Optimization of Smartphone-Based Strain Measurement Algorithm Utilizing Arc-Support Line Segments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of the Sensor and MISS Method
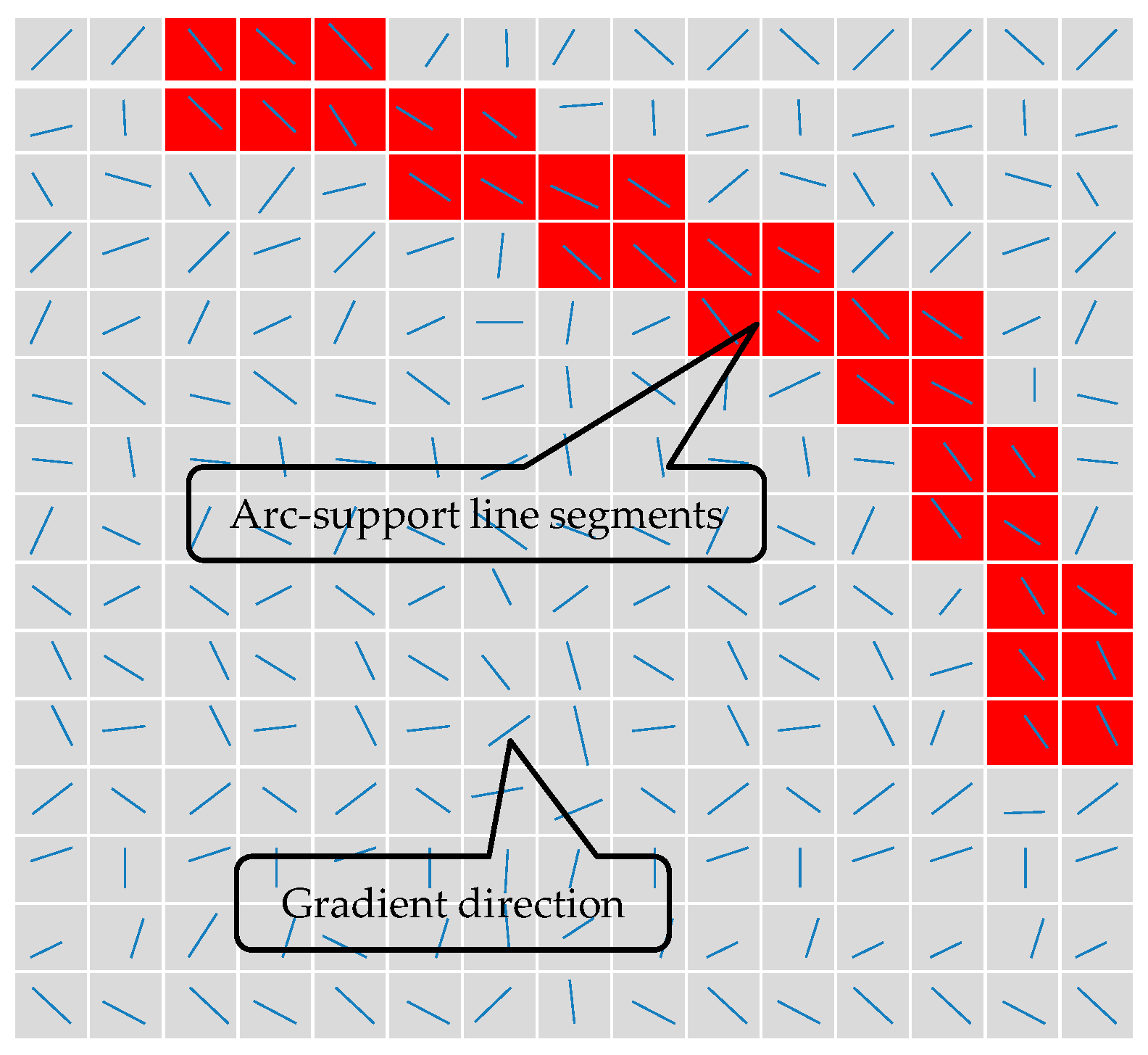
3. Introduction to the ASLS Algorithm
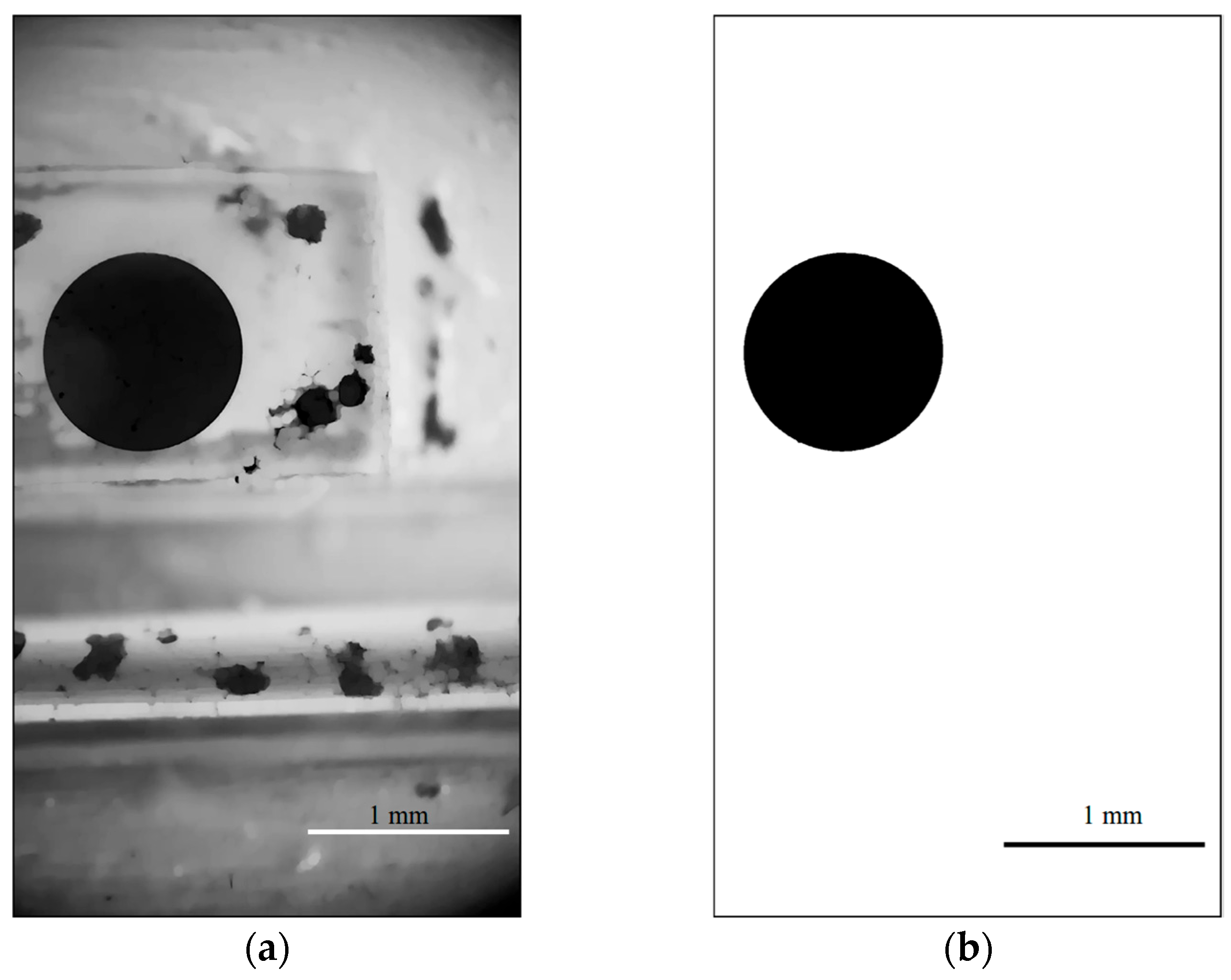
4. Comparison of Circular Detection Methods
4.1. Algorithm Comparison Experimental Setup
4.2. Detection Performance Comparison
4.3. Computational Results Comparison
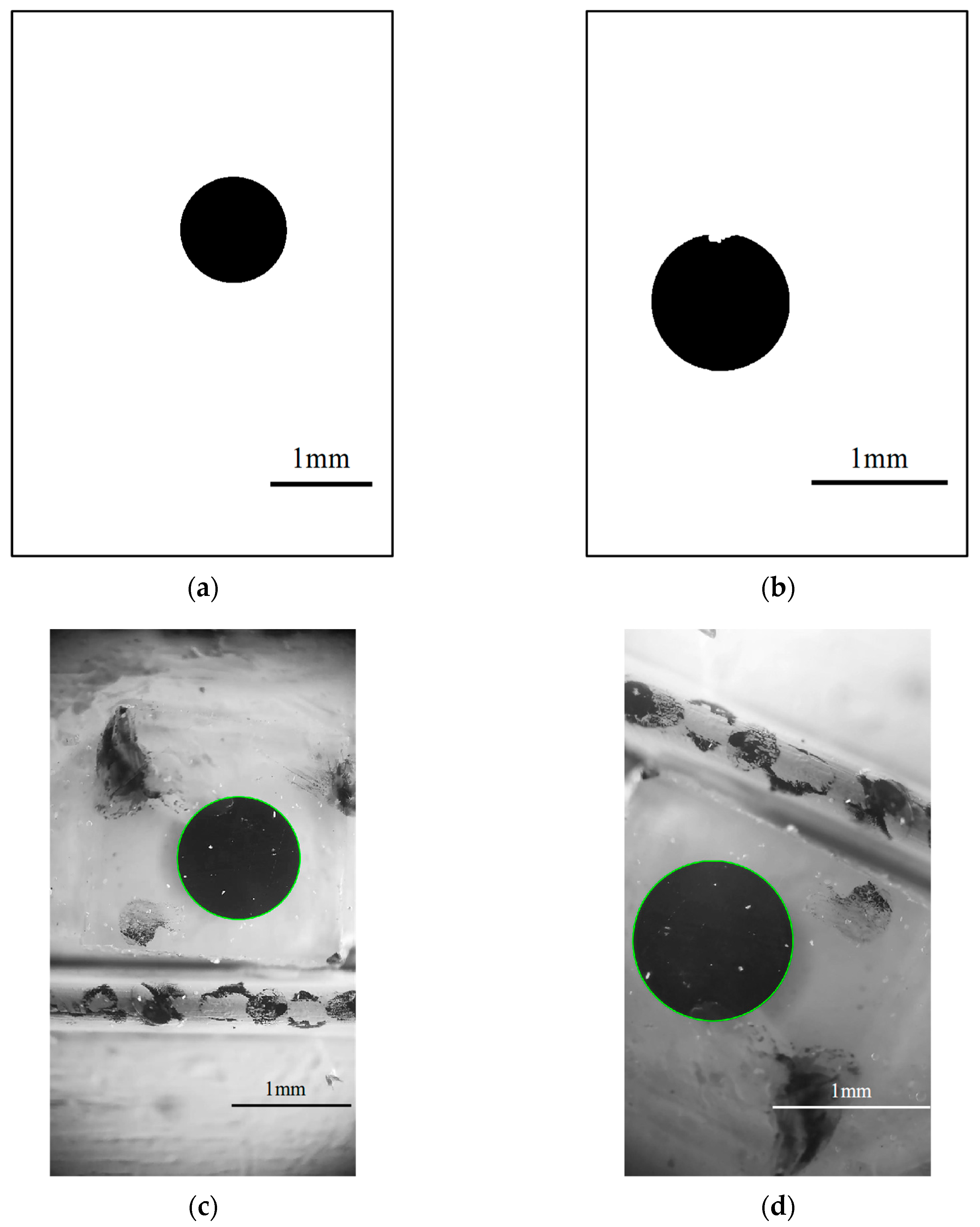
5. Analysis of Illumination Variation Effects
5.1. Illumination Variation Experimental Setup
5.2. Static Test Results Analysis
5.3. Dynamic Test Results Analysis
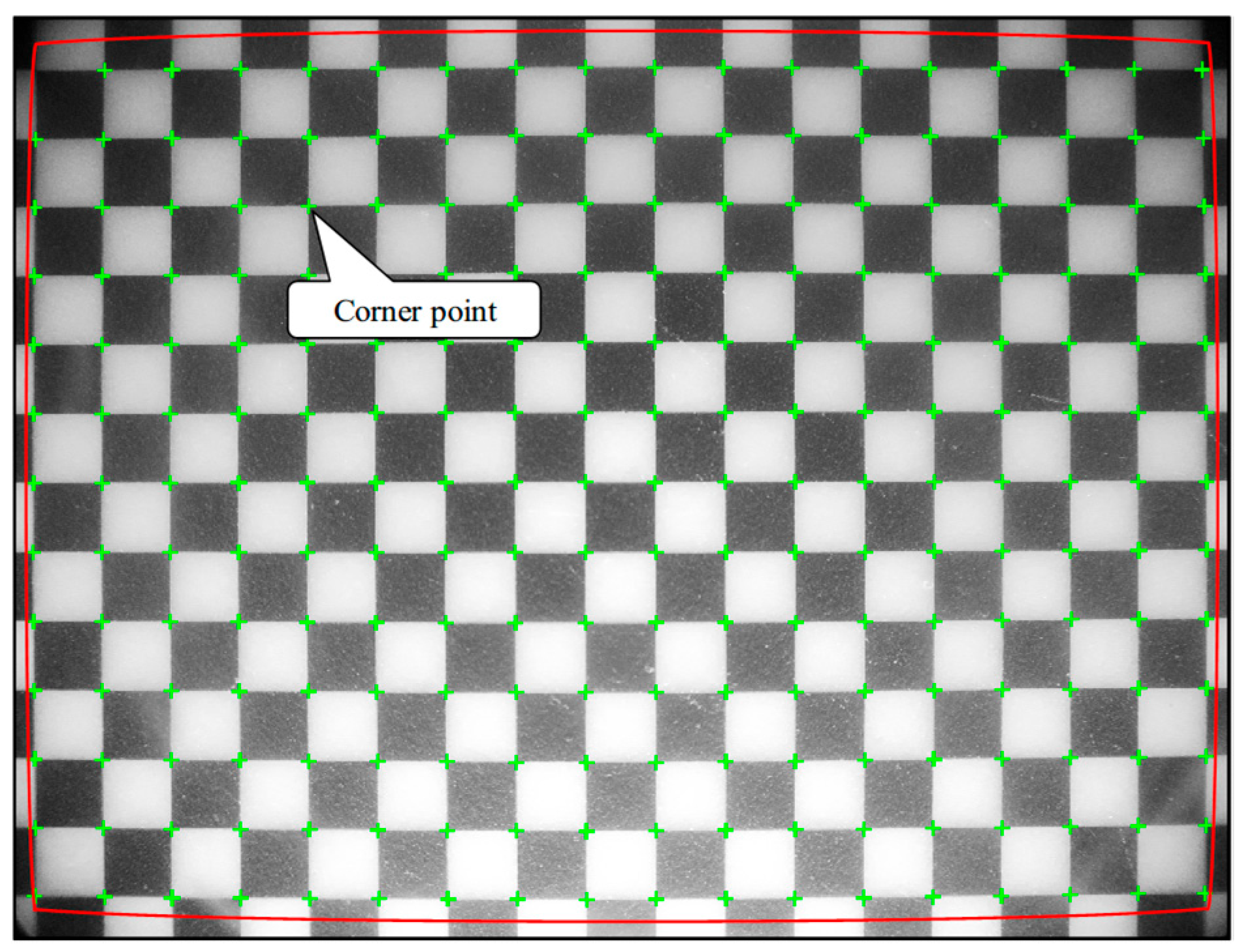
6. Analysis of Image Distortion Effects
6.1. Forms of Distortion
6.2. Pixel Variability
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MISS | Micro Image Strain Sensing |
| SURF | Speeded-up Robust Feature |
| CCL | Connected Component Labeling |
| ASLS | Arc-Support Line Segments |
References
- Vijayan, D.S.; Sivasuriyan, A.; Devarajan, P.; Krejsa, M.; Chalecki, M.; Żółtowski, M.; Kozarzewska, A.; Koda, E. Development of Intelligent Technologies in SHM on the Innovative Diagnosis in Civil Engineering—A Comprehensive Review. Buildings 2023, 13, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ren, Y.; He, S.; Gao, Z.; Li, B.; Song, J. A Review of Methods and Applications in Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) for Bridges. Measurement 2025, 245, 116575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, W.; Gao, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Research Progress of SHM System for Super High-Rise Buildings Based on Wireless Sensor Network and Cloud Platform. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Hou, Y.; Xiao, W.; Fan, L.; Cai, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, Y. Strain Response Analysis and Experimental Study of the Cross-Fault Buried Pipelines. Symmetry 2025, 17, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Shi, B.; Zhu, Y. Structural Monitoring and Performance Assessment of Shield Tunnels during the Operation Period, Based on Distributed Optical-Fiber Sensors. Symmetry 2019, 11, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Yu, T. Crack Identification Method for Prefabricated Concrete Pavement Based on Distributed Strain Monitoring. Buildings 2024, 14, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, L.; Li, D.; Zhao, X. Design of Smart Cable for Distributed Cable Force Measurement in Cable Dome Structures and Its Application. Buildings 2023, 13, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Du, H.; Zhao, F.; Hong, M. Damage Identification in a Plate Structure Based on a Cross-Direction Strain Measurement Method. Measurement 2020, 158, 107714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Choi, S.W.; Jung, D.J.; Park, H.S. Analytical Model for Estimation of Maximum Normal Stress in Steel Beam-Columns Based on Wireless Measurement of Average Strains from Vibrating Wire Strain Gages. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2013, 28, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Pan, B. In-Plane Displacement and Strain Measurements Using a Camera Phone and Digital Image Correlation. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 054107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Tao, R.; Lubineau, G. Accurate 3D Shape, Displacement and Deformation Measurement Using a Smartphone. Sensors 2019, 19, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Bekdullayev, N.; Lubineau, G. Smartphone-Based Single-Camera Stereo-DIC System: Thermal Error Analysis and Design Recommendations. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 9567–9576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromanis, R.; Xu, Y.; Lydon, D.; Martinez del Rincon, J.; Al-Habaibeh, A. Measuring Structural Deformations in the Laboratory Environment Using Smartphones. Front. Built Environ. 2019, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Yan, X.; Lv, X. Research on 2D Digital Image Correlation Measurement Based on Smartphones. In Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures + Nondestructive Evaluation, Denver, CO, USA, 3–7 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Stoilov, G.; Pashkouleva, D.; Kavardzhikov, V. Smartphone Application for Structural Health Monitoring. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 951, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Li, J.; Zhao, X. Accuracy and Sensibility Analysis of Strain Measurement Based on Microimages Captured by Smartphone with a Microscope. Struct Control. Health Monit 2021, 2, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Li, J.; Zhao, X. Strain Measurement Based on Speeded-up Robust Feature Algorithm Applied to Microimages from a Smartphone-Based Microscope. Sensors 2020, 20, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Chen, X.; Ding, M.; Zhou, G.; Zhao, X. Design and Development of a New Strain Measuring Method Based on Smartphone and Machine Vision. Measurement 2021, 182, 109724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Xie, B.; Zhou, G.; Zhao, X. Critical Experiments for Structural Members of Micro Image Strain Sensing Sensor Based on Smartphone and Microscope. Buildings 2022, 12, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, G.