Abstract
To address challenges posed by waste tires and greenhouse gas emissions associated with ordinary Portland cement, exploring eco-friendly construction materials is critical for sustainability. This study examines the workability and mechanical properties of straight steel fiber-reinforced rubberized geopolymer concrete (SFRRGC), where rubber powder is derived from recycled waste tires. The experimental variables included rubber powder (RP) content (0%, 6%, 12%, and 20% by volume of fine aggregate) and steel fiber (SF) content (0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, and 1.5% by volume). The results show that incorporating RP and SFs reduced the workability of SFRRGC but increased its peak strain. Specifically, RP addition decreased the elastic modulus, compressive strength, and toughness; increasing the SF content enhanced energy dissipation, while the effects of SF and RP contents on Poisson’s ratio were negligible. The specimens showed that a higher RP content would weaken the crack-bridging effect of SF. For example, specimens with 1.0% SF and 6% RP achieved 49.56 MPa compressive strength and 4.04 × 10−3 maximum peak strain; those with 0.5% SF and 20% RP had 118.40 J compressive toughness, which was 5.53% lower than that of the reference specimens (125.33 J). Furthermore, a constitutive model for SFRRGC was proposed, and its theoretical curves aligned well with the experimental results. This proposed model can reliably predict the stress–strain curves of geopolymer concrete with different SF and RP mixture proportions.
1. Introduction
Over the current decade, approximately one billion waste tires are generated globally each year, with more than 500 million discarded in landfills without subsequent reuse—a trend expected to continue [1,2,3]. Improper disposal of waste tires poses substantial risks to society and the environment, including land and water contamination, fire hazards, disease transmission, and the loss of valuable resources such as rubber, steel, and fuel [4]. Recycling waste tires offers an eco-friendly solution, reducing waste volumes, mitigating environmental harm, and generating valuable products for diverse industries [5]. Concurrently, the booming construction sector is depleting natural aggregates, particularly river sand. Excessive sand mining has triggered environmental issues like riverbed erosion and habitat disruption. With global aggregate demand projected to reach 60 billion tons by 2030, the need for alternative aggregates has become critical [6,7]. Studies by El Khouri et al. [8], Sainz-Aja et al. [9], and Zrar et al. [10] highlight that incorporating solid wastes—including recycled aggregates, ground granulated blast furnace slag, and rubber powder (RP) derived from waste tires—provides a practical pathway to sustainable concrete production. RP, in particular, has been shown to effectively substitute fine aggregates in rubberized concrete, aiding environmental protection and conserving natural resources like sand and gravel, which are essential for conventional concrete mixes [11,12].
Over the past decade, significant progress has been made in the comprehensive utilization of solid waste worldwide [13,14,15]. Growing awareness of products derived from solid waste utilization has spurred in-depth investigations into the properties of rubberized concrete and the development of relevant theories [16,17,18]. Recycled rubber, primarily obtained by shredding waste tires, is used to partially or fully replace fine aggregates in traditional concrete, enhancing the material’s resistance to impact, freeze–thaw cycles, abrasion, and thermal conductivity [19], as well as alkali-silica reactions [20]. Research by Akter et al. [21] and Duarte et al. [22] show that rubberized concrete mixtures containing up to 30% RP (by mass) exhibit marked improvements in ductility (70.0%) and energy dissipation capacity (27.7%) compared to standard mixtures. Karunarathna et al. [23] suggested that concrete with a low RP content can be effectively used in impact-resistant structures, promoting sustainable construction. Furthermore, Zhang et al. [24] emphasized that integrating RP reduces both steel corrosion and concrete deterioration. Nonetheless, rubberized concrete predominantly relies on ordinary Portland cement (OPC) as its primary binder, owing to OPC’s favorable mechanical properties, cost-effectiveness, and durability. However, OPC production is linked to significant environmental concerns, including extensive consumption of natural resources and substantial greenhouse gas emissions. Notably, OPC production accounts for 6–9% of global greenhouse gas emissions [25,26], and its worldwide output is projected to reach 4.4 billion tons by 2050 [27,28]. In response to these environmental challenges, there is a growing focus on developing eco-friendly alternative materials.
Alkali-activated materials (AAMs) are regarded as a promising alternative, primarily due to their lower CO2 emissions and superior engineering properties compared to OPC-based concrete [29,30]. AAMs are characterized by high levels of aluminum and alkali elements [31] and are synthesized using precursors such as fly ash, bottom ash, metakaolin, and ground granulated blast furnace slag. These aluminosilicate-rich precursors undergo activation with highly alkaline solutions and soluble silicates within appropriate temperature ranges, leading to polymerization and the formation of AAMs [32,33]. AAMs, categorized into high-calcium and low-calcium types, exhibit excellent engineering properties, including high early strength, resistance to chemical attack, low creep, and exceptional acid resistance [34,35,36,37]. Geopolymerization results in three-dimensional networks for low-calcium AAMs, which are composed of SiO4 and AlO4 tetrahedrons [38]. Combining AAMs with recycled tire materials represents a promising approach to significantly enhance the sustainability of construction materials and mitigate associated environmental issues.
To date, several studies have explored the effects of RP on the engineering properties of AAMs. Dehdezi et al. [39] examined the microstructure, physical, mechanical, and dynamic properties of lightweight fly ash-based geopolymers incorporating RP, finding that substituting fine aggregates with RP in AAMs enhances dynamic strength under impact loading. Kokabi and Gandoman [40] demonstrated that metakaolin-based geopolymers containing RP exhibit significantly improved noise reduction and sound absorption compared to traditional rubberized concrete. Park et al. [41] validated the feasibility of using RP in fly ash-based geopolymers, showing that a substantial portion of fine aggregates can be replaced by RP. Wongsa et al. [42] investigated RP’s influence on the mechanical and thermal properties of fly ash-based geopolymers, concluding that AAMs with 100% RP exhibit superior thermal insulation. Aly et al. [43] evaluated the impact of various RP replacement ratios for natural aggregates on AAM properties, determining that the proposed steel slag-based geopolymers containing RP are suitable for structural components subjected to dynamic loads. However, significant reductions (up to 93%) in compressive and flexural strength have been observed in both OPC and AAMs incorporating RP [44,45].
To address RP-induced strength reductions while retaining its beneficial effects, steel fibers (SFs) are typically added to rubberized concrete to enhance its overall mechanical properties [46,47]. In recent years, extensive research has focused on how SFs influence the mechanical and durability properties of SF-reinforced concrete [48,49,50]. Multiple studies have investigated the impacts of various fiber types—including polypropylene, polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene terephthalate, and steel fibers—and fabric [51]—on the mechanical properties of concrete. For example, Medina et al. [19] explored the thermal properties of SF-reinforced rubberized concrete, finding that SF inclusion significantly improves mechanical properties and toughness due to strong bonding between the SFs and the concrete matrix. This aligns with research by Alsaif et al. [52], which showed that adding either recycled or manufactured SFs effectively mitigates RP-induced strength loss while enhancing the flexural strength of rubberized concrete. These studies indicate that fibers create a bridging effect within concrete, leading to notable improvements in flexural toughness and ductility [53,54,55]. Integrating RP and SFs is crucial for enhancing the sustainability of construction materials and reducing production costs by maximizing the use of recycled materials that address environmental concerns. However, comprehensive research on the properties of AAMs incorporating both RP and SFs remains limited.
