Experimental and DEM Investigation of Shear Behaviors of a Loess and Rough Concrete Interface
Abstract
1. Introduction
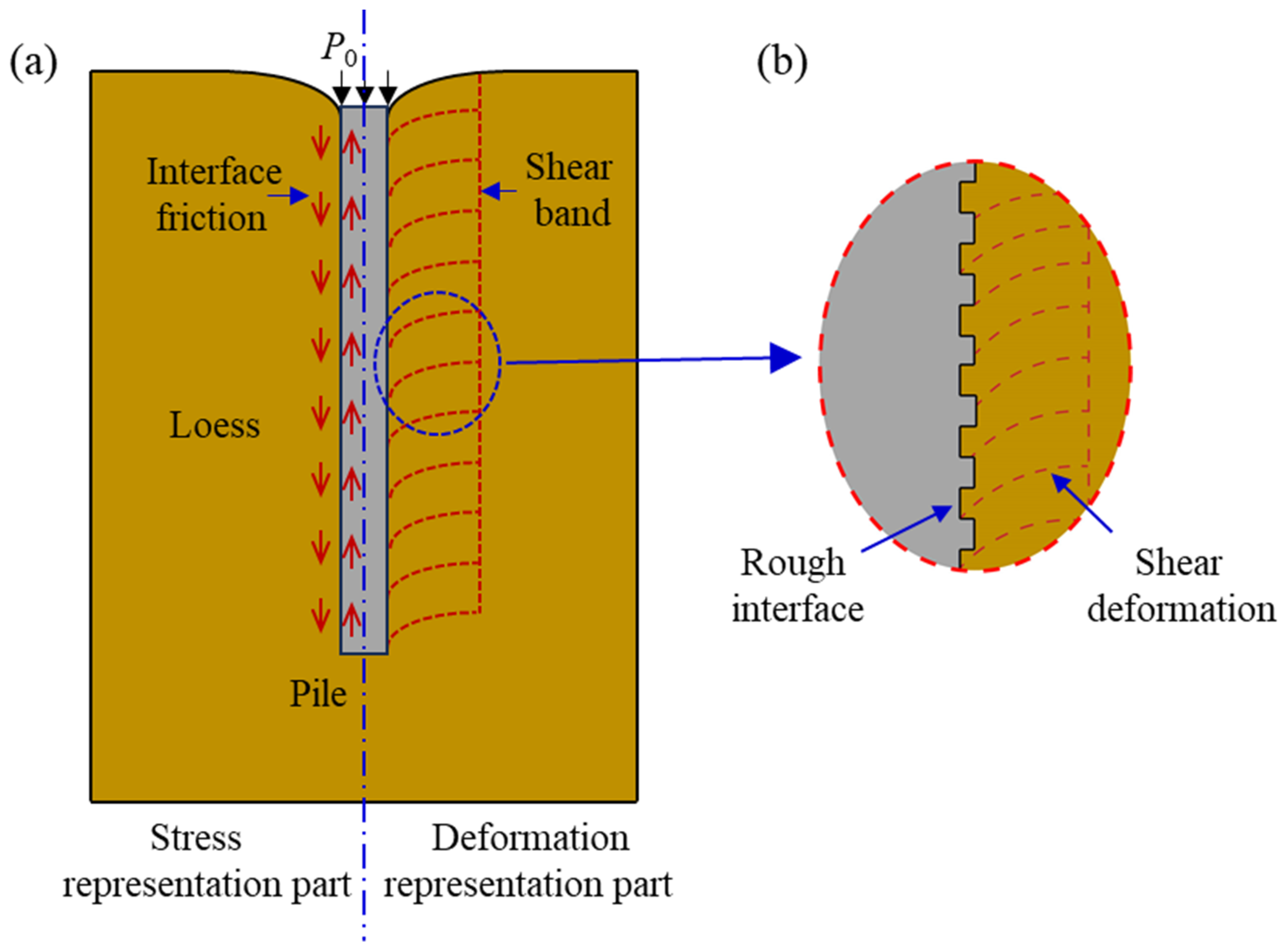
2. Shear Tests of Loess-Concrete Interfaces
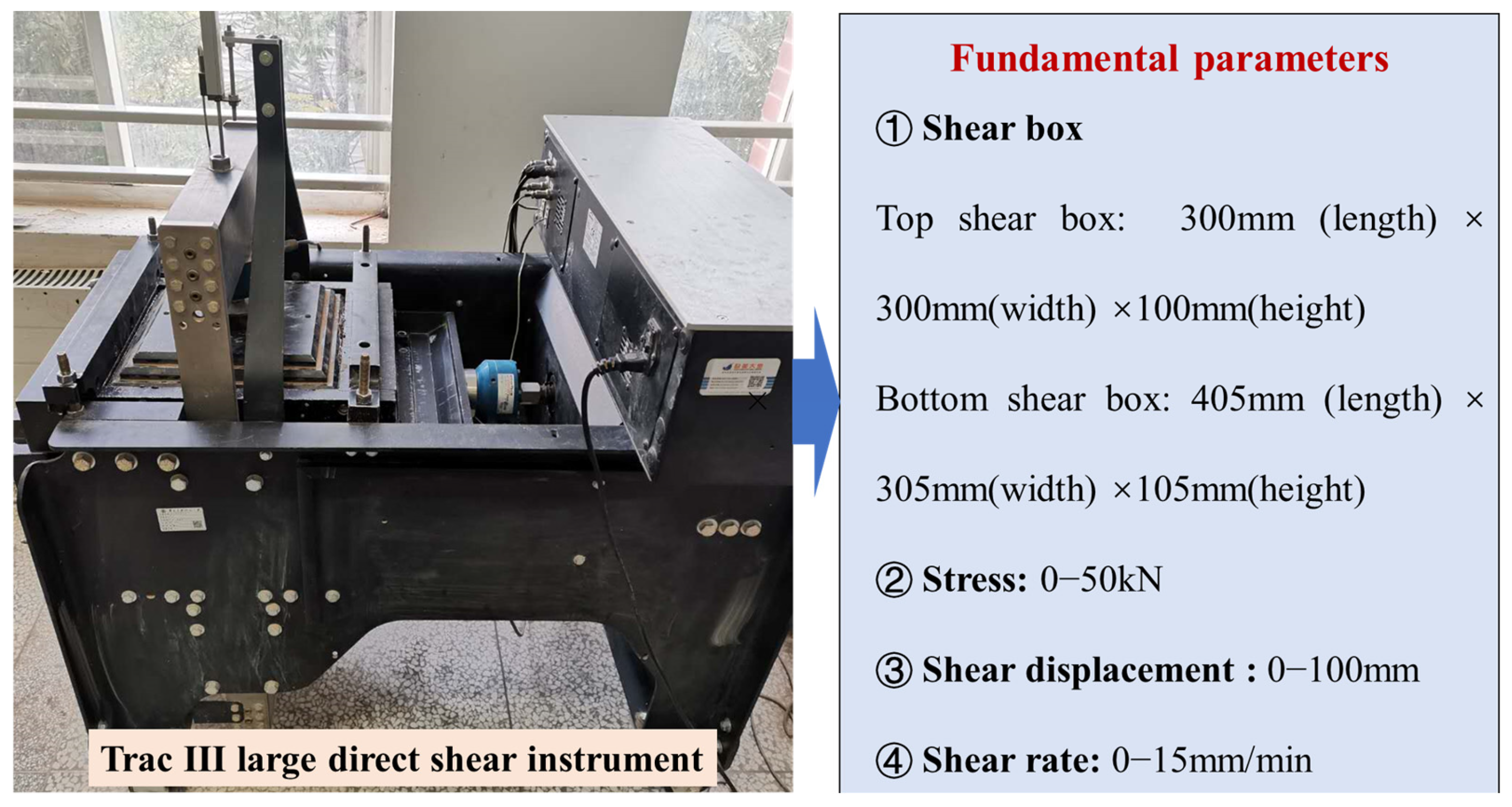
2.1. Experimental Apparatus
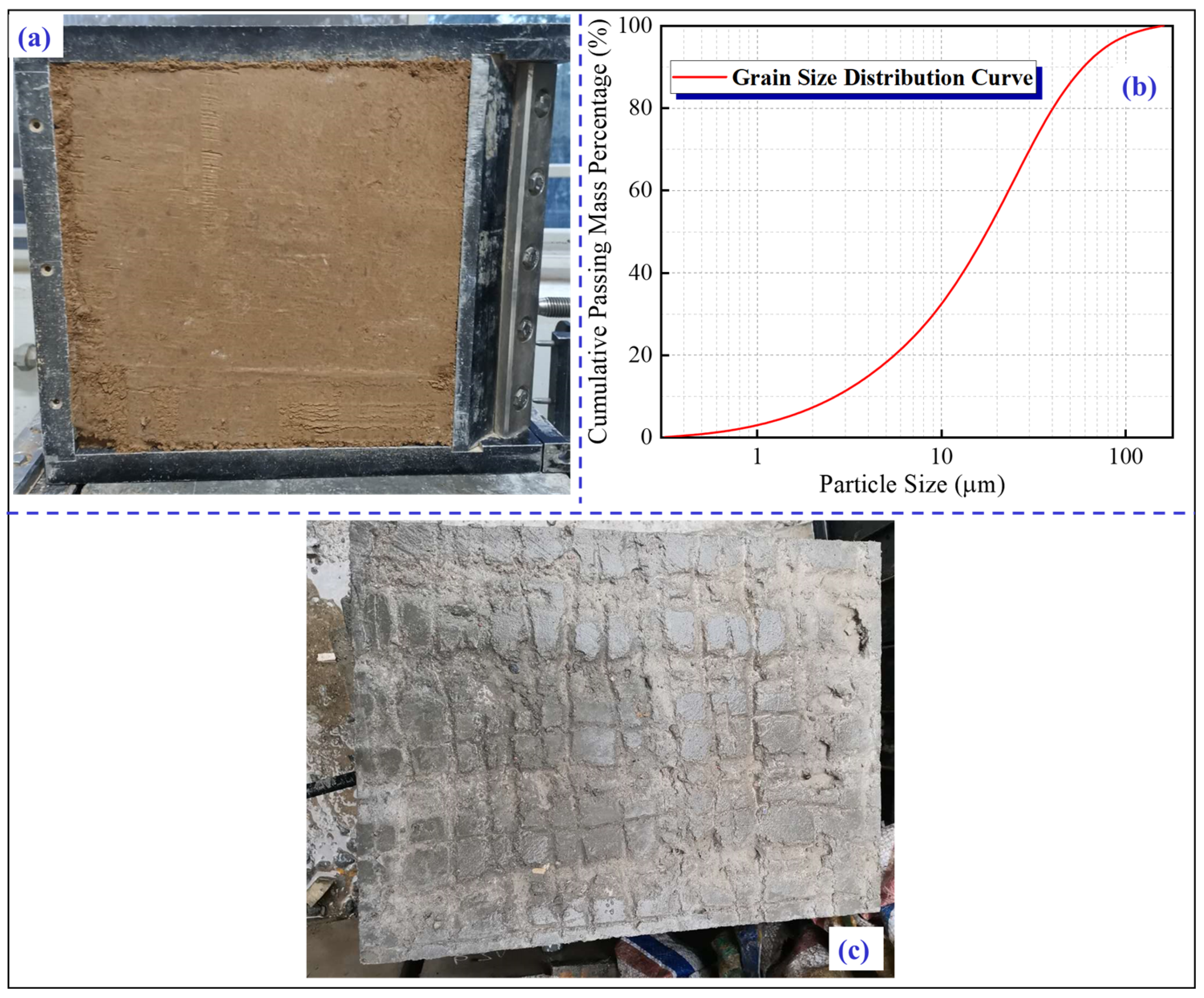
2.2. Experimental Materials
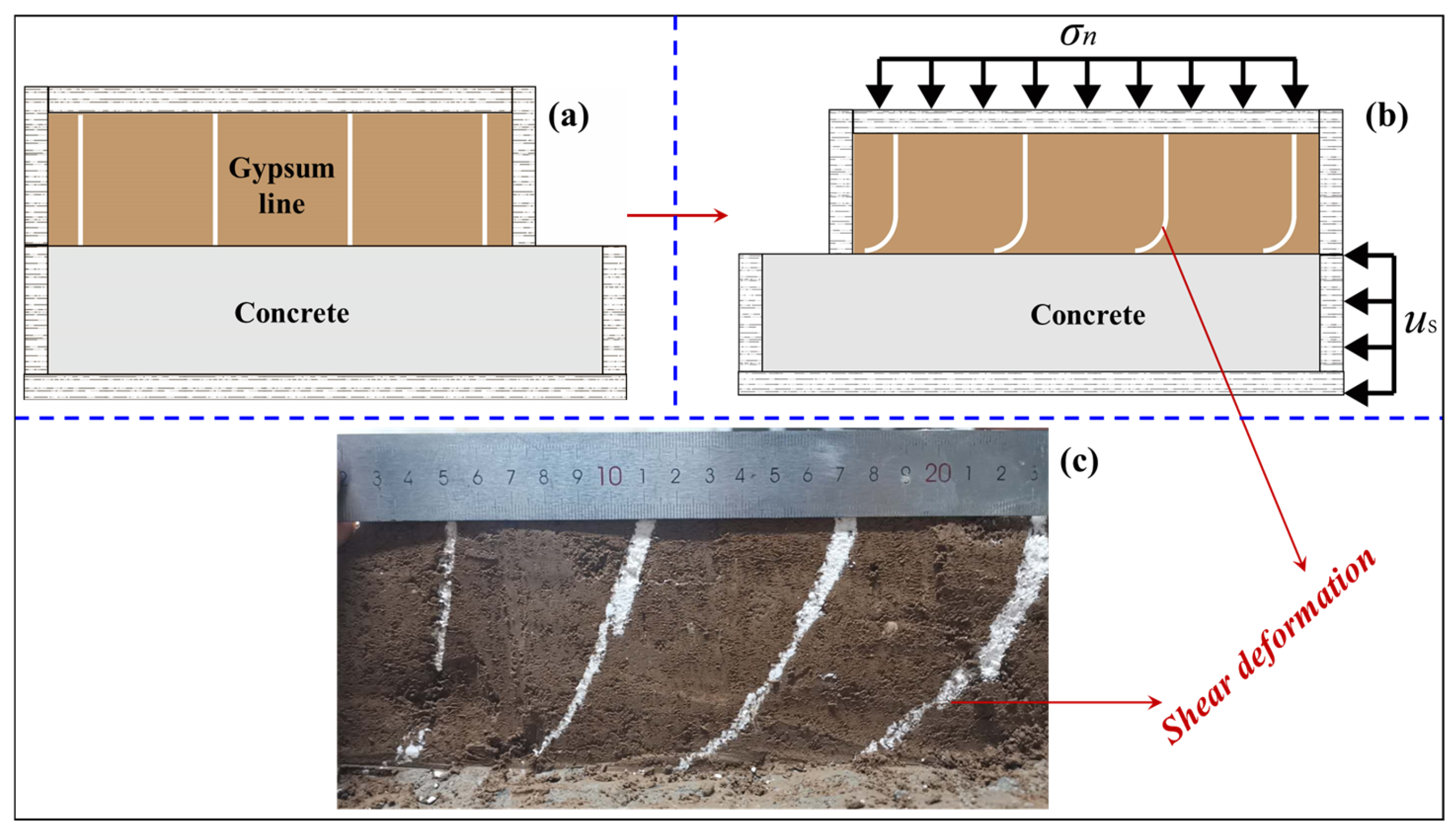
