Research on the Optimization Design of Natural Ventilation in University Dormitories Based on the Healthy Building Concept: A Case Study of Xuzhou Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
Literature Review
| Design Parameters | Wind Environment Indicators | Research Methods | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Window-to-wall ratio (WWR) and window wind catcher (WWC) | Ventilation efficiency, airflow organization and patterns, CO2 concentration | CFD simulation | [30] |
| Orientation and number of floors | Indoor-outdoor pressure difference, turbulence effects and pollutant concentration | Wind tunnel experiment and CFD simulation | [31] |
| Building geometry, window geometry, and wind angle | Ventilation efficiency and indoor air velocity | Wind tunnel experiment | [32] |
| Room geometry, window geometry, occupant position | Indoor air velocity, SF6 concentration and air changes per hour | CFD simulation | [19] |
| Building form and layout, window type and opening control, wind direction and wind angle | Ventilation efficiency, Air age and indoor air velocity | CFD simulation | [16] |
| Building form and layout, orientation, window opening state | Indoor air velocity | CFD simulation | [33] |
| Window position, orientation, window opening size and type | Indoor air velocity | CFD simulation | [21] |
| Window opening behavior, orientation, window position and building envelope | Air changes per hour, Ventilation rate per person and CO2 concentration | Field measurement | [34] |
| Building type, window opening behavior and orientation | Ventilation efficiency, Air changes per hour and CO2 concentration | Field measurement | [35] |
| Window opening area and per capita space | Ventilation efficiency and CO2 concentration | Field measurement and mathematical model | [22] |
| Window type and window orientation | Air changes per hour | Field measurement and CFD simulation | [36] |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Methodology
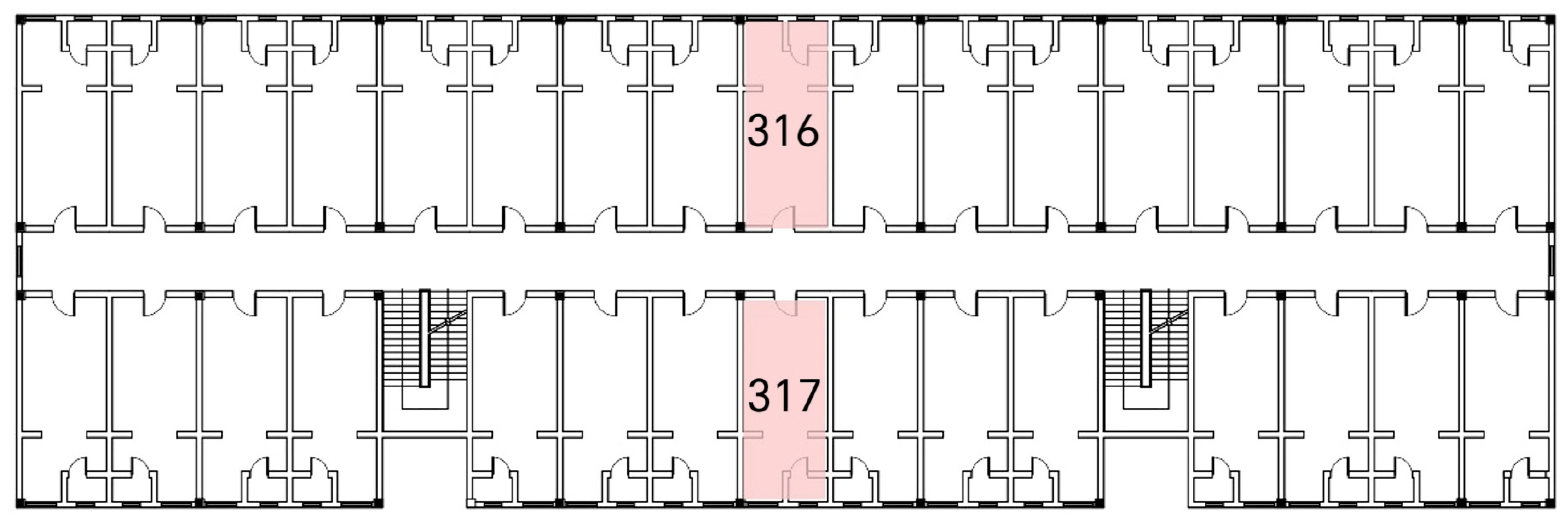
2.2. Case Overview
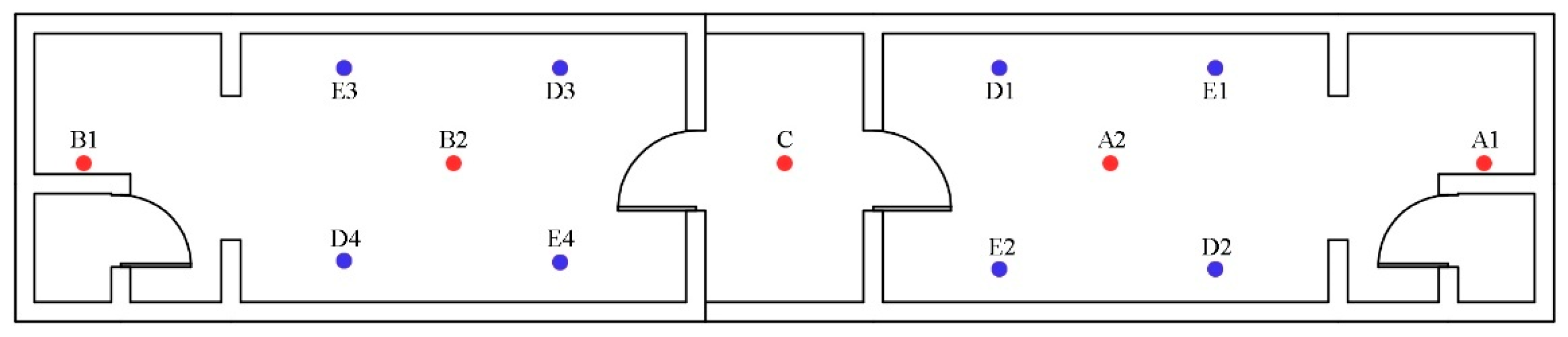
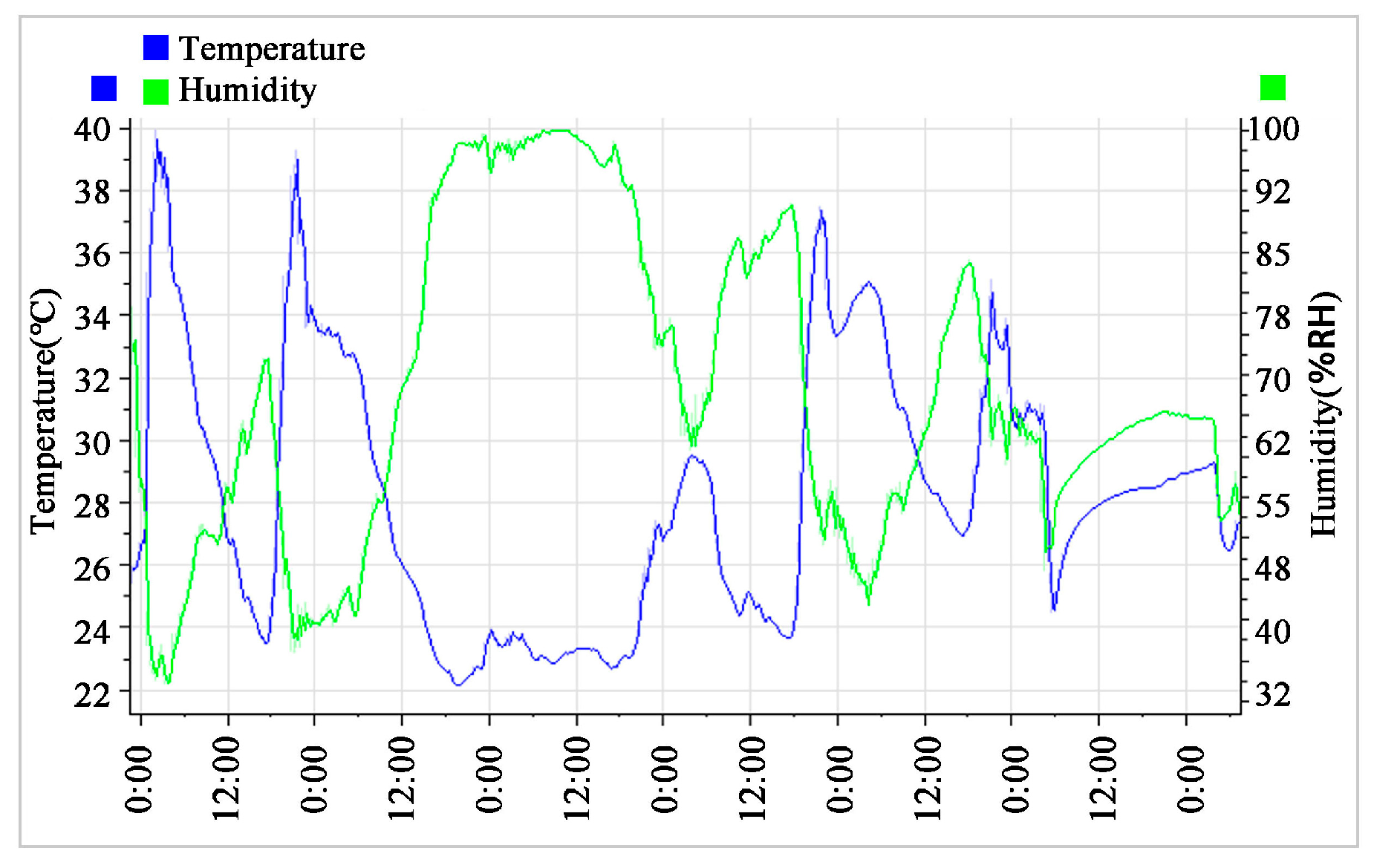
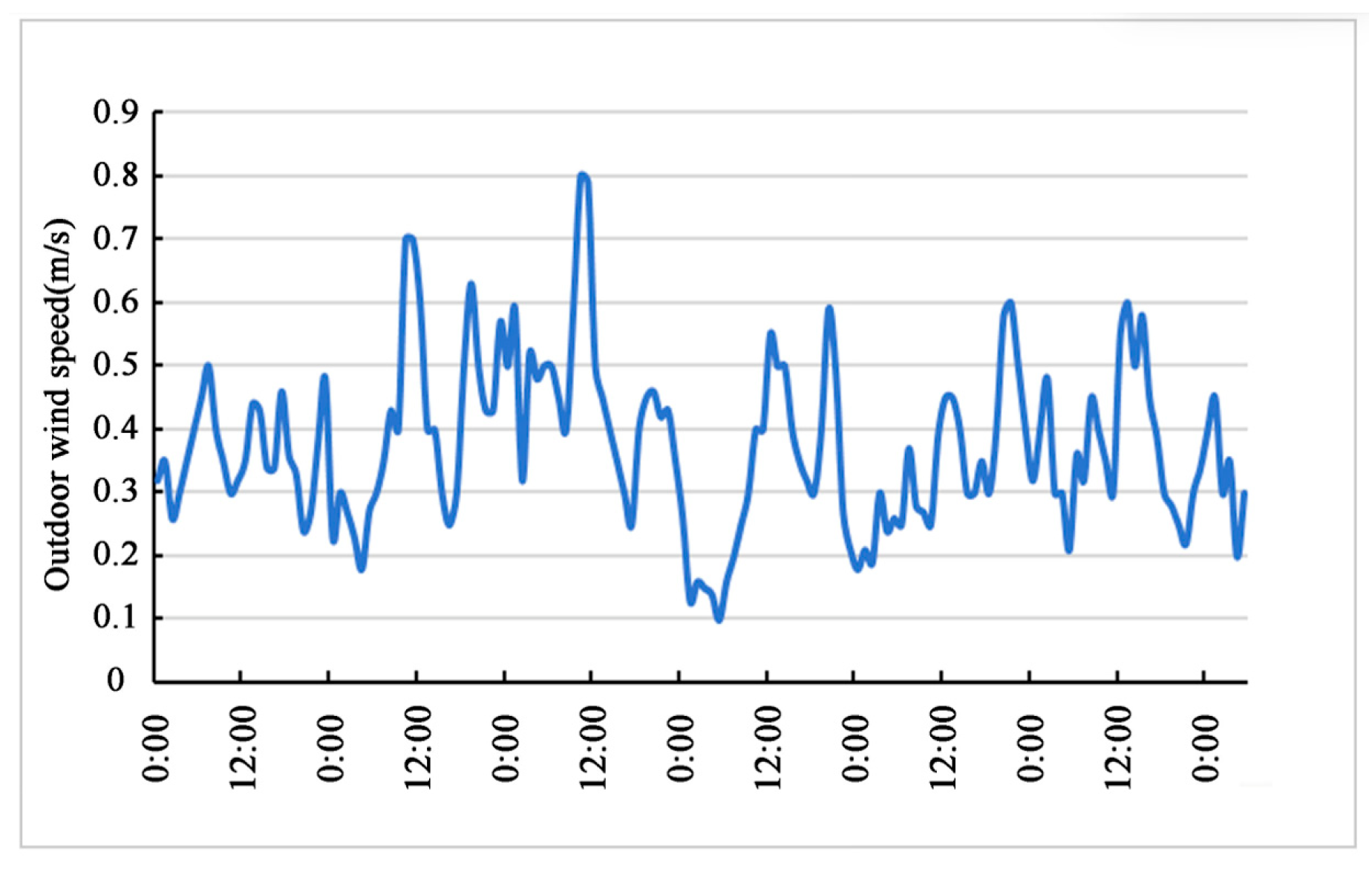
2.3. Field Measurement Scheme
2.4. Evaluation Criteria for Wind Environment
2.5. Simulation of University Dormitory Buildings in Xuzhou
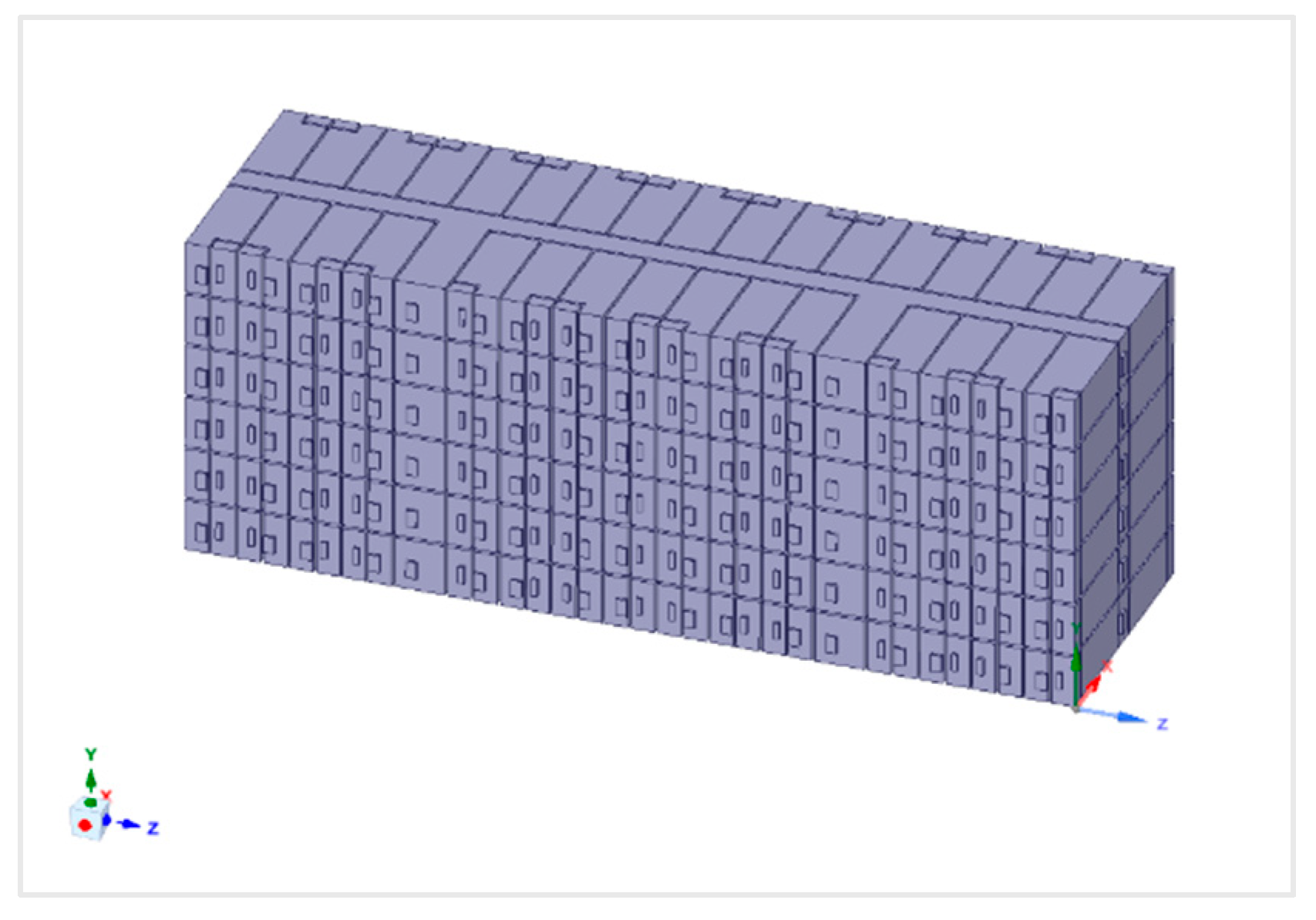
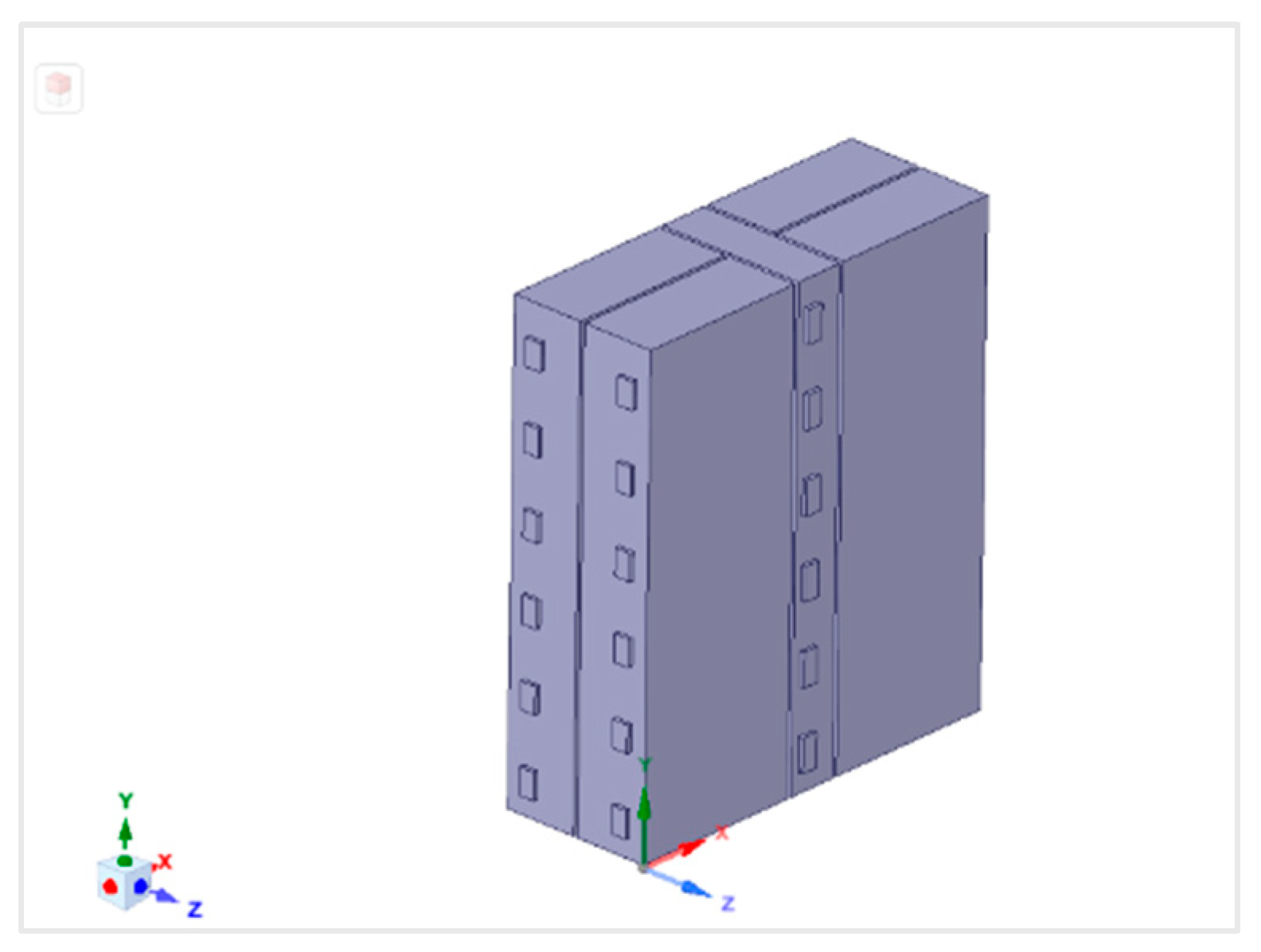
2.5.1. Establishment and Simplification of the Physical Model
2.5.2. Mesh Generation
2.5.3. Boundary Condition Settings
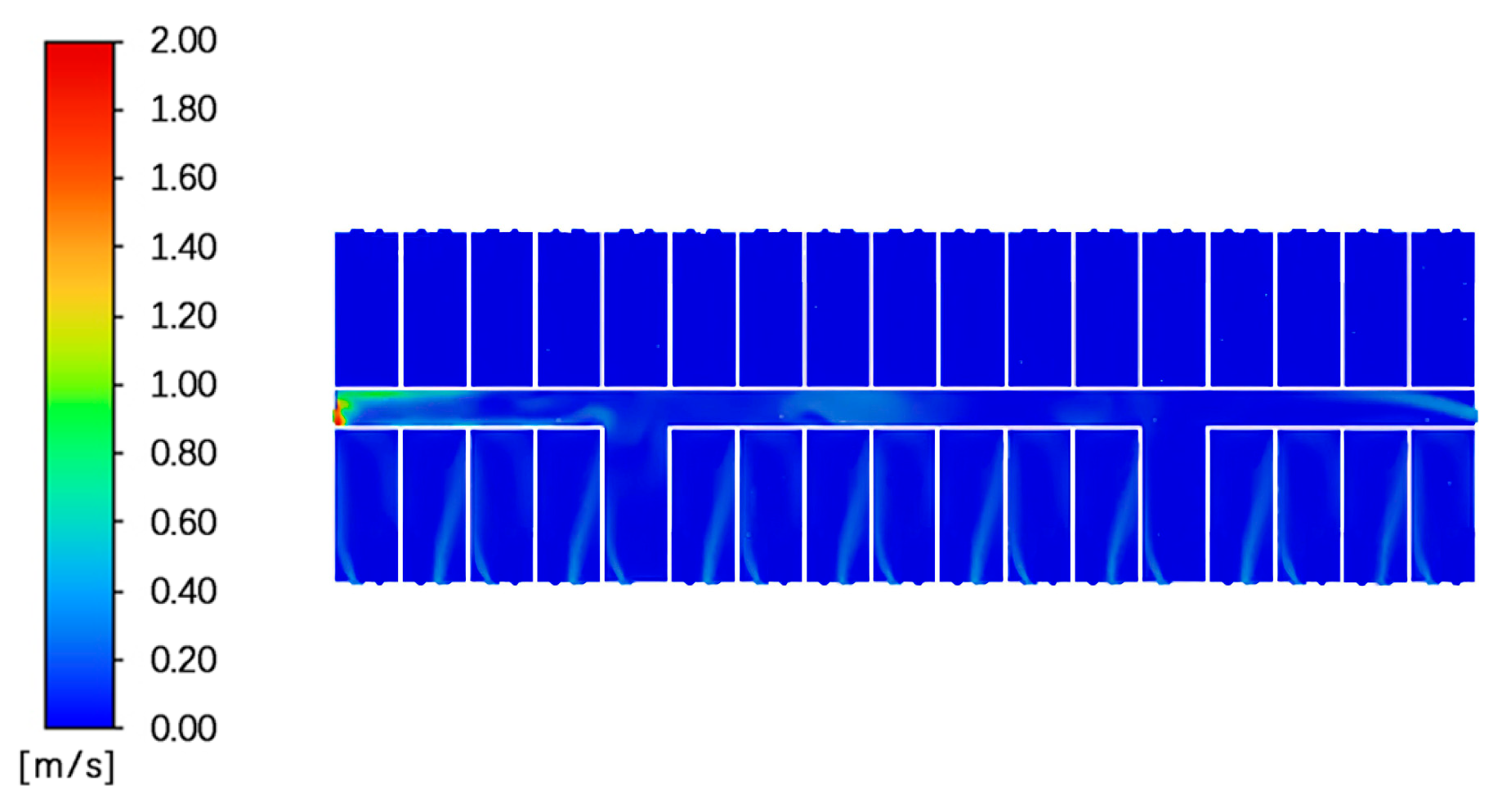
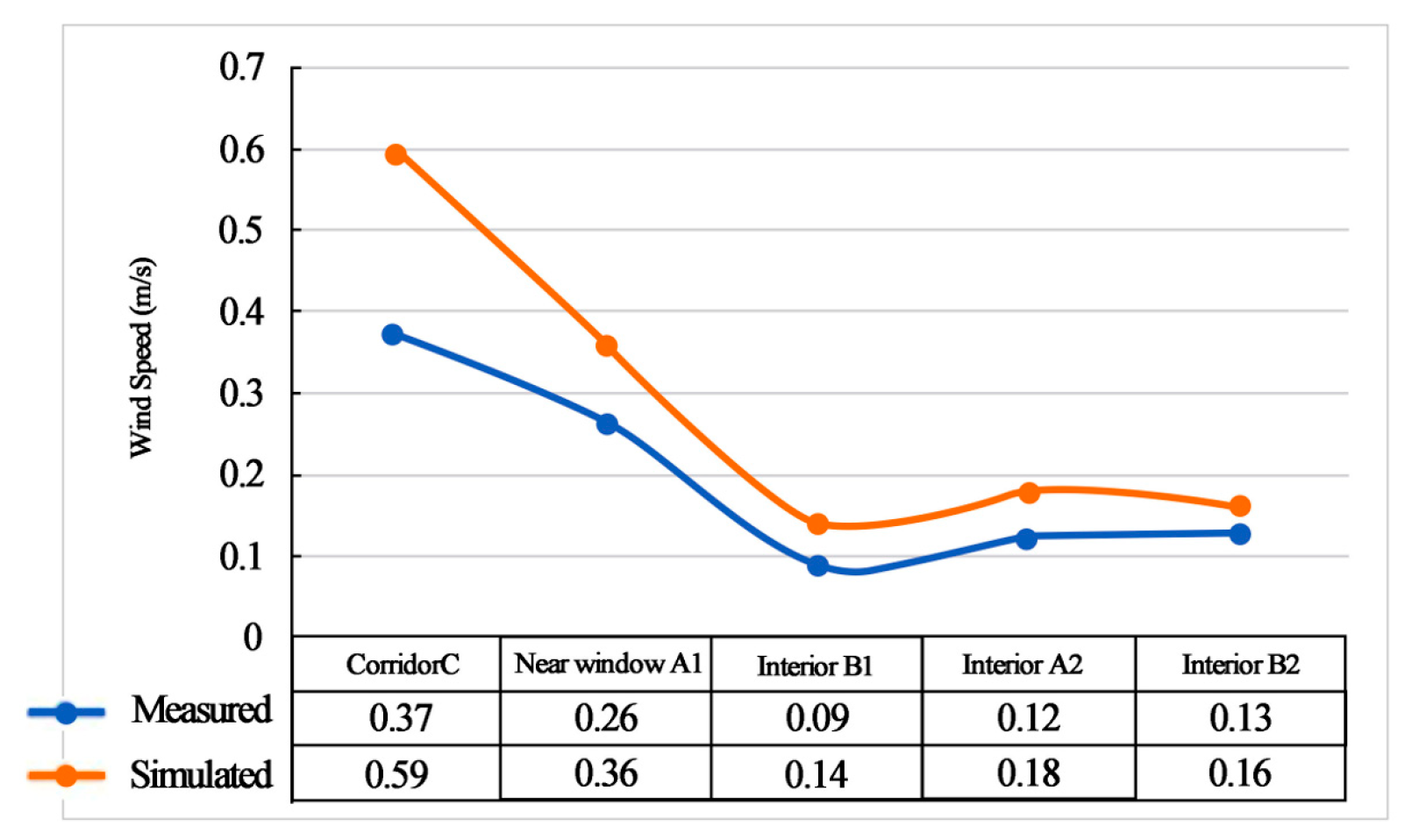
2.5.4. Validation of Software Accuracy
2.6. Introduction to the Orthogonal Simulation Method
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Factors Influencing the Wind Environment
3.1.1. Effect of Building Orientation on Natural Ventilation in Dormitories
3.1.2. Effect of Corridor Width on Natural Ventilation in Dormitories
3.1.3. Effect of Window Width on Natural Ventilation in Dormitories
3.1.4. Effect of Internal Window Height on Natural Ventilation in Dormitories
3.1.5. Effect of Window Types on Natural Ventilation in Dormitories
3.2. Analysis of Orthogonal Simulation Results
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Orthogonal Simulation Results
3.4. Analysis of Influencing Factors
3.5. Simulation of Optimal Combination Schemes