This study develops an environmentally friendly steel fiber-reinforced rubberized geopolymer concrete (SFRRGC) and designs sixteen different mixes with varying RP contents (0%, 6%, 12%, and 20% by volume of fine aggregate) and SFs (0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, and 1.5% by volume). The AAMs used in this research are prepared using coal gangue (low-calcium) and ground granulated blast furnace slag (high-calcium) activated by alkaline solutions. The experimental program focuses on evaluating workability, failure modes, compressive strength, peak strain, and compressive toughness through a series of tests, with additional analysis of SFRRGC stress–strain curves. The findings aim to enhance the mechanical properties and achieve high ductility in geopolymer concrete through the combined use of SFs and RP reinforcement.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Alkali-activated materials (AAMs) are categorized into high-calcium and low-calcium systems based on the calcium content in raw materials [56]. High-calcium systems, including those based on ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBFS), primarily generate calcium-aluminosilicate hydrate (C-A-S-H) gel [57]. In contrast, low-calcium systems utilizing materials like fly ash (FA) and coal gangue (CG) produce sodium (or potassium) aluminosilicate hydrate (N-A-S-H) gel, characterized by a zeolite-like structure and a higher degree of Si-O tetrahedron polymerization. In this study, geopolymers were prepared using CG and GGBFS as precursors, with sodium silicate and sodium hydroxide solutions as alkaline activators. The particle size distributions of CG and GGBFS are illustrated in Figure 1a, while their chemical compositions can be found in Table 1. The median particle sizes of CG and GGBFS were 20.29 μm and 13.59 μm, respectively. Sodium hydroxide with a purity exceeding 96% was used, and the sodium silicate solution had mass fractions of 27.3% Na2O, 8.5% SiO2, and 64.2% H2O.
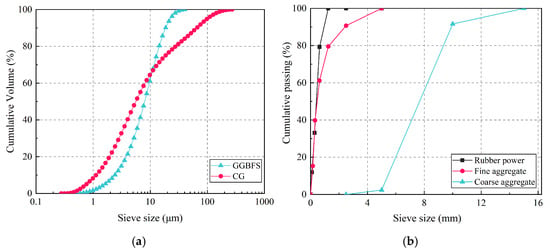
Figure 1.
Particle size distribution: (a) precursors; (b) aggregates.

Table 1.
Main chemical composition of the precursors (wt%).
Fine aggregates consisted of rubber powder (RP) from waste tires and river sand, while crushed granite served as the coarse aggregate. The particle sizes of these aggregates are illustrated in Figure 1b, determined via sieve analysis following ASTM D5644 standards [58]. River sand had a maximum particle size of approximately 5 mm with continuous grading; crushed granite ranged from 5 to 15 mm; and RP was 20-mesh. Their densities were 2.64 g/cm3 (river sand), 2.66 g/cm3 (crushed granite), and 0.76 g/cm3 (RP), as listed in Table 2. Ordinary straight steel fibers (SFs) had a length of 13 mm, and the diameter, tensile strength, and elastic modulus were 0.2 mm, 2800 MPa, and 200 GPa, respectively. Laboratory water was used to control the liquid-to-solid ratio, and retarder (BaCl2) was added to prevent rapid setting of SFRRGC. All materials were sourced from both laboratory stocks and commercial suppliers.

Table 2.
Properties of fine and coarse aggregates.
2.2. Design of Concrete Mix
Table 3 displays the composition ratios of all mixtures, with the CG:GGBFS ratio fixed at 50:50, retarder dosage at 1.0% by mass of precursors, and water-to-binder ratio at 0.55. The investigated parameters were RP and SF contents: RP partially replaced sand by volume at 0%, 6%, 12%, and 20%; SFs were incorporated at 0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, and 1.5% by volume, resulting in 16 SFRRGC mixes. The mix nomenclature uses “SF” and “R” to denote steel fiber and rubber powder contents (e.g., SF0R0 is the reference mix without SFs or RP).

Table 3.
Mixture proportions of SFRRGC (kg/m3).
2.3. Specimen Preparation
Figure 2 shows the mixing procedures: (1) Prepare the alkali activator by blending sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate solutions for 5 min, then cool to room temperature. (2) Dry-mix CG, GGBFS, SF, RP, sand, and crushed granite in a planetary mixer for 180 s to ensure uniformity. (3) Add the alkaline activator and extra water, mixing for 3 min. Workability of fresh SFRRGC was assessed via slump test before casting into 100 × 200 mm cylindrical molds. Specimens were compacted on a vibrating table, covered with polyethylene film to minimize moisture loss, and cured at approximately 25 °C. They were demolded after 24 h and stored in a 20 ± 2 °C curing room for 28 days; the humidity was ≥95%.
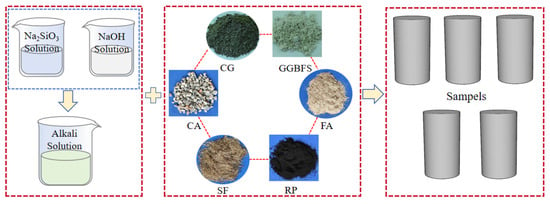
Figure 2.
Preparation procedure of SFRRGC.
2.4. Testing Method
Figure 3 shows the compressive strength test setup of SFRRGC, and triplicate specimens per mix were tested for compressive strength. The 28-day cured 100 × 200 mm cylinders were tested using a compression machine following ASTM C469M [59], under displacement control at a loading rate of 0.18 mm/min. Axial strain was measured using two 80 mm longitudinal strain gauges symmetrically attached at mid-height; transverse strain was measured with two 50 mm gauges at the same location. To capture full-range strain (pre-peak to post-peak), two linear variable differential transducers (LVDTs) were installed at mid-height over 80 mm, addressing potential gauge damage during cracking.
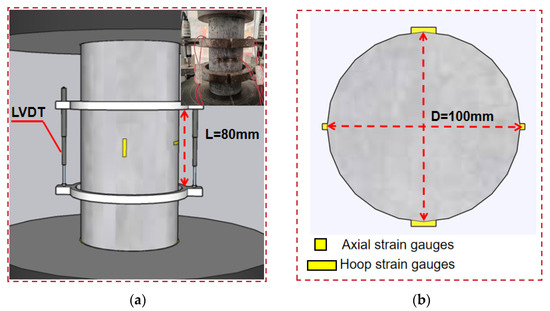
Figure 3.
Compressive strength test setup: (a) the setup; (b) the strain gauges.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Workability
Slump tests were conducted to evaluate the workability of different mixtures, where higher slump values indicate enhanced fluidity, mobility, and workability. The effects of steel fibers (SFs) and rubber powder (RP) on slump values of all mixtures are illustrated in Figure 4, with the SF0R0 mixture (0% SF and 0% RP) serving as the reference, and it was observed that the addition of both SFs and RP reduced the workability.
