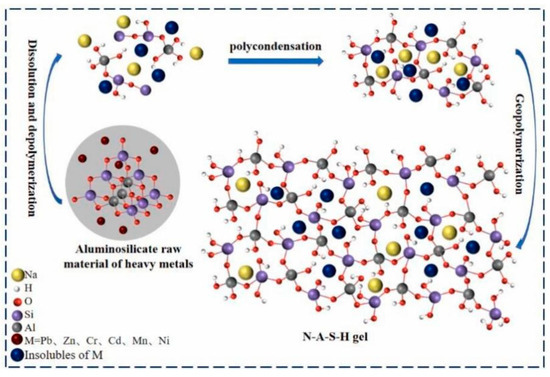
Figure 9.
Physical encapsulation of ions by geopolymer [85].
Compared to physical encapsulation, chemical bonding takes place at the nanometer scale, making a more contribution to immobilize. As shown in Figure 10, the cations can be solidified by charge balancing for [AlO4]− or formation of covalent bonding with Si-O− and Al-O− [56,86]. Recent studies indicate that the immobilization of ions occurs via isomorphous substitution [83]. Huang et al. [87] proposed that the positions of Al3+ in geopolymers can be substituted by similar ions, such as (Cr6+ (44 p.m.), Mn7+ (46 p.m.), and Fe3+ (55 p.m.). In addition, the solidification mechanism of geopolymers for ions also includes complexation and micro-precipitation [56].
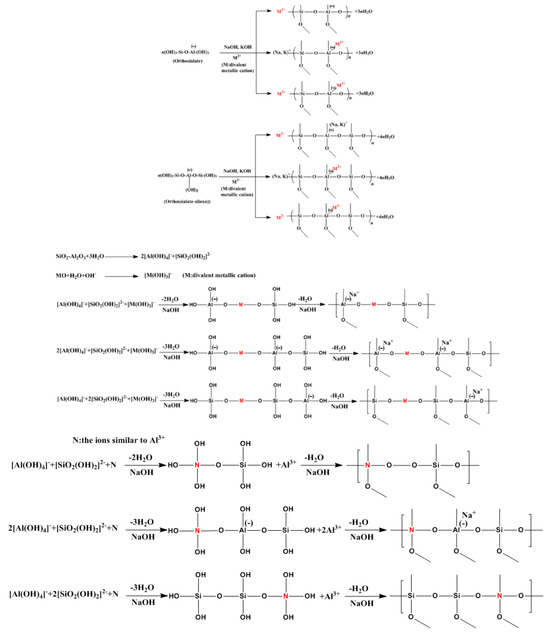
Figure 10.
Chemical mechanisms of ions solidification in geopolymers [56,65,87]. The red M and N represents metals ion.
Recently, molecular dynamics study has been applied for insight into the immobilization mechanism. Wang et al. [88] reported that thanks to the large radius of Cs+ and high charge density of Sr2+, NASH gel can solidify these ions (Figure 11). The incorporation of Cs+ decreased the geopolymers’ strength and increased the fracture strain. In contrast, the inclusion of Sr ions increased the number of AlV, which thus increased the geopolymers’ strength and ductility. Wang et al. [89] investigated the effect of Si/Al ratios on the adsorption and diffusion of CsCl2 using molecular dynamics simulation. Density distribution demonstrated that Cs+ and Cl− will aggregate on the channel surface. Meanwhile, the adsorption capacity of geopolymer channel for these two ions enhanced, and diffusion capacity decreased as the decrease in Si/Al ratio based on the result of mean square displacement.
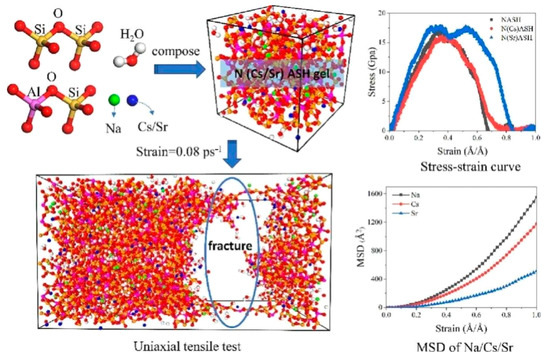
Figure 11.
Molecular dynamics study on structural characteristics of ions solidification in geopolymers [88].
Besides the solidification mechanisms based on the fundamental structure of geopolymers, there are also mechanisms based on the unreacted materials. El-Eswed et al. [90] demonstrated through Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and SEM tests that, in addition to the aforementioned chemical bonding, the formation of hydroxides, carbonates, silicates, and aluminates is also a potential mechanism for immobilization. Under alkaline conditions, the precipitation of ions inhibits the reaction between ions and Si/Al ions. These results indicate that ions are not completely immobilized by silicates or aluminates alone; other components also influence the curing process.
The immobilization of hazardous ions is a hot topic in the application research of geopolymers, warranting in-depth understanding and attention, and should be extended to the solidification/stabilization studies of other hazardous matters, which has profound significance for environmental protection and management.
3. Adsorption of Ions Using Geopolymer
As stated in the Introduction section, a geopolymer possesses a 3D structure, which consists of tetrahedral silicate and aluminate units connected by covalent bonds. In this structure, negatively charged Al-O tetrahedra must be charge-balanced by alkali metal cations (Na+, or K+) [22]. Due to its weak bond, these cations can be exchanged by other cations, which show similar ion exchange mechanism of zeolites [91].
Generally, the smooth and flat surface of geopolymers contributes to increased mechanical properties. However, in certain cases, geopolymers can be prepared to have rough and irregular surfaces for a higher specific surface area and thus better adsorption capacity. In this way, cations can be adsorbed onto the porous structure and surfaces of the geopolymer, thereby reducing the transport of hazardous cations. Additionally, the high alkalinity of alkali-activation geopolymers can lead to an increase in the pH of the solution, allowing for the removal of some cations through precipitation [92]. In addition to adsorbing ions in the solution, recent studies have also explored the use of geopolymers for organic dye adsorption and CO2 capture. In this section, geopolymers as absorbent for hazardous ions, organic dye, CO2 gas, etc., absorption will be reviewed.
3.1. Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions by Geopolymer
As mentioned in Section 2.1, heavy metals such as Cd, Pb, Cu, Zn, Cr, Ni, As, etc., are harmful to humans (Table 1) [93,94,95]. These metals originate from various industrial processes (e.g., electroplating wastewater) and other human activities, as well as from the dissolution of natural geological deposits. Exposure to environments contaminated with these heavy metals can lead to severe health issues in humans [96,97]. How to immobilize these metals, especially in solutions, raises an important issue. Existing studies have shown that geopolymers exhibit high removal efficiency and regenerative ability for the harmful ions.

Table 1.
Representative regulatory limits for heavy metal concentrations in leachates according to international environmental standards [93,94,95].
Normally, the geopolymers will be crushed to powder before they are used as absorbent. The results of Al-Harahsheh et al. [98] demonstrate that geopolymers can effectively adsorb Cu2+, with a maximum adsorption capacity of 152 mg/g. Cheng et al. [99] conducted adsorption experiments using MK-based geopolymers for Pb2+, Cu2+, Cr3+, and Cd2+. The results indicated that the adsorption reaction was endothermic, with heavy metal cations undergoing ion exchange with Na+ in the geopolymer. Meanwhile, the adsorption kinetics followed a pseudo-second-order model, and the adsorption isotherms adhered to the Langmuir model, with the order of adsorption capacities being Pb2+ > Cd2+ > Cu2+ > Cr3+. The geopolymer demonstrated the best adsorption performance for Pb, which may be related to the ionic radii of the ions. Arokiasamy et al. [100] prepared MK/silica fume-based geopolymer powder adsorbents for removal of Cu2+. They found that the replacement of 75% MK by silica fume can generate more reactive Si and Al binding sites for Cu2+ adsorption. Kumar et al. [101] synthesized ternary-blended geopolymer for Mn2+ removal, for which the uptake capacity from the model was found to be 17 mg/g at 35 °C, with working solutions at pH = 4 within 40 min of contact time. Ghafri et al. [102] developed a highly effective geopolymer sorbent for the removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater through Taguchi-TOPSIS hybrid method. They found that FA is beneficial to Pb2+ and Cd2+ removal while GGBFS is Ni2+ and Co2+. Kara et al. [103] utilized MK-based geopolymers to adsorb Zn2+ and Ni2+. The amounts of Zn2+ and Ni2+ adsorbed onto the geopolymer increased with contact time, reaching adsorption equilibrium at 40 and 50 min, respectively. As the dosage of the adsorbent increased, the adsorption capacity decreased, with maximum monolayer adsorption capacities for Zn2+ and Ni2+ of 1.14 × 10−3 and 7.26 × 10−4 mol/g, respectively.
However, in some application scenarios, powder shape absorbent is limited. Therefore, bulk-type geopolymers are also used for absorption. In order to increase absorption efficiency of these absorbents, creating foam in geopolymer bulk is a frequent method. Carvalheiras et al. [104] prepared geopolymer foam for Pb removal, where the maximum Pb removal reached 30.7 mg/g (Figure 12). Meanwhile, this monolith could be regenerated post-sorption without significantly affecting their performance. Novais et al. [105] also prepared porous geopolymer blocks for the adsorption of Pb2+. When the porosity increased from 52.0% to 78.4%, the adsorption efficiency improved by 68% with a faster adsorption rate. Prior to the adsorption reaction, the removal of OH− ions from the geopolymer significantly increased the single-pore porosity, thereby enhancing their adsorption capacity. Jiang et al. [106] adjusted the foaming agent (H2O2) and stabilizer to prepare geopolymer foam for Pb2+ and Cu2+ removal, where adsorption capacity of Pb2+ increased from 7.49 mg/g to 24.95 mg/g after foaming. Alshaaer et al. [107] utilized MK and wollastonite as precursors, Na2SiO4 as alkali activator, Al powder as foaming agent, and olive oil as foaming stabilizer to prepare geopolymer foam for the removal of heavy metal ions from water. The addition of wollastonite increased the mechanical properties and the adsorption rate of Cr, Co, Cu, Zn, Pd, and As in the as-prepared geopolymer.
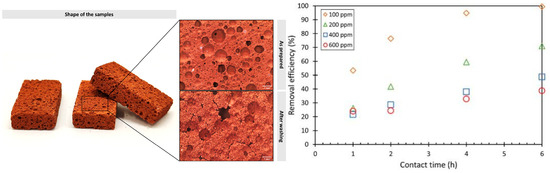
Figure 12.
Geopolymer foams and their removal efficiency for heavy metals [104].
The design of absorbent with a spherical shape can further increase absorption efficiency. Tang et al. [108] utilized MK and an organic foaming agent to prepare spherical porous geopolymers for the adsorption of Cu2+, Ca2+, and Pb2+. This geopolymer demonstrated good adsorption performance for all three kinds of ions, with the adsorption order being Pb2+ > Cu2+ > Ca2+, and the adsorption process consisting of both chemical and physical adsorption components. Yan et al. [109] explored a spherical porous carbon nanotube-reinforced geopolymer with amorphous phases and BET surface area of 73.06 m2/g (Figure 13). The maximum absorption of Pb2+ and Ni2+ was 52.74 mg/g and 8.92 mg/g, respectively.
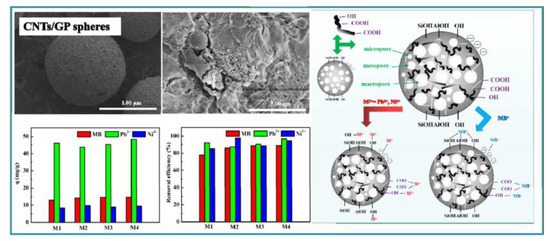
Figure 13.
Geopolymer foam sphere and its absorption mechanism of heavy metal ions [109].
As known to us, zeolite molecular sieves are a promising absorbent for its special structure. Meanwhile, geopolymer is an amorphous zeolite which show similar properties [110]. Recently, to increase the adsorption capacity of geopolymer, the addition of zeolites into geopolymer or the transformation of geopolymer to zeolite are studies. Andrejkovicová et al. [111] investigated the effects of clinoptilolite as a filler on the mechanical properties and heavy metal ions adsorption capacity of MK-based geopolymers. The addition of clinoptilolite contributes to an increase in strength, and the geopolymer with 25% zeolite shows the best adsorption performance for Pb2+, Cd2+, and Zn2+. The order of heavy metal adsorption by the geopolymer is Pb2+ > Cd2+ > Zn2+, while the highest adsorption for Cu2+ and Cr3+ occurs without the addition of zeolite. This order may be attributed to several factors, including the reactivity of ions, the free energy of hydration, the size of hydrated ions, changes in available coordination sites, and the pore size distribution on the geopolymer surface. However, El-Eswed et al. [112] used kaolin/zeolite-based geopolymers to adsorb heavy metal ions, obtaining different adsorption capacity results: Cu2+ > Cd2+ > Ni2+ > Zn2+ > Pb2+. Liu et al. [113] alkali activated nature clinoptilolite, where the partial clinoptilolite and impurity (montmorillonite, illite and albite) were transformed to geopolymer. This clinoptilolite-based zeolite-geopolymer foam can absorb heavy metal ions with the capacity order: Cr3+ > Pb2+ > Ni2+ > Cu2+ > Cd2+, which is related with Hard-Soft-Acid-Base principle and the speciation and radii of the hydrated metal ions.
In the case of transformation of geopolymer as zeolite, Li et al. [114] in situ synthetized zeolite microsphere based on MK-based geopolymer (Figure 14). The maximum adsorption capacities for Cu2+ were 698.14 and 523.84 mg/g, depending on the type of zeolite. They also used this kind of geopolymer-based zeolite for Pb2+ absorption with static removal of 584 mg/g and dynamic removal of 880 mg/g [115]. He et al. [116] obtained bulk analcime and zeolite P by a facile hydrothermal treatment and geopolymer precursor technique. In addition, these geopolymer-based zeolite shows outstanding adsorption performance for Cs+ with an adsorption efficiency of 93.3%.
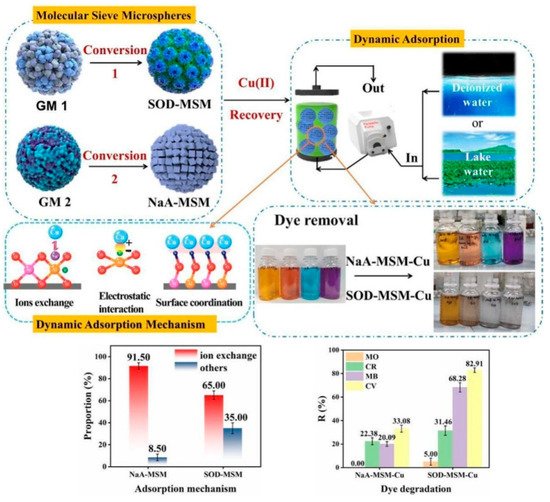
Figure 14.
In situ transformation of geopolymer to zeolite for absorption of Cu2+ [114].
As a promising adsorbent, geopolymers are designed for real application in recent studies, like highly porous, inorganic self-supporting membranes, filters, and columns [117,118,119], which can reduce production costs compared to traditional ceramic materials and organic polymers. For instance, Ge et al. [120] developed a novel self-supporting inorganic membrane for wastewater treatment, which exhibited good adsorption performance for Ni2+ (Figure 15). Xu et al. [121] used MK-based geopolymers as filter membranes to treat green liquor, with the filtered effluent meeting China’s wastewater discharge standards. Amari et al. [122] prepared an innovative porous geopolymer membrane made from waste natural zeolite powder for Pb(II) removal. To obtain controlled porous architecture, polyvinyl acetate (PVA) (10, 20, and 30 wt.%) was added and then thermally treated at 300 °C. Adding 20 wt% PVA can achieve a permeation rate of 78.5 L/(m2·h) and an 87% absorption rate at an initial Pb2+ concentration of 50 ppm. De et al. [123] developed a porous, phosphate mine tailings-based geopolymer membrane, which can adsorb Cu2+ and humic acid from aqueous solutions.
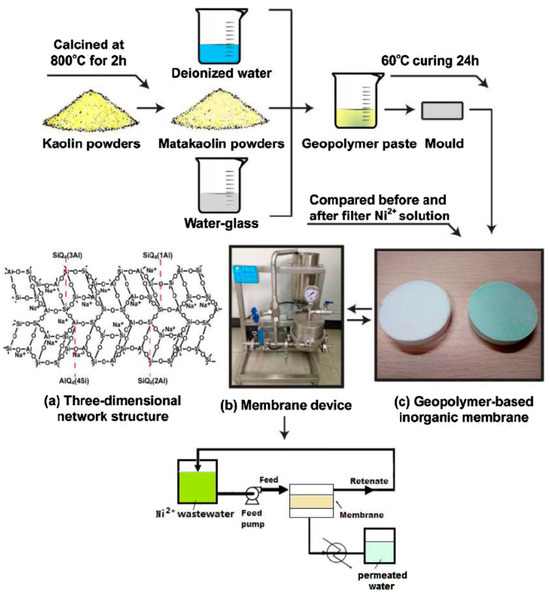
Figure 15.
