Evolution of the Damping Ratio Considering Cyclic Confining Pressure Under Intermittent Cyclic Loading
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Descriptions
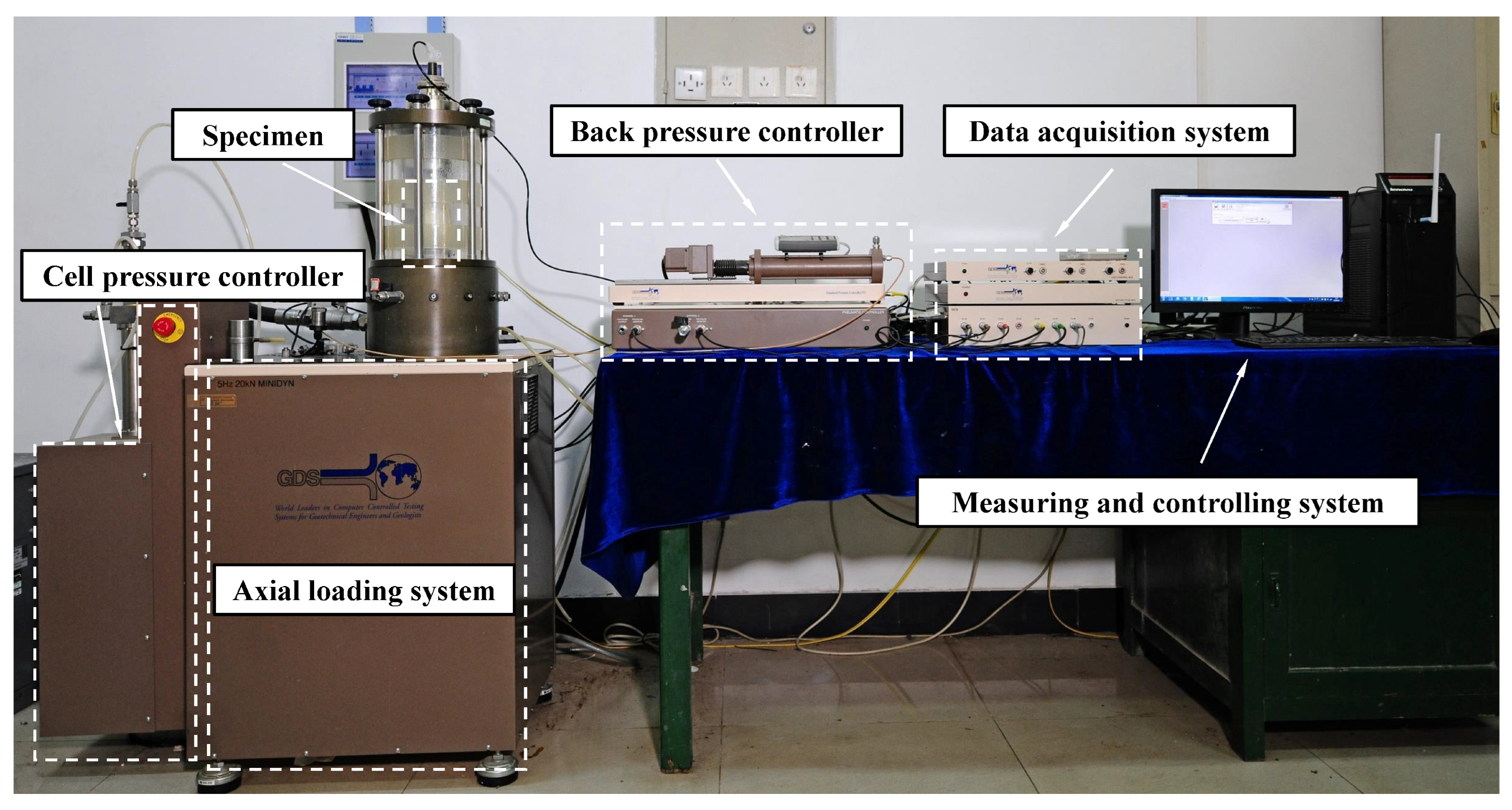
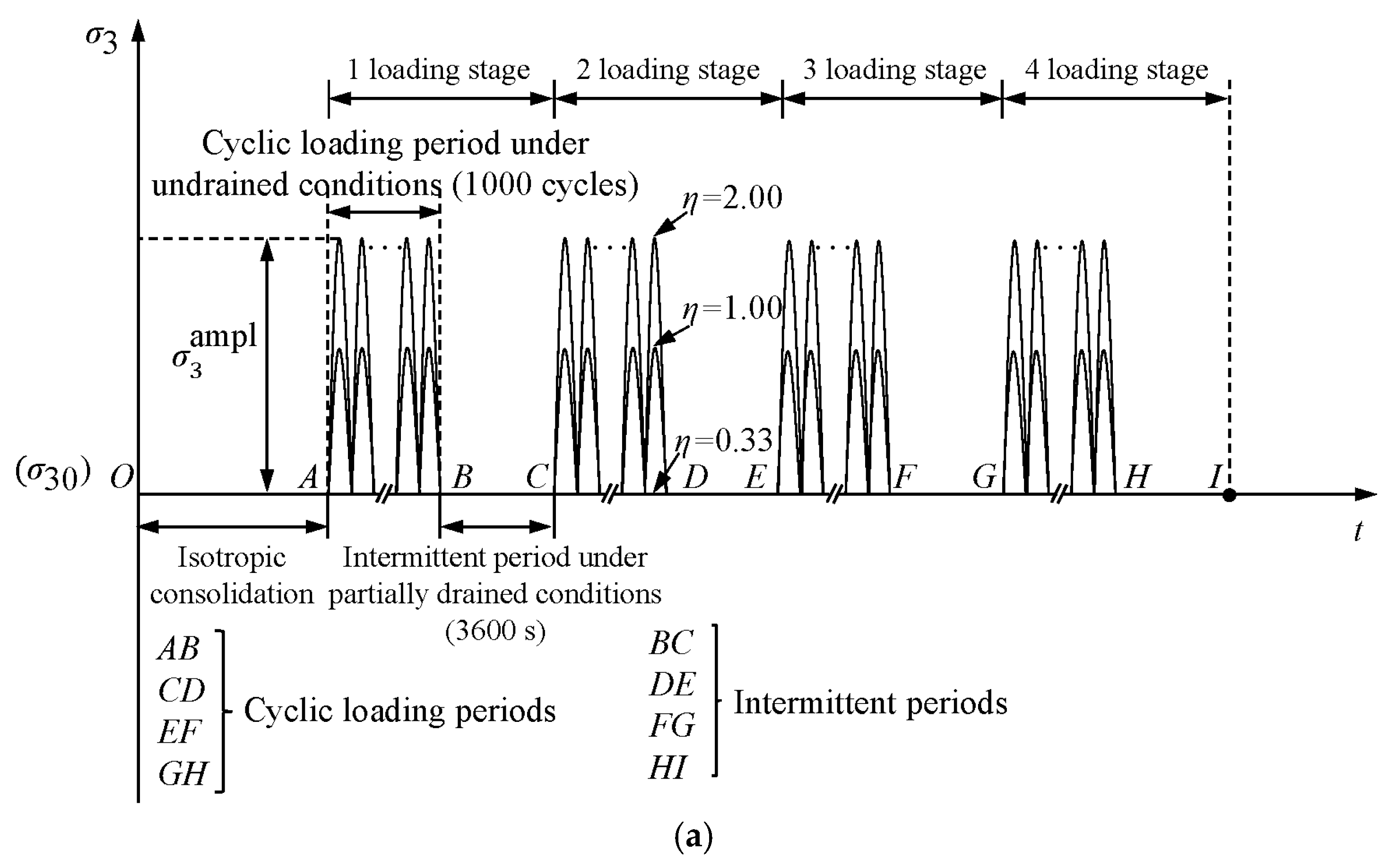