3.6. Comparative Analysis of Optimal Retrofit Strategies
4. Discussion
Limitations and Future Directions
- (1)
- Building group planning and layout: Moving beyond single buildings, studies should explore how group layouts—especially in large campuses or residential complexes—affect overall ventilation efficiency and reduce wind interference.
- (2)
- Robustness and uncertainty analysis: The results of this study are based on a limited number of CFD simulation scenarios and an orthogonal experimental design, without statistical significance testing or uncertainty analysis. This to some extent restricts the systematic quantification of result robustness. Future research may incorporate sensitivity analysis and related methods to more comprehensively assess the influence and uncertainty of different parameters on ventilation performance, thereby enhancing the credibility and generalizability of the conclusions.
- (3)
- Integration of standard floors with communal spaces: Research should address how the design of standard floors, social areas, and public activity zones collectively shape airflow patterns and influence comfort and health.
- (4)
- Multi-climate validation: Key design parameters such as orientation and window angle should be tested across different climate zones to improve generalizability and adaptability.
- (5)
- Furniture and external obstructions: The omission of furniture arrangements and surrounding obstructions in the CFD simulations may introduce certain deviations in airflow predictions. Therefore, future studies could incorporate these factors into CFD models to enable a more precise evaluation of local comfort conditions and pollutant dilution.
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Through simulation analysis of how building orientation affects the outdoor wind environment—considering Xuzhou’s prevailing wind direction—it was found that orienting the building between 8° and 23° yields superior wind conditions.
- (2)
- For linear-form dormitories, a corridor width of 2700–3000 mm improves indoor ventilation and air quality.
- (3)
- In unit dormitory layouts, under standard window-to-wall and window-to-floor ratios, wider windows result in better ventilation, ranked in descending order: 950 mm > 850 mm > 750 mm > 650 mm. Optimal ventilation was observed with interior corridor wall windows at a height of 2000–2100 mm. Horizontal center-hung windows offered the best ventilation performance, with 39% of the indoor area falling within comfortable wind speed ranges. Performance by window type ranked as follows: center-hung at 90° > side-hung at 60° > side-hung at 45° > typical sliding window > top-hung outward at 30° > bottom-hung inward at 30°.
- (4)
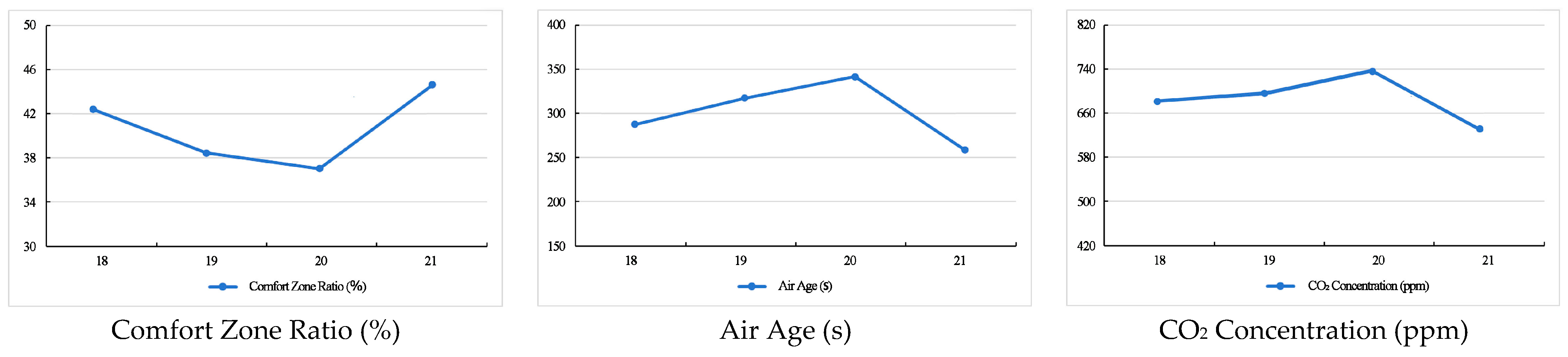
- Subsequently, orthogonal simulation was applied to combine these factors, and the optimal retrofit scheme was derived under the premise of healthy building orientation. The study yields the following conclusion: the optimal scheme obtained from the orthogonal simulation was the combination A2 + B2 + C2 + D2 + E2, corresponding to a building orientation of 15.5°, a corridor width of 2850 mm, a sash width of 850 mm, an internal window height of 2000 mm, and a casement window opening angle of 60°. Compared with other combinations, this scheme provided the highest proportion of indoor comfort wind speed area, while achieving lower air age and CO2 concentration.