Numerical Study on the Flexural Performance of Fully Bolted Joint for Panelized Steel Modular Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Establishment and Validation of the FE Model
2.1. FE Model Information
2.2. Load and Boundary Conditions
2.3. Validation
3. Parametric Joint Optimization
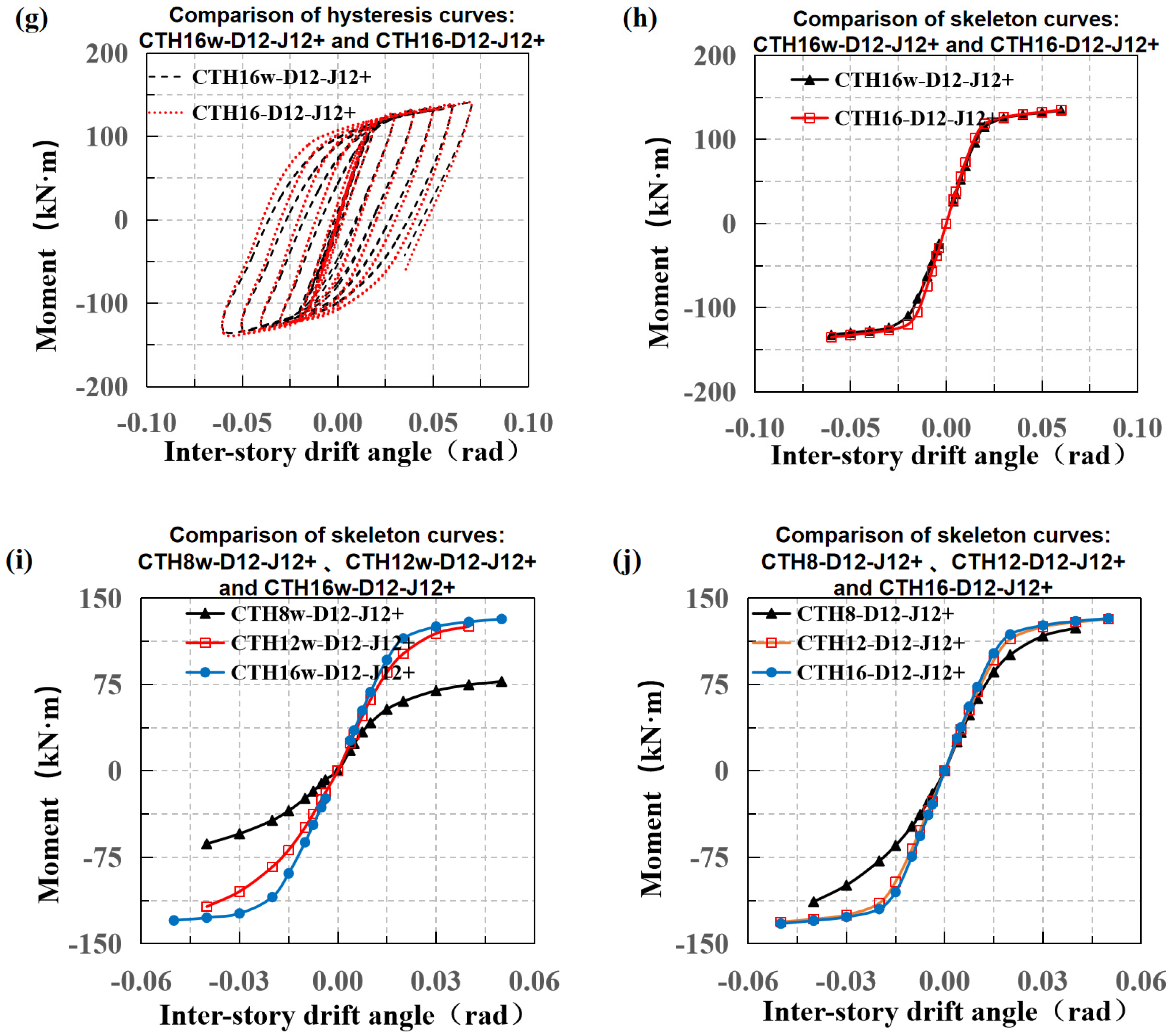
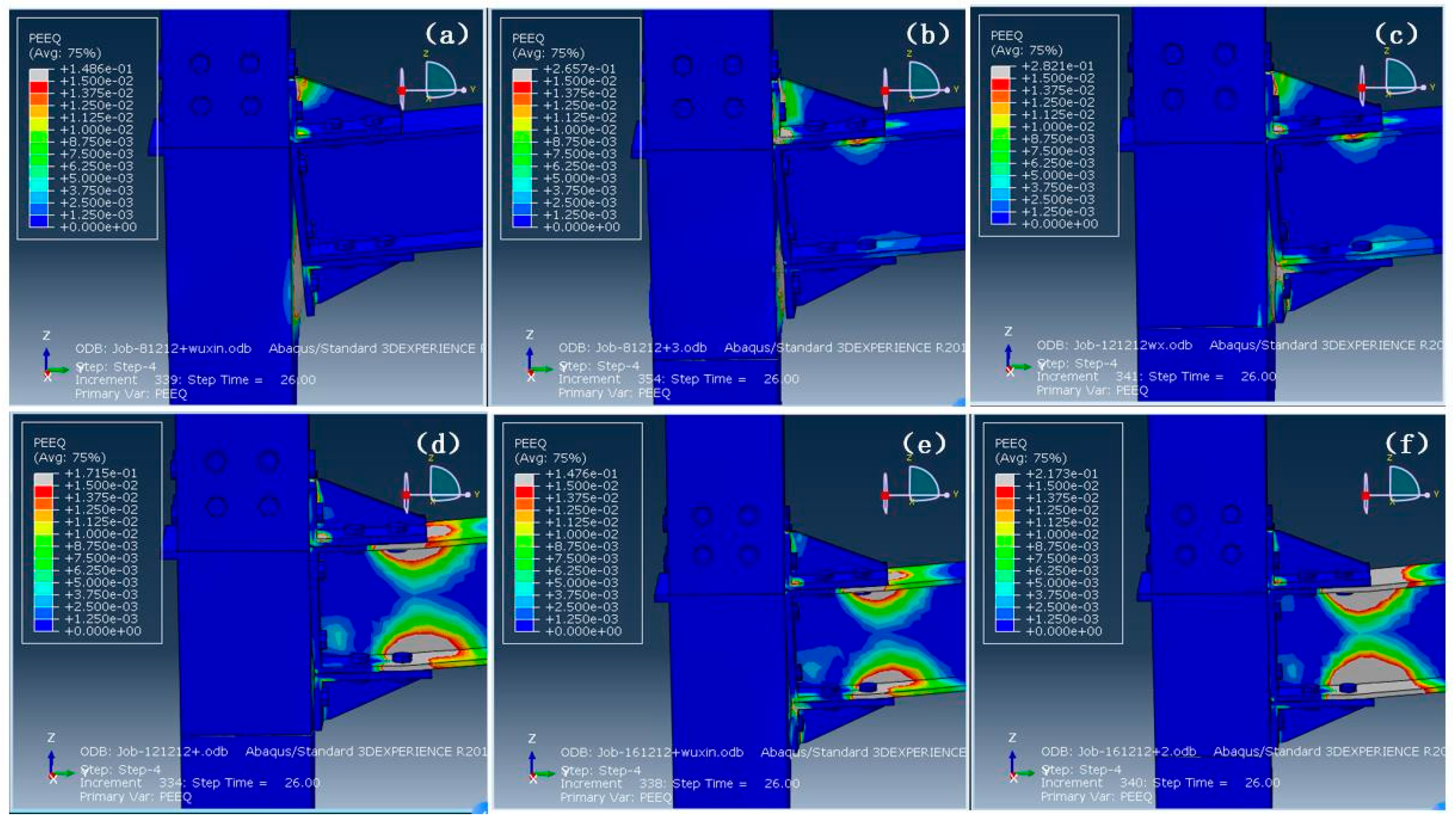
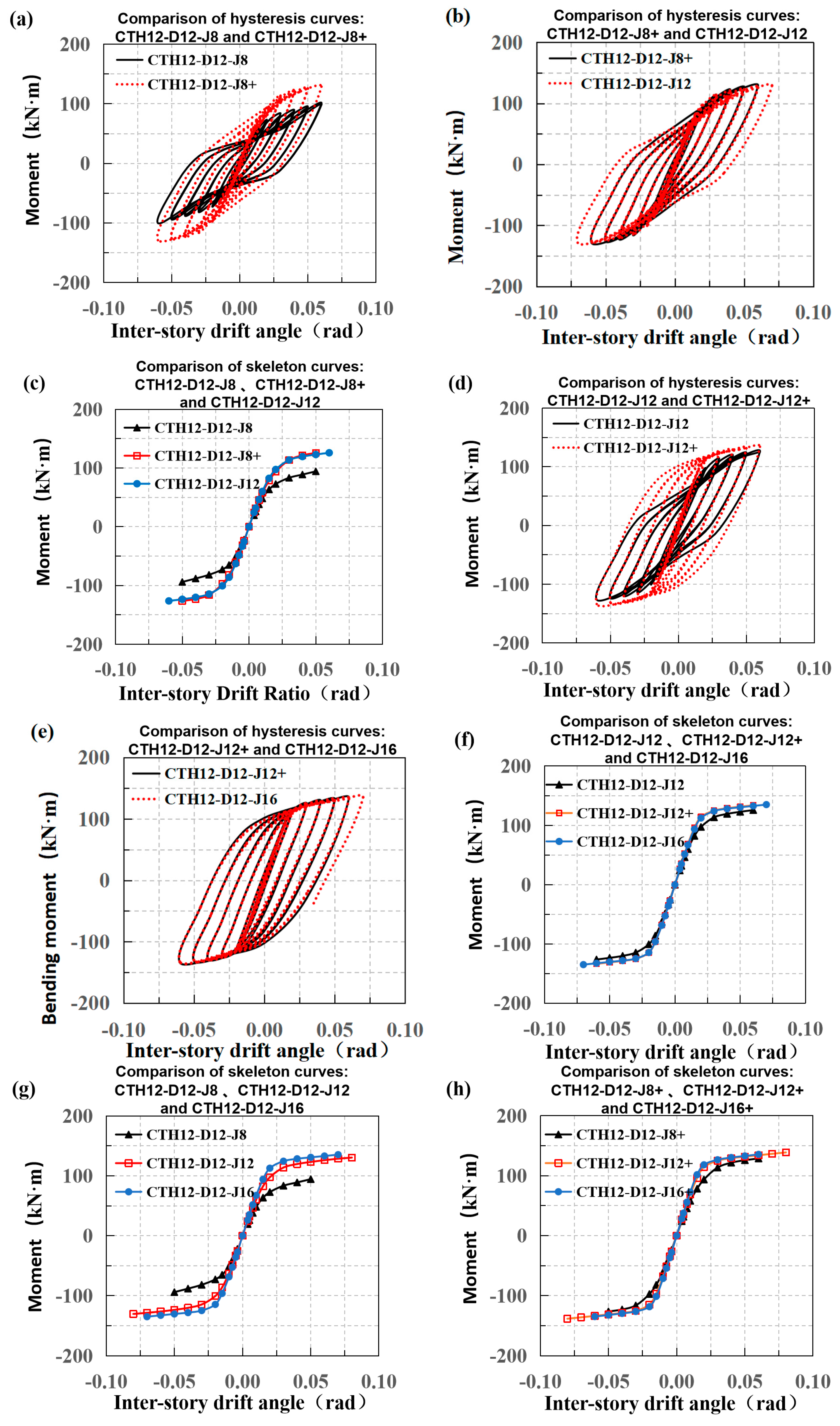