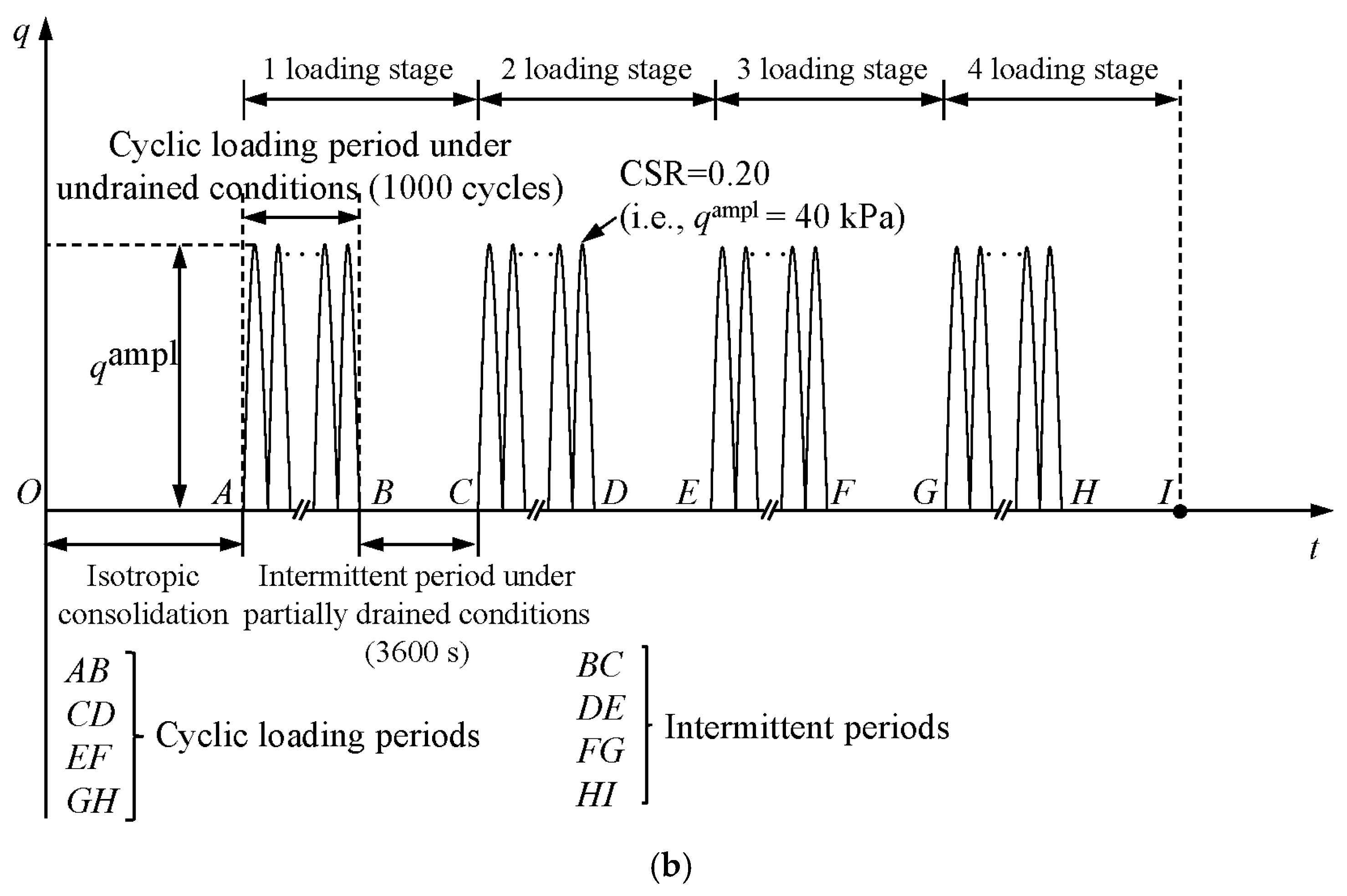
2.2. Test Procedures
3. Test Results
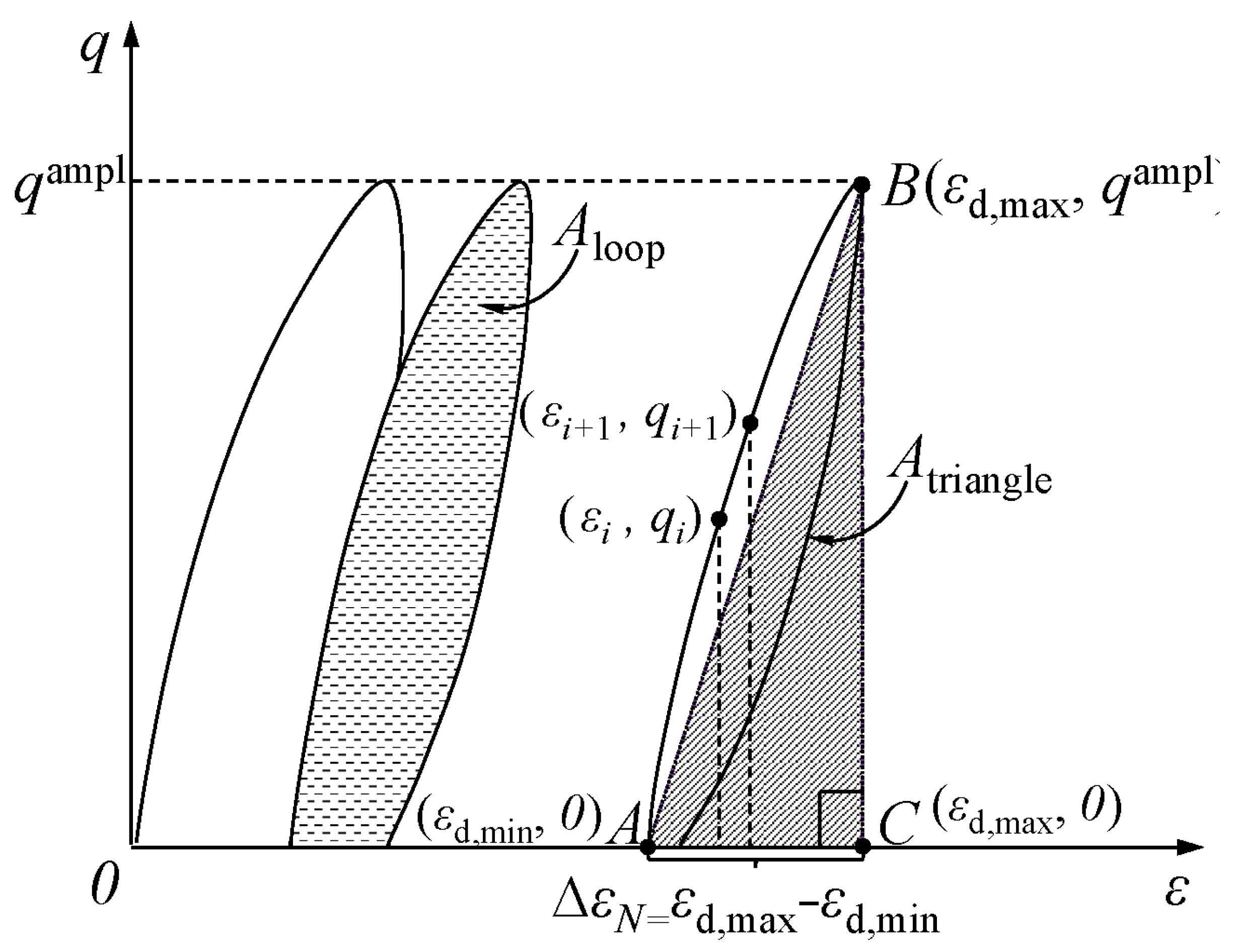
3.1. Determination of the Damping Ratio Under Cyclic Loading
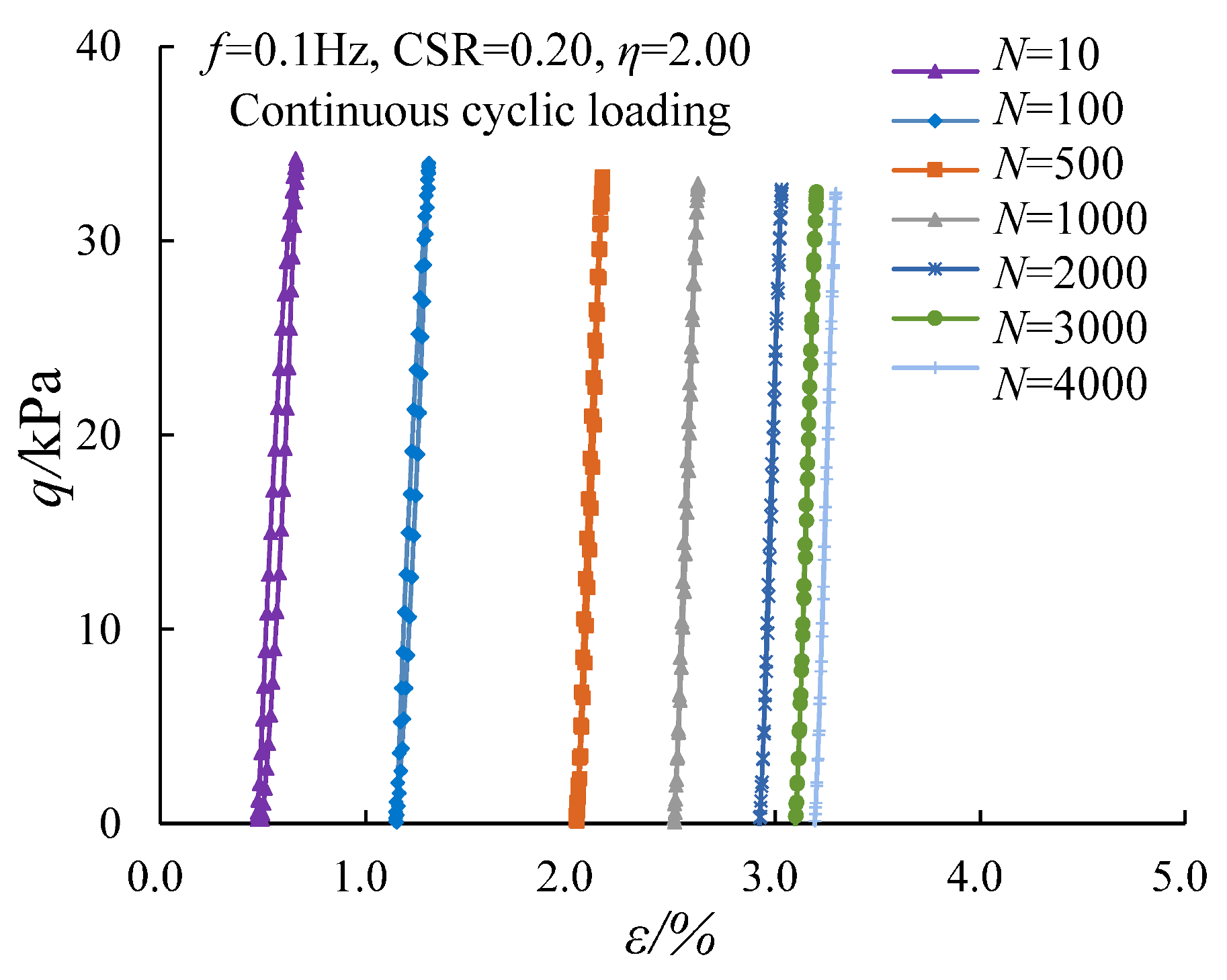
3.2. Evolution of the Damping Ratio Under Continuous Cyclic Loading