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klepeis, N.E.; Nelson, W.C.; Ott, W.R.; Robinson, J.P.; Tsang, A.M.; Switzer, P.; Behar, J.V.; Hern, S.C.; Engelmann, W.H. The National Human Activity Pattern Survey (NHAPS): A Resource for Assessing Exposure to Environmental Pollutants. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2001, 11, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šujanová, P.; Rychtáriková, M.; Sotto Mayor, T.; Hyder, A. A Healthy, Energy-Efficient and Comfortable Indoor Environment, a Review. Energies 2019, 12, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Huang, X.; Shi, D.; Lin, W.E.; Fan, S.; Linden, P.F. Natural Ventilation in London: Towards Energy-Efficient and Healthy Buildings. Build. Environ. 2021, 195, 107722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.; Rijal, H.B. Investigation on Summer Thermal Comfort and Passive Thermal Improvements in Naturally Ventilated Nepalese School Buildings. Energies 2023, 16, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, F.; Xu, Y. Building Performance Optimization for University Dormitory through Integration of Digital Gene Map into Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm. Appl. Energy 2022, 307, 118211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Qi, M. Field Testing of Natural Ventilation in College Student Dormitories (Beijing, China). Build. Environ. 2014, 78, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.; Ren, J. Application of an Architect-Friendly Digital Design Approach to the Wind Environment of Campus Dormitory Buildings. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, S.; Li, S.-W.; Hu, Z.-Z.; Wu, H.-Y.; Li, B.-B. Development of a Micro-in-Meso-Scale Framework for Simulating Pollutant Dispersion and Wind Environment in Building Groups. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 364, 132661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Yi, M.; Liu, H.; Cao, K. Numerical Simulation Study on the Influence of Building Layout on Pollutant Dispersion in Industrial Parks Under Different Degrees of Stability. Int. J. Comput. Fluid. Dyn. 2024, 38, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Jiang, M.; Liu, M.; He, T.; Jiang, N.; Huan, X. An Investigation into the Effects of Primary School Building Forms on Campus Wind Environment and Classroom Ventilation Performance. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, P.; Mathur, S.; Mathur, J. Thermal Performance Prediction of Office Buildings Using Direct Evaporative Cooling Systems in the Composite Climate of India. Build. Environ. 2019, 157, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, R.; Arashpour, M.; Golafshani, E.M.; Hosseini, M.R.; Chang, V.; Zhou, J. Machine Learning-Based Analysis of Occupant-Centric Aspects: Critical Elements in the Energy Consumption of Residential Buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 46, 103846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalua, A.; Jo, S.J.; Fateminasab, S.; Al-Rciaibat, S.; Opitz, C. Impact of Ventilation Method on Residential Indoor PM Dispersion during Dust Storm Events in Saudi Arabia. Archit. Eng. Des. Manag. 