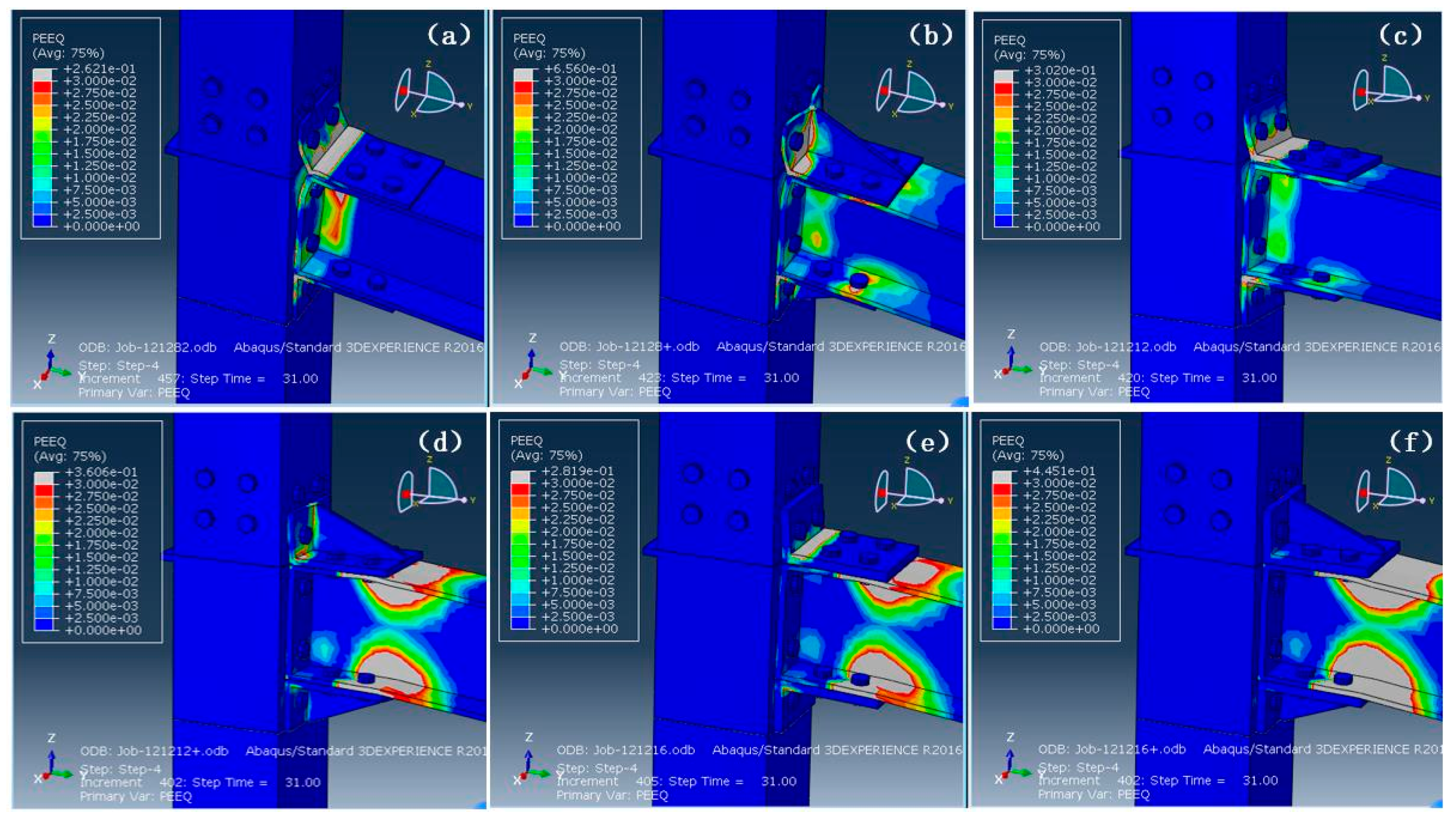
3.1. Core Column Wall Thickness and Inner Diaphragm
3.2. Angle Thickness and Stiffener Presence
3.3. Effect of Endplate Thickness on Joint Performance
3.4. Bolt Diameter
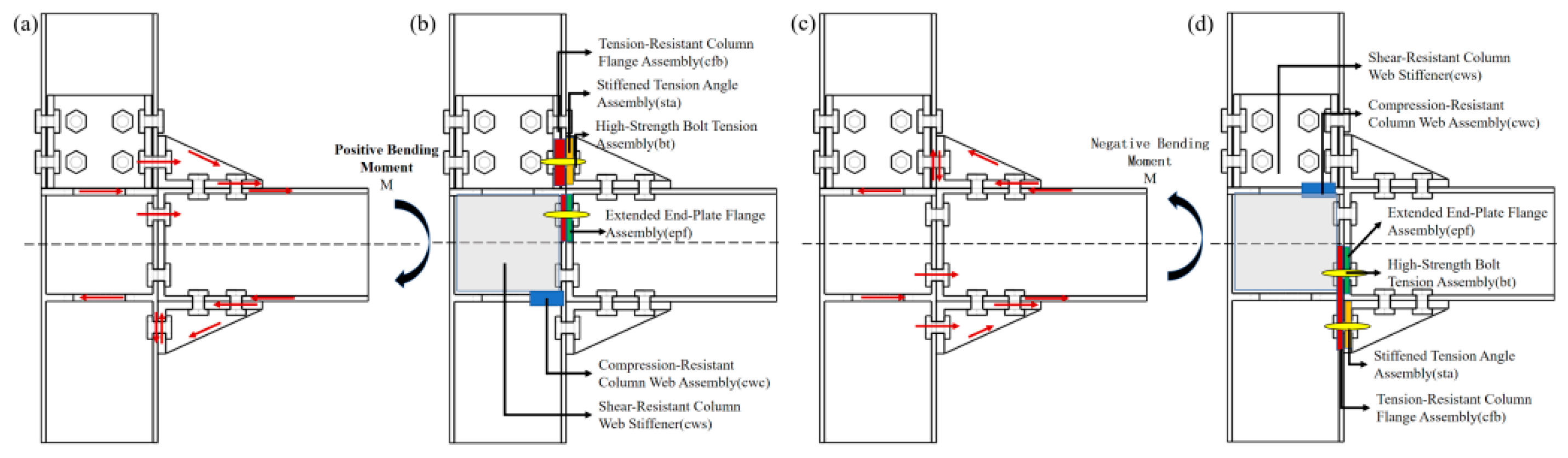
4. Mechanical Model of Fully Bolted Joints
4.1. Initial Rotational Stiffness of Joints
4.2. Determination of Effective Components
4.3. Stiffness Calculation of Effective Components
4.3.1. Compressive Stiffness of Column Web Component (kcwc)
- E: Elastic modulus of the material;
- tc: Wall thickness of the square tubular column;
- ta: Thickness of the stiffener angle leg;
- bc: Flange width of the square tubular column;
- tsp: Thickness of the horizontal stiffener in the joint panel;
- hc: Sectional height of the square tubular column.
