Modeling Compressive and Flexural Strength of Cement Grouts with Fly Ash, Silica Fume, and Polyethylene Terephthalate: A Correlated Multivariate Regression Approach in Compositional Data Analysis
Abstract
1. Background Study
2. Data Collection and Methodology
2.1. Experimentation
2.2. Compositional Structure and Data Preparation
2.3. Statistical Modeling: Multivariate Linear Mixed Model
- is the 1 × p vector of fixed-effect predictors (e.g., ALR log-ratios, flow value).
- is the p × 1 coefficient vector for the hth outcome.
- is the random intercept for outcome h in mix j, capturing between-mix variability.
- is the within-mix residual error.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Multivariate Linear Mixed Model
3.2. Combined Graphical Analyses
3.2.1. Influence of PET and Fly Ash on Compressive and Flexural Strength
3.2.2. Influence of PET and Silica Fume on Compressive and Flexural Strength
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Oss, H.G.; Padovani, A.C. Cement manufacture and the environment: Part I: Chemistry and technology. J. Ind. Ecol. 2002, 6, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunuweera, S.; Rajapakse, R. Cement types, composition, uses and advantages of nanocement, environmental impact on cement production, and possible solutions. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Atroush, M.E.; Marouf, A.; Aloufi, M.; Marouf, M.; Sebaey, T.A.; Ibrahim, Y.E. Structural performance assessment of geothermal asphalt pavements: A comparative experimental study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, T.R. Sustainability of the cement and concrete industries. In Sustainable Construction Materials and Technologies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- da Rocha Gomes, S.; Ferrara, L.; Sánchez, L.; Moreno, M.S. A comprehensive review of cementitious grouts: Composition, properties, requirements and advanced performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 375, 130991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Li, X.; Sun, T.; Chen, Y.; Xu, F.; Yan, G.; Xu, M.; Tian, K. Utilization of waste glass powder as partial replacement of cement for the cementitious grouts with superplasticizer and viscosity modifying agent binary mixtures: Rheological and mechanical performances. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 286, 122953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nawasir, R.I.; Al-Humeidawi, B.H. Efficient use of ceramic waste powder in Cementitious Grout for the Development of Sustainable Semi-Flexible Pavement Surfaces. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1232, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albusaisi, K.M.; Al-Busaltan, S.F.; Kadhim, M.A. Characterizing the Mechanical Properties of Sustainable Modified Cementitious Grout for Semi-Flexible Mixture. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 856, 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Sutanto, M.H.; Napiah, M.B.; Zoorob, S.E.; Al-Sabaeei, A.M.; Rafiq, W.; Ali, M.; Memon, A.M. Investigating the mechanical properties and fuel spillage resistance of semi-flexible pavement surfacing containing irradiated waste PET based grouts. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 304, 124641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spathi, C. Novel Applications for Paper Sludge Ash; Imperial College London: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mavroulidou, M.; Feruku, B.; Boulouki, G. Properties of structural concrete with high-strength cement mixes containing waste paper sludge ash. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2022, 24, 1317–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.K.; Sanchaya, M.; Harikaran, M.; Krishna, J.G.; Kaviyarasan, V.; Venkatesh, N. Effective utilization of waste paper sludge ash as a supplementary material for cement. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremani, M.; Aghayan, I.; Hosseini, S.A.; Lu, Q.; Behzadian, R. Laboratory assessment of the impact of modified asphalt binder on mechanical properties of grouted macadam mixtures under various performance conditions. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2024, 25, 2347986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Khan, M.I.; Khan, J.H.; Ahmad, S.; Azfar, R.W. Exploring waste marble dust as an additive in cementitious grouts for semi-flexible pavement applications: Analysis and optimization using RSM. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Khan, N.; Hashmi, S.R.Z.; Yazid, M.R.M.; Yusoff, N.I.M.; Azfar, R.W.; Ali, M.; Fediuk, R. Prediction of compressive strength of cementitious grouts for semi-flexible pavement application using machine learning approach. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Taghipoor, M.; Karimi, M.M. A state of the art of semi-flexible pavements: Introduction, design, and performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 253, 119196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, S.