2.3. Experimental Methods
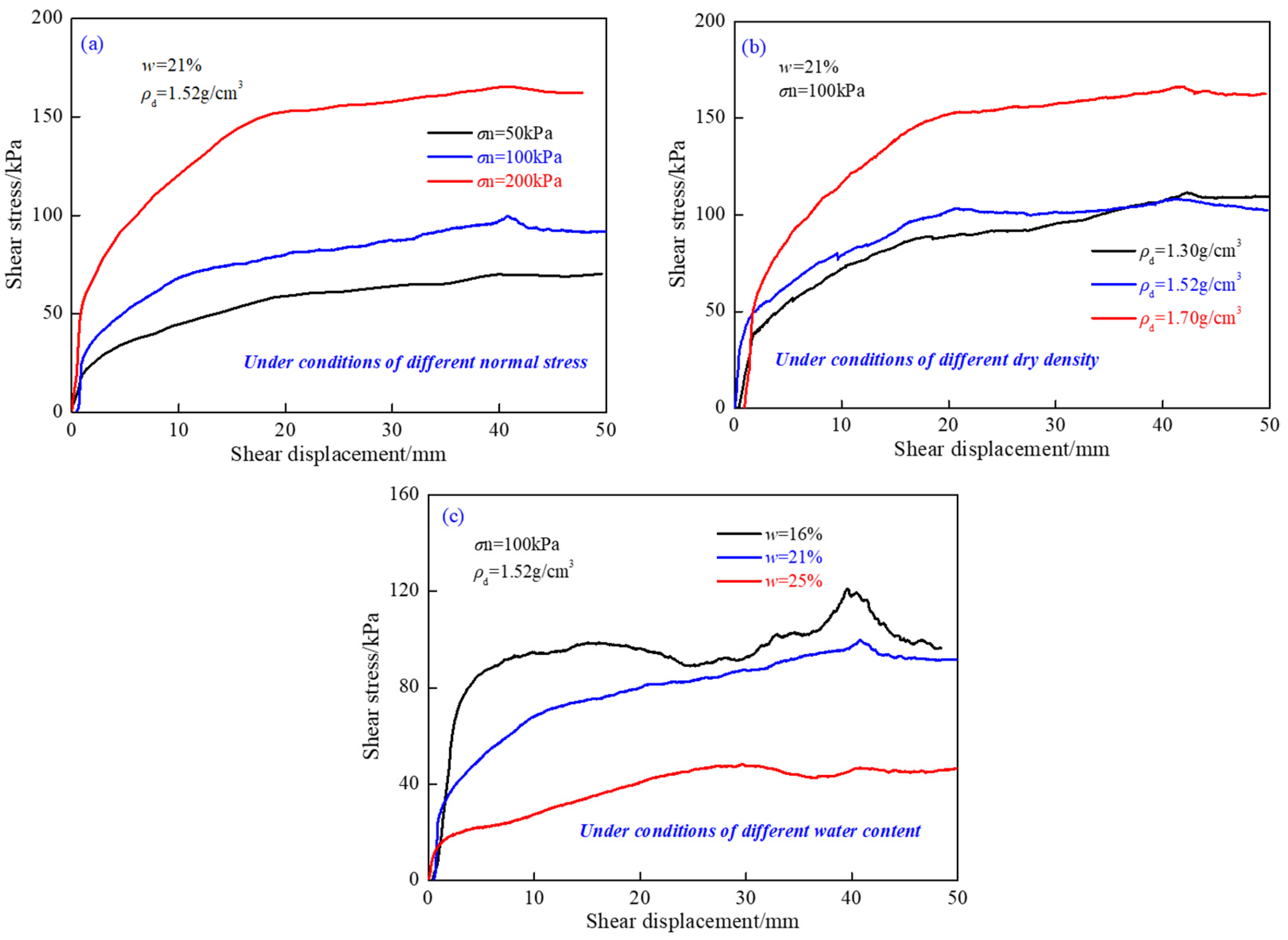
2.4. Experimental Results
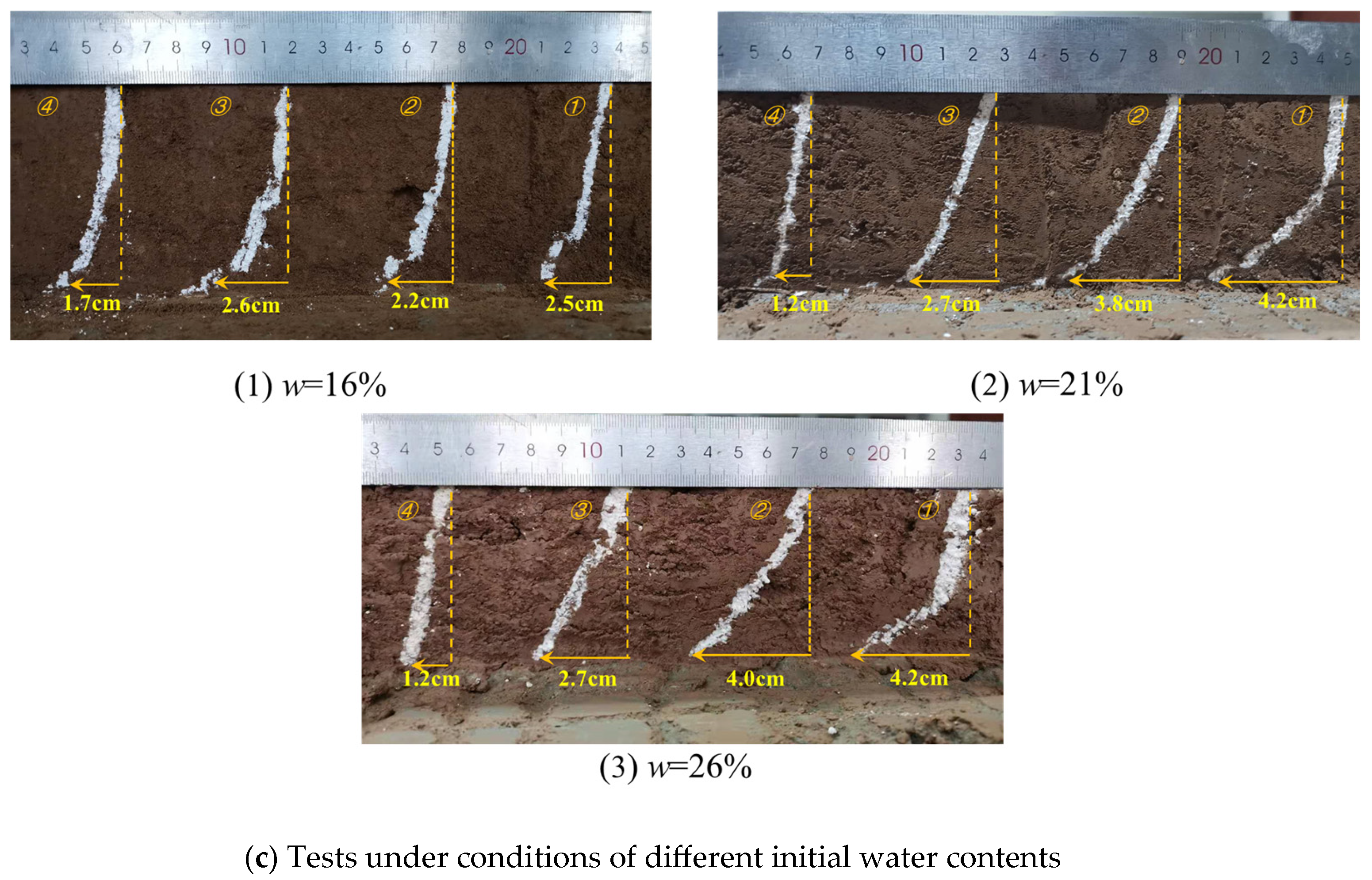
2.4.1. Shear Deformation Characteristics
2.4.2. Shear Strength Characteristics
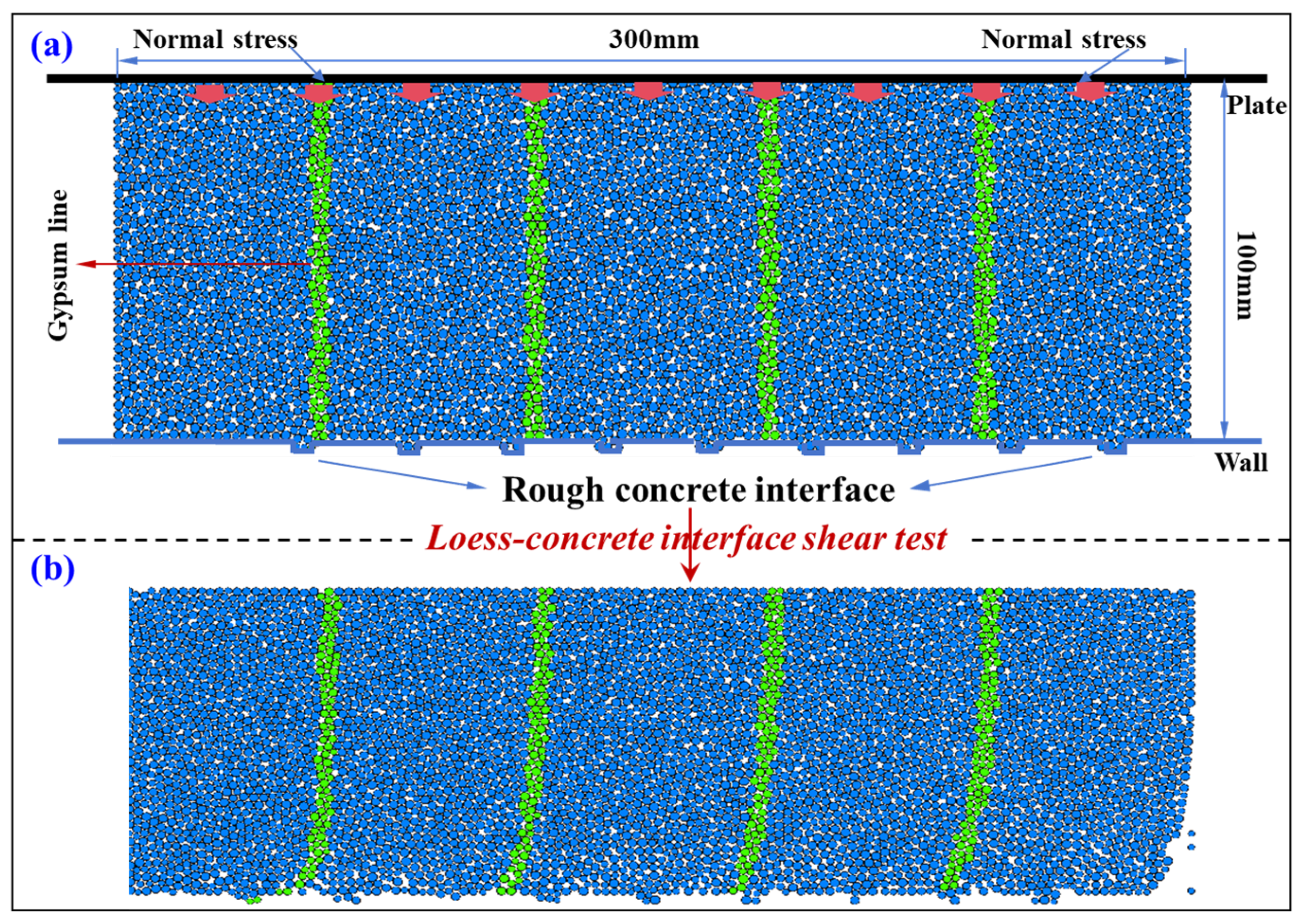
3. DEM Simulation for Interface Shear Test
3.1. DEM Model Establishment
3.2. DEM Model Calibration
3.3. DEM Simulation Results