Process of preparing a geopolymer filter membrane [120].
In addition, Wang et al. [124] applied a dispersion-suspension-solidification method to prepare solid wastes (electrolytic manganese residue/GGBFS) based geopolymer microspheres, aiming at resource utilization of electrolytic manganese residue and Cr-containing wastewater disposal. In the column experiments, the competitive absorption effects were in the following order: Mg2+ > Ca2+ > Na+ > K+ > Mn2+. Through the synergistic effects of ion exchange and chemisorption.
3.2. Adsorption of Radioactive Elements
Geopolymers have been studied for the adsorption of several radioactive isotopes, including Cs, Sr, Ra, Co, etc. Since the Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan in 2011, the removal of radioactive isotopes from wastewater has become increasingly attractive [125]. Cesium exists in aqueous environments as Cs+, is highly soluble and stable, and has garnered attention due to the long half-life (30.2 years) of radioactive 137Cs [126]. Strontium, which primarily exists as Sr2+ in aquatic environments, has several radioactive isotopes, with 90Sr (half-life of 28.9 years) being the most significant [127]. All isotopes of radium (which typically exist as Ra2+ under low salinity conditions) are radioactive, with half-lives ranging from a few days to 1600 years [128]. Therefore, the removal of such radioactive ions is essential.
Compared to heavy metal ions, like Pb2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+, MK-based geopolymers demonstrate better selectivity for the adsorption of Cs+, and their adsorption efficiency is not affected by NaCl concentrations in comparison with the aforementioned heavy metals. López et al. [129] prepared a porous geopolymer using kaolinite and rice husk ash to adsorb Cs+, finding that the removal rate of Cs+ increased with the increasing silicon content in the geopolymer. Lee et al. [130] used mesoporous geopolymers to remove Cs+ from solutions. The removal rate of Cs+ significantly increases from 85% to 96% with the presence of nano-crystalline zeolites and can be enhanced by longer contact times and increased solution pH, while it decreases with lower initial Cs+ concentrations. The adsorption kinetics fit both the pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order models, indicating that the adsorption process of Cs+ involves both physical and chemical adsorption. Zheng et al. [131] concluded that the NaNO3 concentration in solution will affect the adsorption performance of geopolymer.
Wang et al. [132] prepared NaA zeolite microspheres using MK-based geopolymers (Figure 16). The NaA zeolite microspheres exhibited excellent removal efficiency for Sr2+. These microspheres have high Sr removal efficiency, excellent regeneration, and recyclability performance. Deng et al. [133] applied an in situ self-reduction in graphene oxide method by adding geopolymer for treatment of the simulated high salt liquid radioactive waste (Figure 17). The removal ratios of radioactive I−, Cs+, and Sr2+ in the simulated wastewater reached 99.62%, 99.71%, and 99.99%, respectively.
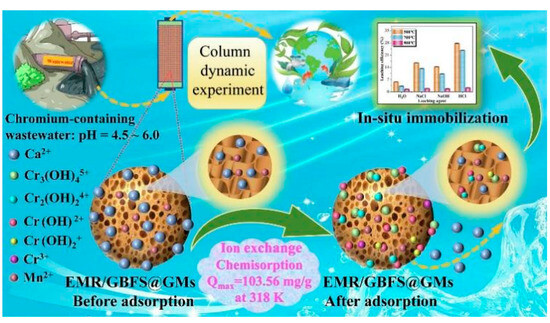
Figure 16.
Process of geopolymer sphere for filler in column filter [124].
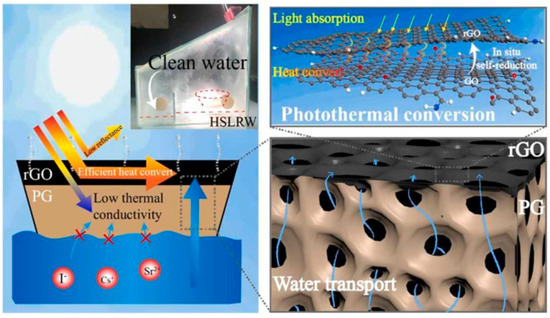
Figure 17.
Absorption mechanism of graphene oxide-modified porous geopolymer [133].
For other radioactive ions, Panda et al. [134] prepared a pyrophyllite mine waste-based geopolymer using waste to adsorb Co2+. This geopolymer exhibited a strong adsorption capacity for Co2+ in water, primarily through chemical adsorption. Kara et al. [135] demonstrated that MK-based geopolymers possess good adsorption property for Mn2+ and Co2+, with adsorption occurring on the homogeneous surface of the MK-based geopolymers. Li et al. [136] used MK-based geopolymer microspheres prepared by vacuum infusion and dispersion-pelletizing-solidification methods for the efficient adsorption of ReO4−, in which ReO4− is removed by electrostatic and coordination synergism with quaternary ammonium salts after ion exchange.
3.3. Adsorption of Organic Dyes
Dye pollution mainly comes from industries such as textile printing and dyeing, leather manufacturing, papermaking, food processing, and cosmetics production. The dyes are carcinogenic and poisonous, which requires decontamination [137]. Absorption is an effective way to remove dye, and as stated before, geopolymers can also be used to remove different kinds of ionic dyes, such as methylene blue and crystal violet, through ion exchange reactions.
Methylene blue (MB) is widely used as a model cationic dye in adsorption research and is chosen here for several practical reasons: it is strongly cationic and water-soluble, has a well-defined chemical structure, and can be accurately quantified by UV–Vis spectroscopy. MB is commonly employed as a surrogate for cationic contaminants present in textile effluents, so MB adsorption tests provide a convenient benchmark to assess ion-exchange capacity, surface adsorption, and pore accessibility of geopolymer adsorbents. It should be noted, however, that MB mainly represents cationic dye behavior; adsorption of anionic dyes or complex real wastewaters may follow different mechanisms and require additional testing [138,139,140]. Novais et al. [141] fabricated a FA-based geopolymer block for the adsorption of MB, observing a maximum adsorption of 20.5 mg/g, with the removal efficiency controllable by adjusting pore volume and connectivity (Figure 18). The adsorbent can be used in packed beds, regenerated, and reused (at least 5 times). Ozkan et al. [142] prepared a porous geopolymer by adding Zn and Al, achieving an adsorption efficiency for MB as high as 97.4% in 50 ppm solution. En-naji et al. [143] explored acid-activation geopolymers for MB removal. The geopolymer prepared by 75% MK/25% calcined clay had the highest efficiency in removing MB with a rate of 98%. Eshghabadi et al. [144] fabricated MK-based geopolymer for MB absorption. Pseudo-second-order kinetic with an equilibrium time of 120 min and Freundlich isotherm models fits the adsorption behavior, with the highest MB adsorption >90%.
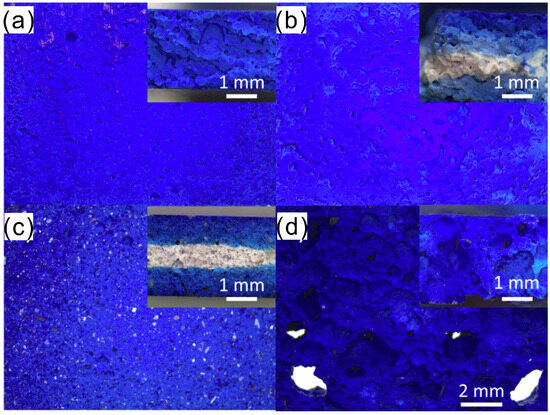
Figure 18.
Photos of different proportions of polymers for removing methyl blue. (a–d) Different samples [141].
Crystal violet dye (CVD) is another normally used dye in removal study. Barbosa et al. [143,144,145] prepared geopolymers from kaolinite, rice husk ash, and soybean oil for the adsorption of CVD, achieving a relatively high maximum capacity of 276.9 mg/g. Marubini et al. [146] prepared vermiculite-based geopolymer for CVD removal, where the absorption kinetic and isotherm models were suitable in the pseudo-second order and Temkin models. This adsorption process was endothermic and spontaneous through the calculation of ΔH and ΔS.
Other cationic dyes are also attracting attentions gradually. Tochetto et al. [147] pretreated geopolymer by sulfuric acid and calcination for improved adsorption of the direct red dye 28. The Elovich model describes the kinetics, while the Sips model represents the isotherms. El-Apasery et al. [148] used two kinds of geopolymer to remove reactive yellow 145. Taquieteu et al. [149] synthesized geopolymer–lignin composites for methyl orange absorption and found that these composites are eco-adsorbents for the removal of azo dyes in a continuous adsorption system.
Similarly to the case of heavy metal ions, the adsorption of anionic dye for geopolymer appears to less effective than cationic dye [150]. Açışlı et al. [151] modified geopolymer using CTAB for anionic acid blue 185 adsorption (Figure 19). This modification increased removal efficiency from 0.29% up to 79.36% in 40 min. Purbasari et al. [152] compared the adsorption of cationic (methyl violet) and anionic (eriochrome black T) dyes on porous FA-based geopolymer. Both adsorption of methyl violet and eriochrome black T followed pseudo-second-order kinetics model and Langmuir isotherm model, with maximum adsorption capacity of 49.26 and 45.45 mg/g, respectively.
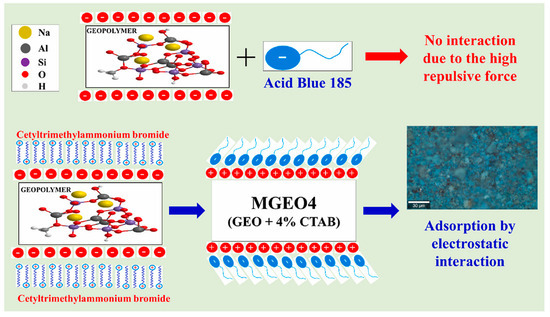
Figure 19.
Absorption mechanism of anionic dye for geopolymers [151].
Recently, 3D printing technology was used to strengthen the absorption efficiency of dyes [153]. Liu et al. [154] combined geopolymer, g-C3N4, and different contents of GO for preparing geopolymer composites. Through 3D printing, a geopolymer-based scaffold was manufactured for MB removal (Figure 20). They also found that the introduction of Fe3+ into this composite could further improve the MB removal efficiency.
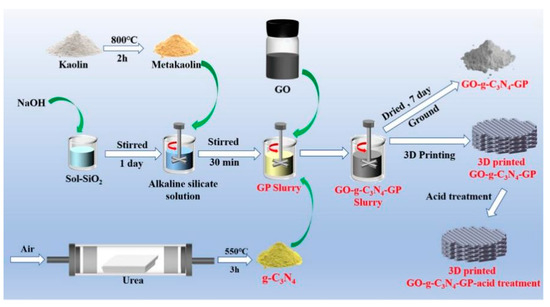
Figure 20.
Preparation of 3D printing GO-g-C3N4-geopolymer composites [154].
Although geopolymers have certain advantages in removing organic dyes (such as strong regeneration ability), their reported adsorption capacities are currently lower than those of commercially available activated carbon or other experimental adsorbents, meaning that it requires further optimization research.
3.4. Adsorption of CO2
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is an indispensable gas on earth. However, too much CO2 emission in the air leads to the greenhouse effect, which will increase the temperature around the world and finally cause a global disaster. The capture and storage of CO2 has become a hot topic recently. In fact, zeolites, with porous structure, have been used to absorb CO2 because zeolites exhibit acidity due to the presence of Lewis and Brønsted acid sites [155]. As an amorphous zeolite, geopolymers have also been attempted to be used as adsorbents for CO2 capture. Freire et al. [156] invented a kind of MK/phosphate sludge-based geopolymer, where the existence of Fe2O3 in geopolymer enhanced the chemical interaction with CO2, forming iron bicarbonate, monodentate carbonate, and bidentate carbonate. Hossain et al. [157] fabricated a lightweight scaffold via extrusion-based 3D printing for CO2 capture. By hydrothermally treated, 3D printed geopolymer showed a CO2 adsorption effect of 1.22 mmol/g, which higher than conventionally casted geopolymer. Minelli et al. [158] prepared porous kaolinite-based geopolymer blocks and investigated the effects of the H2O/K2O ratio and gas pressure on CO2 adsorption. The results showed that the geopolymer with an H2O/K2O ratio of 13 exhibited the best CO2 adsorption (0.6 mmol/g), as it had finer pores and a larger specific surface area, providing greater contact points for gas adsorption. Additionally, the adsorption capacity of the geopolymer for CO2 was significantly greater than that for other lighter gases, with the order of adsorption capacity being CO2 > CH4 > N2.
Although geopolymer shows comparable CO2 adsorption to other solid adsorbents but lower than most well-performing zeolites or MOFs. To improve the CO2 adsorption performance of the geopolymer, Minelli et al. [159] also added zeolite during the preparation of geopolymer to create zeolite/geopolymer blocks. The geopolymer composite prepared with 27% Na13X zeolite showed the best CO2 adsorption performance at 0.1 bar, reaching 1.1 mmol/g. The study found that the composite of geopolymer and zeolite exhibited a synergistic effect on CO2 adsorption, effectively combining the functional micropores of zeolite with the mesopores of the geopolymer matrix, thereby reinforcing the zeolite phase. Han et al. [160] synthesized zeolite X in foam geopolymer as a CO2 adsorbent and the results showed that the maximum CO2 absorbance reached 7.91 mmol/g. Wang et al. [161] prepared a geopolymer/zeolite composite from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash (MSWIFA) for CO2 adsorption. The results indicated that the as-obtained composite possessed a CO2 uptake for 2.06 mmol/g, due to the new formed analcime and the high specific surface area and porosity. In the study of Wu et al. [162], they pointed out that geopolymer/zeolite composites exhibit a CO2 adsorption capacity of 4.18 mmol/g by the zwitterion reaction mechanism by forming carbamate.
In addition, Papa et al. [163] developed a new geopolymer/ hydrotalcite composite with suitable mechanical and thermal properties for CO2 adsorption. However, due to the limited capacity of the geopolymer matrix, especially under moderate temperature conditions, the CO2 absorption capacity of the composite primarily depends on the hydrotalcite content. Chen et al. [164] added activated carbon in geopolymer (Figure 21), which can improve the CO2 adsorption by 2.25 times. The intercalation of –C=O, –OK, and –COOK functional groups on the activated carbon surface during geopolymerization favored the CO2 adsorption. In addition, the incorporation of carbonic anhydrases, a kind of metalloenzyme that can catalyze the hydration of CO2, into geopolymer microspheres can enhance their capacity for CO2 capture with excellent reproducibility [165,166].
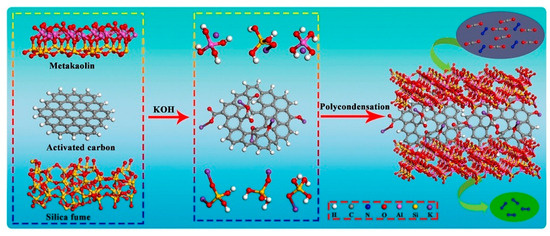
Figure 21.
Activated carbon-geopolymer composites for CO2 absorption [164].
3.5. Adsorption of Other Matters
Rare earth elements (REEs) are critical resources for many high-tech applications, and their demand is increasing [167]. Rare earth elements typically exist in relatively low concentrations in minerals, necessitating effective extraction technologies. However, some REEs are also harmful to human health when they enter body in high concentrations. Fiket et al. [168] reported a preliminary study where they used a fly ash-based geopolymer to adsorb Ce, La, Nd, Pm, Dy, Er, Eu, Gd, Ho, Lu, Sc, Sm, Tb, Tm, Y, and Yb from multi-element solutions. Their experimental results showed that all the studied rare earth elements were very effectively adsorbed at 120 min. Reis et al. [169] explored the rice husk/MK-based geopolymer for absorbing Ce3+, La3+, Pr3+, Sm3+, and Nd3+ from phosphogypsum leachate, which recovery were 86.33%, 79.64%, 53.33%, 71.25%, and 95.03%, respectively.
