Research on the Contagion Paths and Blocking Strategies of Schedule Risk in Prefabricated Buildings Under the EPC Mode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Questions
2.1. Existing Problems
2.2. The Limitations of Single-Model Analysis and Its Innovative Approaches
2.3. A Multi-Model Integration Approach for Schedule Risk Analysis in EPC Prefabricated Building Projects
3. Research Method
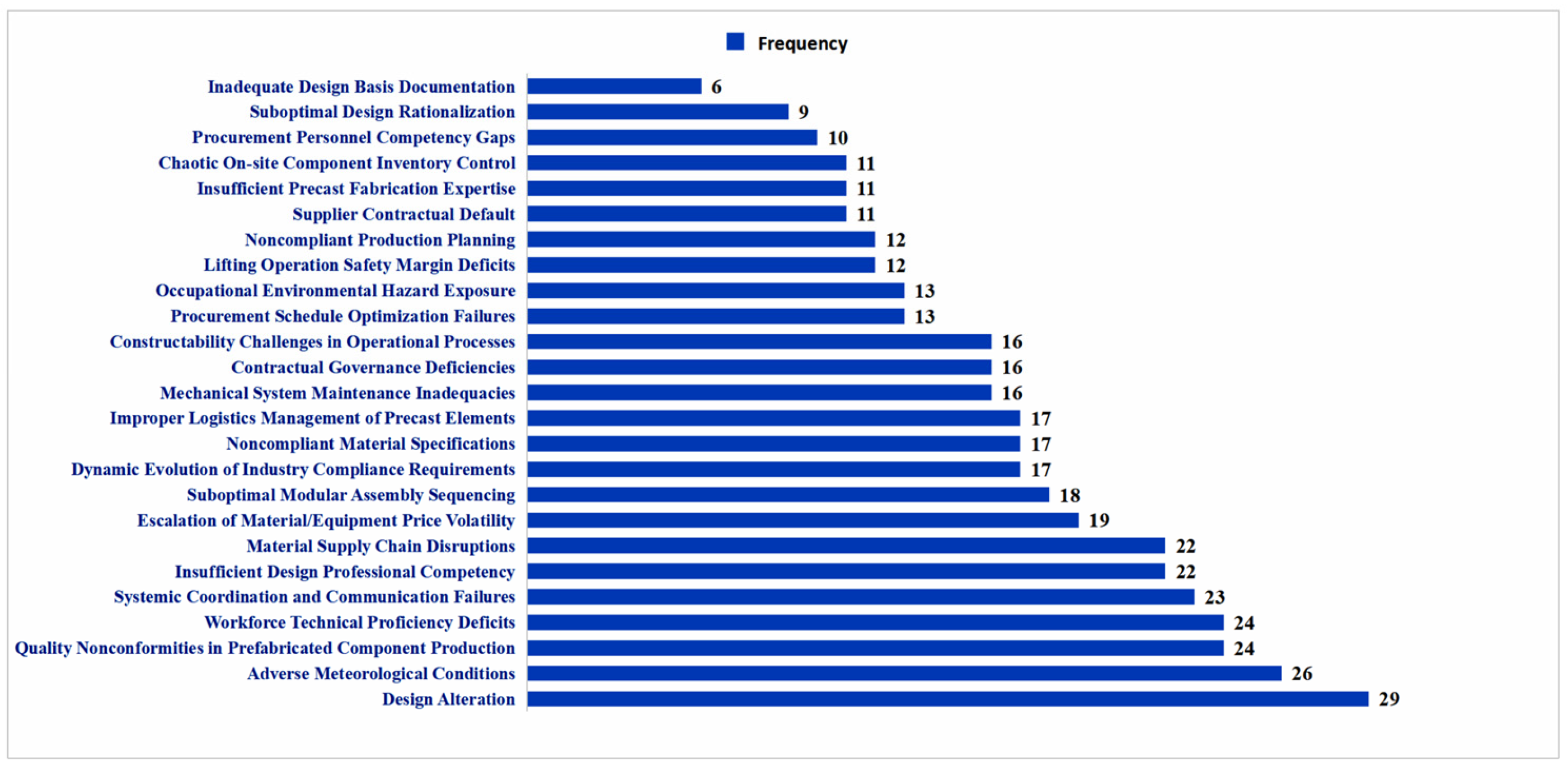
