Abstract
As a well-known World Cultural Heritage Site, the Historic Centre of Macao’s historical buildings possess a wealth of decorative patterns. These patterns contain cultural esthetics, geographical environment, cultural traditions, and other elements from specific historical periods, deeply reflecting the evolution of religious rituals and political and economic systems throughout history. Through long-term research, this article constructs a dataset of 11,807 images of local decorative patterns of historical buildings in Macau, and proposes a fine-grained image classification method using the ConvNeXt-L model. The ConvNeXt-L model is an efficient convolutional neural network that has demonstrated excellent performance in image classification tasks in fields such as medicine and architecture. Its outstanding advantages lie in limited training samples, diverse image features, and complex scenes. The most typical advantage of this model is its structural integration of key design concepts from a Transformer, which significantly enhances the feature extraction and generalization ability of samples. In response to the objective reality that the decorative patterns of historical buildings in Macau have rich levels of detail and a limited number of functional building categories, ConvNeXt-L maximizes its ability to recognize and classify patterns while ensuring computational efficiency. This provides a more ideal technical path for the classification of small-sample complex images. This article constructs a deep learning system based on the PyTorch 1.11 framework and compares ResNet50, EfficientNet-B7, ViT-B/16, Swin-B, RegNet-Y-16GF, and ConvNeXt series models. The results indicate a positive correlation between model performance and structural complexity, with ConvNeXt-L being the most ideal in terms of accuracy in decorative pattern classification, due to its fusion of convolution and attention mechanisms. This study not only provides a multidimensional exploration for the protection and revitalization of Macao’s historical and cultural heritage and enriches theoretical support and practical foundations but also provides new research paths and methodological support for artificial intelligence technology to assist in the planning and decision-making of historical urban areas.
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background and Significance
Historical buildings are decorated with patterns that serve as a vibrant language of visual culture. These motifs enhance the esthetic appeal of the structures, but also contain multi-layered cultural data, such as the geographical environment, humanistic beliefs, religious beliefs, and social systems of specific historical periods [1]. Architectural heritage is an important medium to solidify cultural narratives, and for intergenerational transmission. The Historic Centre of Macao was included on the World Heritage list as a key hub of exchange between Eastern and Western cultures. The architectural heritage in this area is a unique collage of Chinese and Portuguese elements. This is most evident in the decorative patterns. The traditional Chinese auspicious motifs, such as the characters for prosperity, happiness, and longevity, as well as pomegranates and peonies, are interwoven with classical Western columns, arches, bas-reliefs, and Portuguese blue and white ceramic tiles that depict story scenes, creating a harmony in the coexistence of both cultures [2]. This study focuses on traditional decorative patterns in Macau (sourced from the website of the Macau Cultural Bureau, https://www.culturalheritage.mo/gb/list/9?area=0&building=1 (accessed on 31 July 2022)). These patterns blend the characteristics of China and Portugal. The samples are concentrated mainly on building facades and interior spaces such as rooftops, walls, and podiums, as well as shadow walls and detailed components like stone column bases, door and window frames, and eaves. These elements do not only reflect the craftsmanship and esthetic tendencies of the period but also serve as a visual representation of social identity and hierarchical systems. They vividly illustrate the historical depth and culture complexity of Macau’s multicultural heritage [3].
The research on the decorative patterns in the historical architecture of Macau is based on a traditional methodology system that combines manual surveying, image capture, a compilation of the literature, and oral history. These methods are indispensable for obtaining high-precision data on the field, documenting craft details, and interpreting humanistic values and cultural context. They are the foundation of heritage research and recording. There are limitations to processing efficiency, scalability, and objective consistency. This makes it difficult to support large-scale, multi-category pattern recognition and cultural element analyses. Traditional methods need new technological tools to complement them [4]. Recent advances in artificial intelligence have opened up new approaches for the intelligent recognition and analysis of architectural cultural heritage. convolutional neural networks (CNNs), a deep learning technique, have shown outstanding performances in image classification. This is a method that can be used to automatically identify and interpret architectural decorative elements [5]. The classification results should be integrated into decision-making processes for heritage management and conservation, restoration, or adaptive reuse. This integration requires a deep fusion of the element interpretation, value assessments, and historical context analysis provided by experts in the domain.
This study primarily explores Macau’s architectural structures that are monuments or have architectural artistic value. We created a large-scale dataset of images from Macau that includes 11,807 images. The images are divided into six categories of decorative patterns, each corresponding to a different architectural function. A method of image classification based on the ConvNeXt model is also proposed. This method evaluates the performance of deep models and their feasibility in complex small-sample image classification [6].
1.2. Research Status and Problem Analysis
Academic research on decorative patterns of historical architecture has evolved from esthetic appreciation and cultural interpretation to technical domains, such as image recognition and data modeling. Intelligent reconstruction is also included [7]. Computer vision has been used in a number of studies to explore architectural-style recognition, façade classification, and pattern generation. These studies have made significant progress. Despite this, there are still some critical limitations in practical applications.
First of all, as a World Cultural Heritage Site, the Historic Centre of Macao has had a long-term accumulation of research. However, existing research has mostly focused on the overall form and decorative style of historical heritage buildings, with limited research on architectural decorative patterns: especially the decorative pattern dataset that reflects the integration of Chinese and Portuguese cultures. There is a lack of standardized and detailed datasets with comprehensive labeling and geographic location information. These contents are helpful for in-depth research on the historical origins and cultural intentions behind decorative patterns and are more conducive to the development of information technology and digital application of Macao’s World Cultural Heritage status in protection and renewal.
Second, the model’s generalization ability is limited. Existing models are good at classifying architectural styles, but their understanding of the details of decorative patterns, cultural meanings, and structural relationships is limited. This limits their ability to generalize in practical scenarios, limiting their application in real-world heritage management contexts.
Thirdly, the interpretability of visual and elemental elements is insufficient. Decorative patterns not only present visual patterns but also serve as carriers of cultural connotations and symbolic features, presenting spatial logic and hierarchical patterns. Existing models often focus on the accuracy of classification, while neglecting the explanatory power of research design elements. In the actual decision-making of historical urban area protection, the precise and appropriate definition of decorative patterns is limited, and the evolution of cultural elements and design styles cannot be effectively analyzed.
Therefore, there is an urgent need for an intelligent recognition framework that can combine deep feature extraction with element connotation, which can effectively support the accurate classification of decorative patterns of historical buildings in Macau, while also modeling the differentiation of cultural elements. Through digital heritage protection and artificial-intelligence-driven urban decision-making, it can provide objective and accurate technical support [8].
1.3. Research Objectives and Content
This study aims to overcome the limitations of traditional classification techniques in terms of accuracy and objectivity. The purpose is to establish a framework based on deep learning for the classification of decorative patterns in different functional buildings in the Historic Centre of Macao. The ConvNeXt model highlights high-performance image classification methods that combine visual interpretability to improve the overall model’s configuration applicability and ability for cultural understanding.
The main research content includes the following: First, dataset construction. The buildings studied in this study are located within the Historic Centre of Macao. They span over 400 years of history, from the Ming Dynasty up to the Republic of China. The study sample is made up of 11,807 images based on data from the Macao Cultural Affairs Bureau’s website. It focuses on two categories of buildings: monuments and structures with architectural artistic value. The classification is based upon Mr. Chen Zecheng’s Memorandum of Macao’s Historical Architecture. Appendix 1: Construction Years Table of Heritage Buildings of the Historic Centre of Macao provides further clarification. The data are annotated in a multi-layered system. There are six categories in total: cultural attribute labels (Chinese and Western) and Sino-Western Fusion; and key point and region annotations (highlighting culturally significant feature areas). This approach is intended to provide richer supervision signals.
Second, model training and design. A classification model based on ConvNeXt-L was developed and benchmarked with mainstream architectures, including ResNet50, EfficientNet-B7, ViT-B/16, Swin-B, and RegNet-Y-16GF, to validate its superiority.
Third, visual analysis. The study introduced Grad CAM heatmap to analyze the focus area of the visualization model, exploring the perception patterns and features of architectural decoration patterns in historical buildings with different functions. Not only does this reveal the recognition rules of architectural decoration patterns, but it also deeply reflects their historical and cultural accumulation and connotation. In the context of historical heritage conservation, this provides interpretable research progress for the development of the link between urban cultural analysis and artificial intelligence.
1.4. Literature Review
1.4.1. Current Research on Decorative Patterns in Macau’s Historical Architecture
Architectural Cultural Heritage of Macau authors Liu Xianjue and Chen Zecheng wrote the pioneering book on the subject that systematically offers 400 years of Sino-Portuguese architectural accord. The categorization of decorative arts found in religious architecture, civil architecture, and defensive architecture provided the research of architectural forms (Liu and Chen, 2005) for later study [9]. Building on this, the Memoir of Macau’s Historic Architecture further refines the functional typology by incorporating architectural ornamentation into five categories—residential, civic, educational and others—thereby reinforcing the functional–functional correlation and providing a complete inventory of Macau’s Historic Buildings (Chen 9& Long, 2019) [10]. The architectural landscape of Macau, according to Macau Narratives, reflects the localized blending of Portuguese and Chinese civilizations that exemplifies various multi-layered structures of cultural coexistence (Spiteri, 2013) [11], especially in its religious sites, urban morphology, and decorative elements.
Australian historian Geoffrey C. Gunn’s History of Macau 1557–1999 provides valuable historical context for the study of decorative patterns through a global–historical lens [12]. Yin Muzi (2014) [13] conducted a systematic analysis of Macau’s historical architecture in terms of historical development, stylistic features, ornamentation, and cultural context, identifying the distinctive characteristics of decorative forms shaped by multicultural integration, as well as the influence of cultural transplantation on architectural expression. She Meixuan et al. (2011) [14] focused on the harmonious blending of Chinese and Western architectural garden decorations, highlighting the intricacy of decorative craftsmanship and the vibrancy of the colors. Feng Jingzhao (2022) [15] centered on the gray sculpture (hui su) decorative technique, discussing its multifunctional roles in vernacular architecture—including esthetics, fire prevention, and symbolic protection—while proposing strategies for digital preservation. Xiang Liqun (2023) [16] reinterpreted the interdisciplinary and cross-media application of historical architectural themes by studying the characteristic themes of decorative patterns in historical buildings and applying them to contemporary jewelry design.
Existing research has established a foundational framework encompassing “cultural connotation–typological characteristics–application-oriented exploration”, which provides a rigorous academic basis for the classification of decorative patterns in Macau’s historical architecture and enriches the understanding of their humanistic and esthetic values. Nonetheless, there are still shortcomings regarding the systematic organization of pattern data, the degree of digitalization, and the application of artificial intelligence for decision-making support [17].
1.4.2. Advances in the Intelligent Analysis and Real-Time Processing of Architectural Decoration Patterns
Many scholars have systematically sifted through the databases and models of artificial intelligence (AI), which have significantly improved the efficiency of computer vision tasks such as image recognition and generation. Digital cultural heritage is a relatively new direction for applying image synthesis as such, which can provide a new perspective for this study.
In recent years, deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have made remarkable advances in image classification tasks. Rawat and Wang (2017) conducted a comprehensive review of over 300 publications on CNNs, summarizing major achievements and proposing several improvement strategies [18]. A comparative study involving five pretrained CNN models (DenseNet121, InceptionV3, VGG16, GoogLeNet, and AlexNet) was conducted to assess their efficiency in classifying ceramic patterns from the Sukhothai Ceramics Center (Pitikan Kuntitan and Orawan Chaowalit, 2021) [19]. Yuji Yoshimura (2019) measured visual similarities between architectural designs of different architects using DCNN models [20]. Llamas (2017) demonstrated the effectiveness of CNNs in digital heritage document retrieval, comparing representative architectures under full training and fine-tuning settings [21]. Obeso et al. (2017) applied deep learning and visual attention predictions to classify architectural styles within Mexican heritage buildings [22]. Lin, C. studied the application of traditional cultural symbols in art design against the background of artificial intelligence. [23]. Chen, L., Feng, J., Lin, M., et al. (2016) constructed a dataset and implemented recognition and classification methods for Li brocade patterns [24]. Sun, Zhang, Ren, Wang, and Jin (2015) applied Convolutional Neural Networks for author classification of Chinese ink paintings [25]. Chu et al. (2012) applied visual pattern recognition to architectural image classification and product image retrieval, demonstrating a superior performance to traditional bag-of-words approaches [26].