Ammonium (NH4+) is a common nitrogen-containing species in wastewater, which will destroy aquatic ecosystems by eutrophication, which required removal before emitting wastewater [170]. Luukkonen et al. [171] used MK-based geopolymers to adsorb NH4+ from solution, achieving an adsorption capacity of 21.07 mg/g, which is higher than that of typical natural zeolites. They also demonstrated that the adsorption mechanism is ion exchange, and the material can be regenerated using 0.2 M NaCl and 0.1 M NaOH solutions. Furthermore, the adsorbent can effectively treat landfill leachate on-site at low temperatures. In another study [172], they optimized the NH4+ adsorption capacity by using a high content of alkali activator, a small amount of MK, with the maximum adsorption capacity increasing from 21.07 to 31.70 mg/g. Clausi et al. [173] replaced MK by two types of sludge to prepare geopolymer composites. This composite can absorb NH4+ efficiently (66.6% of NH4+ removal and 18 mg/g adsorption capacity) after optimization. Savoir et al. [174] treated MK-based geopolymer using HCl solution to enhance its ability to adsorb NH4+. In acidic environments and at low ionic strength, NH4+ will be absorbed more easily, while the presence of co-existing species (bicarbonate, humic acid, and sulfate) hinders its adsorption.
In the research of Naghsh and Shams [175], the MK-based geopolymer was used for the removal of Mg2+ and Ca2+ from water. Their materials were comparable to commercial water softening agents (such as 4A zeolite) in both synthesis and actual groundwater adsorption experiments.
Besides the cation, many oxyanions were also studied. Sulfate (SO42−) is a commonly and naturally occurring anion that, although non-toxic, can lead to the salinization of water bodies. Therefore, the removal of sulfates is necessary in some large-scale industrial processes, such as mining (acid mine drainage) and seawater desalination plants. Runtti et al. [176] synthesized modified slag-based geopolymer by ion exchange, replacing Na+ with Ba2+. The resulting material was used to remove sulfate (SO42−~1000 mg/L) from synthetic wastewater and mine wastewater (SO42−~900 mg/L). The adsorption capacity was approximately 119 mg/g, and it could achieve very low sulfate concentrations (<2 mg/L). Their study suggested that the removal mechanism was surface complexation or the formation of BaSO4 precipitation. Zhang et al. [177] demonstrated through molecular dynamics simulations that cations such as Na+ or Mg2+ adsorbed onto the hydroxyl groups on the surface of N-A-S-H gel can attract SO42− ions. In addition, Zhang et al. [178] explored the sulfamethoxazole removal using copper slag-based geopolymer.
Phosphate (PO43−) is also a pollutant that will cause eutrophication in water. Sun et al. used eggshells and FA to prepare geopolymer (Figure 22) [179]. Eggshells after high-temperature pyrolysis can provide active sites (CaO) and porous structure (CO2) for phosphate adsorption. When eggshell: FA ratio was 40%, the phosphate adsorption performance reached maximum of 49.92 mg P/g. The adsorption process was well described by the pseudo-second-order model and the Langmuir model. Savoi et al. [180] found that loading La in geopolymer can significantly increase the PO43− removal through inner-sphere complexation and adsorption. Karmil et al. [181] produced a low-cost porous geopolymer using reverse osmosis (RO) reject brine as mixing water for PO43− removal.
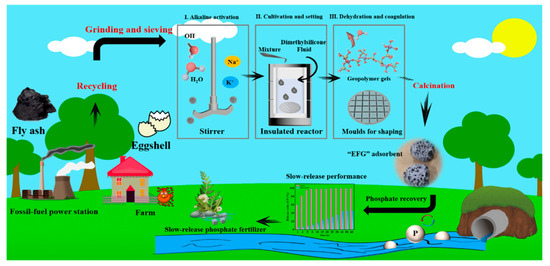
Figure 22.
Eggshell–fly ash-based geopolymer for phosphate absorption [179].
4. Resource Utilization of Solid Wastes by Geopolymerization
In the process of human activity, a significant amount of solid waste is generated. Such waste includes wastewater treatment sludge, various tailings, fly ash, slag, etc. Some solid wastes may not be toxic, but their accumulation occupies large areas of land and cause water and air pollution. Some solid wastes contain substantial amounts of hazardous composites like heavy metals or radioactive species. If not properly treated, these species can cause significant damage to geological and ecological environments. As an environmentally friendly technology, geopolymerization thus has also been used to treat solid wastes, for not only resource utilization but also stabilization of hazardous composites. This section reviews the current research status on the non-hazardous and hazardous solid wastes treated with geopolymerization technology.
4.1. Utilization of Common Solid Wastes
4.1.1. Mine Tailings
Mining and mineral processing tailings are among the most scrutinized industrial by-products due to their large volume. Tailings are one of the largest waste materials globally, and they are typically stored in dammed ponds along with process water or stacked nearby as thickened slurries [182]. It is estimated that approximately 2.025 billion tons of solid waste are produced globally each year, of which 500 to 700 million tons are tailings. Furthermore, with the increasing utilization of low-grade ores, this figure is bound to rise in the future [183]. Therefore, finding efficient ways to utilize tailings has become an urgent issue for achieving a circular economy and minimizing waste. Research has shown that many tailings contain reactive aluminosilicates, making them suitable raw materials for geopolymer production. Therefore, directly utilizing such tailings to produce geopolymers can effectively utilize solid waste and provide significant guidance for practical production applications.
(1) Red mud. Red mud is the red solid waste left after extracting Al2O3 from bauxite ore, characterized by large production, high alkalinity, fine particle size, large specific surface area, and strong adsorption capacity. The combination of very fine particle size, plate-like mineral phases, and high soluble-alkali content (Na+/OH−) stabilizes colloidal suspensions and increases water demand. This leads to difficulties in dewatering, pumping, and mixing, and can negatively affect geopolymerization by increasing porosity and decreasing strength; it also raises environmental concerns related to alkaline leachate.
Typically, 1.5–2.5 tonnes of red mud are generated per tonne of alumina produced, depending on ore quality and process efficiency [184]. In 2023, global alumina production was approximately 141.8 Mt, generating an estimated 177 Mt of red mud, with cumulative global stockpiles exceeding 4 billion tonnes [185]. However, the high dispersion characteristics of red mud particles pose challenges for recovery and potential secondary pollution. How to consume such amounts of solid waste attracts attention.
Disposal methods [186,187,188] include (i) wet storage in tailings ponds with engineered liners and drainage systems, (ii) dry stacking after mechanical dewatering to minimize land footprint, (iii) neutralization with acidic agents followed by soil cover and revegetation for ecological rehabilitation, and (iv) resource utilization such as incorporation into geopolymer binders, cement, ceramics, or recovery of Fe, Ti, and REEs.
Direct utilization is one of the best options for treating red mud, and there have been numerous reports on using red mud as a precursor for geopolymers. Yang et al. [189] optimized activation, activator, and water-to-binder ratio condition to prepare RM-based geopolymer with a maximum 28 d compressive strength of 181.6 kPa. Ascensao et al. [190] prepared porous geopolymers using red mud, which exhibited high buffering capacity and long-lasting performance, making them suitable as pH buffering materials. Hertel et al. [191] prepared porous geopolymers from red mud for the adsorption of MB, and the synthesized porous blocks demonstrated high adsorption capacity (17 mg/g at an initial concentration of 75 mg/L). The higher the porosity of the geopolymer blocks, the higher the pH value and porosity.
Due to the low strength for geopolymer based on solely RM, the addition of higher-reactivity precursors has also been studied. Liu et al. [192] compared five kinds of calcined RM as geopolymer precursors. The silica dissolved from RM favored the strength development of RM/FA-based geopolymer. In contrast, Hao et al. [193] increased the RM’s reactivity through mechanical activation instead thermal activation. They found that crystal structure of mineral phase in RM is destroyed by mechanical grinding, resulting in a large increase in strength and resistivity. Xu et al. [194] used RM to produce high-strength high-ductility engineered geopolymer composites. After optimization, the geopolymers’ compressive strength is over 100 MPa, and a tensile strain capacity is over 5%, even though the utilization rate of RM is as high as 50%, which is better than in many other studies (Figure 23).
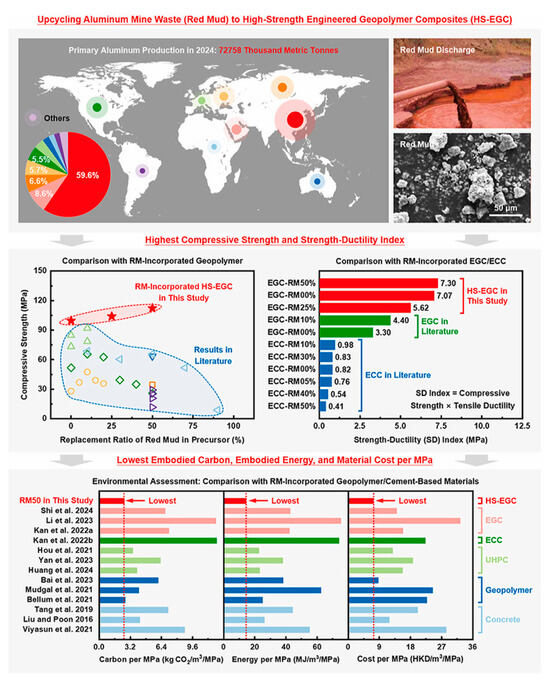
Figure 23.
Red mud-based engineered geopolymer composites [194].
(2) Coal gangue. Coal gangue is a solid waste generated during coal mining and beneficiation, accounting for approximately 10–15% of the total solid waste in China. It is estimated that the accumulation of coal gangue in China has exceeded 5 billion tons, with an annual increase of 152 million tons, which also required utilization.
The main components of coal gangue are kaolinite, illite, and quartz; calcining CG can produce a large number of amorphous aluminosilicates, making it a very promising precursor for geopolymer preparation. Cheng et al. [195] utilized coal gangue as a raw material for geopolymers and investigated the effects of Na2SiO3 modulus and L/S ratio on their mechanical properties and microstructure, achieving a maximum strength of 70 MPa at 28 days, providing experimental and theoretical support for the development of CG-based binders. Geng et al. [196] compared the effects of thermally activated and mechanically activated CG-RM as precursors on the properties of geopolymers. The study indicates that mechanically activated CG exhibits better geopolymer reactivity than thermally activated one. Wang et al. [197,198] investigated the effect of alkali activators and GGBFS on the mechanical properties of CG-based geopolymer. The compressive strength can reach 24.75 MPa after adjusting alkali activators and 54.59 MPa after adding GGBFS. Zhao et al. [199] concluded that the amorphous SiO2 and Al2O3 phases are critical factors for the geopolymerization of CG, and that the geopolymer, mainly N-A-S-H gels, can fill the existing cavities and increase strength.
To increase the utilization efficiency and high-value utilization of CG, many efforts have been posed. Zhao et al. [200] used CG as both a binder and an aggregate for preparing ultra-high-performance geopolymer concrete (UHPGC) with a 28 d compressive strength of 143.1 MPa. Bakil et al. [201] improved the specific surface area of CG by grinding, which can provide more reactive sites for geopolymerization and thus improved strength and microstructure of CG-based geopolymer. Zeng et al. [202] applied machine learning method to predict the mechanical properties of CG-based geopolymers and offers guidance for mix design tailored to CG from different sources. Li et al. [203] fabricated porous CG-based geopolymer for pH regulator (Figure 24). All these efforts provide more ways to use CG-based geopolymer.
Figure 24.
Coal gangue-based geopolymer for pH regulator [203].
(3) Other tailings. In addition to red mud and coal gangue, a wide variety of tailings from metallic and non-metallic mineral processing can serve as potential geopolymer precursors. The most significant include iron ore tailings (~500 Mt/year in China), copper tailings (~200–300 Mt/year globally), lead–zinc tailings (~100 Mt/year in China), and smaller volumes of nickel, molybdenum, and tungsten tailings [204,205,206]. Non-metallic tailings such as quartz, fluorite, and phosphate also contribute to the global solid waste stream. However, these tailings are geographically scattered and vary greatly in chemical composition and reactivity. In many cases, the resulting geopolymers exhibit lower compressive strength than those derived from fly ash or slag. For this reason, this section provides only a general overview of these materials, emphasizing their resource utilization potential and environmental significance.
Many other mineral processing tailings, like metallic tailing have also been studied as precursors for geopolymers. Duan et al. [207] synthesized a porous alkali activation geopolymer using iron tailings, fly ash, and H2O2 (total porosity: 74.6%) for the removal of Cu2+. Due to the clear pore size distribution and high total porosity, this geopolymer achieved a Cu2+ removal rate of 90.7%. Carvalho et al. [208] prepared acid-activated iron tailing-based geopolymer with maximum compressive strength of only ~22.5 MPa. Jiao et al. [209] used tungsten tailings and MK to synthesize geopolymers and found that curing in a steam autoclave can effectively enhance the compressive strength (7-day compressive strengths reaching 86 MPa) of geopolymers and inhibit efflorescence behavior in a shorter time. Karrech et al. [210] used lithium ore residue as a raw material (containing spodumene, lepidolite, quartz, kaolinite, and other minerals) to produce geopolymers with relatively low strength; after calcination, by adding varying proportions of kaolinite, MK, steel slag, and fly ash, geopolymer composites were created, achieving a maximum 28-day strength close to 100 MPa. Zhang et al. [86] firstly used ion-adsorption rare earth mine tailings to prepare geopolymer for Pb2+ and Cd2+ immobilization. Clay minerals, like kaolinite, play an important role in geopolymerization and provide strength and absorption capacity for geopolymer.
Other non-metallic tailings are also promising geopolymer precursors. Wang et al. [211] used garnet tailings as raw materials, adding a certain amount of MK to produce high-strength geopolymers. Kızıltepe et al. [212] developed one-part geopolymer by co-alkali fusion with boron mine tailing, where new crystalline phases (merwinite, monticellite, sodium peroxide, and magnesium oxide) appeared. The highest compressive strength reached 24.2 MPa, and the highest flexural strength reached 4.3 MPa. Qiu et al. [213] utilized fluorite tailings for one-part geopolymer preparation. However, due to the low reactivity, the compressive strength was only 7.2 MPa, even when the calcination temperature reached 1000 °C. Haddaji et al. [214] reinforced phosphate mine tailing/MK-based geopolymer with fibers. The addition of 1% of polypropylene and glass fibers increased the flexural strength by 278% and 26%, respectively. Wang et al. [215] prepared sulfur tailings/GGBFS-based geopolymer with a compressive strength of 32.2 MPa by using CaO-Na2SiO3 composite as activator.
4.1.2. Construction and Demolition Wastes
Approximately 800, 700, and 1800 million tons of CDW are produced annually in European Union countries, the United States, and China, respectively [216]. Although CDW does not emit hazardous elements, the burial or are dumped in the open air caused serious environmental pollution and the consumption of land resources [217,218]. In recent years, recycling these wastes after crushing and sorting as aggregates or active powder for preparing recycled geopolymer (concrete) is a hotspot. Recycled powder (RP) has small particle size; this means it can easily become suspended in air, thereby functioning as a pollutant that poses a health hazard. Considering that RP is mainly composed of silica (SiO2) and alumina (Al2O3), it can be used as geopolymer precursor.
The geopolymer obtained from alkali-activation of sole RP showed low mechanical properties [219,220,221]. Therefore, pretreatment techniques such as grinding [221,222], calcination [223,224], acidification [225,226], and carbonation [227,228] have been applied for enhancing the properties of RP.
Carbonation can reduce the porosity and water absorptivity of RP owing to the reaction between hydration products and CO2 [227,229]. Lu et al. [227] demonstrated that RP subjected to carbonation increased compressive strength of geopolymer by 21.9% and 12.1% and decreased >25% porosity. Calcination can not only condense the RP microstructure but also decompose its hydration products to increase reactivity [216,228]. Sui et al. [230] pre-treated RP by calcinating at different temperatures. They reported that 700 °C was the suitable calcination temperature compared to other temperatures. Zhang et al. [231] investigated the effects of the replacement ratio, pretreatment methods (carbonization and calcination), and alkali modulus on the properties and microstructure of recycled FA/GGBFS-based geopolymer. The results show that calcination at 600 °C exhibited better effects (mechanical properties and lower critical pore size) than carbonization pretreatment, due to the active clay minerals.
Mechanical activation can decrease the particle size and SSA of RP, which can also increase RP’s reactivity. Xu et al. [232] synergistically activated RP by using mechanical-thermal methods. When grinding time was 10 min and calcination temperature was 750 °C, the 3-day, 7-day, and 28-day compressive strength increased 77.91%, 109.88%, and 108.18%, respectively. Ma et al. used recycled brick powder and fine aggregates to prepare geopolymer mortar. In an appropriate replacement ratio, RBP as fine aggregate can refine the microstructure and enhance the mechanical strength and permeability resistance of geopolymer, where the compressive strength can reach 78.1 MPa (Figure 25) [233].
