Research on Intelligent Generation of Line Drawings from Point Clouds for Ancient Architectural Heritage
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background
1.2. Research Significance
2. Related Work
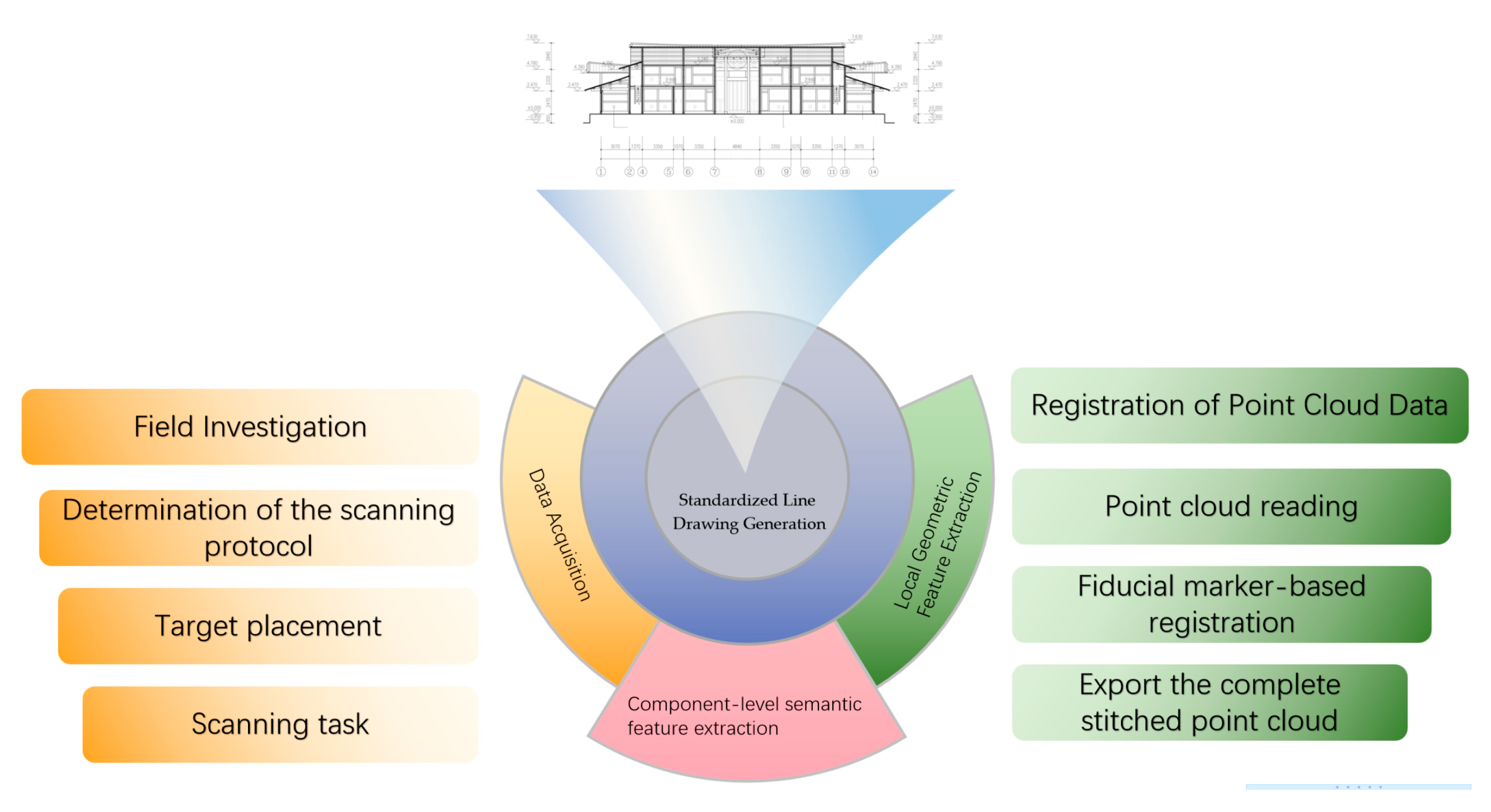
3. Methods
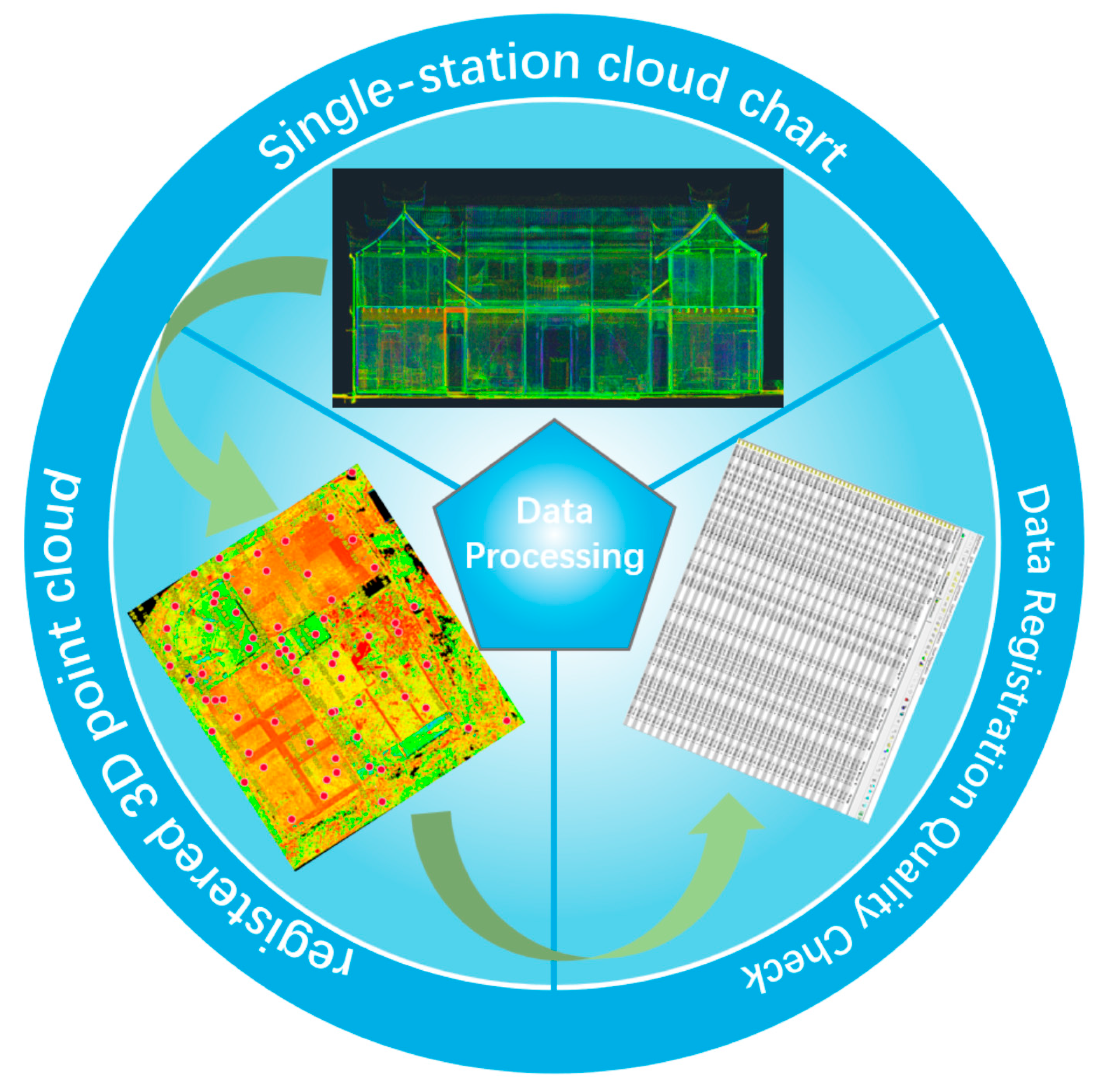
3.1. Intelligent Multi-Granularity Feature Learning
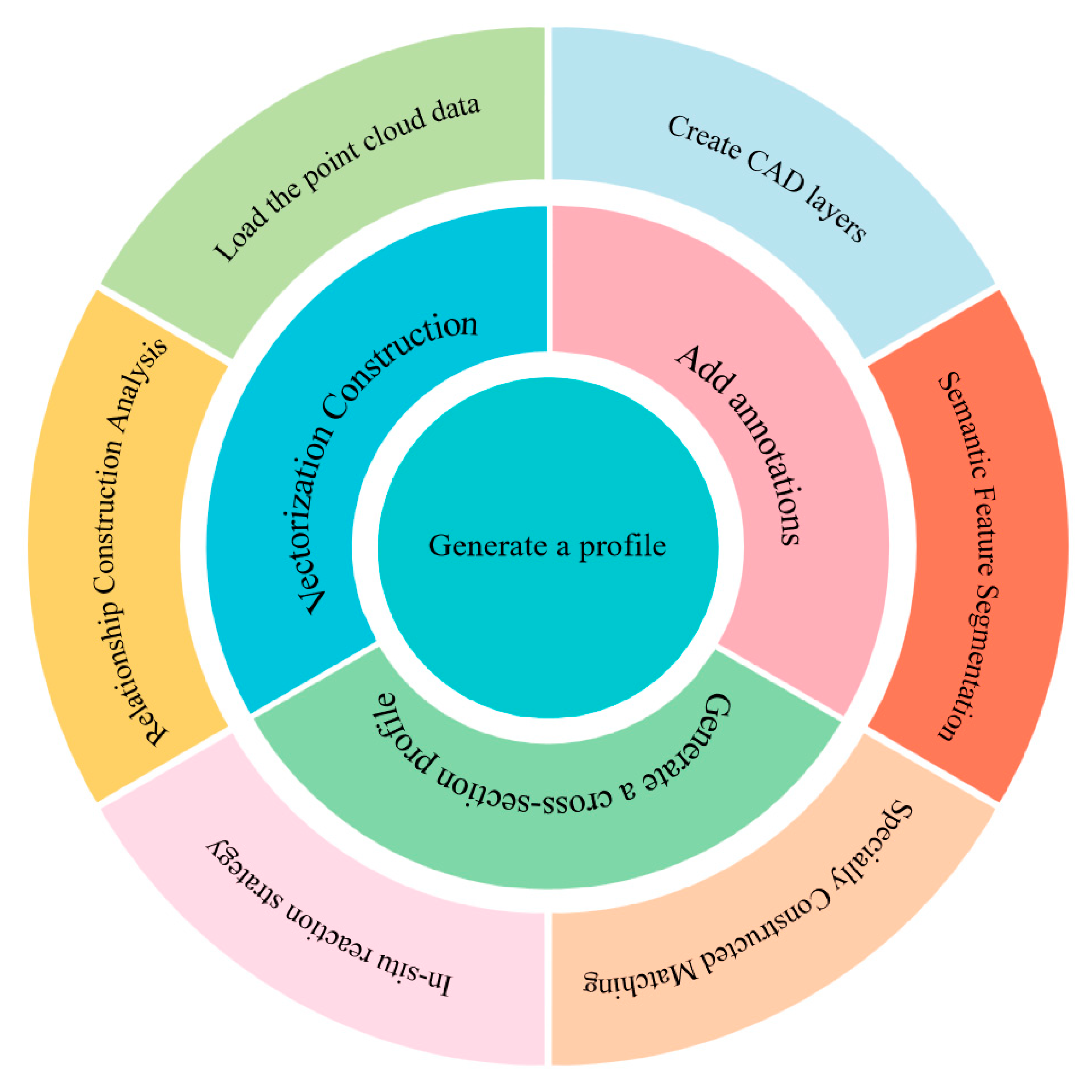
3.2. AI-Driven Structured Line Drawing Generation
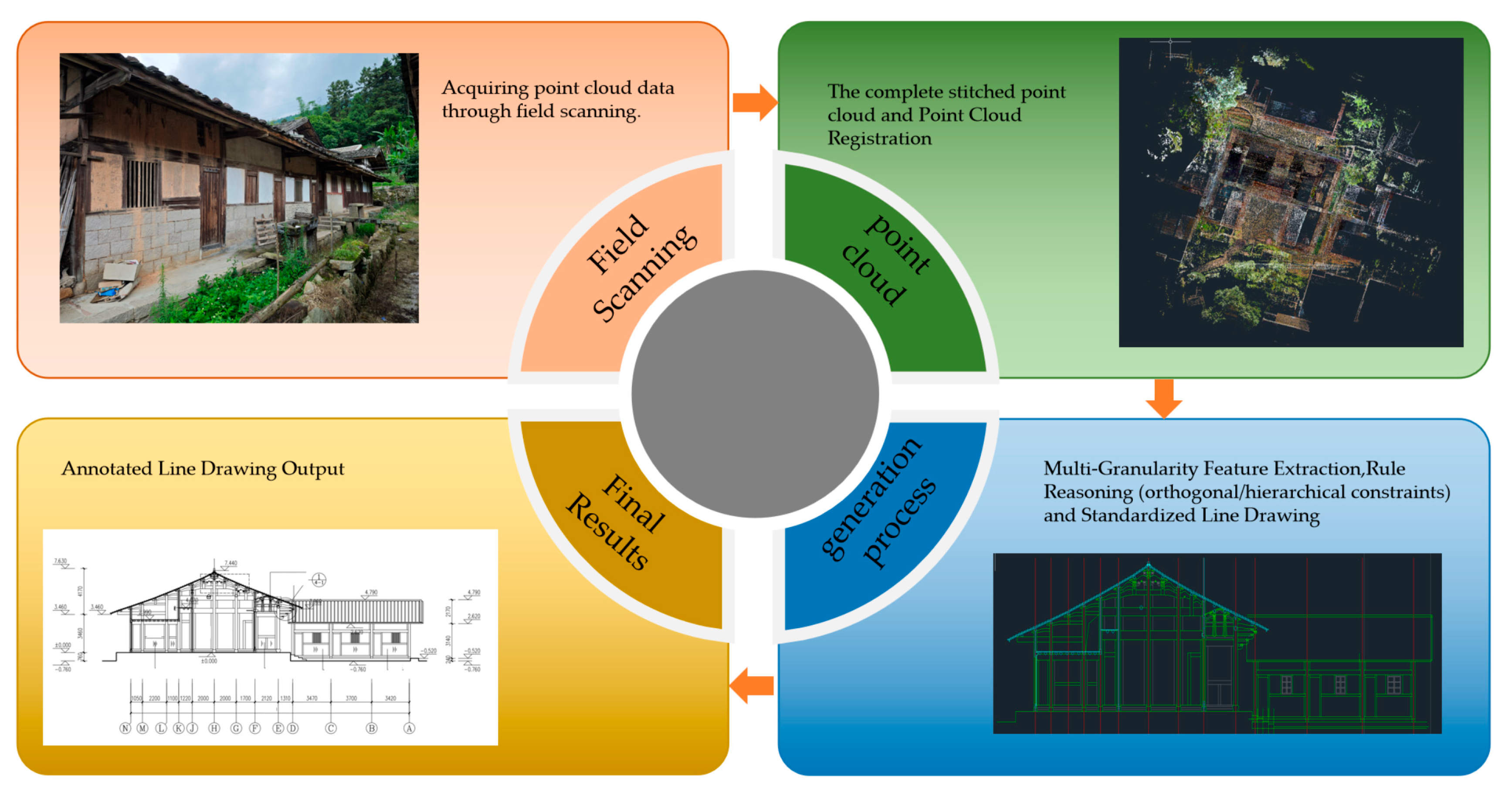
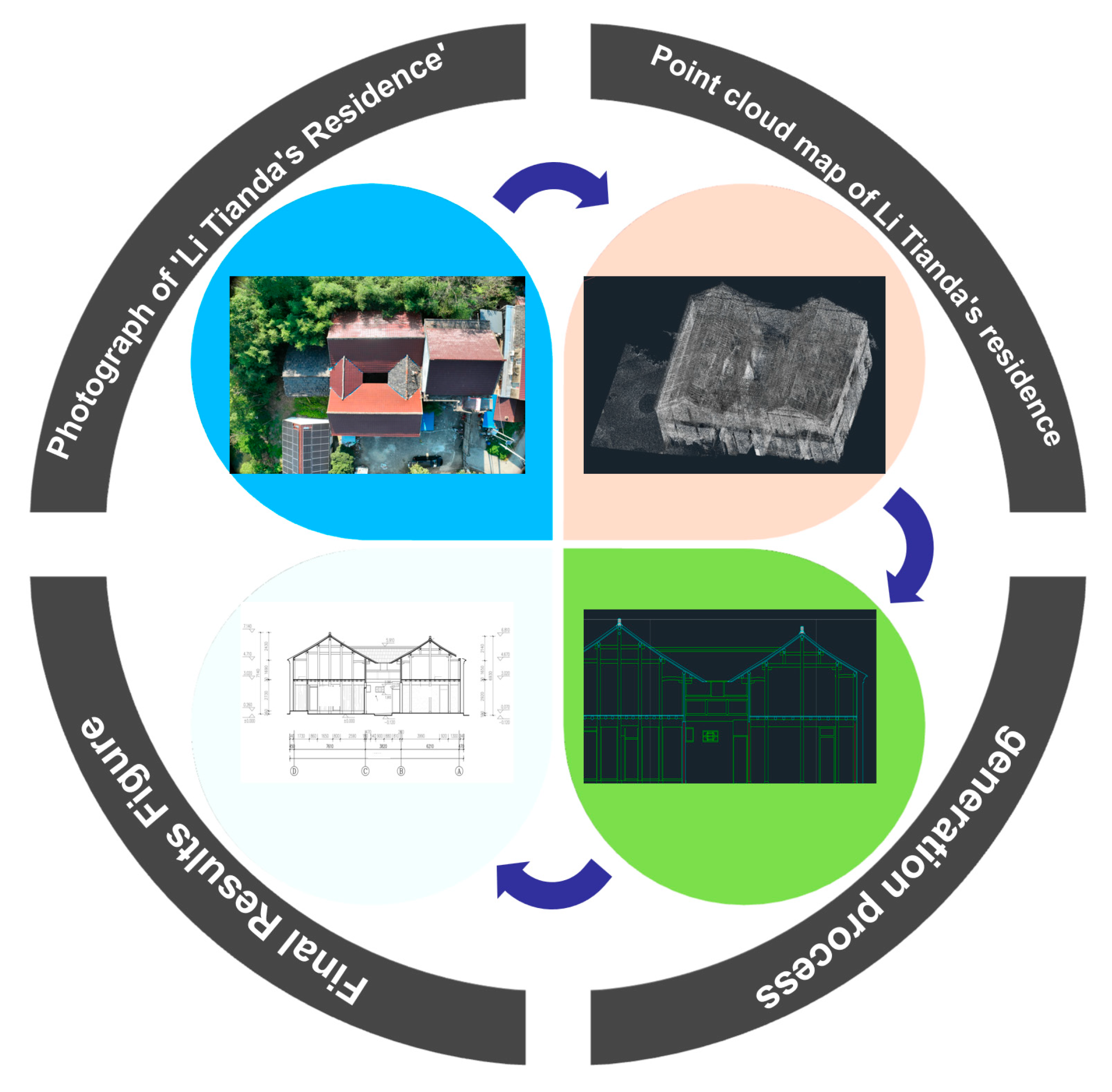
4. Case Study
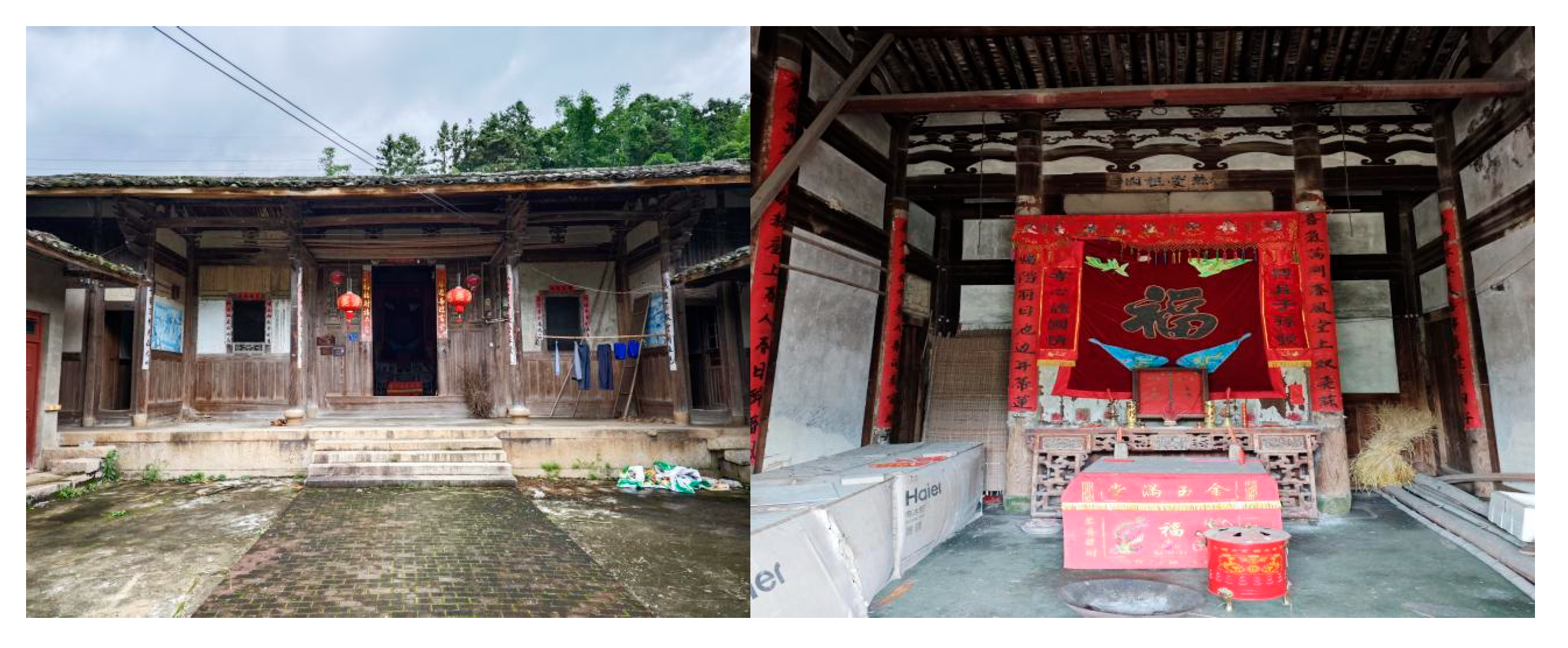
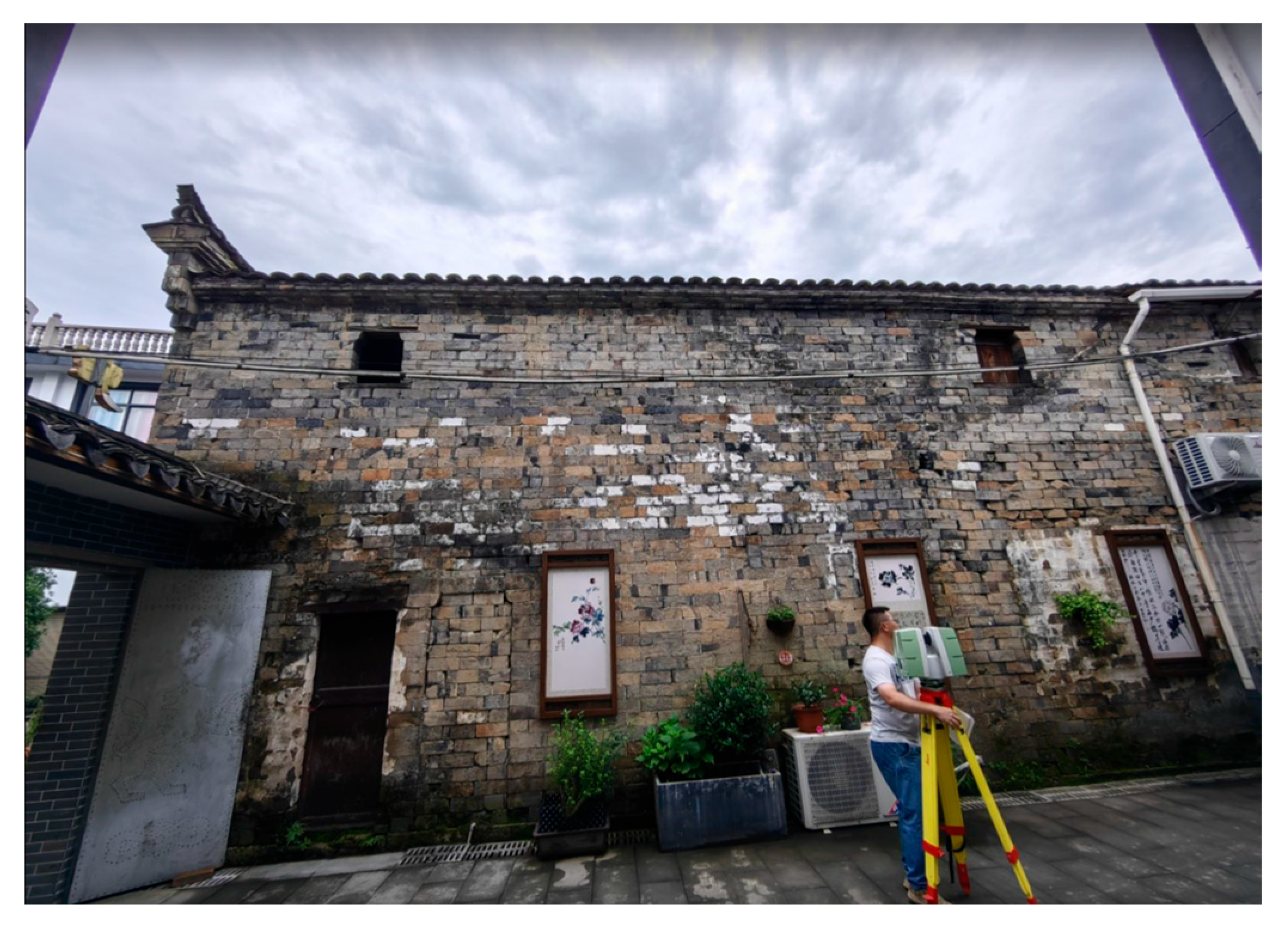
4.1. Guancang No. 11, Luoyuan County, Fujian
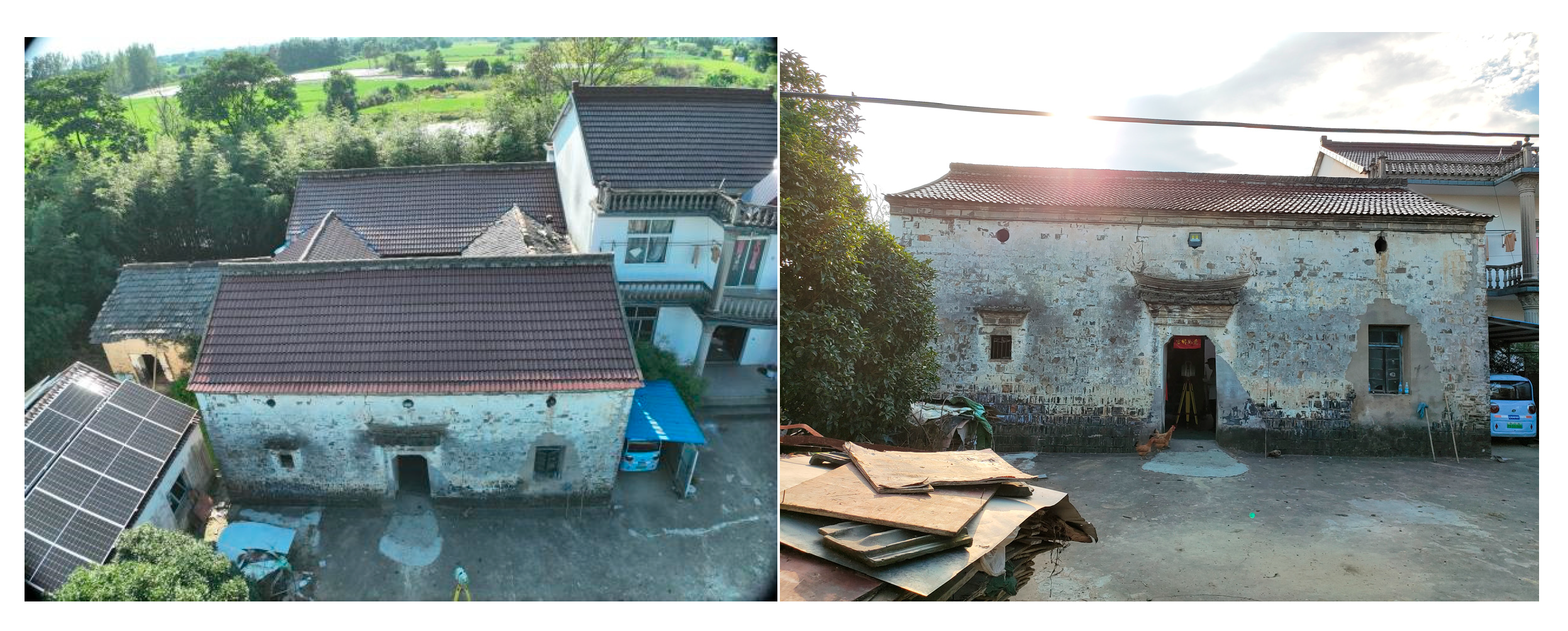
4.2. Langxi County, Anhui Province
4.3. Validation and Comparison with Traditional Methods
4.4. Complex Component Testing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, K.; Xu, Y.; Wang, R. A Preprocessing Method for 3D Point Cloud Registration in Urban Environments. Opto-Electron. Eng. 2018, 45, 180266. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Feng, P.; Li, H.; Du, J.; Cheng, W. Intelligent Generation of Single-Line Diagrams in Power Distribution Networks Using Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 102345–102356. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Tuzel, O. VoxelNet: End-to-End Learning for Point Cloud Based 3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7830–7839. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zu, X. Machine Intelligence for Interpretation and Preservation of Built Heritage. Autom. Constr. 2025, 16, 104567. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, T.; Li, R.; Zha, H. 3D Line Drawing for Archaeological Illustration. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2011, 94, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, Y.; Song, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Line-Based 3D Building Abstraction and Polygonal Surface Reconstruction From Images. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2022, 28, 4877–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Dong, Y.; Hou, M.; Qi, Y. An Extraction Method for Roof Point Cloud of Ancient Building Using Deep Learning Framework. ISPRS Arch. 2021, XLVI-M-1-2021, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Semantic Segmentation of Point Clouds of Ancient Buildings Based on Weak Supervision. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, R.B.; Cousins, S. 3D is Here: Point Cloud Library (PCL). In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Lv, P.; Li, D. A New Shape Reconstruction Method for Monitoring the Large Deformations of Offshore Wind Turbine Towers. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 312, 119253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Li, S.; Mao, J. Research on VMD-SSA-LSTM Mine Surface Deformation Prediction Model Based on Time-Series InSAR Monitoring. Chem. Miner. Process. 2023, 52, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Shi, R.; Kuang, K. Openshape: Scaling up 3D Shape Representation Towards Open-World Understanding. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 44860–44879. [Google Scholar]
- Gumhold, S.; Bærentzen, J.A. Curvature Estimation for Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques in Australasia and South East Asia (GRAPHITE), Melbourne, Australia, 11–14 February 2002; pp. 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhao, C.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. PV-RCNN: Point-Voxel Feature Set Abstraction for 3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10526–10535. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Geng, S.; Zhang, R.; Ma, T.; Fang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Qiao, Y. Clip-Adapter: Better Vision-Language Models with Feature Adapters. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2024, 132, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Tang, X.; Liu, Y. Ground Deformation Analysis Along the Island Subway Line by Integrating Time-Series InSAR and LiDAR Techniques. Opt. Eng. 2023, 62, 1988–1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; He, L.; Li, H. Multi-Scale Debris Flow Warning Technology Combining GNSS and InSAR Technology. Water 2025, 17, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosselman, G.; Dijkman, S. 3D building model reconstruction from point clouds and ground plans. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2001, 34, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Dai, A. Regional Dynamic Point Cloud Completion Network (RD-Net). Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2024, 147, 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Wang, J.; Li, H. TurboReg: TurboClique for Robust and Efficient Point Cloud Registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Honolulu, HI, USA, 19–23 October 2025; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zai, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Pairwise Registration of TLS Point Clouds Using Covariance Descriptors and a Non-Cooperative Game. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 195, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuhan University of Technology Team. Large-Scale Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation with Density-Based Grid Decimation. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, H.; Wang, B.; An, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z. Voxel-FPN: Multi-Scale Voxel Feature Aggregation for 3D Object Detection from LIDAR Point Clouds. Sensors 2020, 20, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Mao, Y.; Li, B. SECOND: Sparsely Embedded Convolutional Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. (NeurIPS) 2017, 30, 5099–5108. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Litany, O.; He, K.; Guibas, L.J. VoteNet: Deep Hough Voting for 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9288–9297. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Kim, S.; Li, Z.; Pfrommer, B.; Bär, A.; Schneider, J.; Geiger, A.; Oehmcke, S.; Gisler, C.; Omari, S.; et al. 3D Semantic Segmentation in the Wild: Learning Generalized Models for Adverse-Condition Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 15644–15653. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, R.; Wang, W.; Ren, F.; Zhang, P.; Hu, P. LiDAR2Map: In Defense of LiDAR-Based Semantic Map Construction Using Online Camera Distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 18048–18057. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Lai, Y. Dynamic Graph CNN for Learning on Point Clouds. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2019, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Leung, G.; Jia, K. PointCNN: Convolution on X-Transformed Points. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. (NeurIPS) 2019, 32, 8243–8253. [Google Scholar]
- Achlioptas, P.; Diamanti, O.; Mitliagkas, I.; Guibas, L.J. Learning Representations and Generative Models for 3D Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–5 May 2018; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Dai, A. DeepVCP: An End-to-End Deep Neural Network for Point Cloud Registration. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. (RA-L) 2019, 4, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Kim, M.; Kwon, T. PointNetLK: Robust & Efficient Point Cloud Registration using PointNet. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4550–4559. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Ma, H.; Wan, J. Multi-View 3D Object Detection Network for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6526–6534. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Segmentation-Aware Convolutional Neural Network for Point Cloud Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. (TGRS) 2020, 58, 1733–1745. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Li, B.; Zhang, J. PointWeb: Enhancing Local Neighborhood Features for Point Cloud Processing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3716–3724. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, X. Point-Line-Plane Feature Fusion for 3D Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. (TIV) 2021, 6, 456–468. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. LineNet: A Deep Neural Network for Line Feature Extraction from Point Clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 183, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J. 3D Line Segment Detection from Point Clouds using Deep Learning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. (GRSL) 2021, 18, 1569–1573. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, D. Point-Line Correspondence for 3D Reconstruction from Sparse Point Clouds. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. (CVIU) 2020, 199, 102987. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J. Fusion of Point Cloud and Line Features for Indoor Layout Estimation. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. (TVCG) 2022, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Chung, W. Optimization of Building Thermal Environment in Industrial Heritage Landscape Regeneration Design Simulation Based on Image Visual Visualization. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2024, 56, 103024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Intelligent Generation of Building Contours from Point Clouds using Deep Learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 178, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J. Line Feature Extraction from Point Clouds using Attention Mechanism. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. (TGRS) 2022, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Z. 3D Line Reconstruction from Point Clouds using Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 3556–3565. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, D. Point-Line-Plane Integrated Network for 3D Object Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (TNNLS) 2023, 34, 2345–2358. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, C.; Dong, Y.; Hou, M. DGPCD: A Benchmark for Typical Official-Style Dougong in Ancient Chinese Wooden Architecture. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R.; Kaul, M. A Survey on Point Cloud Registration Algorithms. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2020, 52, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, D. Noise Removal for Point Clouds using Anisotropic Diffusion. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. (TVCG) 2019, 25, 2941–2954. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W. Point Cloud Simplification using Quadric Error Metrics. Comput.-Aided Des. (CAD) 2018, 102, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Dong, Y.; Hou, M.; Li, X. MP-DGCNN for the Semantic Segmentation of Chinese Ancient Building Point Clouds. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.S.; Deng, Y. Intelligent assessment system of material deterioration in masonry tower based on improved image segmentation model. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J. Quality Assessment of Line Features Extracted from Point Clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 187, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Robust Line Detection in Noisy Point Clouds using Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. (TGRS) 2021, 59, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, J.W.; Kim, Y.J. Recognizing the Correlation of Architectural Drawing Methods between Ancient Mathematical Books and Octagonal Timber-Framed Monuments in East Asia. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2021, 17, 1189–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, D. Evaluation of Point-Line Correspondence Algorithms for 3D Reconstruction. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. (CVIU) 2021, 198, 102956. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J. Adaptive Line Refinement for 3D Reconstruction from Point Clouds. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. (TVCG) 2023, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, D. Uncertainty-Aware Line Feature Extraction from Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 4026–4035. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Cui, H.; Yang, J. Automated Generation of Archaeological Line Drawings from Sculpture Point Cloud Based on Weighted Centroid Projection. npj Herit. Sci. 2025, 3, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Hierarchical Point-Edge Feature Fusion for Indoor 3D Line Drawing Extraction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 200, 152–168. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J. Attention-Guided Point Cloud Simplification for Large-Scale Urban Scenes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J. Deep Learning-Based Line Feature Extraction from Noisy Point Clouds for Heritage Documentation. Autom. Constr. 2024, 162, 105123. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, X.; Huang, W.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Xie, Z. Accurate and complete line segment extraction for large-scale point clouds. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 128, 103728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leica Geosystems. Leica Cyclone 9.1 User Manual: Point Cloud Registration for Cultural Heritage Preservation; Leica Geosystems AG: Heerbrugg, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]






| Reference | Automation Level | Speed (Per Building) | Component Recognition Accuracy | Detail Retention | Output Portability | Laser Scan Setup Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xu et al. [1] (BUPT, 2022) | Semi-automated (needs manual line adjustment) | 8 h | 82% (columns/beams) | Basic (no ornamental details) | WLD format (not industry-standard) | High (requires 5+ control points) |
| Zhou et al. [3] (MP-DGCNN, 2024) | Automated (component segmentation only) | 6 h | 88% (columns/beams/Dougong) | Partial (Dougong sub-components missing) | Point cloud format (no 2D output) | Medium (requires 3+ target spheres) |
| Li et al. [60] (Weighted Centroid Projection, 2025) | Automated (archeological illustrations only) | 4 h | 79% (simple components) | High (contours only) | PNG format (no vector output) | High (requires control network connection) |
| Our Method | Fully automated (end-to-end: point cloud → 2D vector drawing) | 2.5 h | 92% (columns/beams/Dougong/ornaments) | High (structural + ornamental details) | DXF/SVG/DWG (industry-standard) | Low (no control network; 3 target spheres sufficient) |
| Category | Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement | Single-point accuracy | 3 mm @ 50 m, 6 mm @ 100 m |
| Distance accuracy | 1.2 mm + 10 ppm | |
| Angular accuracy (H/V) | 8 arcsec | |
| Range noise (RMS) | 0.4 mm @ 10 m; 0.5 mm @ 50 m | |
| Target acquisition accuracy | 2 mm @ 50 m (HDS-compatible, 45°) | |
| Dual-axis compensator | ±5° range, 1 arcsec accuracy | |
| Laser System | Wavelength | 1550 nm (invisible)/658 nm (visible) |
| Laser safety class | Class 1 | |
| Scan rate | 1,000,000 points/s | |
