Tilt Monitoring of Super High-Rise Industrial Heritage Chimneys Based on LiDAR Point Clouds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
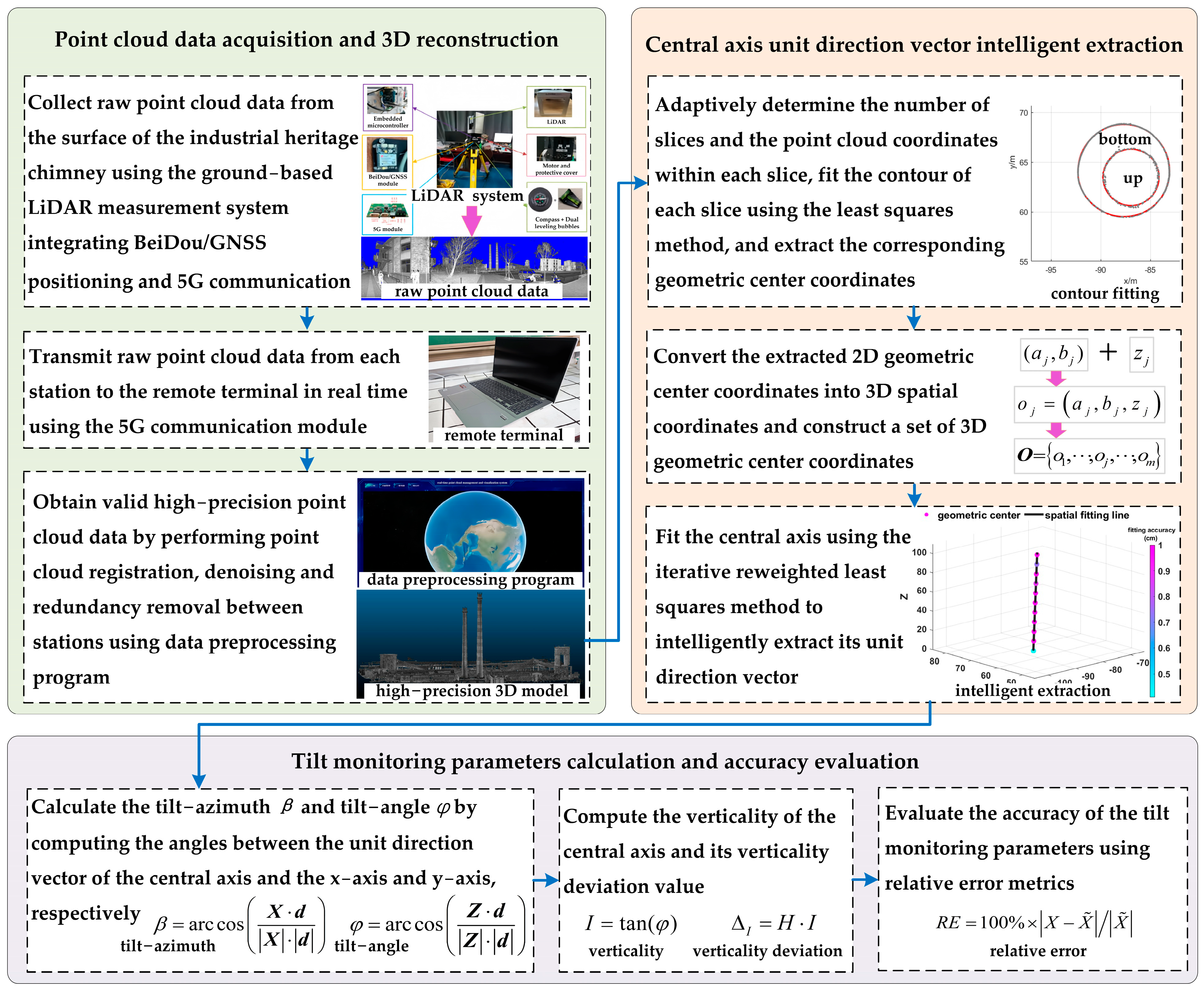
2.1. Acquisition and 3D Reconstruction of Point Cloud Data
2.1.1. Acquisition of Raw Point Cloud Data
2.1.2. 3D Reconstruction of Point Cloud Data
2.2. Extraction of Slice Shape Contours and Geometric Center Coordinates
2.2.1. Cross-Section Slicing Segmentation of the Point Cloud
2.2.2. Projection of Point Cloud Data onto the Slice Plane
2.2.3. Extraction of Slice Shape Contours
2.2.4. Calculation of the Geometric Center Coordinates of the Contour