2020, 16, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; An, Y. Green Residential Building Design Scheme Optimization Based on the Orthogonal Experiment EWM-TOPSIS. Buildings 2024, 14, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, S. Retrofitting Strategies Based on Orthogonal Array Testing to Develop Nearly Zero Energy Buildings. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xie, S.; Yang, M.; Ma, Y.; He, Y.; Zheng, S. A Study on Natural Ventilation of Dormitories for College Students in Northeast China during Spring: A Case of Linear-Shaped Dormitory Buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 90, 109402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, X. A Framework for Optimizing the Indoor Spatial Layout of Outpatient Building Focusing on Respiratory Infection Control by Improving Natural Ventilation. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 104, 112352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aflaki, A.; Mahyuddin, N.; Baharum, M.R. The Influence of Single-Sided Ventilation towards the Indoor Thermal Performance of High-Rise Residential Building: A Field Study. Energy Build. 2016, 126, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahpour, M.; Naeini, H.G.; Mirzaei, P.A. Generic Geometrical Parametric Study of Wind-Driven Natural Ventilation to Improve Indoor Air Quality and Air Exchange in Offices. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 84, 108528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, B.; Song, B. Study on Ventilation Rates at University Dormitories in Winter. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Heating, Ventilation And Air Conditioning (Ishvac) Joint with the 3rd International Conference on Building Energy and Environment (Cobee); Sun, Y., Pei, J., Eds.; Elsevier Science Bv: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 121, pp. 743–748. [Google Scholar]
- Bramiana, C.N.; Aminuddin, A.M.R.; Ismail, M.A.; Widiastuti, R.; Pramesti, P.U. The Effect of Window Placement on Natural Ventilation Capability in a Jakarta High-Rise Building Unit. Buildings 2023, 13, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Li, N. Effect of Natural Ventilation on Indoor Air Quality and Thermal Comfort in Dormitory during Winter. Build. Environ. 2017, 125, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Alexander, D.; Jenkins, H.; Arthur, R.; Chen, Q.Y. Natural Ventilation in Buildings: Measurement in a Wind Tunnel and Numerical Simulation with Large-Eddy Simulation. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2003, 91, 331–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Kumar, P.; Mottet, L. Natural Ventilation in Warm Climates: The Challenges of Thermal Comfort, Heatwave Resilience and Indoor Air Quality. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2021, 138, 110669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, S.; Garcia-Hansen, V.; Capra, B.R.; Drogemuller, R. Effect of Natural Ventilation Mode on Thermal Comfort and Ventilation Performance: Full-Scale Measurement. Energy Build. 2017, 156, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choi, Y.; Song, D.; Kim, E.K. Natural Ventilation Strategy and Related Issues to Prevent Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Airborne Transmission in a School Building. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, S.; Shah, A.N. Prediction of Comfort Parameters for Naturally Ventilated Underground Car Parks. Nucleus 2016, 53, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikul, N.; Hokpunna, A.; Chawana, P. Improving Indoor Air Quality in Primary School Buildings through Optimized Apertures and Classroom Furniture Layouts. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 62, 105324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poshtiri, A.H.; Mohabbati, S.M. Performance Analysis of Wind Catcher Integrated with Shower Cooling System to Meet Thermal Comfort Conditions in Buildings. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma’bdeh, S.N.; Hamasha, A.A.; Al-Shawabkeh, M.; Alali, R.O.; Almomani, R.M.; Obeidat, L.M.; Alrebei, O.F. Enhancing Office Air Quality: The Role of Window to Wall Ratio with Window-Wind Catchers Using CFD Analysis. Energy Rep. 2025, 13, 1508–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Owen, J.S.; Almazmumi, S.; Liu, C.; Mohammadi, M.; Dik, A.; Jimenez-Bescos, C.; Calautit, J.K. Pollutant Cross-Transmission in Courtyard Buildings: Wind Tunnel Experiments and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Evaluation. Build. Environ. 2024, 264, 111919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenech, M.; Decitre, G.; Brenn, G.; Irrenfried, C. Experimental Investigation of the Ventilation Efficiency for Single-Sided Ventilation in Suburban Areas. Build. Environ. 2025, 283, 113280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.-Y.; Xia, Y.; Lao, H.; Ye, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H. Natural Ventilation Potential of Teaching Building Complexes with Different Block Shapes and Layout Patterns. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 110420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turanjanin, V.; Vutiaevic, B.; Jovanovic, M.; La Mirkov, N.; Lazovic, I. Indoor CO2 Measurements in Serbian Schools and Ventilation Rate Calculation. Energy 2014, 77, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Ji, Z.; Ma, L.; Hui, Y. Test on Ventilation Rates of Dormitories and Offices in University by the CO2 Tracer Gas Method. Procedia Eng. 2015, 121, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lee, W.L. Influence of Window Opening Degree on Natural Ventilation Performance of Residential Buildings in Hong Kong. Sci. Technol. Built Environ. 2020, 26, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Cui, X.; Shen, P. Coupled Building Simulation and CFD for Real-Time Window and HVAC Control in Sports Space. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 97, 110731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ling, H.; Jia, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Hua, J. Utilizing Periodic Boundary Conditions to Save Computational Resources for Assessing Building Natural Ventilation in Urban Areas. Urban. Clim. 2024, 55, 101925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Qin, H.; Lin, B. Prediction of Wind Environment and Indoor/Outdoor Relationships for PM2.5 in Different Building-Tree Grouping Patterns. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormigos-Jimenez, S.; Angel Padilla-Marcos, M.; Meiss, A.; Alonso Gonzalez-Lezcano, R.; Feijo-Munoz, J. Computational Fluid Dynamics Evaluation of the Furniture Arrangement for Ventilation Efficiency. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 2018, 39, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Wind Speed (m/s) | Effect |