The various models and research methods based on artificial intelligence have achieved certain results, laying a solid theoretical foundation for this study. However, the digitalization of architectural decoration patterns is still in its early stages of exploration, and the results are relatively scattered, requiring further integration and deepening.
1.4.3. ConvNeXt Model and Its Application
Facebook AI Research unveiled ConvNeXt in 2022. It is a novel convolutional network architecture inspired by the Vision Transformer. In comparison to earlier convolutional network architectures, ConvNeXt employs deeper network architectures, larger convolutional kernels, simplified activation functions, and optimized normalization layers. These enhancements allow ConvNeXt to reach performance levels similar to ViT, while also being as computationally efficient as classic CNNs [27]. The model has demonstrated excellent performance in computer vision tasks such as image classification and object detection, while also showing promising results in medical image segmentation, achieving high accuracy with fewer parameters (Han, Zhimeng et al., 2022) [28]. By integrating ConvNeXt with UNet, researchers have significantly enhanced the performance of the GASlumNet model, proposing a new technical solution for precise mapping of slum areas (Lu, W. et al., 2023) [29]. Hatem Taha et al. (2023) utilized ConvNeXt as the encoder and UPerNet as the decoder, effectively integrating local and global element features, significantly improving the segmentation accuracy for road crack detection [30]. These results fully demonstrate the high accuracy and strong scalability of the ConvNeXt network [31]. These results fully display the high accuracy and good scalability of the ConvNeXt network. In order to tackle the challenge of limited training data, Hatem Taha et al. (2025) combined the improved ConvNeXt with YOLOv5 for efficient and accurate waste classification [32].
ConvNeXt is a deep learning CNN framework designed with efficiency in mind, and works well with limited training data. Considering the limited quantity, intricate structure, and rich detail of Macau’s historical architectural pattern images, traditional models often suffer from insufficient feature extraction and low classification accuracy. ConvNeXt significantly enhances the discriminative ability of such image data, while maintaining computational efficiency, offering a feasible and effective solution for classifying complex visual patterns in small-sample contexts.
In summary, current research on the decorative patterns of Macau’s historical architecture remains primarily focused on cultural interpretation and typological classification, while digital and intelligent analyses are still in their infancy. Notably, significant gaps remain in the elemental understanding between architectural functions and pattern imagery, automated classification, and the construction of large-scale datasets. Thus, employing deep learning models for systematic modeling and intelligent recognition of Macau’s architectural pattern imagery is not only a necessary step in technological evolution but also plays a vital role in the protection and revitalization of urban cultural heritage.
2. Materials and Methods
After eight years of research, a team of doctoral and graduate students from the City University of Macau and Guangdong Polytechnic Normal University collaboratively completed this study. Through organized field investigations and multi-source data collection utilizing Google Street View, the team systematically screened, cleaned, and annotated the materials to construct an extensive historically verified dataset of decorative pattern images, ensuring both cultural accuracy and structural consistency. The research team classified and integrated patterns according to six architectural functional themes, focusing on key structural components such as roofs, eave ridges, walls, platforms, doors and windows, chi tou (gable walls), screen walls, and stone column bases. The core objective extends beyond documenting pattern morphology toward interpreting the profound socio-economic and cultural narratives embedded within these decorative patterns.
2.1. Data Collection Scope and Target
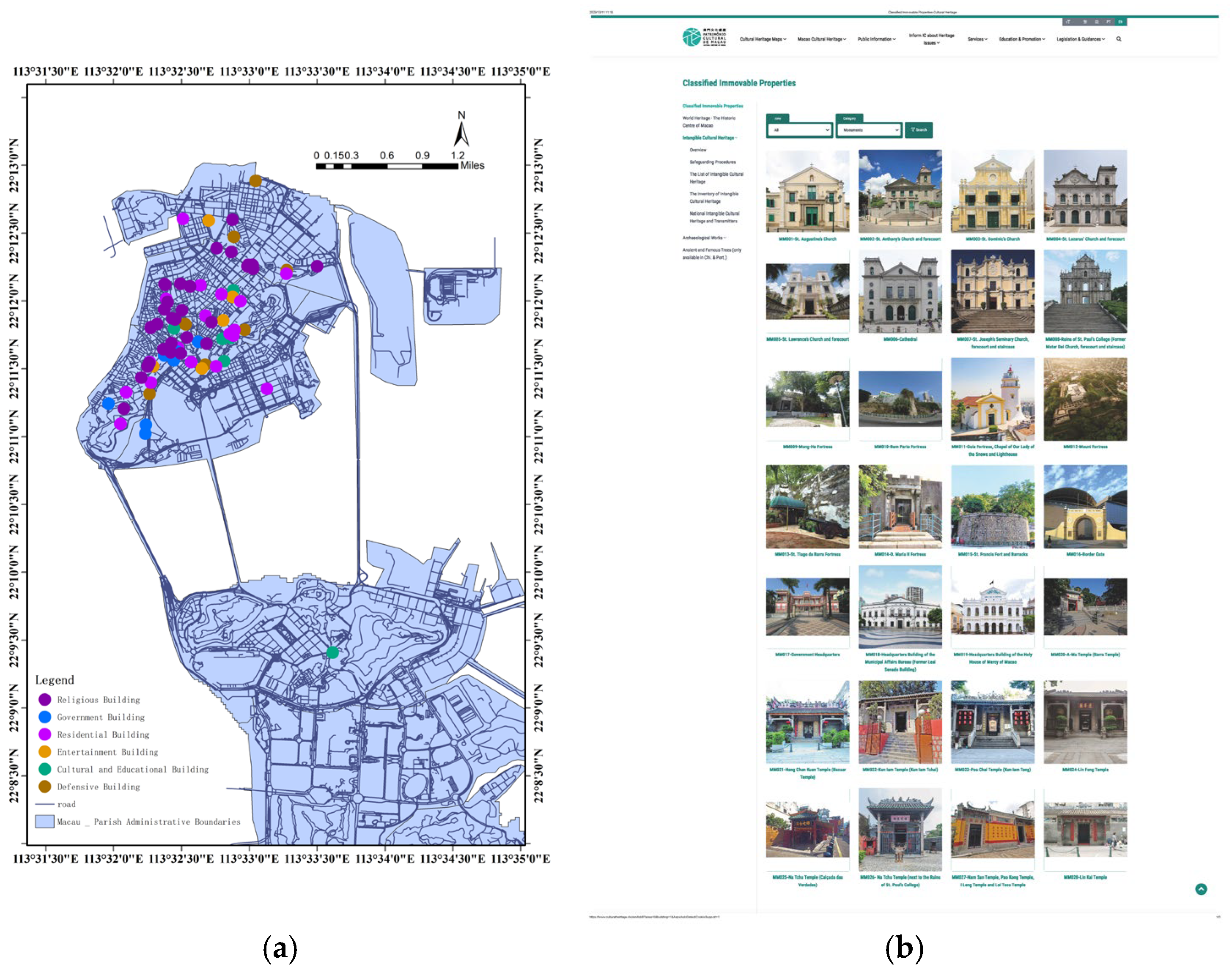
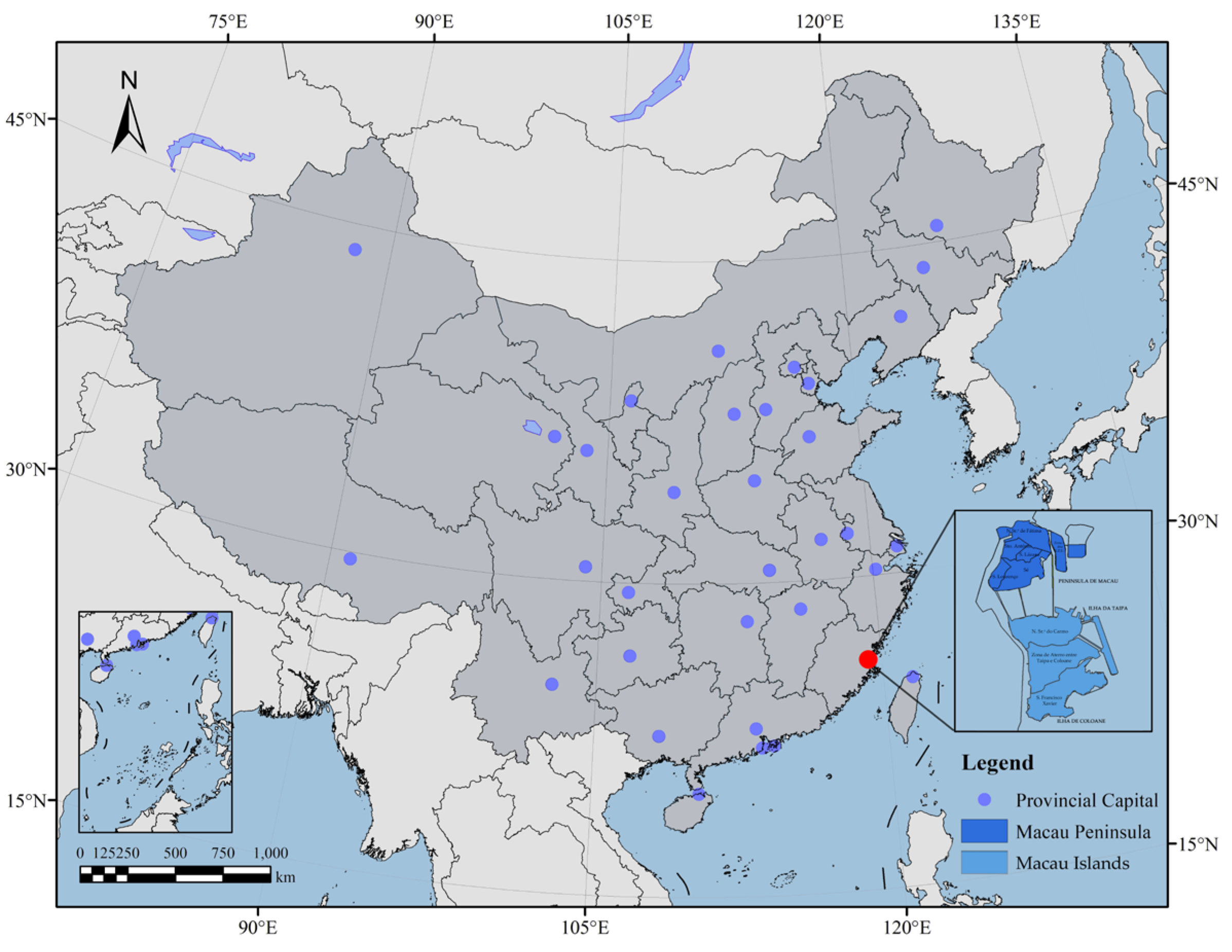
In this study, our data sources mainly refer to the classified historical buildings on the website of the Macao Cultural Bureau, as shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, combined with the published monographs and academic papers on architectural decoration in Macau as the basis for selecting representative historical buildings. This series covers decorative patterns in various functional buildings, including representative decorations of important indoor and outdoor node spaces.
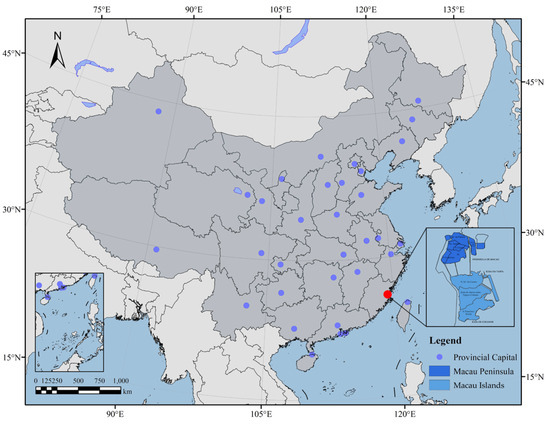
Figure 1.
Geographical location of Macau within China.

Figure 2.
Map and overview of heritage building distribution in the Macao Special Administrative Region. (a) Distribution map of six types of historical buildings in Macau. (b) Properties (cultural heritage buildings) assessed by the Macau Cultural Affairs Bureau website.