4.3.2. Shear Stiffness of Column Web Component (kcws)
- E: Elastic modulus of the steel in the joint panel;
- G: Shear modulus of the steel in the joint panel;
- ν: Poisson’s ratio of the steel;
- hb: Height of the coupled beam;
- hc: Sectional width of the square tubular column;
- tbf: Flange thickness of the coupled beam;
- tc: Wall thickness of the square tubular column.
4.3.3. Tensile Stiffness of Bolt Component (kbt)
- Ebt: Elastic modulus of the bolt material;
- Abt: Effective cross-sectional area of the bolt shaft;
- Lbt: Effective length of the bolt shaft;
- tp: Thickness of the connecting plate;
- dbt: Nominal diameter of the high-strength bolt;
- λ: Ratio of the angle steel/flat endplate thickness to the bolt diameter.
4.3.4. Tensile Stiffness of Column Flange Component (kcfb)
- kcfb1: Stiffness of the flange subpanel between the bolt axis and column web, considering both bending and shear deformation;
- kcfb2: Stiffness of the flange subpanel between the bolt axis and internal diaphragm, considering both bending and shear deformation;
- β1cf, β2cf: Stiffness reduction coefficients for the two flange subpanels, respectively;
- Ecf: Elastic modulus of the column flange steel;
- Gcf: Shear modulus of the column flange steel;
- α: Sectional coefficient for shear deformation (α = 1.2 for rectangular sections);
- efcf: Distance from the bolt center to the internal diaphragm;
- escf: Distance from the bolt center to the column web;
- b1cf, b2cf: Effective lengths of the endplate subpanels, taken as the minimum value between the actual length and (efcf + escf);
- ξcf: Reduction coefficient accounting for the imperfect fixity constraint of the column web on the flange (ξcf = 0.7).
4.3.5. Tensile Stiffness of the Stiffened Angle Component (ksta)
- ksta1: Stiffness of the vertical leg panel between the bolt axis and the horizontal leg of the angle steel;
- ksta2: Stiffness of the vertical leg panel between the bolt axis and the angle steel stiffener;
- β1a, β2a: Stiffness reduction coefficients for the two vertical leg panels, respectively;
- α: Section coefficient for shear deformation calculation, taken as 1.2;
- efa, esa: Distance from bolt center to the inner surface of the horizontal leg and to the stiffener, respectively;
- b1a, b2a: Smaller value between the actual endplate panel length and efa + esa.
4.3.6. Tensile Stiffness of the Flat Endplate Component (kept)
- kep1: Stiffness of the endplate panel between the bolt axis and the beam flange, accounting for both the bending deformation and shear deformation of the flat endplate;
- kep2: Stiffness of the endplate panel between the bolt axis and the beam web, also incorporating bending and shear deformation;
- βep1, βep2: Stiffness reduction coefficients for the two endplate panels, respectively;
- α: Section coefficient for shear deformation calculation, taken as 1.2;
- efep, esep: Distance from bolt center to the beam web and beam flange, respectively;
- b1ep, b2ep: Smaller value between the actual length of the endplate panel and efep + esep.
