Automation and Genetic Algorithm Optimization for Seismic Modeling and Analysis of Tall RC Buildings
Abstract
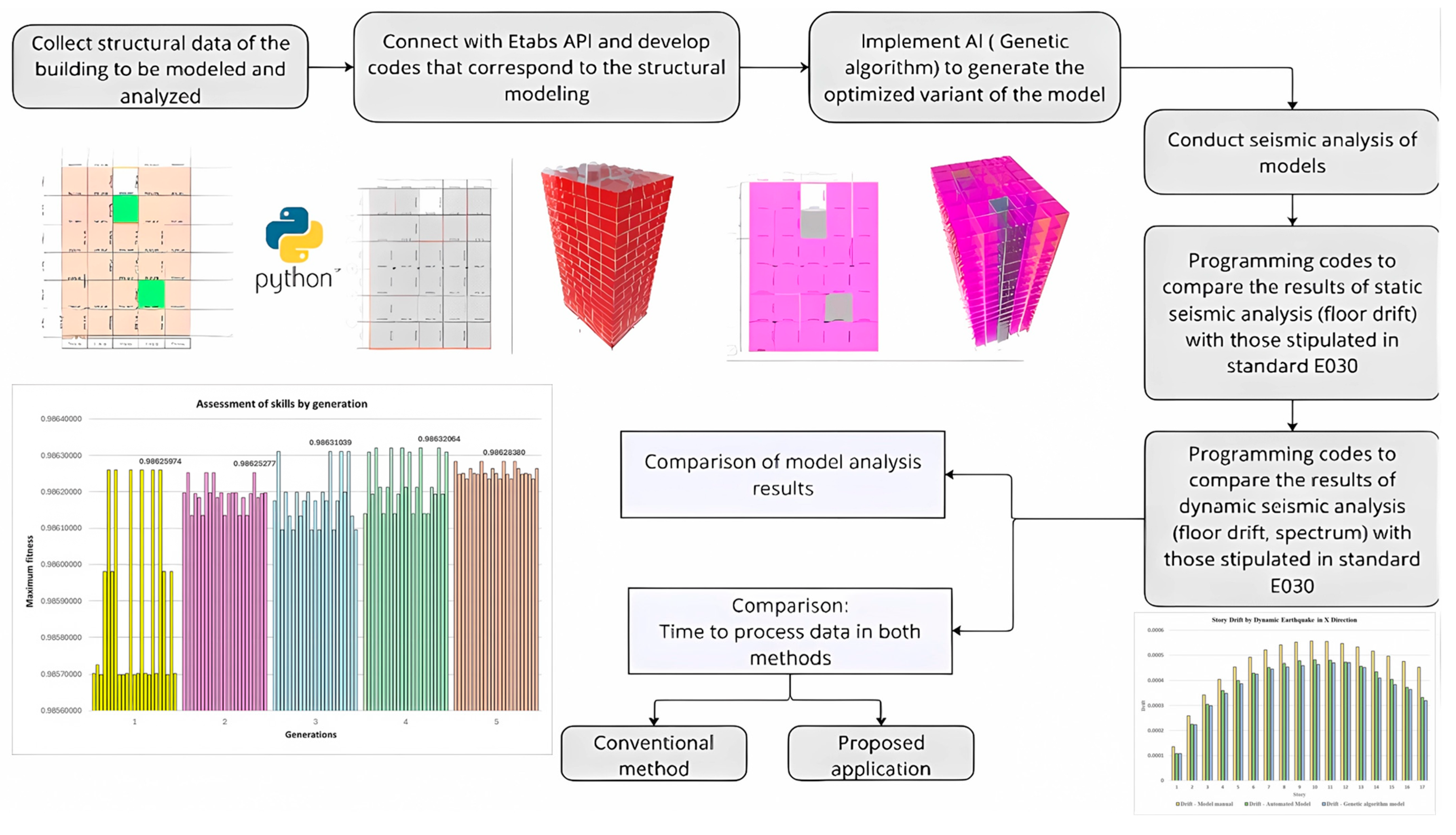
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Mathematical Formulation
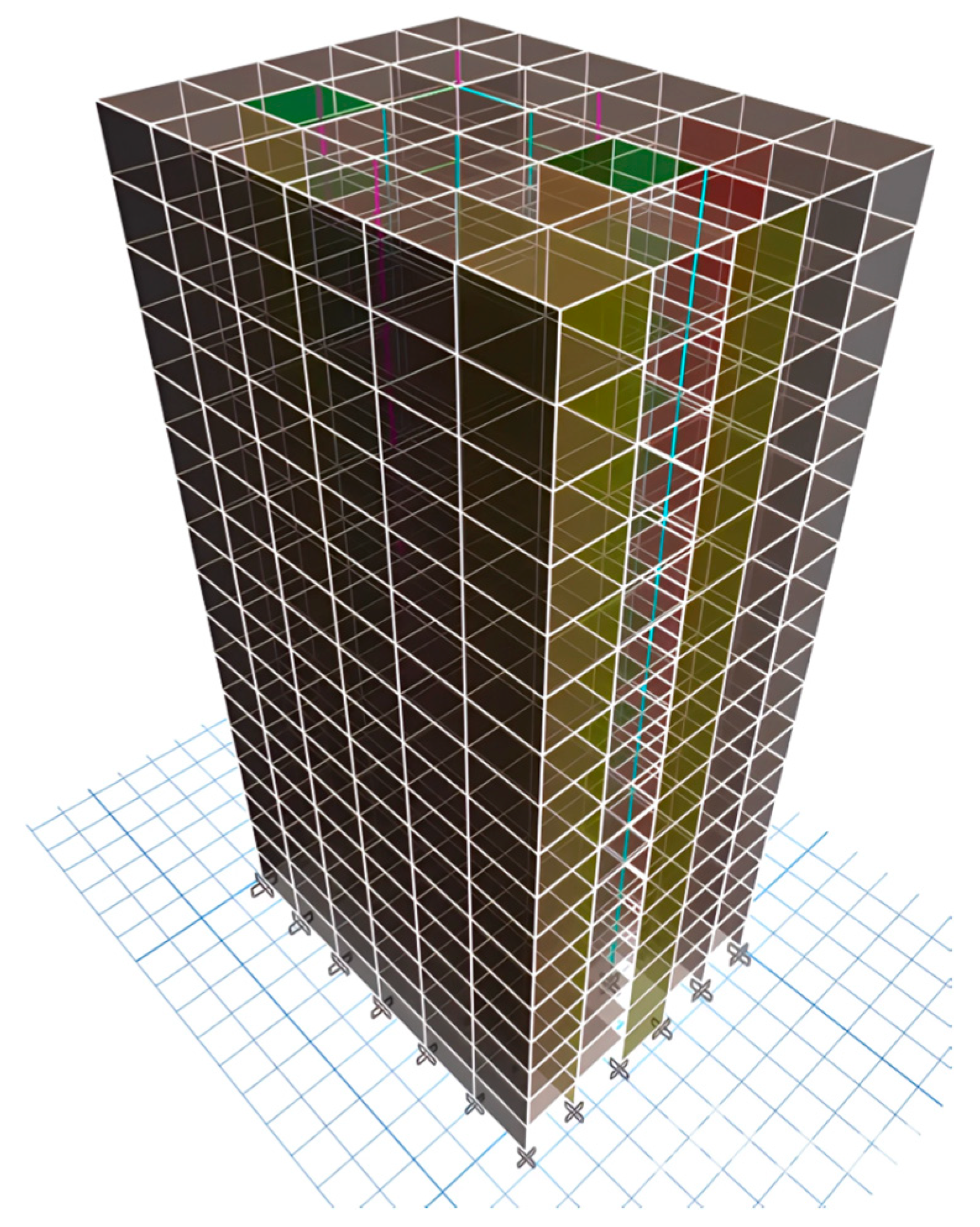
3.1. Modelling in ETABS
Static Analysis
3.2. AI Algorithms
3.2.1. Genetic Algorithm
3.2.2. Fitness
3.3. Model Fit Evaluation and Predictive Accuracy
3.3.1. Coefficient of Determination (R2)
3.3.2. Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE)
4. Empirical Assessment of Tall Buildings—Automated Structural Modelling
4.1. Case Study
4.1.1. Seismic Parameters
Seismic Zone (Z)
Building Use (U)
Building Category (C)
Structural System
4.1.2. Soil and Site Parameters
Soil Type
Site Coefficient (C) and Seismic Amplification Coefficient (S)
4.1.3. Seismic Analysis Parameters
5. Empirical Evaluation of High Buildings—Automated Static Seismic Analysis and Genetic Algorithm
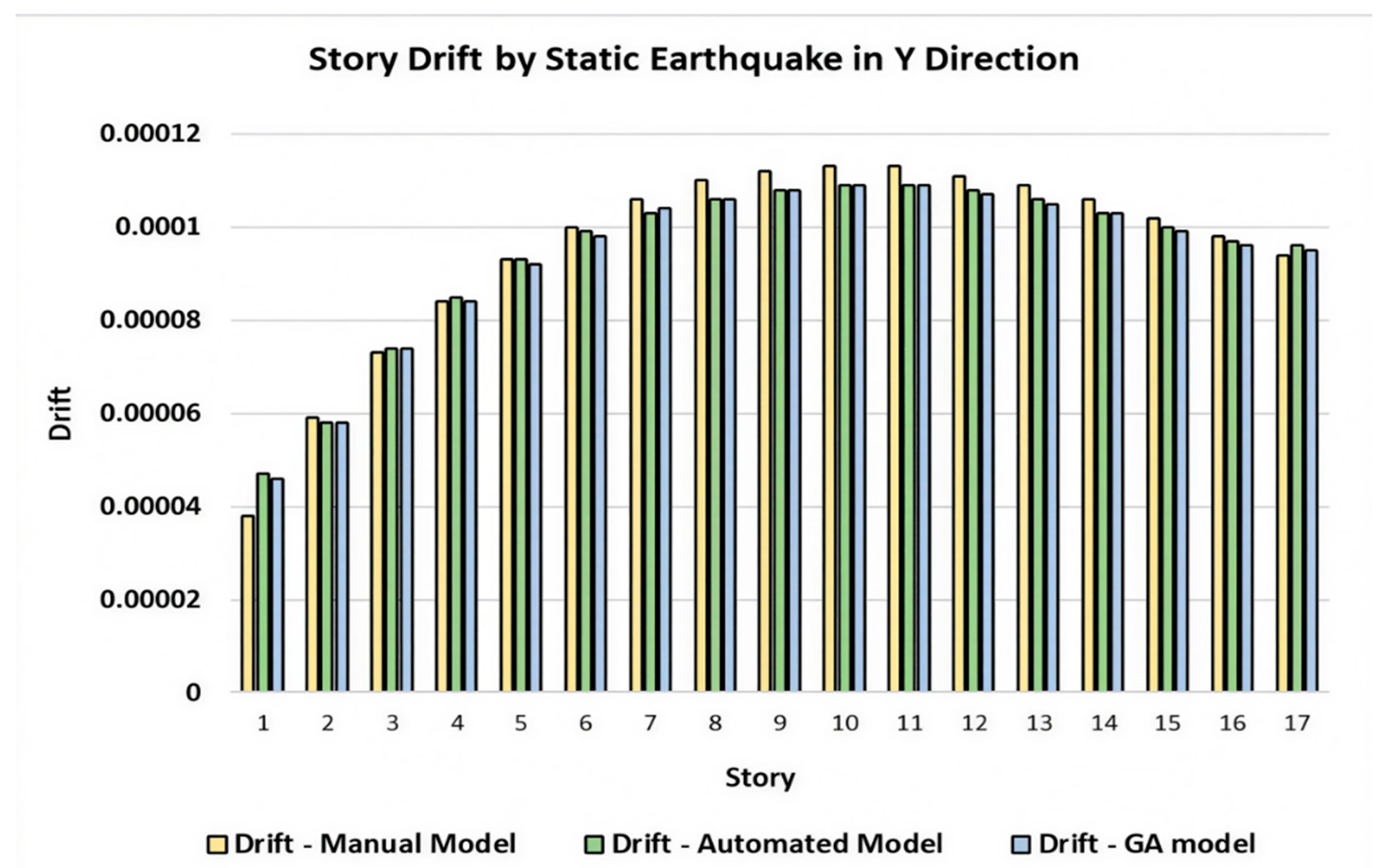
5.1. Derivation Calculation-Static Analysis
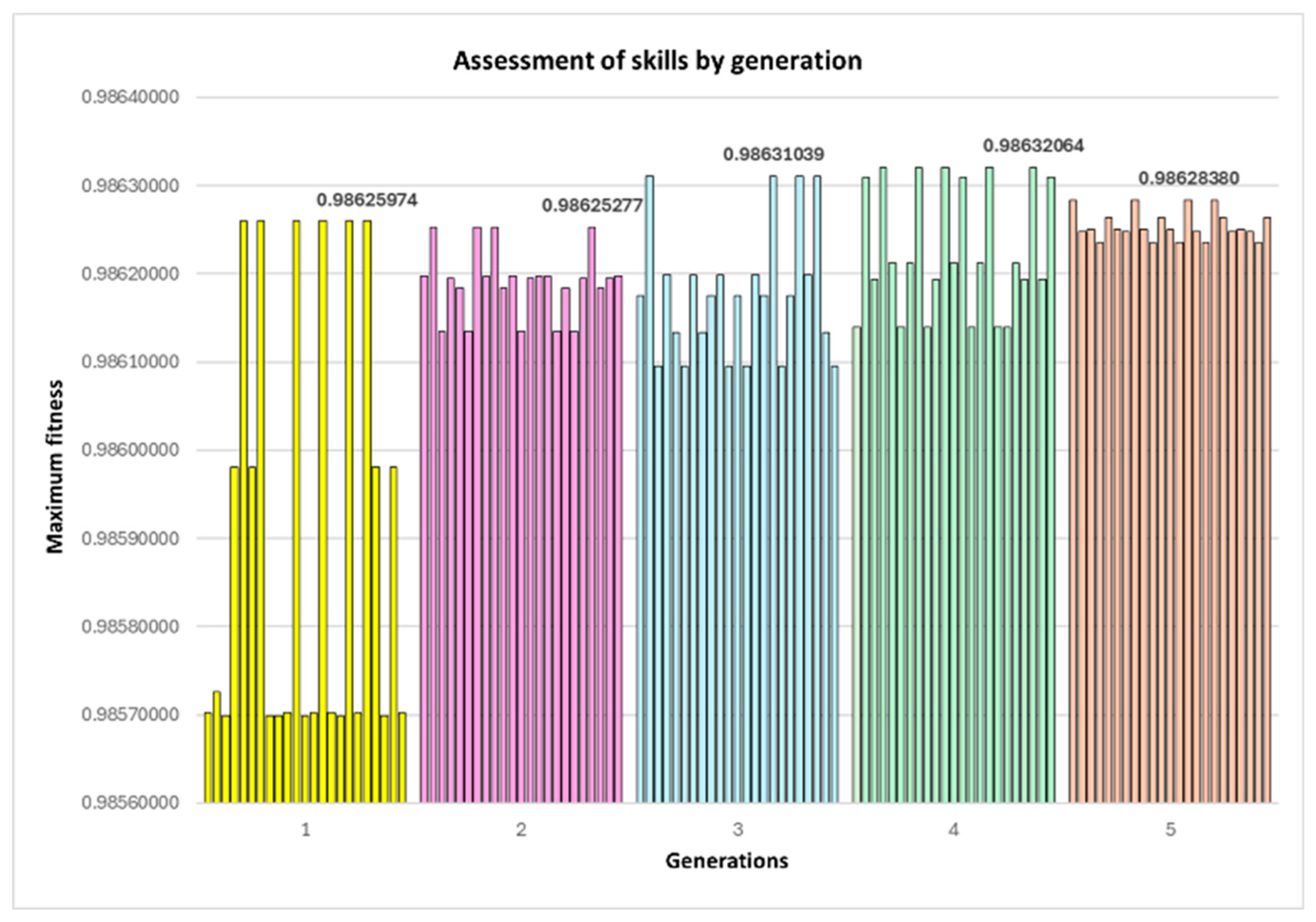
5.2. Genetic Algorithm
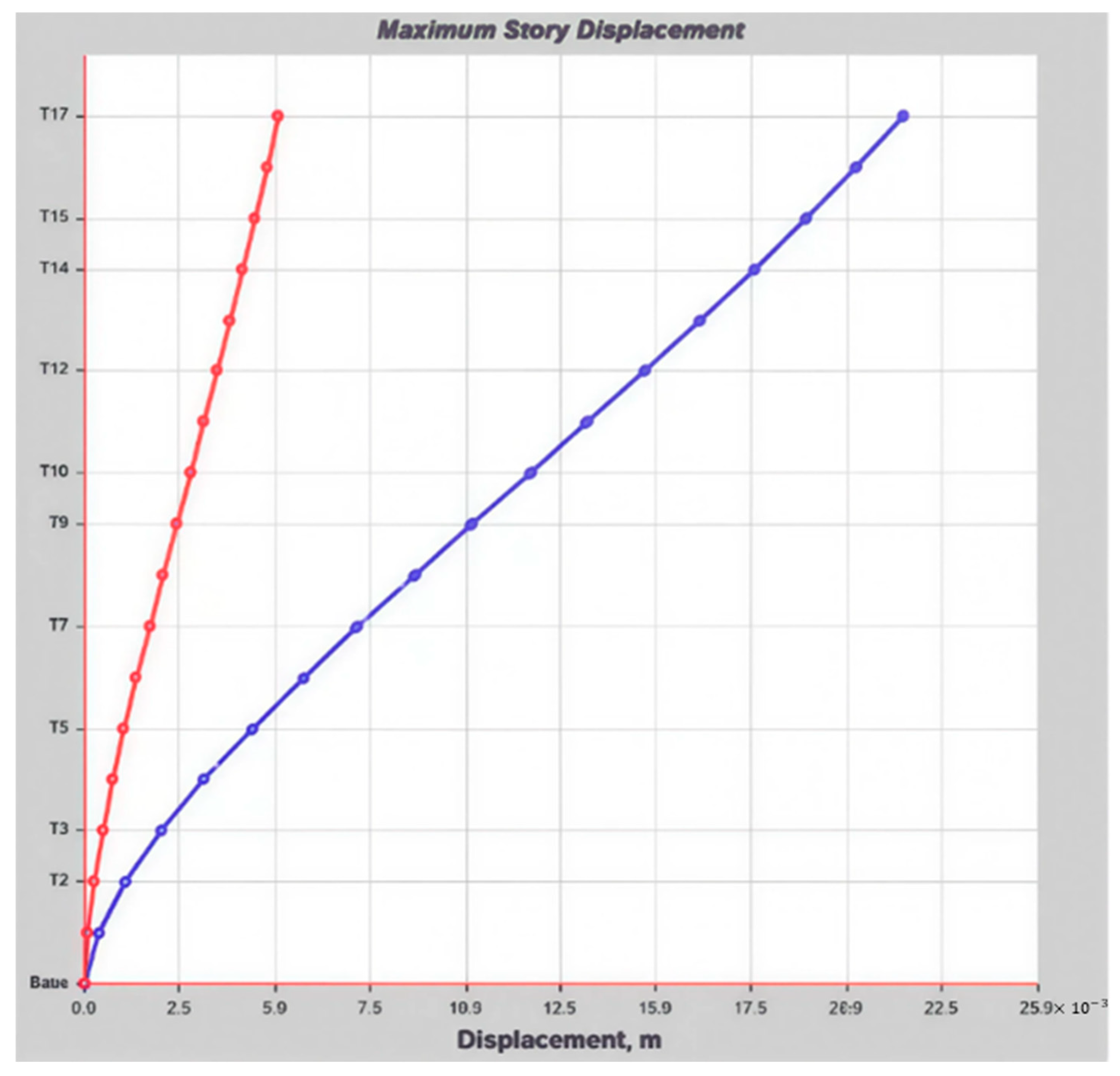
6. Empirical Assessment of Tall Buildings—Automated Dynamic Seismic Analysis
Derivation Calculation-Dynamic Analysis