2.2. Classification of Building Types and Sample Size
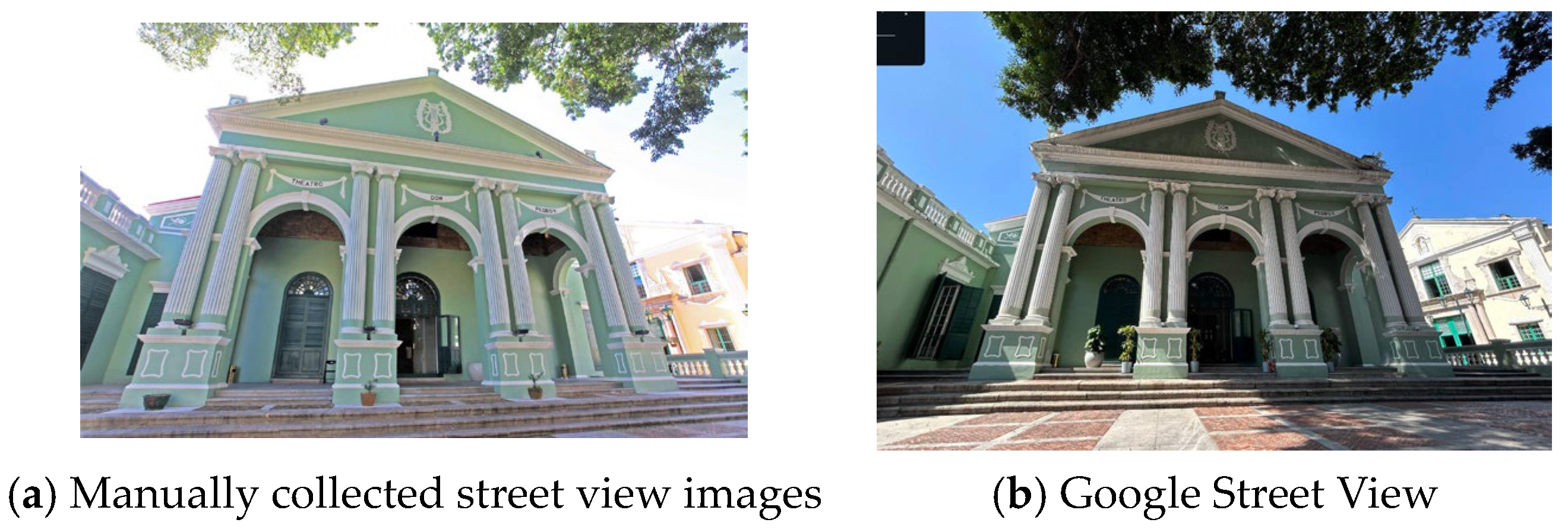
To investigate how different functional attributes influence the style and motifs of architectural decorative patterns, this study categorizes the sampled buildings into six major types based on their historical functions. A data collection team conducted systematic high-resolution photography of decorative patterns from these six types of buildings using professional digital single-lens reflex (DSLR) cameras. During image acquisition, efforts were made to ensure clarity and uniform lighting conditions, and to record metadata such as the building’s location, material, and the approximate historical period associated with each pattern. To supplement street view images that were challenging to collect manually due to obstructions or on-site access limitations, we utilized the Google Street View API to acquire additional data, in compliance with the relevant terms of service. All image usage strictly adhered to Google’s Terms of Service (https://policies.google.com/terms?hl=zh-CN, accessed on 26 March 2025), with clear attribution of the data source and restriction to academic purposes. To ensure data consistency, fixed acquisition parameters were applied: a vertical field of view (fovy) of 90° was set to simulate a natural viewing perspective; the heading angle was aligned perpendicular to the road at each sampling point to focus on the building facade; and the pitch angle was maintained at 0° to simulate a horizontal viewing angle. All images were captured at a resolution of 960 × 960 pixels. Low-quality frames (e.g., those with significant occlusion or abnormal lighting) were excluded, and metadata was recorded to enhance the consistency and reliability of the dataset in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Manually collected street view images vs. Google Street View.
2.3. Image Cropping and Annotation
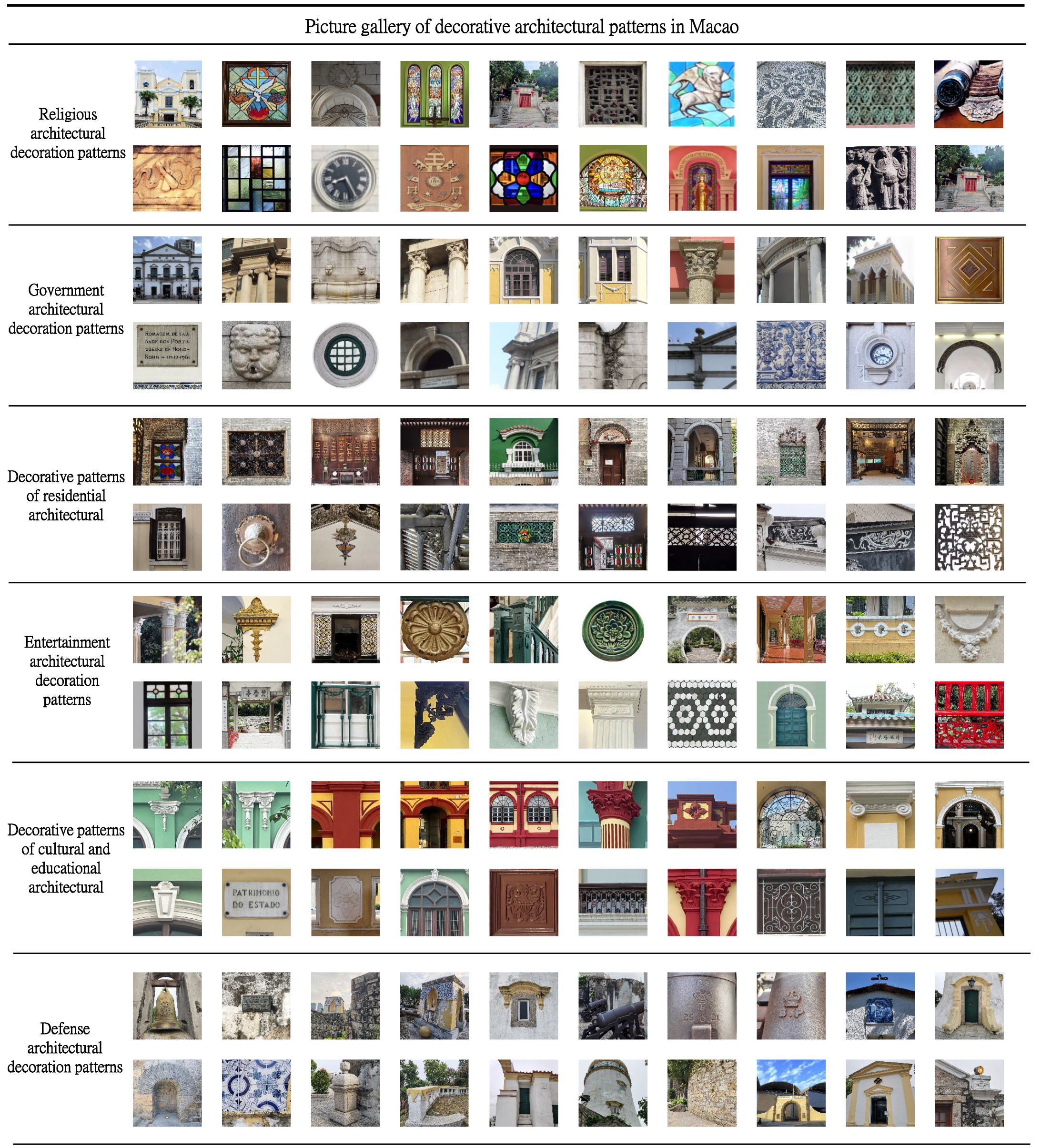
The original photographs often contain broad architectural scenes in which the decorative patterns constitute only a portion of the image. To generate training samples with a focused representation of the patterns themselves, the images underwent manual screening and cropping procedures. Photos exhibiting distortion due to low-angle perspectives, excessive blur, redundancy, or insufficient visual information were excluded. The retained images were cropped to extract regions containing complete and clearly discernible patterns. Following this cropping process, a team of experts with backgrounds in architectural history and design reviewed and annotated the dataset to ensure accurate classification of the image samples. As a result, an annotated dataset of 12,000 images was constructed, with 11,807 valid images selected for model training and evaluation. The number of images per architectural category is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Six functional categories of historical building decoration patterns.
As shown in the table, due to the unique spatial attributes of the Historic Centre of Macao, the number of functional types of buildings is not evenly distributed in the development process, as influenced by the urban planning and design concepts and techniques of China and Portugal in different periods. Overall, there is a relatively large number of religious buildings, accounting for over 50% of the total sample. Although defensive buildings occupy a large area, their quantity is limited. The representativeness of educational buildings is insufficient, accounting for less than 1% and 2%, respectively. This objective imbalance may lead to biased model performance during the training and evaluation stages, and appropriate strategies are needed to address this issue in order to improve the generalization ability and classification accuracy of deep learning models [33].
2.4. Image Preprocessing
To address the class imbalance issue in the dataset (as shown in Table 1), in this study, we employ a comprehensive strategy based on intensive data augmentation, aimed at artificially increasing the diversity and quantity of minority-class samples in the training set. The augmentation pipeline consists of a series of stochastic transformations, including random cropping, random rotation within ±45°, horizontal and vertical flipping, brightness and contrast adjustment, and scale jittering. These operations are applied spontaneously during training to each batch of minority-class samples, thereby significantly increasing their effective number and compelling the model to learn more robust feature representations, rather than memorizing a limited set of examples. All performance metrics of the reported models, along with the subsequently presented confusion matrices and precision–recall curves, were obtained after training on this augmented dataset. The results demonstrate that the data augmentation strategy effectively mitigates overfitting and markedly improves the recall and F1-score for minority classes, confirming its efficacy in tackling class imbalance.
To improve model training performance and enhance generalization capability, this study performs standardized preprocessing on the image data prior to training. The main steps are as follows.
Image Scaling: All images are uniformly adjusted to 224 × 224 pixels using bilinear interpolation to preserve details. Data augmentation: The training set incorporates horizontal and vertical flips (50% probability), random rotation (±15°), brightness contrast perturbation, and cropping operations to enhance the robustness of the model for structural and lighting changes [34]. Normalization: Pixel values are scaled to the range [0, 1]. When loading pretrained weights, further normalization is performed based on ImageNet’s mean and standard deviation (mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]; std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) [35]. Format conversion and loading: PyTorch’s Dataset and DataLoader classes are used to construct efficient data pipelines supporting batch processing and concurrent loading.