2.3. Extraction of the Unit Direction Vector of the Central Axis
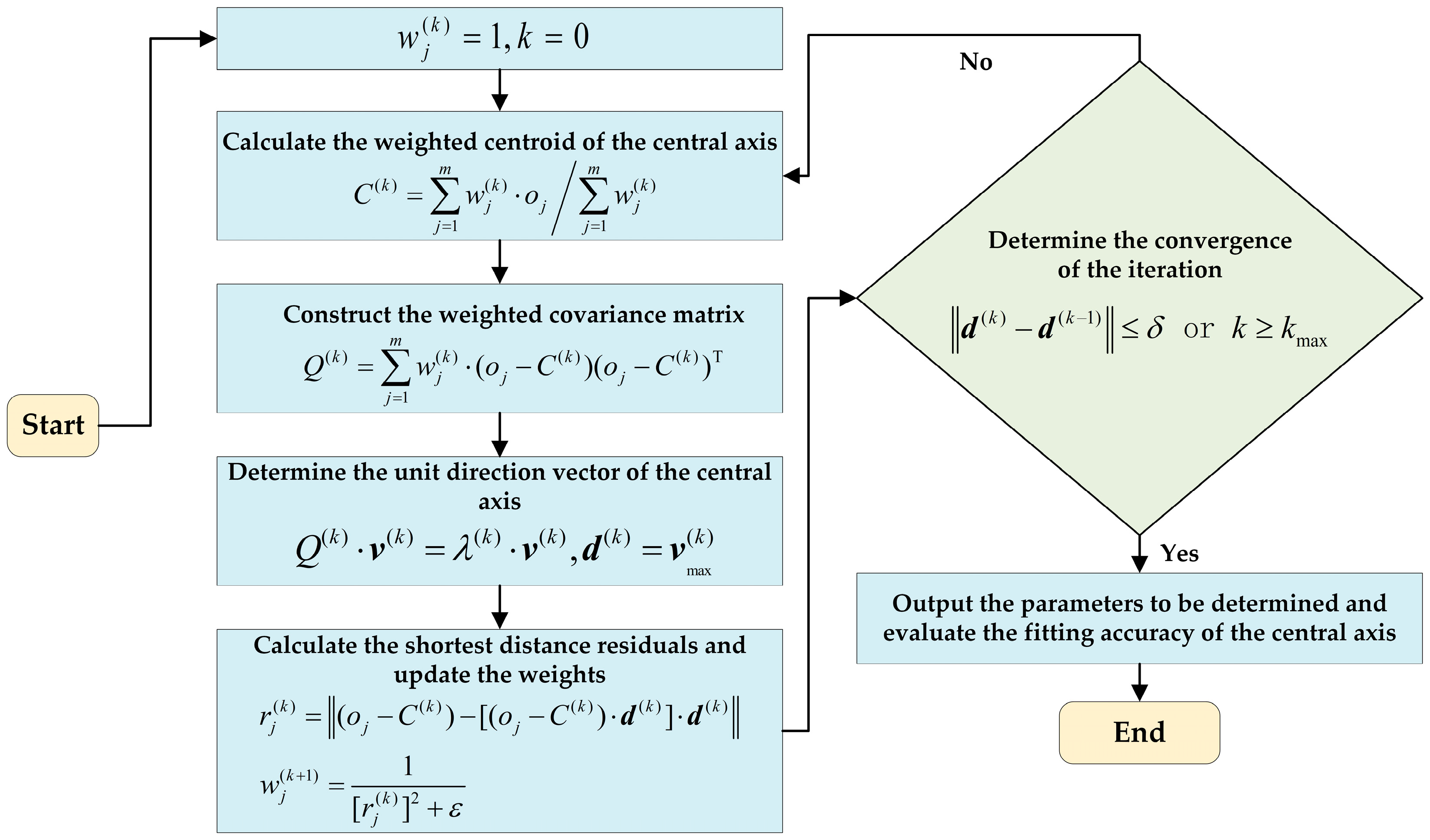
2.3.1. Listing of the Equation Expression of the Central Axis
2.3.2. Calculation of the Weighted Centroid of the Central Axis
2.3.3. Construction of the Weighted Covariance Matrix
2.3.4. Calculation of the Unit Direction Vector of the Central Axis
2.3.5. Calculation of the Shortest Distance Residuals and Updating of the Weights
2.3.6. Convergence Criterion of Iteration
2.3.7. Evaluation of Fitting Accuracy
2.4. Calculation of the Tilt Monitoring Parameters of the Central Axis