4.4. Stiffness Calculation Model of Modular Joints
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaillon, L.; Poon, C. Life cycle design and prefabrication in buildings: A review and case studies in Hong Kong. Autom. Constr. 2014, 39, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, A.; Chen, W.; Hao, H.; Bi, K. Review of bolted inter-module connections in modular steel buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 23, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Choi, Y.; Choi, C. Development and testing of precast concrete beam-to-column connections. Eng. Struct. 2013, 56, 1820–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, H.; Ngo, T.; Uy, B. A review on modular construction for high-rise buildings. Structures 2020, 28, 1265–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ban, H. Research on seismic behaviour of square steel tubular columns with deconstructable splice joints. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 191, 107204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Uy, B.; Aslani, F.; Patel, V. Behaviour and design of demountable CFST column-column connections under tension. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2017, 138, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, W.; Bai, Y.; Ngo, T.; Manalo, A.; Mendis, P. New advancements, challenges and opportunities of multi-storey modular buildings-a state-of-the-art review. Eng. Struct. 2019, 183, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Bai, Y.; Hou, J.; Huang, Y. Progressive collapse analysis and structural robustness of steel-framed modular buildings. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 104, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Xia, J.; Chang, H.; Ma, R.; Zhang, L. Flexural behaviour of pairs of laminated unequal channel beams with different interfacial connections in cornersupported modular steel buildings. Thin Walled Struct. 2020, 154, 106792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, A.; Pu, S.; Chai, S.; Wu, L. Seismic performance of H-section beam to HSS column connection in prefabricated structures. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2017, 138, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cui, F.; Zhan, X.; Yu, C.; Jiang, Z. Seismic performance of bolted connection of H-beam to HSS-column with web end-plate. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 156, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, A. Analysis of bolted connection for H-section beam and square steel tube column. Structures 2024, 60, 105945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, X. Seismic performance of joint for H-beam to CFST column with field-bolted flange-splicing. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 196, 107375. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Liu, J.; Tan, W.; Wang, P. Seismic behavior of composite interior joints of prefabricated H-shaped steel reinforced concrete column—Steel beam. Structures 2020, 23, 558–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yu, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, G. Development and testing of hybrid precast steel-reinforced concrete column-to-H shape steel beam connections under cyclic loading. Eng. Struct. 