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, W.; Zhao, Y. Experimental analysis of semi-flexible pavement by using an appropriate cement asphalt emulsion paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 116994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Yang, X.; Zhong, K.; Yin, J. Open-graded asphalt concrete grouted by latex modified cement mortar. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Huang, W.; Wu, K. Study of the self-healing performance of semi-flexible pavement materials grouted with engineered cementitious composites mortar based on a non-standard test. Materials 2019, 12, 3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, G.; Shukla, M.; Nagabushana, M.; Chandra, S.; Shaw, A. Laboratory and field evaluation of cement grouted bituminous mixes. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 1694–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Xiong, Z.; Chen, H.; Deng, C.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Zhu, H.; Hong, J. Evaluation on the cracking resistance of semi-flexible pavement mixture by laboratory research and field validation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 207, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zerejawy, H.K.; Al-Humeidawi, B.H. Evaluation of the performance of semi-flexible pavement contained sustainable grout material. AIP Conf. Proc. 2024, 3079, 060019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitsangiam, P.; Nusit, K.; Chummuneerat, S.; Chindaprasirt, P.; Pichayapan, P. Fatigue Assessment of Cement-Treated Base for Roads: An Examination of Beam-Fatigue Tests. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2016, 28, 04016095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedrigo, W.; Heller, L.F.; Brito, L.A.T.; Núñez, W.P. Fatigue of Cold Recycled Cement-Treated Pavement Layers: Experimental and Modeling Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedrigo, W.; Kleinert, T.R.; Núñez, W.P.; Graeff, Â.G.; Pinto da Silva Filho, L.C.; Brito, L.A.T. Shrinkage of Cold Recycled Cement-Treated Mixtures of Asphalt Pavement Materials. J. Test. Eval. 2023, 51, 2230–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Kodikara, J. Basaltic Crushed Rock Stabilized with Cementitious Additives: Compressive Strength and Stiffness, Drying Shrinkage, and Capillary Flow Characteristics. Transp. Res. Rec. 2003, 1819, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.S.; Sharma, S.K. A review of mechanical and durability properties and microstructure of semi-flexible pavement. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2024, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nawasir, R.; Al-Humeidawi, B.; Shubbar, A. Influence of Sustainable Grout Material on the Moisture Damage of Semi-Flexible Pavement. Period. Polytech. Civ. Eng. 2024, 68, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, A.; Cerni, G.; D’Alessandro, A.; Ubertini, F. Improved understanding of grouted mixture fatigue behavior under indirect tensile test configuration. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, M.L.; Dinis-Almeida, M.; Pereira-de-Oliveira, L.A.; Castro-Gomes, J.; Zoorob, S.E. Development of a semi-flexible heavy duty pavement surfacing incorporating recycled and waste aggregates–Preliminary study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 102, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboo, N.; Ranjeesh, R.; Gupta, A.; Suresh, M. Development of hierarchical ranking strategy for the asphalt skeleton in semi-flexible pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Cai, J.; Zou, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Chen, X.; Jin, L. Design and performance validation of high-performance cement paste as a grouting material for semi-flexible pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Xu, T.; Huang, K. Aggregate gradation influence on grouting results and mix design of asphalt mixture skeleton for semi-flexible pavement. J. Test. Eval. 2017, 45, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Weng, X. The influence on the durability of semi-flexible airport pavement materials to cyclic wheel load test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Qiao, J.; Yang, X.; Sun, Y.; Sun, D. A review of grouting materials for pouring semi-flexible pavement: Materials, design and performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 379, 131235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmrabet, R.; El Harfi, A.; El Youbi, M.S. Study of properties of fly ash cements. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 13, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistratov, A.V.; Klimenko, N.N.; Pustynnikov, I.V.; Vu, L.K. Thermal regeneration and reuse of carbon and glass fibers from waste composites. Emerg. Sci. J. 2022, 6, 967–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Du, R.; Li, H. Material innovation and performance optimization of multi-solid waste-based composite grouting materials for semi-flexible pavements. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlail, S.H.; Al-Busaltan, S.; Shaban, A.M. Durability Evaluation: Sustainable Semi-flexible Pavement Mixtures. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1067, 012076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, K.; Al-Busaltan, S.; Kadhim, M.A. Cracking Evaluation of Semi-Flexible Mixture Comparison Sustainable Modified Cementitious Grout. Kerbala J. Eng. Sci. 2021, 1, 216–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I. Robust prediction models for flow and compressive strength of sustainable cement grouts for grouted macadam pavement using RSM. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 448, 138205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alani, A.H.; Bunnori, N.M.; Noaman, A.T.; Majid, T.A. Durability performance of a novel ultra-high-performance PET green concrete (UHPPGC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.W.; Moon, D.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lachemi, M. Characteristics of mortar and concrete containing fine aggregate manufactured from recycled waste polyethylene terephthalate bottles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2829–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraternali, F.; Ciancia, V.; Chechile, R.; Rizzano, G.; Feo, L.; Incarnato, L. Experimental study of the thermo-mechanical properties of recycled PET fiber-reinforced concrete. Compos. Struct. 2011, 93, 2368–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, R.P.; Baldacchino, O.; Ferrara, L. Early age performance and mechanical characteristics of recycled PET fibre reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 108, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.Y.; Dheilly, R.M.; Queneudec, M. Valorization of post-consumer waste plastic in cementitious concrete composites. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remadnia, A.; Dheilly, R.M.; Laidoudi, B.; Quéneudec, M. Use of animal proteins as foaming agent in cementitious concrete composites manufactured with recycled PET aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 3118–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.A.; Betioli, A.M.; Gleize, P.J.P.; Roman, H.R.; Gómez, L.A.; Ribeiro, J.L.D. Degradation of recycled PET fibers in Portland cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, C.E.; Kupwade-Patil, K.; Ortega, M.; Soriano, C.; Büyüköztürk, O.; White, A.E.; Short, M.P. Irradiated recycled plastic as a concrete additive for improved chemo-mechanical properties and lower carbon footprint. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Sutanto, M.H.; Napiah, M.B.; Khan, K.; Rafiq, W. Design optimization and statistical modeling of cementitious grout containing irradiated plastic waste and silica fume using response surface methodology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 271, 121504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Wen, L.S.; Sutanto, M.H.; Napiah, M.B.; Zoorob, S. Effect of cement grouts containing irradiated polyethylene terephthalate on properties of semi-flexible mixtures. Key Eng. Mater. 2021, 888, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Sutanto, M.H.; Khan, K.; Iqbal, M.; Napiah, M.B.; Zoorob, S.E.; Klemeš, J.J.; Bokhari, A.; Rafiq, W. Effective use of recycled waste PET in cementitious grouts for developing sustainable semi-flexible pavement surfacing using artificial neural network (ANN). J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filzmoser, P.; Hron, K.; Templ, M. Applied Compositional Data Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraris, C.F.; Hackley, V.A.; Avilés, A.I.; Buchanan, C. Analysis of the ASTM Round-Robin test on particle size distribution of portland cement: Phase I. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. Rep. 2002, 6883, 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Rajiv, K.N.; Reddy, Y.R.; Kumar, G.S.; Ramaraju, H.K. Predictive modelling of mechanical properties of concrete using machine learning with secondary treated waste water and fly ash. Clean. Waste Syst. 2025, 11, 100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Sutanto, M.H.; Napiah, M.B.; Zoorob, S.E.; Yusoff, N.I.M.; Usman, A.; Memon, A.M. Irradiated polyethylene terephthalate and fly ash based grouts for semi-flexible pavement: Design and optimisation using response surface methodology. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 2515–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTMC-305-14; Standard Practice for Mechanical Mixing of Hydraulic Cement Pastes and Mortars of Plastic Consistency. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003.
- ASTM, C939; Standard Test Method for Flow of Grout for Preplaced-Aggregate Concrete (Flow Cone Method). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2002.
- ASTM-C109; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008.