2.4.1. Calculation of the Tilt Azimuth of the Central Axis
2.4.2. Calculation of the Tilt-Angle of the Central Axis
2.4.3. Calculation of the Verticality of the Central Axis
2.4.4. Calculation of the Verticality Deviation of the Central Axis
2.5. Accuracy Assessment of the Tilt Monitoring of the Central Axis
3. Experiment
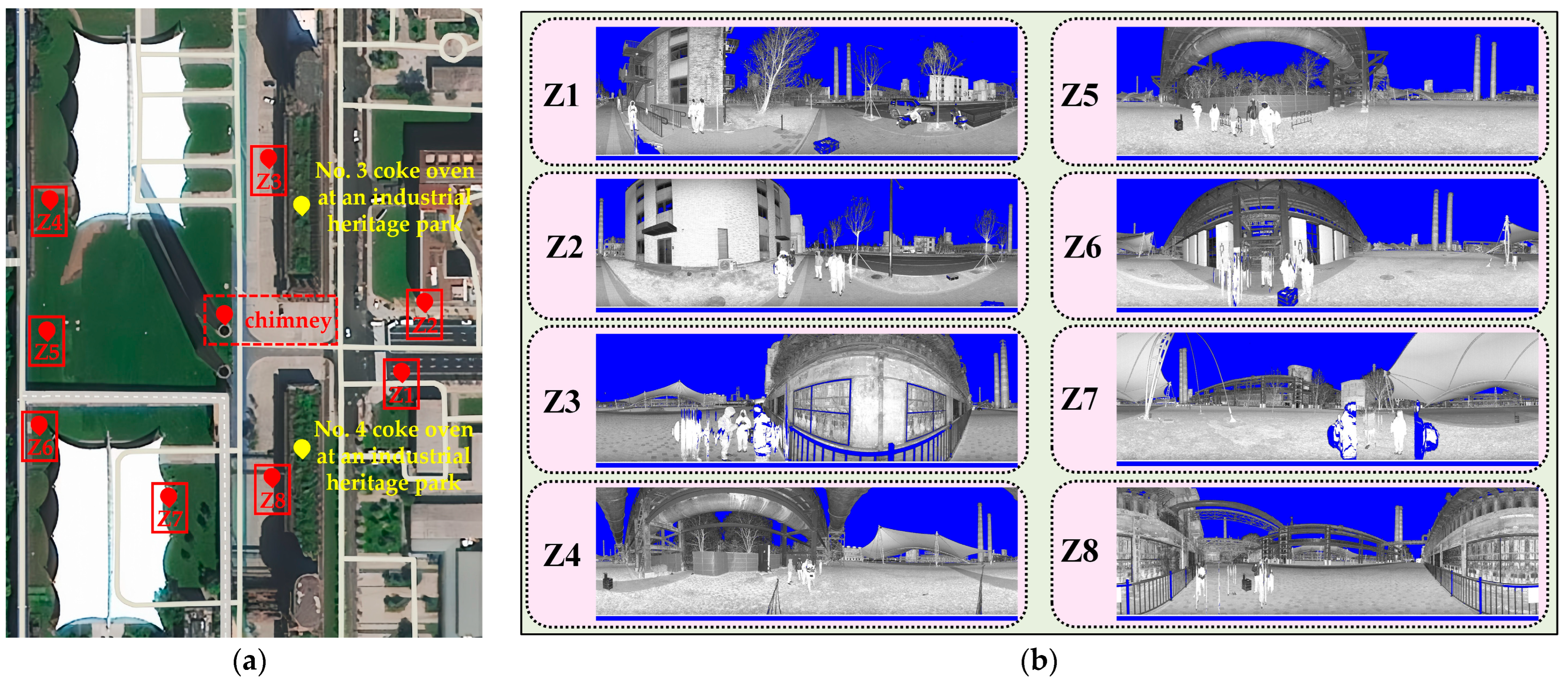
3.1. Experimental Design
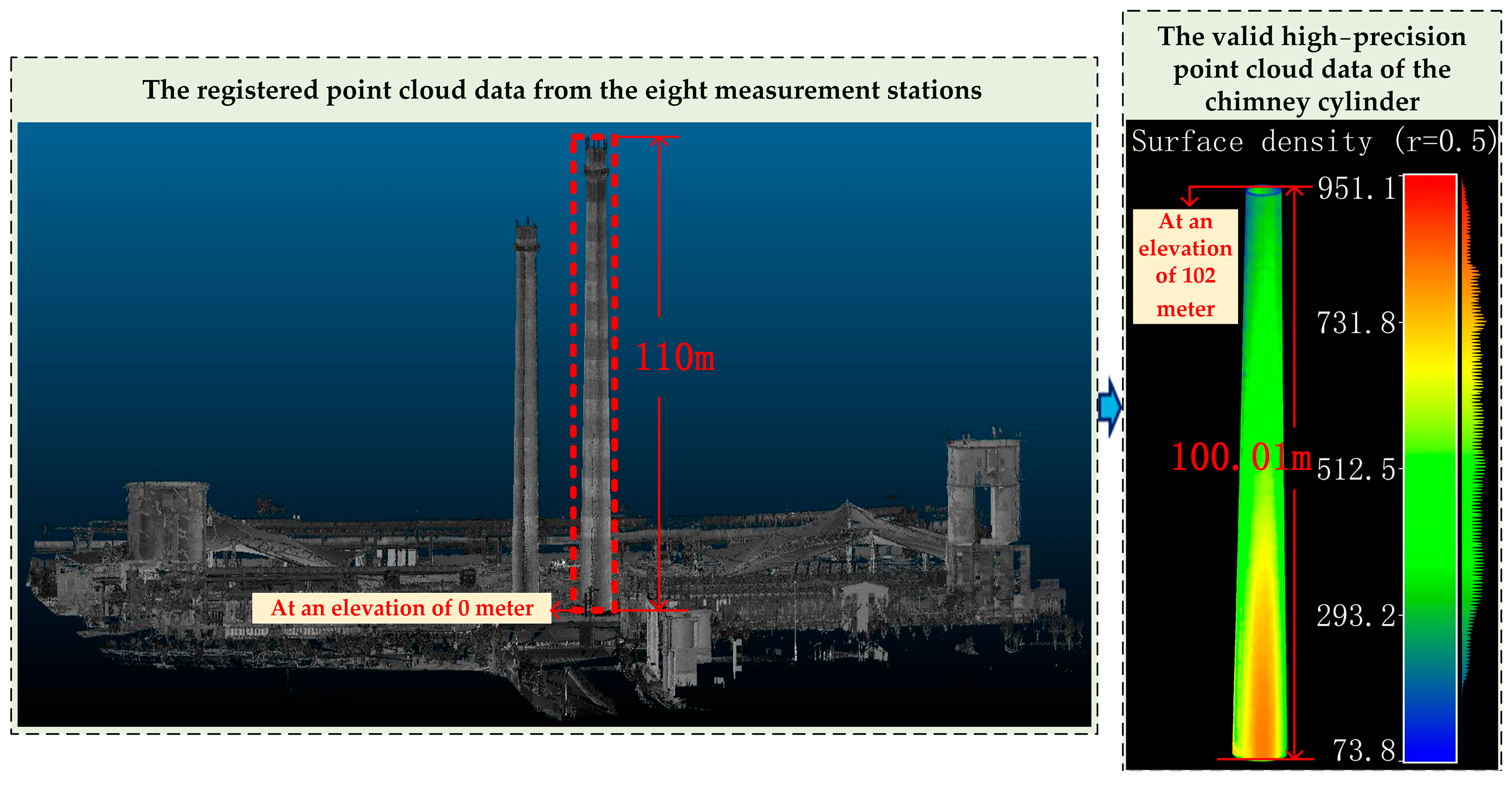
3.2. Point Cloud Data Preprocessing
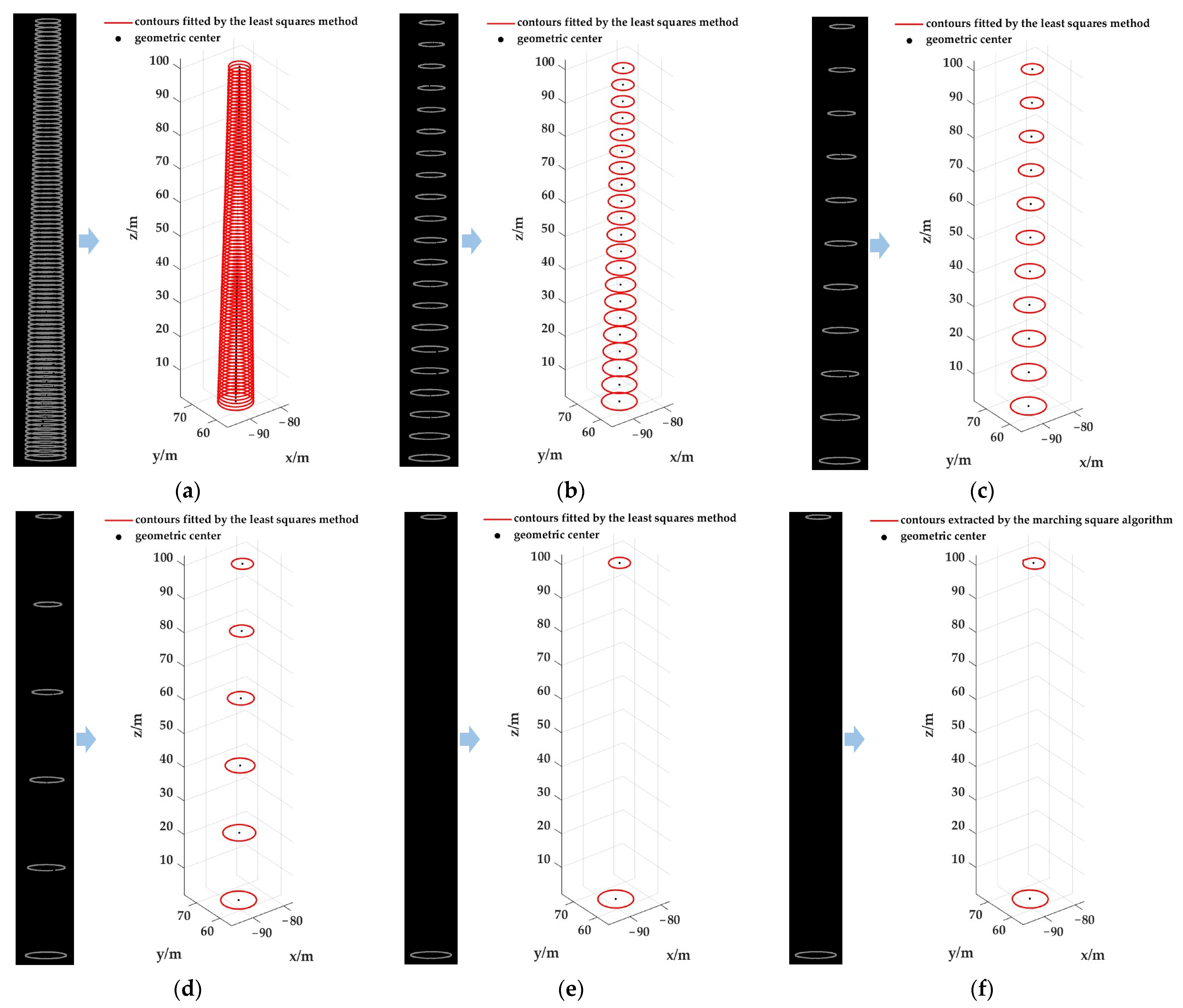
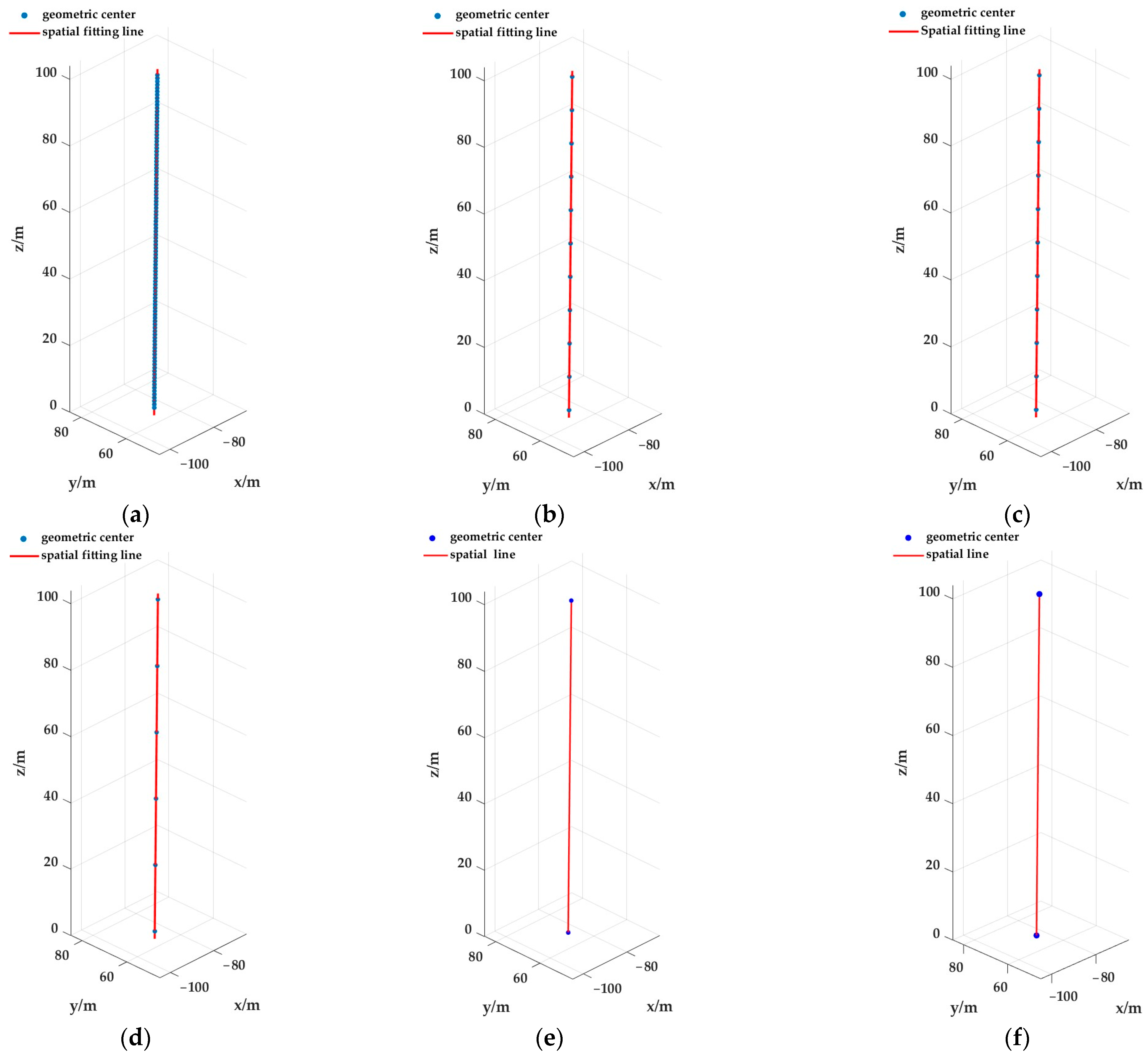
3.3. Design of Cross-Section Slicing Segmentation Strategies
- 1.
- Scheme A: Using the proposed method, the chimney cylinder is sliced horizontally along the z-axis at 1 m intervals. The contours of each slice are extracted to obtain its geometric center coordinates. These centers are then used to fit the central axis, and the corresponding unit direction vector is determined.
- 2.
- Scheme B: Using the proposed method, the chimney cylinder is sliced horizontally along the z-axis at 5 m intervals. The contours of each slice are extracted to obtain its geometric center coordinates. These centers are then used to fit the central axis, and the corresponding unit direction vector is determined.
- 3.
- Scheme C: Using the proposed method, the chimney cylinder is sliced horizontally along the z-axis at 10 m intervals. The contours of each slice are extracted to obtain its geometric center coordinates. These centers are then used to fit the central axis, and the corresponding unit direction vector is determined.
- 4.
- Scheme D: Using the proposed method, the chimney cylinder is sliced horizontally along the z-axis at 20 m intervals. The contours of each slice are extracted to obtain its geometric center coordinates. These centers are then used to fit the central axis, and the corresponding unit direction vector is determined.
- 5.