7. Discussions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aloisio, A.; Santis, Y.; De Irti, F.; Pasca, D.P.; Scimia, L.; Fragiacomo, M. Machine learning predictions of code-based seismic vulnerability for reinforced concrete and masonry buildings: Insights from a 300-building database. Eng. Struct. 2024, 301, 117295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, G.; Quaranta, G.; Mollaioli, F.; Kunnath, S.K. Interpretable machine learning models for displacement demand prediction in reinforced concrete buildings under pulse-like earthquakes. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgarkhani, N.; Kazemi, F.; Jakubczyk-Gałczyńska, A.; Mohebi, B.; Jankowski, R. Seismic response and performance prediction of steel buckling-restrained braced frames using machine-learning methods. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 128, 107388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S. Optimization of the seismic resistance of school buildings using artificial intelligence and sensitivity analysis theories—A Taiwan case study. Structures 2023, 54, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgun, C. Machine learning for the prediction of evaluation of existing reinforced concrete structures performance against earthquakes. Structures 2023, 50, 1994–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Iuliis, M.; Miceli, E.; Castaldo, P. Machine learning modelling of structural response for different seismic signal characteristics: A parametric analysis. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 164, 112026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demertzis, K.; Kostinakis, K.; Morfidis, K.; Iliadis, L. An interpretable machine learning method for the prediction of R/C buildings’ seismic response. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 63, 105493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmen, A.B.; Avci, Y. Development of novel artificial intelligence functions based on 3D finite element method using February 6 Kahramanmaraş Seismic Records for earthquake effects prediction in various soils. Eng. Geol. 2024, 336, 107570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, R.; Ciaramella, A.; Carrabs, F.; Strisciuglio, N.; Martinelli, E. Artificial neural network for technical feasibility prediction of seismic retrofitting in existing RC structures. Structures 2022, 41, 1220–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Lu, W.; Fan, Y.; Gao, Y. Automated simplified structural modeling method for megatall buildings based on genetic algorithm. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 77, 107485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.; Jia, J.; Pan, X. Prediction framework of slope topographic amplification on seismic acceleration based on machine learning algorithms. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, F.; Asgarkhani, N.; Jankowski, R. Machine learning-based seismic response and performance assessment of reinforced concrete buildings. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2023, 23, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, F.; Asgarkhani, N.; Jankowski, R. Optimization-based stacked machine-learning method for seismic probability and risk assessment of reinforced concrete shear walls. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Paal, S.G. Artificial intelligence-enhanced seismic response prediction of reinforced concrete frames. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 52, 101568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Chi, J.W.; Kong, F.C.; Zhou, S.H.; Lu, D.C.; Liao, W.Z. Prediction on the seismic performance limits of reinforced concrete columns based on machine learning method. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 177, 108423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.S.; Mol, M.B. Enhancing seismic performance prediction of RC frames using MFF-ANN model approach. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 42285–42318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, F.; Ruggieri, S.; Lovreglio, R.; Fanti, M.; Uva, G. On the use of mechanics-informed models to structural engineering systems: Application of graph neural networks for structural analysis. Structures 2024, 59, 105712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanini, L.; Badini, L.; Mochi, G.; Predari, G.; Ferrante, A. Neural networks for the rapid seismic assessment of existing moment-frame RC buildings. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 67, 102677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, H.; Noori, M.; Ghiasi, R.; Kuok, S.C.; Altabey, W.A. Probabilistic Seismic Response Prediction of Three-Dimensional Structures Based on Bayesian Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2022, 22, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhai, C. Rapid seismic response prediction of RC frames based on deep learning and limited building information. Eng. Struct. 2022, 267, 114638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, W.; Yu, D.; Zhao, Y. Seismic fragility analysis of RC frame structures based on IDA analysis and machine learning. Structures 2024, 65, 106774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, W.; Wang, S.; Du, D.; Miao, Q. Study on the evolution of dynamic characteristics and seismic damage of a self-centering concrete structure based on data-driven methods. Eng. Struct. 2024, 316, 118529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, W.; Wang, S.; Du, D.; Tang, J. Seismic response prediction of a damped structure based on data-driven machine learning methods. Eng. Struct. 2024, 301, 117264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E.030; Reglamento Nacional de Edificaciones: Diseño Sismorresistente. Ministerio de Vivienda, Construcción y Saneamiento: Lima, Peru, 2020.