- ASTM C348; Standard Test Method for Flexural Strength of Hydraulic-Cement Mortars. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Smithson, M.; Broomell, S.B. Compositional data analysis tutorial. Psychol. Methods 2024, 29, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, M.E.; Kristensen, K.; Van Benthem, K.J.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.W.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, H.J.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M. glmmTMB balances speed and flexibility among packages for zero-inflated generalized linear mixed modeling. R J. 2017, 9, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
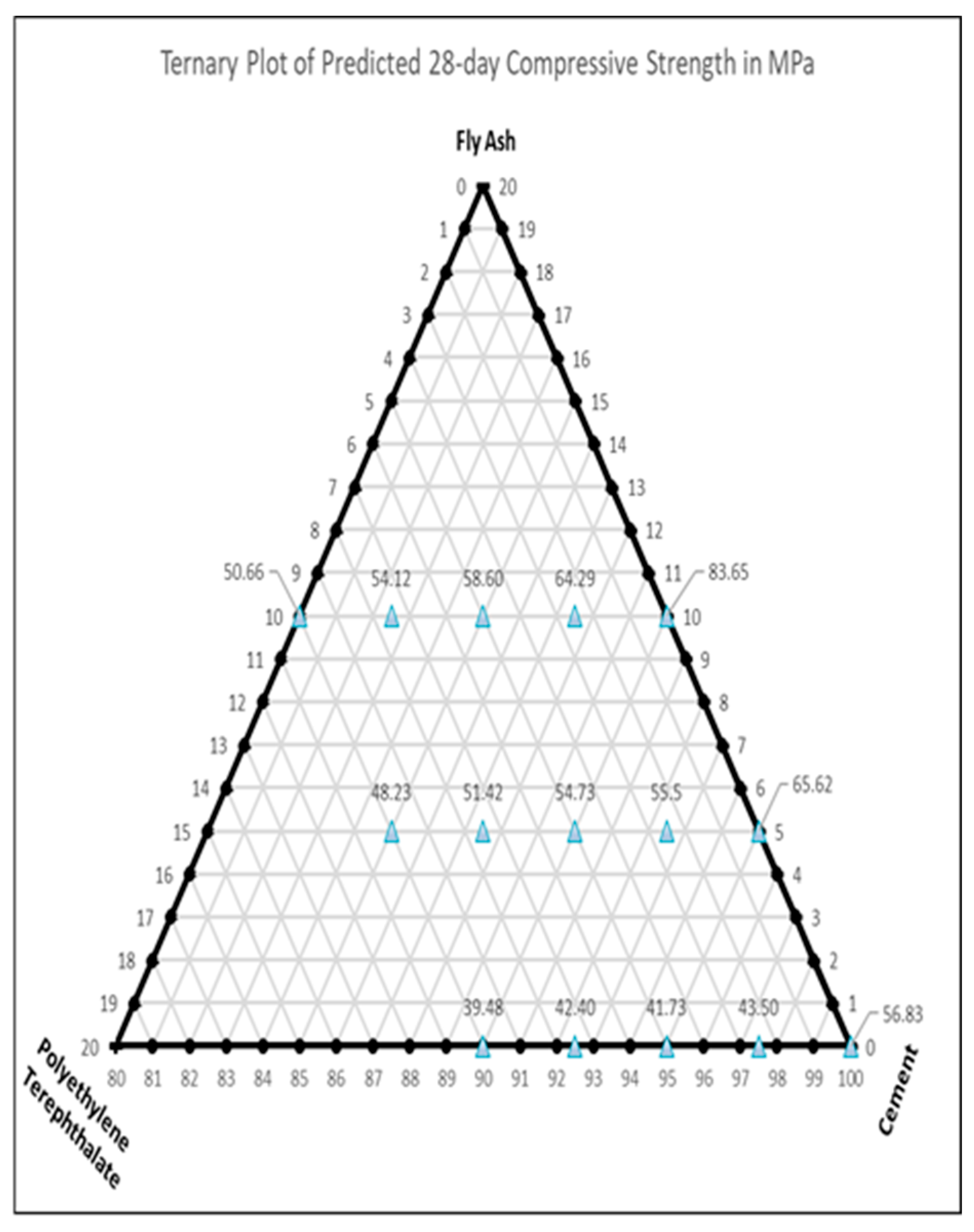
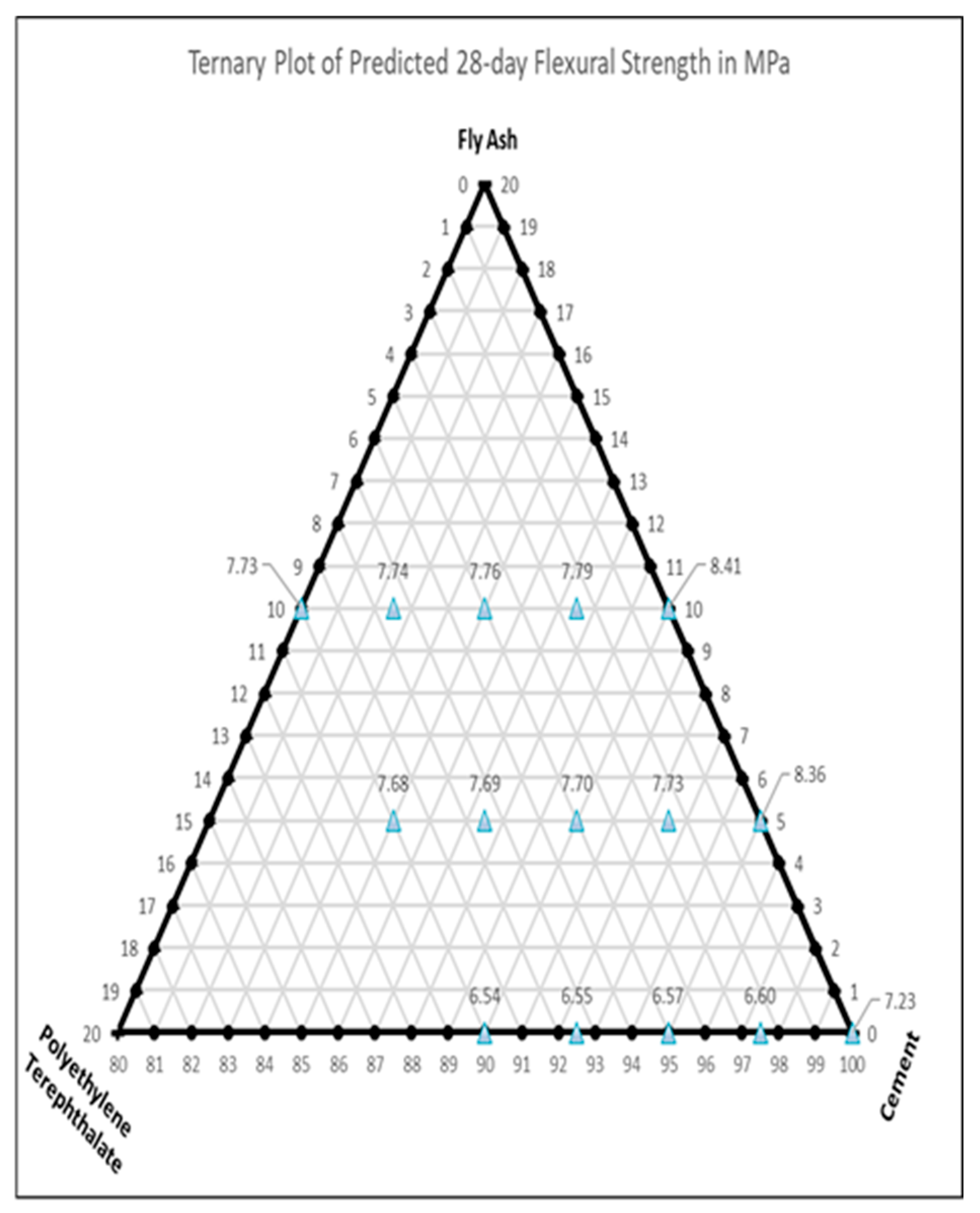
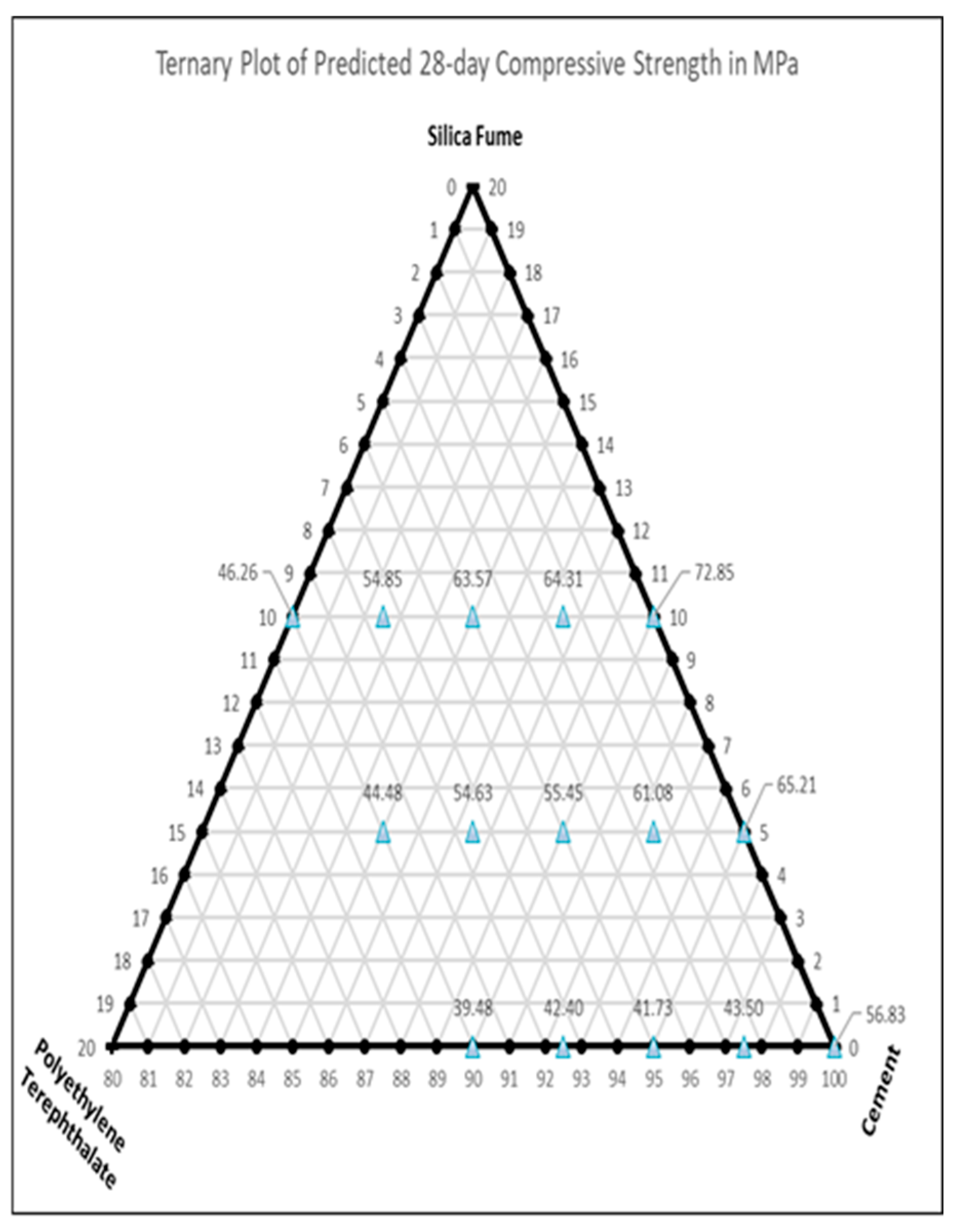

| Variable | Mean | Range | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Response variables | |||
| 1-day compressive strength (MPa) | 16.64 | 5.64–33.32 | 7.62 |
| 7-day compressive strength (MPa) | 34.92 | 19.19–61.81 | 9.65 |
| 28-day compressive strength (MPa) | 51.85 | 33.64–82.54 | 11.73 |
| 28-day flexural strength (MPa) | 7.19 | 5.43–9.98 | 1.04 |
| Predictor variables | |||