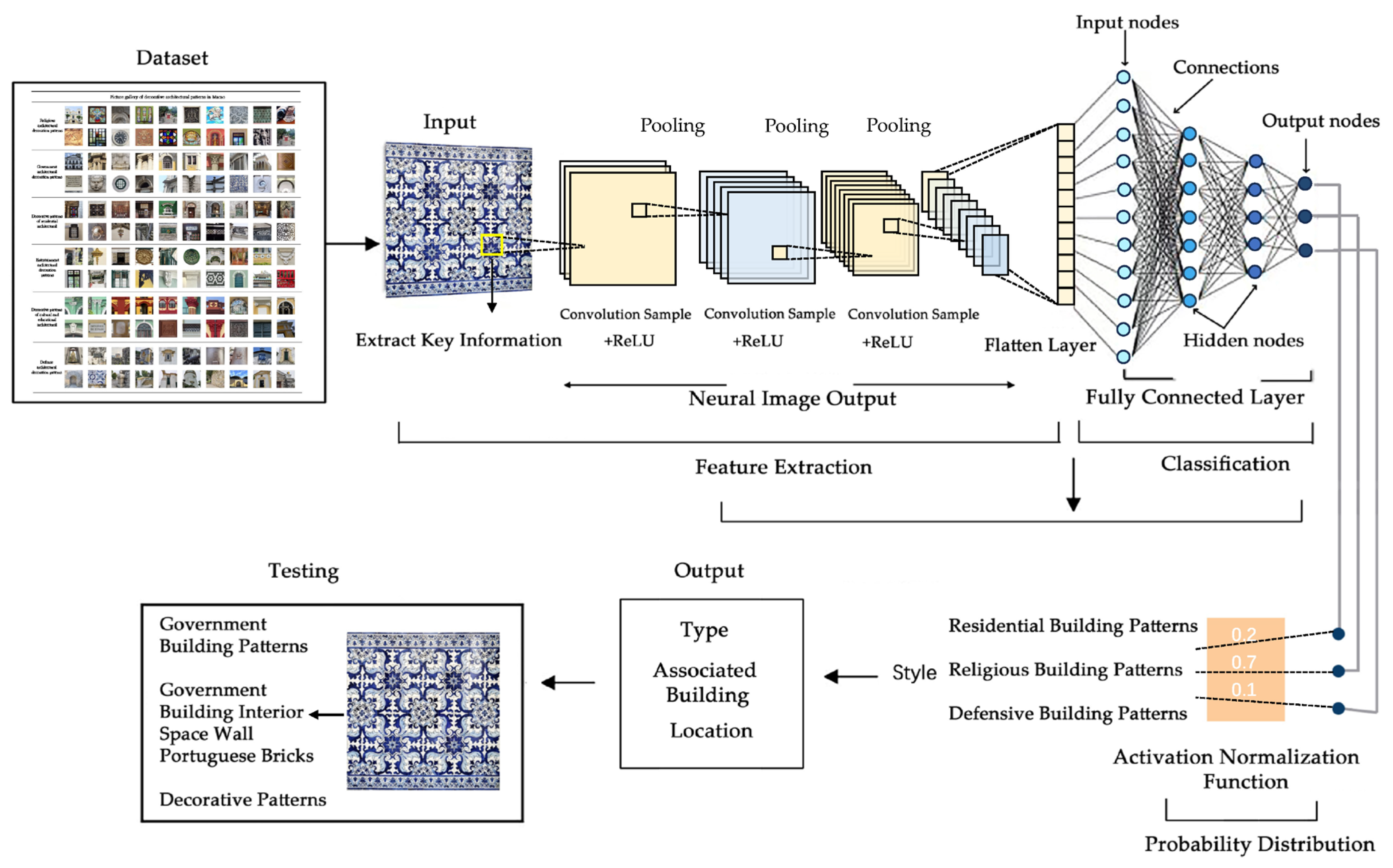
The above dataset construction and preprocessing procedures provide a solid data foundation for the subsequent model training and evaluation in this study, as shown in Figure 4.
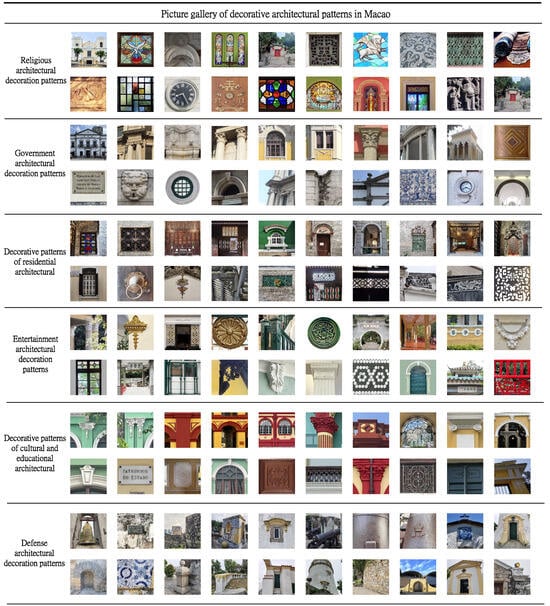

Figure 4.
Dataset of decorative patterns on historical buildings in Macau.
2.5. Transfer Learning
This study leverages transfer learning into the model-training process to further enhance the classification model’s generalization capability and training efficiency. This is because the scale and category distribution of the decorative patterns image dataset for Macau historical buildings is relatively limited [36]. In this study, a ConvNeXt-L pre-trained on ImageNet was chosen and adjusted to adapt to the specific operational tasks of the study. Transfer learning helps the model to extract structural, textural and symbolic features of patterns efficiently under few-shot conditions, which increases the recognition accuracy of historical heritage images. To maintain fairness among the various comparative experiments conducted using the intelligent decision support system, the same transfer learning strategy was applied to all the baseline models (ResNet50, Effi-cientNet-B7, ViT-B/16, etc.).
Transfer learning speeds up the training process and improves the classification performance. It shows the technological utility value of AI in heritage conservation and decision-making for urban planning [37].
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Design and Modeling Methods
3.1.1. ConvNeXt-L Model Construction
Given the intricate textures and high-detail features of decorative patterns in historical architecture in Macau, in this study, we adopt ConvNeXt-L as the primary classification model. ConvNeXt-L is an enhanced convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture that incorporates design elements inspired by Transformers, such as Layer Normalization, simplified activation functions (GELU instead of ReLU), and large-kernel convolutions (e.g., 7 × 7 convolutions), to improve modeling capacity and generalization performance in image recognition tasks [38].
This model consists of multiple ConvNeXt blocks, each receiving an input feature map size of h × w × dim. As shown in Table 2, local features are extracted through large-kernel deep convolution, and then channel information, fusion, and dimension up/down processing are performed using 1 × 1 point convolution. Finally, a feature map of the same size as the input is the output [39]. The overall structure of the model is divided into four stages: the input of the entire model is an RGB image with a size of 224 × 224 × 3. The image first undergoes a 4 × 4 convolution operation to output a feature map with a size of 56 × 56 × 96. Then, through four stages of ConvNeXt Block and downsampling operations, the feature map size is sequentially changed to Stage 1: 56 × 56 × 96; Stage 2: 28 × 28 × 192; Stage 3: 14 × 14 × 384; and Stage 4: 7 × 7 × 768. Finally, the classification prediction is performed using Global Average Pooling, Layer Normalization, and Fully Connected Layers (Linear), resulting in a six-dimensional vector output.

Table 2.
Construction of the ConvNeXt-L model.
This architecture maintains the efficiency and local perception capabilities of conventional convolutional models while introducing deeper feature representation mechanisms, thereby enhancing the classification performance for complex decorative patterns [40].
3.1.2. ConvNeXt-L Model Training
Experimental Design:
This study implements the ConvNeXt-L model using the PyTorch 1.11 framework for the classification task of decorative patterns in historical architecture in Macau. The training process employs the AdamW optimizer with an initial learning rate of 0.001 and a weight decay coefficient of 0.01. The loss function is set to cross-entropy loss, with a batch size of 64 and a total of 300 training epochs. During training, the ConvNeXt model, benefiting from its convolutional enhancements inspired by the Transformer architecture (such as depth-wise separable convolutions and Layer Normalization), effectively captures fine-grained details in decorative patterns [41]. In particular, it demonstrates a strong discriminative power when recognizing traditional textures, color schemes, and symbolic cultural features, thereby achieving high classification accuracy [42].
Environment configuration:
The hardware environment consists of an Intel Core i9-10900K processor, 64 GB of RAM, and an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 GPU, providing substantial parallel computing capabilities and memory bandwidth for efficient training and inference on large-scale image datasets. The software environment includes the 64-bit Windows 10 operating system, the PyTorch 1.11 deep learning framework, CUDA 11.4, and cuDNN 8.2.4. All development work was conducted using PyCharm 2021 Professional Edition. During training, TensorBoard was integrated for real-time monitoring of model loss, accuracy, and weight dynamics, ensuring the traceability of the experimental process and the objectivity of performance evaluation [43].
3.1.3. Dataset Partitioning and Training Process
To ensure the scientificity and generalization ability of model training, we divided the image dataset into a training set (Train), a validation set (Validation), and a test set (Test), in a ratio of 7:2:1 [44]. Among them, the training set contains 8265 images, the validation set contains 2361 images, and the test set contains 1181 images. The data sources cover local historical architectural decoration images and non-local samples in Macau with a ratio of approximately 1:1 to enhance the model’s adaptability and discriminative ability under regional differences, as shown in Figure 5. During the training process, the accuracy of the validation set continues to increase, while the loss value steadily decreases. After about 300 rounds of training, the model converged without significant overfitting or underfitting, verifying the rationality of the training strategy and the stability of the model’s performance [45].
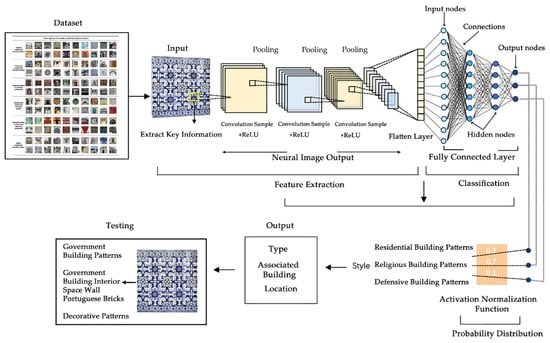
Figure 5.
AI recognition workflow of decorative patterns from six types of historical buildings in Macao.
3.2. Training Results
3.2.1. Evaluation Metrics for Classification Performance
To comprehensively evaluate the model’s performance in the classification of decorative patterns from historical buildings in Macau, four commonly used classification metrics were adopted: accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. A systematic evaluation was conducted, based on the results on the test set. The ConvNeXt-L model achieved an overall accuracy of 82.0% on the test set, indicating strong general recognition capability. However, there is still room for improvement in certain architectural categories, particularly in distinguishing between government and defensive buildings.
The experimental results are as follows:
- (1)
- Accuracy
The model achieved an accuracy of 81.0% on the religious building subset of the test set. This category-specific accuracy reflects the influence of class imbalance in the dataset, which contributes to the model’s superior performance in certain dominant categories [46].
- (2)
- Precision
Precision measures the proportion of correctly predicted samples among all samples predicted as a given class. The model demonstrated the highest precision for religious buildings, while the precision for government buildings was relatively lower, indicating a tendency toward misclassification of government-related patterns as other categories.
- (3)
- Recall rate
Recall assesses the model’s ability to correctly identify all instances of a specific class. The recall for religious buildings was the highest, suggesting strong detection capability for this class. In contrast, the recall for defensive buildings was the lowest, indicating the model’s limited ability to identify this class—likely due to insufficient training samples or less distinctive visual features.
- (4)
- F1-score
The F1-score, as the harmonic mean of precision and recall, provides a balanced evaluation of classification performance. The highest F1-score was achieved for religious buildings, indicating the best overall classification results in this category. Conversely, the relatively lower F1-scores for government and defensive buildings reveal classification bias, likely stemming from class imbalance or insufficient feature representation. Future improvements may involve strategies such as data augmentation, class reweighting, or enhanced feature-extraction mechanisms to improve performance in challenging categories [47].
3.2.2. Overall Classification Results
Upon completion of training on the training and validation sets, the model was evaluated with the test set to assess its performance. Here, True Positive (TP) denotes the number of correctly predicted positive instances for class *i*, False Positive (FP) refers to the number of incorrectly predicted positive instances for class *i*, False Negative (FN) indicates the number of positive instances for class *i* that were incorrectly predicted as negative, and True Negative (TN) represents the number of correctly predicted negative instances for class *i*.
The formulas are as follows:
This metric is widely used in tasks such as object detection and image classification to evaluate the overall performance of a model. Religious buildings achieved the highest F1-score, indicating a superior comprehensive performance of the model in this category. In contrast, government and military buildings obtained relatively lower F1-scores, suggesting that the model’s performance in these two categories requires further improvement [48].
The evaluation metrics are formally defined as follows (applicable to all six categories). Given the issue of class imbalance, both macro-average and weighted average metrics are reported in this study.
Macro-average:
Weighted average (weighted by the number of samples in the test set):
The classification performance evaluation results of the ConvNeXt-L model are presented in Table 3. A comprehensive analysis of various metrics indicates significant performance disparities across different architectural categories.

Table 3.
Classification performance of ConvNeXt-L model on test set.
In terms of macro-average metrics, the model demonstrates a moderate overall classification performance, with a macro-precision of 49.57%, a macro-recall of 46.83%, and a macro-F1-score of 45.80%. These results suggest that there is substantial room for improvement in the six-class architectural image classification task.