- Fogel, D.B. Evolutionary Computation: Toward a New Philosophy of Machine Intelligence, 3rd ed.; IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, L. Heuristic Artificial Intelligent Algorithm for Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Advanced Measurement and Test (AMT 2010), Sanya, China, 15–16 May 2010; Volume 439–440, pp. 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormen, T.H.; Leiserson, C.E.; Rivest, R.L.; Stein, C. Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd ed.; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; Available online: https://mitpress.mit.edu/9780262033848/introduction-to-algorithms/ (accessed on 25 September 2025).
- Cheng, C.-L.; Shalabh; Garg, G. Coefficient of determination for multiple measurement error models. J. Multivar. Anal. 2014, 126, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, T.O. Root-mean-square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE): When to use them or not. Geosci. Model Dev. 2022, 15, 5481–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Base Reactions—Model Manual | |||||||
| Output Case | Case Type | FX | FY | FZ | MX | MY | MZ |
| kN | kN | kN | kN·m | kN·m | kN·m | ||
| SISMO X | LinStatic | −4647.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −143,682.4 | 59,761.2 |
| SISMO Y | LinStatic | 0 | −4647.6 | 0 | 143,682.6 | 0 | −4692.2148 |
| Base Reactions—Automated Model | |||||||
| Output Case | Case Type | FX | FY | FZ | MX | MY | MZ |
| kN | kN | kN | kN·m | kN·m | kN·m | ||
| SISMO X | LinStatic | −4647.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −143,682.3 | 54,191.0 |
| SISMO Y | LinStatic | 0 | −4647.6 | 0 | 143,682.3 | 0 | −41,807.5 |
| Base Reactions—Genetic algorithm model | |||||||
| Output Case | Case Type | FX | FY | FZ | MX | MY | MZ |
| kN | kN | kN | kN·m | kN·m | kN·m | ||
| SISMO X | LinStatic | −4647.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −143,682.3 | 54,191.0 |
| SISMO Y | LinStatic | 0 | −4647.6 | 0 | 143,682.3 | 0 | −41,807.5 |
| Generation | Maximum Fitness | Maximum Displacement |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.98625974 | 0.01393169 |
| 2 | 0.98625277 | 0.01393885 |
| 3 | 0.98631039 | 0.01387962 |
| 4 | 0.98632064 | 0.01386908 |
| 5 | 0.98628380 | 0.01390696 |
| Manual | Genetic Algorithm | Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete volume (m3) | 454.57 | 456.7 | +0.47% |
| Weight of steel (t) | 40.37 | 38.75 | −4.01% |
| Fundamental period T1 (s) | 0.459 | 0.464 | +1.09% |
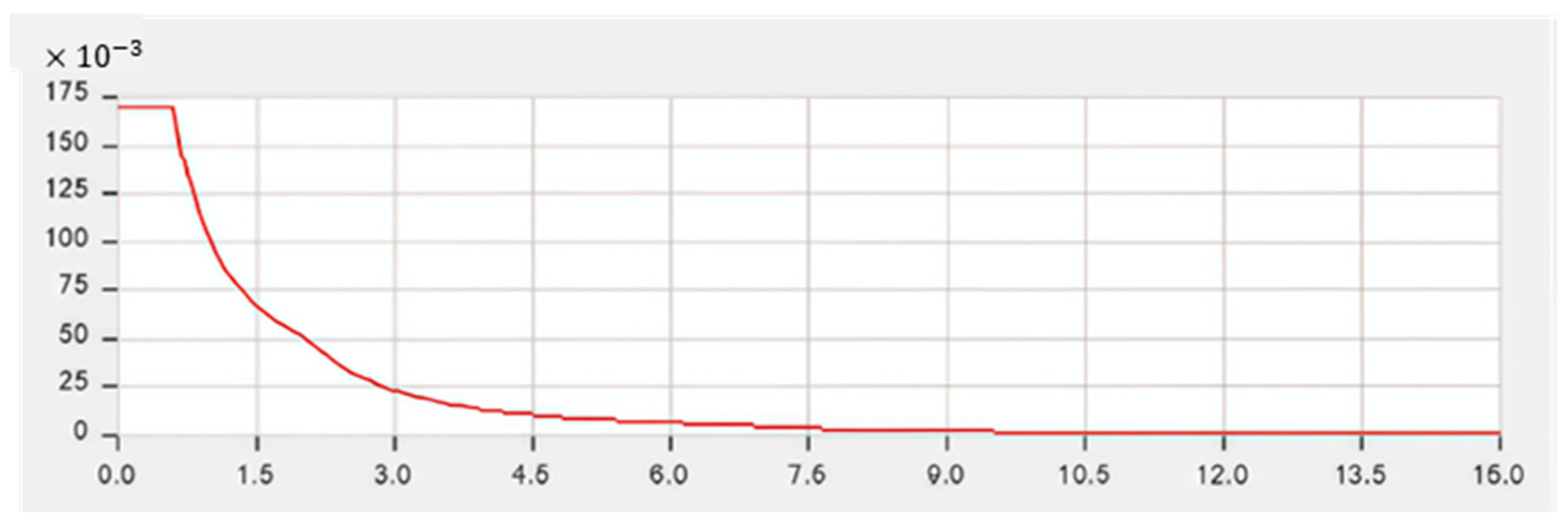
| Period (Sec.) | Acceleration (m/s2) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0.1688 |
| 0.1 | 0.1688 |
| 0.2 | 0.1688 |
| 0.3 | 0.1688 |
| 0.4 | 0.1688 |
| 0.5 | 0.1688 |
| 0.6 | 0.1688 |
| 0.7 | 0.1446 |
| 0.8 | 0.1266 |
| 0.9 | 0.1125 |
| 1 | 0.1012 |
| 1.2 | 0.0844 |
| 1.5 | 0.0675 |
| 1.7 | 0.0596 |
| 2 | 0.0506 |
| 2.5 | 0.0324 |
| 3 | 0.0225 |
| 3.5 | 0.0165 |
| 4 | 0.0127 |
| 5 | 0.008100 |
| 8 | 0.003164 |
| 11 | 0.001674 |
| 15 | 0.000900 |
| Case | Mode | Period | UX | UY | UZ | RX | RY | RZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MODAL | 1 | 0.459 | 0.6304 | 0.0000183 | 0 | 0.00001025 | 0.2749 | 0.0652 |