2020, 211, 110460. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Mou, B.; Pan, W. Mechanical properties of modular prefabricated steel-concrete composite internal joints under cyclic loading. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 178, 106463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Fan, M.; Song, H.; Mou, B.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Liu, C.; Men, J. Elastic-plastic analysis of a novel prefabricated SRC column-steel beam composite frame structure. Structures 2024, 68, 107208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, P.; Chen, X.; Xia, H. Experimental study on the seismic performance of the new fully-bolted beam-column joint. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 199, 107619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhong, Y.; Xia, H. Seismic fragility analysis of the steel frame with new layered assembled joints. Structures 2023, 58, 105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhong, Y.; Xia, H. Seismic fragility analysis of steel frames with fully-bolted core tube joints. Structures 2024, 20, 208–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Qian, H.; Gao, K.; An, B.; Fan, F. Design and mechanical performance analysis of a new type of column-column-beam prefabricated steel frame joint. Struct. Eng. Int. 2021, 31, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Li, D.; Wang, H.J.; Qian, H.L.; Fang, W.Q.; Jing, X.F.; Fan, F. Study of mechanical properties of a novel column-beam-column prefabricated steel frame joint. Adv. Steel Constr. 2024, 20, 330–344. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wu, F.; Tan, M. Static performance of non-through one-side bolted end-plate joint for floor-by-floor assembled steel structures. Structures 2023, 48, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; An, Q. Moment resistance and stiffness of an assembled beam-column joint with high-strength bolt and external diaphragm. J. Tianjin Univ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Bending capacity of prefabricated beam-column joints with external diaphragm high-strength bolted connections. Ind. Build. 2020, 50, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; An, Q. Experimental study on seismic behavior of prefabricated beam-to-column high-strength bolted joint with external diaphragms. China Civil. Eng. J. 2020, 53, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Lei, P.; Ban, H. Experimental study on demountable and reusable steel beam-to-column joints with bolted-pinned connections. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2024, 214, 108450. [Google Scholar]