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X. Smartphone-Based Method for Measuring Maximum Peak Tensile and Compressive Strain. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2024, 39, 2330–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, H.K.; Princen, J.; Lllingworth, J.; Kittler, J. Comparative Study of Hough Transform Methods for Circle Finding. Image Vis. Comput. 1990, 8, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata Hassanein, A.; Mohammad, S.; Sameer, M.; Ehab Ragab, M. A Survey on Hough Transform, Theory, Techniques and Applications. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.02160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Fan, C.; Zhao, Z. The Center of the Circle Fitting Optimization Algorithm Based on the Hough Transform for Crane. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H. Improved Randomized Hough Transform Based on Circular Power Theory. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Image Processing, Computer Vision and Machine Learning, ICICML 2023, Chengdu, China, 3–5 November 2023; pp. 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.C.; Chung, K.L. An Efficient Randomized Algorithm for Detecting Circles. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2001, 83, 172–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.Q.; Peng, C.Z.; Liu, H.M.; Wang, Z.H. A Fast Randomized Circle Detection Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 4th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, CISP 2011, Shanghai, China, 15–16 October 2011; Volume 2, pp. 820–823. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, K.L.; Huang, Y.H.; Shen, S.M.; Krylov, A.S.; Yurin, D.V.; Semeikina, E.V. Efficient Sampling Strategy and Refinement Strategy for Randomized Circle Detection. Pattern Recognit. 2012, 45, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Chung, K.L.; Yang, W.N.; Chiu, S.H. Efficient Symmetry-Based Screening Strategy to Speed up Randomized Circle-Detection. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2012, 33, 2071–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grompone von Gioi, R.; Jakubowicz, J.; Morel, J.-M.; Randall, G. LSD: A Line Segment Detector. Image Process. Line 2012, 2, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Duan, Y. Circle Detection on Images by Line Segment and Circle Completeness. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, ICIP 2016, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 3648–3652. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Xia, S.; Huang, W.; Shao, M.; Fu, Y. Circle detection by arc-support line segments. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; pp. 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Xia, S.; Shao, M.; Fu, Y. Arc-Support Line Segments Revisited: An Efficient and High-Quality Ellipse Detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 768–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Q. A Fast Circle Detector with Efficient Arc Extraction. Symmetry 2022, 14, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.; Stephens, M. A Combined Corner and Edge Detector. In Proceedings of the AVC, Manchester, UK, 31 August–2 September 1988; pp. 23.1–23.6. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.M.; Brady, J.M. SUSAN-A New Approach to Low Level Image Processing. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1997, 23, 45–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awrangjeb, M.; Lu, G. Robust Image Corner Detection Based on the Chord-to-Point Distance Accumulation Technique. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2008, 10, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtarian, F.; Suomela, R. Robust image corner detection through curvature scale space. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.W.; Najmus Sadat, R.M.; Lu, G. Effective and Efficient Contour-Based Corner Detectors. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 2185–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat, R.M.N.; Teng, S.W.; Lu, G. An Effective and Efficient Contour-Based Corner Detector Using Simple Triangular Theory. In Proceedings of the Pacific Conference on Computer Graphics and Applications, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 21–23 September 2011; pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, A.; Moosmann, F.; Car, Ö.; Schuster, B. Automatic Camera and Range Sensor Calibration using a single Shot. In Proceedings of the ICRA 2012: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, St. Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; ISBN 9781467314053. [Google Scholar]






| Para | Illustration | Value |
|---|---|---|
| ξrd | Radial distance tolerance | 10 |
| α | Normal tolerance | 6° |
| Tni | Ratio of support edge pixels on a circle | 0.5 |
| Tac | Angle of circular completeness | 165° |
| Device | Manufacturer Name, City, and Country | Main Camera Resolution (Megapixels) | Type | Frame Rate (Fps) | Pixel Count | Number of Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HONOR 7X | Honor Device Co., Ltd. Shenzhen, China | 8 | Video 1 | 30 | 1920 × 1280 | 1834 |
| HUAWEI P30pro | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. Shenzhen, China | 10 | Video 2 | 60 | 1920 × 1280 | 3798 |
| HUAWEI nova 13 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. Shenzhen, China | 13 | Video 3 | 30 | 1920 × 1280 | 1871 |
| Redmi Note 11 | Xiaomi Corporation. Beijing, China | 16 | Video 4 | 30 | 1920 × 1280 | 1975 |
| Type | Circle Detection Algorithm | Number of Images | Circle Diameter (Mean, in Pixels) | Detection Error (Diameter) | Computational Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Video 1 | CCL | 1834 | 426.1803 | 0.27% | 105 |
| ASLS | 1834 | 427.3447 | 898 | ||
| Video 2 | CCL | 3798 | 556.9113 | 0.23% | 249 |
| ASLS | 3798 | 555.6267 | 1698 | ||
| Video 3 | CCL | 1871 | 553.8449 | 0.94% | 102 |
| ASLS | 1871 | 548.6437 | 726 | ||
| Video 4 | CCL | 1975 | 794.2364 | 0.58% | 110 |
| ASLS | 1975 | 789.6595 | 783 |
| Type | Circle Detection Algorithm | Circle Diameter (The First Image, in Pixels) | Circle Diameter (Mean, in Pixels) | Detection Error (Diameter) | Computational Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Video 1 | CCL | 426.0778 | 426.1803 | 0.024% | 123 |
| ASLS | 427.0857 | 427.3447 | 0.061% | 102 | |
| Video 2 | CCL | 555.7184 | 556.9113 | 0.21% | 524 |
| ASLS | 555.9828 | 555.6267 | 0.064% | 589 | |
| Video 3 | CCL | 554.3392 | 553.8449 | 0.089% | 134 |
| ASLS | 548.8398 | 548.6437 | 0.036% | 147 | |
| Video 4 | CCL | 790.7721 | 794.2364 | 0.44% | 138 |
| ASLS | 786.2929 | 789.6595 | 0.43% | 154 |