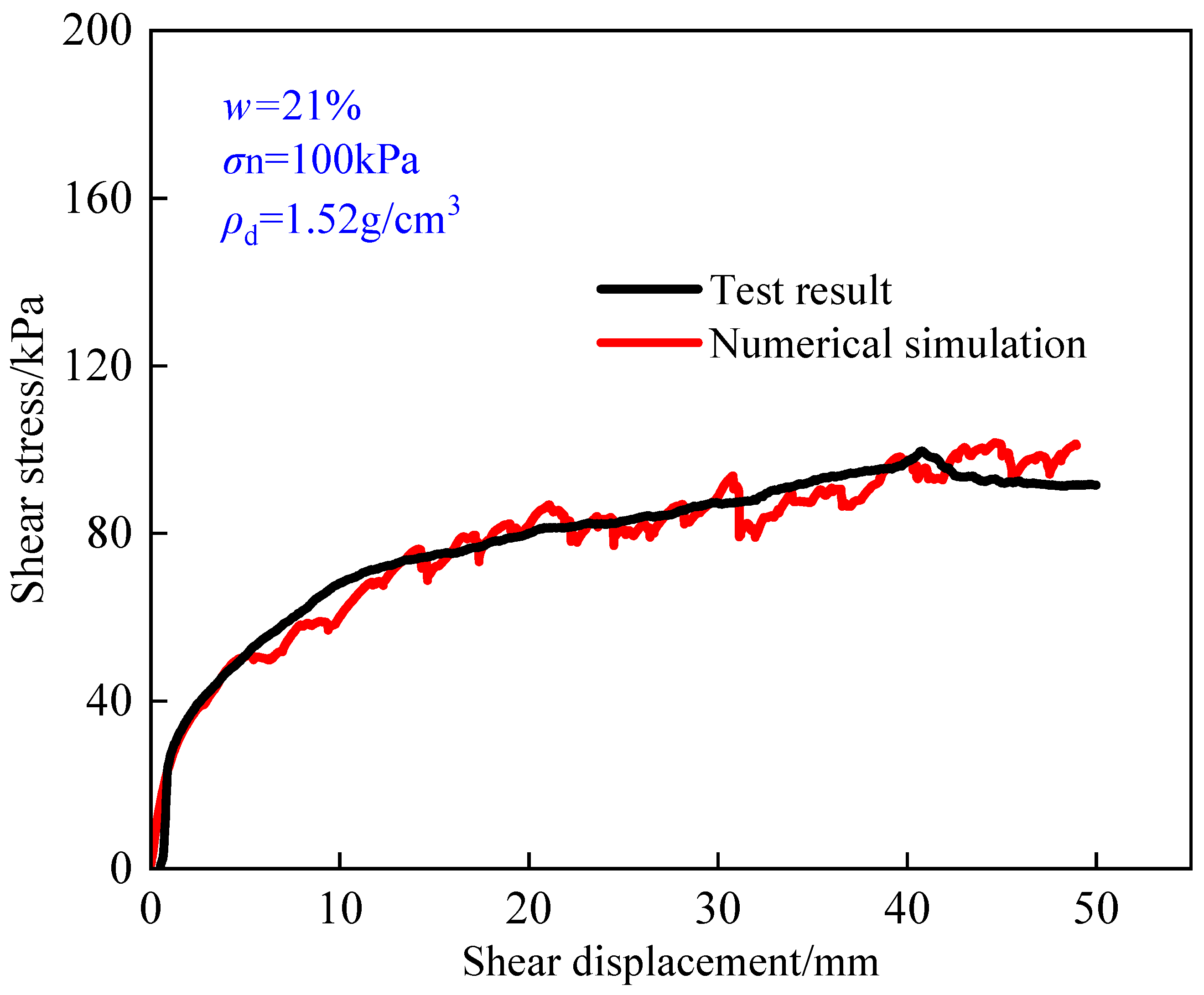
3.3.1. Numerical Results Verification
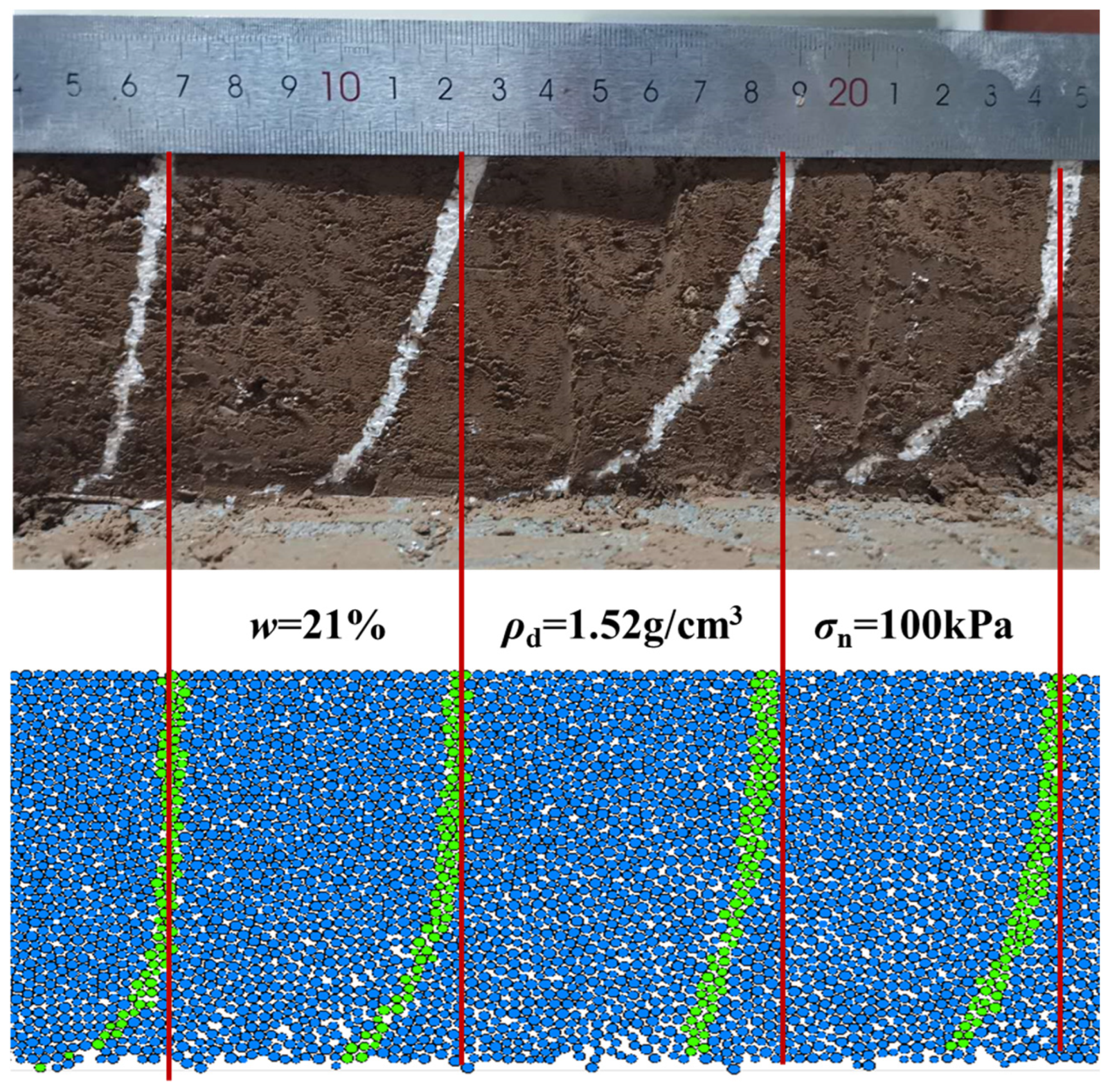
3.3.2. Simulated Deformation Evolutions of Loess Samples
3.3.3. Contact Force Chain Evolutions of Loess Sample
3.3.4. Fabric of Loess Sample
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The maximum shear deformation of the loess increased with the increase in initial moisture content, and decreased with the increase in dry density and normal stress;
- (2)
- The shear strength of loess-concrete rough interface increased with the increase in dry density and normal stress, and decreased with the increase in initial moisture content;
- (3)
- The DEM model can be capable of simulating the shear behaviors of interface shear test on loess and rough concretes.