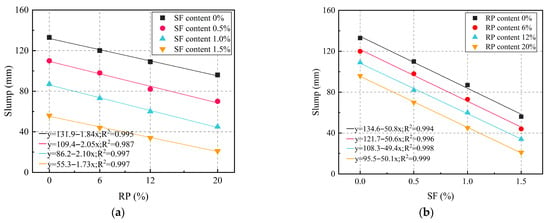
Figure 4.
Workability of SFRRGC: (a) RP; (b) SFs.
The reference mixture (SF0R0) exhibited a maximum slump value of 133.1 mm. As shown in Figure 4a,b, slump values decreased with increasing SF or RP content, with SFs having a more pronounced effect. Increasing SF content from 0% to 1.5% (SF1.5R0) reduced slump by 57.93%, while a 0% to 20% RP addition decreased slump by 27.87%. Specifically, slump values dropped to 110 mm, 87 mm, and 56 mm at 0.5%, 1.0%, and 1.5% SF, respectively. For RP, slump reductions of 9.69%, 18.11%, and 27.87% were observed at 6%, 12%, and 20% replacement levels. The combined addition of SFs and RP caused a notable slump decrease: SF1.5R20 showed a slump of 21 mm, an 84.22% reduction compared to SF0R0. This workability decline is attributed to increased shear resistance from fibers [60,61] and higher water absorption by RP, which reduces effective water content in the mixtures [62].
3.2. Failure Modes
The failure modes of specimens are illustrated in Figure 5. The reference specimen (SF0R0, Figure 5a) initially developed cracks at mid-height, which propagated to both ends under increasing load. At peak load, a vertical crack connected these fractures, followed by extensive cracking and minor spalling post-peak. For specimens without SFs (0% SF) but with increasing RP (Figure 5a–d), more parallel cracks formed along the loading direction. These multiplied with deformation and propagated rapidly post-peak, indicating slight ductility improvement from RP. Higher RP content increased surface cracking, consistent with literature [63] linking RP addition to increased porosity and bubble formation.
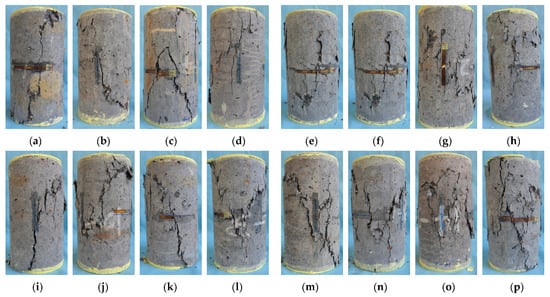
Figure 5.
Failure modes of SFRRGC: (a–d) SF0R0, SF0R6, SF0R12, and SF0R20; (e–h) SF0.5R0, SF0.5R6, SF0.5R12, and SF0.5R20; (i–l) SF1.0R0, SF1.0R6, SF1.0R12, and SF1.0R20; and (m–p) SF1.5R0, SF1.5R6, SF1.5R12, and SF1.5R20.
In RP-free specimens (0% RP) with increasing SFs (Figure 5a,e,i,m), cracks appeared at higher loads with minimal deformation. Post-peak, diagonal cracks widened without spalling, and load-bearing capacity diminished gradually with larger displacements, as SF bridging preserved structural integrity. Specimens containing both SFs and RP exhibited combined failure characteristics. For example, at 20% RP, increasing SFs from 0% to 1.5% (Figure 5d,h,l,p) resulted in significant deformation and numerous fine surface cracks. Higher RP content expanded the geopolymer–aggregate interface, increasing matrix fractures and weakening SF bridging, thereby reducing compressive strength and toughness.
3.3. Compressive Strength
It is widely acknowledged that RP incorporation tends to reduce concrete compressive strength; thus, evaluating the combined effects of RP and SFs on the compressive strength of SFRRGC is essential. Figure 6 illustrates the influences of RP and SFs on the compressive strength of all specimens. The reference mixture (SF0R0, without SFs or RP) exhibited a compressive strength of 47.83 MPa. Compared to SF0R0, strength reductions of 6.82%, 14.84%, and 24.98% were observed at 6%, 12%, and 20% RP replacement, respectively. The lowest strength (35.88 MPa) occurred at 20% RP, indicating significant strength degradation at this replacement level. These findings align with previous studies [42,43], which reported strength reductions of up to 35.0% in AAMs with RP, depending on replacement ratios. The mechanisms underlying strength reduction are consistent with those in RP-modified traditional concrete [64,65,66]: (1) RP’s hydrophobic nature impairs bonding with geopolymer gels; (2) RP exhibits a significantly lower elastic modulus compared to sand, resulting in greater deformation and increased stress concentration, thereby accelerating compressive failure; (3) RP’s low specific gravity increases SFRRGC heterogeneity; and (4) air entrapment by RP during mixing elevates porosity. Notably, SF0.5R6 (0.5% SF and 6% RP) exhibited a strength only 2.01% lower than SF0R0, indicating SFs effectively offset RP-induced strength loss.
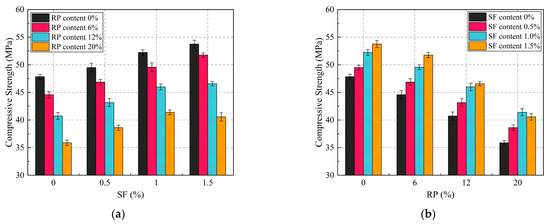
Figure 6.
Compressive strength of SFRRGC: (a) RP; (b) SFs.
As illustrated in Figure 6b, maintaining constant RP content and increasing SFs from 0% to 1.5% significantly improved 28-day compressive strength. For instance, at 6% RP, the 28-day compressive strength increased by 16.13%, while SF1.0R20 (1.0% SF and 20% RP) showed an improvement of approximately 15.38%. This aligns with prior research demonstrating that optimal SF content enhances AAMs’ compressive strength [67,68], attributed to strengthened fiber–matrix bonding and stress redistribution via high-modulus SFs, which restricts tensile crack development and improves load-bearing capacity. SF’s crack-bridging effect further contributes by distributing stress during fiber pullout, inhibiting crack initiation and propagation [69]. Notably, all mixtures exceeded the 35 MPa minimum compressive strength required for basic engineering applications (Figure 6b). This confirms that 1.0% SF effectively mitigates RP-induced strength loss in SFRRGC, ensuring suitability for practical applications.
3.4. Modulus of Elasticity
The elastic modulus of SFRRGC was determined according to ASTM C469M [59] and is presented in Figure 7. The elastic modulus decreased with increasing RP content (0–20%), exhibiting an inverse trend with SF content. For SF0R20 specimens, elastic modulus decreased by 23.62% (Figure 7a). Conversely, SF1.5R0 specimens showed an enhanced elastic modulus (Figure 7b) of approximately 18.97 GPa (Figure 7b), representing a 7.54% increase compared to SF0R0. This indicates that independent incorporation of RP or SFs significantly affected the elastic modulus of SFRRGC.