- Scheme E: Using the proposed method, one horizontal slice is taken at each end along the z-axis. The contours of these slices are extracted to obtain their geometric center coordinates. The direction vector of the central axis is then directly calculated from these center coordinates, and after normalization, the corresponding unit direction vector is obtained.
- 6.
- Scheme F: Using the traditional method described in reference [9], one horizontal slice is taken at each end along the z-axis. The contours of these slices are extracted, and the center coordinates are obtained by averaging the vertex coordinates of each contour. The direction vector of the central axis is then directly calculated from these centers, and after normalization, the corresponding unit direction vector is obtained.
4. Results
4.1. Extraction Results of Slice Contours
4.2. Results of Tilt Monitoring Parameters
4.3. Accuracy Analysis of Tilt Monitoring Parameters
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Y.; Chung, W. Optimization of building thermal environment in industrial heritage landscape regeneration design simulation based on image visual visualization. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2024, 56, 103024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertacchini, E.; Frontuto, V. Economic valuation of industrial heritage: A choice experiment on Shanghai Baosteel industrial site. J. Cult. Herit. 2024, 66, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.; Huang, P.; Xiong, G.; Li, H. Renewal strategies of industrial heritage based on placeness theory: The case of Guangzhou, China. Cities 2024, 155, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chang, M.; Wu, H.; Zhuo, Y.; Djerrad, A.; Lu, X. Numerical investigation on the characteristics of dynamic response and damage of a RC tall chimney considering vertical ground motions. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 175, 108224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, M. Sectional properties and overall performance of FRP-wrapped RC chimneys. Structures 2025, 76, 108938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Li, Z.; Peng, S.; Uematsu, Y. Interference effects on aeroelastic responses and design wind loads of twin high-rise reinforced concrete chimneys. Eng. Struct. 2021, 233, 111925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.S. Chimney Fires: Causes, Effects & Evaluation; Chimney Safety Institute of America: Plainfield, IN, USA, 2007; pp. 11–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Ma, D.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, H.; Gui, L. A novel measurement method based on silhouette for chimney quasi-static deformation monitoring. Measurement 2012, 45, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Q. LiDAR-based non-destructive detection algorithm of tower crane verticality. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2024, 2, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Qin, Y.; Meng, Q.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Song, Q.; Wang, J. A LiDAR inspection method of tower verticality based on marching cubes algorithm. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2025, 50, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Lu, W.; Hu, W.; Teng, J. Real-time estimation method for horizontal displacement of high-rise buildings based on fusion of inclination and acceleration monitoring data. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 103, 112083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Nieto, M.C.; Huesca-Tortosa, J.A.; Martínez-Segura, M.A.; Gea, A.E.; Navarro, M. Structural deformation monitoring using UAV photogrammetry to assess slender historic buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 100, 111766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Sun, M.; Huang, M.; Yan, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y. High-precision measurement of steel structure based on LiDAR and UAV. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2021, 29, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Yan, B.; Zhou, T.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y. Application of LiDAR Technology in Deformation Analysis of Yingxian Wooden Pagoda. J. Archit. Civ. Eng. 2020, 37, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowski, P.S. Novel PCSE-based approach of inclined structures geometry analysis on the example of the Leaning Tower of Pisa. Measurement 2022, 189, 110462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhang, W.; Ye, P.; Chen, J.; Du, Z. Improvement of axial deformation prediction in high-rise buildings with field monitoring and adaptive unscented Kalman filter. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 83, 108432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Luo, X.; Ye, P.; Zhang, W.; Qin, L.; Du, Z. Bayesian-based prediction and real-time updating of axial deformation in high-rise buildings during construction. Eng. Struct. 2023, 297, 116992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, M.; Cheng, S.; Wang, M. Research on transmission line tower tilting and foundation state monitoring technology based on multi-sensor cooperative detection and correction. Energy Eng. 2023, 121, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Ma, B.; Bao, H.; Shi, J.; Luo, D. GNSS-based verticality intelligent detection in rounds for construction tower crane. J. Data Acquis. Process. 2020, 35, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Bao, H.; Zhang, W.; Ma, B. GNSS-based lateral perpendicularity intelligent detection for construction tower crane. Laser J. 2021, 42, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, S.; Kwok, T.; Hui, W.; Li, H.; Chin, C.W.; Ju, S.; Heo, J.; Wong, S. Tree tilt monitoring in rural and urban landscapes of Hong Kong using smart sensing technology. Trees For. People 2020, 2, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, J. Monitoring and research on tilt of transmission line tower based on optical fiber sensing. J. Electron. Meas. Instrum. 