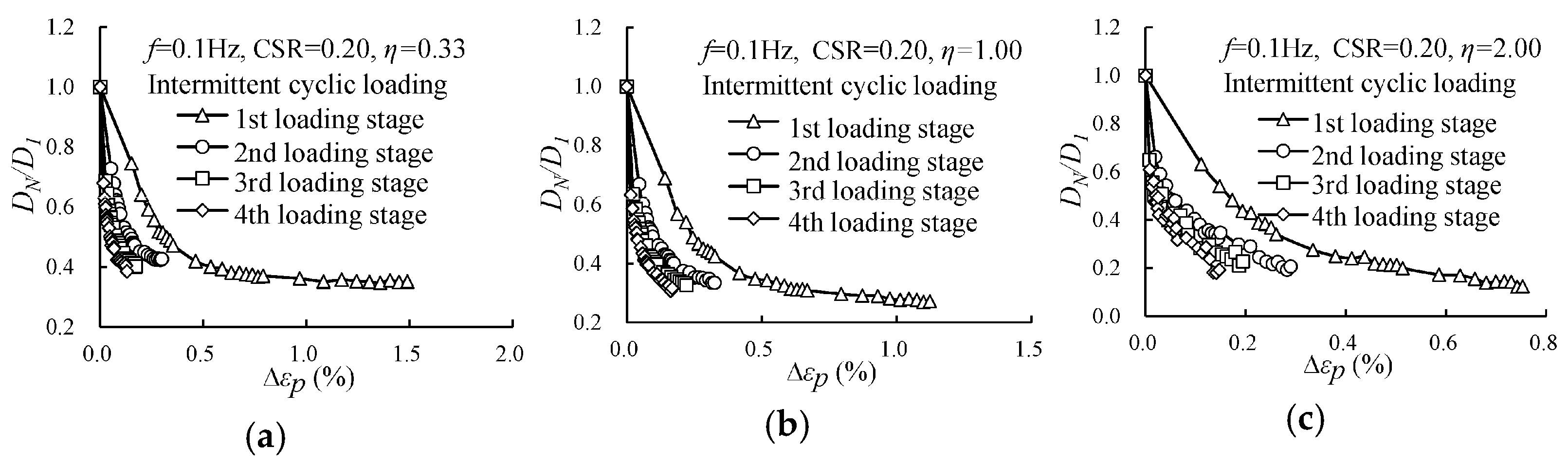
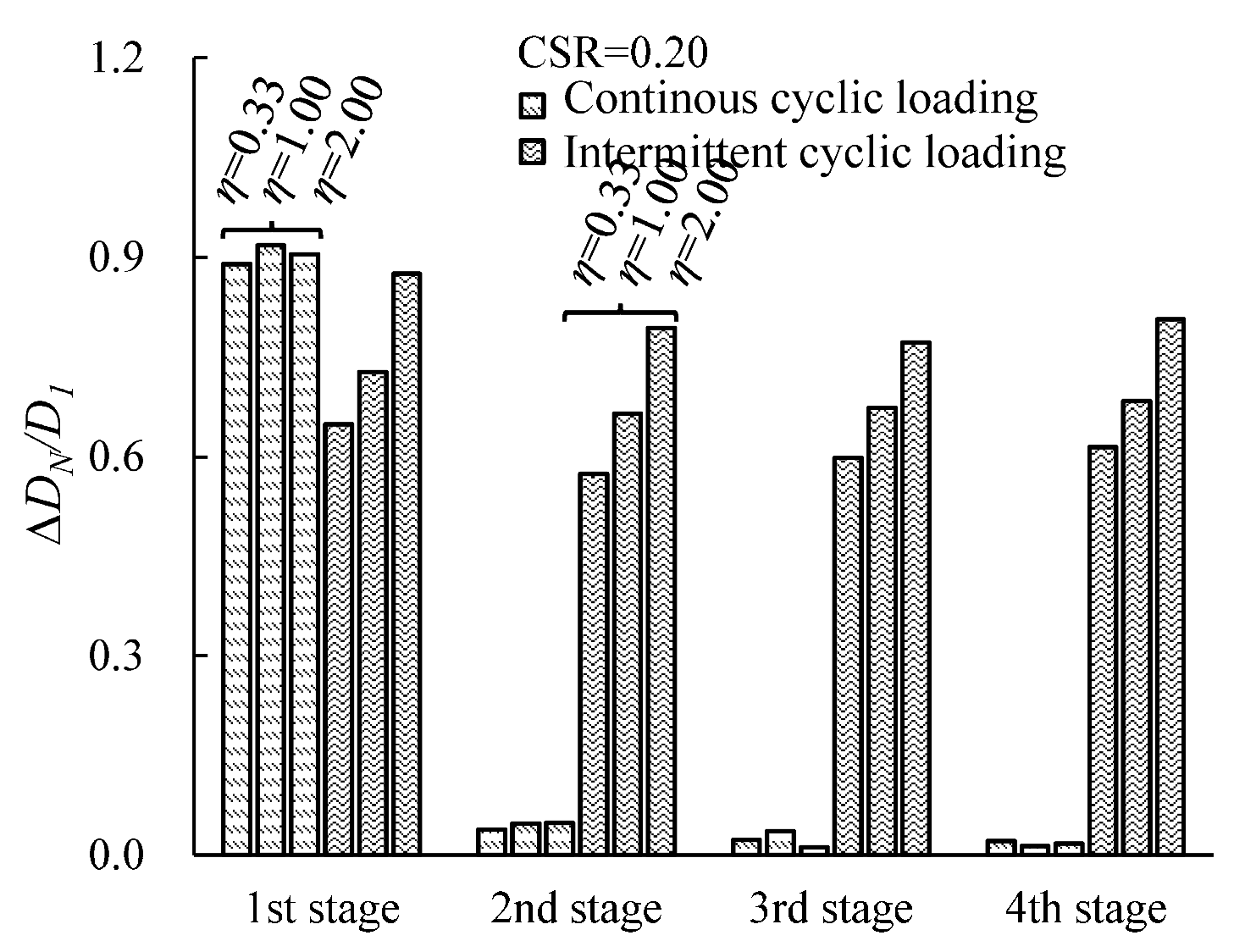
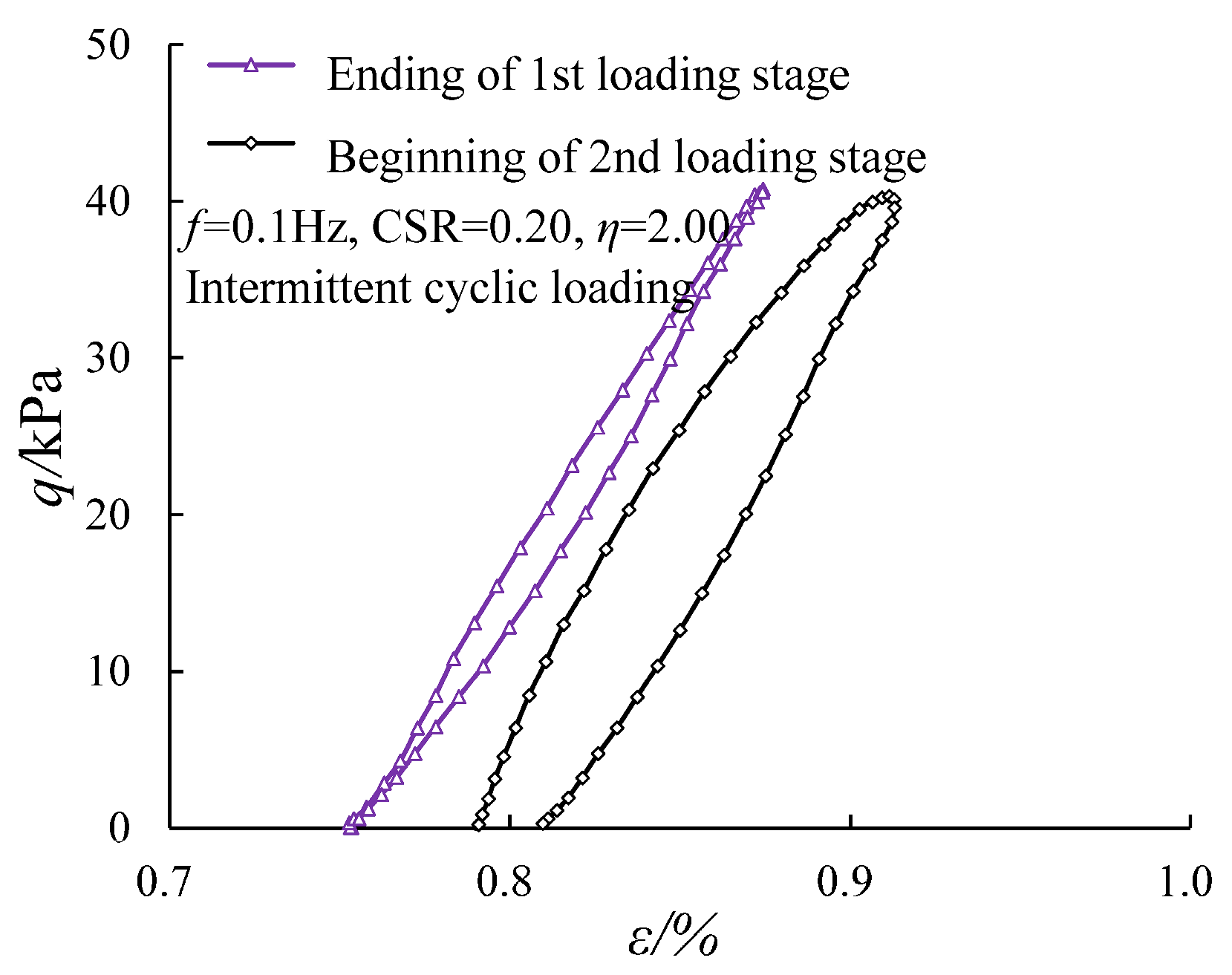
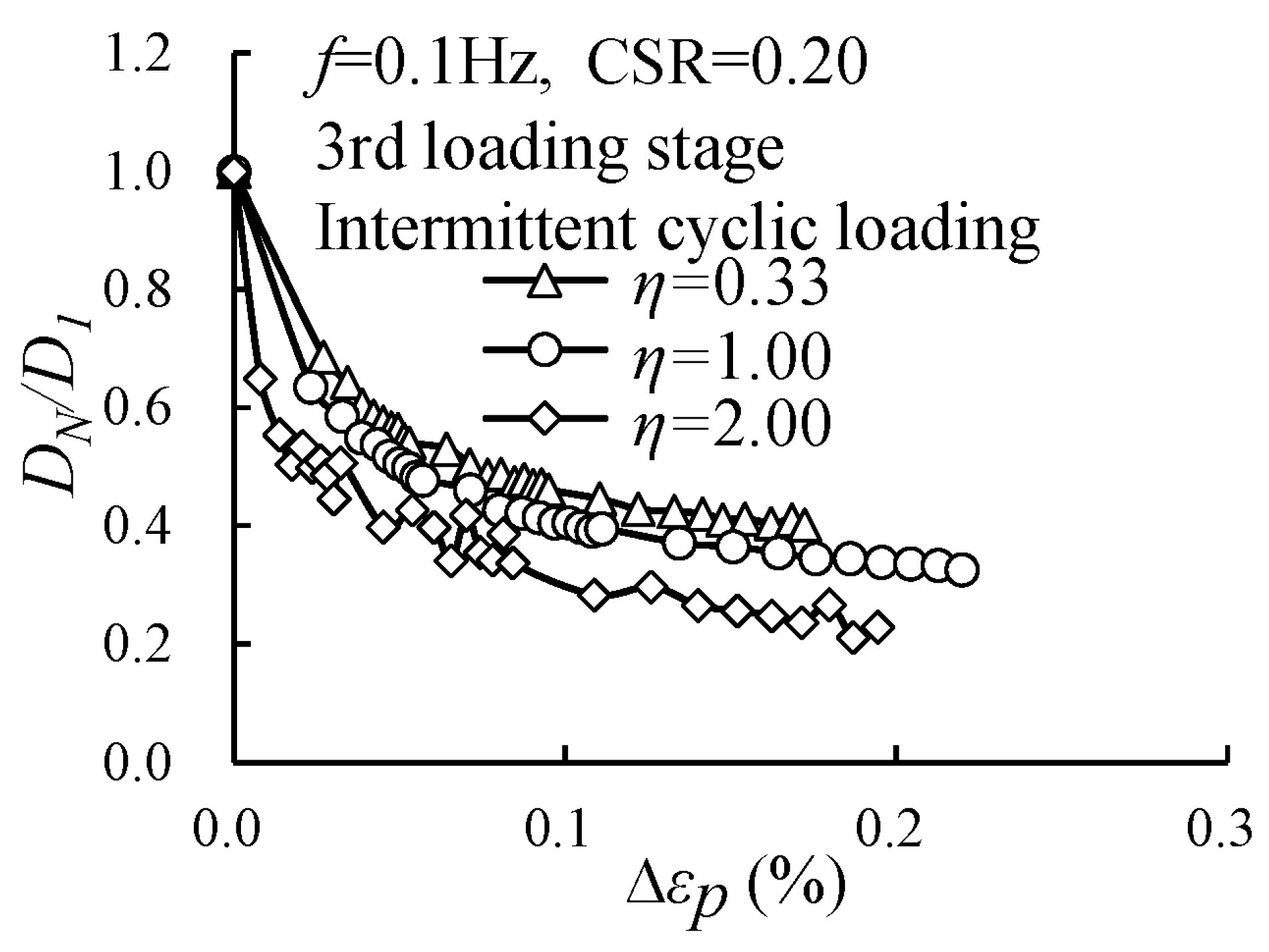
3.3. Evolution of the Damping Ratio Under Intermittent Cyclic Loading
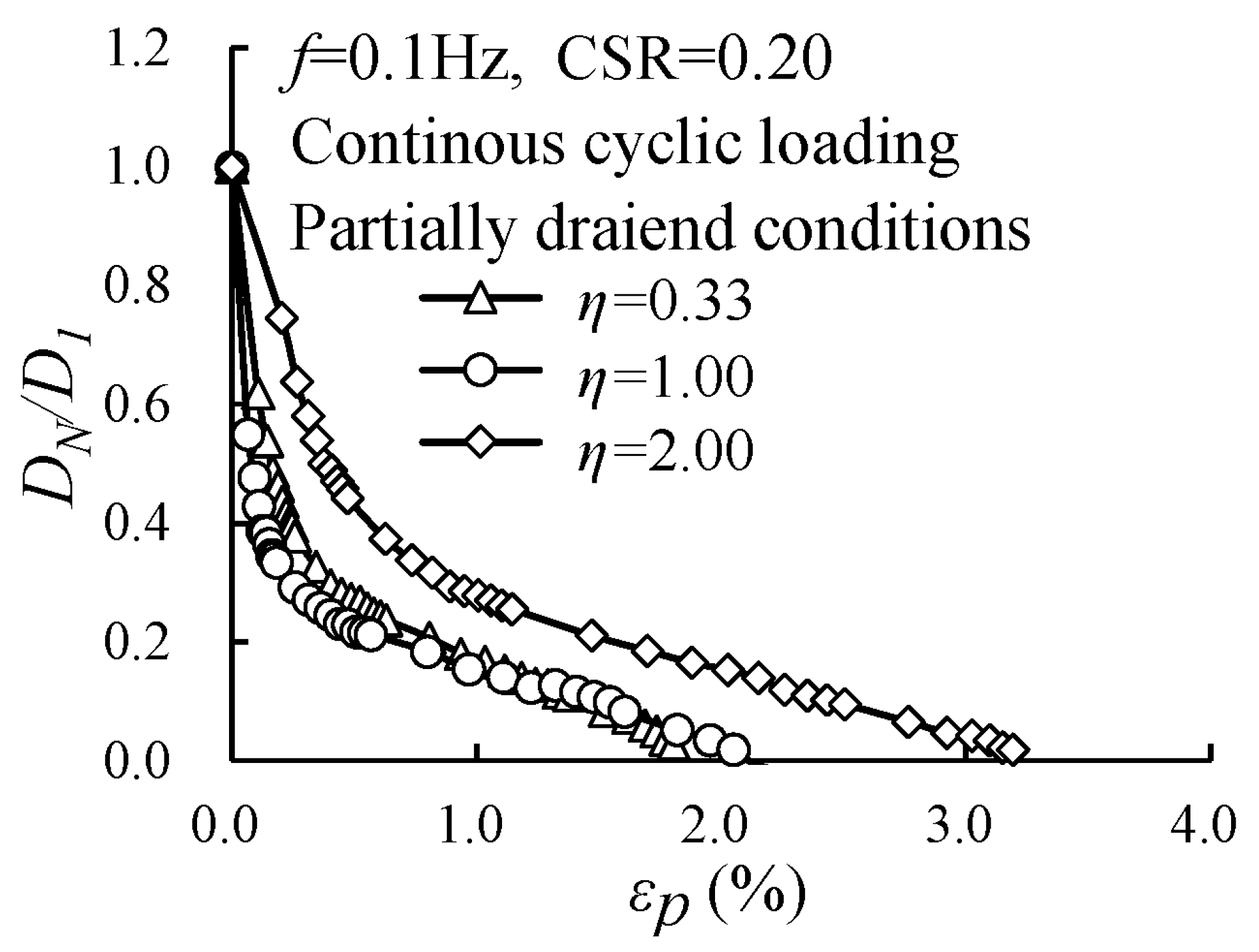