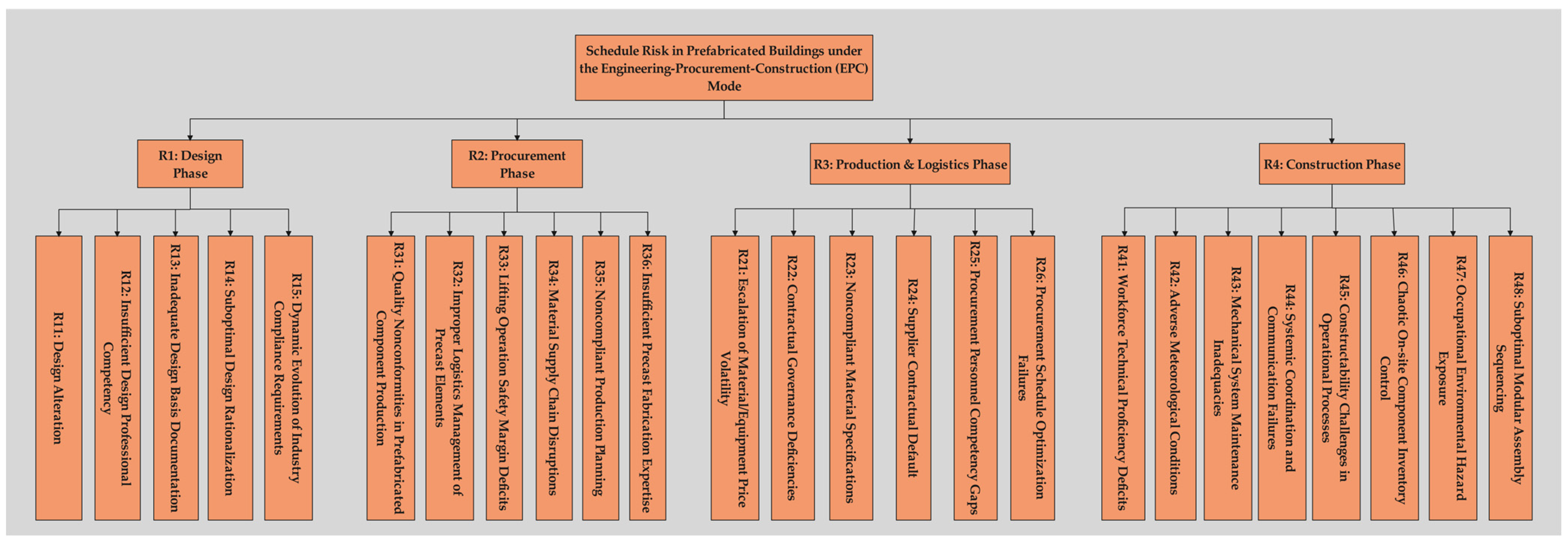
3.1. Identification of Schedule Risk Chain Factors
3.2. Construction of the Indicator System
3.3. Analysis of the Schedule Risk Chain in EPC Prefabricated Buildings
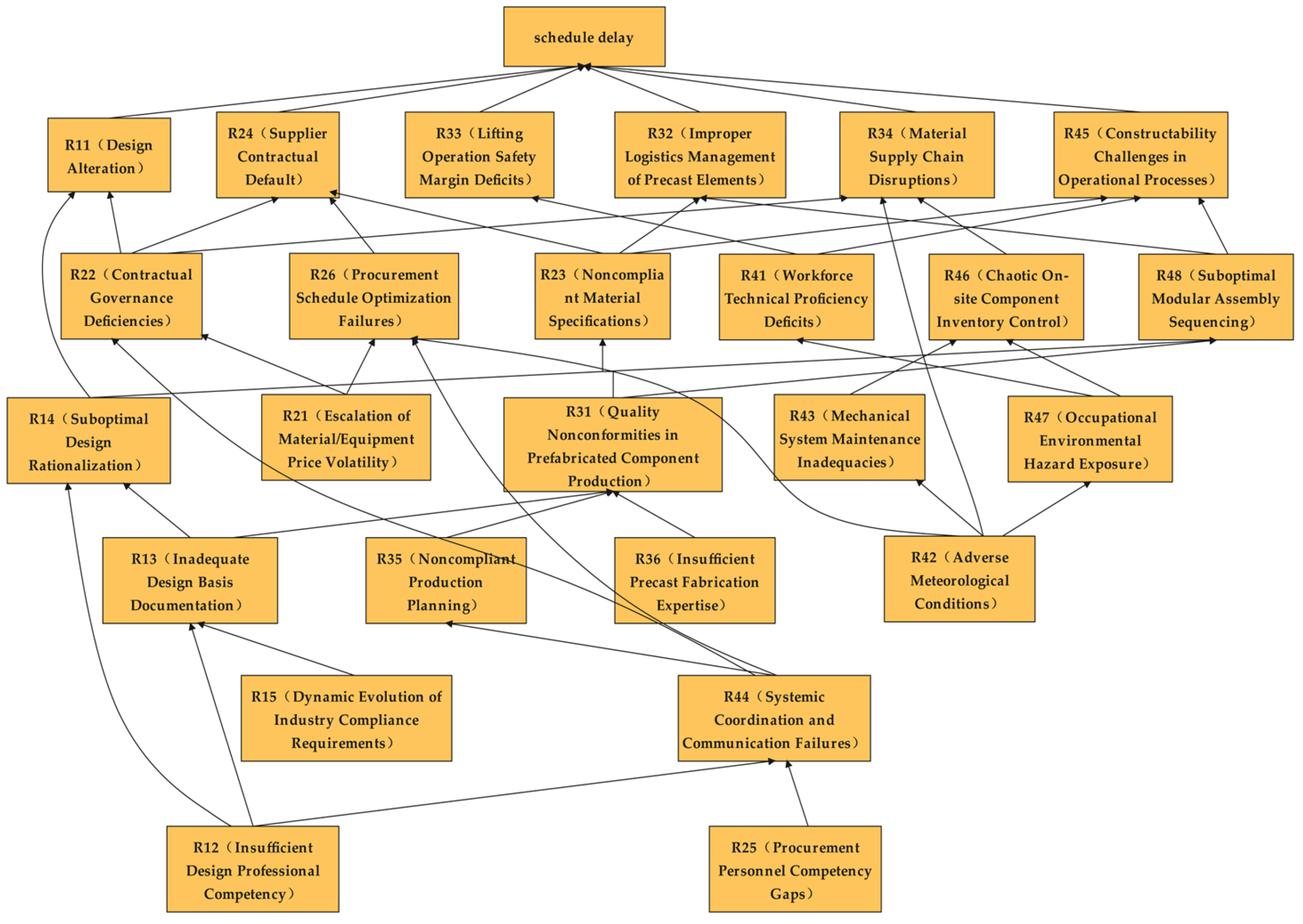
3.3.1. Construction of Schedule Risk Chain Based on FISM
- (1)
- Define Research Objectives and Identify Key Factors
- (2)
- Construct Fuzzy Adjacency Matrix
- (3)
