Optimized Plant Configuration Designs for Wind Damage Prevention in Masonry Heritage Buildings: A Case Study of Zhen Guo Tower in Weihui, Henan, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
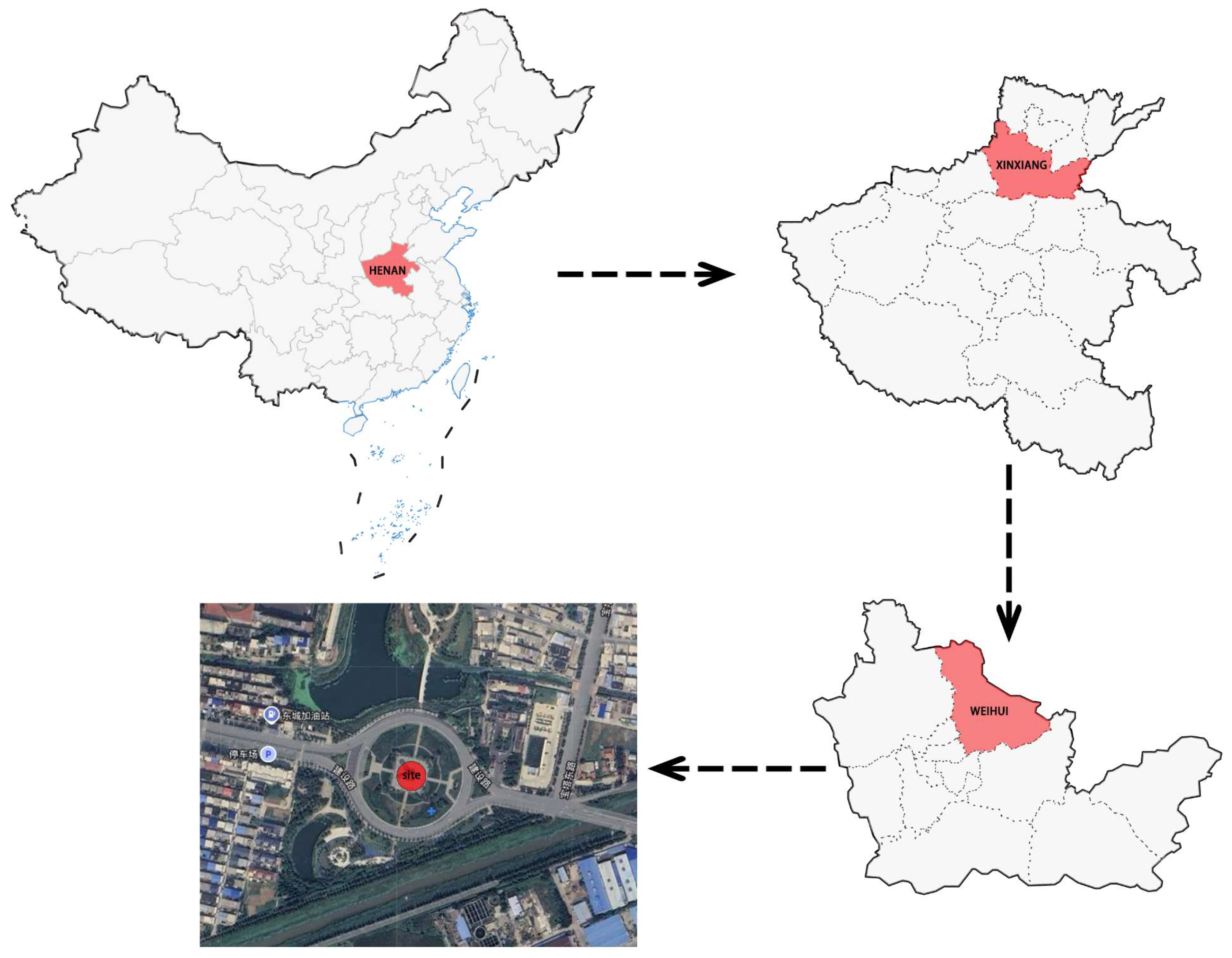
2. Regional Context and Research Subject
2.1. Overview of Zhen Guo Tower
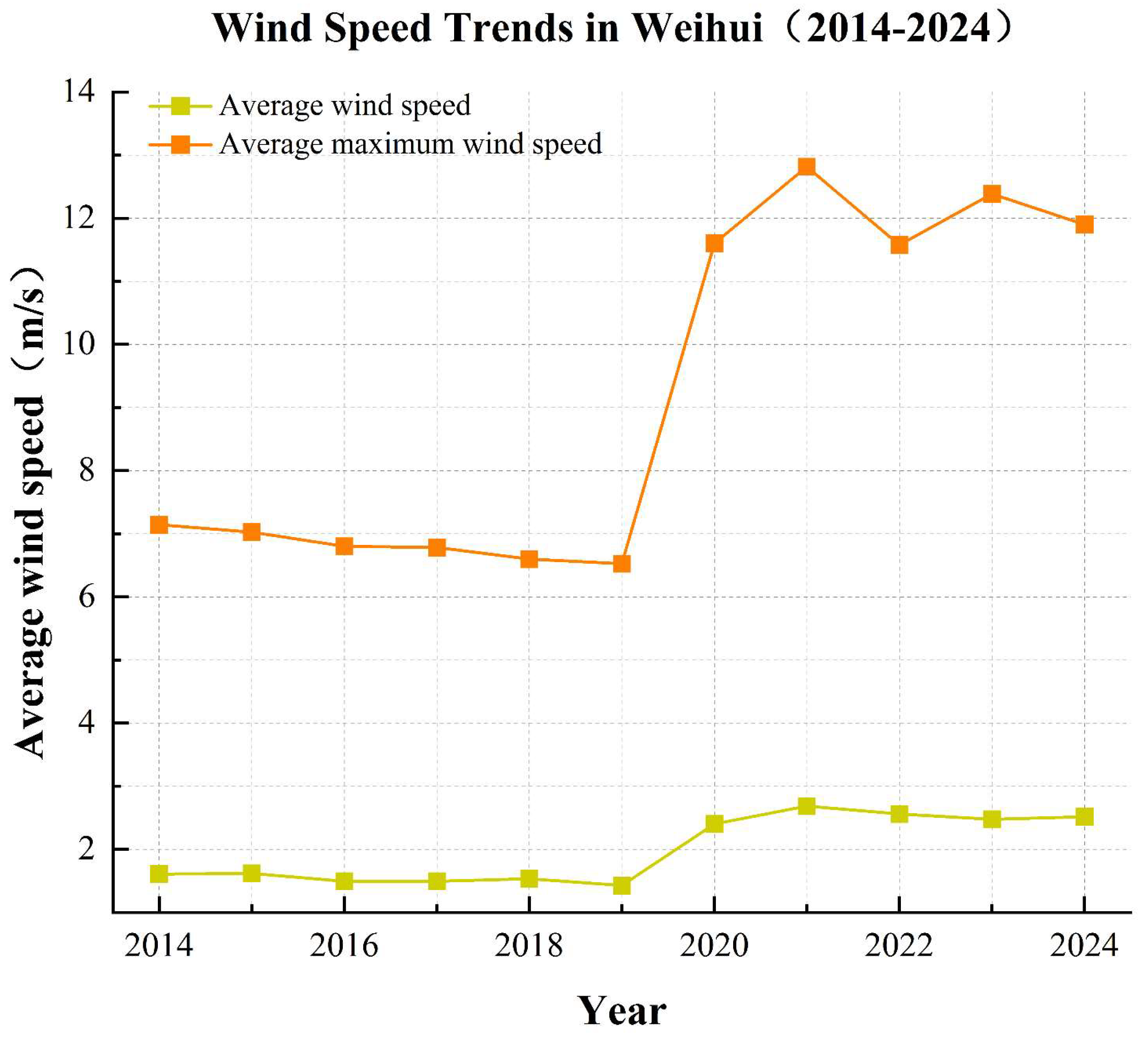
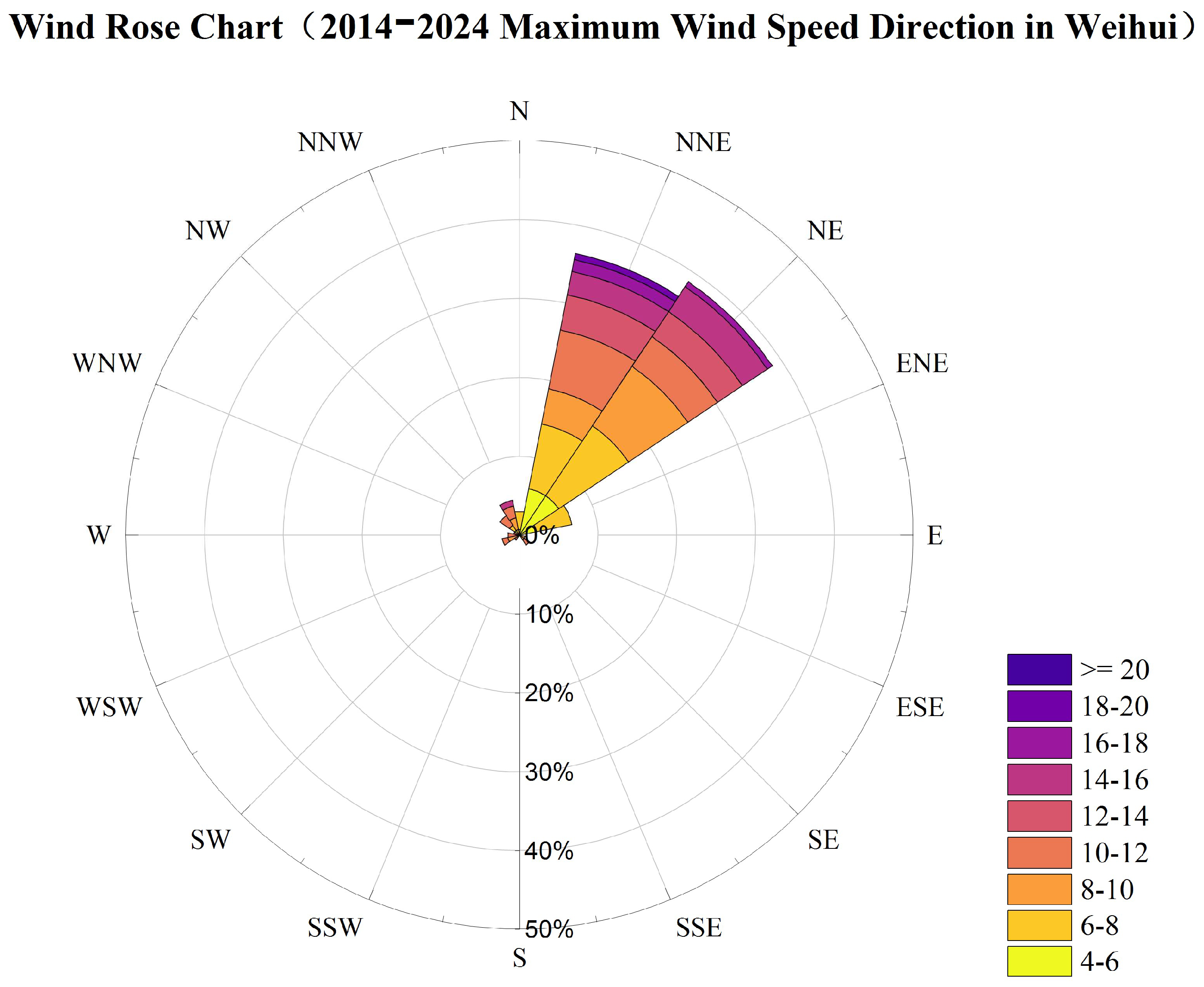