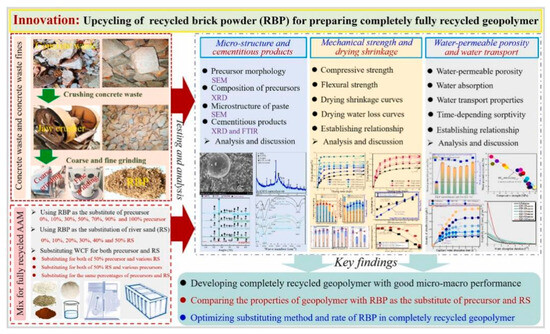
Figure 25.
Upcycling of recycled brick powder for geopolymer preparation [233].
In addition, the incorporation of GGBFS, FA, or any other high-reactivity raw materials can also increase the mechanical properties and durability of geopolymer derived from RP [234,235,236].
4.1.3. Engineering Muck
Engineering muck (EM) is also a kind of construction solid wastes, which is generated by excavating rock and soil underground construction activities [237]. In different places and depths, the mineral composition of EM will be different. The improper dispose of these solid wastes may cause severe geological disaster [238]. Considering the abundant aluminosilicate minerals in EM, geopolymerization is no doubt a suitable technology to treat these solid wastes.
Compared to other places, the EM in subtropical/tropical areas contains more clay minerals (clay minerals like kaolinite, halloysite, and illite) due to the fact that rocks will go through strongly weathering in these places [239]. This endows EM with a high geopolymerization reactivity. Yuan et al. [240,241] used alkali solution to reinforce EM (mainly granite residual soil) to improve its soil strength. Studies show that under the action of alkali, kaolinite in EM underwent geopolymerization. Through processes of dissolution–rearrangement–polycondensation, a small amount of geopolymer gel is formed, which bonds mineral particles and fills the pores between them, thereby reducing the porosity of the soil and enhancing its static mechanical properties (Figure 26). The addition of fibers further strengthens the connections among mineral particles. Through the synergistic interaction between unreacted kaolinite and glass fibers, the dynamic performance of the improved EM is significantly enhanced. When a small amount (2%) of cement is added, the mechanical properties of the treated EM are further improved. This is because highly reactive minerals provide an important source of Al for cement hydration, leading to the formation of calcium aluminosilicate hydrate gels with higher strength. These gels couple with geopolymer, forming a denser structure. In the other studies [242,243,244], they took EM as precursors for preparing geopolymer and optimized their compressive strength by adjust the alkali activator, calcination temperatures, and particle sizes of raw materials. Under appropriate thermal treatment (850 °C), kaolinite in EM converts into MK with high reactivity, which can be dissolves in alkaline solution extensively, generating a large number of aluminosilicate monomers that further polymerize into geopolymer. Quartz and feldspar act as filler particles. The resulting geopolymer can reach a compressive strength of up to 58 MPa. The content of soluble silica and the concentration of alkali affect both the dissolution rate and amount of clay minerals, thereby controlling the microstructure and performance development of the geopolymer.
Figure 26.
(a–c) SEM images of geopolymer-reinforced engineering muck, (d) EDX result of selected area and (e) Schematic diagram of fiber-reinforced engineering muck [241].
Besides granite residual soil, other types of EMs also need to be recycled. Dassekpo et al. [245] calcined weathered granite-type EM at 650 °C, and the 7-day strength of the resulting geopolymer increased by nearly twofold compared to uncalcined EM. They [246] also explored loess-type EM for geopolymer preparation. However, FA has to be added to improve the strength. Zhou et al. [247] calcined residual soil-type EM at 800 °C and, by adjusting alkali concentration, alkali modulus, and liquid-to-solid ratio, obtained geopolymers with relatively high 28-day strength (~55 MPa). Bao et al. [248] verified the feasibility of using EM, FA, and slag for preparing greener geopolymer. Wang et al. [249] proposed a synergistic multi-activation strategy, integrating mechanical, thermal, and chemical activation to enhance the reactivity of shield tunneling EM as a geopolymer precursors. An L16(4^5) orthogonal experimental design was employed to quantitatively assess the effects of particle fineness, calcination temperature, holding time, Na2SiO3 modulus, and alkali content on the compressive strength of EM-based geopolymer. They reported that this activation method can significantly enhance the reactivity of EM, with the compressive strength of the geopolymer reaching up to 31.2 MPa. The thermal activation efficiency of EM is highly sensitive to temperature. Meanwhile, appropriate mechanical activation markedly increases the hydration reaction surface area and the amorphous phase content of the EM, but excessive activation may lead to the formation of a protective film covering the particle surfaces, which could delay or even hinder subsequent reactions. More importantly, with increasing alkali content, N-A-S-H gels rapidly precipitate around unreacted particles and fill adjacent pores, accompanied by the increase in silica-rich N-A-S-H phases.
4.2. Solidification/Stabilization of Hazardous Solid Waste
4.2.1. Hazardous Mine Tailings
In addition to the mine tailing mentioned in Section 4.1.1, there are many mine tailings that contain hazardous composites, especially for some non-ferrous metal ores. The release of heavy metals from tailings causes pollution in groundwater and air and finally enters the human body. Therefore, the stabilization of toxic composites for these mine tailings should be considered when reuse them [250].
Sun et al. [251] investigated the effect of adding Na2S during the preparation of geopolymers using MK mixed with selected Cr tailings. The addition of S2− can reduce Cr(VI) to Cr(III), enhancing the solidification of Cr in the tailings, but it leads to a decrease in strength. XRD and XPS analyses indicate that during the geopolymerization, Cr3+ is fixed within the Al-O tetrahedral units ([−OAl(OH)3]−). Wei et al. [252] used mechanically activated vanadium tailings as raw materials to study the impact of milling time on geopolymer properties, obtaining a geopolymer with a compressive strength of 25 MPa. Wan et al. [253] used zinc tailings as raw materials and enhanced the mechanical properties of the resulting geopolymers by adding calcined kaolinite; the resulting geopolymers exhibited good solidification capacity for Pb2+, with Pb2+ content within a certain range (2%) increasing their compressive strength. Zhou et al. [254] alkali-activated hazardous solid wastes (tin mine tailings and fuming) to synthesize geopolymer. During geopolymerization, the heavy metals in tailings and slag can be stabilized through oxidization, precipitation, with immobilization efficiency for As and Cr of 95% and Cu2+, Zn2+, and Mn2+ for nearly 100%. Hassani et al. [255] produced a green bricks using copper ming tailing, where Cu2+ can be immobilized. These geopolymer bricks showed just 7.5% weight loss after 14 wet-dry cycles, mainly due to minor leaching of unreacted Na+ ions, which slightly increased porosity but caused no structural damage, and just 1.3% weight loss after 50 freeze–thaw cycles with small surface cracks but still high compressive strength.
Lu et al. [256] combined steel slag, FA, and MK to obtain geopolymer for immobilization of mercury tailings (Figure 27). The tri-angle mixture design and potting experiments were conducted. The results indicated that the inclusion of 50% geopolymer reduced Hg2+ transport to the surface soil by ~90% and mercury concentration of herbaceous plant samples by 78%. Opiso et al. [257] combined palm oil fuel ash (POFA), as a high Al-bearing waste, and gold mine tailing for geopolymer synthesis. The heavy metals it contains can also be stabilized. In contrast, Pan et al. [258] used 5% FA/GGBFS/MK-based geopolymer for immobilization of 95% gold mine tailing. All harmful elements were well immobilized by precipitation, physical encapsulation, adsorption, and ion substitution. They also found that geopolymers show higher mechanical strength than OPC in stabilizing tailings.
Figure 27.
Preparation of geopolymer for mercury tailings immobilization [256].
Recently, geopolymerization based on acid-activation is also applied to dispose of hazardous mine tailings. Chen et al. [259] used phosphoric acid to activate copper tailing. However, the as-obtained acid-based geopolymers show low compressive strength of ≤8 MPa although they have good durability in both neutral and acidic environments and Cu2+ solidification effect. Zhao et al. [260] optimized the immobilization effect of uranium tailings by acid-based geopolymer using machine learning. The maximum compressive strength was ~18.9 MPa, with uranium leaching rate of 0.70 × 10−6 cm/d.
4.2.2. Municipal Solid Waste Ash
Municipal solid waste (MSW) is generated in large quantities during daily human activities. Since solid waste occupies vast amounts of land resources, contaminates soil and water bodies, and poses significant risks to human health, it is imperative to adopt harmless and volume-reduction treatments. Among available treatment technologies, incineration is recognized as one of the most effective methods for MSW management [261,262]. It not only substantially reduces the volume of waste but also enables energy recovery through power generation. Nevertheless, during the incineration process, fine particulate matter suspended in the flue gas can be captured by dust removal devices, resulting in the generation of incineration fly ash, which accounts for approximately 5% of the original waste mass. These fly ashes typically contain large amounts of heavy metal ions (e.g., Pb, Cu, Cr, Zn), and long-term exposure to such metals can cause severe health disorders in humans. In addition, toxic organic pollutants such as dioxins are also present in fly ash. Comparatively, the incineration bottom ash is the primary residue generated during MSW incineration, which is coarser in particle size and generally contains a heterogeneous mixture of slag, glass, ceramics, unburned carbon, and metallic fragments [263,264]. Although the leaching potential of toxic components in bottom ash is relatively lower than that of fly ash, bottom ash still contains significant amounts of heavy metals, soluble salts, and persistent organic pollutants. Therefore, incineration fly ash must be properly treated prior to landfilling. Based on these, geopolymerization can be considered as a good tool to dispose of MSW ash.
(1) Municipal solid waste fly ash (MSWIFA). Lancellotti et al. [265] prepared geopolymers using MK and MSWIFA to solidify the heavy metal ions it contains (Cd, Cr, Cu, Mn, Pb, Zn). The MSWIFA is encapsulated within the geopolymer matrix, and the leaching amounts of heavy metal ions meet the safety leaching standards, allowing for safe landfill disposal. Zhang et al. [266] used RM and MSWIFA to prepare geopolymer with strength of 13.11 MPa. The heavy metals can be physically wrapped and chemically bonded by gel networks consisting of N-A-S-H and C-(A)-S-H gels. Tan et al. [267] used CDW and MSWIFA to prepare geopolymer with an immobilization efficiency of Pb > Ba > Zn > Cd > Ni > Cr > Cu. Labianca et al. [268] used GGBFS/MK-based geopolymer to solidify MSWIFA, allowed up to 70% reduction in global warming potential compared to OPC. Qin et al. [269] regarded MSWIFA as Ca resource to enhance properties of MK-based geopolymer. Results show that when the active Ca/Si ratio is <0.048, the early compressive strengths are enhanced, and when active Ca/Si ratio is 0.048, 28-day compressive strength can reach 34.66 MPa. Meanwhile, the heavy metals were effectively solidified by physical coating and chemical precipitation. Tian et al. [270] regarded MSWIFA as a foaming agent (the presence of Al) to prepare MK-based geopolymer foam. When MSWIFA content was increased from 20 to 50%, the porosity of geopolymer foam increased from 63.5% to 73.7% and bulk density decreased from 890 to 690 kg/m3. More importantly, at the same level of thermal conductivity, geopolymer foam prepared with MSWIFA as a foaming agent shows a higher compressive strength than previous studies. Sun et al. [271] fabricated a functional MSWIFA-based geopolymer based on experimental and computational simulation studies. The results indicate that the mineral phases and the degree of compactness affect mechanical properties. Quantum chemical calculations show that [Si(OH)4], [Al(OH)3(OH2)], and [Al(OH)4]− are hydration products (Figure 28). Meanwhile, the heavy metals are embedded in the hydrated silica-aluminate by electrostatic interaction or chemisorption.
Figure 28.
Electrostatic potential energies of Si- and Al-species during geopolymerizaiton of MSWIFA [271].
(2) Municipal solid waste bottom ash (MSWIBA). The utilization of MSWIBA to prepare geopolymer is less studied compared to MSWIFA because of the coarser particle size and more complex composites of MSWIBA. Yang et al. [272] added GGBFS into MSWIBA to increase the mechanical properties of geopolymer. The compressive strength can be increased by 663.7% after adding GGBFS, and the gel formation and porosity are also optimized, with increased Cr solidification efficiency. Jin et al. [273] investigated the solidification law, polymerization, and strength development mechanism of alkali activation of GGBFS/MSWIBA (Figure 29). Wang et al. [274] introduced steel slag, instead of GGBFS, to prepare MSWIBA-based geopolymer. The active Ca supplemented by steel slag promotes the formation of C-(A)-S-H gels. Increasing the alkali content promoted the dissolution of precursors, which contributed to the development of the geopolymers’ compressive strength. The solidification efficiency of heavy metals after the introduction of SS can be >90%. Feng et al. [275] explored GGBFS/MSWIBA-based geopolymer to solidify/stabilized high-salt sludge. The results show that high-salt sludge can be immobilized more efficiently after adding MSWIBA, and the solidified high-salt sludge with 20% GGBS and MSWIBA-based geopolymer exhibits good water stability, with a compressive strength of 2.33 MPa after 28d of water immersion.
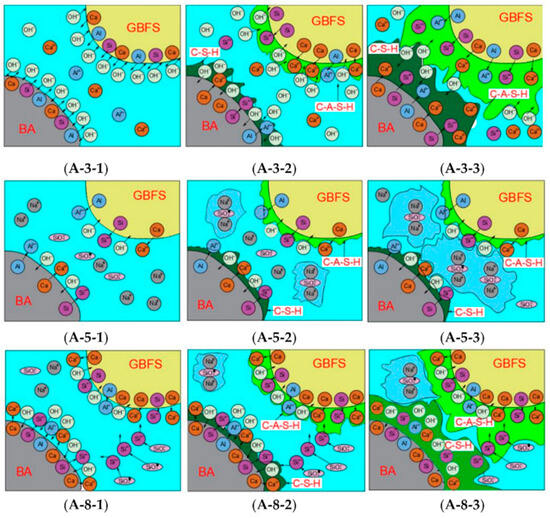
Figure 29.
Geopolymerization mechanism of alkali-activation of MSWIBA and GGBFS [273].
(3) Combination of MSWIFA and MSWIBA. In some studies, co-dispose of MSWIFA and MSWIBA appears to be more efficient and may achieve synergy effect. Liu et al. [276] synthesized MSWIFA/MSIWBA-based geopolymer based on Ca/Si ratio design (Figure 30). The results showed more MSWIFA required low concentration of alkali solution for geopolymerization, which mainly produced C-S-H gels. While, more MSWIFA required high concentration of alkali solution, where C-(A)-S-H gels and N-A-S-H gels coexist. Meanwhile, the immobilization efficiency of heavy metals was above 98%, whose leaching concentrations were below the limits of the Chinese standards. Irshidat et al. [277] partially replaced fly ash by MSWIFA and river sand by MSWIBA to prepare geopolymer mortar.
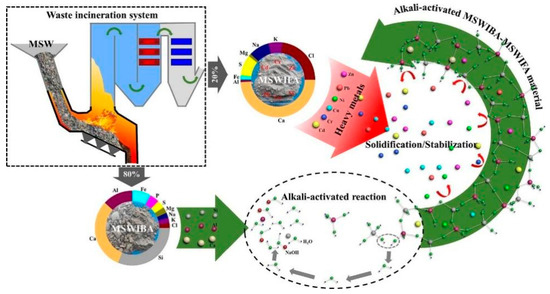
Figure 30.
Solidification mechanism of MSWIBA-MSWIFA-based geopolymer [276].
4.2.3. Other Hazardous Wastes
There are also many other hazardous materials that need to be carefully treated. For example, radioactive solid wastes contain radioactive components. Carelessly disposing these solid wastes will lead to disaster. El-Naggar et al. [278] prepared geopolymers for the solidification of ion exchange resin waste by adjusting the proportions of kaolinite, feldspar, and blast furnace slag, with the ion exchange resin loaded with varying concentrations of radioactive nuclides 134Cs, 60Co, and 152+154Eu. The geopolymer with the resin addition exhibited high strength, exceeding 45 MPa. The solidification experimental results indicated the leaching order was 152+154Eu > 134Cs > 60Co. Samples loaded with multiple components exhibited greater leaching than those with single components, and γ-rays enhanced the leaching of radionuclides. Shin et al. [279] explored MK-based geopolymer for spent ion-exchange resin immobilization. The geopolymer prepared with 20 wt% of simulated spent resin met the criterion in South Korea, where the leachability index >6, depending on the size and wastes loading. Hasnaoui et al. [280] firstly applied MK-based geopolymer for radioactive tributyl phosphate/dodecane (TBP/dodecane) wastes solidification. Three surfactants were tested to determine the best one to achieve desired rheological, mechanical, and microstructural properties. They found that MK-based geopolymer adding Brij O10 is the best for TBP/dodecane immobilization. The above 8 MPa compressive strength of this product can achieve industrial storage specifications.