Notably, the weighted-average metrics are significantly higher than the macro-average values, with a weighted precision of 68.06%, a weighted recall of 67.13%, and a weighted F1-score of 61.97%. This discrepancy primarily stems from the inherent class imbalance in the dataset: religious architecture (52.37%) and residential architecture (28.63%) collectively account for over 80% of the total samples, and the model performs relatively well in these categories (achieving F1-scores of 0.736 and 0.538, respectively), thereby elevating the overall weighted performance.
At the category level, religious architecture achieves the most outstanding classification performance, with both precision and recall reaching 81.0%, and an F1-score of 0.736, indicating high recognition accuracy and consistency for this category. In contrast, government and military buildings show considerably poorer classification results, with F1-scores of only 0.335 and 0.320, respectively, reflecting the model’s weaker discriminative capability in these categories. This performance gap arises from their limited sample sizes (collectively comprising less than 5% of the dataset), which hinders the model’s ability to learn effective distinctive features.
In summary, the ConvNeXt-L model exhibits a clear category-dependent performance in the architectural image classification task, performing well in categories with sufficient samples and distinctive features, but requiring further improvement on categories with limited samples and high inter-class similarity.
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Model Performance
3.3.1. Overall Performance Comparison
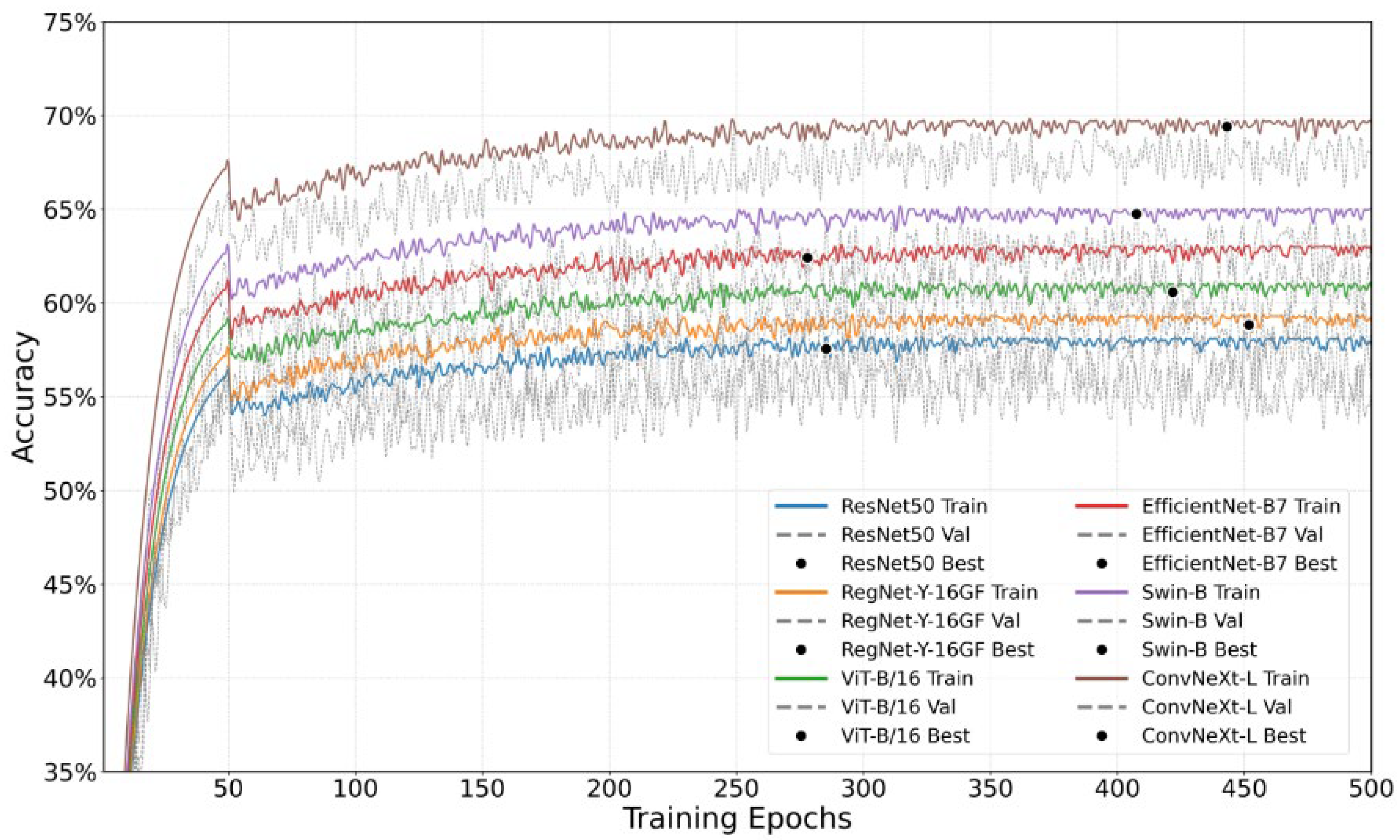
To comprehensively evaluate the performance of the ConvNeXt-L model in the classification of decorative patterns in historical buildings in Macau, we conducted a comparative experiment with consistent dataset and training configurations. Six state-of-the-art deep learning models were selected for benchmarking: ResNet50, EfficientNet-B7, ViT-B/16, Swin-B, RegNet-Y-16GF, and the proposed ConvNeXt-L. These models differ significantly in terms of architectural design, receptive field control, parameter complexity, and representational capacity, and collectively reflect the latest developments in both convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs). The test results for each model—focusing on the “Religious Building” category as a representative case—are shown in Figure 6.
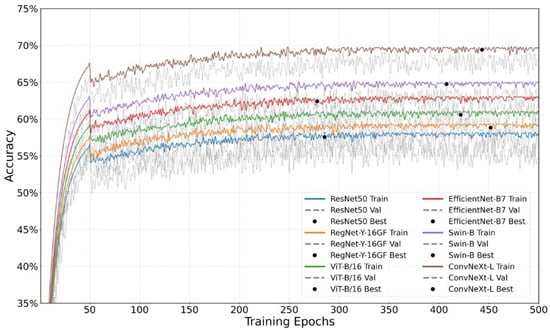
Figure 6.
Comparison of accuracy between different networks in training set and validation set. Note: Gray represents the training set, while color indicates the validation set.
To ensure the reliability of the results and statistical significance, each model was independently trained and evaluated using five different random seeds (42, 2024, 1024, 2048, and 4096). The mean values and standard deviations of the performance metrics are reported. A paired t-test was conducted to assess the statistical significance of differences between ConvNeXt-L and other models across all evaluation metrics, with the significance level set at α = 0.05.
As shown in Table 4, ConvNeXt-L achieved the best classification performance in the test set, with an accuracy of 69.7 ± 0.7%, a macro-average precision of 49.57 ± 0.6%, and a macro-average recall of 46.83 ± 2%. Statistical testing confirmed that its performance was significantly superior to all baseline models (p < 0.05). The Swin-B model ranked second, with corresponding values of 63.0 ± 1.1%, 47.2 ± 0.5%, and 46.73 ± 0.5%, yet it still showed a significant performance gap compared to ConvNeXt-L. Among traditional CNN models, EfficientNet-B7 outperformed ViT-B/16 and ResNet50, benefiting from its neural architecture search-based design optimization. In contrast, RegNet-Y-16GF and ResNet50 delivered relatively weaker results, highlighting the consistent improvement in classification performance brought by advances in model architecture.

Table 4.
Test evaluation results of each model.
The superior performance of ConvNeXt-L can be attributed to its integration of modern Transformer-inspired design elements, including depth-wise separable convolutions, Layer Normalization (Layer Norm), and more advanced downsampling strategies. These innovations enhance the model’s capacity to represent multi-scale decorative pattern features, while maintaining the efficiency and scalability of convolutional operations.
These results consistently demonstrate that the ConvNeXt-L model not only exhibits a strong discriminative capability but also delivers a robust generalization performance in the task of classifying decorative patterns of historical architectures in Macao. It thereby offers a more reliable technical pathway for the automated identification and digital preservation of cultural heritage.
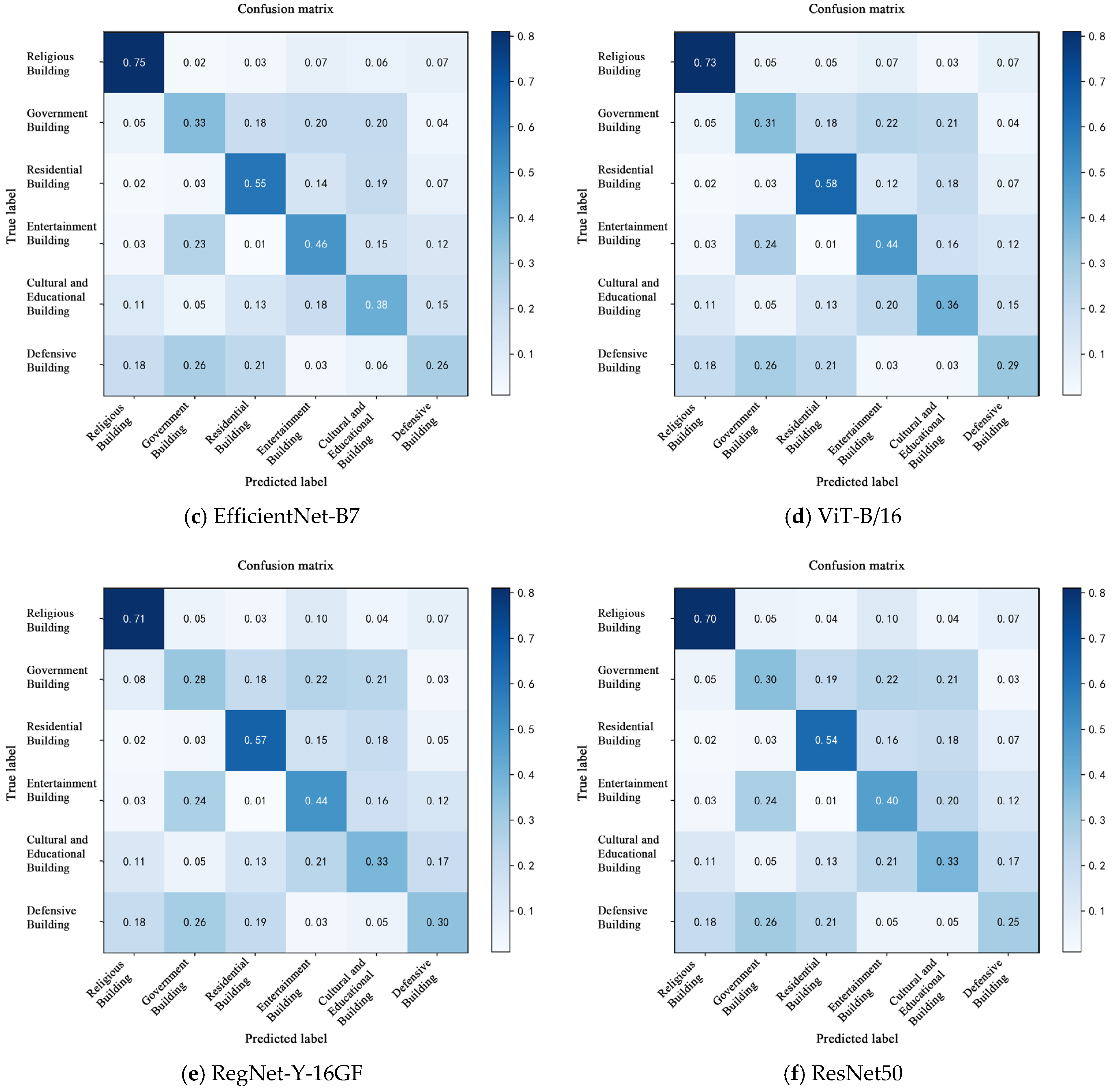
3.3.2. Confusion Matrix
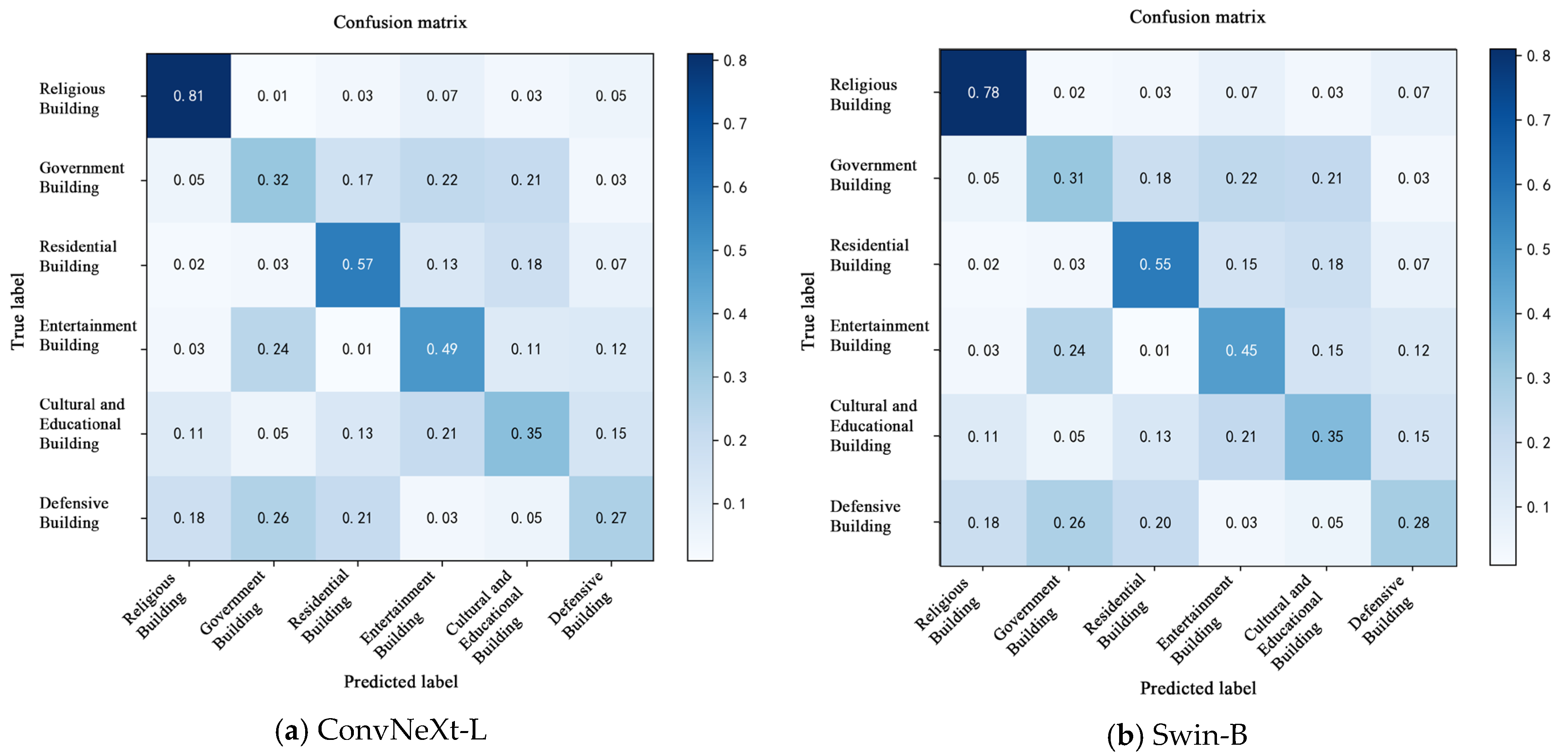