2.2. Wind Environment and Meteorological Data
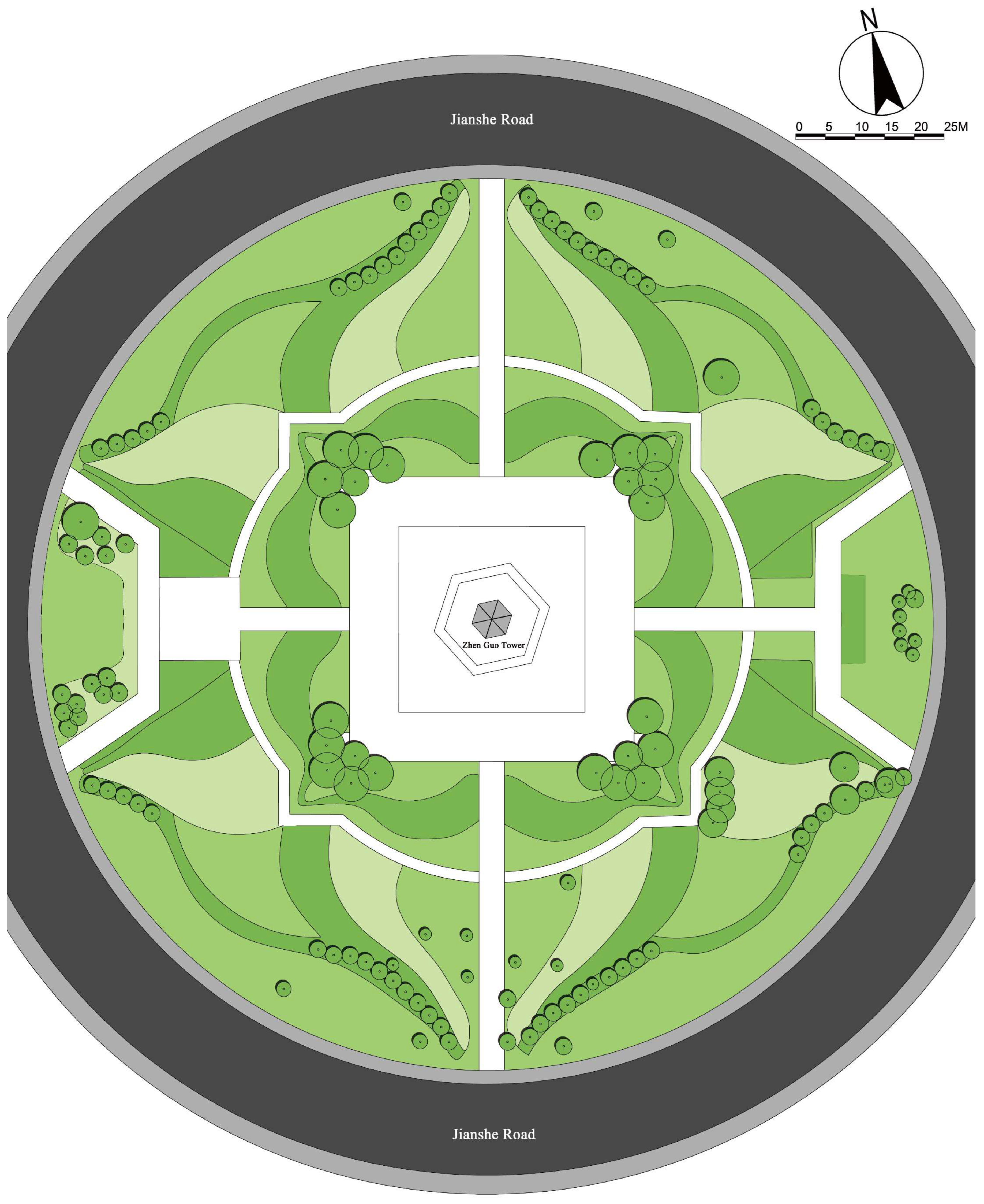
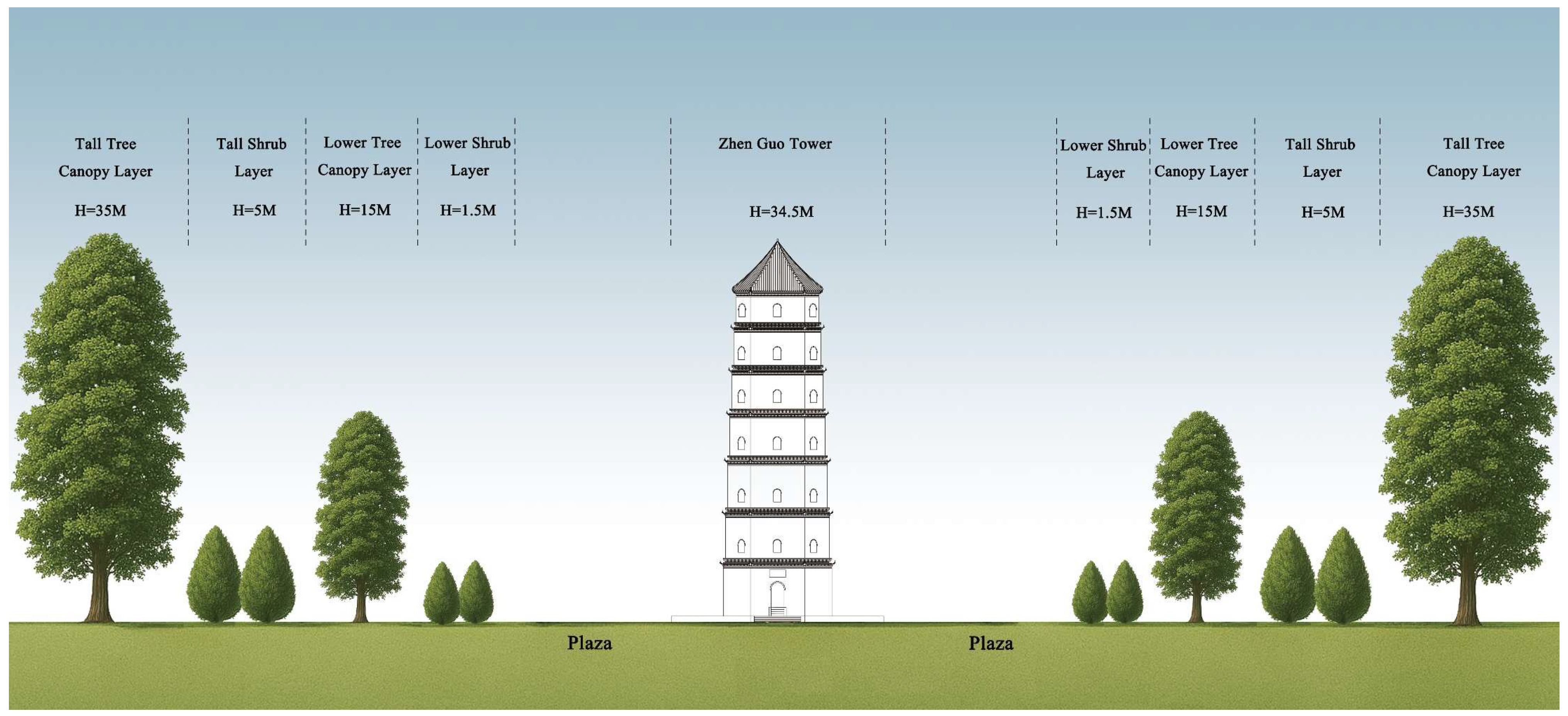
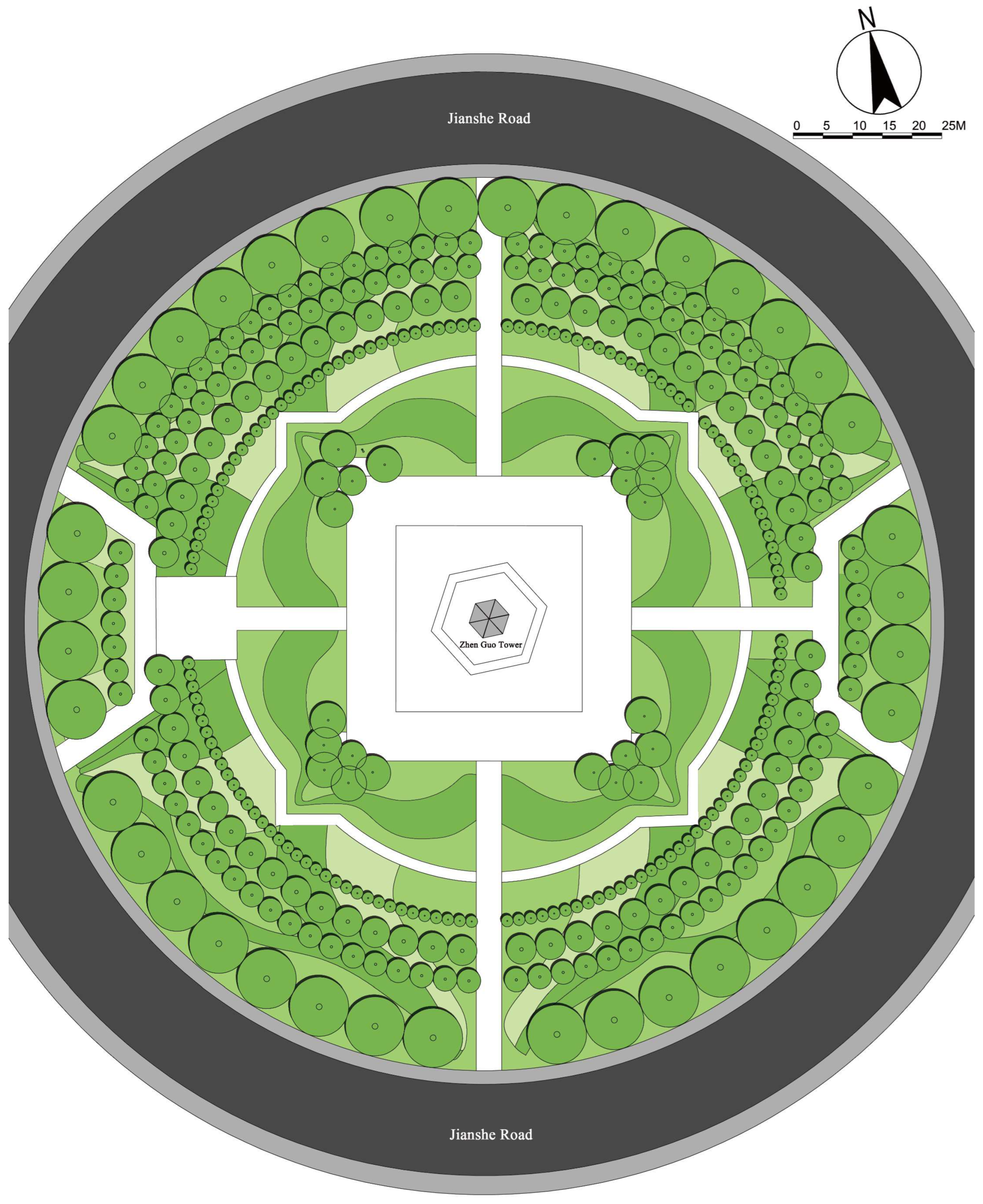
2.3. Existing Vegetation Layout Around Zhen Guo Tower
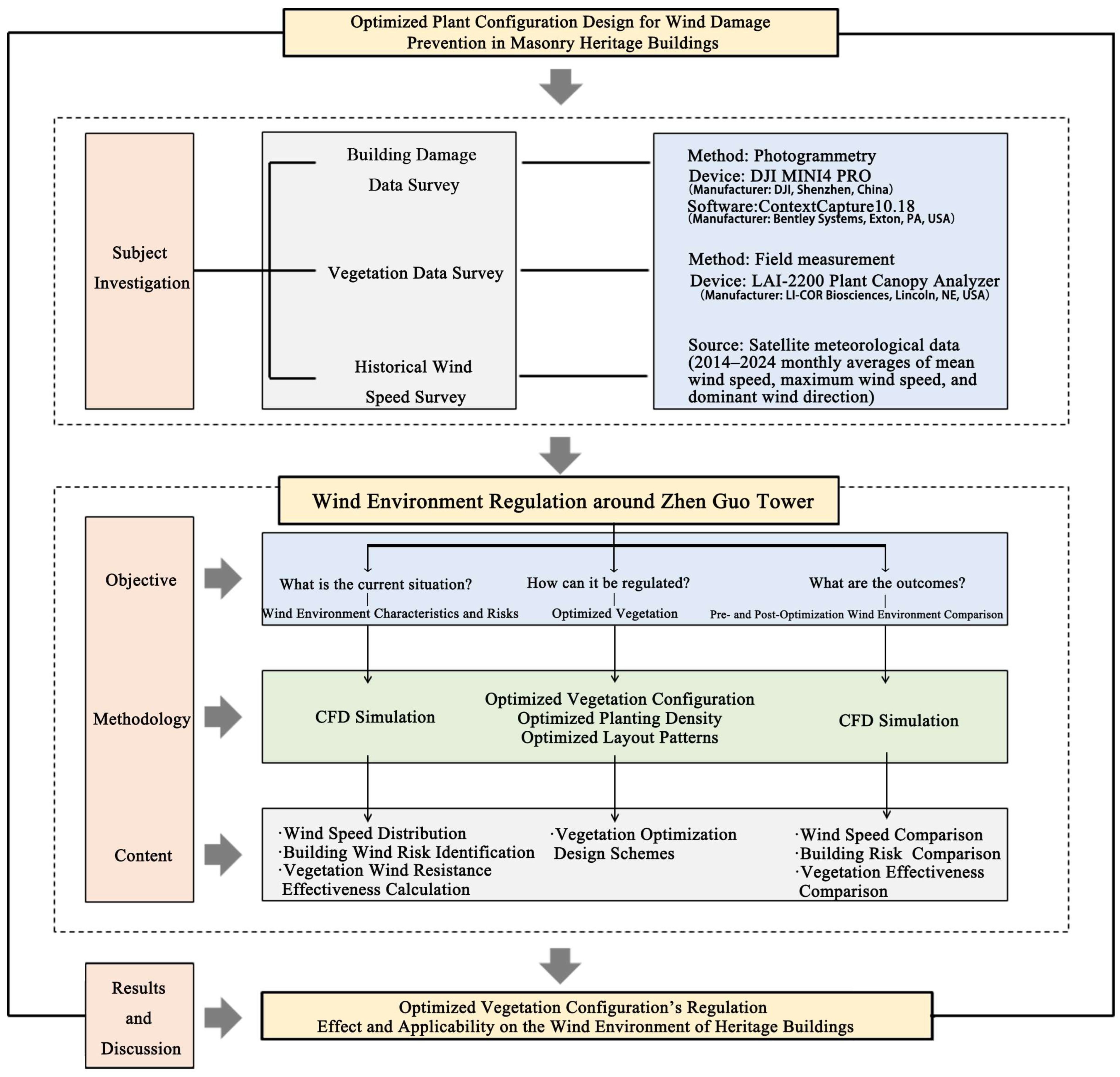
3. Methodology
3.1. Wind Damage Threshold Determination
- Warning wind speed: 10–18 m/s;
- Hazardous wind speed: ≥18 m/s.
3.2. CFD Simulation Method