- Select Membership Function
- (4)
- Determine Threshold λ
- (5)
- Derive Reach ability Matrix M
- (6)
- Hierarchical Partitioning Based on M, compute:
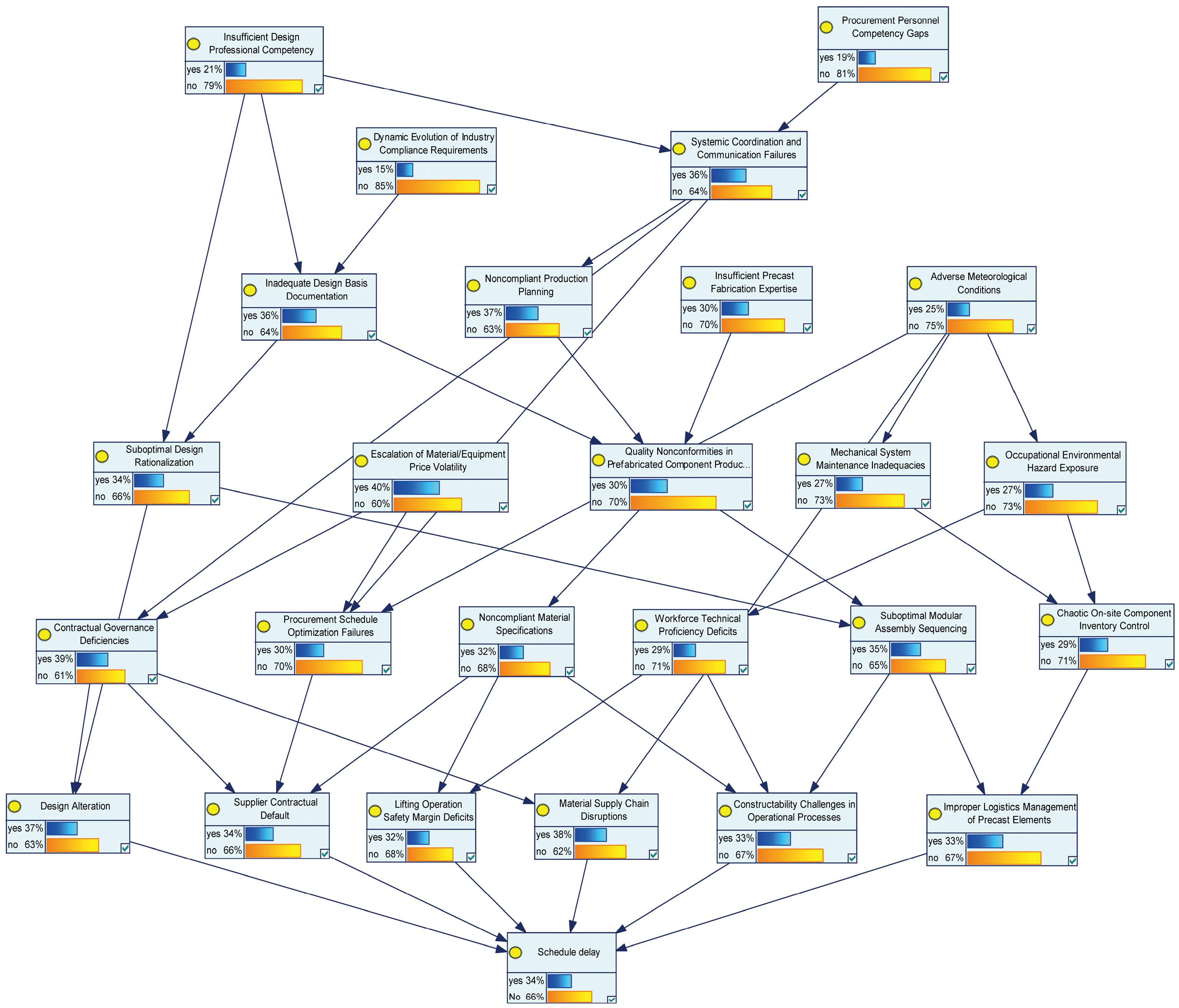
3.3.2. Analysis of Critical Schedule Risk Chains Based on Bayesian Network
- (1)
- By examining the hierarchical network structure constructed through the Fuzzy Interpretive Structural Model, pairs of interacting schedule risk factors are identified. Building on the fuzzy relational matrix from the FISM, a modified coupling degree model [21] is incorporated to quantitatively calculate the coupling degree between paired risk factors.where C denotes the coupling strength, with higher values indicating stronger correlations between associated factor pairs; Ui represents the initial direct influence magnitude of individual factors. Both C and Ui are bounded within the interval [0, 1].