- (4)
- The evolution of the shear deformation, contact force chain and fabric of the loess-concrete rough interface were explored by DEM simulation from micro-structural perspective.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, L.E.; Li, H.W.; Feng, Y.Z.; Huang, L.K.; Yang, J.; Ma, F.Y.; Fan, C.Q. Study on natural grounding of helical anchor foundations for ±800 kV overhead transmission lines in self-weight collapsible loess, China. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2025, 248, 111886. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhang, D.H.; Zhang, M.; Gu, X.Q.; Xu, L.F. Load transfer model of pile-unsaturated loess interface considering hydro-mechanical coupling effects. Rock Soil Mech. 2025, 46, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Xin, L.L.; Ye, S.H.; Wu, J.; Ye, W.A.; Li, J.B. Study on negative friction of pile foundation in homogeneous layered soil in collapsible loess area. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.Z.; Guo, B.W.; Wang, Z.Z.; Liu, Z.P. Settlement Analysis of Single Piles Incorporating Effective Pile Length and Interface Behavior. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2025, 43, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolisetti, C.; Whittaker, A.S. Numerical investigations of structure-soil-structure interaction in buildings. Eng. Struct. 2020, 215, 110709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.X.; Huang, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.H.; Liu, Y.H. A calculation method for uneven collapsible deformation of soil between compaction piles in loess area. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2025, 84, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Wang, G.; Guan, C.; Feng, D.; Zhang, F. Experimental study on the shear characteristics of different pile-soil interfaces and the influencing factors. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2023, 206, 103739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Fauchille, A.-L.; Vasilescu, R.; Dano, C.; Kotronis, P.; Sciarra, G. Influence of clay fraction on the shear behavior of an interface between sand-clay mixture and concrete. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2024, 38, 100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, Y.; Islam, M.R. Effects of water content and interface roughness on the shear strength of silt–cement mortar interface. Soils Found. 2021, 61, 1615–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sumelka, W.; He, S.; Gao, Y. Enhanced Fractional Model for Soil–Structure Interface Considering 3D Stress State and Fabric Effect. J. Eng. Mech. 2022, 148, 4022054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Wang, B.; Pan, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ling, X. Effect of concrete surface roughness on shear strength of frozen soil–concrete interface based on 3D printing technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 366, 130158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fu, S.; Zhu, D.; Li, G.; Shen, S. Experimental study on the effects of triangular groove inclination angles on the mechanical behavior of sand–concrete interfaces. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, B.; Li, Z.; Yin, W.; Lou, Q. Study on surface roughness effect on shear behavior of concrete-soil interface. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 145, 107050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Mu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ma, W.; Dong, J.; Huang, Y. Freeze-thaw cycling impact on the shear behavior of frozen soil-concrete interface. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2020, 173, 103024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Fei, K.; Dai, D. Modeling of granular soil-structure interface under monotonic and cyclic loading with the nonlinear approach. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 159, 105480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Liu, J.X.; Bayat, M.; Feng, W.Q.; Fang, Y.F.; Mousavi, Z. Comparison study of silty clay-gravel mixture-geotextile interface without and with polyurethane foam adhesive injection. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Xiao, Y.; Shu, S.Z.; He, X.; Liu, H.L. A constitutive model incorporating particle breakage for gravelly soil-structure interface under cyclic loading. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2022, 65, 2846–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoltz, G.; Nicaise, S.; Veylon, G.; Poulain, D. Determination of geomembrane—Protective geotextile friction angle: An insight into the shear rate effect. Geotext. Geomembr. 2020, 48, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, H.; Abbas, S. DEM-aided study of Coulomb and Roscoe theories for shear band inclination. Acta Geotech. 2022, 17, 3357–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, Q.; Ling, X.; Fang, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z. Thickness of the shear band of silty clay–concrete interface based on the particle image velocimetry technique. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 388, 131712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, C. An analytical method for predicting the soil-structure interaction of axially loaded piles in sands incorporating the two-surface plasticity model. Eng. Struct. 2023, 295, 116841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, A.; Hassani, H.; Shahriar, K.; Shahrabi, M.J.A. Thermo-hydro-mechanical modeling of fault discontinuities using zero-thickness interface element. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 12, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yin, Z.Y. Soil-structure interface modeling with the nonlinear incremental approach. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2021, 45, 1381–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Wu, D.; Fan, M.