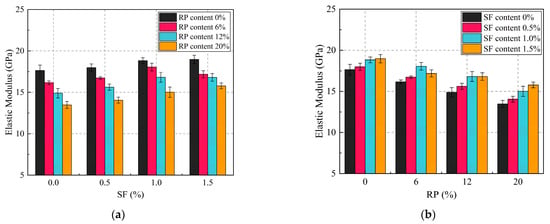
Figure 7.
Elastic modulus of SFRRGC: (a) RP; (b) SFs.
In specimens containing both SFs and RP, the elastic modulus decreased gradually with increasing RP; the specimens SF0.5R20, SF1.0R20, and SF1.5R20 exhibited elastic moduli of 14.05, 15.01, and 15.49 GPa, corresponding to reductions of 21.86%, 20.29%, and 18.34%, respectively. The elastic modulus increased with SFs at a constant RP: the specimens SF1.5R6, SF1.5R12, and SF1.5R20 showed moduli of 17.18, 16.80, and 15.78 GPa, with reductions of 6.31%, 12.83%, and 17.06% relative to SF0R0. These results indicate a synergistic effect of combined SFs and RP on the elastic modulus, consistent with mechanisms observed for compressive strength and peak strain. RP introduces voids in the matrix, weakening the SFRRGC structure [64], while SFs—with a higher elastic modulus than the matrix—enhance the overall modulus as their content increases [69].
3.5. Poisson’s Ratio
Poisson’s ratios of SFRRGC were calculated following ASTM C469/C469M [59] and are shown in Figure 8. Ranging from 0.209 to 0.238, Poisson’s ratios increased with both RP and SF content. The minimum value (0.209) was observed in SF0R0 (no RP or SFs). Increasing RP from 0% to 20% notably raised Poisson’s ratios: In the SF0Ry series (no SFs), SF0R20 exhibited a 10.53% increase compared to SF0R0 (Figure 8a). In the SFxR0 series (no RP), Poisson’s ratios also increased with SF content (0–1.5%), with SF1.5R0 showing the maximum value of 2.21, approximately 5.74% higher than SF0R0 (Figure 8b). This suggests RP and SFs both influence Poisson’s ratios, consistent with the materials’ deformation characteristics.
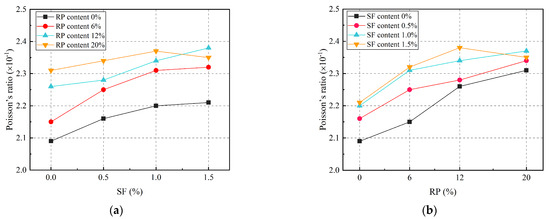
Figure 8.
Poisson’s ratios of SFRRGC: (a) RP; (b) SFs.
In specimens with combined SFs and RP, Poisson’s ratios were synergistically influenced, with the maximum value (0.238) observed in SF1.5R12. Increasing SFs from 1.0% to 1.5% caused a slight rise in Poisson’s ratios (from 0.235 to 0.238). RP addition (0–20%) had a more pronounced effect on Poisson’s ratios than SFs. Overall, the Poisson’s ratios remained within a narrow range (0.224 ± 0.015), indicating that the influence of SFs and RP on the SFRRGC Poisson’s ratio is minimal and negligible for practical engineering design.
3.6. Peak Strain
Peak strains of the specimens were determined following the method described in previous research [70] and are presented in Figure 9. Increasing RP content from 0% to 20% led to higher peak strains, with a similar positive correlation observed for SF content. In the series without SFs (SF0Ry), the maximum peak strain reached 3.70 at 20% RP (SF0R20, Figure 9a). For the RP-free series (SFxR0, Figure 9b), peak strains increased with SF content (0–1.5%), with SF1.5R0 exhibiting the highest value (3.62)—12.42% higher than SF0R0. These results indicate that both RP and SFs independently promote peak strain in SFRRGC.
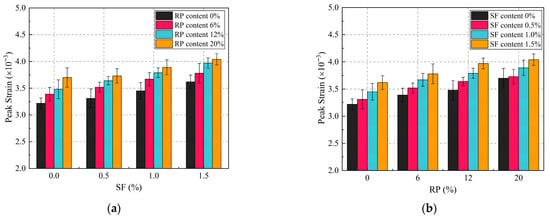
Figure 9.
Peak strains of SFRRGC: (a) RP; (b) SFs.
In specimens containing both SFs and RP, peak strains at maximum stress were significantly enhanced by increasing either component. For series with fixed 20% RP and increasing SFs, the peak strains of SF0.5R20, SF1.0R20, and SF1.5R20 were 3.73, 3.89, and 4.04, respectively—representing increases of 12.69%, 12.75%, and 11.60% compared to their RP-free counterparts (SF0.5R0, SF1.0R0, and SF1.5R0). For series with fixed 1.5% SF and increasing RP, the peak strains of SF1.5R6, SF1.5R12, and SF1.5R20 were 3.78, 3.97, and 4.04, showing increases of 11.50%, 14.08%, and 9.19% relative to SF0R6, SF0R12, and SF0R20. The maximum peak strain (4.04) was observed in SF1.5R20, a 25.47% increase compared to SF0R0 (3.22) (Figure 9), confirming that combined SF and RP incorporation enhances deformation at maximum stress.
3.7. Compressive Toughness
Compressive toughness, which effectively characterizes a material’s energy dissipation capacity [71], is critical for structural applications as it provides clearer pre-failure warnings compared to abrupt brittle failure. The compressive toughness (T) of all SFRRGC specimens was calculated using Equation (1):
where T is defined as the integral of compressive stress (σ) over strain (ε) up to 80% of the peak stress in the post-peak phase. Figure 10 displays the toughness values of the specimens. It was observed that the effects of SF and RP content on the compressive toughness of SFRRGC varied. Generally, SF significantly improved toughness, while RP had a negative impact. The reference mixture (SF0R0) exhibited a toughness of 125.33 J. In the SF-free series (SF0Ry), increasing RP to 6%, 12%, and 20% (SF0R6, SF0R12, and SF0R20) reduced toughness by 15.54%, 21.03%, and 31.79%, respectively (Figure 10a). Conversely, in the RP-free series (SFxR0, Figure 10b), SF addition at 0.5%, 1.0%, and 1.5% increased toughness by 38.23%, 51.63%, and 80.97%, respectively, confirming SF’s positive effect on energy dissipation.
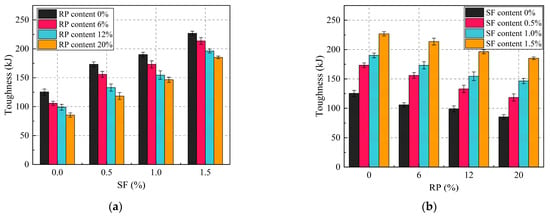
Figure 10.