2018, 32, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.; Kim, I.; Park, J.; Kim, Y.; Sohn, H.; Park, H. Evaluation of Stiffness Changes in a High-Rise Building by Measurements of Lateral Displacements Using GPS Technology. Sensors 2013, 13, 15489–15503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, M.; Wang, D.; Chen, B.; Song, K. A transmission line tower tilt detection method based on BeiDou positioning signals and UAV inspection images. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2024, 17, 101192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwiec, J.; Lenda, G. Integration of terrestrial laser scanning and structure from motion for the assessment of industrial chimney geometry. Measurement 2022, 199, 111404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, J.; Pandžić, J.; Pejić, M.; Vranić, P.; Milovanović, B.; Martinenko, A. Quantifying tall structure tilting trend through TLS-based 3D parametric modelling. Measurement 2022, 188, 110533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrinjski, M.; Tupek, A.; Barkovic, D.; Polovic, A. Industrial Masonry Chimney Geometry Analysis: A Total Station Based Evaluation of the Unmanned Aerial System Photogrammetry Approach. Sensors 2021, 21, 6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleterski, Ž.; Rak, G.; Kregar, K. Determination of Chimney Non-Verticality from TLS Data Using RANSAC Method. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Zhao, L. Modified boosting and bagging for building tilt rate prediction in tunnel construction. Autom. Constr. 2023, 155, 105059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Lv, P.; Li, D. A new shape reconstruction method for monitoring the large deformations of offshore wind turbine towers. Ocean Eng. 2024, 312, 119253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górski, P. Dynamic characteristic of tall industrial chimney estimated from GPS measurement and frequency domain decomposition. Eng. Struct. 2017, 148, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, A.; Sangoor, A.; Al-Rkaby, A. Behavior of tall masonry chimneys under wind loadings using CFD technique. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 13, e00451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzaniga, N.; Pinto, L.; Forlani, G.; Abruzzi, P. Monitoring Oscillations of Slender Structures with GPS and Accelerometers. In Proceedings of the From Pharaohs to Geoinformatics FIG Working Week 2005 and GSDI-8, Cairo, Egypt, 16–21 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Mi, K.; Li, X.; Shu, J.; Chen, C.; Lan, H.; Wang, J. Application of robust least-square in perpendicularity analysis of wind turbine tower. Therm. Power Gener. 2021, 50, 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, K.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Bao, D.; Dong, J. Research on non-contact rapid inspection method of high pier bridge verticality and its precision analysis. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2019, 6, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, F.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; Su, Z.; Guan, B.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Q. Stereo vision-based health monitoring method for wind turbine towers. Measurement 2024, 226, 114148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdi, F.; Lewandowicz, E.; Gharineiat, Z.; Shan, J. Modeling Multi-Rotunda Buildings at LoD3 Level from LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3324. [Google Scholar]
- Helming, P.; Poeck, N.; Freyberg, A.; Sorg, M.; Fischer, A. Dynamic optical deformation measurements on wind turbines. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2265, 022100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D. Terrestrial laser scanning for area based deformation analysis of towers and water damns. In Proceedings of the 3rd IAG/12th FIG Symposium, Baden, Austria, 22–24 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Muszynski, Z.; Milczarek, W. Application of Terrestrial Laser Scanning to Study the Geometry of Slender Objects. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 95, 042069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zheng, X.; Li, J.; Pan, C.; Li, J.; He, C.; Yan, D.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Hou, Z.; et al. Long-term high-precision monitoring system for laser parameters in large-aperture dual-wavelength LiDAR. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 182, 112200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Zhou, J.; Chu, X.; Ma, W.; Meng, J. 3D deformation monitoring method for temporary structures based on multi-thread LiDAR point cloud. Measurement 2022, 200, 111545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Guo, J.; Jiang, Y. Monitoring tunnel deformations by means of multi-epoch dispersed 3D LiDAR point clouds: An improved approach. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2013, 38, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cai, D.; Wang, R. Bridge Pier Verticality Detection Considering Surface Point Cloud Curvature Characteristics. Sens. Mater. 2024, 36, 5395–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gražulis, Ž.; Krikštaponis, B.; Neseckas, A.; Popovas, D.; Putrimas, R.; Šlikas, D.; Zigmantiene, E. The Horizontal Deformation Analysis of High-rise Buildings. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference, Environmental Engineering, Vilnius, Lithuania, 27–28 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Barazzetti, L.; Previtali, M.; Roncoroni, F. The use of terrestrial laser scanning techniques to evaluate industrial masonry chimney verticality. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W11, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kaszowska, O.; Gruchlik, P.; Mika, W. Industrial chimney monitoring—Contemporary methods. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 36, 01005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głowacki, T.; Grzempowski, P.; Sudoł, E.; Wajs, J.; Zając, M. The assessment of the application of terrestrial laser scanning for measuring the geometrics of cooling towers. Geomat. Landmanag. Landsc. 