Borate and boric acid appear in this section not merely as chemical additives but as components of specific hazardous solid wastes. In nuclear power plants and other nuclear facilities, boric acid and sodium borates are commonly employed as neutron absorbers and pH control agents in cooling systems. As a result, borate-bearing residues are generated during operation, maintenance, and decommissioning, forming a distinctive class of radioactive or hazardous wastes that require stabilization. The disposal of borate wastes is becoming popular. Kim et al. [281] adjusted the Si/Al ratios (1.0–1.4) and curing temperatures (26 °C and 60 °C) to optimize the properties of boron waste-containing MK-based geopolymer. All geopolymers had compressive strengths (>3.445 MPa) meeting waste acceptance criteria. The leaching mechanism of boron was diffusion, and its leachability index of boron was higher than 6.0. The physically bound or unincorporated boron was leached out of the geopolymer, while the chemically bound boron with silicon remained as an inert phase. Owing to the bad behavior of sodium borate anhydrous during geopolymeriztion, Chung et al. [282] introduced CaO to improve the properties of sodium borate anhydrous. After performing this, the mechanical, thermal circulation, immersion, and leaching properties in all cases satisfied the criteria value. Kim et al. [283] firstly applied acid-activation geopolymer for borate waste disposal (0–50 wt%). The formation of a new amorphous boron phosphate phase corresponded to the increase in the compressive strength and immobilization of boron.
Many sludges contain hazardous matters. Waijarean et al. [284] prepared geopolymers using water treatment residues and employed them to solidify electroplating sludge. Although the compressive strength is below 10 MPa, the heavy metal ions in the sludge are effectively solidified. The primary heavy metals (Zn, Fe, and Cr) in electroplating sludge precipitate as insoluble oxides in alkaline solutions, leading to solidification. Genua et al. [285] investigated factors affecting the immobilization effect of galvanic sludge that contains Cr, Ni, Fe. The addition of MK during geopolymerization of galvanic sludge increased Cr immobilization effect from 83% to 89%.
Han et al. [286] took electrolytic manganese dioxide residue as raw material for preparing acid-activation geopolymer mortar. They obtained a geopolymer with a strength of 96.3 MPa and Mn stabilization efficiency of 95.4%. Narani et al. [287] used wood fly ash and GGBFS as precursors for geopolymer preparation. ICP-MS results indicate that the alkali-activated composites effectively immobilize a wide range of heavy metals, including As, Cd, Ba, Cr, Pb, Mo, Se, Hg, Sr, Cu, and Zn. However, Co and V were found to remain partially soluble after leaching tests, suggesting that these two elements cannot be efficiently immobilized in the current system. This behavior is mainly related to their high mobility and oxyanion formation in alkaline conditions, which hinder their incorporation into the aluminosilicate gel framework. Huang et al. [288] synthesize polyvalent Mn-based (hydro)oxide-functionalized nanosilica by nonthermal plasma irradiation. Then, they loaded these nanosilica onto geopolymers for efficient solidification and stabilization (S/S) of Tl-containing soils (Figure 31).
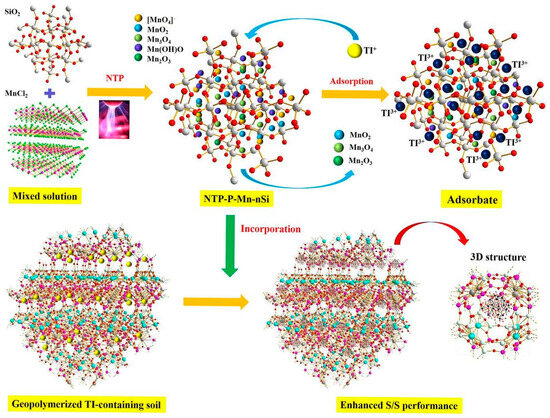
Figure 31.
Solidification mechanism of polyvalent Mn-based (hydro)oxide-functionalized nanosilica/geopolymer for Tl-containing soil [288].
5. Conclusions
Geopolymers have emerged as promising low-carbon binders with excellent mechanical performance, chemical resistance, and capability to immobilize hazardous wastes and adsorb pollutants. However, translating laboratory results into industrial practice faces several significant barriers. First, the cost and availability of alkali activators remain major issues; large-scale production will require supply chain optimization and cost reduction strategies. Second, long-term durability under real-world conditions—including variable pH, freeze–thaw cycles, wet–dry cycling, and radiation exposure—must be validated through extended leaching tests and pilot-scale field trials. Third, regulatory approval and standardization are still in early stages, and the absence of widely accepted codes or performance specifications hinders widespread adoption. Addressing these challenges through systematic research, life-cycle assessment, and collaboration between academia, industry, and regulatory bodies will be essential for accelerating the commercialization of geopolymer technology in environmental applications.
Current research has demonstrated that both alkali- and acid-activation geopolymers are effective in stabilizing toxic pollutants and valorizing solid wastes into high-performance environmental materials. Furthermore, advances in tailoring their microstructure, porosity, and surface chemistry have broadened their applications in wastewater purification, air pollution control, and circular economy practices. Despite these achievements, challenges remain in understanding reaction mechanisms, optimizing precursor activation, and scaling up technologies for industrial deployment.
Overall, geopolymers currently hold significant research and application value. The application of geopolymerization or geopolymers in the environmental field not only addresses environmental issues but also holds significant implications for energy conservation, resource utilization, and environmental protection. Looking forward, the future of geopolymers in environmental applications lies in the integration of multi-functional design, large-scale solid waste utilization, and process optimization for commercial feasibility. By bridging fundamental research with engineering practice, geopolymers are expected to play a pivotal role in sustainable development, offering innovative pathways for pollution control, carbon neutrality, and resource efficiency in the coming decades.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. (Yonglei Zhang); methodology, Y.Z. (Yonglei Zhang); validation, T.Y. and Y.Z. (Yang Zhou); formal analysis, Y.Z. (Yonglei Zhang); investigation, P.L., Y.H. and Y.P.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z. (Yonglei Zhang); writing—review and editing, Y.Z. (Yonglei Zhang), T.Y. and Y.Z. (Yang Zhou); funding acquisition, Y.Z. (Yonglei Zhang). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2022A1515111008).
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the anonymous reviewers for their insightful and constructive comments and suggestions on the earlier version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Loáiciga, H.A. Energy and Water Provision for a Growing Population; SSRN: Rochester, NY, USA, 2024; Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=5422068 (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Habert, G.; Miller, S.A.; John, V.M.; Provis, J.L.; Favier, A.; Horvath, A.; Scrivener, K.L. Environmental Impacts and Decarbonization Strategies in the Cement and Concrete Industries. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Muhammad, F.; Yu, T.; Fahimizadeh, M.; Hassan, M.A.S.; Liang, J.; Ning, X.; Yuan, P. Harnessing Iron Tailings as Supplementary Cementitious Materials in Limestone Calcined Clay Cement (LC3): An Innovative Approach towards Sustainable Construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 453, 139111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Huang, X.; Zhong, S.; Zhou, J. Advancing toward a Low-Carbon Infrastructure: Emission Reduction Potential of Geopolymer Road Maintenance. Mater. Today Sustain. 2025, 30, 101121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, K.; Shen, P.; Poon, C.S. Utilization of Granite Sludge in the Production of Low Carbon Cement Composites after Coupled Mechanical and CO2 Activation (CMCA). Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 164, 106284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Guo, H.; Yuan, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Deng, L.; Liu, D. Geopolymerization of Halloysite via Alkali-Activation: Dependence of Microstructures on Precalcination. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 185, 105375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Deng, G.; Yang, T.; Yang, Y. Effect of Different Curing Methods on the Preparation of Carbonized High-Titanium Slag Based Geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 128023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhan, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, B.; Li, R.; Dong, Z.; Kua, H.W. Eco-Sustainable Design of Seawater Sea-Sand Slag-Based Geopolymer Mortars Incorporating Ternary Solid Waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 431, 136512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, H.A.; Cilla, M.S.; Walkley, B.; Ribeiro Dias, C.M. Durability of Geopolymer Composites Reinforced with Vegetable Fibers: Effects of Alkaline Activator, Matrix Dosage, and Aging on the Composite. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 107, 112693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Guo, H.; Deng, L.; Fan, W.; Yu, T.; Wang, Q. Undehydrated Kaolinite as Materials for the Preparation of Geopolymer through Phosphoric Acid-Activation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 199, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Lang, L.; Dong, C.; Huang, K. Preparation and Properties of Geopolymer Containing Phosphoric Acid-Activated Fly Ash and Mechanically-Milled Kaolinite: Experiments and Density Function Theory. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 441, 140992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Li, L.; He, P.; Chen, Z.; Lao, C.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. Effects of Kinds of Alkali-Activated Ions on Geopolymerization Process of Geopolymer Cement Pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 293, 123536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djobo, J.N.Y.; Tome, S. Insights into Alkali and Acid-Activated Volcanic Ash-Based Materials: A Review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 152, 105660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Huang, X.; Huang, Q.; Shiau, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, B.; Sabri, M.M. Effects of Particle Size on Properties of Engineering Muck-Based Geopolymers: Optimization through Sieving Treatment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 492, 142967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishna, B.; Dinakar, P. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and the Influence of Alkaline Activator Content on Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Geopolymer Mortar. J. Eng. Res. 2024, 13, 1462–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Provis, J.L.; Dai, J.-G. Role of Soluble Aluminum Species in the Activating Solution for Synthesis of Silico-Aluminophosphate Geopolymers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 93, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Synthesis of New High-Temperature Geo-Polymers for Reinforced Plastic/Composites. In Proceedings of the PACTEC ‘79 Society of Plastics Engineers, Costa Mesa, CA, USA, 31 January–2 February 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Dong, T.; Ouyang, G. Structural and Mechanical Properties of Geopolymers Made of Aluminosilicate Powder with Different SiO2/Al2O3 Ratio: Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Microstructural Experimental Study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 240, 117935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Pour-Ghaz, M.; Park, S. Compressive Strength Degradation of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer with an Excessively High S/A Ratio: Insights from Nanoindentation on N-A-S-H Gel Structure. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 108, 112870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deventer, J.; Provis, J.; Duxson, P.; Lukey, G. Reaction mechanisms in the geopolymeric conversion of inorganic waste to useful products. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Lin, W.; Zheng, K.; Sha, J.; Liu, S. In-situ Quantitative Tracking of the Hydration Process in the Interfacial Transition Zone of K-PSDS Geopolymer Concrete by Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 31, 806–810. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, B.; Rees, G.J.; San Nicolas, R.; Van Deventer, J.S.J.; Hanna, J.V.; Provis, J.L. New Structural Model of Hydrous Sodium Aluminosilicate Gels and the Role of Charge-Balancing Extra-Framework Al. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 5673–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Cao, K.; Chen, K.; Mao, N. Interfacial Characteristics and Mechanical Behavior of Geopolymer Stabilizers with Clay Mineral: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2024, 250, 107286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisard, S.; Serdar, M.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Multiscale X-Ray Tomography of Cementitious Materials: A Review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 128, 105824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H. Geopolymer from kaolin in China: An overview. Appl Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, I.H.; Li, Q.; Hu, H.; Onyekwena, C.C.; Hou, Y.; Hakuzweyezu, T.; Iftikhar, S.; Chen, B. A Critical Review of the Advancements in Acid-Activated Metakaolin Geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Liu, Y.; Le, H. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Phosphoric Acid Activated Geopolymer Materials Reinforced with Mullite Fibers. Materials 2022, 15, 4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmani, S.; Sdiri, A.; Bouaziz, S.; Joussein, E.; Rossignol, S. Effects of Metakaolin Addition on Geopolymer Prepared from Natural Kaolinitic Clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 146, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Guo, H.; Yuan, P.; Deng, L.; Zhong, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, D. Novel Acid-Based Geopolymer Synthesized from Nanosized Tubular Halloysite: The Role of Precalcination Temperature and Phosphoric Acid Concentration. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 110, 103601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Yang, Z.; Li, N.; Zhu, X.; Fu, B.; Ou, Z. Strength, Microstructure, CO2 Emission and Economic Analyses of Low Concentration Phosphoric Acid-Activated Fly Ash Geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 374, 130920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M. Properties and Mechanism of High-Magnesium Nickel Slag-Fly Ash Based Geopolymer Activated by Phosphoric Acid. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, D. High Temperature Performance of High Magnesium Nickel Slag Based Geopolymers with Different P/Al Molar Ratios Prepared by Acidic Activator. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguang, C.; Dageng, S.U.; Bo, L.U.; Yunxia, Y. Synthesis and Structure Characterization of Geopolymeric Material Based on Metakaolinite and Phosphoric Acid. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 33, 1385–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Louati, S.; Baklouti, S.; Samet, B. Acid Based Geopolymerization Kinetics: Effect of Clay Particle Size. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 132–133, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louati, S.; Hajjaji, W.; Baklouti, S.; Samet, B. Structure and Properties of New Eco-Material Obtained by Phosphoric Acid Attack of Natural Tunisian Clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 101, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathivet, V.; Jouin, J.; Gharzouni, A.; Sobrados, I.; Celerier, H.; Rossignol, S.; Parlier, M. Acid-Based Geopolymers: Understanding of the Structural Evolutions during Consolidation and after Thermal Treatments. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 512, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Liu, L.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J. A Novel Aluminosilicate Geopolymer Material with Low Dielectric Loss. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 130, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Yan, C.; Zhou, W. Compressive Strength and Microstructure of Fly Ash Based Geopolymer Blended with Silica Fume under Thermal Cycle. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 78, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yuan, Y.; Wen, S.; Wang, Y.; Tan, B. Research on Ambient-Temperature Synthesis of High-Strength Geopolymer Concrete: Parameter Optimization and Strength Prediction Model. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 23, e05123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivenko, P.V.; Guziy, S.G. Aluminosilicate Coatings with Enhanced Heat- and Corrosion Resistance. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 73, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, H.; Chai, X.; Jia, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, G.; Li, W. Study on Corrosion Resistance and Microstructure of Modified Sediment Geopolymer Materials. Mater. Today Sustain. 2025, 29, 101048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Liu, L.; Cui, X.; He, Y.; Zheng, G.; Shi, C. Effect of Fuller-Fine Sand on Rheological, Drying Shrinkage, and Microstructural Properties of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Grouting Materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 104, 103381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyrek, Y.; Rudić, O.; Juhart, J.; Grengg, C.; Charry, E.M.; Freytag, B.; Mittermayr, F. On Drying Shrinkage of Geopolymer and How to Mitigate It with Vegetable Oil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 436, 137013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandanayake, M.; Gunasekara, C.; Law, D.; Zhang, G.; Setunge, S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Different Fly Ash Based Geopolymer Concretes in Building Construction. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lai, D.; Zhong, H.; Yu, T.; Liang, J.; Xie, J. Dynamic Mechanical Behaviour and Life Cycle Assessment of Rubberised Solid Waste-Based Geopolymer Concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 501, 145247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, C.; Peng, X. Immobilization of Radioactive Borate Liquid Waste Using Calcined Laterite–Phosphoric Acid–Fe3O4-Based Geopolymer Waste Forms. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 48164–48173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Guo, B.; Sasaki, K. Immobilization Mechanism of Se Oxyanions in Geopolymer: Effects of Alkaline Activators and Calcined Hydrotalcite Additive. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, D.; Hao, H. Cementitious Binders Modified with Halloysite Nanotubes for Enhanced Lead Immobilization. Powder Technol. 2022, 395, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ke, Y.; Cao, L.; Yang, J.; Liang, S.; Xiao, K.; Hu, J.; Hou, H. Lead Immobilization in Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers: The Role of Microwave Irradiation and Chemical Forms. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 481, 141557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaolong, Z.; Shiyu, Z.; Hui, L.; Yingliang, Z. Disposal of Mine Tailings via Geopolymerization. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basar, I.A.; Eskicioglu, C. Continuous-Flow Aerobic Co-Treatment of Municipal Sludge Derived Hydrothermal Liquefaction Aqueous Phase with Wastewater in Treatment Plants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wei, Z. Interaction Mechanism of Multiple Heavy Metals Removal in Sludge Incineration Flue Gas by Thermophilic Membrane Bioreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 520, 166196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, A.; Rayhan, M.M.; Sarker, M.S.A.; Saha, A.; Hamrani, A.; McDaniel, D. A Systematic Review on Grout in Nuclear Waste Management: Advancement, Composition and Performance. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2025, 443, 114281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, J.; Lu, J.