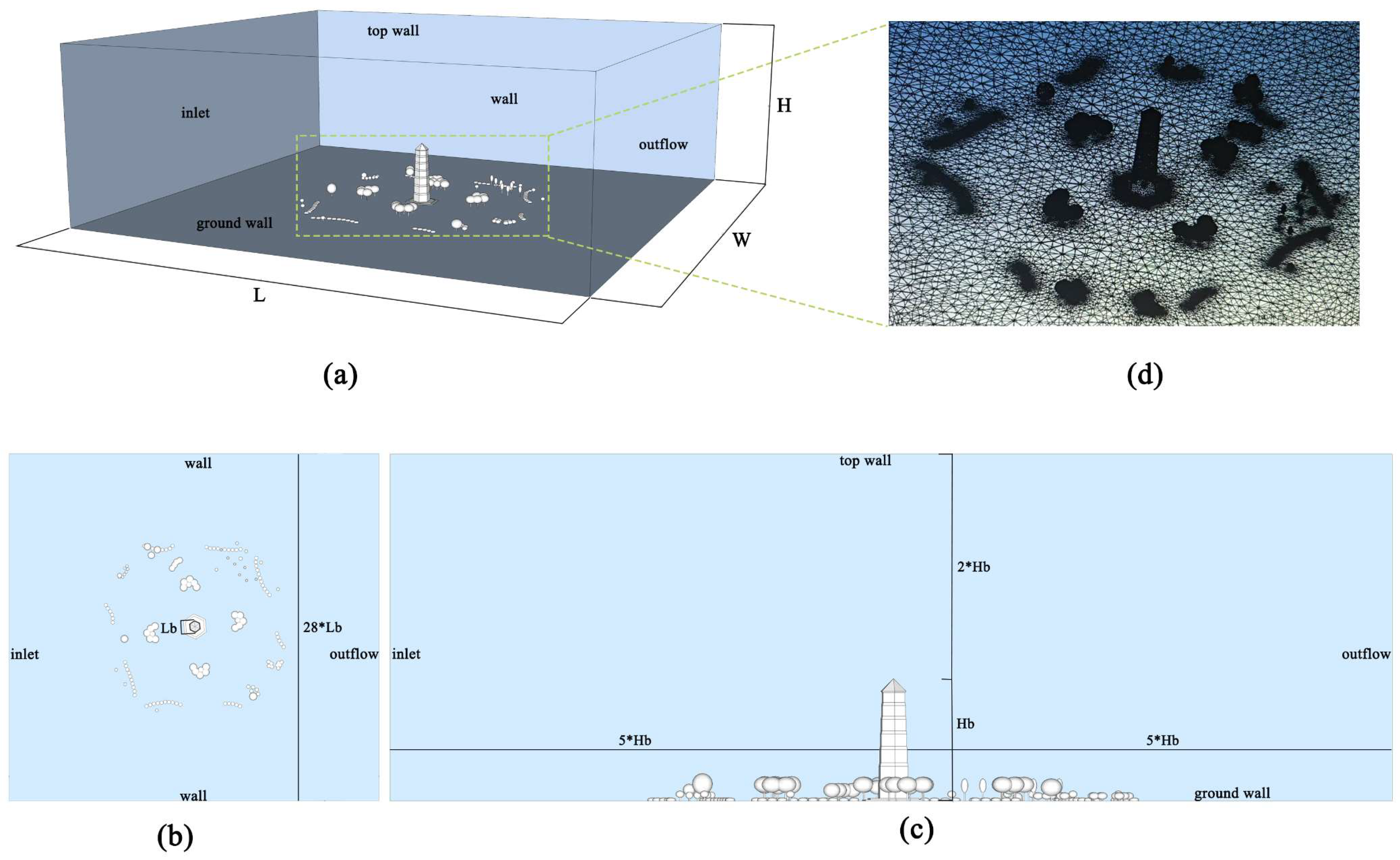
3.2.1. Computational Domain, Boundary Conditions, and Grid Settings
- Inlet and outlet boundaries were set at approximately 5 × Hb (≈170 m) from the tower to allow for a fully developed flow and to minimize wake interference;
- The domain width was set to approximately 28 × Lb (≈270 m);
- The top boundary height was defined as 2 × Hb to ensure upper-level flow development.