Compression toughness of SFRRGC: (a) RP; (b) SFs.
In specimens with combined SFs and RP, a higher RP content significantly impaired toughness. At 20% RP, the toughness values of SF0.5R20, SF1.0R20, and SF1.5R20 were 118.40, 146.51, and 185.29 J—decreases of 31.66%, 22.91%, and 18.31% compared to their 0% RP counterparts. However, increasing SFs to 1.5% markedly offset RP-induced toughness loss: SF1.5R6, SF1.5R12, and SF1.5R20 exhibited toughness values of 213.65, 196.28, and 185.29 J, representing increases of 101.83%, 98.32%, and 116.76% relative to SF0R6, SF0R12, and SF0R20. This indicates that SFs enhance load-bearing capacity and energy dissipation, enabling greater energy absorption during failure. Notably, SF0.5R20 showed a 5.53% toughness reduction compared to SF0R0 (118.40 J vs. 125.33 J), suggesting that RP content should be limited to ensure adequate toughness in SFRRGC.
4. Mechanism Analysis
Concerning the SF incorporation, it is clear that the compressive strength, toughness, elastic modulus, and peak strain of SFRRGC were enhanced. Its effects are attributed to three mechanisms: (1) the SFs could effectively improve the compressive strength of SFRRGC because of the high strength and rigidity of SFs, which increased the failure load for the concrete [69]; (2) the high elastic modulus of SFs and the skeletal structure were formed within the SFRRGC, thereby improving the deformation ability and altering failure modes by inhibiting crack propagation of SFRRGC [72,73,74]; (3) the inclusion of SFs negatively influences the workability of fresh SFRRGC, potentially increasing internal porosity and slightly compromising compressive strength [67]. These factors collectively govern the compressive performance of SF-reinforced SFRRGC.
Concerning the RP incorporation, it is evident that the compressive strength, elastic modulus, and toughness of SFRRGC were reduced, and the peak strain and Poisson’s ratio were improved with the addition of RP. The influence of RP on the mechanism behavior of SFRRGC primarily involved two aspects: (1) RP-induced internal porosity degraded strength but mitigated brittle failure [65]; and (2) the lower elastic modulus of RP enhanced deformation capacity and altered failure modes [75]. These effects collectively characterize the compressive behavior of RP-modified SFRRGC.
Integrating SFs and RP produced synergistic improvements in compressive performance, particularly in peak strain and toughness, transforming SFRRGC from brittle to ductile failure. Compressive strength, Poisson’s ratio, and peak strain also showed moderate enhancements, demonstrating the potential of SFs/RP combinations to optimize SFRRGC properties. However, SFs significantly reduced workability, affecting handling during testing—an aspect requiring further investigation into underlying mechanisms.
5. Constitutive Analysis
5.1. Stress–Strain Curves
The stress–strain curves of all SFRRGC mixtures are plotted in Figure 11, and the curves can be divided into three phases: elastic ascending phase (from beginning to 40% of peak stress), inelastic ascending phase (from 40% to 100% of peak stress), and post-peak descending phase (from peak stress to failure). Clearly, the addition of SFs and RP significantly altered curve morphology. Increasing RP reduced the slope of the ascending phase, lowered maximum load, and increased peak strain—effects attributed to RP’s low elastic modulus and air entrapment, which promote crack propagation and deformation. At peak load, RP-containing specimens showed increased deformation as microcracks widened gradually. Increasing SF content (0.5–1.5%) enhanced the slope of the ascending phase and smoothed the descending phase while increasing peak strain, due to improved strain capacity from fiber reinforcement. SFs bridged cracks and filled voids, enhancing compressive strength and delaying failure. Combined SF and RP addition produced a synergistic effect, significantly improving deformation and ductility—consistent with previous findings. A constitutive model to predict the stress–strain behavior of SFs/RP-modified SFRRGC, based on these results, will be presented in subsequent sections.
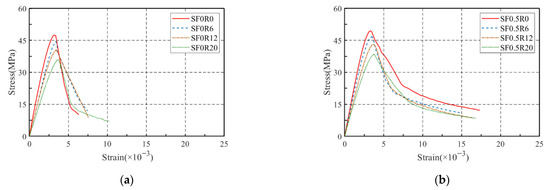
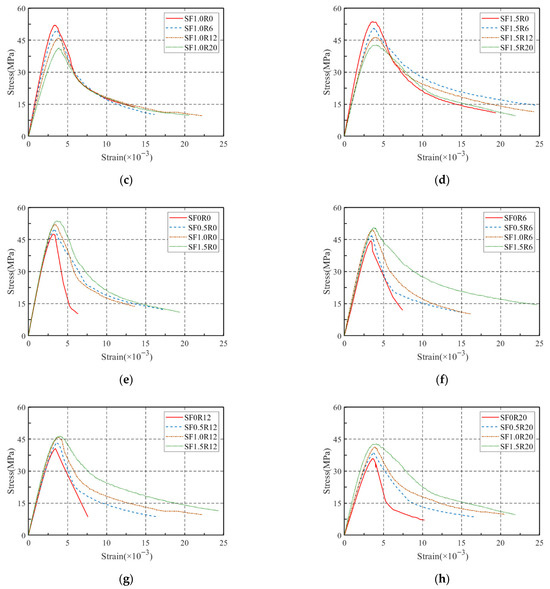
Figure 11.
Stress–strain curves: (a) SF0Ry; (b) SF0.5Ry; (c) SF1.0Ry; (d) SF1.5Ry; (e) SFxR0; (f) SFxR6; (g) SFxR12; and (h) SFxR20.
5.2. Constitutive Model
Currently, three primary empirical models are used to describe the stress–strain relationship of concrete: the polynomial model, the improper rational fraction model, and the proper rational fraction model. In this study, the effectiveness of applying a geopolymer concrete-based stress–strain relationship model—introduced by Ouyang et al. [76]—is evaluated. The proposed model has been modified based on the framework established in previous research [77], and its formulation is presented in Equations (2) and (3).
where fc denotes the compressive strength, εc refers to the strain at the maximum stress, and a and b are parameters that influence the result. Equations (2) and (3) illustrate the ascending phase prior to peak stress and the descending phase following the peak stress, respectively [76]. The controlling parameters a and b were determined via curve fitting. All R2 values exceeded 0.948, indicating that the constitutive model effectively predicts the stress–strain curve of SFRRGC.
Second, the incorporation of SFs and RP significantly affected the compressive behavior of SFRRGC; the coefficients (IS and IR) were determined via regression analysis, which was calculated using Equations (4) and (5), where x and y were the contents of SFs and RP, respectively.
Finally, using the following polynomial formula, the compressive strength (fc), strain at peak stress (εc), and controlling parameter a, and b of SFRRGC were correlated with IS and IR.
where Ri (i = 1, 2, 3, 4) denotes the compressive strength (fc), the strain at peak stress (εc), and the parameters a and b, respectively. The coefficients αij (i = 1, 2, 3, 4; j = 1, 2, …, 10) were determined through regression analysis for each indicator, with the results displayed in Table 4. It is important to highlight that, based on the experimental data obtained with SFs and RP, a distinct set of coefficients αij was derived from the regression analysis.