| Experiment No. | Peak Value of LVDT (με) | Peak Value of Smartphone (με) | Error (με) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 336.3 | 341.9 | 5.6 |
| 2 | 336.2 | 341.6 | 5.4 |
| 3 | 335.1 | 342.1 | 7.0 |
| 4 | 335.5 | 341.8 | 6.3 |
| 5 | 325.4 | 322.2 | −3.2 |
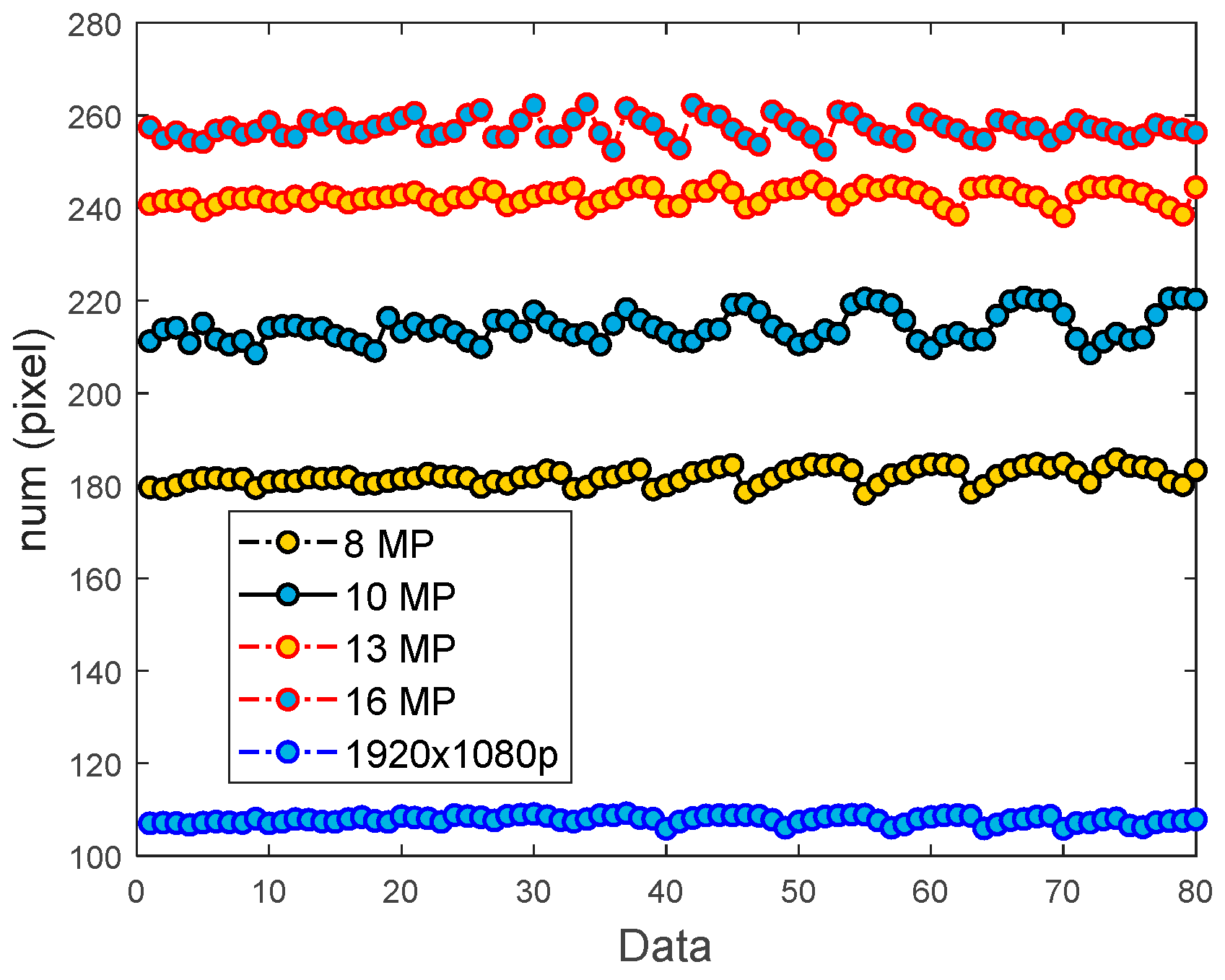
| Image Pixels | Pixel Count Between Corner Points (Maximum) | Pixel Count Between Corner Points (Minimum) | Pixel Count Between Corner Points (Average) | Errors (Absolute) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 MP | 185.7746 | 178.2364 | 182.1527 | 4.12% |
| 10 MP | 220.7116 | 208.5724 | 214.4623 | 5.66% |
| 13 MP | 244.3574 | 237.4262 | 242.5094 | 2.86% |
| 16 MP | 262.4204 | 252.4495 | 257.2798 | 3.88% |
| 1920 × 1280 | 109.1786 | 105.4875 | 107.5891 | 3.43% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, Q.; Gou, C.; Lu, S.; Xie, B. Optimization of Smartphone-Based Strain Measurement Algorithm Utilizing Arc-Support Line Segments. Buildings 2025, 15, 3407. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183407
Cui Q, Gou C, Lu S, Xie B. Optimization of Smartphone-Based Strain Measurement Algorithm Utilizing Arc-Support Line Segments. Buildings. 2025; 15(18):3407. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183407
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Qiwen, Changfei Gou, Shengan Lu, and Botao Xie. 2025. "Optimization of Smartphone-Based Strain Measurement Algorithm Utilizing Arc-Support Line Segments" Buildings 15, no. 18: 3407. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183407
APA StyleCui, Q., Gou, C., Lu, S., & Xie, B. (2025). Optimization of Smartphone-Based Strain Measurement Algorithm Utilizing Arc-Support Line Segments. Buildings, 15(18), 3407. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183407