| Flow value (s) | 16.54 | 9.1–26 | 4.16 |
| Cement (%) | 90 | 80–100 | 5.32 |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (%) | 5.2 | 0–10 | 3.62 |
| Fly ash (%) | 2.6 | 0–10 | 4.05 |
| Silica fume (%) | 2.2 | 0–10 | 3.50 |
| Mix No | Cement (%) | PET (%) | FA or SF (%) | ALR_PET [ln (PET/Cement)] | ALR_FA/SF [ln ((FA or SF)/Cement)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 0 | 0 | −18.42 | −18.42 |
| 2 | 97.5 | 2.5 | 0 | −3.66 | −18.40 |
| 3 | 95 | 5 | 0 | −2.94 | −18.37 |
| 4 | 92.5 | 7.5 | 0 | −2.51 | −18.34 |
| 5 | 90 | 10 | 0 | −2.20 | −18.32 |
| 6 | 95 | 0 | 5 | −18.37 | −2.94 |
| 7 | 92.5 | 2.5 | 5 | −3.61 | −2.92 |
| 8 | 90 | 5 | 5 | −2.89 | −2.89 |
| 9 | 87.5 | 7.5 | 5 | −2.46 | −2.86 |
| 10 | 85 | 10 | 5 | −2.14 | −2.83 |
| 11 | 90 | 0 | 10 | −18.32 | −2.20 |
| 12 | 87.5 | 2.5 | 10 | −3.56 | −2.17 |
| 13 | 85 | 5 | 10 | −2.83 | −2.14 |
| 14 | 82.5 | 7.5 | 10 | −2.40 | −2.11 |
| 15 | 80 | 10 | 10 | −2.08 | −2.08 |
| Outcomes, MPa | 1-Day CS (7-Day CS) | 28-Day CS (28-Day FS) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Parameter | Estimate | Std. Error | Z-Stat | Estimate | Std. Error | Z-Stat |