Table 4.
Coefficients in the constitutive model.
A comparative analysis of the proposed constitutive model and the experimental stress–strain curves are illustrated in Figure 12. From this analysis, it is evident that the theoretical curves align well with the experimental results, suggesting that the proposed constitutive model effectively predicts the stress–strain behavior of SFRRGC. This alignment (or the observed complexity in behavior) arises from the interplay between SFs and RP in regulating the compressive properties of geopolymer concrete. In this research, all Ri values (corresponding to SF and RP combinations) were treated as variables and fitted concurrently. While extensive experimental investigations are still necessary to thoroughly explore the failure mechanisms and optimize the constitutive model of SFRRGC, the findings of this study indicate that Equations (4) and (5) can reliably predict the stress–strain characteristics of the composite. Furthermore, the proposed model is capable of forecasting the stress–strain curves of SFRRGC with different SF and RP mixture proportions.
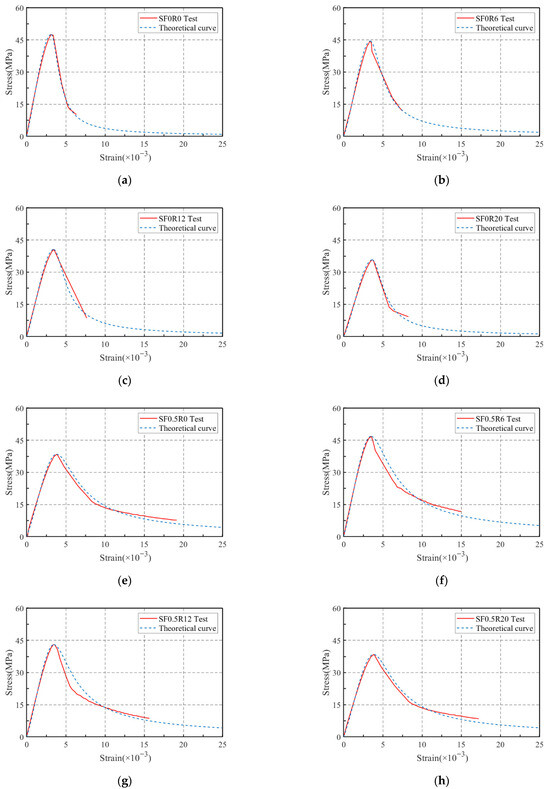
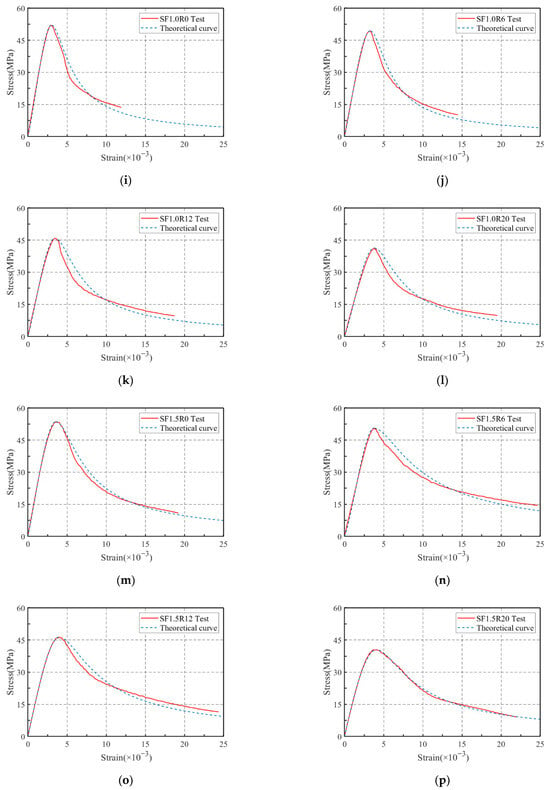
Figure 12.
Constitutive model: (a–d) SF0R0, SF0R6, SF0R12, and SF0R20; (e–h) SF0.5R0, SF0.5R6, SF0.5R12, and SF0.5R20; (i–l) SF1.0R0, SF1.0R6, SF1.0R12, and SF1.0R20; and (m–p) SF1.5R0, SF1.5R6, SF1.5R12, and SF1.5R20.
6. Conclusions
This study investigated the workability and mechanical properties of rubber powder geopolymer concrete, reinforced with steel fibers (SFRRGC). The concrete mixture incorporated rubber powder (RP) from waste tires as a partial sand replacement (0%, 6%, 12%, and 20% by volume) and steel fibers (SFs) as reinforcement (0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, and 1.5% by volume). The experimental findings lead to the following conclusions:
The workability of SFRRGC decreased with increasing RP and SF replacement. For specimens with SFs and RP, the minimum slump value was 21 mm for SF1.5R20, representing an 84.22% reduction compared to the reference mixture (SF0R0). As the RP content increased, more surface microcracking occurred in the specimens, and the deformation and structural integrity were maintained by the addition of SFs due to their bridging effect.
The compressive strength of SFRRGC at 28 days decreased by 24.98% for SF0R20; however, this reduction was compensated by reinforcing with SFs. Specifically, SF1.0R6 exhibited a comparable strength (46.87 MPa) to SF0R0 (47.83 MPa). Although the elastic modulus and compressive toughness decreased with increasing RP content, the peak strain increased (maximum 4.04 × 10−3) in SF1.5R20. The compressive toughness was 118.40 J for SF0.5R20, which was improved by SF reinforcement. The influence on Poisson’s ratio was negligible with increasing RP or SF content. Moreover, a constitutive model for SFRRGC was proposed, and the theoretical predictions were aligned well with the experimental results. The proposed model could reliably predict the stress–strain curves of geopolymer concrete with other SF and RP mixture proportions.