|---|---|
| 0–0.25 | Hardly perceptible |
| 0.25–0.5 | Pleasant, does not interfere with work |
| 0.5–1.0 | Relatively comfortable, but may cause paper displacement |
| 1.0–1.5 | Slightly disturbing airflow, unpleasant draught, paper easily blown off |
| >1.5 | To maintain work efficiency and a healthy environment, ventilation volume should be adjusted and airflow paths effectively managed when significant draught occurs |
| Thermal Sensation | Cold | Cool | Slightly Cool | Neutral | Slightly Warm | Warm | Hot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMV Index | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Air Age T (s) | T < 225 | 225 ≤ T < 400 | T ≥ 400 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Freshness | Fresh | Relatively Fresh | Not Fresh |
| Corridor Width (mm) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Air Age (s) | CO2 Concentration (ppm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2100 mm | 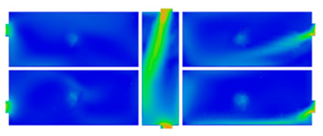 |  |  | 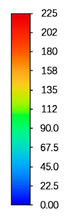 | 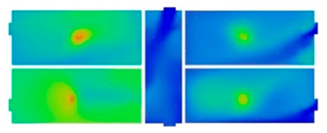 | 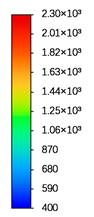 |
| 2400 mm | 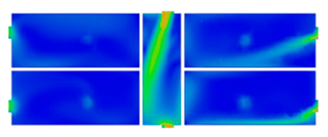 |  | 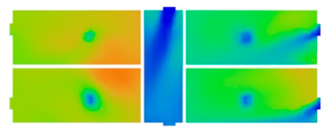 |  | 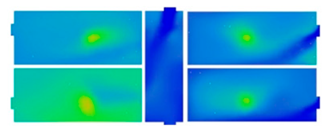 |  |
| 2700 mm | 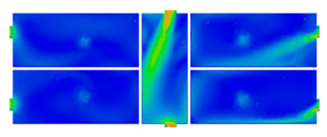 |  | 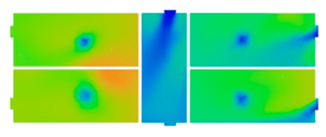 |  | 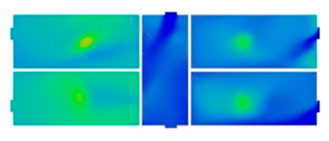 |  |
| 3000 mm | 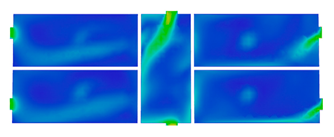 | 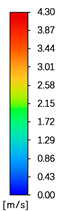 | 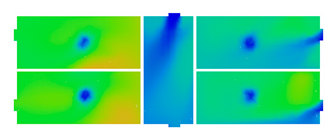 | 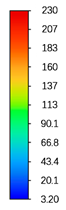 |  | 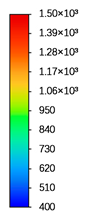 |
| Window Sash Width (mm) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Air Age (s) | CO2 Concentration (ppm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 650 mm | 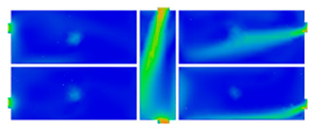 |  | 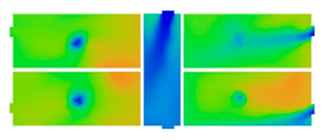 |  | 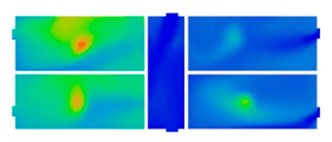 |  |
| 750 mm | 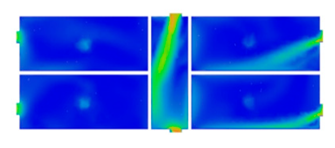 |  | 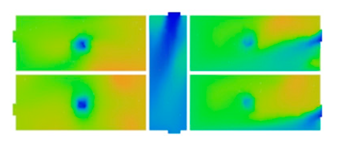 |  | 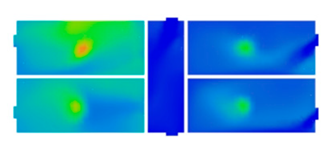 | 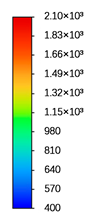 |
| 850 mm | 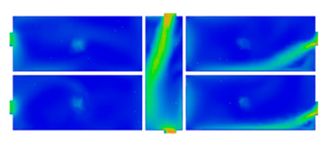 |  | 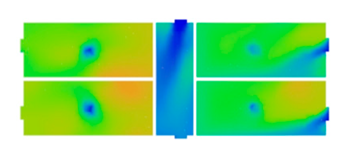 |  |  |  |
| 950 mm | 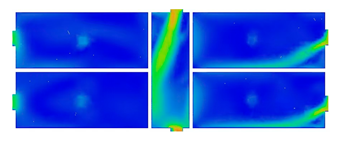 |  | 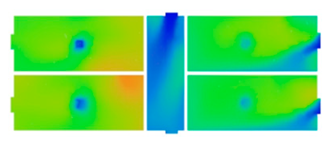 |  | 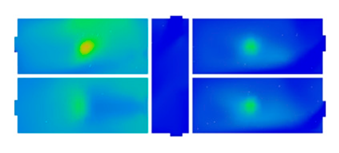 |  |
| Type | Example | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Lateral | 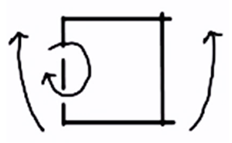 | Poor performance in introducing outdoor wind, resulting in unsatisfactory indoor ventilation |
| Sequential | 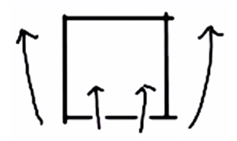 | Small pressure difference between windows; even if wind enters through openings, effective ventilation is difficult to achieve |
| Reverse | 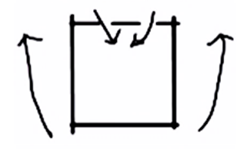 | Side openings on the leeward side hinder indoor air circulation; only limited airflow exits, leading to poor ventilation |
| Vertical | 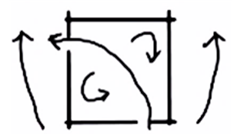 | Indoor ventilation is obstructed; airflow is turbulent in corner zones, forming vortices |
| Staggered | 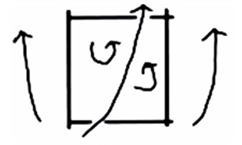 | Large ventilation area ensures smooth airflow into the interior, effectively reducing vortices |