-X.; Ma, B.; Peng, L.; Du, H.; Fan, D.; Yao, J.; Xing, B.; Poon, C.S. Hydration and Physicochemical Immobilization Mechanisms of Pozzolanic-Hazardous Waste in Supersulfated Cement. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 158, 105970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, D.; Rizzo, F.; Palma, L.D. Lime and Pozzolan-Based Matrices for an Efficient Immobilization of Hazardous Waste. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 313, 121735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Pei, Y. Bibliographic and Visualized Analysis of Geopolymer Research and Its Application in Heavy Metal Immobilization: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; He, X.; Gong, S.; Cai, G.; Lang, L.; Ma, H.; Niu, Z.; Zhou, F. Influence Mechanism of Fulvic Acid on the Strength of Cement-Solidified Dredged Sludge. Water 2022, 14, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, E.; Kunze, C.; Gatzweiler, R.; Kießig, G.; Davidovits, J. Solidification of Various Radioactive Residues by Géopolymère with Special Emphasis on Long-Term-Stability. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Geopolymer’99, Saint-Quentin, France, 30 June–2 July 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Jomova, K.; Alomar, S.Y.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Heavy Metals: Toxicity and Human Health Effects. Arch. Toxicol. 2025, 99, 153–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phair, J.W.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Effect of Silicate Activator pH on the Leaching and Material Characteristics of Waste-Based Inorganic Polymers. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, F.; Mu, J. Solidification/Stabilization Mechanism of Pb(II), Cd(II), Mn(II) and Cr(III) in Fly Ash Based Geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatello, S.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. An Assessment of Mercury Immobilisation in Alkali Activated Fly Ash (AAFA) Cements. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213–214, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Luo, H.; Wang, S.; Ou, X.; Su, J.; Lyu, Z.; Chen, J.; Wei, D. Synthesis of Tailing Slurry-Based Geopolymers for the Highly Efficient Immobilization of Heavy Metals: Behavior and Mechanism. Appl. Clay Sci. 2024, 247, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pereira, C.; Luna-Galiano, Y.; Pérez-Clemente, M.; Leiva, C.; Arroyo, F.; Villegas, R.; Vilches, L.F. Immobilization of Heavy Metals (Cd, Ni or Pb) Using Aluminate Geopolymers. Mater. Lett. 2018, 227, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Pan, D.; Liu, B.; Volinsky, A.A.; Fincan, M.; Du, J.; Zhang, S. Immobilization Mechanism of Pb in Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, H. Detoxification and Solidification of Heavy Metal of Chromium Using Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer with Chemical Agents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mashqbeh, A.; Abuali, S.; El-Eswed, B.; Khalili, F.I. Immobilization of Toxic Inorganic Anions (Cr2O72-, MnO4- and Fe(CN)63-) in Metakaolin Based Geopolymers: A Preliminary Study. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 5613–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Pei, Y. Immobilization Efficiency and Mechanism of Metal Cations (Cd2+, Pb2+ and Zn2+) and Anions (AsO43- and Cr2O72-) in Wastes-Based Geopolymer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Wei, X.; Chen, H.; Xie, F.; Shen, X.; Zheng, P.; Yan, F.; Bai, W.; Zhang, Z. Microstructural Evolution and Immobilization Mechanisms of Geopolymers Incorporating Cationic and Oxyanionic Heavy Metals (Pb2+, Zn2+, Cr2O72−, and AsO2−). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymer: Chemistry & Applications, 5th ed.; Institut Géopolymère: Saint-Quentin, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.; Wang, H.; Pan, Y.; Bai, Y.; Chen, C.; Yao, S.; Guo, B.; Zhang, H. Immobilization Mechanism of Cesium in Geopolymer: Effects of Alkaline Activators and Calcination Temperature. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Wang, R.; Fu, S.; Wang, M.; Cai, D.; Ma, G.; Wang, M.; Yuan, J.; Yang, Z.; Duan, X.; et al. Safe Trapping of Cesium into Doping-Enhanced Pollucite Structure by Geopolymer Precursor Technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 367, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; An, H.; Cui, H.; Pan, Y.; Wang, B.; Mao, L.; Zhai, J. Effects of Gamma-Ray Irradiation on Leaching of Simulated 133 Cs + Radionuclides from Geopolymer Wasteforms. J. Nucl. Mater. 2015, 459, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavor, D.; Wolfson, A.; Shamaev, A.; Shvarzman, A. Recycling of industrial wastewater by its immobilization in geopolymer cement. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 6801–6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackford, M.G.; Hanna, J.V.; Pike, K.J.; Vance, E.R.; Perera, D.S. Transmission Electron Microscopy and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies of Geopolymers for Radioactive Waste Immobilization. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zong, Z.; Dong, Y.; Xie, J.; Cao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, L.; Jiang, Q. Assessing the immobilization performance of fly ash-based geopolymers for removal of cesium and treatment of radioactive wastewater. Mater Today Commun. 2025, 46, 112638. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, X.; Elakneswaran, Y.; Hiroyoshi, N. Surface Chemistry and Radionuclide Anion Immobilisation Potential of Phosphoric Acid-Activated Metakaolin-Based Geopolymers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 181, 107549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Yun, J.-I. Exploring the Longevity of Geopolymer Waste Forms Co-Hosting Cationic and Anionic Radionuclides: A Mechanistic Investigation. J. Nucl. Mater. 2025, 608, 155720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Chai, X.; Bi, X.; Liu, J.; Ohnuki, T. Synthesis and Characterization of Mn-Slag Based Geopolymer for Immobilization of Co. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayenko, S.; Svitlychnyi, Y.; Shkuropatenko, V.; Pancotti, F.; Sandalova, S.; Poulesquen, A.; Giboire, I.; Hasnaoui, A.; Cori, D.; Magugliani, G.; et al. Incorporation of Organic Liquid Waste in Alkali Activated Mixed Fly Ash/Blast Furnace Slag/Metakaolin-Based Geopolymers. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2024, 429, 113608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossini, E.; Santi, A.; Magugliani, G.; Galluccio, F.; Macerata, E.; Giola, M.; Vadivel, D.; Dondi, D.; Cori, D.; Lotti, P.; et al. Pre-Impregnation Approach to Encapsulate Radioactive Liquid Organic Waste in Geopolymer. J. Nucl. Mater. 2023, 585, 154608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wen, Q.; Lu, X.; Xiao, K.; Ekberg, C.; Zhang, S. Application of Geopolymers for Treatment of Industrial Solid Waste Containing Heavy Metals: State-of-the-Art Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 390, 136053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, W.; Gao, X. Solidification and immobilization of MSWI fly ash through aluminate geopolymerization: Based on partial charge model analysis. Waste manag. 2016, 58, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Heponiemi, A.; Runtti, H.; Pesonen, J.; Yliniemi, J.; Lassi, U. Application of Alkali-Activated Materials for Water and Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 271–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Ye, F.; Chen, D.; Liang, S. Research progress on solidification/stabilization of sludge with Alkali‒Activated cementitious materials: A review. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2025, 43, 101904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yu, T.; Deng, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, L.; Peng, Y. Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earth Tailings for Preparation of Alkali-Based Geopolymer with Capacity for Heavy Metals Immobilization. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 134, 104768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, T.; Li, S.; Muhammad, F.; Xu, G.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, L.; Yan, Y.; Li, D.; Jiao, B. Immobilization of Chromite Ore Processing Residue with Alkali-Activated Blast Furnace Slag-Based Geopolymer. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 9538–9549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tu, Y.; Guo, T.; Fang, M.; Shi, P.; Yuan, L.; Wang, C.; Sas, G.; Elfgren, L. Molecular Dynamics Study on Structural Characteristics and Mechanical Properties of Sodium Aluminosilicate Hydrate with Immobilized Radioactive Cs and Sr Ions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 243, 107042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ye, J.; Wang, J.; Peng, X. Adsorption and Diffusion Mechanism of Cesium and Chloride Ions in Channel of Geopolymer with Different Si/Al Ratios: Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2023, 332, 3597–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Eswed, B.I.; Aldagag, O.M.; Khalili, F.I. Efficiency and Mechanism of Stabilization/Solidification of Pb(II), Cd(II), Cu(II), Th(IV) and U(VI) in Metakaolin Based Geopolymers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 140, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siora, I.; Andriyko, L.; Gerashchenko, I.; Borysenko, M.; Pakhlov, E.; Oranska, O.; Lytvynenko, Y.; Tsyba, M.; Odynchenko, R.; Goncharuk, O. Comparative Study of the Structural Characteristics and Adsorption Capacity of Natural and Synthetic Zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2025, 397, 113778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Věžníková, K.; Tolonen, E.-T.; Runtti, H.; Yliniemi, J.; Hu, T.; Kemppainen, K.; Lassi, U. Removal of Ammonium from Municipal Wastewater with Powdered and Granulated Metakaolin Geopolymer. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5085.3-2007; Hazardous Waste Identification Standard—Leaching Toxicity Identification. Ministry of Environmental Protection of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure (TCLP), Method 1311 of SW-846; 40 CFR Part 261.24; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 1992.
- European Union. Commission Decision 2014/955/EU, Amending Decision 2000/532/EC on the List of Waste, Annex III, Section H14; Official Journal of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mazumder, M.A.J.; Al-Attas, O.; Husain, T. Heavy Metals in Drinking Water: Occurrences, Implications, and Future Needs in Developing Countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Orr, M.; Gustave, W.; Ma, C.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, M.; Ouyang, F.; Chesters, D.; Cheng, R.; et al. The Impacts of Agricultural Intensification and Diet Diversity on Solitary Bee Exposure to Heavy Metals. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 394, 109882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harahsheh, M.S.; Al Zboon, K.; Al-Makhadmeh, L.; Hararah, M.; Mahasneh, M. Fly Ash Based Geopolymer for Heavy Metal Removal: A Case Study on Copper Removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.W.; Lee, M.L.; Ko, M.S.; Ueng, T.H.; Yang, S.F. The Heavy Metal Adsorption Characteristics on Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 56, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arokiasamy, P.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Arifi, E.; Jamil, N.H.; Othuman Mydin, M.A.; Abd Rahim, S.Z.; Sandu, A.V.; Ishak, S. Sustainable Geopolymer Adsorbents Utilizing Silica Fume as a Partial Replacement for Metakaolin in the Removal of Copper Ion from Synthesized Copper Solution. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KA, A.K.; Shetty, K.K.; Rashmi, N.; Bhat, P. Adsorptive Removal of Manganese Ion Using Ternary Blended Geopolymer Paste Derived from Industrial and Agricultural Wastes. Mater. Res. Express 2025, 12, 035506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafri, E.A.; Tamimi, N.A.; El-Hassan, H.; Maraqa, M.A.; Hamouda, M. Synthesis and Multi-Objective Optimization of Fly Ash-Slag Geopolymer Sorbents for Heavy Metal Removal Using a Hybrid Taguchi-TOPSIS Approach. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 35, 103721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, İ.; Yilmazer, D.; Akar, S.T. Metakaolin Based Geopolymer as an Effective Adsorbent for Adsorption of Zinc(II) and Nickel(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 139, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalheiras, J.; Novais, R.M.; Labrincha, J.A. Metakaolin/Red Mud-Derived Geopolymer Monoliths: Novel Bulk-Type Sorbents for Lead Removal from Wastewaters. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 232, 106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Buruberri, L.H.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Novel Porous Fly-Ash Containing Geopolymer Monoliths for Lead Adsorption from Wastewaters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Luo, H.; Wang, S.; Ou, X.; Su, J.; Chen, J. Synthesis of Foamed Geopolymers by Substituting Fly Ash with Tailing Slurry for the Highly Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Contaminants: Behavioral and Mechanistic Studies. J. Cent. South Univ. 2024, 31, 1344–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaaer, M.; Alharbi, B.; Alqahtani, O.; Alotaibi, M.S.; Alzayed, A.; Al-Kafawein, J. Synthesis and Characterization of Metakaolin–Wollastonite Geopolymer Foams for Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water. Materials 2025, 18, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Ge, Y.; Wang, K.; He, Y.; Cui, X. Preparation and Characterization of Porous Metakaolin-Based Inorganic Polymer Spheres as an Adsorbent. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 1244–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Ren, X.; Zhang, F.; Huang, K.; Feng, X.; Xing, P. Comparative Study of Pb2+, Ni2+, and Methylene Blue Adsorption on Spherical Waste Solid-Based Geopolymer Adsorbents Enhanced with Carbon Nanotubes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 284, 120234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Do Geopolymers Actually Contain Nanocrystalline Zeolites? A Reexamination of Existing Results. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 3075–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrejkovičová, S.; Sudagar, A.; Rocha, J.; Patinha, C.; Hajjaji, W.; Da Silva, E.F.; Velosa, A.; Rocha, F. The Effect of Natural Zeolite on Microstructure, Mechanical and Heavy Metals Adsorption Properties of Metakaolin Based Geopolymers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 126, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Eswed, B.I.; Yousef, R.I.; Alshaaer, M.; Hamadneh, I.; Al-Gharabli, S.I.; Khalili, F. Stabilization/Solidification of Heavy Metals in Kaolin/Zeolite Based Geopolymers. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 137, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Qiu, X.; Meng, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Qiao, Q.; Yan, C. Clinoptilolite Based Zeolite-Geopolymer Hybrid Foams: Potential Application as Low-Cost Sorbents for Heavy Metals. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, Q.; Ye, Q.; Deng, X.; Su, Q.; Cui, X. Performance of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Molecular Sieve Microspheres on Dynamic Recovery of Cu (II). Appl. Clay Sci. 2024, 255, 107423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; He, Y.; Yang, S.; Wan, H.; Chang, S.; Cui, X. Synthesis of NaA-Zeolite Microspheres by Conversion of Geopolymer and Their Performance of Pb (II) Removal. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 200, 105914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Wang, Q.; Fu, S.; Wang, M.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. Hydrothermal Transformation of Geopolymers to Bulk Zeolite Structures for Efficient Hazardous Elements Adsorption. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liu, R.; Qu, J.; Liu, H. Potential Applications of Solid Waste-Based Geopolymer Materials: In Wastewater Treatment and Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 443, 141144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurlina, N.; Pratama, J.H.; Pambudi, A.B.; Rahmawati, Z.; Subaer, S.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Gusrizal, G.; Fansuri, H. A Review of Geopolymer Membrane for Water Treatment. Appl. Clay Sci. 2024, 251, 107301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Colombo, P. Processing, Properties and Applications of Highly Porous Geopolymers: A Review. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 16103–16118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, K.; He, Y.; Cui, X. Preparation of Geopolymer-Based Inorganic Membrane for Removing Ni2+ from Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; He, Y.; Liu, Z.; Tong, Z.; Cui, X. Preparation of Geopolymer Inorganic Membrane and Purification of Pulp-Papermaking Green Liquor. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 168, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, S.; Darestani, M.; Millar, G.; Boshrouyeh, B. Fabrication and Performance of PVAc-Incorporated Porous Self-Standing Zeolite-Based Geopolymer Membranes for Lead (Pb(II)) Removal in Water Treatment. Polymers 2025, 17, 1155. [Google Scholar]
- De Sousa, F.A.; Della-Rocca, D.; De Amorim, S.M.; Da Silveira Salla, J.; Peralta, R.A.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Peralta Muniz Moreira, R.D.F. Development of Membranes Based on Alkali-Activated Phosphate Mine Tailings for Humic Acid and Copper Removal from Water. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 496. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Yi, M.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lu, C.; Fujita, T.; Cui, X. Fabrication of Electrolytic Manganese Residue/Granulated Blast Furnace Slag-Based Geopolymer Microspheres (EMR/GBFS@GMs) and Enhanced Synergic Adsorption of Cr(III)-Containing Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 355, 129555. [Google Scholar]