| MODAL | 2 | 0.205 | 0.0001 | 0.7019 | 0 | 0.297 | 0.00000421 | 0.00001437 |
| MODAL | 3 | 0.118 | 0.1508 | 0.00001219 | 0 | 0 | 0.342 | 0.0287 |
| MODAL | 4 | 0.104 | 0.0851 | 0.00003778 | 0 | 0.00001247 | 0.0124 | 0.6906 |
| MODAL | 5 | 0.056 | 0.0479 | 0.000007918 | 0 | 0.0000116 | 0.1087 | 0.006 |
| MODAL | 6 | 0.054 | 0 | 0.1894 | 0 | 0.4045 | 0.000001291 | 0.00001382 |
| MODAL | 7 | 0.036 | 0.0256 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0729 | 0.0008 |
| MODAL | 8 | 0.033 | 0.0113 | 0.000004556 | 0 | 0.00001856 | 0.0444 | 0.124 |
| MODAL | 9 | 0.027 | 5.491 × 10−7 | 0.0488 | 0 | 0.1167 | 0.000001345 | 0 |
| MODAL | 10 | 0.026 | 0.0132 | 6.968 × 10−7 | 0 | 0.000002027 | 0.0368 | 0.0017 |
| MODAL | 11 | 0.02 | 0.0092 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0274 | 0.0006 |
| MODAL | 12 | 0.018 | 0.0031 | 0.00001009 | 0 | 0.00003838 | 0.0073 | 0.0346 |
| MODAL | 13 | 0.018 | 0.000002175 | 0.023 | 0 | 0.0687 | 0.000003717 | 0.00003222 |
| MODAL | 14 | 0.016 | 0.006 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0178 | 0.0007 |
| MODAL | 15 | 0.014 | 0.0043 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0134 | 0.0004 |
| MODAL | 16 | 0.013 | 9.161 × 10−7 | 0.0128 | 0 | 0.0371 | 0.000002954 | 0.00001181 |
| MODAL | 17 | 0.013 | 0.0017 | 0.00001719 | 0 | 0.0001 | 0.0063 | 0.0167 |
| MODAL | 18 | 0.012 | 0.0028 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0086 | 0.0006 |
| MODAL | 19 | 0.011 | 0.0023 | 0.000000607 | 0 | 0.000002041 | 0.0073 | 0.0001 |
| MODAL | 20 | 0.011 | 0 | 0.008 | 0 | 0.0252 | 0 | 0.000005205 |
| MODAL | 21 | 0.01 | 0.0007 | 0.000007973 | 0 | 0.00002331 | 0.002 | 0.0097 |
| MODAL | 22 | 0.01 | 0.0016 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.005 | 0.0001 |
| MODAL | 23 | 0.009 | 0.000002933 | 0.0052 | 0 | 0.016 | 0.000008988 | 0.000002463 |
| MODAL | 24 | 0.009 | 0.001 | 0.000006552 | 0 | 0.00001994 | 0.0033 | 0.0002 |
| MODAL | 25 | 0.008 | 0.0008 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0026 | 6.015 × 10−7 |
| MODAL | 26 | 0.008 | 0.0003 | 0.000006353 | 0 | 0.00002113 | 0.0013 | 0.0062 |
| MODAL | 27 | 0.008 | 0.0005 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0015 | 0.00001332 |
| MODAL | 28 | 0.008 | 0 | 0.0036 | 0 | 0.0115 | 0.00000167 | 0.000004874 |
| MODAL | 29 | 0.008 | 0.0002 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0007 | 0.00004932 |
| MODAL | 30 | 0.007 | 0.0001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0004 | 0.000002108 |
| MODAL | 31 | 0.007 | 0.00002342 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0001 | 0.000005299 |
| MODAL | 32 | 0.007 | 0.0003 | 0.0003 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.0007 | 0.0036 |
| MODAL | 33 | 0.007 | 0.0000355 | 0.0021 | 0 | 0.0067 | 0.0001 | 0.0005 |
| MODAL | 34 | 0.006 | 0 | 0.0017 | 0 | 0.0056 | 0 | 0 |
| MODAL | 35 | 0.006 | 0.0002 | 0 | 0 | 8.187 × 10−7 | 0.0007 | 0.0028 |
| MODAL | 36 | 0.006 | 0 | 0.0012 | 0 | 0.0038 | 0 | 5.101 × 10−7 |
| MODAL | 37 | 0.005 | 0.0001 | 0.00000179 | 0 | 0.000005919 | 0.0004 | 0.002 |
| MODAL | 38 | 0.005 | 0 | 0.0008 | 0 | 0.0026 | 7.794 × 10−7 | 0.000004315 |