| Single-sided cross |  | Openings on the same side allow overall airflow, but uneven wind speeds cause vortex formation |
| Through-corridor | 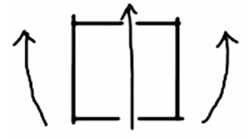 | Strong cross-ventilation effect with reduced vortices, achieving excellent ventilation performance |
| Internal Window Height (mm) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Air Age (s) | CO2 Concentration (ppm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 mm |  |  |  |  | 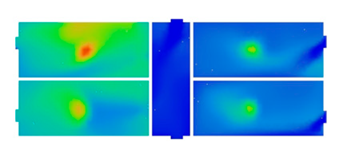 | 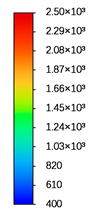 |
| 1900 mm | 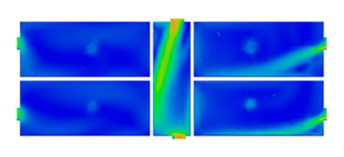 |  |  | 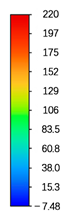 | 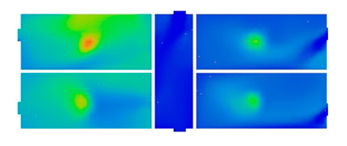 |  |
| 2000 mm | 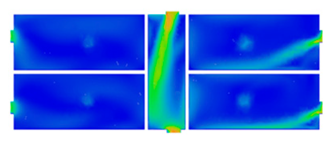 |  | 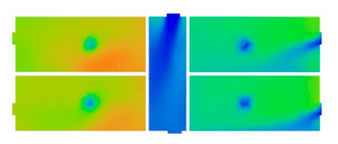 |  | 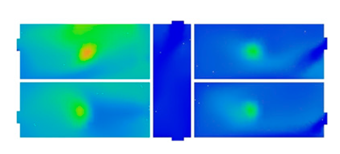 |  |
| 2100 mm | 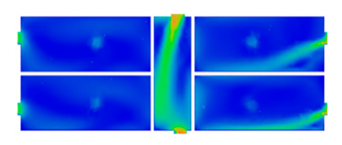 |  |  | 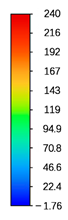 | 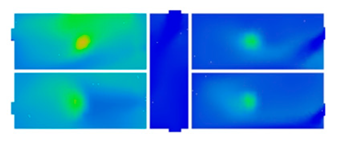 |  |
| 2200 mm | 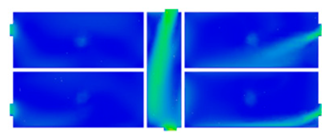 |  | 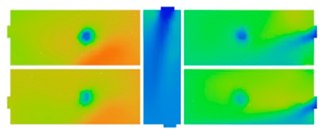 |  | 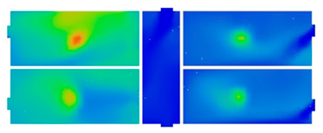 |  |
| Window Type | Wind Speed (m/s) | Air Age (s) | CO2 Concentration (ppm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sliding window |  | 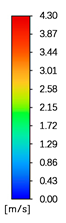 |  | 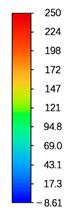 | 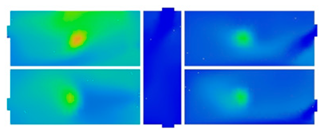 |  |
| Bottom-hung window 30° |  | 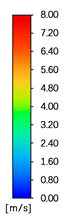 |  |  | 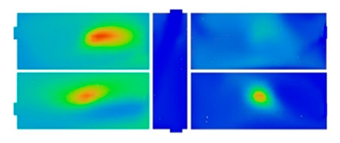 | 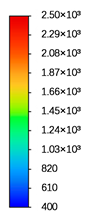 |
| Top-hung window 30° | 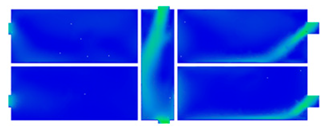 | 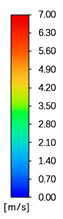 |  | 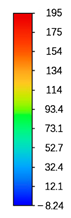 | 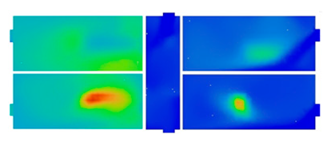 | 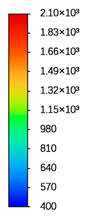 |
| Casement window 45° |  | 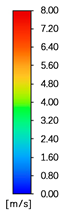 | 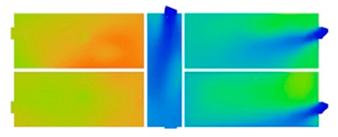 |  | 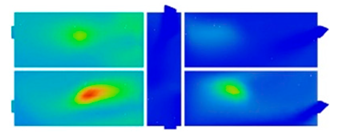 |  |
| Casement window 60° | 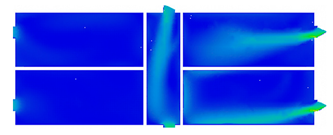 |  | 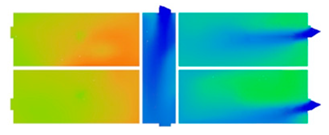 |  | 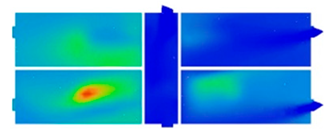 | 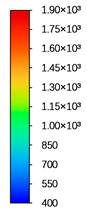 |
| Mid-hung window 90° | 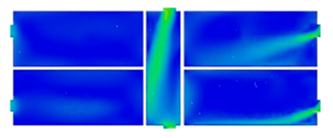 | 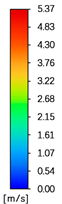 |  | 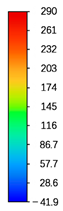 | 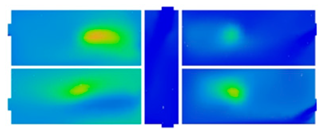 |  |
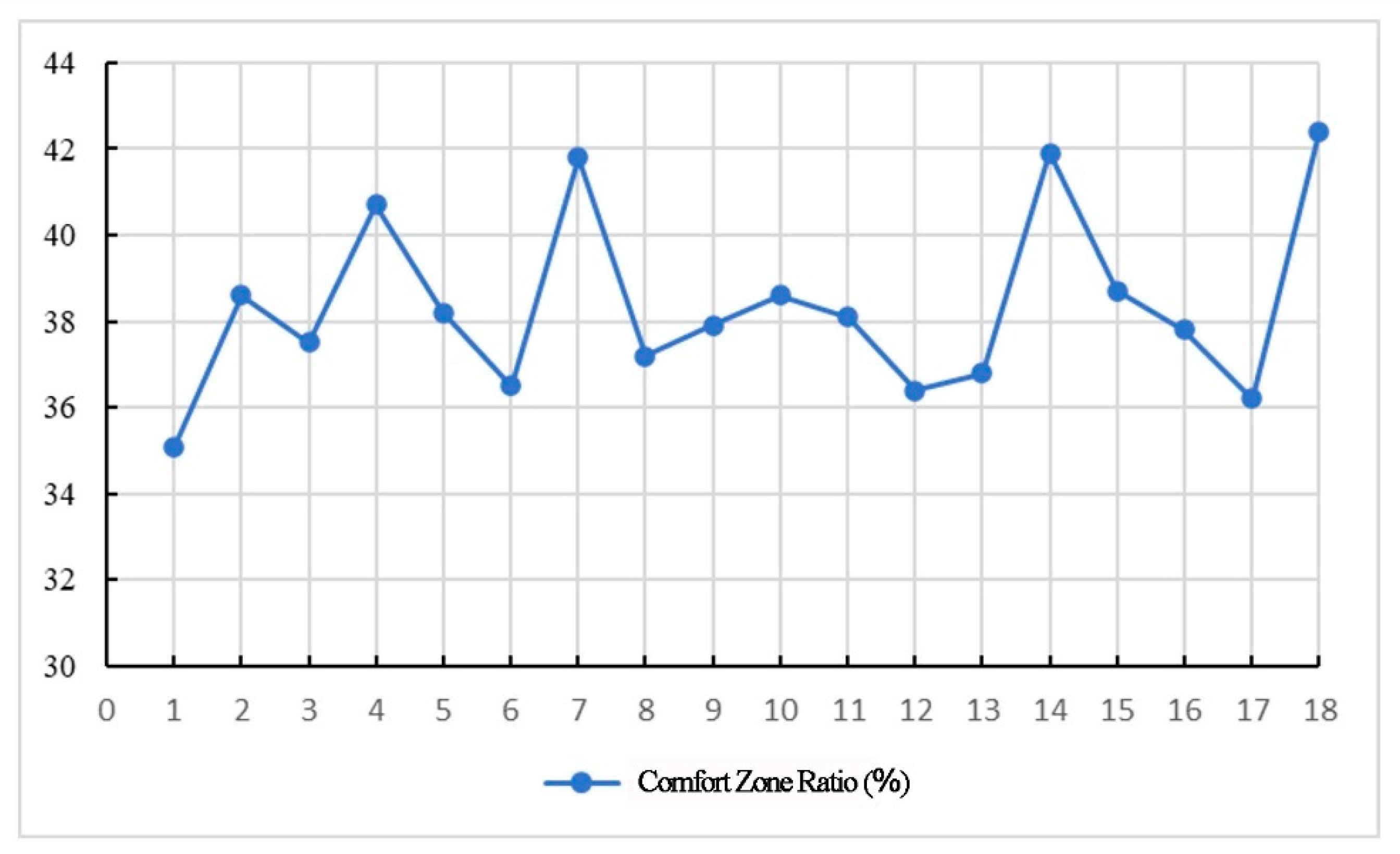
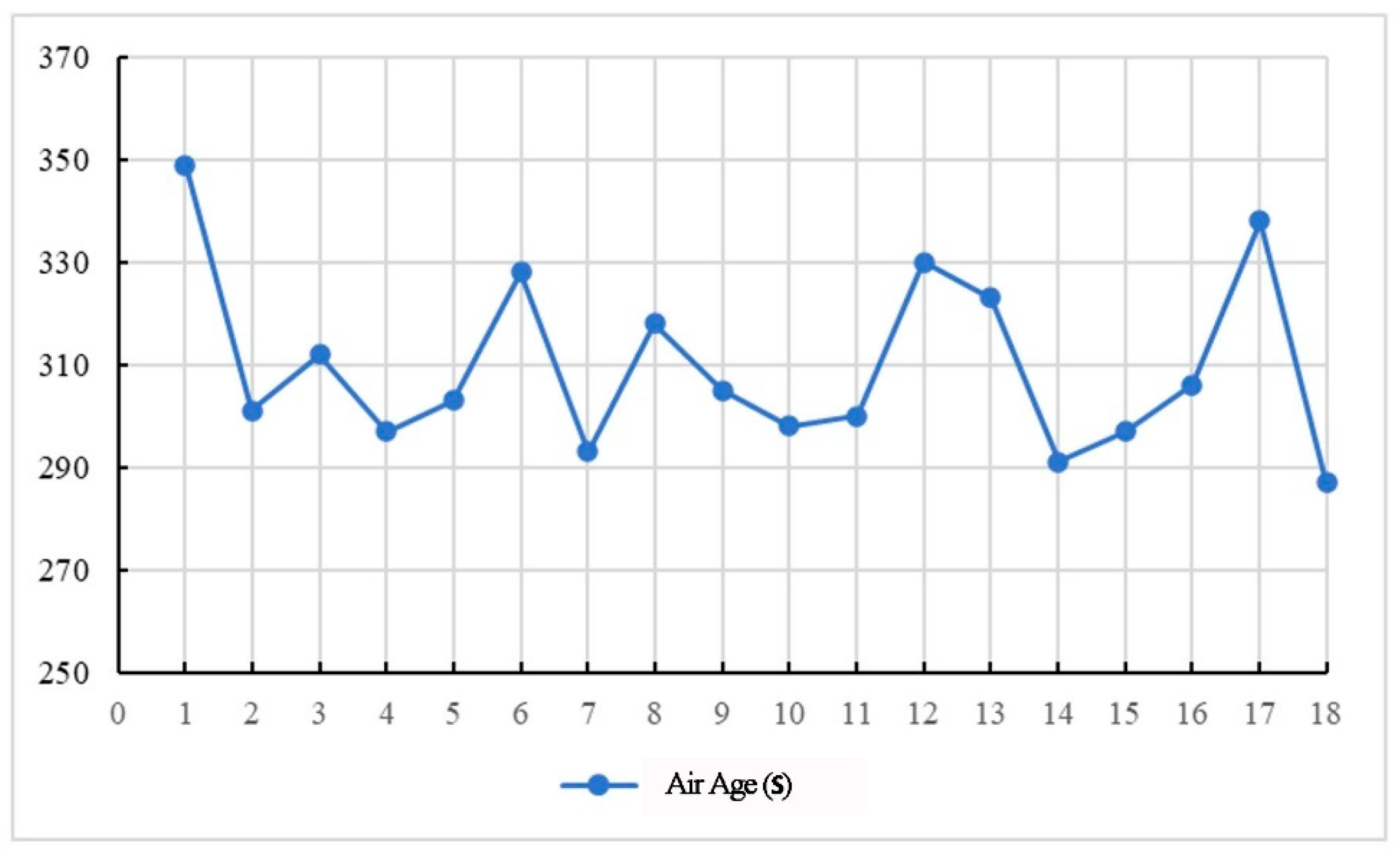
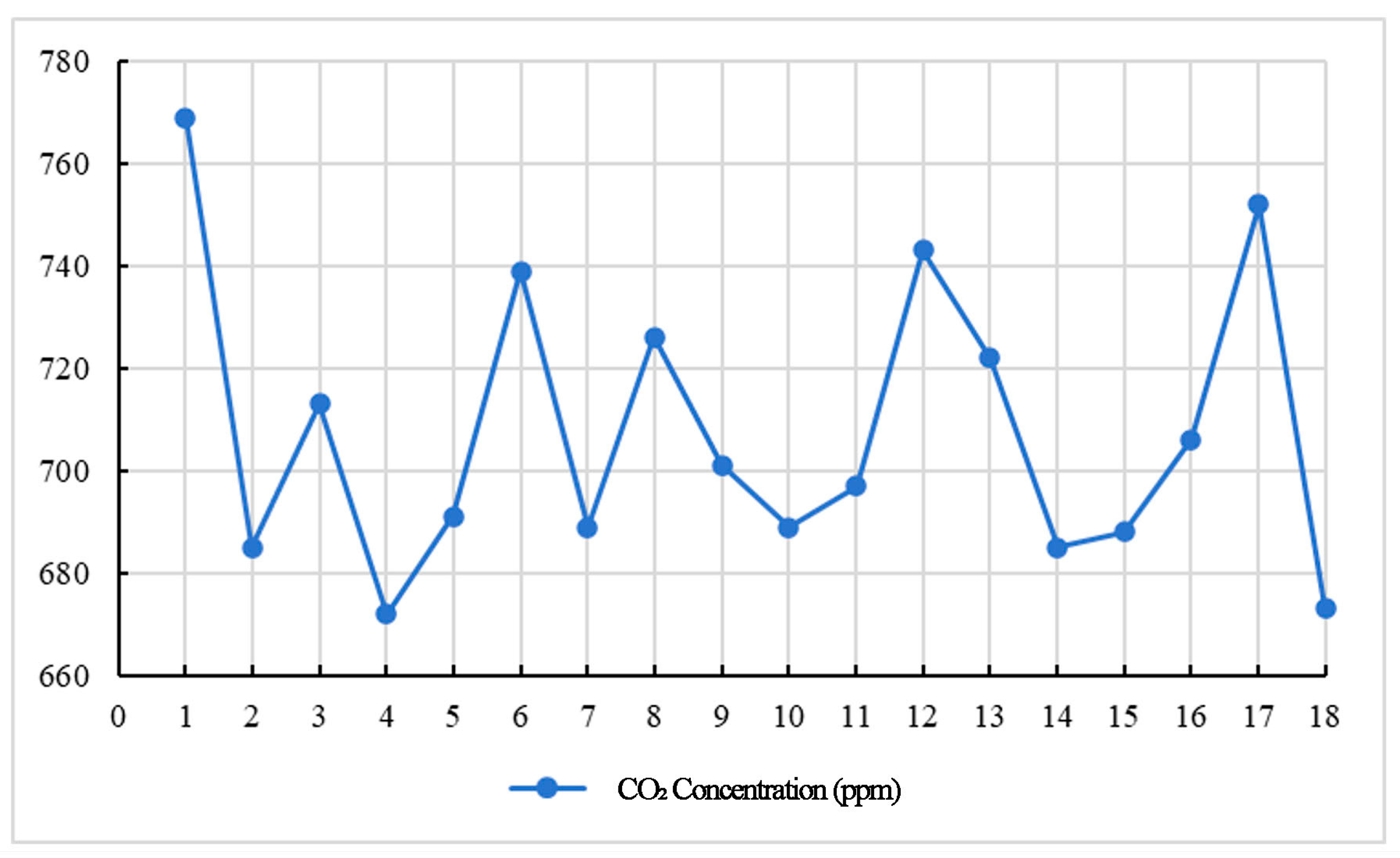
| Group | A | B | C | D | E | Comfort Wind Speed Area (%) | Air Age (s) | CO2 Concentration (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 35.1 | 349 | 769 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 38.6 | 301 | 685 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 37.5 | 312 | 713 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 40.7 | 297 | 672 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 38.2 | 303 | 691 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 36.5 | 328 | 739 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 41.8 | 293 | 689 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 37.2 | 318 | 726 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 37.9 | 305 | 701 |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 38.6 | 298 | 689 |
| 11 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 38.1 | 300 | 697 |