- Tajima, T.; Ikeda, A.; Shigemura, J.; Tanigawa, T. Longitudinal Effects of Disaster-Related Experiences on Concern and Its Impact on Depressive Symptoms among Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant Workers: The Fukushima NEWS Project Study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2025, 184, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Adati, T.; Takahashi, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Takahashi, S. Concentrations and Biological Half-Life of Radioactive Cesium in Epigeic Earthworms after the Fukushima Dai-Ichi Nuclear Power Plant Accident. J. Environ. Radioact. 2018, 192, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Cui, M.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; Chen, Y. Insights into the Effect of NaOH on the Hydration Products of Solidified Cement-NaNO3 Matrices and Leaching Behavior of Sr2+. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; Barandica, J.; Paniagua, J.M.; Rufo, M.; Sterling, A. Using 226Ra/228Ra Disequilibrium to Determine the Residence Half-Lives of Radium in Vegetation Compartments. J. Environ. Radioact. 1999, 43, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, F.J.; Sugita, S.; Kobayashi, T. Cesium-Adsorbent Geopolymer Foams Based on Silica from Rice Husk and Metakaolin. Chem. Lett. 2014, 43, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.K.; Khalid, H.R.; Lee, H.K. Adsorption Characteristics of Cesium onto Mesoporous Geopolymers Containing Nano-Crystalline Zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 242, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Yang, J.; Cui, M.; Yang, K.; Shang, H.; Ma, X.; Li, Y. Adsorption/Desorption Performances of Simulated Radioactive Nuclide Cs+ on the Zeolite-Rich Geopolymer from the Hydrothermal Synthesis of Fly Ash. Energies 2023, 16, 7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, F.; Chen, F.; Cui, X.; Wei, Y.; Shao, L.; Yu, M. One-Pot Preparation of NaA Zeolite Microspheres for Highly Selective and Continuous Removal of Sr(II) from Aqueous Solution. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 2459–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Ge, Y.; He, Y.; Cui, X. A Low-Cost Photo-Evaporation Inorganic Membrane Preparation and Treatment of the Simulated High Salinity Radioactive Waste Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, L.; Rath, S.S.; Rao, D.S.; Nayak, B.B.; Das, B.; Misra, P.K. Thorough Understanding of the Kinetics and Mechanism of Heavy Metal Adsorption onto a Pyrophyllite Mine Waste Based Geopolymer. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 263, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, I.; Tunc, D.; Sayin, F.; Akar, S.T. Study on the Performance of Metakaolin Based Geopolymer for Mn(II) and Co(II) Removal. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yi, M.; Shao, L.; Kou, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, K. CTAB Modified Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Microspheres for the Selective Adsorption and Recovery of TcO4−/ReO4−. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 350, 127853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.K.; Uppaluri, R.V.S. Environmental Sustainability through Adsorption: A Review of Chitosan’s Potential in Dye Pollution Remediation. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2025, 46, 102096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, H.; He, P.Y.; Meng, Q. Development of Porous and Reusable Geopolymer Adsorbents for Dye Wastewater Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 348, 131278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-husseiny, R.A.; Ebrahim, S.E. Effective Removal of Methylene Blue from Wastewater Using Magnetite/Geopolymer Composite: Synthesis, Characterization and Column Adsorption Study. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 139, 109318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmad, J.; BiBi, A.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Application of TiO2-Loaded Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer in Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Water: Waste-to-Value Approach. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 25, 101138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Ascensão, G.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Biomass Fly Ash Geopolymer Monoliths for Effective Methylene Blue Removal from Wastewaters. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, H.; Tugrul, N.; Derun, E.M. Methylene Blue Adsorption by Chemically Foamed Geopolymer Based on Fly Ash. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- En-naji, S.; Ghazi, S.; Mabroum, H.; Mabroum, S.; Khatib, K.; Taha, Y.; Lodeiro, I.G.; Hakkou, R. Design of Acid-Geopolymers Based on Clays by-Products for Methylene Blue Removal from Wastewater. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 245, 107126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshghabadi, F.; Javanbakht, V. Preparation of Porous Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Foam as an Efficient Adsorbent for Dye Removal from Aqueous Solution. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1295, 136639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, T.R.; Foletto, E.L.; Dotto, G.L.; Jahn, S.L. Preparation of Mesoporous Geopolymer Using Metakaolin and Rice Husk Ash as Synthesis Precursors and Its Use as Potential Adsorbent to Remove Organic Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marubini, A.; Mhlarhi, R.; Edokpayi, J.N. Adsorptive Removal of Crystal Violet Dye from Aqueous Solution Using a Vermiculite-Based Geopolymer. Sci. Afr. 2025, 28, e02701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tochetto, G.; Simão, L.; De Oliveira, D.; Hotza, D.; Immich, A.P.S. Chemical and Thermal Modification of Geopolymer for Efficient Dye Removal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Apasery, M.A.; Ahmed, D. A Sustainable Approach for Immobilization Dyeing Bath Effluents of Reactive Yellow 145 by Using Different Types of Eco-Friendly Geopolymer Cement. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 66, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taquieteu, I.K.; Tamaguelon, H.D.; Shikuku, V.; Tome, S.; Njouond, D.K.; Dongmo, M.F.; Othman, H.; Vollrath, A.; Mohabbat, A.; Janiak, C.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Lignin-Modified Geopolymer Composites for Aqueous Phase Sequestration of Methyl Orange Dye in a Fixed-Bed Column. Mater. Adv. 2025, 6, 5074–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathy, S.R.; Bhattacharyya, S. Adsorptive Dye Removal Using Clay-Based Geopolymer: Effect of Activation Conditions on Geopolymerization and Removal Efficiency. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2025, 319, 118348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Açışlı, Ö.; Acar, İ.; Khataee, A. Preparation of a Surface Modified Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer for Removal of an Anionic Dye: Parameters and Adsorption Mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purbasari, A.; Ariyanti, D.; Fitriani, E. Adsorption of Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions on Fly Ash-Based Porous Geopolymer. Glob. NEST J. 2023, 25, 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Ma, S.; He, P.; Wang, M.; Duan, X.; Jia, D.; Colombo, P.; Zhou, Y. 3D Printing of Green and Environment-Friendly rGO@ZnO/GP for Removal of Methylene Blue from Wastewater. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2023, 174, 111158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Li, Q.; He, P.; Duan, X.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. 3D Printed GO-g-C3 N4 -geopolymer Components with Acid Treatment for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Wastewater. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2025, 108, e20377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Zu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Qin, Y.; Song, L. Deciphering the H2O Impact Mechanism in the NaA Zeolite for CO2 Capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 515, 163352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, A.L.; Da Silva, A.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Da Silveira Salla, J.; Castellã Pergher, S.B.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; José, H.J.; De Fátima Peralta Muniz Moreira, R. Synthesis and Characterization of Geopolymers Based on Phosphate Mining Tailings and Its Application for Carbon Dioxide and Nitrogen Adsorption. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 8396–8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.S.; Akhtar, F. Development of Lightweight Architecture of Geopolymer via Extrusion-Based 3D Printing for CO2 Capture. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2025, 45, 117191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelli, M.; Medri, V.; Papa, E.; Miccio, F.; Landi, E.; Doghieri, F. Geopolymers as Solid Adsorbent for CO2 Capture. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 148, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelli, M.; Papa, E.; Medri, V.; Miccio, F.; Benito, P.; Doghieri, F.; Landi, E. Characterization of Novel Geopolymer—Zeolite Composites as Solid Adsorbents for CO2 Capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 341, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, B.; Zhu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. In-Situ Synthesis of Zeolite X in Foam Geopolymer as a CO2 Adsorbent. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z. Synthesis of Geopolymer-Zeolite Composite from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash and Their Performance for CO2 Adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Lv, S.; Zhou, Y. Kinetics and Thermodynamics Study on Low Energy Synthesis of Porous Geopolymer Based Solid Amine Sorbent for Efficient CO2 Capture. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, E.; Medri, V.; Paillard, C.; Contri, B.; Natali Murri, A.; Vaccari, A.; Landi, E. Geopolymer-Hydrotalcite Composites for CO2 Capture. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.J.; He, P.Y.; Liu, L.C. Synthesis, Characterization, and Selective CO2 Capture Performance of a New Type of Activated Carbon-Geopolymer Composite Adsorbent. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 325, 129271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Cui, X. Study on the Immobilization of Carbonic Anhydrases on Geopolymer Microspheres for CO2 Capture. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 316, 128163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Deng, X.; He, Y.; Xiao, P.; Dhmees, A.S.; Cui, X. Carbonic Anhydrase Immobilized on Zn(II)-Geopolymer Membrane for CO2 Capture. Biochem. Eng. J. 2024, 208, 109364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariev, O.; Blueschke, D. Interplay of Chinese Rare Earth Elements Supply and European Clean Energy Transition: A Geopolitical Context Analysis. Renew. Energy 2025, 238, 121986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiket, Ž.; Galović, A.; Medunić, G.; Turk, M.F.; Ivanić, M.; Dolenec, M.; Biljan, I.; Šoster, A.; Kniewald, G. Adsorption of Rare Earth Elements from Aqueous Solutions Using Geopolymers. Proceedings 2018, 2, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis, G.S.; Srivastava, V.; Taleb, M.F.A.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Dotto, G.L.; Rossatto, D.L.; Oliveira, M.L.S.; Silva, L.F.O.; Lassi, U. Adsorption of Rare Earth Elements on a Magnetic Geopolymer Derived from Rice Husk: Studies in Batch, Column, and Application in Real Phosphogypsum Leachate Sample. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 10417–10429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D.; Liang, H.; Wang, J. A Critical Review on Ammonium Recovery from Wastewater for Sustainable Wastewater Management. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luukkonen, T.; Sarkkinen, M.; Kemppainen, K.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U. Metakaolin Geopolymer Characterization and Application for Ammonium Removal from Model Solutions and Landfill Leachate. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Tolonen, E.-T.; Runtti, H.; Kemppainen, K.; Perämäki, P.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U. Optimization of the Metakaolin Geopolymer Preparation for Maximized Ammonium Adsorption Capacity. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 9363–9376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausi, M.; Cofano, V.; Medini, M.; Occhipinti, R.; Pinto, D. Enhancing the Sustainability of Geopolymer Adsorbents for Efficient Ammonium Removal Using Sludges from Water Potabilization and Wastewater Treatment Plants. Environ. Res. 2025, 283, 122161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoir, G.J.; Wu, T. HCl-Treated Metakaolin Geopolymer-Based Adsorbent for Ammonium Removal from Agricultural Runoff. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 71, 107255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghsh, M.; Shams, K. Synthesis of a Kaolin-Based Geopolymer Using a Novel Fusion Method and Its Application in Effective Water Softening. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 146, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runtti, H.; Luukkonen, T.; Niskanen, M.; Tuomikoski, S.; Kangas, T.; Tynjälä, P.; Tolonen, E.-T.; Sarkkinen, M.; Kemppainen, K.; Rämö, J.; et al. Sulphate Removal over Barium-Modified Blast-Furnace-Slag Geopolymer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Hou, D.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, J. Insights on Magnesium and Sulfate Ions’ Adsorption on the Surface of Sodium Alumino-Silicate Hydrate (NASH) Gel: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 18297–18310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tian, S.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Du, S.; Cang, D. Exploration of Sulfamethoxazole Removal Triggered by Copper Slag-Based Geopolymer: Radical versus Nonradical Contributions. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 154310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Huang, C.; Wang, P.; Yin, J.; Tian, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z. Low-Cost Eggshell-Fly Ash Adsorbent for Phosphate Recovery: A Potential Slow-Release Phosphate Fertilizer. Water Res. 2024, 255, 121483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoir, G.J.; Wu, T. Lanthanum-Loaded Geopolymer for Phosphate Removal from Agricultural Runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmil, F.Z.; Mountadar, S.; El Alaoui-Belghiti, H.; Majid, F.; Rich, A.; Mountadar, M. Desalination RO Reject Brine as a Novel-Based Porous Geopolymer for Phosphorus Removal from Contaminated Media. Chemosphere 2024, 358, 142202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceacero-Moreno, M.; Álvarez-Rogel, J.; Nazaret González-Alcaraz, M. What Can Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization Reveal about Soil Functionality in Technically Restored and Spontaneously Colonized Metalliferous Mine Tailings? J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 392, 126832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, P.; Ismailov, A.; Solismaa, S.; Sreenivasan, H.; Räisänen, M.-L.; Levänen, E.; Illikainen, M. Recycling Mine Tailings in Chemically Bonded Ceramics—A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 634–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S.; Ray, A.K.; Bandopadhyay, A. Proposal for Resources, Utilization and Processes of Red Mud in India—A Review. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 118, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, B. Red Mud: An Environmental Challenge but Overlooked Treasure for Critical Rare Earth Metals. MRS Bull. 2022, 47, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.; Wasewar, K.; Mukhopadhyay, J.; Yoo, C.K.; Uslu, H. Neutralization and Utilization of Red Mud for Its Better Waste Management. World 2012, 6, 5410. [Google Scholar]
- Bhumij, R.K. Compaction Characteristics of Red Mud and Pond Ash Mix as Filling and Embankment Material. Ph.D. Dissertation, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, S.V.; Thorat, B.N. Mechanical Dewatering of Red Mud. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 294, 121157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, K. Synergistic Optimization of Synthesis Processes for Geopolymer from Solely Red Mud: Precursor Activation, Activator and Water-to-Binder Ratio. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 118007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascensão, G.; Seabra, M.P.; Aguiar, J.B.; Labrincha, J.A. Red Mud-Based Geopolymers with Tailored Alkali Diffusion Properties and pH Buffering Ability. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, T.; Novais, R.M.; Murillo Alarcón, R.; Labrincha, J.A.; Pontikes, Y. Use of Modified Bauxite Residue-Based Porous Inorganic Polymer Monoliths as Adsorbents of Methylene Blue. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Doh, J.-H.; Ong, D.E.L.; Kiely, F.L. Effect of Thermal Pretreatment on the Reactivity of Red Mud Valorized as Aluminosilicate Precursor for Geopolymer Production. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 445, 137943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Liu, X.; Dong, X.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Chang, S. Study on the Optimal Ratios and Strength Formation Mechanism of Mechanical Activation Red Mud Based Geopolymer. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 104, 112401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.-Y.; Lao, J.-C.; Qian, L.-P.; Shi, D.-D.; Lan, J.; Xie, T.-Y.; Hou, D.; Huang, B.-T. Upcycling Red Mud into High-Strength High-Ductility Engineered Geopolymer Composites (EGC): Toward Superior Performance and Sustainability. Compos. Part B Eng. 2025, 305, 112713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Hongqiang, M.; Hongyu, C.; Jiaxin, W.; Jing, S.; Zonghui, L.; Mingkai, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Coal Gangue Geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, Y.; Wan, S.; Zhou, X.; Hou, H. Comparison of Red Mud and Coal Gangue Blended Geopolymers Synthesized through Thermal Activation and Mechanical Grinding Preactivation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 153, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Pan, Z.; Chen, W.; Muhammad, F.; Zhang, B.; Li, L. Geopolymerization of Coal Gangue via Alkali-Activation: Dependence of Mechanical Properties on Alkali Activators. Buildings 2024, 14, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Li, L.; Chen, W.; Cong, X.; Yu, T.; Zhang, B. Study on the Compressive Strength and Reaction Mechanism of Alkali-Activated Geopolymer Materials Using Coal Gangue and Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag. Materials 2024, 17, 3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, K.; Qu, F.; Yan, C.; Wu, Z. Toward Understanding the Activation and Hydration Mechanisms of Composite Activated Coal Gangue Geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 318, 125999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, A.; Zhu, Y.; Dai, J.-G.; Xu, Q.; Liu, K.; Hao, F.; Sun, D. Manufacturing Ultra-High Performance Geopolymer Concrete (UHPGC) with Activated Coal Gangue for Both Binder and Aggregate. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 284, 111723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakil, S.N.A.; Tóth, M.; Ibrahim, J.-E.F.; Mucsi, G. Influence of Mechanical Activation of Coal Gangue on the Strength and Microstructure of Geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 486, 141977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, D.; Xu, F. Prediction of Compressive and Flexural Strength of Coal Gangue-Based Geopolymer Using Machine Learning Method. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 44, 112076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, K.; Su, F.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, C.; Zheng, T.; Wang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Colombo, P. Rapid Fabrication of Coal Gangue-Based Alkali Activated Foams and Application as pH Regulators. Mater. Lett. 2023, 338, 134020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, K.; Su, Y.; Shi, Y. An Evaluation of Iron Ore Tailings Characteristics and Iron Ore Tailings Concrete Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 286, 122968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yin, Z.; Lin, H. Research Status and Prospects for the Utilization of Lead–Zinc Tailings as Building Materials. Buildings 2023, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zou, A.; Pan, Z. Green Rebirth of Copper Tailings: From Environmental Burden to Efficient Utilization Strategies. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2025, e70075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Yan, C.; Zhou, W.; Ren, D. Development of Fly Ash and Iron Ore Tailing Based Porous Geopolymer for Removal of Cu(II) from Wastewater. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 13507–13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.R.D.; Calderón-Morales, B.R.D.S.; Borba Júnior, J.C.; Oliveira, T.M.D.; Silva, G.J.B. Proposition of Geopolymers Obtained through the Acid Activation of Iron Ore Tailings with Phosphoric Acid. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 403, 133078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Cao, Z.; Li, T.; Yan, Q.; Chen, Q.; Luo, X.P. Effect of Curing on Compressive Strength and Efflorescence of Tungsten Tailing-Based Geopolymer. Non-Met. Mines 2016, 39, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Karrech, A.; Dong, M.; Elchalakani, M.; Shahin, M.A. Sustainable Geopolymer Using Lithium Concentrate Residues. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Liu, H.; Hao, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Z. Geopolymer Synthesis Using Garnet Tailings from Molybdenum Mines. Minerals 2019, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kızıltepe, C.Ç.; Yüksel, İ.; Aydın, S.; Sığındere, A. Development of One-Part Geopolymer Binder Produced from Alkali Fused Boron Mine Tailings. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 111, 113099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Su, H.; Liu, H.