- Montuori, R.; Nastri, E.; Piluso, V.; Troisi, M. Influence of connection typology on seismic response of MRFrames with and without ‘set-backs’. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 46, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Geng, Y.; Li, B.; Lu, W.; Hu, F.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y. Research on lateral load-resisting performance of cruciform cold-formed steel built-up columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2025, 229, 109529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Ma, G. Experimental study on seismic performance of column-column-beam joint in panelised steel-modular structure. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 192, 107240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Malidarreh, N.R.; Ghaseminejad, V.; Asgari, A. Seismic resilience assessment of RC superstructures on long-short combined piled raft foundations: 3D SSI modeling with pounding effects. Structures 2025, 81, 110176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN1993-1-8: 2005; Eurocode 3-Design of Steel Structures-Part 1-8: Design of Joints. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2005.
- Faella, C.; Piluso, V.; Rizzano, G. Structural Steel Semirigid Connections: Theory, Design, and Software; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Shi, G.; Zhao, J.; Yu, H.; Wei, D. Calculation method of moment-rotation curves for ultra-large capacity end-plate joints based on component method. Eng. Mech. 2017, 34, 30–41. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G.; Chen, X. Moment-rotation curves of ultra-large capacity end-plate joints based on component method. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2017, 128, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
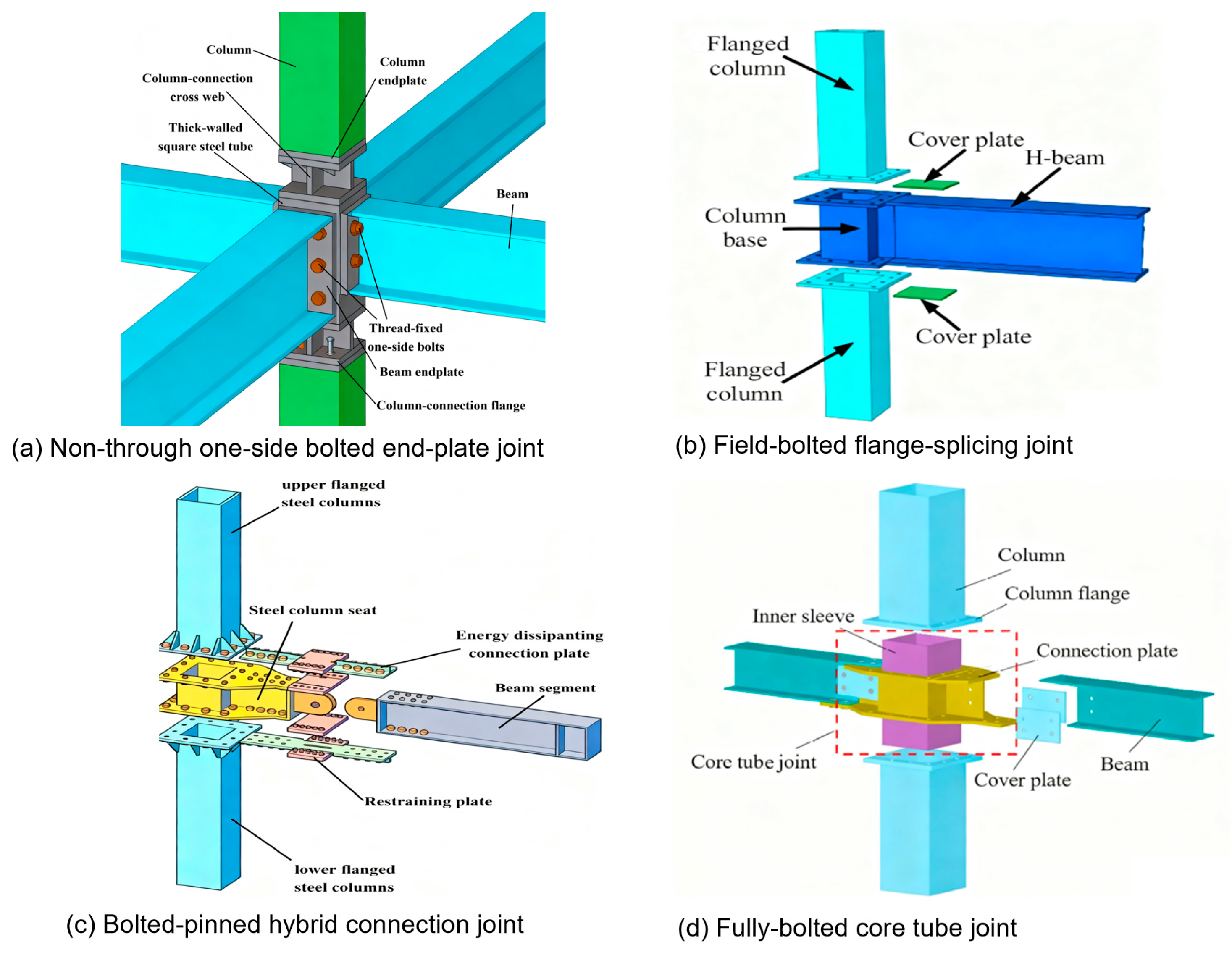
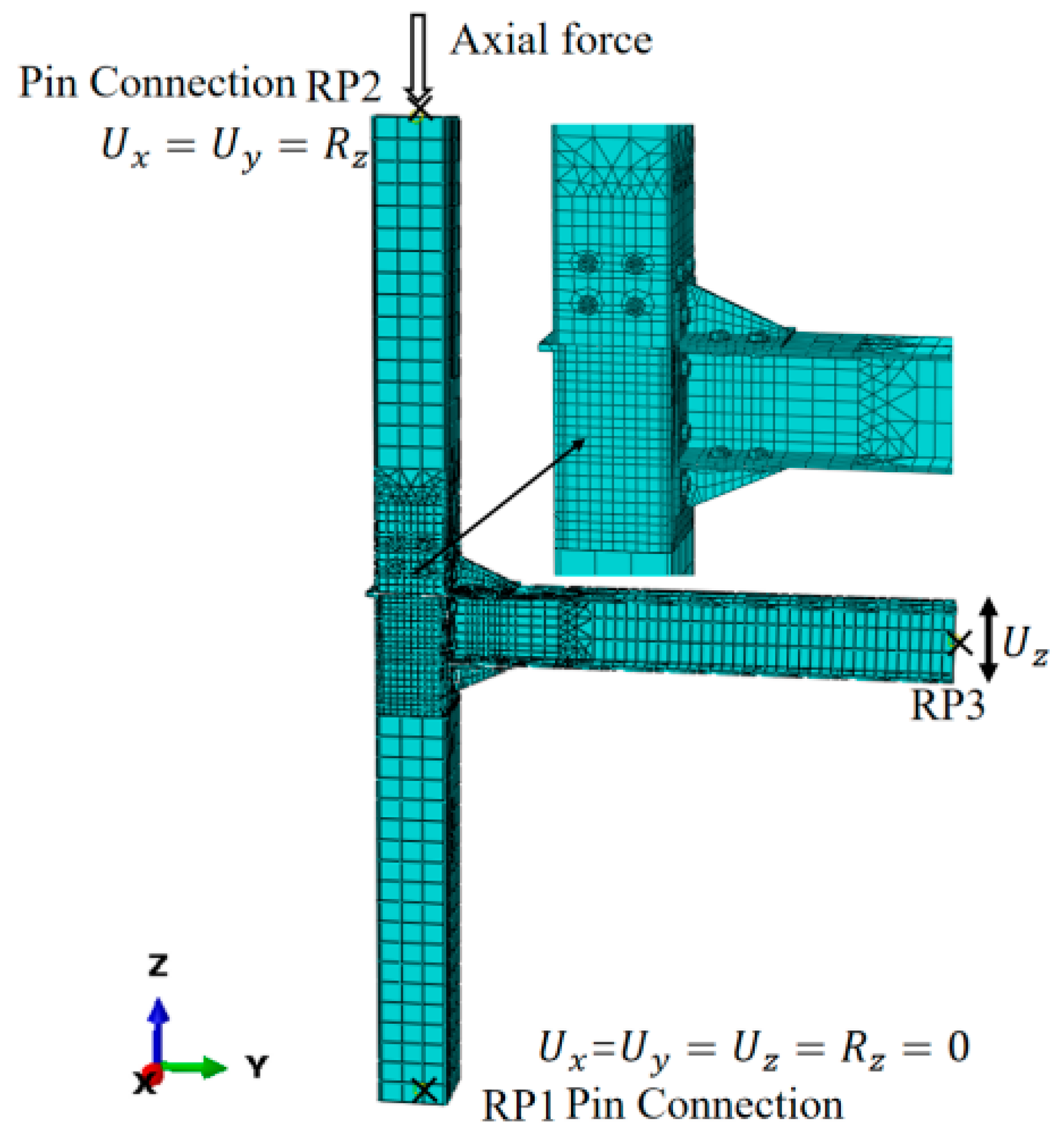



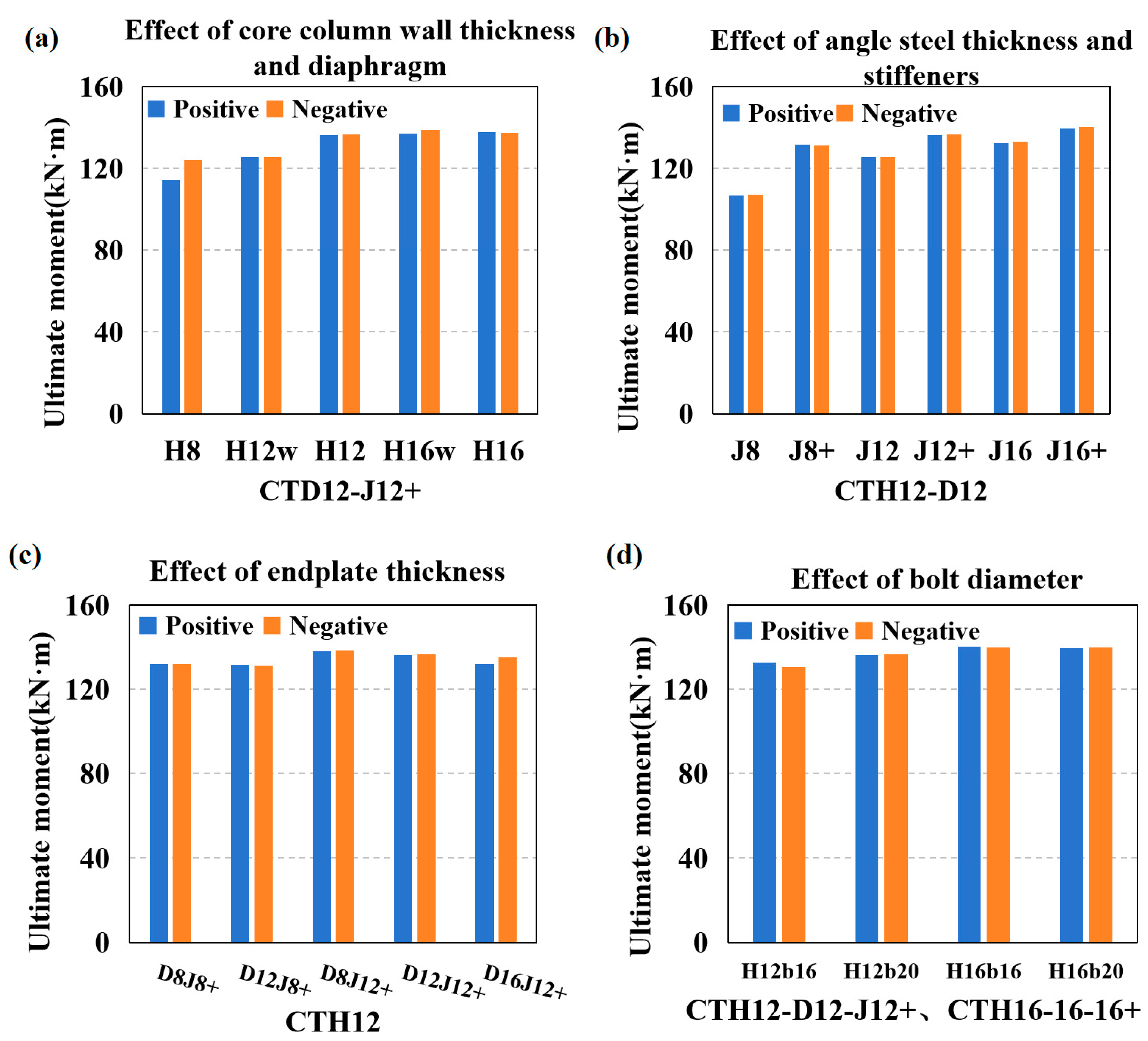
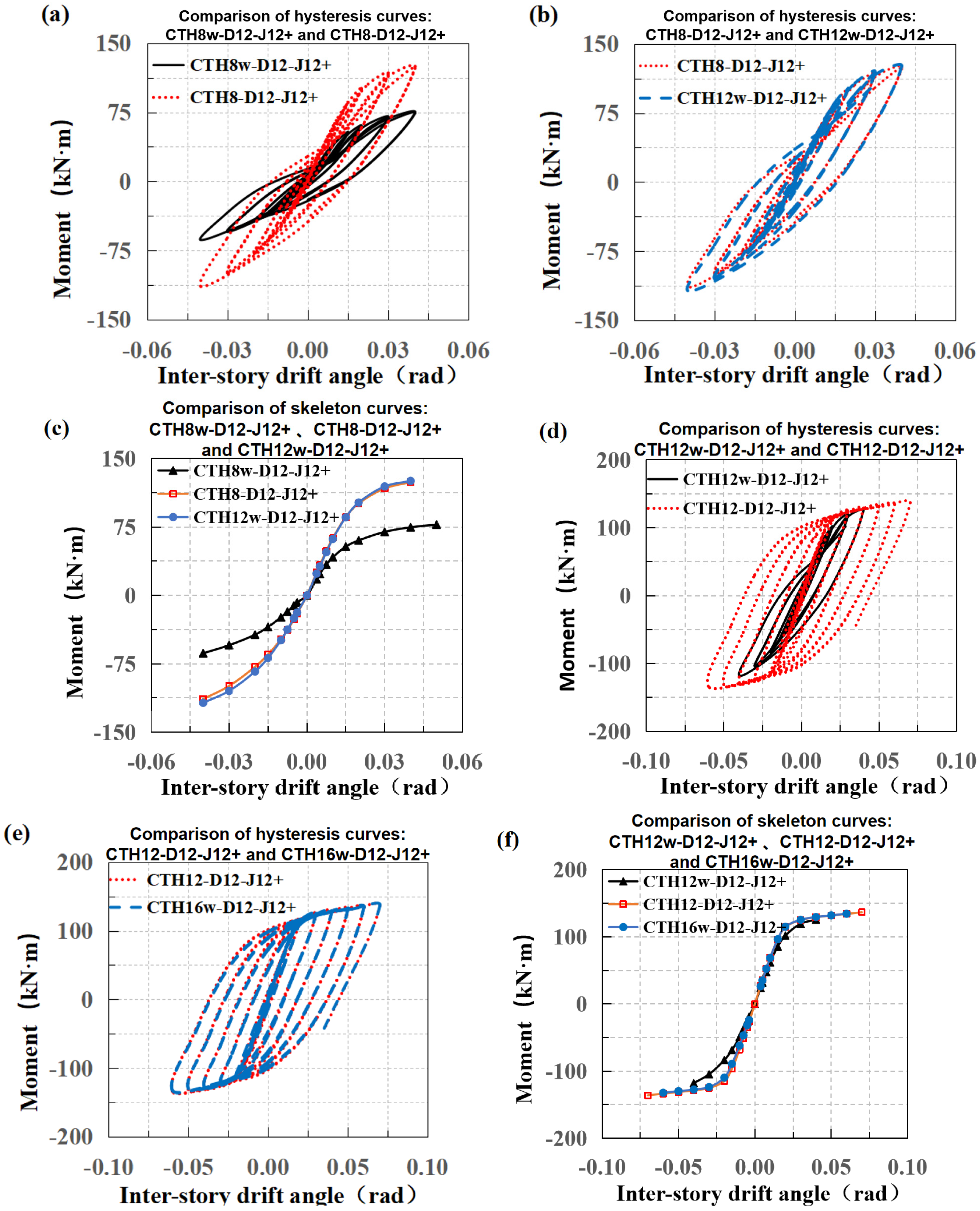
| Model Number | Thickness/mm | Cancellation | Bolt Diameters/mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Column Top | Flush Endplate | Angle Steel | Inner Diaphragm | Rib Stiffener | ||
| CTH8-D8-J8+ | 8 | 8 | 8 | No | No | 20 |
| CTH8-D8-J12+ | 8 | 8 | 12 | No | No | 20 |
| CTH8-D12-J8+ | 8 | 12 | 8 | No | No | 20 |
| CTH8-D12-J12+ | 8 | 12 | 12 | No | No | 20 |
| CTH12-D8-J8+ | 12 | 8 | 8 | No | No | 20 |
| CTH12-D8-J12+ | 12 | 8 | 12 | No | No | 20 |
| CTH12-D12-J8 | 12 | 12 | 8 | No | Yes | 20 |
| CTH12-D12-J8+ | 12 | 12 | 8 | No | No | 20 |
| CTH12-D12-J12+ | 12 | 12 | 12 | No | No | 20 |
| CTH12-D12-J12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | No | Yes | 20 |
| CTH12w-D12-J12+ | 12 | 12 | 12 | Yes | No | 20 |
| CTH12-D12-J16+ | 12 | 12 | 16 | No | No | 20 |
| CTH12-D12-J16 | 12 | 12 | 16 | No | Yes | 20 |
| CTH12-D16-J12+ | 12 | 16 | 12 | No | No | 20 |
| CTH12-D16-J16+ | 12 | 16 | 16 | No | No | 20 |
| CTH16-D12-J12+ | 16 | 12 | 12 | No | No | 20 |
| CTH16w-D12-J12+ | 16 | 12 | 12 | Yes | No | 20 |
| CTH16-D16-J16+ | 16 | 16 | 16 | No | No | 20 |
| CTH12-b16 | 12 | 12 | 12 | No | No | 16 |
| CTH16-b16 | 16 | 12 | 12 | No | No | 16 |
| Model Number | Initial Rotational Stiffness /kN·m/rad | Ultimate Moment /kN·m | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| CTH8-D8-J8+ | 8482 | 11,625 | 105.37 | 110.77 |