3.2.2. Vegetation Modeling Method
- : canopy porosity (dimensionless);
- : extinction coefficient, typically taken as 0.5 for trees and 0.6 for shrubs;
- LAI: leaf area index.
3.3. Wind Protection Efficiency Calculation
- : represents the percentage reduction in wind speed at height hhh (in meters) owing to vegetation;
- : the wind speed at height hhh under the non-vegetated (control) condition (m/s);
- : the wind speed at the same height with vegetation present (m/s).
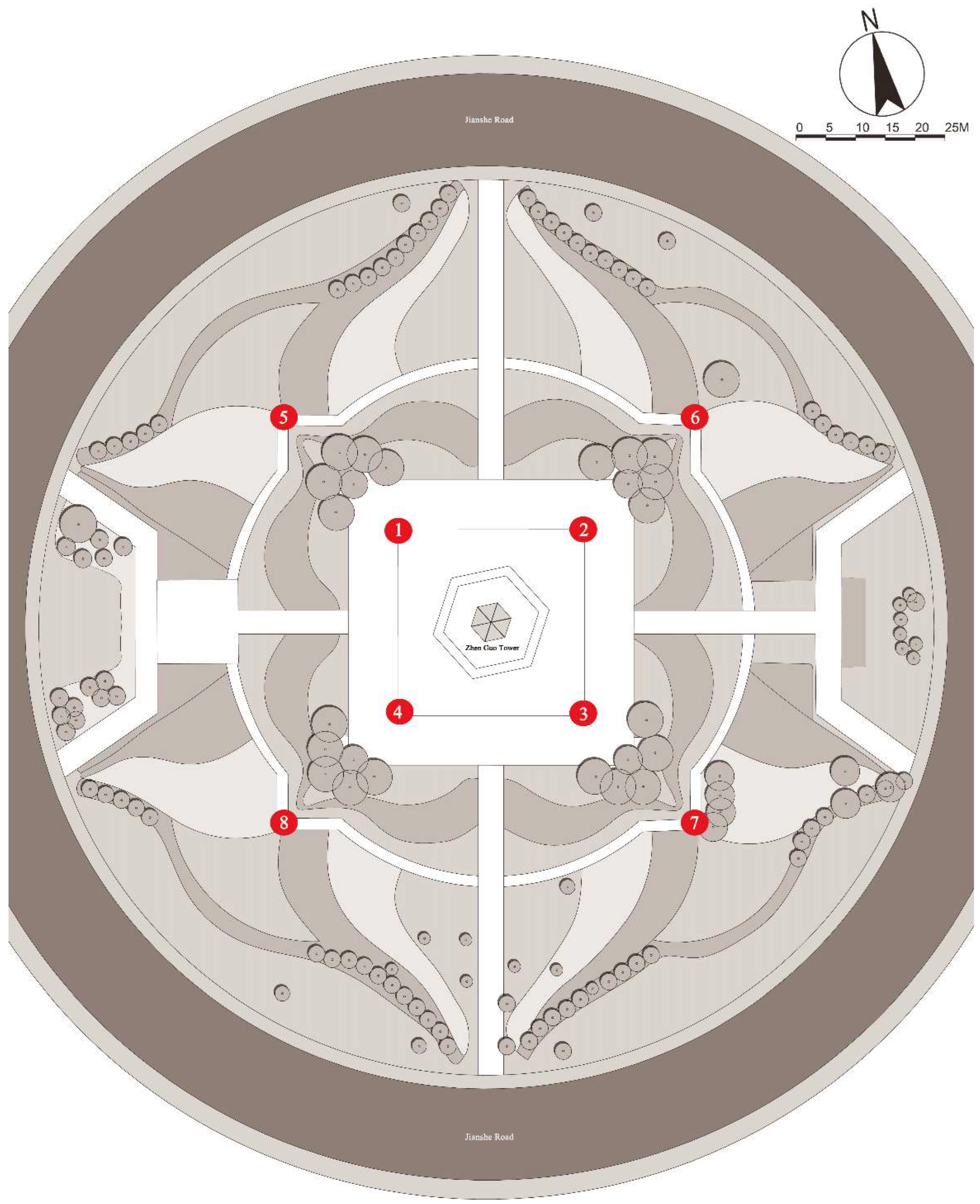
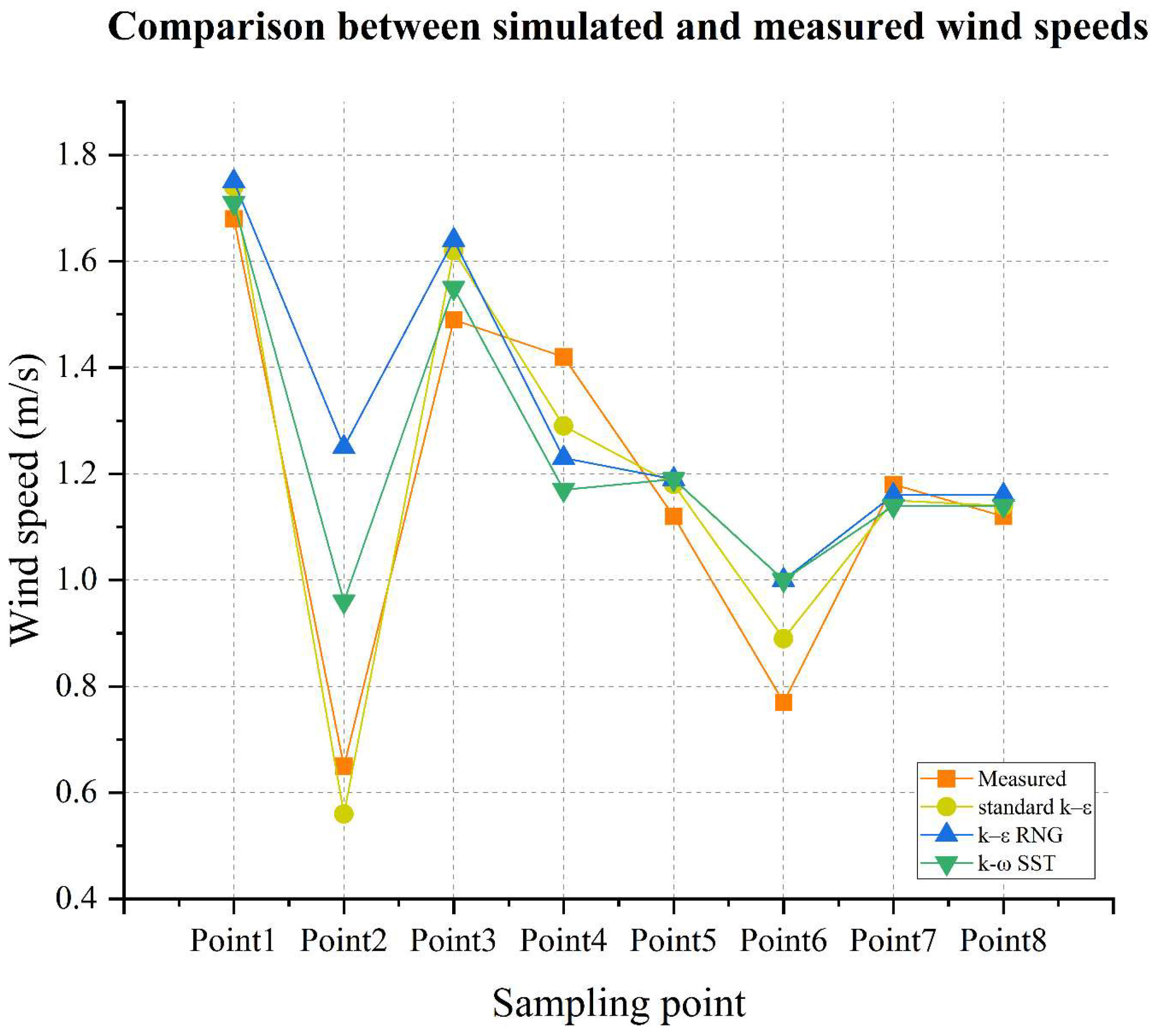
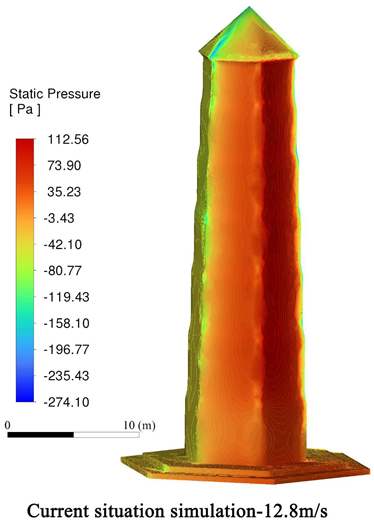
3.4. Model Validation
4. Simulation Results and Analysis
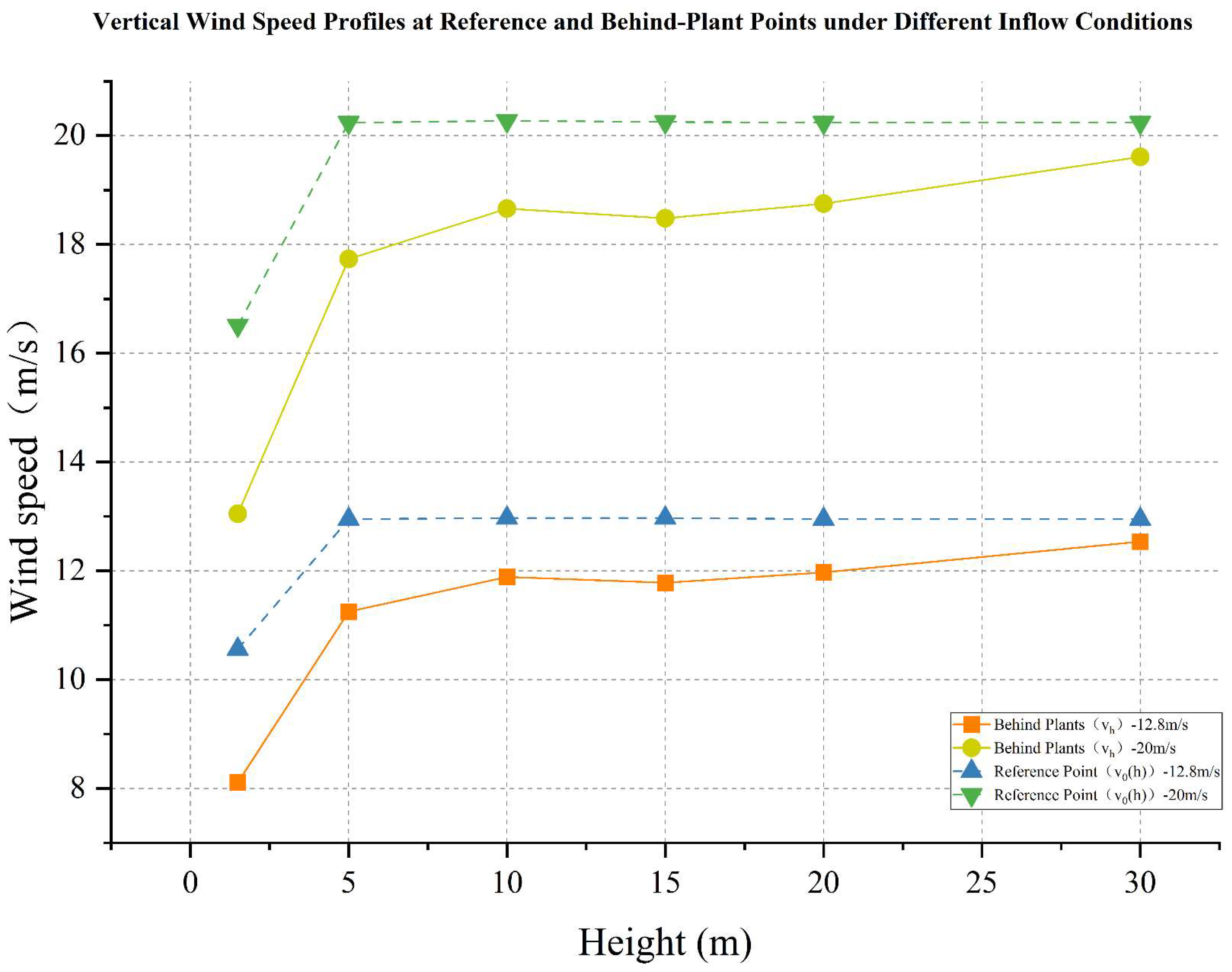
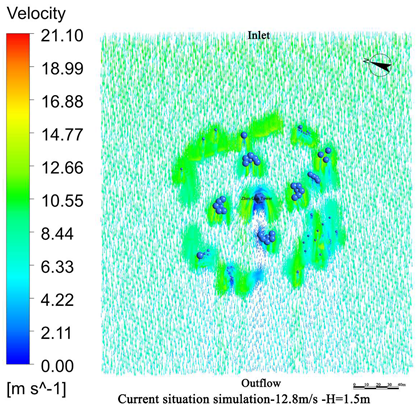
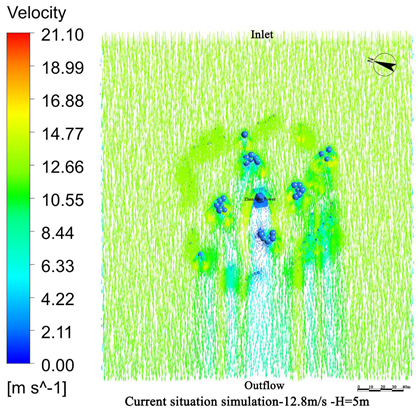
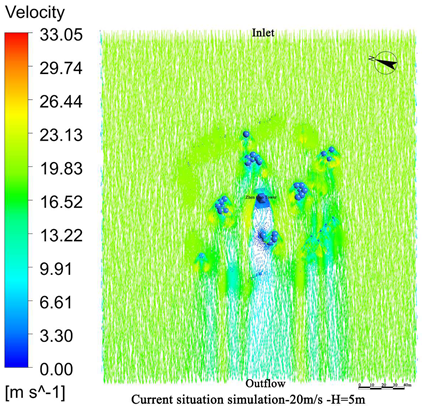