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J.; Wang, X. Preparation and Mechanical Performance of Fluorite Tailings Geopolymer Precursor under Alkaline Heat Activation. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaji, Y.; Majdoubi, H.; Mansouri, S.; Tamraoui, Y.; El Bouchti, M.; Manoun, B.; Oumam, M.; Hannache, H. Effect of Synthetic Fibers on the Properties of Geopolymers Based on Non-Heat Treated Phosphate Mine Tailing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 260, 124147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Lu, L.; Luo, Q.; Lai, J.; Xie, X.; Li, B.; Zhuang, R.; He, Y. Strength Development and Polymerization Reaction Mechanism of Sulfur-Tailings-Based Geopolymer Produced with CaO and Na2SiO3 Composite Activator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Ma, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, W. The Utilization of Eco-Friendly Recycled Powder from Concrete and Brick Waste in New Concrete: A Critical Review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 114, 103807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zuo, J.; Zillante, G.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H. Construction and Demolition Waste Research: A Bibliometric Analysis. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2019, 62, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Ma, Z.; Ding, T. Reclamation Chain of Waste Concrete: A Case Study of Shanghai. Waste Manag. 2016, 48, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Lao, W.; Liu, F.; Zhu, H.; et al. The Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Recycled Metakaolinite-Based Geopolymer: Dependence of Recycled Powder Replacement Ratio. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 85, 108730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Kang, A.; Wu, Z.; Gong, Y.; Xiao, P. The Effect of Mechanical-Thermal Synergistic Activation on the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Recycled Powder Geopolymer. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 327, 129477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, B.; Xiao, J.; Singh, A. Utilization Potential of Aerated Concrete Block Powder and Clay Brick Powder from C&D Waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Tang, Q.; Yang, D.; Ba, G. Durability Studies on the Recycled Aggregate Concrete in China over the Past Decade: A Review. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 4073130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.-S.; Seo, E.-A.; Kim, D.-G.; Yang, K.-H. Efficiency of Dry Calcination and Trituration Treatments for Removing Cement Pastes Attached to Recycled Coarse Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 312, 125412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Xie, J. Effect of the Pretreatment on the Properties of Cement-Based Recycled Powder. Coatings 2024, 14, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Qian, X.; Chen, P.; Xu, Y.; Guo, J. An Environmentally Friendly Method to Improve the Quality of Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkhuda, H.; Shatarat, N. Improving the Mechanical Properties of Recycled Concrete Aggregate Using Chopped Basalt Fibers and Acid Treatment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 140, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Shi, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Effects of Carbonated Hardened Cement Paste Powder on Hydration and Microstructure of Portland Cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; He, Y.; Hu, S. Binding Materials of Dehydrated Phases of Waste Hardened Cement Paste and Pozzolanic Admixture. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater Sci. Ed. 2009, 24, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, B.J.; Xuan, D.X.; Zeng, W.; Poon, C.S. Carbonation Treatment of Recycled Concrete Aggregate: Effect on Transport Properties and Steel Corrosion of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 104, 103360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Ou, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Q. Study on Properties of Waste Concrete Powder by Thermal Treatment and Application in Mortar. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Feng, Y.; Xie, J.; Dai, J.; Chen, W.; Xue, Z.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Effects of Pretreated Recycled Powder Substitution on Mechanical Properties and Microstructures of Alkali-Activated Cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 406, 133360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Kang, A.; Wu, Z.; Peng, X.; Gong, Y. Evaluation of workability, microstructure and mechanical properties of recycled powder geopolymer reinforced by waste hydrophilic basalt fiber. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 396, 136514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yang, D.; Fang, K.; Hou, S.; Dai, Y.; Wang, C. Upcycling of Recycled Brick Powder as a Substitute for Precursor and Sand in Completely Recycled Geopolymer: From Micro to Macro Perspective. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 476, 141300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhu, T.; Yang, Q.; Vandeginste, V.; Li, J. Influence of Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag on Recycled Concrete Powder-Based Geopolymer Cured at Ambient Temperature: Rheology, Mechanical Properties, Reaction Kinetics and Air-Void Characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 438, 137190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Kang, S.; Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Chen, F.; Xu, M. Sulfate Resistance of Recycled Powder-Slag-Based Geopolymers under Different Erosive Environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 462, 139950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazami, D.; Pourabbas Bilondi, M.; Rahnama, A.; Zaresefat, M.; Moretti, L. Recycled Glass Powder and Calcium Carbide Residue Geopolymer to Stabilise Silty Sand Soil: Mechanical Performances and Statistical Analysis. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voit, K.; Kuschel, E. Rock Material Recycling in Tunnel Engineering. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Li, A. The 2015 Shenzhen Catastrophic Landslide in a Construction Waste Dump: Reconstitution of Dump Structure and Failure Mechanisms via Geotechnical Investigations. Eng. Geol. 2018, 238, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-L.; Ma, S.-T.; Kuang, Y.-W.; Xie, J.-B. Effect of Mineral Compositions on Mechanical Properties of Granite Residual Soil. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e02140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Liang, J.; Zhang, B.; Chen, W.; Huang, X.; Huang, Q.; Li, Y.; Yuan, P. Optimized Reinforcement of Granite Residual Soil Using a Cement and Alkaline Solution: A Coupling Effect. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2025, 17, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Chen, W.; Zhao, J.; Li, L.; Liu, F.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, B. Addition of Alkaline Solutions and Fibers for the Reinforcement of Kaolinite-Containing Granite Residual Soil. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 228, 106644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Liang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Luo, Q.; Sabri, S.M.M.; Muhammad, F.; Azzam, W.R.; Rao, F.; Yuan, P. Sustainable Utilization of Clay Minerals-Rich Engineering Muck via Alkali Activation: Optimization of Pore Structure by Thermal Treatment. Appl. Clay Sci. 2024, 258, 107491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Liang, J.; Huang, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, H.; Yuan, P. Eco-Efficient Recycling of Engineering Muck for Manufacturing Low-Carbon Geopolymers Assessed through LCA: Exploring the Impact of Synthesis Conditions on Performance. Acta Geotech. 2024, 257, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yan, Z.; Cao, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, X. Workability and mechanical performance of shield muck–slag-based engineered geopolymer composites modified with chemical admixtures. Case Stud. Constr. Mat. 2025, 23, e05173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassekpo, J.-B.M.; Zha, X.; Zhan, J. Compressive Strength Performance of Geopolymer Paste Derived from Completely Decomposed Granite (CDG) and Partial Fly Ash Replacement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 138, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassekpo, J.-B.M.; Zha, X.; Zhan, J. Synthesis Reaction and Compressive Strength Behavior of Loess-Fly Ash Based Geopolymers for the Development of Sustainable Green Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 141, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Li, K.; Liu, T.; Zou, D.; Peng, X.; Lyu, H.; Xiao, J.; Luan, C. Recycling and Optimum Utilization of Engineering Sediment Waste into Low-Carbon Geopolymer Paste for Sustainable Infrastructure. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Yin, Y.; Mi, W.; Chen, R.; Lin, X. Assessing Performance, Economic Costs and Environmental Benefits of High-Performance Ecological Geopolymer Concrete Incorporating Excavated Rock and Soil from Tunnelling, Fly Ash and Slag as Reclaimed Raw Materials. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Cao, K.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, H. Sustainable Utilization of Shield Muck in Geopolymer Composites: Insights into Activation Mechanisms and Carbon Emission Reduction Strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 520, 146110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ramos, A.O.; Bah, A.; Li, F. Valorization of Lead-Zinc Mine Tailing Waste through Geopolymerization: Synthesis, Mechanical, and Microstructural Properties. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Chen, J.; Lei, X.; Zhou, C. Detoxification and Immobilization of Chromite Ore Processing Residue with Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, S. Preparation of Geopolymers from Vanadium Tailings by Mechanical Activation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Rao, F.; Song, S.; Leon-Patino, C.A.; Ma, Y.; Yin, W. Consolidation of Mine Tailings through Geopolymerization at Ambient Temperature. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 102, 2451–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, H. Stabilization/Solidification Mechanisms of Tin Tailings and Fuming Slag-Based Geopolymers for Different Heavy Metals. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2024, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikvar-Hassani, A.; Hodges, R.; Zhang, L. Production of Green Bricks from Low-Reactive Copper Mine Tailings: Durability and Environmental Aspects. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 337, 127571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Guo, J.; Chen, F.; Tian, M. Synthesis of Ternary Geopolymers Using Prediction for Effective Solidification of Mercury in Tailings. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 147, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opiso, E.M.; Tabelin, C.B.; Maestre, C.V.; Aseniero, J.P.J.; Arima, T.; Villacorte-Tabelin, M. Utilization of Palm Oil Fuel Ash (POFA) as an Admixture for the Synthesis of a Gold Mine Tailings-Based Geopolymer Composite. Minerals 2023, 13, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, C. Solidification/Stabilization of Gold Ore Tailings Powder Using Sustainable Waste-Based Composite Geopolymer. Eng. Geol. 2022, 309, 106793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Nikvar-Hassani, A.; Ormsby, S.; Ramey, D.; Zhang, L. Mechanical and Microstructural Investigations on the Low-Reactive Copper Mine Tailing-Based Geopolymer Activated by Phosphoric Acid. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 393, 132030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Wu, H.; Sun, J.; Wen, X.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, W.; Shen, H.; Hu, Z.; Huang, P. Immobilization of Uranium Tailings by Phosphoric Acid-Based Geopolymer with Optimization of Machine Learning. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2022, 331, 4047–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Tian, T.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; Dong, L. Unpacking the Decision-Making Evolution Mechanism of Governance Actors towards Smart Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Management: An Insight from Game Approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2025, 220, 124319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, E.; Domingues, E.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M.; Leitão, A.; Martins, R.C. European and African Landfilling Practices: An Overview on MSW Management, Leachate Characterization and Treatment Technologies. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 66, 105931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Choi, D.; Lee, J. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Biodegradable Plastic in CO2 Atmosphere Using MSW Incinerator Bottom Ash for PLA Monomer Recovery. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2024, 183, 106839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliem, M.H.; Irshidat, M.; Hassan, M.K.; Manawi, Y.; Al-Ejji, M. Mechanochemical Treatment of Incinerated Municipal Bottom Ash in CO2-Rich Environment for Sustainable Waste Management Practices. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 389, 126171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancellotti, I.; Kamseu, E.; Michelazzi, M.; Barbieri, L.; Corradi, A.; Leonelli, C. Chemical Stability of Geopolymers Containing Municipal Solid Waste Incinerator Fly Ash. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xie, G.; Hu, J.; Niu, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Xing, F. Hazardous Wastes Used as Hybrid Precursors for Geopolymers: Cosolidification/Stabilization of MSWI Fly Ash and Bayer Red Mud. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; De Vlieger, J.; Desomer, P.; Cai, J.; Li, J. Co-Disposal of Construction and Demolition Waste (CDW) and Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash (MSWI FA) through Geopolymer Technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labianca, C.; Ferrara, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; De Feo, G.; Hsu, S.-C.; You, S.; Huang, L.; Tsang, D.C.W. Alkali-Activated Binders—A Sustainable Alternative to OPC for Stabilization and Solidification of Fly Ash from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 134963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Q. Effects of the Ca/Si Ratio on the Structure and Properties of Metakaolin–Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2025, 64, 6530–6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liu, K.; Yang, X.; Jiang, T.; Chen, B.; Tian, Z.; Wu, J.; Xia, L.; Huang, D.; Peng, H. Synthesis of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Foamed Materials Using Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash as a Foaming Agent. Waste Manag. 2023, 169, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Ma, L.; Dai, Q.; Yang, J.; Xie, L.; Hu, Y.; Duan, L.; Yan, X.; Zhou, G.; Zeng, L.; et al. Preparation of Functional Geopolymers from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash: An Approach Combining Experimental and Computational Simulation Studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 355, 120226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Tu, L.; Hu, J.; Tan, C.; Zou, P.; Hu, Z.; Qiu, H.; Zhao, H. Effect of Headed Stud Spacing on Flexural Behavior of Steel Plate-UHPC Composite Beams: Experimental and Numerical Investigation. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Huang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ji, Y.; Xu, Z. Positive Influence of Liquid Sodium Silicate on the Setting Time, Polymerization, and Strength Development Mechanism of MSWI Bottom Ash Alkali-Activated Mortars. Materials 2021, 14, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, G.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Jin, H.; Xing, F. Co-Disposal of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Bottom Ash (MSWIBA) and Steel Slag (SS) to Improve the Geopolymer Materials Properties. Waste Manag. 2023, 171, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liang, S. Experimental Study on Solidification/Stabilisation of High-Salt Sludge by Alkali-Activated GGBS and MSWI Bottom Ash Cementitious Materials. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, G.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, C.; Fan, X.; Li, Z.; Ren, J.; Xing, F.; Zhang, W. Manufacture of Alkali-Activated Cementitious Materials Using Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Ash: Immobilization of Heavy Metals in MSWI Fly Ash by MSWI Bottom Ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 131848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshidat, M.R.; Al-Nuaimi, N.; Rabie, M. Sustainable Alkali-Activated Binders with Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Ashes as Sand or Fly Ash Replacement. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2022, 24, 992–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.R.; El-Masry, E.H.; El-Sadek, A.A. Assessment of Individual and Mixed Alkali Activated Binders for Solidification of a Nuclear Grade Organic Resin Loaded with 134Cs, 60Co and 152+154Eu Radionuclides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 375, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Kim, B.; Kang, J.; Ma, H.; Um, W. Estimation of Radionuclides Leaching Characteristics in Different Sized Geopolymer Waste Forms with Simulated Spent Ion-Exchange Resin. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2023, 55, 3617–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnaoui, A.; McWilliams, J.; Reeb, C.; Hayes, M.; Davy, C.A.; Provis, J.L.; Lambertin, D. Solidification of Tributyl Phosphate/Dodecane Waste Using Metakaolin-Based Potassium Geopolymers. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2025, 442, 114251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Kang, J.; Shin, Y.; Yeo, T.; Heo, J.; Um, W. Effect of Si/Al Molar Ratio and Curing Temperatures on the Immobilization of Radioactive Borate Waste in Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Waste Form. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, D.-Y.; Lee, K.; Sohn, S. Geopolymer-Based Solidification and Stabilization of CaO-Induced Concentrated Borate Waste Arising from Nuclear Power Plant Operation. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2025, 42, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Kang, J.; Shin, Y.; Yeo, T.; Um, W. Immobilization Mechanism of Radioactive Borate Waste in Phosphate-Based Geopolymer Waste Forms. Cem. Concr. Res. 2022, 161, 106959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waijarean, N.; Asavapisit, S.; Sombatsompop, K. Strength and Microstructure of Water Treatment Residue-Based Geopolymers Containing Heavy Metals. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genua, F.; Giovini, M.; Santoni, E.; Berrettoni, M.; Lancellotti, I.; Leonelli, C. Factors Affecting Consolidation in Geopolymers for Stabilization of Galvanic Sludge. Materials 2025, 18, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Cui, X.; Lv, X.; Wang, K. Preparation and Characterization of Geopolymers Based on a Phosphoric-Acid-Activated Electrolytic Manganese Dioxide Residue. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narani, S.S.; Siddiqua, S.; Perumal, P. Wood Fly Ash and Blast Furnace Slag Management by Alkali-Activation: Trace Elements Solidification and Composite Application. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 354, 120341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Song, D.; Fang, Q.; Yang, C.; Wu, D.; Li, S.; Luo, Y.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Z. Synthesis of Nonthermal Plasma-Irradiated Polyvalent Manganese (Hydro)Oxide Functionalized Nanosilica for Intensifying Geopolymerized Solidification/Stabilization of Thallium-Contaminated Soil and Mechanism Exploration. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 469, 143751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).