| 12 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 36.4 | 330 | 743 |
| 13 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 36.8 | 323 | 722 |
| 14 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 41.9 | 291 | 685 |
| 15 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 38.7 | 297 | 688 |
| 16 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 37.8 | 306 | 706 |
| 17 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 36.2 | 338 | 752 |
| 18 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 42.4 | 287 | 673 |
| Group | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 38.200 | 39.000 | 37.383 | 39.267 | 36.367 |
| 2 | 38.367 | 37.783 | 38.850 | 38.233 | 39.983 |
| 3 | 38.467 | 38.250 | 38.800 | 37.533 | 38.683 |
| R | 0.267 | 1.217 | 1.467 | 1.734 | 3.616 |
| Factor ranking of influence | E > D > C > B > A | ||||
| Theoretical optimal combination | A3 + B1 + C2 + D1 + E2 | ||||
| Group | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 311.000 | 313.167 | 314.333 | 307.833 | 331.000 |
| 2 | 308.500 | 308.167 | 306.167 | 306.500 | 296.500 |
| 3 | 309.833 | 308.000 | 308.833 | 315.000 | 301.833 |
| R | 2.500 | 5.167 | 8.166 | 8.500 | 34.500 |
| Factor ranking of influence | E > C > D > B > A | ||||
| Theoretical optimal combination | A1 + B1 + C1 + D3 + E1 | ||||
| Group | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 707.833 | 708.667 | 713.167 | 699.500 | 741.833 |
| 2 | 709.500 | 711.333 | 700.500 | 716.000 | 684.167 |
| 3 | 706.000 | 703.333 | 709.667 | 707.833 | 697.333 |
| R | 3.500 | 8.000 | 12.667 | 16.500 | 57.666 |
| Factor ranking of influence | E > C > D > B > A | ||||
| Theoretical optimal combination | A2 + B2 + C2 + D2 + E2 | ||||
| Group | A | B | C | D | E | Comfort Wind Speed Area (%) | Air Age (s) | CO2 Concentration (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 42.4 | 287 | 673 |
| 19 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 38.5 | 317 | 689 |
| 20 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 37.1 | 341 | 738 |
| 21 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 44.6 | 258 | 613 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, Z.; Zi, Y.; Wang, L.; Dong, S. Research on the Optimization Design of Natural Ventilation in University Dormitories Based on the Healthy Building Concept: A Case Study of Xuzhou Region. Buildings 2025, 15, 3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193630
Duan Z, Zi Y, Wang L, Dong S. Research on the Optimization Design of Natural Ventilation in University Dormitories Based on the Healthy Building Concept: A Case Study of Xuzhou Region. Buildings. 2025; 15(19):3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193630
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Zhongcheng, Yilun Zi, Leilei Wang, and Shichun Dong. 2025. "Research on the Optimization Design of Natural Ventilation in University Dormitories Based on the Healthy Building Concept: A Case Study of Xuzhou Region" Buildings 15, no. 19: 3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193630
APA StyleDuan, Z., Zi, Y., Wang, L., & Dong, S. (2025). Research on the Optimization Design of Natural Ventilation in University Dormitories Based on the Healthy Building Concept: A Case Study of Xuzhou Region. Buildings, 15(19), 3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193630