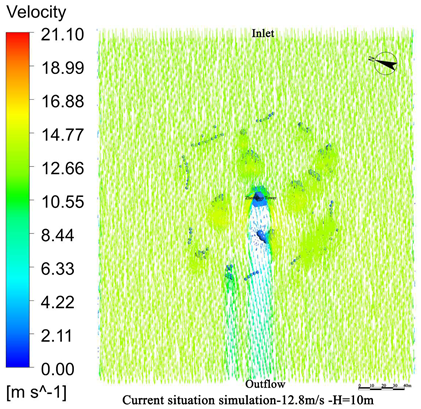
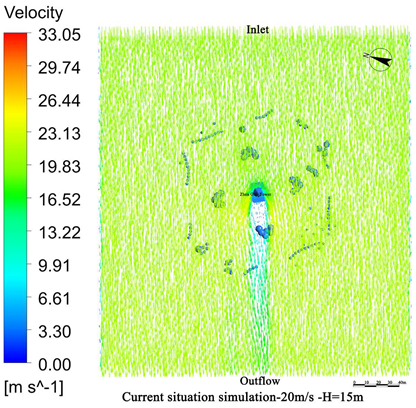
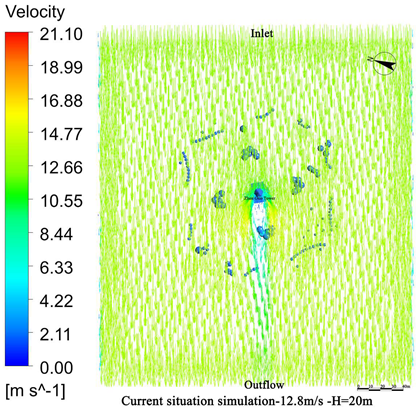
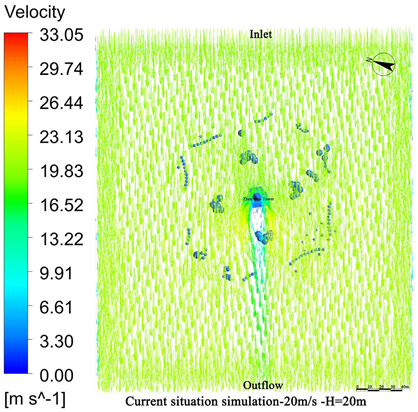
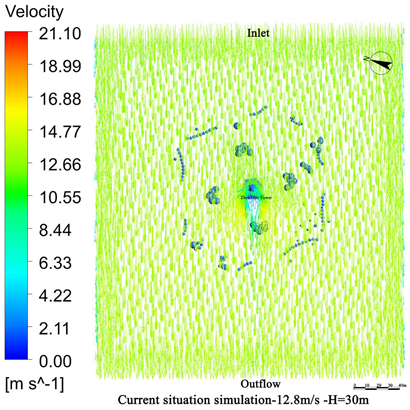
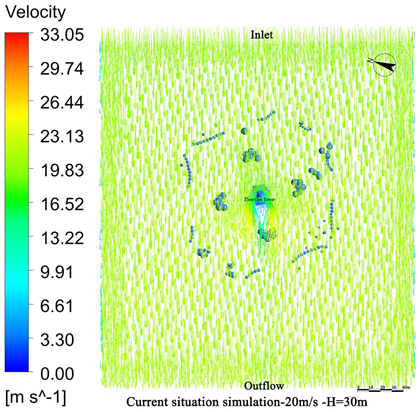
4.1. Wind Field Simulation Under Existing Vegetation Configuration
4.1.1. Wind Field Distribution and Risk Zone Identification
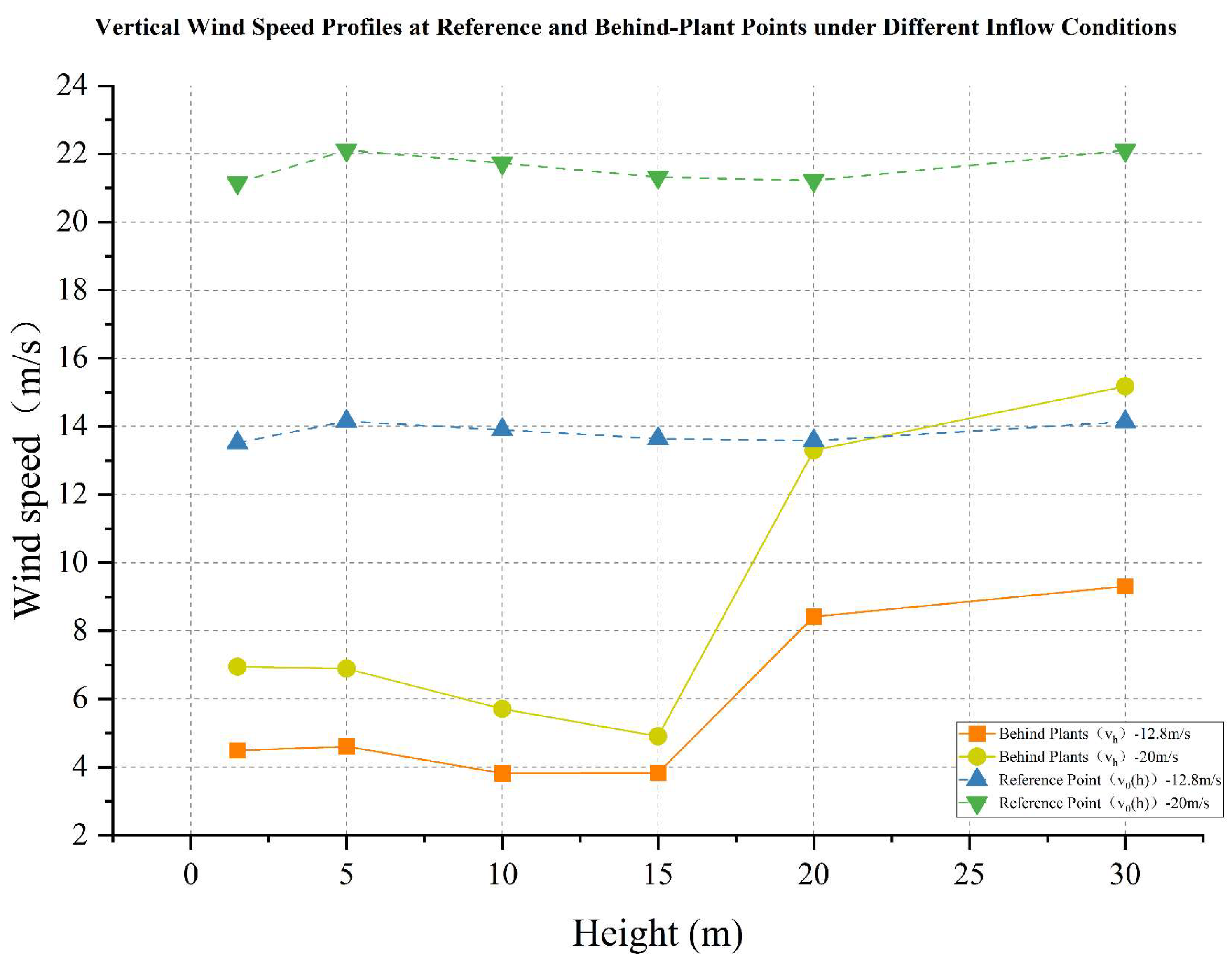
4.1.2. Wind Protection Efficiency of Existing Vegetation
- The average height of the trees planted around Zhen Guo Tower is approximately 6–7 m, while most shrubs are below 1.5 m. Consequently, the vegetation exerts a wind-blocking effect at lower heights (around 1.5 m) but offers little to no attenuation at higher levels, where wind directly impacts the tower surface.