| Intercept | 10.08 (32.82) | 1.58 (1.95) | 6.39 (16.84) | 51.61 (7.61) | 2.67 (0.42) | 19.35 (18.20) |
| ALR_PET | −0.95 (−1.08) | 0.10 (0.12) | −10.00 (−9.22) | −1.10 (−0.04) | 0.16 (0.03) | −6.85 (−1.70) |
| ALR_FA/SF | 0.19 (0.60) | 0.09 (0.11) | 2.07 (5.44) | 0.91 (0.07) | 0.15 (0.02) | 6.00 (3.09) |
| Flow value indicator | 3.16 (2.07) | 1.22 (1.50) | 2.6 (1.38) | 3.48 (0.18) | 2.06 (0.32) | 1.69 (0.55) |
| Silica fume indicator | −0.89 (0.52) | 0.56 (0.69) | −1.59 (0.76) | 0.80 (0.21) | 0.95 (0.15) | 0.84 (1.39) |
| Random parameter | ||||||
| Standard deviation of the intercept | 2.83 (3.54) | 4.90 (---) | ||||
| Correlation between Intercepts | 1d-CS and 7d-CS | 0.88 | 1d-CS and 28d-CS | 0.88 | 7d-CS and 28d-CS | 0.93 |
| Goodness-of-fit measure | Null Model | This Model | ||||
| Deviance | 2844.5 | 1651.2 | ||||
| Degrees of freedom | 5 | 27 | ||||
| AIC | 2854.5 | 1705.2 | ||||
| BIC | 2874.4 | 1813 | ||||
| Accuracy | Fixed-Effect Model Only | This Model | ||||
| R2 | 0.96 | 0.99 | ||||
| RMSE | 3.68 | 1.44 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almutairi, O.; Khan, M.I. Modeling Compressive and Flexural Strength of Cement Grouts with Fly Ash, Silica Fume, and Polyethylene Terephthalate: A Correlated Multivariate Regression Approach in Compositional Data Analysis. Buildings 2025, 15, 3976. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15213976
Almutairi O, Khan MI. Modeling Compressive and Flexural Strength of Cement Grouts with Fly Ash, Silica Fume, and Polyethylene Terephthalate: A Correlated Multivariate Regression Approach in Compositional Data Analysis. Buildings. 2025; 15(21):3976. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15213976
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmutairi, Omar, and Muhammad Imran Khan. 2025. "Modeling Compressive and Flexural Strength of Cement Grouts with Fly Ash, Silica Fume, and Polyethylene Terephthalate: A Correlated Multivariate Regression Approach in Compositional Data Analysis" Buildings 15, no. 21: 3976. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15213976
APA StyleAlmutairi, O., & Khan, M. I. (2025). Modeling Compressive and Flexural Strength of Cement Grouts with Fly Ash, Silica Fume, and Polyethylene Terephthalate: A Correlated Multivariate Regression Approach in Compositional Data Analysis. Buildings, 15(21), 3976. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15213976