To further analyze the model’s classification accuracy and misclassification patterns across different categories, a confusion matrix was constructed based on the predictions on the test set, as shown in Figure 7. By comparing the distribution of true labels and predicted labels among architectural categories, the model’s discriminative capability for each class can be assessed more comprehensively [49]. The model’s prediction results for the test set are summarized.
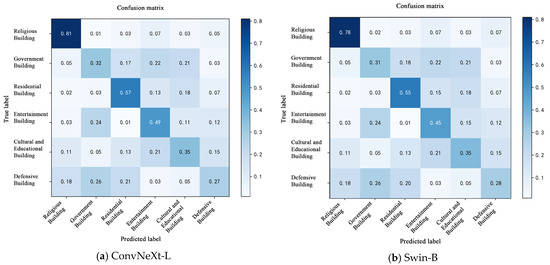
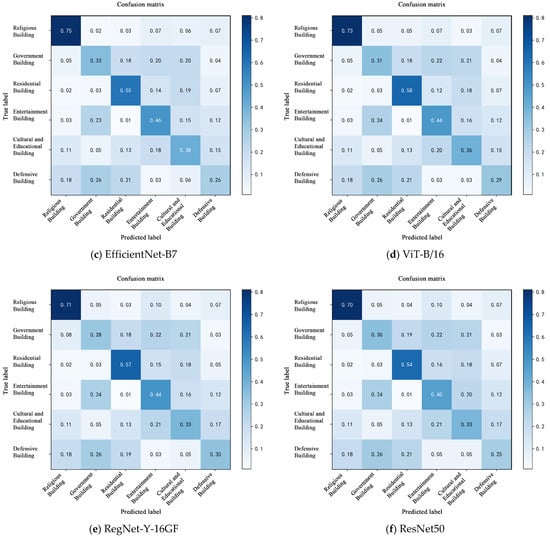
Figure 7.
Confusion matrix of ConvNeXt-L model classification results.
Overall, the proposed ConvNeXt-L model demonstrated higher classification accuracy across all six architectural categories with reduced inter-class confusion. It notably outperformed other models in discriminating between religious and educational structures, highlighting its superior capability for modeling intricate decorative patterns. In contrast, ResNet50 and RegNet-Y-16GF exhibited more pronounced confusion, particularly between government and recreational buildings, indicating their limited ability to differentiate fine-grained local visual features. While EfficientNet-B7 and Swin-B showed competitive performances in certain categories such as residential buildings, they still suffered from high misclassification rates in underrepresented classes like defensive structures, reflecting a sensitivity to class imbalance [50]. It is notable that the Transformer-based ViT-B/16 model demonstrated certain capabilities in global contextual awareness, such as in classifying recreational buildings. However, it exhibited instability in categories with dense patterns or highly textured variations, such as religious structures, indicating a limited generalization capability in fine-grained decorative pattern classification. In contrast, the ConvNeXt-L model not only achieved the highest overall classification accuracy but also outperformed competing models in terms of inter-class distribution balance, sample boundary clarity, and sensitivity to salient regions, validating its effectiveness and robustness in classifying complex decorative patterns of historical architectures.
3.4. Grad-CAM Visualization Analysis
To gain deeper insights into the discriminative mechanisms and element comprehension capabilities of the model in the task of classifying decorative patterns of historical architectures in Macao, in this study, we employ the Grad-CAM (Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping) method. By backpropagating gradients from the final convolutional layer, a class activation heatmap is generated to visualize the image regions that are the most influential for the model’s predictions, thereby providing an intuitive interpretation of the model’s decision criteria [51]. The heatmap is computed by multiplying each feature map by its corresponding weight and summing over all channels, as formalized in Equation (11).
denotes the k-th feature map of the last convolutional layer in a CNN, representing different visual features such as edges and textures. The weight wkcwkc reflects the importance of the k-th feature map for class c, obtained by computing the gradient of the class score with respect to the feature map. The weighted sum yields a coarse heatmap, highlighting relevant regions. A ReLU activation function is applied to filter out negative values, retaining only areas that positively contribute to predicting class c. The resulting heatmap shares the same spatial resolution as the convolutional feature maps and is typically upsampled (e.g., via bilinear interpolation) and overlaid on the original input image to produce the final visualization [52].
3.4.1. ConvNeXt-L Model
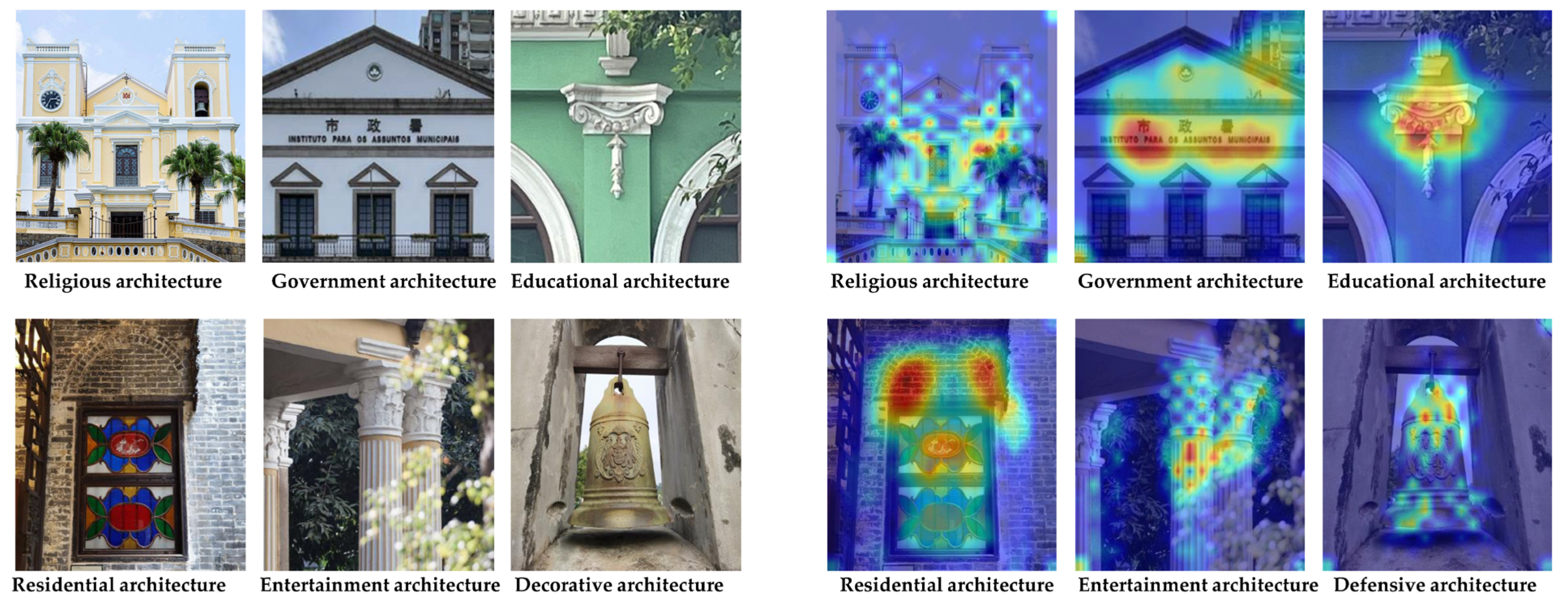
The visualization results demonstrate that the ConvNeXt-L model employed in this study exhibits highly concentrated attention distributions across multiple architectural categories, effectively focusing on representative local pattern regions. As shown in Figure 8, red areas indicate regions of high model attention, while blue areas correspond to regions of lower attention. The features in attention regions for “religious buildings” and “residential buildings” are the most stable and consistent, whereas those for “government buildings” and “defensive buildings” appear more scattered or ambiguous, leading to a reduced classification performance. These findings indicate that the effectiveness of the model in architectural pattern classification not only depends on the depth of the convolutional neural network but is also closely related to the recognition difficulty of patterns across categories and the data distribution. Therefore, for categories with unstable attention regions, future work may incorporate methods, such as pattern region enhancement, comparative learning of features, and data balancing strategies, to further improve model performance [53].

Figure 8.
Grad-CAM heatmaps of the ConvNeXt-L model. Color Semantics: Warm tones (red to yellow) indicate high-density usage and core activity areas; cool tones (blue to green) correspond to areas of low utilization and peripheral zones.
3.4.2. Analysis of Attention Region Characteristics in Grad-CAM Heatmaps Across Models and Building Categories
- (1)
- Analysis of Attention Regions in Grad-CAM Heatmaps.