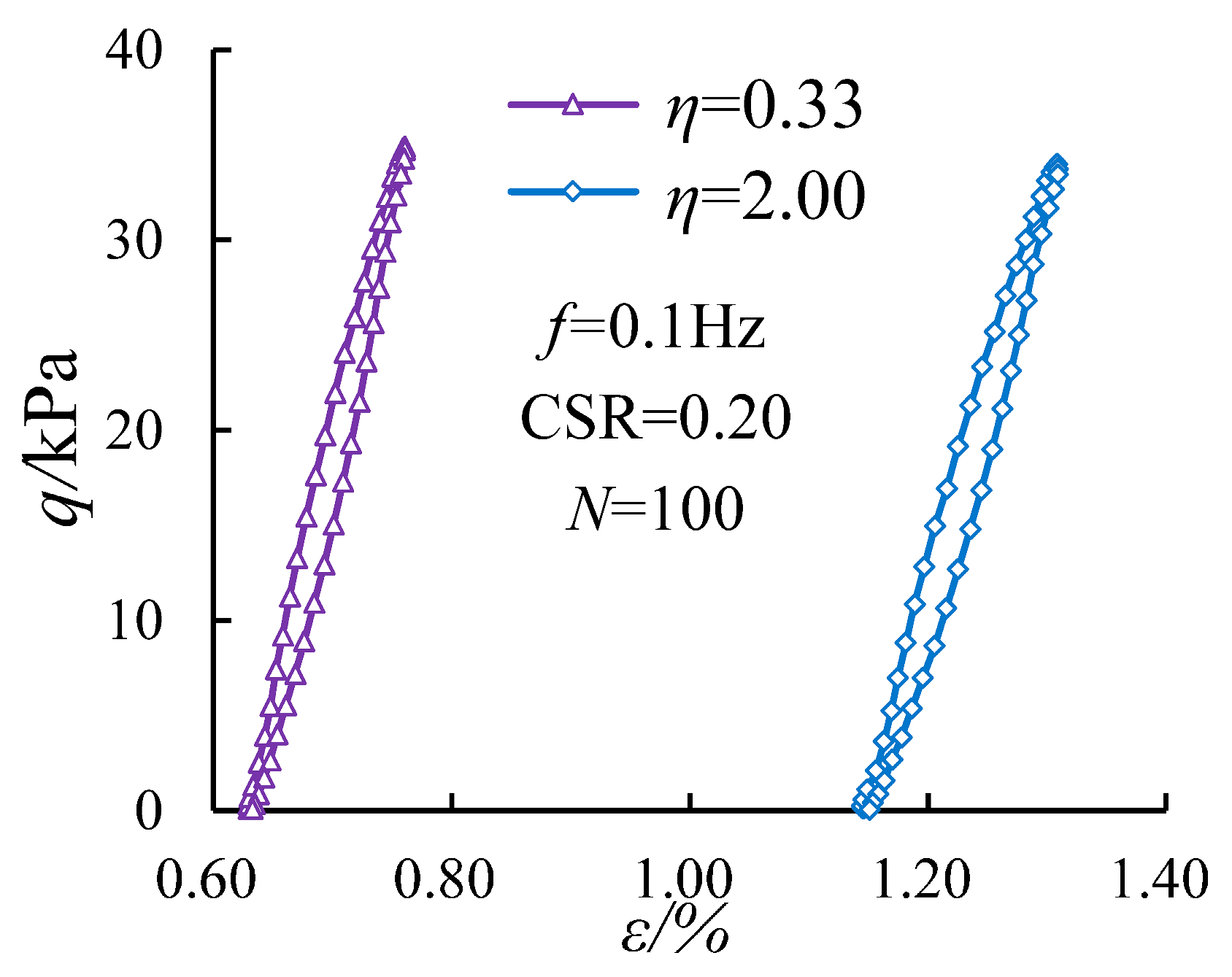
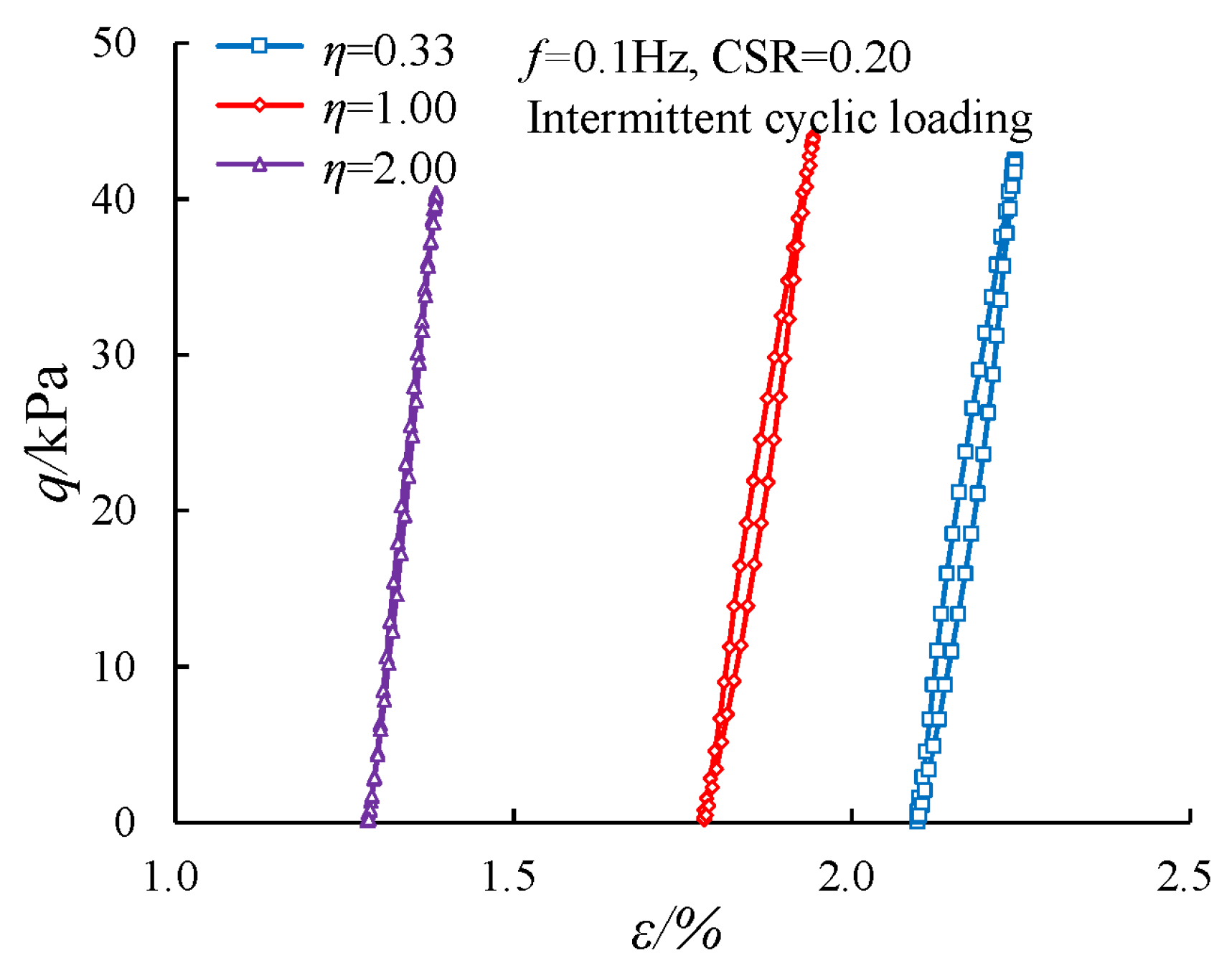
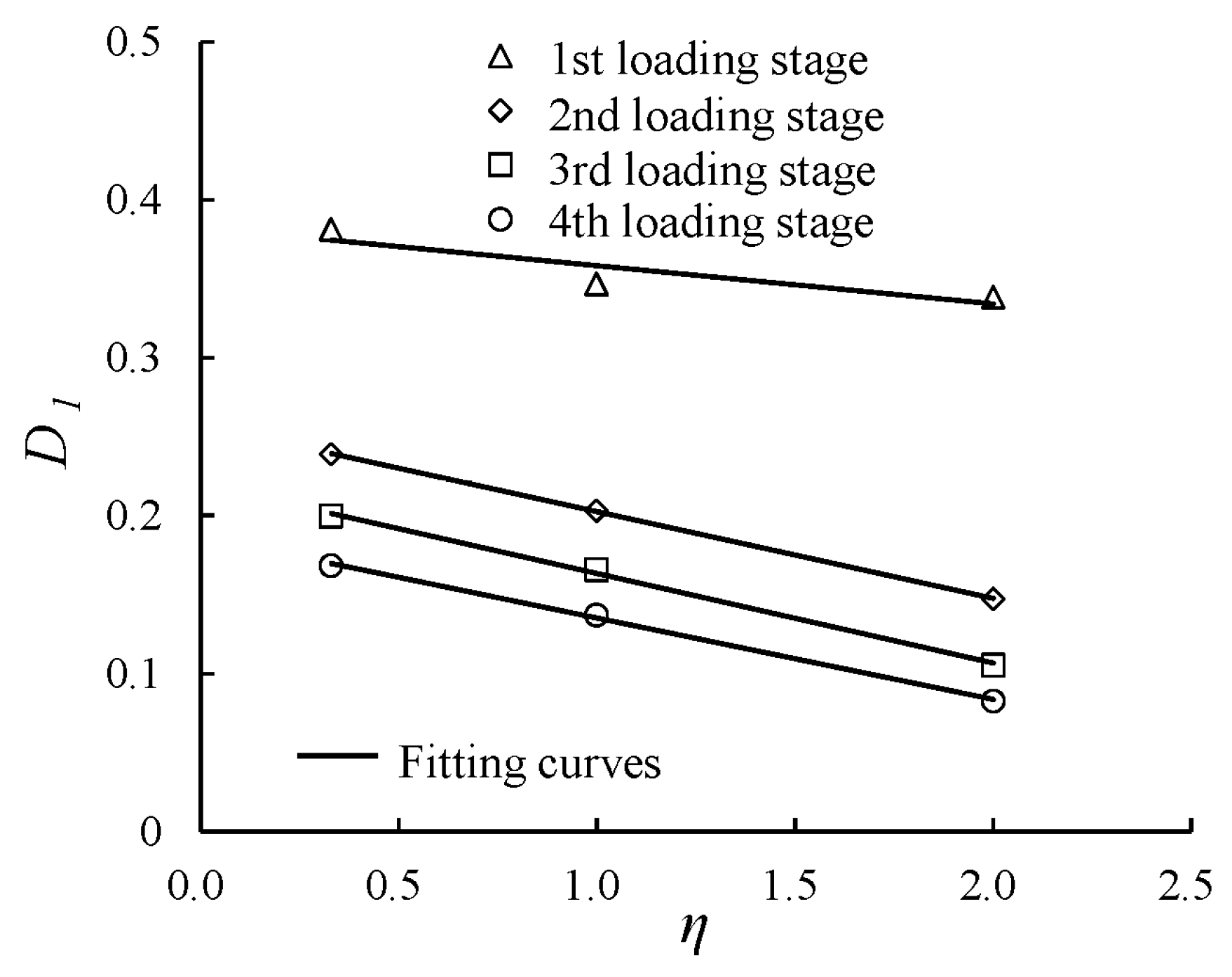
3.4. Evolution of the Damping Ratio with Various Cyclic Confining Pressures
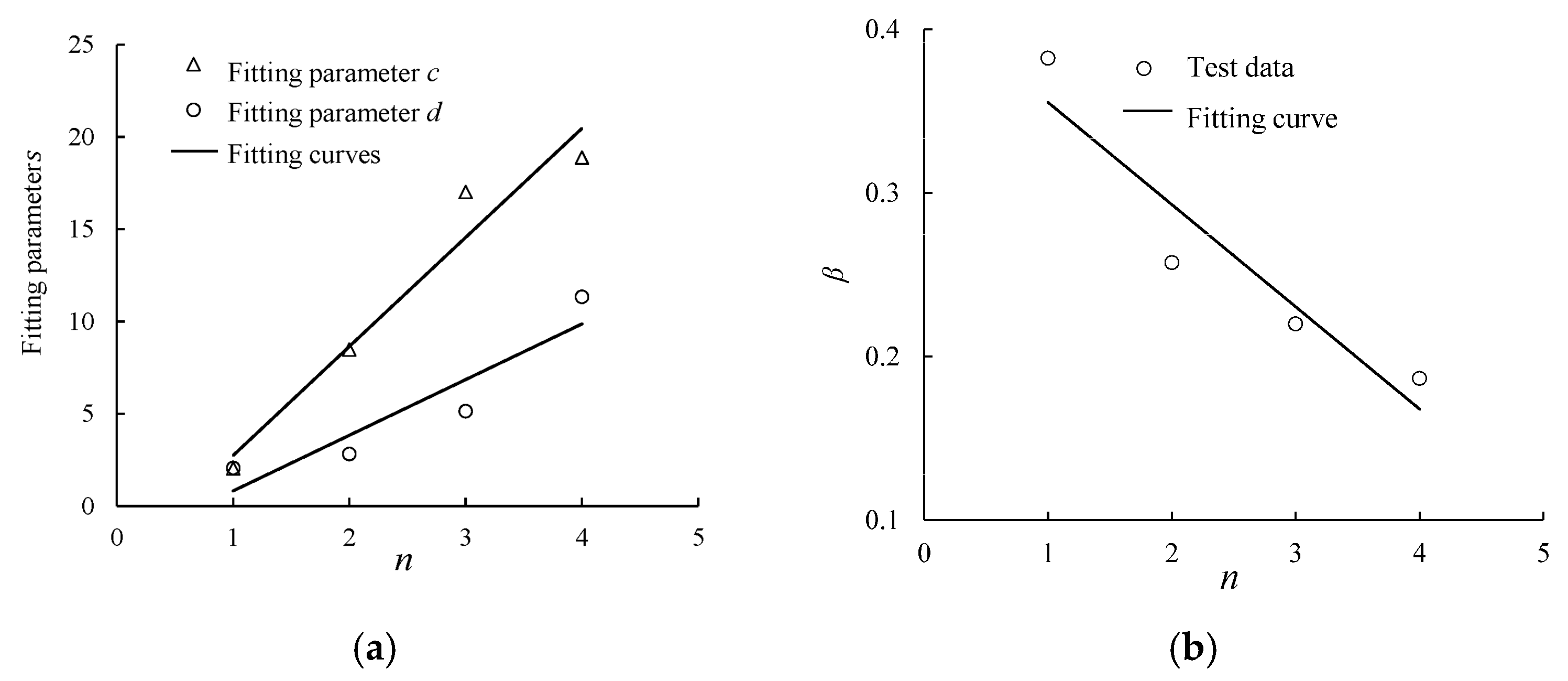
3.5. Damping Ratio Model Under Intermittent Cyclic Loading
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Unlike continuous loading, where the normalized damping ratio progressively decreases, the corresponding variations, except those in the first loading stage, showed similar variation across later stages under intermittent cyclic loading. The normalized damping ratio showed a sudden increase in the initial damping ratio at each restart under intermittent cyclic loading.
- (2)
- Higher cyclic confining pressure reduced the normalized damping ratio. Under intermittent loading, the attenuation was significantly greater at higher cyclic confining pressures; the normalized damping ratio for the specimen with η = 0.33 decayed by 60.0%, while the corresponding attenuation for the specimen with η = 2.00 reached 77.2%.