| MODAL | 39 | 0.005 | 0 | 0.0005 | 0 | 0.0016 | 0 | 0 |
| MODAL | 40 | 0.005 | 0.0001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0003 | 0.0014 |
| MODAL | 41 | 0.005 | 0 | 0.0003 | 0 | 0.001 | 0 | 0 |
| MODAL | 42 | 0.005 | 0 | 0.0002 | 0 | 0.0005 | 0 | 0 |
| MODAL | 43 | 0.005 | 0 | 0.0001 | 0 | 0.0002 | 0 | 0.000001602 |
| MODAL | 44 | 0.005 | 0.0001 | 5.538 × 10−7 | 0 | 0.000001691 | 0.0002 | 0.0009 |
| MODAL | 45 | 0.005 | 0.000001657 | 0.000006002 | 0 | 0.00001654 | 0.000004974 | 0.00002619 |
| MODAL | 46 | 0.004 | 0.00004018 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0002 | 0.0007 |
| MODAL | 47 | 0.004 | 0.00002488 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0001 | 0.0004 |
| MODAL | 48 | 0.004 | 0.00001414 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 |
| MODAL | 49 | 0.004 | 0.000006673 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00001775 | 0.0001 |
| MODAL | 50 | 0.004 | 0.000001994 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.000008984 | 0.00003575 |
| MODAL | 51 | 0.004 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9.394 × 10−7 | 0 |
| Base Reactions—Model Manual | |||||||
| Output Case | Case Type | FX | FY | FZ | MX | MY | MZ |
| kN | kN | kN | kN·m | kN·m | kN·m | ||
| SDx | LinRespSpec | 3159.329 | 35.335 | 0 | 1132.934 | 97,996.780 | 48,485.613 |
| SDy | LinRespSpec | 35.335 | 3466.030 | 0 | 107,739.918 | 982.624 | 34,121.209 |
| Base Reactions—Automated Model | |||||||
| Output Case | Case Type | FX | FY | FZ | MX | MY | MZ |
| kN | kN | kN | kN·m | kN·m | kN·m | ||
| SDx | LinRespSpec | 2697.420 | 34.004 | 0 | 1100.929 | 85,771.947 | 39,296.772 |
| SDy | LinRespSpec | 34.005 | 2959.197 | 0 | 92,254.261 | 944.555 | 26,434.123 |
| Base Reactions—Genetic algorithm model | |||||||
| Output Case | Case Type | FX | FY | FZ | MX | MY | MZ |
| kN | kN | kN | kN·m | kN·m | kN·m | ||
| SDx | LinRespSpec | 2705.823 | 56.131 | 0 | 1814.233 | 84,355.035 | 38,691.561 |
| SDy | LinRespSpec | 56.131 | 2961.589 | 0 | 92,315.328 | 1523.735 | 26,263.629 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabrera, P.A.; Medina, G.M.; Delgadillo, R.M. Automation and Genetic Algorithm Optimization for Seismic Modeling and Analysis of Tall RC Buildings. Buildings 2025, 15, 3618. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193618
Cabrera PA, Medina GM, Delgadillo RM. Automation and Genetic Algorithm Optimization for Seismic Modeling and Analysis of Tall RC Buildings. Buildings. 2025; 15(19):3618. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193618
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabrera, Piero A., Gianella M. Medina, and Rick M. Delgadillo. 2025. "Automation and Genetic Algorithm Optimization for Seismic Modeling and Analysis of Tall RC Buildings" Buildings 15, no. 19: 3618. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193618
APA StyleCabrera, P. A., Medina, G. M., & Delgadillo, R. M. (2025). Automation and Genetic Algorithm Optimization for Seismic Modeling and Analysis of Tall RC Buildings. Buildings, 15(19), 3618. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193618