Future research will comprehensively investigate the dynamic behavior and durability performance of SFRRGC, which is the subject of ongoing work and will be presented in a future publication.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W. and F.L.; data curation, X.W., L.L. (Lei Luo), and B.Z.; formal analysis, X.W.; funding acquisition, F.L., L.L. (Lijuan Li), and X.W.; investigation, X.W.; methodology, X.W. and L.L. (Lei Luo); resources, F.L. and L.L. (Lijuan Li); project administration, F.L. and L.L. (Lijuan Li); software X.W.; supervision, F.L.; writing—original draft preparation, X.W.; writing—review and editing, X.W., L.L. (Lei Luo), and B.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12072080 and 12032009) and the Applied Research Foundation of Huangshan University, (Grant No. hxkt2024260 and hxkt2025138).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank all technical personnel from the Structural Laboratory of Guangdong University of Technology for their assistance during the experiment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zia, A.; Zhang, P.; Holly, I. Long-Term Performance of Concrete Reinforced with Scrap Tire Steel Fibers in Hybrid and Non-Hybrid Forms: Experimental Behavior and Practical Applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 134011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, F.; Pegoretti, A. End-of-Life Options of Tyres. A Review. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2022, 5, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerle, V.; Ustimenko, A. Plasma Processing of Rubber Powder from End-of-Life Tires: Numerical Analysis and Experiment. Processes 2024, 12, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, M.; Meng, X.; Liu, A.; Duo, L. Waste Rubber—Black Pollution Reframed as a Global Issue: Ecological Challenges and Sustainability Initiatives. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 356, 124291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P. Pyrolysis of Waste Tyres: A Review. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1714–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, K.; Subhani, S.; Bahurudeen, A. Cleaner Production of Concrete by Using Industrial By-Products as Fine Aggregate: A Sustainable Solution to Excessive River Sand Mining. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 42, 102415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashish, D. Concrete Made with Waste Marble Powder and Supplementary Cementitious Material for Sustainable Development. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El, K.; Garcia, R.; Mihai, P.; Budescu, M.; Taranu, N.; Toma, I.; Guadagnini, M.; Escolano-Margarit, D.; Entuc, I.S.; Oprisan, G.; et al. Behaviour of Short Columns Made with Conventional or FRP-Confined Rubberised Concrete: An Experimental and Numerical Investigation. Eng. Struct. 2024, 307, 117885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz-Aja, J.; Carrascal, I.; Polanco, J.; Thomas, C. Effect of Temperature on Fatigue Behaviour of Self-Compacting Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 125, 104309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrar, Y.; Abdulrahman, P.; Sherwani, A.; Younis, K.; Mohammed, A.S. Sustainable Innovation in Self-Compacted Concrete: Integrating by-Products and Waste Rubber for Green Construction Practices. Structures 2024, 62, 106234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, A.; Mamun, M.; Alyousef, R.; Amran, Y.; Aslani, F.; Alabduljabbar, H. Properties and Utilizations of Waste Tire Rubber in Concrete: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 711–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Islam, M.; Li, J.; Roychand, R.; Saberian, M.; Chen, F. A Comprehensive Review on the Application of Renewable Waste Tire Rubbers and Fibers in Sustainable Concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 133998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Talukdar, S. Mechanical and Bond Behaviour of High Volume Ultrafine-Slag Blended Fly Ash Based Alkali Activated Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 383, 131368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhi, X.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Wei, L.; Liu, Z. Damage Characteristics and Constitutive Model of Phosphogypsum/Fly Ash/Slag Recycled Aggregate Concrete under Uniaxial Compression. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 138, 104980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J. Effect of Accelerated Carbonation of Fully Recycled Aggregates on Fracture Behaviour of Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 148, 105442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, C.; Shehata, B.; Derogar, S.; Ball, R. Towards the Development of Sustainable Concrete Incorporating Waste Tyre Rubbers: A Long-Term Study of Physical, Mechanical & Durability Properties and Environmental Impact. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaidi, S.; Dinkha, Y.; Haido, J.; Ali, M.; Tayeh, B. Engineering Properties of Sustainable Green Concrete Incorporating Eco-Friendly Aggregate of Crumb Rubber: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 324, 129251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssf, O.; Swilam, A.; Tahwia, A. Performance of Crumb Rubber Concrete Made with High Contents of Heat Pre-Treated Rubber and Magnetized Water. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 2160–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, N.; Medina, D.; Hernández-Olivares, F.; Navacerrada, M. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Concrete Incorporating Rubber and Fibres from Tyre Recycling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, R.; Wang, J.; Guo, S.; Dai, Q.; Han, S. Evaluation of Laboratory Performance of Self-Consolidating Concrete with Recycled Tire Rubber. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.; Sulong, N.; Ayough, P.; Tafsirojjaman, T.; Fawzia, S. Flexural Behavior of Circular Rubberized Concrete-Filled Double-Skin Steel Tubular Beams: Experiments. Eng. Struct. 2024, 306, 117816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.; Silvestre, N.; de Brito, J.; Júlio, E. Computational Modelling of the Cyclic Behaviour of Short Rubberized Concrete-Filled Steel Tubes. Eng. Struct. 2021, 248, 113188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunarathna, S.; Ngo, T.; Linforth, S.; Kashani, A.; Liu, X.; Lu, G.; Ruan, D. Evaluation of the Effect of Recycled Rubber Aggregate Size on Concrete for Sustainable Applications of Rubberised Concrete in Impact Resistant Structures: Experimental and Numerical Study. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 133648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Dong, B.; Ma, H. Quantitative Evaluation of Steel Corrosion Induced Deterioration in Rubber Concrete by Integrating Ultrasonic Testing, Machine Learning and Mesoscale Simulation. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 128, 104426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindasiriphan, P.; Yokota, H.; Kawabata, Y.; Pimpakan, P. Combined Effect of Rice Husk Ash and Superabsorbent Polymer on Self-Healing Capability of Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 338, 127588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Abdollahnejad, Z.; Yliniemi, J.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. One-Part Alkali-Activated Materials: A Review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 103, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Romer, M.; Tschudin, M.; Bolio, H. Sustainable Cement Production—Present and Future. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhawat, M.; Ashour, A.; Yildirim, G.; Aldemir, A.; Sahmaran, M. Properties of Geopolymers Sourced from Construction and Demolition Waste: A Review. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 50, 104104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, H.; Hamcumpai, K.; Nuaklong, P.; Jongvivatsakul, P.; Likitlersuang, S.; Pothisiri, T.; Chintanapakdee, C.; Wijeyewickrema, A. Enhancing Fire Resistance in Geopolymer Concrete Containing Crumb Rubber with Graphene Nanoplatelets. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 426, 136115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, S.; Sadowski, Ł.; Shree, N. Geopolymer and Alkali-Activated Permeable Concrete Pavements: Bibliometrics and Systematic Current State of the Art Review, Applications, and Perspectives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, H.; Tuyan, M.; Nehdi, M. Alkali-Activated and Geopolymer Materials Developed Using Innovative Manufacturing Techniques: A Critical Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 303, 124483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeh, B.; Zeyad, A.; Agwa, I.; Amin, M. Effect of Elevated Temperatures on Mechanical Properties of Lightweight Geopolymer Concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, P.; Chen, W.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; Xiang, X.; Wang, G.; Wu, J. Effects of Red Mud, Desert Sand, and Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag on the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 468, 140471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Elsakhawy, Y.; Abu el-hassan, K.; Abdelsalam, B.A. Behavior Evaluation of Sustainable High Strength Geopolymer Concrete Based on Fly Ash, Metakaolin, and Slag. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradikhou, A.; Safehian, M.; Golafshani, E. High-Strength Geopolymer Concrete Based on Coal Washing Waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 362, 129675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liang, X.; Granja, J.; Azenha, M.; Ye, G. Internal Curing of Alkali-Activated Slag-Fly Ash Paste with Superabsorbent Polymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmonem, A.; El-Feky, M.; Nasr, E.; Kohail, M. Performance of High Strength Concrete Containing Recycled Rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 116660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakara, E.; Nacar, S.; Sevim, O.; Korkmaz, S.; Demir, I. Determination of Compressive Strength of Perlite-Containing Slag-Based Geopolymers and Its Prediction Using Artificial Neural Network and Regression-Based Methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 359, 129518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehdezi, P.; Erdem, S.; Blankson, M. Physico-Mechanical, Microstructural and Dynamic Properties of Newly Developed Artificial Fly Ash Based Lightweight Aggregate—Rubber Concrete Composite. Compos. Part B 2015, 79, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandoman, M.; Kokabi, M. Sound Barrier Properties of Sustainable Waste Rubber/Geopolymer Concretes. Iran. Polym. J. 2015, 24, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Abolmaali, A.; Kim, Y.; Ghahremannejad, M. Compressive Strength of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete with Crumb Rubber Partially Replacing Sand. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 118, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsa, A.; Sata, V.; Nematollahi, B.; Sanjayan, J.; Chindaprasirt, P. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Lightweight Geopolymer Mortar Incorporating Crumb Rubber. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.; El-Feky, M.; Kohail, M.; Nasr, E.-S. Performance of Geopolymer Concrete Containing Recycled Rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 207, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrak, H.; Gümüş, M.; Yakut, R.; Erkmen, J. A Comprehensive Experimental Investigation on Tire Char Replacement in Geopolymer Concrete: Mechanical and Fracture Features. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 164, 106286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tu, G.; Lan, C.; Liu, F. Mechanical Characterization of Waste-Rubber-Modified Recycled-Aggregate Concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 124, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, S.; Kuang, Y.; Zou, Q.; Wang, L.; Fu, B. Rubber Concrete Reinforced with Macro Fibers Recycled from Waste GFRP Composites: Mechanical Properties and Environmental Impact Analysis. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematzadeh, M.; Hosseini, S.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. The Combined Effect of Crumb Rubber Aggregates and Steel Fibers on Shear Behavior of GFRP Bar-Reinforced High-Strength Concrete Beams. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 102981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Deng, L.; Feng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B. Experimental Investigation on Monotonic and Cyclic Pullout Performance of Expansion Anchors in High-Performance Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (HPSFRC) with Different Fiber Types. Structures 2025, 76, 108992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.; Woo, J.; Yun, H.; Kim, S.; Park, W.; Choi, W. Influence of Concrete Strength and Fiber Properties on Residual Flexural Strength of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 489, 142366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Xu, Z. 3D Mesoscale Model of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete Based on Equivalent Failure of Steel Fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 450, 138579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascardi, A.; Verre, S.; Ombres, L.; Aiello, M.A. Carbon Fabric Reinforced Cementitious Mortar Confinement of Concrete Cylinders: The Matrix Effect for Multi-Ply Wrapping. Compos. Struct. 2024, 332, 117919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, T.; Li, H.; Dong, T.; Li, Z.; Guo, X. Study of the Flexural Behavior of Basalt Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Beams with Basalt Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Bars and Steel Bars. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Poon, E.; Chen, K.; Zhang, M. Engineering Properties of Crumb Rubber Alkali-Activated Mortar Reinforced with Recycled Steel Fibres. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dai, Q.; Si, R.; Guo, S. Investigation of Properties and Performances of Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Fiber-Reinforced Rubber Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 193, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hadithi, A.; Noaman, A.; Mosleh, W. Mechanical Properties and Impact Behavior of PET Fiber Reinforced Self-Compacting Concrete (SCC). Compos. Struct. 2019, 224, 111021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.; Bernal, S. Geopolymers and Related Alkali-Activated Materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2014, 44, 299–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C. Strength, Pore Structure and Permeability of Alkali-Activated Slag Mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 1996, 26, 1789–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D5644; Standard Test Method for Rubber Compounding Materials—Determination of Particle Size Distribution of Recycled Vulcanizate Particulate Rubber. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- ASTM C469/C469M; Standard Test Method for Static Modulus of Elasticity and Poisson’s Ratio of Concrete in Compression. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Su, H.; Yang, J.; Ling, T.; Ghataora, G.; Dirar, S. Properties of Concrete Prepared with Waste Tyre Rubber Particles of Uniform and Varying Sizes. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 91, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaif, A.; Albidah, A. Production of Rubberized Concrete Utilizing Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Aggregates and Recycled Tire Steel Fibers. Structures 2024, 68, 107174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yang, C.; Huang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Xu, F. Effects of Hybrid Fibers on Workability, Mechanical, and Time-Dependent Properties of High Strength Fiber-Reinforced Self-Consolidating Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 277, 122325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukontasukkul, P.; Tiamlom, K. Expansion under Water and Drying Shrinkage of Rubberized Concrete Mixed with Crumb Rubber with Different Size. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turki, M.; Bretagne, E.; Rouis, M.; Queneudec, M. Microstructure, Physical and Mechanical Properties of Mortar-Rubber Aggregates Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2715–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaif, A.; Koutas, L.; Bernal, S.; Guadagnini, M.; Pilakoutas, K. Mechanical Performance of Steel Fibre Reinforced Rubberised Concrete for Flexible Concrete Pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, W.; Zhong, H.; Chi, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M. Experimental Study on Dynamic Compressive Behaviour of Recycled Tyre Polymer Fibre Reinforced Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 98, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Pan, X. Mechanical Properties and Mechanisms of Fiber Reinforced Fly Ash–Steel Slag Based Geopolymer Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 179, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Hao, Y.; Hao, H.; Shaikh, F. Mechanical Properties of Ambient Cured High Strength Hybrid Steel and Synthetic Fibers Reinforced Geopolymer Composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 85, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Hassan, A. Shear Behaviour of Large-Scale Rubberized Concrete Beams Reinforced with Steel Fibres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 140, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Tam, V.; Li, W. Uniaxial Compressive Behaviors of Fly Ash/Slag-Based Geopolymeric Concrete with Recycled Aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 104, 103375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhuge, Y.; Gravina, R.; Mills, J. Compressive Stress Strain Behavior of Crumb Rubber Concrete (CRC) and Application in Reinforced CRC Slab. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 166, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrazik, A.; Khayat, K. Effect of Fiber Characteristics on Fresh Properties of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete with Adapted Rheology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 116852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, K.; Bassurucu, M.; Bitkin, R.E. Workability, Strength and Flexural Toughness Properties of Hybrid Steel Fiber Reinforced SCC with High-Volume Fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 266, 120944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Cao, M.; Gao, Q. Workability, Strength and Shrinkage of Fiber Reinforced Expansive Self-Consolidating Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, N.; Talebian, S.; Mehrali, M.; Kuenzel, C.; Cornelis Metselaar, H.; Jumaat, M.Z. Mechanisms of Interfacial Bond in Steel and Polypropylene Fiber Reinforced Geopolymer Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 122, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Wu, Z.; Shan, B.; Chen, Q.; Shi, C. A Critical Review on Compressive Behavior and Empirical Constitutive Models of Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 323, 126572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Standard-GB/T 50081-2019; Standard for Test Methods of Concrete Physical and Mechanical Properties. General Administration of Quality Supervision: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese)
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).