| Beam divergence | <0.23 mrad | |
| Max. effective range | 120 m (18% reflectivity) | |
| 270 m (34% reflectivity) | ||
| Field of View | Horizontal FOV | 360° |
| Vertical FOV | 290° | |
| Imaging | Integrated camera | 4 MP (17° × 17° FOV); 70 MP panorama |
| External camera support | Canon EOS 60D/70D/50D (Canon Inc., Tokyo, Japan) | |
| Operational | Data storage | 256 GB SSD + external USB |
| Control interface | Touchscreen (640 × 480 VGA) | |
| Operating temperature | −20 °C to +50 °C | |
| Environmental protection | IP54 | |
| Battery life (dual batteries) | >5.5 h |
| Metric | Proposed Method | Traditional Manual Drafting | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time consumption | 2.5 h | 36 h | 93.1% faster |
| Dimensional error | 0.8% | 3.2% | 75% reduction |
| Capture of irregularities | 100% (e.g., non-orthogonal beam angles in Guancang No.11) | 72% (missed 8 out of 25 irregularities) | 28% improvement |
| Completeness of dimensions | 100% (all load-bearing component dimensions included) | 85% (missed 7 out of 47 critical dimensions) | 15% improvement |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, S.; Wu, D.; Kong, W.; Liu, W.; Xia, N. Research on Intelligent Generation of Line Drawings from Point Clouds for Ancient Architectural Heritage. Buildings 2025, 15, 3341. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183341
Dong S, Wu D, Kong W, Liu W, Xia N. Research on Intelligent Generation of Line Drawings from Point Clouds for Ancient Architectural Heritage. Buildings. 2025; 15(18):3341. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183341
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Shuzhuang, Dan Wu, Weiliang Kong, Wenhu Liu, and Na Xia. 2025. "Research on Intelligent Generation of Line Drawings from Point Clouds for Ancient Architectural Heritage" Buildings 15, no. 18: 3341. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183341
APA StyleDong, S., Wu, D., Kong, W., Liu, W., & Xia, N. (2025). Research on Intelligent Generation of Line Drawings from Point Clouds for Ancient Architectural Heritage. Buildings, 15(18), 3341. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183341