- (2)
- Perform normalization based on the following equation:where Wi denotes the influence weight of parent nodes on child nodes; Ci represents the coupling degree between risk factor pairs.where j denotes the node state, with j = T indicating occurrence and j = F non-occurrence; Zij represents the distance between the child node and the parent node; if the child node occurs while the parent node does not, Zij = 1; if both nodes share the same state, Zij = 0; if the child node does not occur while the parent node does, Zij = −1; Wi denotes the influence weight of the i-th parent node on the child node; Pj signifies the conditional probability of the child node being in risk state “j”; and R quantifies the expert-evaluated result distribution index.
3.3.3. Research on Blocking Strategies Based on Schedule Risk Chain
4. Empirical Analysis and Results
4.1. Overview of the EPC Prefabricated Building Project
4.2. Construction of the Schedule Risk Chain Based on the FISM
4.2.1. Determination of the Fuzzy Correlation Matrix of Factors
4.2.2. Membership Function Selection
4.3. Analysis of the Critical Schedule Risk Chain Based on Bayesian Network
4.3.1. Network Structure Formation
4.3.2. Probability Determination
- (1)
- Prior Probability Determination
- (2)
- Conditional Probability Determination
4.3.3. Comprehensive Analysis
- (1)
- Adverse weather (R42) → Poor construction work environment (R47) → Low technical proficiency of workers (R41) → Inadequate component lifting safety (R33) + Poor operability of construction techniques (R45) → Project delay (R);
- (2)
- Adverse weather (R42) → Insufficient maintenance of mechanical equipment (R43) → Disorganized on-site component management (R46) → Unreasonable transportation, loading/unloading, and stacking (R32) → Project delay (R).
4.4. Research on Blocking Strategies
4.4.1. Management and Control Measures for Key Causative Risks
4.4.2. Measures for Blocking the Critical Schedule Risk Chain
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Using the literature research method, 25 schedule risk factors for prefabricated construction under the EPC model were objectively and effectively extracted, and an indicator system was constructed after scientific classification. Considering the interrelationships among these schedule risk factors, the FISM was applied to theoretically analyze the correlation effects of risk factors, ultimately yielding a network diagram formed by the interweaving of 46 schedule delay risk chains.
- (2)
- Optimization of the Bayesian network conditional probability calculation process. Given that the hierarchical network diagram obtained from the FISM only reflects the mutual influence relationships among schedule risk factors but cannot quantify the influence intensity, a modified coupling degree model was introduced to quantify the correlation of risk factors using a fuzzy correlation matrix. To address the difficulty of weighting due to the large number of Bayesian network nodes, the coupling strength of risk factors was innovatively transformed into the influence weight of parent nodes on child nodes, calculated using the probability allocation method. This reduces the number of expert decisions, lowers error rates, and significantly improves computational efficiency and accuracy.
- (3)
- Based on the Bayesian network model, simulation analysis was conducted on the top 15 schedule risk factors by hazard degree, identifying two critical transmission paths and other potential key causal factors. For the critical transmission paths, simulations were carried out using the GeNIe platform to locate key blocking nodes, reducing the probability of schedule delay risk by 23%, avoiding the resource consumption of full-node blocking, and effectively improving engineering profits. For key causal factors, targeted control measures were formulated to block risk transmission and prevent schedule delays.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, S.L.; Hou, Z.W.; Chen, H.B. Network model analysis of quality control factors of prefabricated buildings based on the complex network theory. Buildings 2022, 12, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, H.; Steinle, A. Precast Concrete Structures; Ernst & Sohn: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, J.D.; Hu, Z.Y. Review and thinking on development of building industrialization in China. China Civ. Eng. J. 2016, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Sun, R.; Ren, L.Y.; Geng, X.X.; Wang, X.M.; Lv, L. Risk Propagation Model and Simulation of an Assembled Building Supply Chain Network. Buildings 2023, 13, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.X.; Fu, X.W.; Chen, X.X.; Wen, X. Supply Chain Management for the Engineering Procurement and Construction (EPC) Model: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Lee, E.B.; Choi, H.S. A forecast and mitigation model of construction performance by assessing detailed engineering maturity at key milestones for offshore EPC mega-projects. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Gao, S.H. Study on Factors Affecting the Progress of Engineering Projects under the EPC Model. E3S Web Conf. 2024, 565, 01015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldhaheri, M.; Bakchan, A.; Sandhu, M.A. A structural equation model for enhancing effectiveness of engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) major projects: End-user’s perspective. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2018, 25, 1226–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaming, P.F.; Koesmargono, A.; Aji, B.W. Delay model for Engineering Procurement Construction (EPC): A case of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) projects in Indonesia. MATEC Web Conf. EDP Sci. 2019, 270, 05010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.; Kermanshachi, S.; Rouhanizadeh, B. Identifying and measuring engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) key performance indicators and management strategies. Infrastructures 2019, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Sun, C.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Xue, J.; Zhang, G. Hierarchical schedule risk structures and mitigation strategies in prefabricated building projects: An integrated SNA-ISM approach. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2025; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Geng, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, R. Research on the Risk-Inducing Factors of Prefabricated Building Design Change Based on Improved DEMATEL-ISM. Buildings 2023, 13, 3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Binchao, D.; Yin, Y. Hierarchical structure and transfer mechanism to assess the scheduling-related risk in construction of prefabricated buildings: An integrated ISM–MICMAC approach. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023, 30, 2991–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Zhang, S. Schedule Risk Analysis of Prefabricated Building Projects Based on DEMATEL-ISM and Bayesian Networks. Buildings 2025, 15, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, W.; Arashpour, M.; Yang, Z.; Shao, C.; Li, C. Predicting delays in prefabricated projects: SD-BP neural network to define effects of risk disruption. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2022, 29, 1753–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, L. A Comprehensive Risk-Assessment Method for Prefabricated Buildings Using EPC: A Case Study from China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Lei, X. Evaluating Risk in Prefabricated Building Construction under EPC Contracting Using Structural Equation Modeling: A Case Study of Shaanxi Province, China. Buildings 2023, 13, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Duan, L.; Du, X. Risk Assessment of Prefabricated Building Projects Based on the G1-CRITIC Method and Cloud Model: A Case Study from China. Buildings 2025, 15, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, J. Research on Key Risk Factors and Risk Transmission Path of Procurement in International Engineering Procurement Construction Project. Buildings 2022, 12, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yu, D.; Wang, T.; Xu, C. Coupling Analysis of Tunnel Construction Safety Risks Based on N-K Model and SD Causality Diagram. Buildings 2023, 13, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kong, W.; Ren, L.; ZHI, D. Research on misuses and modification of coupling coordination degree model in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Gou, H.; Wan, Z.; Ren, C.; Chen, M.; Gou, T.; Luo, Z. Research on coupling degree model of safety risk system for tunnel construction in subway shield zone. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 5783938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Song, Z.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, L. Coupling analysis of tunnel construction risk in complex geology and construction factors. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2022, 148, 04022097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tang, Y.J.; Zhang, W.J.; Wang, H.J. Study on engineering progress risk analysis methods under perspective of risk chain. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2023, 42, 96–107. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yuan, H.; Huang, P.Y.; Zhou, Z.L.; Wang, B. Safety risk evaluation of tunnel collapse based on Bayesian network of improving conditional probability. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2023, 54, 327–340. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Kou, X.; Yin, D.; Mi, R.; Li, L. Railway dangerous goods transportation system risk analysis: An Interpretive Structural Modeling and Bayesian Network combining approach. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 204, 107220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, N.; Seth, N. Analysis of Supply Chain Resilience Enablers and Business Outcomes Using Delphi and Fuzzy ISM for Indian Automobile Industry. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2024, 25, 763–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roed, W.; Mosleh, A.; Vinnem, J.E.; Aven, T. On the use of the hybrid causal logic method in offshore risk analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2009, 94, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.L.; Zhou, J. Analysis of influence factors of prefabricated building cost based on FISMM-ANP. Chang. Univ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 57–65+98. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidan, G.; Dikemen, I.; Tanyer, A.M.; Birgonul, M.T. Ontology for relating risk and vulnerability to cost overrun in international projects. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2011, 25, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.G. Key Risk Transmission Paths During the Construction Phase and Blocking Strategies of Green Retrofit Project in Public Buildings. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2024. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichsan, M.; Isvara, W.; Karim, S. Monte Carlo Simulation for Enhancing the Schedule Completion Forecast of Jakarta Central Railway Station Construction Project. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakolan, M.; Etemadinia, H. Fuzzy weighted interpretive structural modeling: Improved method for identification of risk interactions in construction projects. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2017, 143, 04017084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | R11 | R12 | R13 | R14 | R15 | R21 | R22 | R23 | R24 | R25 | R26 | R31 | R32 | R33 | R34 | R35 | R36 | R41 | R42 | R43 | R44 | R45 | R46 | R47 | R48 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R11 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.42 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| R12 | 0.68 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.76 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.61 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.22 |
| R13 | 0.76 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.72 | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.25 | 0.65 | 0.19 | 0.32 | 0.15 | 0.66 | 0.33 | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.22 |
| R14 | 0.62 | 0.17 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.32 | 0.72 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.61 |
| R15 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.13 |
| R21 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.82 | 0.10 | 0.72 | 0.21 | 0.50 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.34 | 0.23 | 0.33 | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.30 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.31 |
| R22 | 0.58 | 0.20 | 0.33 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.70 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.66 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.21 |
| R23 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.32 | 0.26 | 0.10 | 0.32 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.85 | 0.17 | 0.41 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.66 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.20 | 0.71 | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.23 |
| R24 | 0.27 | 0.23 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.26 | 0.10 | 0.41 | 0.25 | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.10 |
| R25 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.62 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.32 | 0.31 |
| R26 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.18 | 0.51 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.33 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.32 | 0.22 |
| R31 | 0.20 | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.74 | 0.10 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.57 | 0.10 | 0.39 | 0.31 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.24 | 0.69 |
| R32 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.43 | 0.10 | 0.24 |
| R33 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.31 | 0.10 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.21 |
| R34 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.10 |
| R35 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.32 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.69 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.66 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.22 | 0.00 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.48 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.32 |
| R36 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.59 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.65 | 0.32 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.30 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.42 |
| R41 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.11 | 0.23 | 0.65 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.30 | 0.54 | 0.10 | 0.18 | 0.33 |
| R42 | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.70 | 0.10 | 0.77 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.30 | 0.90 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.65 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.70 | 0.80 | 0.10 |
| R43 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.30 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.51 | 0.23 | 0.11 |
| R44 | 0.40 | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0.35 | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0.72 | 0.10 | 0.50 | 0.28 | 0.62 | 0.10 | 0.38 | 0.45 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.21 | 0.40 |