2016, 4, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kregar, K.; Ambrožic, T.; Kogoj, D.; Vezocnik, R.; Marjetic, A. Determining the inclination of tall chimneys using the TPS and TLS approach. Measurement 2015, 75, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliga, K.; Kurałowicz, Z. Comparison of Different Measurement Techniques as Methodology for Surveying and Monitoring Stainless Steel Chimneys. Geosciences 2019, 9, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Qi, H.; Guo, K.; Zhou, Y.; Li, D. Ground-based LiDAR measurement system integrating BeiDou/GNSS positioning and 5G communication. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2023, 31, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Qi, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y. Design and Management of a Spatial Database for Monitoring Building Comfort and Safety. Buildings 2023, 13, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Guo, M.; Liu, Y. Research on installation surveying method of steel structures in architecture engineering for site protection. Geotech. Investig. Surv. 2020, 48, 52–56,74. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 50051-2021; Technical Standard for Chimney Engineering. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Ahn, S.J.; Rauh, W.; Warnecke, H. Least-squares orthogonal distances fitting of circle, sphere, ellipse, hyperbola, and parabola. Pattern Recognit. 2001, 34, 2283–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, H.; Wei, W. The performance analysis of extending iterative reweighted least squares algorithm compressed sensing theory. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2014, 53, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, P.J. Robust Statistics; Wiley, John & Sons Inc. Pub.: New York, NY, USA, 1981; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
| Indicator | Scheme A | Scheme B | Scheme C | Scheme D | Scheme E | Scheme F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of geometric centers involved in the fitting | 101 | 21 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 2 |
| Number of fitting iterations | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | -- * | -- |
| Update weight ratio of geometric centers | 21.8% | 19.0% | 27.3% | 33.3% | -- | -- |
| Mean deviation and its average value (mm) | 11.0 | 12.3 | 13.1 | 12.1 | -- | -- |
| 12.1 | -- | -- | ||||
| Root mean square error and its average value (mm) | 13.3 | 15.4 | 15.7 | 14.4 | -- | -- |
| 14.7 | -- | -- | ||||
| Indicator | Scheme A | Scheme B | Scheme C | Scheme D | Scheme E | Scheme F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cross-section slices | 101 | 21 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 2 | |
| Number of slice contour | 101 | 21 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 2 | |
| Number of geometric centers of contour | 101 | 21 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 2 | |
| Unit direction vector of the central axis | [0.00734720, −0.00703179, 0.99994828] | [0.00733996, −0.00697344, 0.99994874] | [0.00733933, −0.00699452, 0.99994860] | [0.00731785, −0.00684513, 0.99994979] | [0.00726479, −0.00666181, 0.99995142] | [0.00725774, −0.00570779, 0.99995737] | |
| Tilt monitoring parameters | Tilt-azimuth | 90°25′15″ | 90°25′14″ | 90°25′14″ | 90°25′09″ | 90°24′58″ | 90°24′57″ |
| Tilt-angle | 0°34′58″ | 0°34′48″ | 0°34′51″ | 0°34′27″ | 0°33′53″ | 0°31′45″ | |
| Verticality | 10.17‰ | 10.12‰ | 10.14‰ | 10.02‰ | 9.86‰ | 9.23‰ | |
| Verticality deviation | 1.0373 m | 1.0322 m | 1.0343 m | 1.0220 m | 1.0057 m | 0.9415 m | |
| Indicator | Scheme A | Scheme B | Scheme C | Scheme D | Scheme E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tilt-azimuth and its mean value | 90°25′15″ | 90°25′14″ | 90°25′14″ | 90°25′09″ | 90°24′58″ |
| 90°25′10″ | |||||
| Reference value of the tilt-azimuth | 90°24′57″ | ||||
| Relative error (%) of the tilt-azimuth and its mean value | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0 |
| 0.004 | |||||
| Tilt-angle and its mean value | 0°34′58″ | 0°34′48″ | 0°34′51″ | 0°34′27″ | 0°33′53″ |
| 0°34′45″ | |||||
| Reference value of the tilt-angle | 0°31′45″ | ||||
| Relative error (%) of the tilt-angle and its mean value | 10.13 | 9.60 | 9.76 | 8.50 | 6.71 |
| 9.45 | |||||
| Verticality and its mean value (‰) | 10.17 | 10.12 | 10.14 | 10.02 | 9.86 |
| 10.06 | |||||
| Reference value of verticality (‰) | 9.23 | ||||
| Relative error (%) of verticality and its mean value | 10.13 | 9.60 | 9.76 | 8.50 | 6.71 |
| 9.45 | |||||
| Verticality deviation and its mean value (m) | 1.0373 | 1.0322 | 1.0343 | 1.0220 | 1.0057 |
| 1.0263 | |||||
| Reference value of verticality deviation (m) | 0.9415 | ||||
| Relative error (%) of verticality deviation and its mean value | 10.13 | 9.60 | 9.76 | 8.50 | 6.71 |
| 9.45 | |||||
| Allowable verticality deviation (m) | 0.0605 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, M.; Qin, Y.; Xie, Q.; Song, Q.; Lin, S.; Qin, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, G.; Yan, P. Tilt Monitoring of Super High-Rise Industrial Heritage Chimneys Based on LiDAR Point Clouds. Buildings 2025, 15, 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173046
Zhou M, Qin Y, Xie Q, Song Q, Lin S, Qin L, Zhou Z, Wu G, Yan P. Tilt Monitoring of Super High-Rise Industrial Heritage Chimneys Based on LiDAR Point Clouds. Buildings. 2025; 15(17):3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173046
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Mingduan, Yuhan Qin, Qianlong Xie, Qiao Song, Shiqi Lin, Lu Qin, Zihan Zhou, Guanxiu Wu, and Peng Yan. 2025. "Tilt Monitoring of Super High-Rise Industrial Heritage Chimneys Based on LiDAR Point Clouds" Buildings 15, no. 17: 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173046
APA StyleZhou, M., Qin, Y., Xie, Q., Song, Q., Lin, S., Qin, L., Zhou, Z., Wu, G., & Yan, P. (2025). Tilt Monitoring of Super High-Rise Industrial Heritage Chimneys Based on LiDAR Point Clouds. Buildings, 15(17), 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173046