- The tree layout surrounding the tower primarily adopts a “clustered” configuration, while the shrubs, though arranged in “row-wise” patterns, are planted at a relatively low density. The substantial gaps between the plants prevent the formation of an effective windbreak barrier. Consequently, even in the 1.5 m and 5 m height zones, the wind protection effect remains limited.
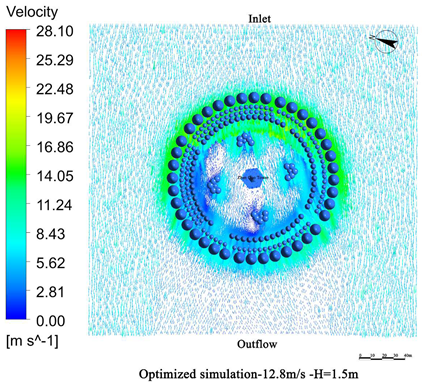
4.2. Optimized Vegetation Configuration Design
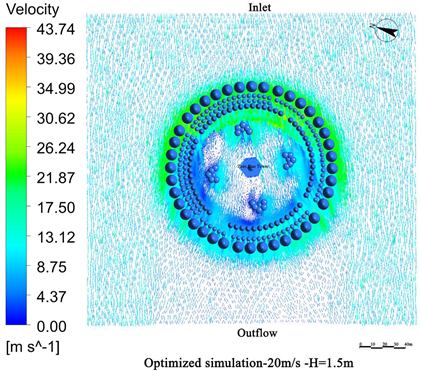
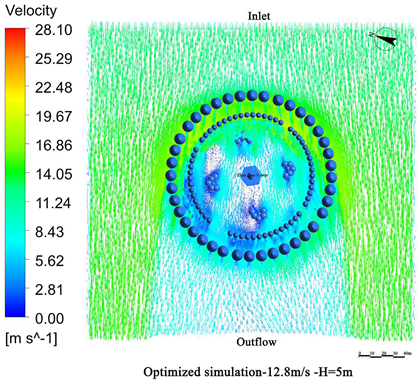
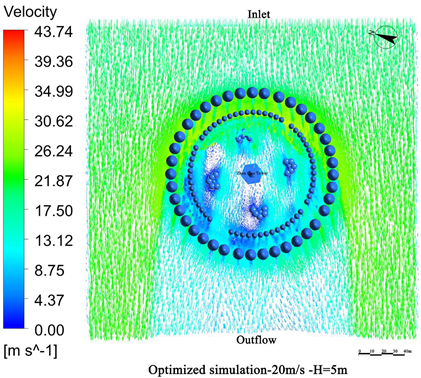
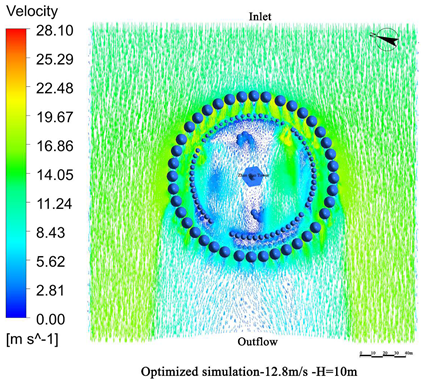
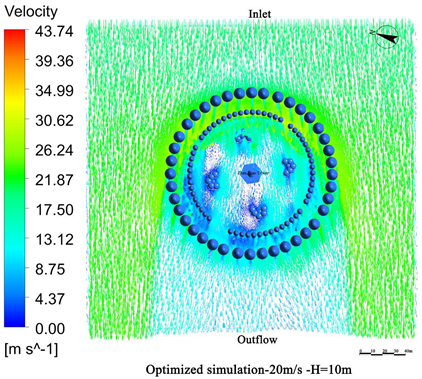
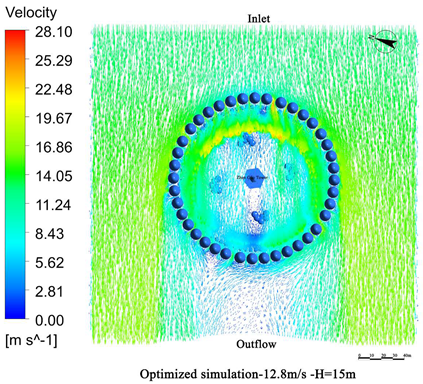
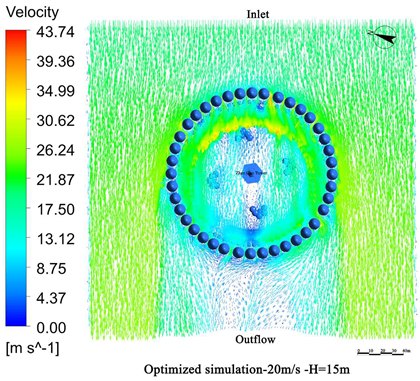
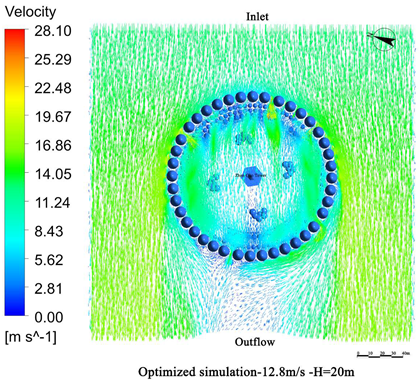
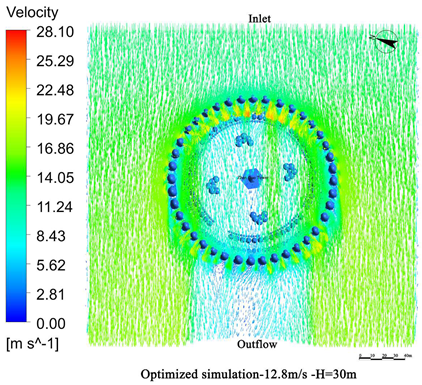
- Vegetation structure adjustment:Tall trees (covering the 3.5 m–15 m height range) and densely planted tall shrubs (covering the 1.5 m–5 m range) are added around the tower. A stratified vegetation structure composed of trees and shrubs is used to create a progressive wind speed attenuation zone, thereby enhancing the overall effectiveness of the windbreak (Figure 13).
- Vegetation density enhancement:The planting density is increased, particularly in areas exposed to high-frequency and high-velocity winds. Densely planted vegetation acts as an effective “green barrier” to obstruct the incoming airflow.
- Vegetation layout adjustment:The existing “clustered” layout, primarily designed for esthetic purposes, is replaced with a “row-wise” layout oriented toward wind protection. A concentric, layered windbreak forest belt is formed to encircle the tower and improve the wind shielding performance (Figure 14).
4.3. Comparative Analysis of Pre- and Post-Optimization Results
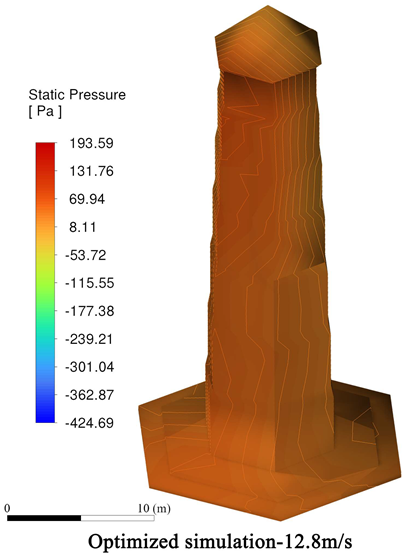
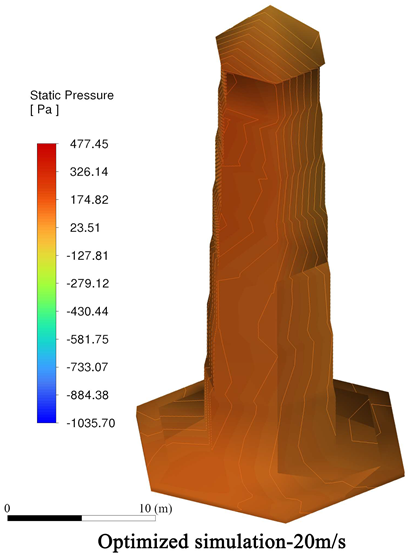
4.3.1. Wind Speed Reduction Before and After Optimization
4.3.2. Comparison of Wind Protection Efficiency Before and After Optimization
- Under elevated wind speed conditions, the risk of wind erosion on the tower façade is notably reduced;
- Under extreme wind scenarios, the likelihood of direct structural damage to the tower is significantly reduced.
5. Discussion
5.1. Limitations of Wind Protection Performance and Potential Adverse Scenarios
- Limitations in vertical wind protectionWhile the optimized vegetation layout shows a considerable wind mitigation capacity at low and mid-height levels, localized wind speed exceedances persist in the upper parts of the tower owing to the height limitations of the vegetation. This indicates that although optimized vegetation can effectively regulate wind at specific elevations, its performance is inherently constrained by the plant height. For tall heritage structures, further design refinements are needed, such as optimizing the height ratio between the vegetation and the building or integrating supplementary wind protection measures for upper-level zones.
- Potential risks under extreme wind conditionsThe current simulation assumes an ideal structural integrity of the vegetation during high-wind events. However, under extreme wind conditions, vegetation itself is susceptible to damage, which could lead to two adverse outcomes:
- First, the loss or destruction of vegetation would reduce the wind protection performance;
- Second, damaged or uprooted plants may collapse onto the heritage structure, causing additional physical harm.