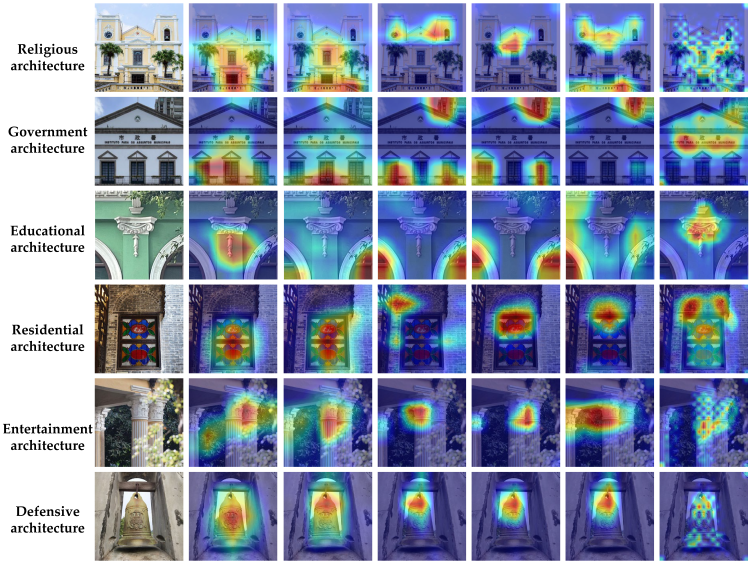
Table 5 presents the Grad-CAM visualization results of six architectural categories across different models. The heatmaps highlight the regions within the input images that are the most critical for the model’s classification decisions. These visualizations were generated from the final convolutional layer of each model. A unified color bar (on the right) is applied across all heatmaps, where warm colors (red) indicate higher importance and cool colors (blue) represent lower relevance.

Table 5.
Original image and visualized feature heat map of six types of historical building decoration patterns.
As shown in the heatmaps, the ConvNeXt-L model demonstrates superior interpretability and stability in recognizing decorative patterns of Macau’s historical buildings across all six categories [54]. This model exhibits not only highly concentrated attention regions that are closely aligned with elementally critical areas—such as gables, bell towers, and window decorations—but also enhanced clarity in boundary localization and spatial layout modeling. This enables a more effective differentiation of architecture types that feature dense details or stylistic similarity, confirming the model’s strong capabilities in deep element extraction and structural perception. In contrast, conventional CNN architectures such as ResNet50 and RegNet-Y-16GF suffer from issues such as misaligned attention, scattered heatmaps, and lack of consistency. These problems are particularly evident in the residential and defensive categories, where the response to structural details is unstable, indicating limitations in their element representation of complex decorative elements [55]. Although EfficientNet-B7 has a good alignment of hot zones in some categories (such as government buildings), boundary blurring and oversimplification of patterns still affect the interpretability of the model. The ViT-B/16 and Swin-B structures of a Transformer have certain advantages in modeling the overall contour of buildings, but their performance in fine-grained image tasks is limited by the problems of scattered hot zones and insufficient attention to key decorative parts [56]. Overall, the results indicate that ConvNeXt-L not only outperforms other models in quantitative performance metrics but also demonstrates greater stability and discriminative power in terms of model interpretability, making it the most effective model for decorative pattern recognition in this study.
- (2)
- Performance Characteristics of Different Model Architectures.
According to both the experimental results presented in Table 6 and the Grad-CAM visualizations, ResNet50, as a classical residual network, performs stably in shallow pattern recognition tasks and demonstrates certain capabilities in edge and texture extraction. However, its limited ability to represent complex structures reduces classification accuracy in building types rich in decorative elements [57]. EfficientNet-B7, which utilizes a compound scaling strategy, achieves high parameter efficiency and performs well on standard samples. Nevertheless, it tends to underfit on densely patterned or structurally complex images, often resulting in blurred and diffuse prediction regions. RegNet-Y-16GF maintains a good balance between model depth and computational efficiency, making it suitable for tasks of moderate complexity. However, its class activation maps tend to be widely distributed, and focus misalignment remains a challenge in fine-grained classification. Transformer-based models such as ViT-B/16 and Swin-B excel at modeling global relationships within images and outperform conventional convolutional models in spatial structure modeling. However, they are more sensitive to small datasets, exhibit slower convergence during training, and are less precise in recognizing local decorative patterns [58]. In contrast, ConvNeXt-L integrates the strengths of convolutional structures and self-attention mechanisms, significantly enhancing the model’s ability to perceive multi-scale structural information in architectural decorative patterns. Its Grad-CAM heatmaps across all six building categories show well-focused attention regions and clearly defined classification boundaries. Overall, ConvNeXt-L outperforms the other models in both quantitative metrics and interpretability, demonstrating stronger discriminative and generalization capabilities.

Table 6.
Comparative analysis table of Grad-CAM visualizations across different models.
Furthermore, Grad-CAM visualizations reveal that the model’s attention regions align closely with the elemental structure of decorative patterns, demonstrating strong cultural-element consistency. For instance, in government buildings, the model accurately focuses on emblematic and power-symbolic elements, such as insignias and gables; in religious structures, it consistently identifies faith-related motifs, including altars and spires; and in residential and cultural buildings, it exhibits clear element awareness toward daily life and identificatory decorations, such as window lattices and inscribed tablets. This sensitivity to cultural elements not only validates the model’s effectiveness for structural recognition but also indicates its potential to discern the cultural connotations behind decorative patterns, thereby offering a novel approach for symbolic interpretations and value explorations of architectural heritage.
At the same time, in order to further elaborate on the cultural element dimensions of patterns and the induction and analysis of visual features, the following characteristics can be summarized:
- (1)
- Pattern scale and structure.
The relative scale characteristics and structural features of patterns are two important indicators. The relative scale feature can define the area ratio between the pattern and the attached building’s structural components and can measure the level attributes of the pattern. In residential buildings, the scale and proportion of patterns such as lintels and window frames are more diverse, reflecting the flexibility and regional characteristics of folk craftsmanship. The decorative patterns in government buildings are more regular and are mostly concentrated at the central axis of the building space, creating a sense of solemnity in the patterns.
- (2)
- Surface texture and material.
In response to the lack of corresponding physical materials in pattern classification, this study focuses on the visual representation characteristics of wood carvings, with a focus on capturing the direction of surface materials, the particle state of stone carvings, and the degree of reflection on the surface of the material. By optimizing texture features and classification objectives, establishing implicit mappings between visual features and material processes, and completing the inference of material cultural attributes, cultural dimensions are ensured to run through the entire process of feature extraction, interaction, and decision-making.
- (3)
- Grad CAM verification corresponds to cultural elements.
According to Grad CAM visualization, the attention area of the model is closely integrated with the element structure of decorative patterns, exhibiting a certain degree of cultural element consistency. In government buildings, models often focus on symbolic and power symbolic elements, such as badges and mountain walls. In religious architecture, it is easy to identify patterns related to faith, including altars and spires. In residential and cultural buildings, it exhibits a clear element awareness towards daily life and iconic decorations, such as window frames and plaques. However, the consistency of this cultural element is still limited to feature extraction at the visual level, and a deep understanding of material craftsmanship and historical context has not yet been fully achieved. Therefore, further expansion is needed in future research.
3.4.3. Quantitative Analysis of Grad-CAM Interpretability
To objectively quantify the interpretability of different models, in this study, we introduced the Top-K localization score as a quantitative evaluation metric. This metric aims to measure the overlap between the model’s Grad-CAM attention maps and human-annotated “salient regions”. Specifically, Grad-CAM visualizations were generated for all models across the six architectural categories, and the Intersection over Union (IoU) was computed with the top 10% most activated pixels in each attention map and the manually annotated bounding boxes of decorative patterns. These quantitative results corroborate our earlier qualitative analysis (see Figure 6 and Table 6), providing more compelling objective evidence for interpreting the decision-making process of the models.
As shown in the table below, ConvNeXt-L achieved the highest average localization score across all six categories, with an overall mean IoU of 86.1%, confirming its superior ability to focus on and discriminate complex decorative patterns. Its heatmaps not only highly concentrate on key element regions but also exhibit clear boundaries that align closely with human-annotated salient areas. In contrast, other models showed various limitations in localization precision. Traditional CNN models (e.g., ResNet50 and RegNet-Y-16GF) generally yielded lower localization scores, indicating dispersed attention distributions and difficulty in effectively capturing fine-grained decorative details, particularly in categories such as “defensive structures” and “geometric patterns”.
While demonstrating certain advantages in some categories (e.g., “government buildings”), Transformer-based models (e.g., ViT-B/16 and Swin-B) often produced attention regions that were too broad or imprecise, resulting in overall lower localization scores compared to ConvNeXt-L. This reflects their limitations in handling fine-grained textures and complex local patterns. Although EfficientNet-B7 achieved higher localization scores than some models, its heatmaps suffered from blurred boundaries and a lack of sharpness, consistent with the underfitting issues observed in qualitative analysis.
In summary, the quantitative results further validate the superiority of ConvNeXt-L in model interpretability. While maintaining high classification accuracy, it more precisely localizes core decorative patterns in images, thereby providing strong support for the reliability of model predictions.
4. Discussion
This study mainly focuses on the classification and recognition of decorative patterns in historical buildings in Macau. We have constructed an image dataset with regional characteristics of China and Portugal and combined it with ConvNeXt-L’s deep learning model to visualize and analyze the generation process and core elements of pattern recognition using Grad CAM, in order to assist urban planning and development decision-making. With the increasing penetration of artificial intelligence, this study provides a new method and approach for digital protection and intelligent identification for urban heritage protection and planning decision-making. The main conclusions are as follows.
The ConvNeXt-L model can outperform existing mainstream architecture and achieves 82.0% classification accuracy and better interpretability. This validates the effectiveness and robustness of the model as a stronger alternative for tackling complex decorative pattern recognition challenges. Based on the experimental results, the performance of a model is correlated with the scale of the parameters. Thus, the model exhibits strong scalability. It can also adapt to varying parameter scales. Decorative building patterns in historical Macau are typically complex in shape, dense in texture, and a mixture of Chinese and Western styles, which has a greater demand on the model to learn local and global contexts. Because the ConvNeXt-L model integrates depth-wise separable convolutions with self-attention like mechanisms, it naturally adapts to capture multi-level element features. Parameter scaling helps the system adapt better to the dataset’s multi-feature and multi-style distribution patterns, improving recognition stability.
Grad-CAM results show that the model’s attention area is highly consistent with the elemental structure of decorative patterns in classification and recognition. Training shows that the model has strong element perception ability. This further validates the effectiveness of the research method and its practical potential for the identification and digital protection of historical, architectural, and cultural heritage. We ensured that these data reflect both spatial structure and esthetic value.
From the perspective of the practice of protecting and updating historical urban areas, the research results are of great significance for the decision-making of cultural heritage protection and the transformation of architectural archives and decorative pattern design with the assistance of artificial intelligence. Through the effective recognition of artificial intelligence, the high-precision automatic recognition efficiency of historical building decoration patterns has been improved, reducing the dependence upon manual classification records, accelerating the collection of heritage resources, and providing further in-depth research foundations for design innovation. In addition, frameworks based on graph neural networks, multimodal fusion, or multitask learning can address the ability to generalize across different architectural styles, promoting the transition of digital preservation from traditional “static archiving” to “dynamic revival”.
For future research, we will identify more robust methods for discovering underrepresented pattern categories, use information on elements with manual annotations, and use generative models to sample new traits/elements that are not in the data but still validate the traits within the data. While the existing architecture achieves a satisfactory performance in several metrics, multimodal extension and the regional attention mechanism will be the focus of future work for further enhancing its discriminative ability. Simultaneously, as the unique maritime culture of Macau and the trade culture of the Maritime Silk Road is reflected in these elements, the cultural narratives, layered meanings, and symbolic connotations will feel much more sophisticated and will reveal the true value of semantic understanding. Future research will develop interdisciplinary interpretive paradigms. The paradigms will integrate quantitative analysis of visual narrative elements with richer materials. The materials will include historical documents, oral history, and navigation logs to form a deep semantic knowledge map of Macau World Cultural Heritage. These improvements will help to develop trustworthy and transparent decision-making tools in the context of heritage in the smart city context and lead to the establishment of sustainable data-driven cultural heritage plans.