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Xiong, H.; Chen, X. DEM investigation into the coupling effects of particle asphericity and interface roughness on shear behaviour of soil-structure interface. Particuology 2025, 97, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xu, Z.; Chai, J.; Qin, Y.; Cao, J. Numerical investigation of the seepage mechanism and characteristics of soil-structure interface by CFD-DEM coupling method. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 159, 105430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yin, Z.Y.; Zhou, W.H.; Chen, W. Micro-mechanical analysis of soil–structure interface behavior under constant normal stiffness condition with DEM. Acta Geotech. 2022, 17, 2711–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yin, Z.-Y. Effect of particle breakage on the behavior of soil-structure interface under constant normal stiffness condition with DEM. Comput. Geotech. 2022, 147, 104766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, F.; Zhu, J.; Shahab, K.M. Mesoscopic shear evolution characteristics of frozen soil-concrete interface. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2025, 229, 104342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.K.; Zhou, G.Q.; Vandeginste, V.; Zhou, Y. Thermal-hydraulic-mechanical coupling behavior and frost heave mitigation in freezing soil. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 2701–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Fauchille, A.L.; Filippo, E.; Kotronis, P.; Sciarra, G. A review of sand–clay mixture and soil–structure interface direct shear test. Geotechnics 2021, 1, 260–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Song, Z. An elastoplastic model for unsaturated soil-structure interfaces considering different initial states, boundary conditions and suctions. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 167, 106123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yang, Y.; Bian, X.; Zhu, G. Study on dynamic shear properties of sulfate saline soil- geotextile interface with different salt content. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 183, 108807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, V.; Eskandari., S. Comparing a single pile’s axial bearing capacity using numerical modeling and analytical techniques. Results Eng. 2023, 17, 100893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.J.; Xu, J.M.; Xiong, H.R. Thermo-hydro-mechanical dynamic response of a cylindrical lined tunnel in a poroelastic medium with fractional thermoelastic theory. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 130, 105960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Lu, Y.Y.; Li, W.Y.; Dang, F.; Wang, Y.; Luo, X.Q. Dry-shrinkage of sandy clay improved by ecological fibers based on experiment and DEM simulation. Results Eng. 2025, 27, 106058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Li, X.; Du, Y.; Bao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J.; Hu, Y. Macro-micro numerical analysis of granular materials considering principal stress rotation based on DEM simulation of dynamic hollow cylinder test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, F.; Ma, Y. Numerical investigation of the tensile strength of loess using discrete element method. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2021, 247, 107610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.J.; Chen, J.N.; Chen, H.X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, A. Analysis of sand-woven geotextile interface shear behavior using discrete element method (DEM). Can. Geotech. J. 2020, 57, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitka, M.; Grabowski, A. Shear band evolution phenomena in direct shear test modelled with DEM. Powder Technol. 2021, 391, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


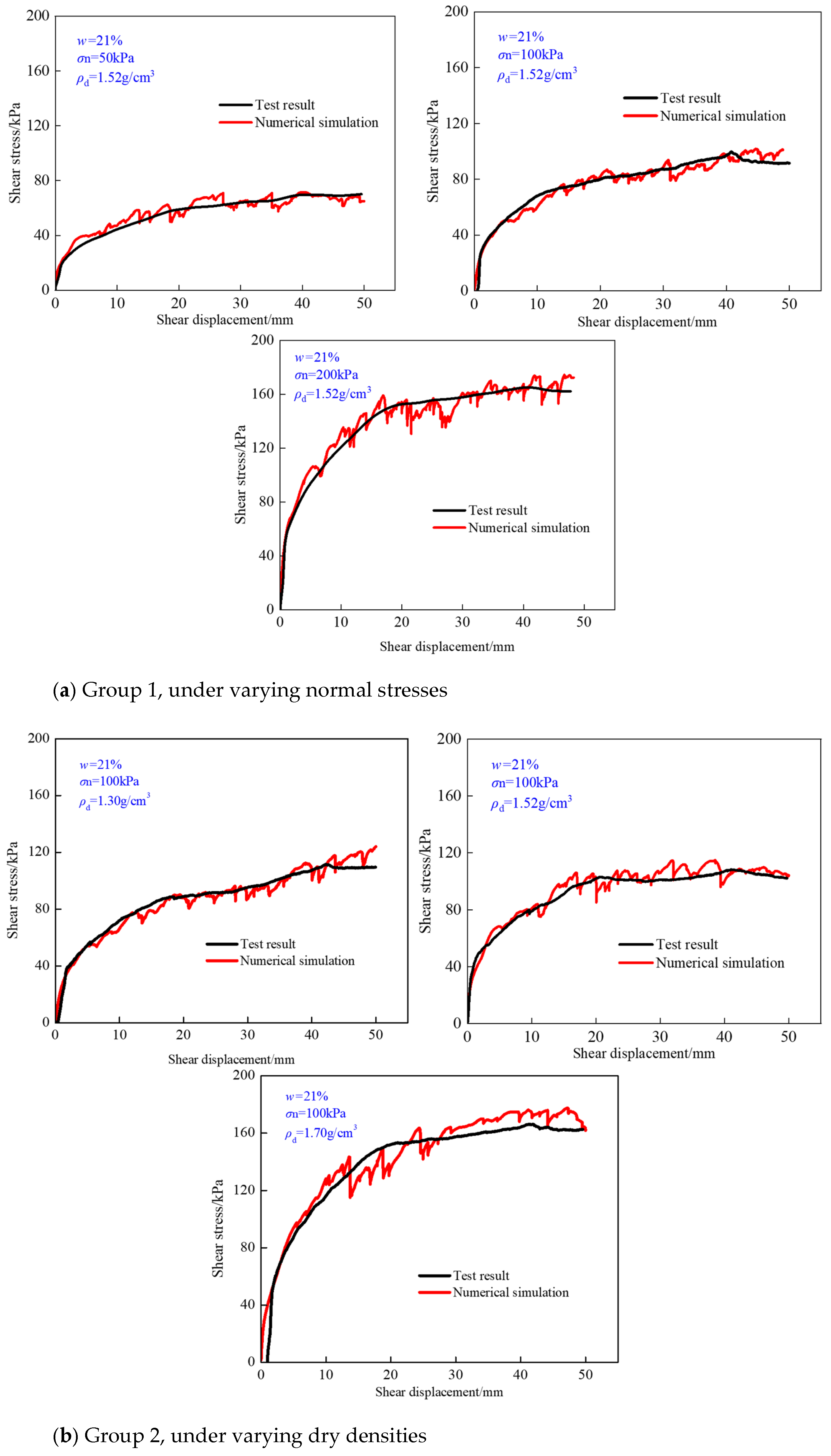
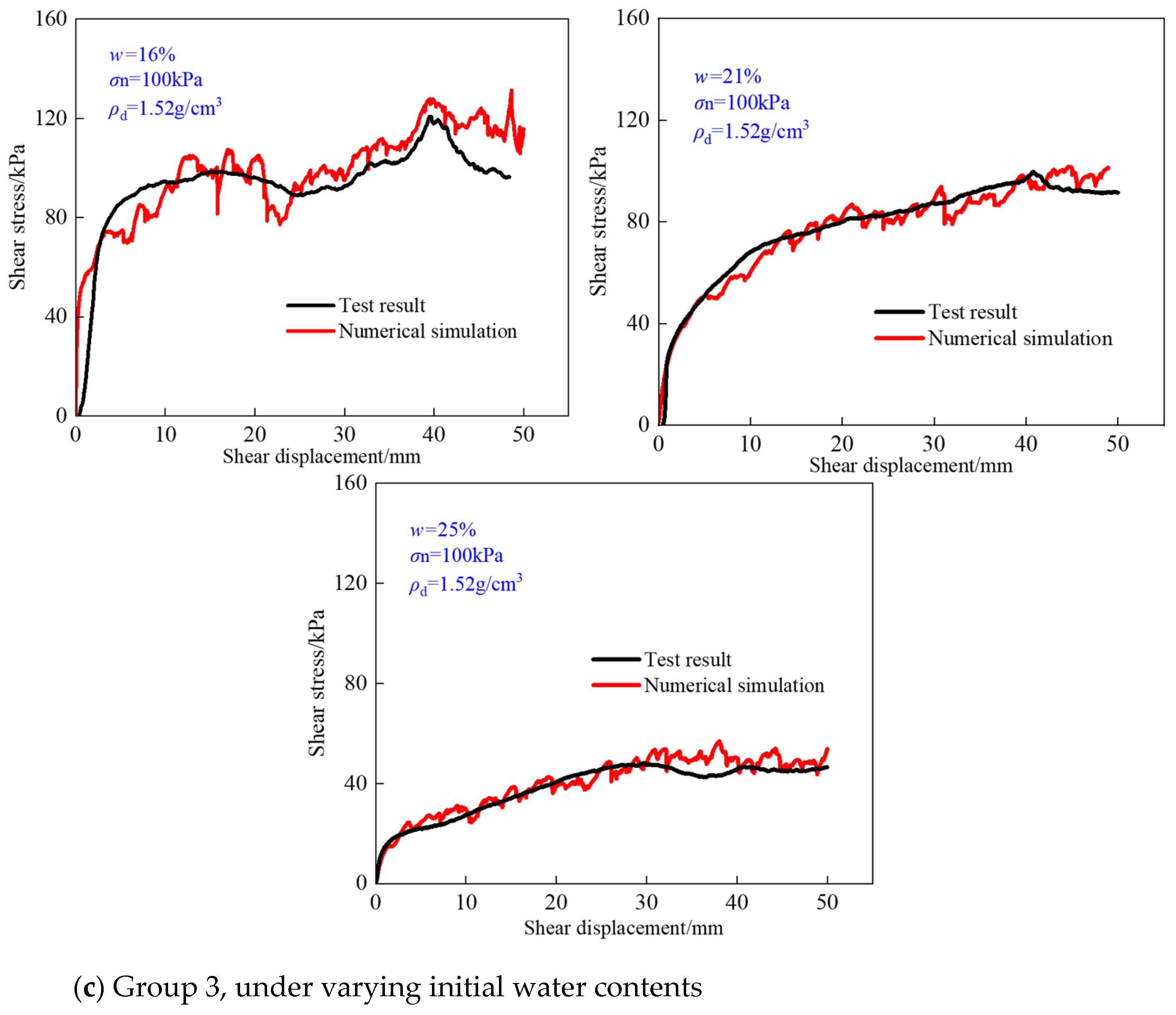
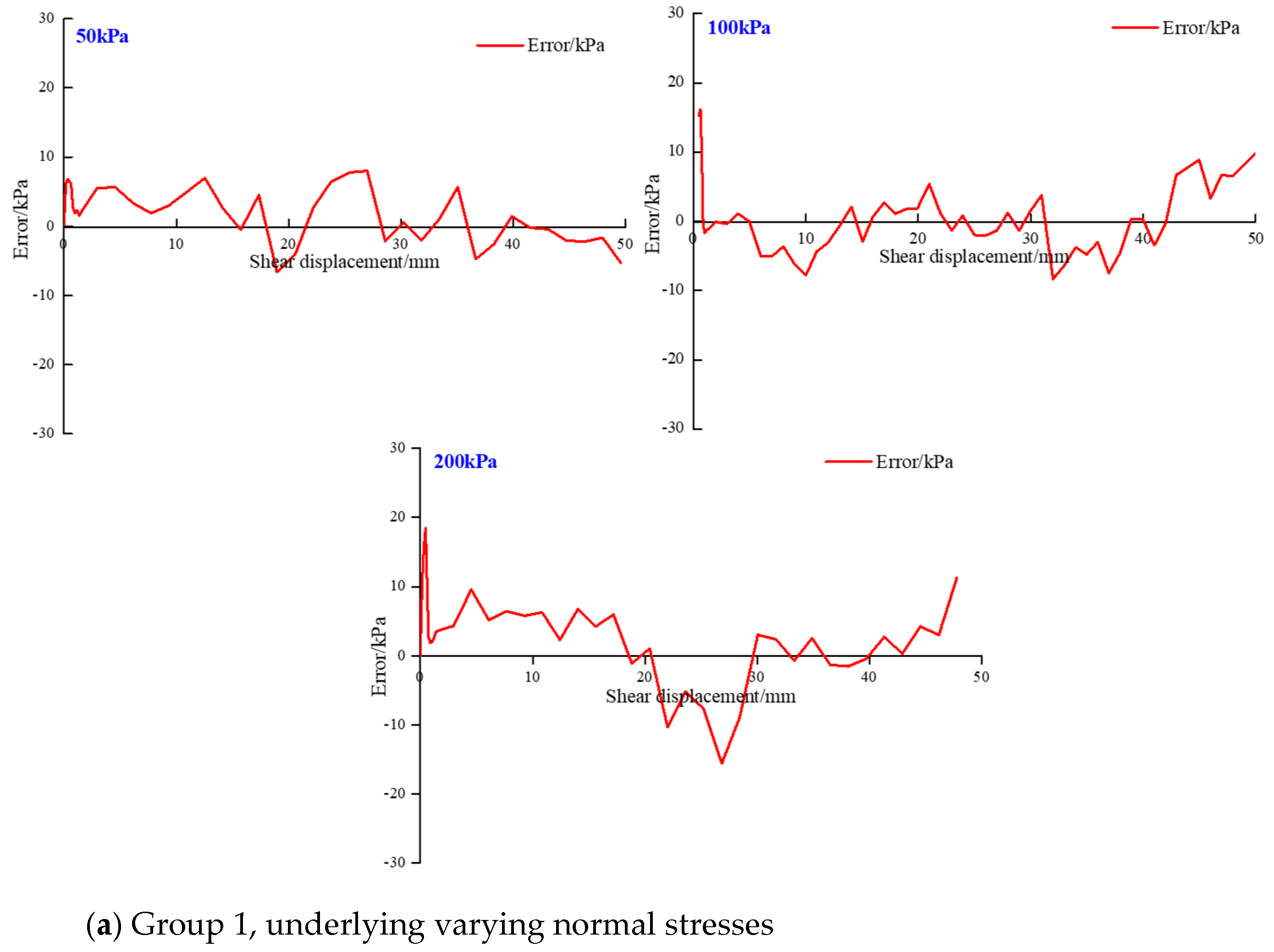

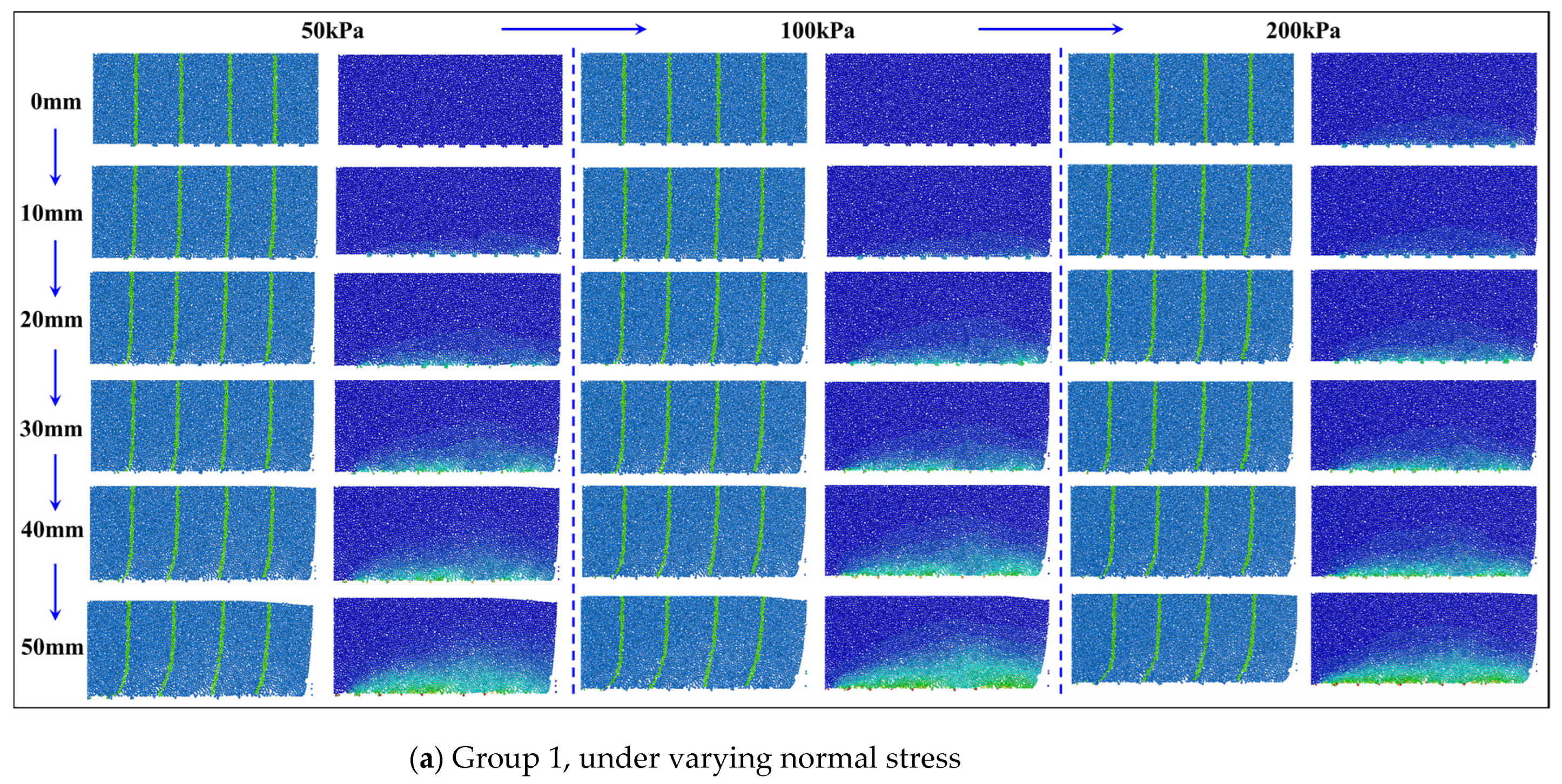

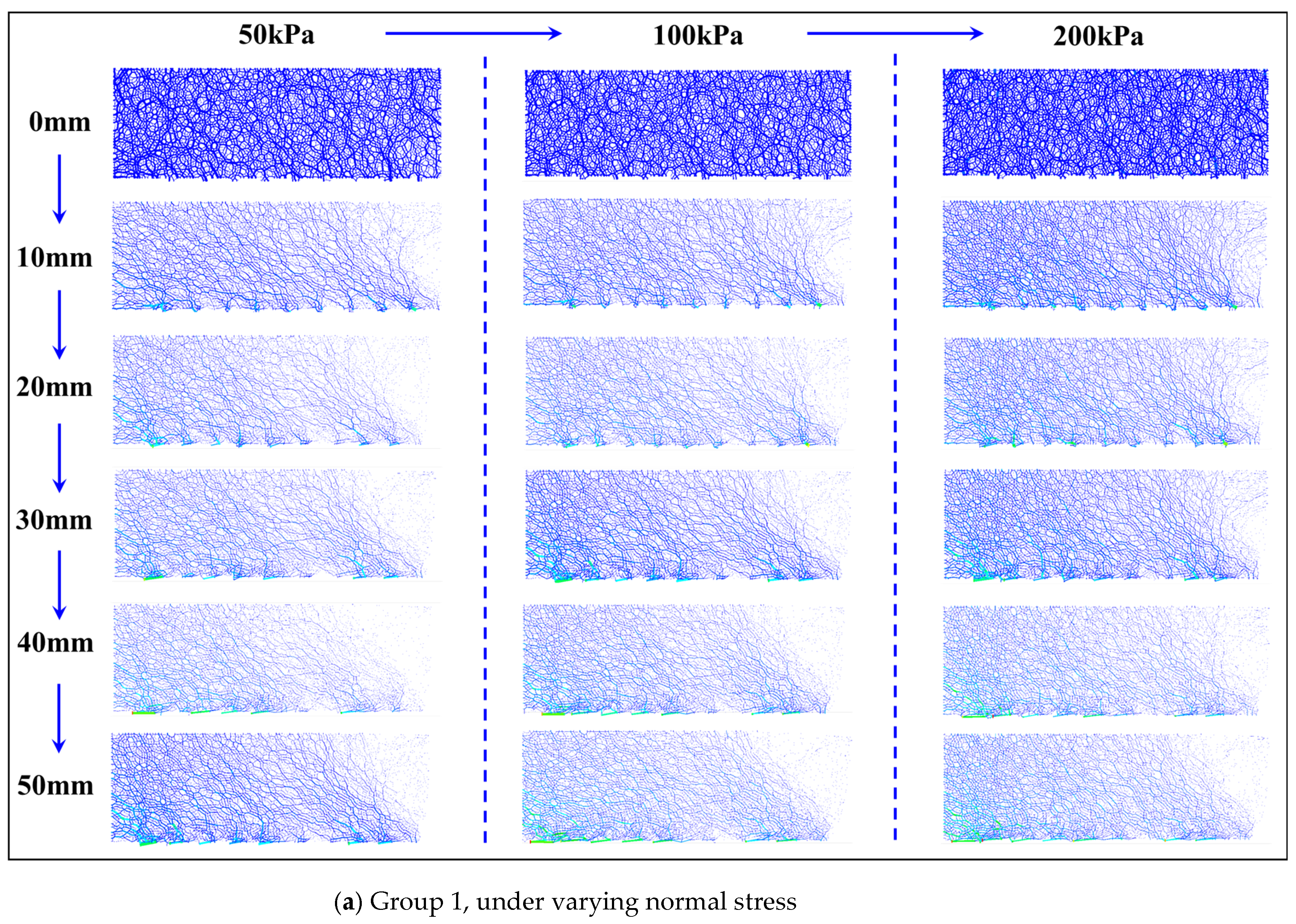
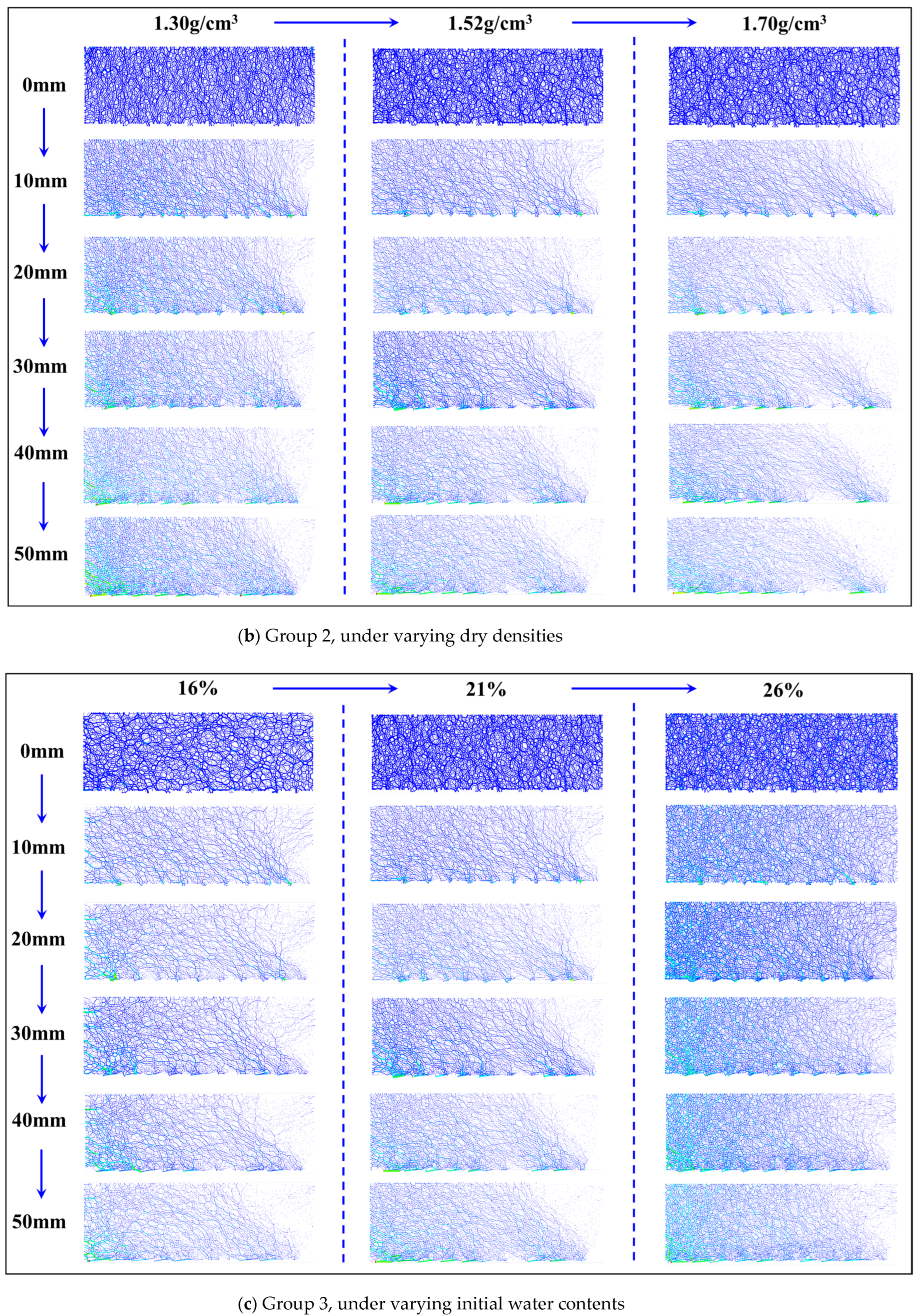
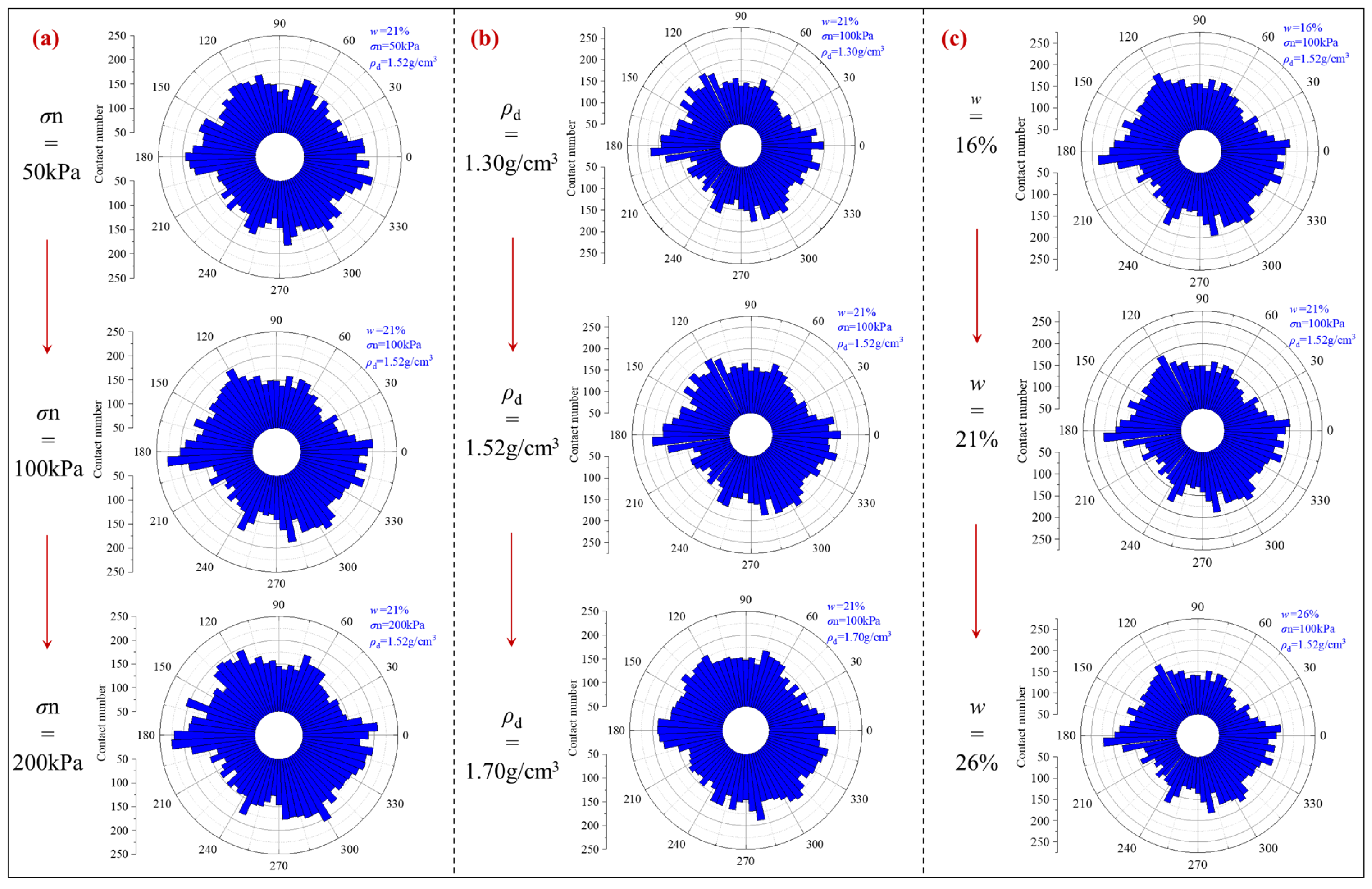
| Group 1 | Moisture content (%) | Dry density (g/cm3) | Normal stress (kPa) |
| 21.0 | 1.52 | 50 | |
| 100 | |||
| 200 | |||
| Group 2 | Moisture content (%) | Normal stress (kPa) | Dry density (g/cm3) |
| 21 | 100 | 1.30 | |
| 1.52 | |||
| 1.70 | |||
| Group 3 | Dry density (g/cm3) | Normal stress (kPa) | Moisture content (%) |
| 1.52 | 100 | 16 | |
| 21 | |||
| 26 |
| Parameters for Loess Particles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| emod | pb_deform emod | pb_coh | pb_ten | pb_fa | fric |
| 2.5 × 107 N/m | 3 × 105 N/m | 1 × 108 N/m | 1 × 108 N/m | 15° | 0.22 |
| Parameters for rough loess-concrete interface | |||||
| Ks | Kn | emod | fric | ||
| 1 × 107 N/m | 1 × 107 N/m | 1 × 107 N/m | 0.25 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Experimental and DEM Investigation of Shear Behaviors of a Loess and Rough Concrete Interface. Buildings 2025, 15, 3178. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173178
You Z, Wang T, Zhang L, Wang J. Experimental and DEM Investigation of Shear Behaviors of a Loess and Rough Concrete Interface. Buildings. 2025; 15(17):3178. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173178
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Zhilang, Tiehang Wang, Liang Zhang, and Juanjuan Wang. 2025. "Experimental and DEM Investigation of Shear Behaviors of a Loess and Rough Concrete Interface" Buildings 15, no. 17: 3178. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173178
APA StyleYou, Z., Wang, T., Zhang, L., & Wang, J. (2025). Experimental and DEM Investigation of Shear Behaviors of a Loess and Rough Concrete Interface. Buildings, 15(17), 3178. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173178