| CTH8-D8-J12+ | 9979 | 15,664 | 105.39 | 110.80 |
| CTH8-D12-J8+ | 9355 | 12,311 | 108.26 | 112.64 |
| CTH8-D12-J12+ | 10,904 | 16,547 | 114.49 | 124.21 |
| CTH12-D8-J8+ | 14,126 | 15,073 | 132.00 | 131.85 |
| CTH12-D8-J12+ | 17,767 | 20,014 | 138.00 | 138.46 |
| CTH12-D12-J8 | 11,101 | 12,855 | 106.85 | 106.96 |
| CTH12-D12-J8+ | 16,329 | 17,007 | 131.55 | 131.42 |
| CTH12-D12-J12+ | 19,666 | 21,265 | 136.45 | 136.81 |
| CTH12-D12-J12 | 16,529 | 17,856 | 125.67 | 125.47 |
| CTH12w-D12-J12+ | 8584 | 14,030 | 112.08 | 124.02 |
| CTH12-D12-J16+ | 21,384 | 23,772 | 139.43 | 140.18 |
| CTH12-D12-J16 | 19,412 | 21,210 | 132.30 | 133.07 |
| CTH12-D16-J12+ | 21,384 | 23,968 | 131.87 | 135.20 |
| CTH12-D16-J16+ | 22,786 | 24,230 | 137.36 | 137.78 |
| CTH16-D12-J12+ | 25,759 | 24,623 | 137.68 | 137.32 |
| CTH16w-D12-J12+ | 16,148 | 27,299 | 136.97 | 138.97 |
| CTH16-D16-J16+ | 30,228 | 29,023 | 139.49 | 139.90 |
| MT16w-RBS | 16,995 | 18,667 | 132.81 | 130.56 |
| MT16w-RWS | 27,156 | 26,255 | 140.38 | 139.93 |
| Specimen | Loading Direction | Theoretical Value (kN·m/rad) | Finite Element Value (kN·m/rad) | Finite Element Value/Theoretical Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTH8-D8-J8+ | Positive | 9223 | 8482 | 0.92 |
| Negative | 14,411 | 11,625 | 0.81 | |
| CTH8-D12-J12+ | Positive | 11,328 | 10,904 | 0.96 |
| Negative | 20,428 | 16,547 | 0.81 | |
| CTH12-D8-J8+ | Positive | 15,019 | 14,126 | 0.94 |
| Negative | 16,670 | 15,073 | 0.90 | |
| CTH12-D12-J12+ | Positive | 21,386 | 19,666 | 0.92 |
| Negative | 24,441 | 21,265 | 0.87 | |
| CTH12-D12-J16+ | Positive | 25,085 | 22,786 | 0.91 |
| Negative | 27,729 | 24,230 | 0.87 | |
| CTH16-D12-J12+ | Positive | 29,848 | 25,759 | 0.86 |
| Negative | 27,783 | 24,623 | 0.89 | |
| CTH16-D16-J16+ | Positive | 31,898 | 30,228 | 0.95 |
| Negative | 32,236 | 29,023 | 0.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Li, X.; Tian, C.; Cui, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Li, Y. Numerical Study on the Flexural Performance of Fully Bolted Joint for Panelized Steel Modular Structure. Buildings 2025, 15, 3807. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203807
Wang H, Li X, Tian C, Cui J, Wang X, Zhao C, Li Y. Numerical Study on the Flexural Performance of Fully Bolted Joint for Panelized Steel Modular Structure. Buildings. 2025; 15(20):3807. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203807
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hao, Xuetong Li, Conghe Tian, Jintao Cui, Xuyue Wang, Chuan Zhao, and Yanlai Li. 2025. "Numerical Study on the Flexural Performance of Fully Bolted Joint for Panelized Steel Modular Structure" Buildings 15, no. 20: 3807. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203807
APA StyleWang, H., Li, X., Tian, C., Cui, J., Wang, X., Zhao, C., & Li, Y. (2025). Numerical Study on the Flexural Performance of Fully Bolted Joint for Panelized Steel Modular Structure. Buildings, 15(20), 3807. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203807