5. Conclusions
The conservation of urban heritage and the landscape is greatly affected by the decorative patterns. The UNESCO World Cultural Heritage Site in Macau serves as a testimony to the successful blending of Chinese and Western decorative architectural styles. The complexity and stylistic diversity of these patterns make it very challenging to classify them accurately.
In this study, we proposed a ConvNeXt-L–based framework to classify decorative patterns according to the functional typology of the buildings. Comparative experiments involving six mainstream models—ResNet50, EfficientNet-B7, ViT-B/16, Swin-B, RegNet-Y-16GF, and ConvNeXt-L—demonstrated that ConvNeXt-L achieved the best performance in accuracy (82.0%), precision (80.2%), and recall (82.3%), highlighting its sensitivity to small-sample datasets and robust feature extraction capabilities. Through normalization and learning-rate scheduling, noise can be reduced, and model convergence can be accelerated, while transfer learning and contrastive learning pre-training further improve classification and recognition accuracy performance. Future research should integrate multimodal data sources, including literature, pattern and structural analysis, material properties, and spatial distribution, while exploring advanced methods such as region-based attention mechanisms and enhanced contrastive learning to improve discrimination ability. A historical architectural decoration pattern database, which integrates Chinese and Portuguese cultures, will be established in combination with new artificial intelligence technologies. This will not only facilitate the protection of historical buildings and regional culture dissemination but also extend its application to modern urban architectural design and cultural tourism experience upgrading, as well as public science education through derivative innovative design. These traditional decorative elements can be integrated into contemporary architectural creation, fostering a deeper integration of cultural heritage and modern urban development and ultimately enabling a holistic approach to heritage preservation.
This study not only achieved accurate recognition of decorative patterns in historical buildings from multicultural backgrounds, but also provided a reference for the protection of cultural heritage data in other cities. The development of objective parameter indicators can help smart city planning and cultural heritage policy formulation based on data, which benefits the sustainable protection and innovative development of the World Cultural Heritage Site of Macau.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.F. and L.X.; Data Curation, J.Z., L.X. and K.L.; Formal Analysis, J.Z. and L.X.; Funding Acquisition, J.Z.; Investigation, L.X.; Methodology, J.Z. and P.F.; Project Administration, P.F., L.X. and K.L.; Resources, P.F.; Software, J.Z.; Supervision, L.X. and K.L.; Validation, J.Z. and L.X.; Visualization, L.X. and K.L.; Writing—Original Draft, J.Z. and L.X.; Writing—Review and Editing, J.Z., P.F., L.X. and K.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by (1) Key Project of the Ministry of Education’s Special Project for Outstanding Traditional Chinese Culture (Category A): “Interweaving and Symbiosis: A Study on Architectural Decoration in the Historic Centre of Macao” (Project of the Nishan World Center for Confucian Studies/China Confucius Foundation (23JDTCA010). (2) Guangdong Province Philosophy and Social Sciences Planning Project: “Innovative Application Research on Decorative Patterns of Macao’s Historic Buildings from the Perspective of Artificial Intelligence (AI)” (Lingnan Culture Project of the Guangdong Provincial Philosophy and Social Sciences Planning Leading Group Office (GD25LN32). (3) 2024 Guangdong Provincial Higher Education Innovation Team Project (Social Sciences) Platform and Project: “Cultural Heritage and Intelligent Design Innovation Team” (2024WCXTD029). (4) Research Capacity Enhancement Project for the 2022 Doctoral Program Construction Units at Guangdong Polytechnic Normal University (22GPNUZDJS59 and 22GPNUZDJS58). (5) 2020 Provincial First-Class Undergraduate Program of the Ministry of Education (Environmental Design Major), Provincial First-Class Undergraduate Course “Landscape Design Foundation” (991710368). (6) 2021 University-Level Research Project Talent Special Fund of Guangdong Polytechnic Normal University—Research on the Optimization of Public Green Space Layout in Macao (2021SDKYB058). (7) Guangdong Polytechnic Normal University Scientific Research Start-up Fund (99166990233). (8) Guangdong Polytechnic Normal University Horizontal Research Project—Research and Development of Green, Eco-friendly, and Energy-Saving Landscape Lighting Devices (1747379).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
This research was assisted by the City University of Macau.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Kuan Liu was employed by the company Pelli Clarke & Partners. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Liang, S. History of Chinese Architecture; Guizhou People’s Publishing House: Guiyang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F. Stories of Macau Historic Architecture; Guangdong Economic Publishing House: Guangzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J. The application of traditional patterns in the decoration of Ming and Qing architecture. Art Stud. 2015, 31, 116–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Q.; Cao, Y.; Li, Q.; Huang, C.; Wang, S. Chronological Classification of Ancient Paintings Using Appearance and Shape Features. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2014, 49, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, G.; Odobez, J.-M.; Gatica-Perez, D. How to Tell Ancient Signs Apart? Recognizing and Visualizing Maya Glyphs with CNNs. J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2018, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajol, S.I.; Hasan, A.S.M.J.; Islam, S.; Rahman, S. A ConvNeXt V2 Approach to Document Image Analysis: Enhancing High-Accuracy Classification. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 3rd Conference on Information Technology and Data Science (CITDS), Debrecen, Hungary, 26–28 August 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condoroici, R.G.; Florea, C.; Vertan, C. Automatically Classifying Paintings with Perceptually Inspired Descriptors. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2015, 26, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Johnson, B.; Lee, C. Automated Building Anomaly Detection and Degradation Prediction Using AI Models. Buildings 2023, 13, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Z. Macau Architectural Cultural Heritage; Southeast University Press: Nanjing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.-C.; Long, F.-Z. Aomen Lishi Jianzhu Beiwang Lu (Yi) (Memorandum of Macau Historical Buildings. Part 1); Yi Chan Xue Hui: Macau, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, B.B. Chronicle of Macao («Macau Chronicle»); Macao Foundation: Macao, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gunn, G.C. History of Macao, 1557–1999; Hong Kong University Press: Hong Kong, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, M. Study on Decorative Forms of Macau Architecture under Multicultural Integration. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- She, M.; Li, M.; Liang, M. Study on the Characteristics of Garden Architecture and Decorative Pieces in Macau. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2011, 27, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J. Research on Grey Sculpture Decoration of Macau Residential Buildings—Taking Lou Kau Mansion as an Example. In China Creative Design Yearbook 2020–2021; Macau University of Science and Technology, School of Humanities and Arts: Macau, 2022; pp. 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, L. Application of Elements of Macau Historical Architecture in Jewelry. Shanghai Light Ind. 2023, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, D. AI Model for Construction Waste Classification Using Data Augmentation. Buildings 2022, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, W.; Wang, Z. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Image Classification: A Comprehensive Review. Neural Comput. 2017, 29, 2352–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaowalit, O.; Kuntitan, P. Using Deep Learning for the Image Recognition of Motifs on the Center of Sukhothai Ceramics. Curr. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2021, 21, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Cai, B.; Wang, Z.; Ratti, C. Deep Learning Architect: Classification for Architectural Design through the Eye of Artificial Intelligence. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llamas, J.; Lerones, P.M.; Medina, R.; Zalama, E.; Gómez-García-Bermejo, J. Classification of Architectural Heritage Images Using Deep Learning Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeso, A.M.; Vázquez, G.M.S.; Acosta, A.A.R.; Benois-Pineau, J. Connoisseur: Classification of Styles of Mexican Archi-tectural Heritage with Deep Learning and Visual Attention Prediction. In Proceedings of the 15th International Workshop on Content-Based Multimedia Indexing (CBMI), Florence, Italy, 19–21 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C. Application of Traditional Cultural Symbols in Art Design under the Background of Artificial Intelligence. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Feng, J.; Lin, M.; Zhou, Y. Research on processing technology of Hainan Li brocade pattern elements based on MATLAB. Comput. Knowl. Technol. 2016, 12, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, D.; Ren, J.; Wang, Z.; Jin, J.S. Brushstroke based sparse hybrid convolutional neural networks for author classification of Chinese ink-wash paintings. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015; pp. 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.-T.; Tsai, M.-H. Visual Pattern Discovery for Architecture Image Classification and Product Image Search. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, Hong Kong, China, 5–8 June 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, J.L.; Kiros, J.R.; Hinton, G.E. Layer Normalization. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.06450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, H.; Feng, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, F.; Wu, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, S. MSDEnet: Multi-scale detail enhanced network based on human visual system for medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 170, 108010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Hu, Y.; Peng, F.; Feng, Z.; Yang, Y. A Geoscience-Aware Network (GASlumNet) Combining UNet and ConvNeXt for Slum Mapping. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, H.; El-Habrouk, H.; Bekheet, W.; El-Naghi, S.; Torki, M. Pixel-Level Pavement Crack Segmentation Using UAV Remote Sensing Images Based on the ConvNeXt-UPerNet. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 124, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Wu, J.; Meng, J.; Wang, W.; Wu, J. Screening of Retired Batteries with Gramian Angular Difference Fields and ConvNeXt. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 123 Part B, 106397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, Y.; Wan, T.; Yang, L.; Yu, X. A Waste Classification Model in Low-Illumination Scenes Based on ConvNeXt. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 199, 107274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Zou, Q.; Huang, K.; Li, Q. Multi-View Feature Combination for Ancient Paintings Chronological Classifi-cation. J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2017, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todi, A.; Narula, N.; Sharma, M.; Gupta, U. ConvNext: A Contemporary Architecture for Convolutional Neural Networks for Image Classification. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Innovative Sustainable Computational Technologies (CISCT), Dehradun, India, 8–9 September 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S. Batch Renormalization: Towards Reducing Minibatch Dependence in Batch-Normalized Models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 1942–1950. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.Y. Poverty Level Classification Post-Rural Flooding Disasters Using Deep Neural Networks and Transfer Learn-ing. Earth Sci.-J. China Univ. Geosci. 2023, 48, 112–125. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, C. Image Retrieval Algorithm Based on Transfer Learning. Comput. Sci. 2019, 46, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, P.; Cisse, M. ConvNets and ImageNet Beyond Accuracy: Understanding Mistakes and Uncovering Biases. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 498–512. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Q. CI-UNet: Melding ConvNeXt and Cross-Dimensional Attention for Robust Medical Image Segmentation. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2024, 14, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A ConvNet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11976–11986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; Sun, W.; Zhu, C.; Mo, Y.; Yan, S.; Zhang, C. Real-Time ConvNext-Based U-Net with Feature Infusion for Egg Microcrack Detection. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudouri, Y.E.; Bohi, A. EmoNeXt: An Adapted ConvNeXt for Facial Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE 25th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP), Poitiers, France, 27–29 September 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y. Practical Recommendations for Gradient-Based Training of Deep Architectures. In Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 437–478. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, K.; Huo, Y.; Yao, M.; Xue, L.; Wang, H. Mushroom Image Classification and Recognition Based on Improved ConvNeXt V2. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e70133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.; Debnath, S.; Hu, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Kweon, I.S.; Xie, S. ConvNeXt V2: Co-designing and Scaling ConvNets with Masked Autoencoders. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 16133–16142. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, P.; Lu, J.; Sun, Y. A ConvNeXt-Based Network for Aerial-View Geo-Localization in Multiple Environments. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on UAVs in Multimedia: Capturing the World from a New Perspective, New York, NY, USA, 28 October–1 November 2024; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Deng, H.; Xu, Q.; Lan, X. CNTR-YOLO: Improved YOLOv5 Based on ConvNext and Transformer for Aircraft Detection in Remote Sensing Images. Electronics 2023, 12, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer Using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhay, A.; Sarkar, A.; Howlader, P.; Balasubramanian, V.N. Grad-CAM++: Improved Visual Explanations for Deep Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; Hinton, G. A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Virtual, 12–18 July 2020; pp. 1597–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Donahue, J.; Jia, Y.; Vinyals, O.; Hoffman, J.; Zhang, N.; Tzeng, E.; Darrell, T. Decaf: A Deep Convolutional Activation Feature for Generic Visual Recognition. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Beijing, China, 21–26 June 2014; PMLR: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 647–655. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Du, M.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, S.; Mardziel, P.; Hu, X. Score-CAM: Score-Weighted Visual Explana-tions for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Lapedriza, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Learning Deep Features for Discriminative Localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2921–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image Is Worth 16×16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS); Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 33, pp. 11929–11942. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).