5.2. Comparison with Existing Studies
5.3. The Generalization of the Vegetation-Based Wind Mitigation Approach for Masonry Heritage Buildings
- High-rise buildings (>20 m)Due to the relatively unobstructed airflow at upper elevations, wind mitigation vegetation should be concentrated in the 5–15 m range, using stratified arrangements of trees and shrubs to reduce ground-level wind speeds. For upper zones, green-compatible measures, such as tall-canopy species, reversible climbing plant systems, or facade-integrated greenery, can be considered. If simulation results indicate that these are insufficient, carefully selected supplementary interventions may be explored—provided they adhere to principles of reversibility, minimal intrusion, and heritage compatibility.
- Low-rise buildings (<10 m)For low-rise structures, an effective wind reduction can generally be achieved across the full height using only vegetation, provided that appropriate species selection, layout design, and planting density are applied—making additional interventions unnecessary in most cases.
- Medium-rise or architecturally complex buildings (10–20 m)A hybrid yet vegetation-dominant strategy is recommended, combining a CFD-based diagnosis with layered vegetation configurations. Design adjustments should be flexibly tailored to accommodate the architectural features, site topography, and local wind conditions. Where critical wind zones cannot be effectively mitigated through vegetation alone, auxiliary interventions may be cautiously introduced—strictly adhering to principles of sustainability, reversibility, and minimal impact on heritage integrity.
6. Conclusions
- The optimized vegetation configuration significantly reduces wind speeds, particularly in the lower and mid-height regions of the tower. Under extreme wind conditions, the maximum wind speed reduction reached 13.57 m/s.
- The wind protection efficiency on the windward side was substantially improved after optimization, especially along the vertical profile of the tower, with efficiency increases ranging from 28% to 68%.
- Wind attenuation in the upper regions of the tower remained limited, and the effects of high wind speeds could not be completely eliminated.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cassar, M. Preventive conservation and building maintenance. Mus. Manag. Curatorsh. 1994, 1, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.S.; Ciantelli, C.; Cassar, J.; Hughes, J. Climate change impacts on cultural heritage: A literature review. Wire’s Clim. Change 2021, 12, e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolin, C. Preservation of cultural heritage and resources threatened by climate change. Geosciences 2019, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipekoglu, B.; Boke, H.; Cizer, O. Assessment of material use in relation to climate in historical buildings. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, M. An assessment for the conservation mechanism of masonry architectural heritage based on material deterioration analysis: A case study of the Xuhai Dao Shu screen wall (Xuzhou, China). J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2023, 22, 3403–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q. Study on the Risk Assessment and Prediction of Deterioration of the Bottom Wall of Xi’an Dayan Pagoda. Master’s Thesis, Southeast University, Nanjing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blavier, C.L.S.; Huerto-Cardenas, H.E.; Aste, N.; Del Pero, C.; Leonforte, F.; Della Torre, S. Adaptive measures for preserving heritage buildings in the face of climate change: A review. Build. Environ. 2023, 245, 110832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Meng, J.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, J. Prediction of wind erosion over a heritage site: A case study of Yongling Mausoleum, China. Built Herit. 2019, 3, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegyi, D.; Armuth, M.; Halmos, B.; Marotzy, K. The effect of wind on historical timber pagodas analyzed by plastic limit analysis in the focus of a collapse. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 134, 105852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkal, A.; D’Ayala, D.; Sequeira, L. Assessment of wind-driven rain impact, related surface erosion and surface strength reduction of historic building materials. Build. Environ. 2012, 57, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzima-Nyarko, M.; Ademovic, N.; Pavic, G.; Sipos, T.K. Strengthening techniques for masonry structures of cultural heritage according to recent Croatian provisions. Earthq. Struct. 2018, 15, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artesani, A.; Di Turo, F.; Zucchelli, M.; Traviglia, A. Recent advances in protective coatings for cultural heritage—An overview. Coatings 2020, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.S. Retrofitting of cracked and damaged walls of historical buildings with reinforced concrete materials. Int. J. Eng. Res. Afr. 2020, 51, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakul, Ö. An integrated methodology for the conservation of traditional craftmanship in historic buildings. Int. J. Intang. Herit. 2015, 10, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, M.; Chen, Y.F.; Zhai, Z.; Du, J. Investigating the critical issues in the conservation of heritage building: The case of China. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 51, 104319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, A.J.; Macías-Bernal, J.M.; Chávez, M.J.; Alejandre, F.J.; Silva, A. Impact of maintenance, rehabilitation, and other interventions on functionality of heritage buildings. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2019, 33, 04019011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribera, F.; Nestico, A.; Cucco, P.; Maselli, G. A multicriteria approach to identify the highest and best use for historical buildings. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 41, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Lu, S.; Zhong, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, L. Numerical Analysis of Roof Wind Pressure Distribution in Renovated Historical Buildings: Preventive Protection Measures to Mitigate Typhoon Damage. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, P.; Iranzo, A. Analysis of sand-loaded air flow erosion in heritage sites by computational fluid dynamics: Method and damage prediction. J. Cult. Herit. 2016, 25, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lang, J.; Wang, X. A numerical study of the effect of vegetative windbreak on wind erosion over complex terrain. Forests 2022, 13, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nord, M. Shelter effects of vegetation belts—results of field measurements. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1991, 54, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhen, L.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, H. The effects of different types of vegetation restoration on wind erosion prevention: A case study in Yanchi. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 115001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosevic, D.D.; Bajsanski, I.V.; Stevan, S.M. Influence of changing trees locations on thermal comfort on street parking lot and footways. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 23, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartesaghi-Koc, C.; Osmond, P.; Peters, A. Quantifying the seasonal cooling capacity of ‘green infrastructure types’ (GITs): An approach to assess and mitigate surface urban heat island in Sydney, Australia. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 203, 103893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, A. Nondestructive Tree Planting for Reducing the Wind Loads of a Historical Wooden Pagoda. ASCE 2024, 38, 04024033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICOMOS Climate Change and Cultural Heritage Working Group. The Future of Our Pasts: Engaging Cultural Heritage in Climate Action; International Council on Monuments and Sites: Paris, France, 2019; Available online: https://openarchive.icomos.org/id/eprint/2459/1/CCHWG_final_print.pdf (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Fujita, T.T. Proposed Characterization of Tornadoes and Hurricanes by Area and Intensity; University of Chicago SMRP Research Project: Chicago, IL, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, S.A.; Miller, C.S.; Sills, D.M.L.; Kopp, G.A.; Rhee, D.M.; Lombardo, F.T. Assessment of wind speeds along the damage path of the Alonsa, Manitoba EF4 tornado on 3 August 2018. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2023, 238, 105422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment Canada. Environment and Climate Change Canada: Enhanced Fujita Scale. 2013. Available online: https://ec.gc.ca/meteo-weather/default.asp?lang=En&n=41E875DA-1 (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Mosoarca, M.; Keller, A.I.; Bocan, C. Failure analysis of church towers and roof structures due to high wind velocities. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 100, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocken, B. Computational fluid dynamics for urban physics: Importance, scales, possibilities, limitations and ten tips and tricks towards accurate and reliable simulations. Build. Environ. 2015, 91, 219–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocken, B. LES over RANS in building simulation for outdoor and indoor applications: A foregone conclusion? Build. Simul. 2018, 11, 821–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Mochida, A.; Yoshie, R.; Kataoka, H.; Nozu, T.; Yoshikawa, M.; Shirasawa, T. AIJ guidelines for practical applications of CFD to pedestrian wind environment around buildings. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2008, 96, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocken, B.; Hout, A.V.; Dekker, J.; Weiler, O. CFD Simulation of Wind Flow over Natural Complex Terrain: Case Study with Validation by Field Measurements for Ria de Ferrol, Galicia, Spain. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerod. 2015, 147, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Ishihara, T. Numerical Study of Turbulent Flow Fields around of a Row of Trees and an Isolated Building by Using Modified K–Model and LES Model. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerod. 2018, 177, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, S.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, Q.; Li, L.; Chan, P.W. Effects of Inflow Conditions on Mountainous/Urban Wind Environment Simulation. Build. Simul. 2017, 10, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, P. Appropriate Boundary Conditions for Computational Wind Engineering Models Using the K–Turbulence Model. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerod. 1993, 46, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gatto, E.; Gao, Z.; Buccolieri, R.; Morakinyo, T.E.; Lan, H. The “plant evaluation model” for the assessment of the impact of vegetation on outdoor microclimate in the urban environment. Build. Environ. 2019, 159, 106151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccolieri, R.; Santiago, J.-L.; Rivas, E.; Sanchez, B. Review on urban tree modelling in CFD simulations: Aerodynamic, deposition and thermal effects. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 31, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J. The influence of wind-induced response in urban trees on the surrounding flow field. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, J.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, K. Research on the windproof efficiency of polygonal straw sand barrier. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2017, 39, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacek, Z.; Řeháček, D.; Cukor, J.; Vacek, S.; Khel, T.; Sharma, R.P.; Kučera, J.; Král, J.; Papaj, V. Windbreak efficiency in agricultural landscape of the Central Europe: Multiple approaches to wind erosion control. Environ. Manag. 2018, 62, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Patruno, L.; Zhao, G.; Tamura, Y. Windbreak effectiveness of shelterbelts with different characteristic parameters and arrangements by means of CFD simulation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 61, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Patruno, L.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Q.; Tamura, Y. Windbreak Effectiveness of Single and Double-Arranged Shelterbelts: A Parametric Study Using Large Eddy Simulation. Forests 2024, 344, 109813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


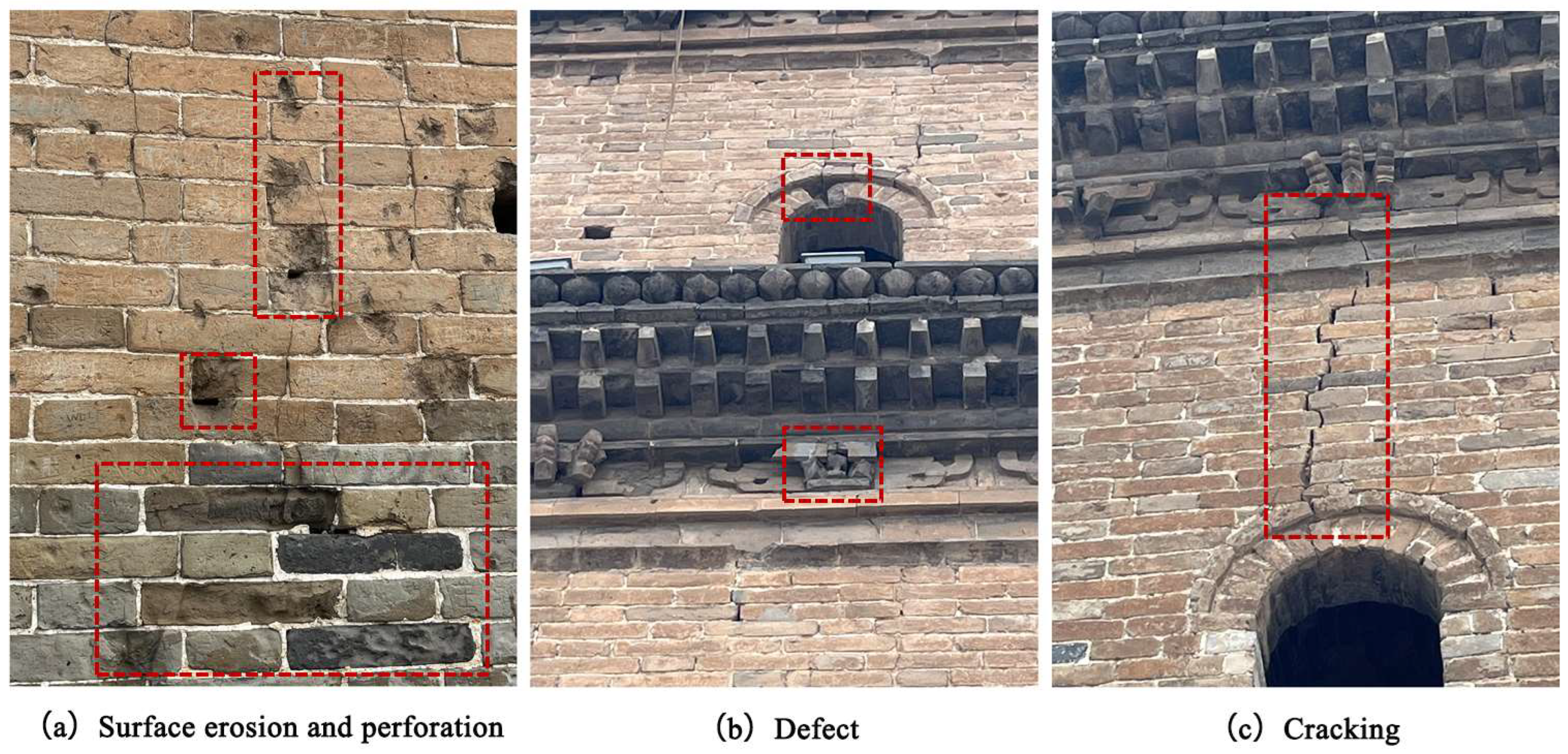
| Orientation | Damage Description | Defect Points (Count) | Cracks (Count) | Deteriorated Wall Area (m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| North | There is a waterline at the base of the tower, where the brickwork has turned black owing to moisture staining. The main body of the tower shows extensive material deterioration, with significant discoloration and surface spalling. Five major cracks are clearly visible on the tower surface, and nearly all the projecting eaves feature noticeable structural defects or missing components. | 32 | 5 | 89 |
| Northwest | There is a visible waterline at the base of the tower, where the bricks have turned black owing to prolonged moisture exposure. At the upper part of the tower, particularly on the north-facing side, the bricks exhibit signs of deterioration, including mottling and discoloration. Three prominent cracks are present on the tower body, and the ornamental eaves display substantial localized damage with numerous missing or broken components. | 16 | 3 | 35 |
| Southwest | There is a waterline at the base of the tower, where the brick surface has darkened owing to moisture staining. The upper part of the tower shows partial deterioration and discoloration, with minor, inconspicuous cracks and slight material loss observed on the brickwork. Localized damage is also present on sections of the ornamental eaves. | 9 | 0 | 21 |
| South | There is a visible waterline at the base of the tower, with brick surfaces darkened owing to moisture exposure. Minor and inconspicuous cracks and small-scale material loss are observed on the tower body. Partial damage is present on the ornamental eaves. | 6 | 0 | 20 |
| Southeast | There is a waterline at the base of the tower, with the bricks exhibiting blackening owing to moisture exposure. The brickwork on the tower body shows minor, inconspicuous cracks and slight material loss. Localized damage is also observed on parts of the ornamental eaves. | 9 | 0 | 14 |
| Northeast | There is a waterline at the base of the tower, with bricks darkened owing to moisture exposure. The brickwork on the tower body shows extensive deterioration, with severe mottling and discoloration. One prominent crack is visible, and the ornamental eaves exhibit significant structural loss with numerous damaged or missing sections. | 14 | 1 | 79 |
| Plant Type | Species | Average Height (m) | Crown Diameter (m) | Number of Plants | Average Height Below Canopy (m) | Planting Distance (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tree | Sophora japonica | 6.5 | 6.0 | 20 | 2.2 | 4.22 |
| Tree | Ginkgo biloba | 6.5 | 2 | 7 | 2.5 | 7 |
| Tree | Pinus massoniana | 2.7 | 2.2 | 6 | 1.2 | 2.45 |
| Shrub | Ligustrum quihoui | 2.5 | 3 | 14 | 0.45 | 2.8 |
| Shrub | Photinia fraseri | 1.5 | 2.8 | 64 | — | 2.8 |
| DOD | Description of Damage | Wind Speed Estimates [km/h] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Expected | Upper Bound | ||
| 1 | Threshold of visible damage | 70 | 90 | 110 |
| 2 | Loss of roof covering material (up to 20%) | 90 | 115 | 140 |
| 3 | Loss of significant roof covering material (more than 20%); light damage on the bell pagoda summit | 115 | 145 | 175 |
| 4 | More than 50% of roof structure removed; collapse of the bell pagoda summit (spire); walls remain standing | 150 | 185 | 220 |
| 5 | More than 80% of roof structure removed; walls partly collapsed; bell pagoda structure damaged | 190 | 225 | 260 |
| 6 | Roof structure totally removed and blown away; many walls collapsed; bell pagoda structure mostly destroyed | 230 | 270 | 310 |
| 7 | Complete destruction of building | 275 | 315 | 355 |
| Project | Parameter Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Simulation type | Steady state | Chosen for convergence efficiency and suitability for mean flow analysis |
| Inlet condition | Uniform velocity inlet | Constant inlet velocity (12.8 m/s and 20.0 m/s); vertical profile simplified for comparative analysis |
| Wind direction | NNE | Represents prevailing wind in the region |
| Turbulence intensity | 10% | Typical value for low-rise urban or suburban terrain |
| Surface roughness | z0 = 0.5 m | Reflecting conditions of vegetated surfaces and low-rise buildings |
| Outlet boundary | Pressure outlet | Atmospheric pressure outlet to ensure numerical continuity |
| Wall condition | No-slip rough wall + standard wall function | Applied to ground and building surfaces |
| Top and sides | Symmetry boundary | Minimize reflection and maintain domain stability |
| Mesh type | Unstructured tetrahedral | Local refinement near tower façade and vegetation canopy |
| Minimum mesh size | 0.2 m | Enhanced resolution in critical zones |
| Mesh count | ~5.3–6.0 million | Slight variation depending on vegetation configuration |
| Geometry source | Measured data | The building and vegetation geometry was modeled in Rhino |
| Sampling Point | Standard k–ε Model Error (%) | RNG k–ε Model Error (%) | k–ω SST Model Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 3.57 | 4.17 | 1.79 |
| P2 | 13.85 | 92.31 | 47.69 |
| P3 | 8.72 | 10.07 | 4.03 |
| P4 | 9.15 | 13.38 | 17.61 |
| P5 | 5.36 | 6.25 | 6.25 |
| P6 | 15.58 | 29.87 | 29.87 |
| P7 | 2.54 | 1.69 | 3.39 |
| P8 | 1.79 | 3.57 | 1.79 |
| Average Error | 8.57 | 21.41 | 14.06 |
| 12.8 m/s Wind Condition Simulation | 20 m/s Wind Condition Simulation |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
| 12.8 m/s Wind Condition Simulation | 20 m/s Wind Condition Simulation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Height (m) | Windbreak Effectiveness (%) | Height (m) | Windbreak Effectiveness (%) |
| 1.5 | 23% | 1.5 | 21% |
| 5 | 13% | 5 | 12% |
| 10 | 8% | 10 | 8% |
| 15 | 9% | 15 | 9% |
| 20 | 8% | 20 | 7% |
| 30 | 3% | 30 | 3% |
| 12.8 m/s Wind Condition Simulation | 20 m/s Wind Condition Simulation |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
| 12.8 m/s Wind Condition Simulation | 20 m/s Wind Condition Simulation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height (m) | Windbreak Effectiveness (%) | Increment (%) | Height (m) | Windbreak Effectiveness (%) | Increment (%) |
| 1.5 | 67% | 44% | 1.5 | 67% | 46% |
| 5 | 67% | 54% | 5 | 69% | 56% |
| 10 | 73% | 64% | 10 | 74% | 66% |
| 15 | 72% | 63% | 15 | 77% | 68% |
| 20 | 38% | 30% | 20 | 37% | 30% |
| 30 | 34% | 31% | 30 | 31% | 28% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, Z.; Ma, K.; He, D.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y. Optimized Plant Configuration Designs for Wind Damage Prevention in Masonry Heritage Buildings: A Case Study of Zhen Guo Tower in Weihui, Henan, China. Buildings 2025, 15, 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15172999
Mao Z, Ma K, He D, Guo Z, Zhao X, Zhang Y. Optimized Plant Configuration Designs for Wind Damage Prevention in Masonry Heritage Buildings: A Case Study of Zhen Guo Tower in Weihui, Henan, China. Buildings. 2025; 15(17):2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15172999
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Zhiyuan, Ke Ma, Dong He, Zhenkuan Guo, Xuefei Zhao, and Yichuan Zhang. 2025. "Optimized Plant Configuration Designs for Wind Damage Prevention in Masonry Heritage Buildings: A Case Study of Zhen Guo Tower in Weihui, Henan, China" Buildings 15, no. 17: 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15172999
APA StyleMao, Z., Ma, K., He, D., Guo, Z., Zhao, X., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Optimized Plant Configuration Designs for Wind Damage Prevention in Masonry Heritage Buildings: A Case Study of Zhen Guo Tower in Weihui, Henan, China. Buildings, 15(17), 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15172999