| R45 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.32 | 0.26 | 0.12 | 0.27 | 0.37 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.40 |
| R46 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.71 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.00 | 0.39 | 0.31 |
| R47 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.30 | 0.21 | 0.33 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.62 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 0.63 | 0.00 | 0.22 |
| R48 | 0.41 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.45 | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.82 | 0.27 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.63 | 0.31 | 0.23 | 0.00 |
| No. | R11 | R12 | R13 | R14 | R15 | R21 | R22 | R23 | R24 | R25 | R26 | R31 | R32 | R33 | R34 | R35 | R36 | R41 | R42 | R43 | R44 | R45 | R46 | R47 | R48 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R11 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R12 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R13 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R14 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| R15 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R22 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R23 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R26 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| R32 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R34 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R35 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R36 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R41 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R42 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| R43 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| R44 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R45 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R46 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| R47 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| R48 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Node | Prior Probability |
|---|---|
| S12 | P (S12 = T) = 0.209, P (S12 = F) = 0.791 |
| S25 | P (S25 = T) = 0.189, P (S25 = F) = 0.811 |
| S15 | P (S15 = T) = 0.243, P (S15 = F) = 0.757 |
| S36 | P (S36 = T) = 0.302, P (S36 = F) = 0.698 |
| S42 | P (S42 = T) = 0.249, P (S42 = F) = 0.750 |
| S21 | P (S21 = T) = 0.173, P (S21 = F) = 0.827 |
| R13-R31 | 0.63 | 0.25 | 0.4727 | 0.278 |
| R35-R31 | 0.60 | 0.39 | 0.6663 | 0.392 |
| R36-R31 | 0.65 | 0.31 | 0.5610 | 0.330 |
| Node | Conditional Probability |
|---|---|
| S31 | P (S31 = T|S13 = T, D35 = T, E36 = T) = 0.953 |
| P (S31 = T|S13 = T, D35 = T, E36 = F) = 0.753 | |
| P (S31 = T|S13 = T, D35 = F, E36 = T) = 0.657 | |
| P (S31 = T|S13 = T, D35 = F, E36 = F) = 0.209 | |
| P (S31 = T|S13 = F, D35 = T, E36 = T) = 0.791 | |
| P (S31 = T|S13 = F, D35 = T, E36 = F) = 0.343 | |
| P (S31 = T|S13 = F, D35 = F, E36 = T) = 0.265 | |
| P (S31 = T|S13 = T, D35 = F, E36 = F) = 0.047 |
| Risk | Sensitivity Analysis | Impact Strength Analysis | Diagnostic Analysis | Risk Factor Hazard Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R45 | 0.0940 | 0.2228 | 0.2751 | 0.5919 |
| R33 | 0.0940 | 0.2295 | 0.2604 | 0.5839 |
| R44 | 0.1190 | 0.3078 | 0.1405 | 0.5674 |
| R11 | 0.0500 | 0.3271 | 0.1737 | 0.5508 |
| R42 | 0.2570 | 0.1145 | 0.1438 | 0.5153 |
| R24 | 0.0320 | 0.2844 | 0.1732 | 0.4897 |
| R41 | 0.1560 | 0.1161 | 0.1731 | 0.4452 |
| R47 | 0.1600 | 0.1164 | 0.1590 | 0.4354 |
| R26 | 0.0120 | 0.2935 | 0.1148 | 0.4202 |
| R23 | 0.1120 | 0.1043 | 0.1869 | 0.4032 |
| R32 | 0.0270 | 0.1843 | 0.1885 | 0.3998 |
| R34 | 0.0730 | 0.1299 | 0.1939 | 0.3968 |
| R48 | 0.0410 | 0.1998 | 0.1554 | 0.3962 |
| R25 | 0.0410 | 0.3357 | 0.0186 | 0.3953 |
| R43 | 0.0180 | 0.2428 | 0.1337 | 0.3945 |
| R12 | 0.1270 | 0.1943 | 0.0627 | 0.3840 |
| R13 | 0.0860 | 0.1745 | 0.1142 | 0.3747 |
| R36 | 0.0590 | 0.2772 | 0.0372 | 0.3734 |
| R46 | 0.0300 | 0.1613 | 0.1392 | 0.3306 |
| R22 | 0.1000 | 0.0659 | 0.1643 | 0.3302 |
| R21 | 0.0950 | 0.1826 | 0.0404 | 0.3180 |
| R35 | 0.0450 | 0.1349 | 0.1371 | 0.3169 |
| R14 | 0.0740 | 0.1079 | 0.1301 | 0.3120 |
| R31 | 0.0470 | 0.0427 | 0.1802 | 0.2699 |
| R15 | 0.0170 | 0.1378 | 0.0093 | 0.1640 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Y.; Tang, Y. Research on the Contagion Paths and Blocking Strategies of Schedule Risk in Prefabricated Buildings Under the EPC Mode. Buildings 2025, 15, 3948. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15213948
Tian Y, Tang Y. Research on the Contagion Paths and Blocking Strategies of Schedule Risk in Prefabricated Buildings Under the EPC Mode. Buildings. 2025; 15(21):3948. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15213948
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Yong, and Yanjuan Tang. 2025. "Research on the Contagion Paths and Blocking Strategies of Schedule Risk in Prefabricated Buildings Under the EPC Mode" Buildings 15, no. 21: 3948. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15213948
APA StyleTian, Y., & Tang, Y. (2025). Research on the Contagion Paths and Blocking Strategies of Schedule Risk in Prefabricated Buildings Under the EPC Mode. Buildings, 15(21), 3948. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15213948