- (3)
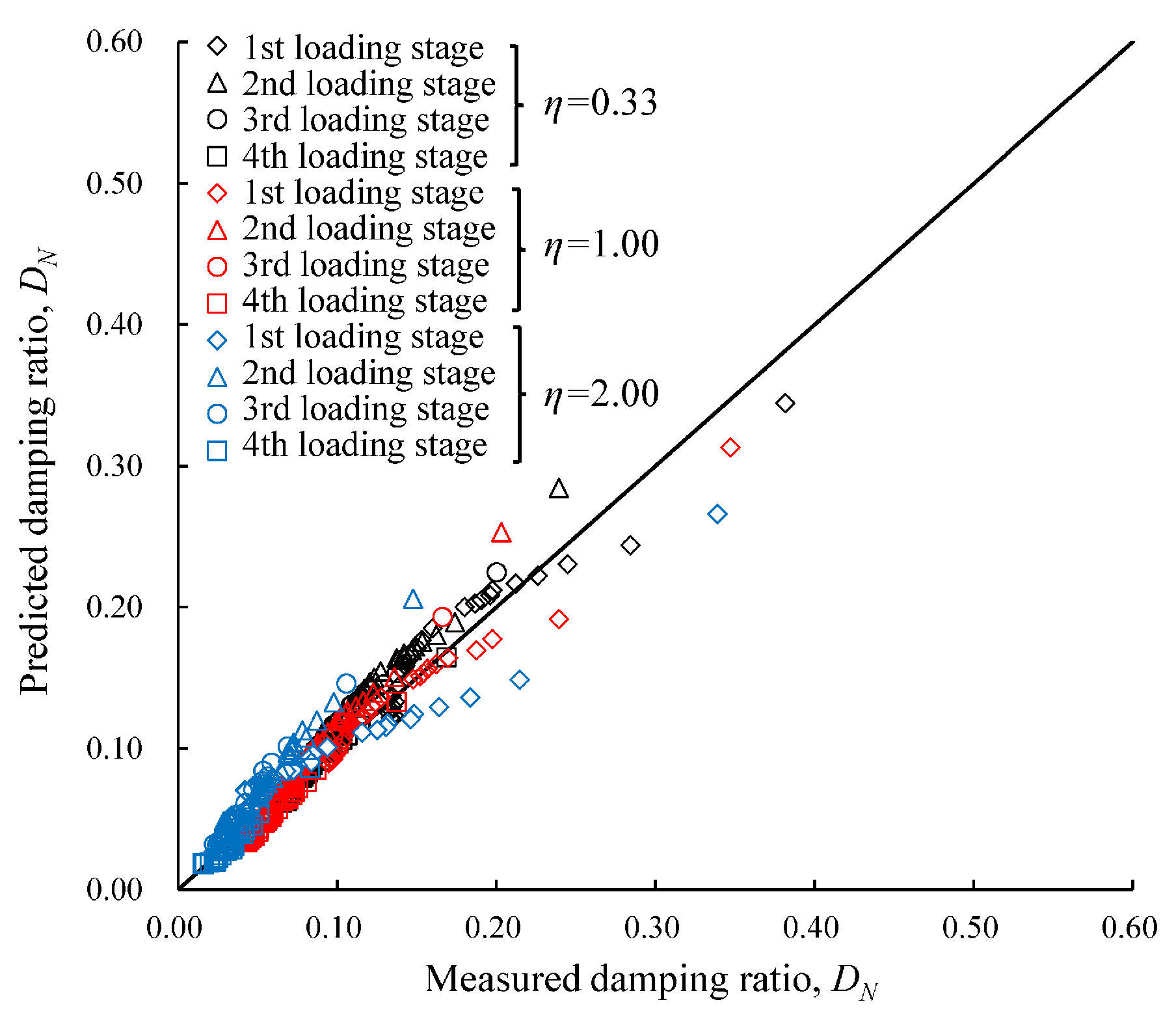
- The developed model accurately predicted the damping ratio under intermittent loading, and it was validated against test and literature data. Fitting parameters linking the effects of cyclic confining pressure and intermittent loading were analyzed.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cerni, G.; Cardone, F.; Virgili, A.; Camilli, S. Characterisation of permanent deformation behaviour of unbound granular materials under repeated triaxial loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.Q.; Gu, C.; Wang, J.; Juang, C.H.; Xu, C.J.; Hu, X.Q. One-way cyclic triaxial behavior of saturated clay: Comparison between constant and variable confining pressure. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2013, 139, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.Z.; Li, Q.L.; Wang, L.N.; Zhang, F.; An, L.S.; Xu, P.J. Stiffness and damping ratio evolution of frozen clays under long-term low-level repeated cyclic loading: Experimental evidence and evolution model. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2013, 86, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, Y.C.; Chen, J.; Du, J.S.; Peng, X.; Zhou, Z.L.; Zhu, C. Optimizing microseismic sensor networks in underground space using Cramér–Rao Lower Bound and improved genetic encoding. Undergr. Space 2025, 23, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, Y.C.; Chen, J.; Pu, Y.Y.; Du, X.M. An innovative analytical solution of AE/MS source location with singular value decomposition and weight estimation. Measurement 2025, 253, 117652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Krishna, M.A.; Dey, A. Evaluation of dynamic properties of sandy soil at high cyclic strains. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2017, 99, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okur, D.V.; Ansal, A. Stiffness degradation of natural fine-grained soils during cyclic loading. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2007, 27, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, I.; Zhang, X. Unified dynamic shear moduli and damping ratios of sand and clay. Soils Found. 1993, 33, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, B.O.; Drnevich, V.P. Shear modulus and damping in soils: Design equation and curves. J. Soil Mech. Found. ASCE 1972, 98, 667–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, P.; Banerjee, S. Shear modulus degradation model for cohesive soils. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2013, 53, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondon, H.A.; Wichtmann, T.; Triantafyllidis, T.; Lizcano, A. Comparison of cyclic triaxial behavior of unbound granular material under constant and variable confining pressure. J. Transp. Eng. 2009, 135, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Wang, J.; Cai, Y.Q.; Sun, L.; Wang, P.; Dong, Q.Y. Deformation characteristics of overconsolidated clay sheared under constant and variable confining pressure. Soils Found. 2016, 56, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichtmann, T.; Niemunis, A.; Triantafyllidis, T.H. On the influence of the polarization and the shape of the strain loop on strain accumulation in sand under high-cyclic loading. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2007, 27, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Wang, J.; Cai, Y.Q.; Yang, Z.X.; Gao, Y.F. Undrained cyclic triaxial behavior of saturated clays under variable confining pressure. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2012, 40, 118–128. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Wang, P. Effects of cyclic confining pressure on the deformation characteristics of natural soft clay. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2015, 78, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.H.; Chen, J.; Ke, W.H.; Zhong, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yi, S. Damping ratio evolution of saturated Ningbo clays under cyclic confining pressure. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 143, 106581. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.H.; Chen, J.; Ke, W.H.; Zhong, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yi, S. Post-cyclic mechanical behaviors of laterite clay with different cyclic confining pressures and degrees of reconsolidation. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 151, 106986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.S.; Li, Y.F.; Leng, W.M.; Mei, H.H.; Dong, J.L.; Chen, X.X. Deformation characteristics of fine-grained soil under cyclic loading with intermittence. Acta Geotech. 2020, 15, 3041–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.S.; Mei, H.H.; Leng, W.M.; Ruan, B.; Li, Y.F.; Chen, X.X. Characterization of permanent deformation of fine-grained subgrade soil under intermittent loading. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 139, 106395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamou, A.; Powrie, W.; Priest, J.A.; Clayton, C. The effects of drainage on the behaviour of railway track foundation materials during cyclic loading. Géotechnique 2017, 67, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Xia, T.; Ding, Z.; He, S. The effect of periodic intermittency on the cyclic behavior of marine sedimentary clay. Mar. Georesour. Geotec. 2019, 37, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.Y.; Liu, M.; Feng, S.X.; Liu, J.J.; Jiang, M.J. Cyclic behavior of Tianjin soft clay under intermittent combined-frequency cyclic loading. Int. J. Geomech. 2020, 20, 04020186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.X.; Nie, R.S.; Li, Y.F.; Guo, Y.P.; Dong, J.L. Resilient modulus of fine-grained subgrade soil considering load interval: An experimental study. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 142, 106558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, H.; Ersan, H. Settlements under consecutive series of cyclic loading. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2007, 27, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cai, Y.Q.; Guo, L.; Yang, F. Pore pressure and strain development of Wenzhou saturated soft soil under cyclic loading by stages. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2012, 34, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 50123-2019; Standard for Geotechnical Testing Method. MWR (Ministry of Water Resources): Beijing, China, 2019.
- ASTM D2487; Standard Practice for Classification of Soils for Engineering Purposes (Unified Soil Classification System). ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Sakai, A.; Samang, L.; Miura, N. Partially-drained cyclic behavior and its application to the settlement of a low embankment road on silty-clay. Soils Found. 2003, 43, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Ding, H.; Chen, Y.M.; Bian, X.C. Experimental study of undrained strength property of saturated silty clay after traffic load. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2010, 29, 3986–3993. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.B.; Yin, J.H.; Feng, W.Q.; Borana, L.; Chen, R.P. Accumulated permanent axial strain of a subgrade fill under cyclic high-speed railway loading. Int. J. Geomech. 2018, 18, 04018018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyodo, M.; Hyde, A.F.L.; Yamamoto, Y.; Fujii, T. Cyclic shear strength of undisturbed and remoulded marine clays. Soils Found. 1999, 39, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simomsen, E.; Isacsson, U. Soil behavior during freezing and thawing using variable and constant confining pressure triaxial tests. Can. Geotech. J. 2001, 38, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.H.; Chen, J.; Yu, S.; Fu, X.D.; Zhang, G.C.; Tian, N. Dynamic behaviors of overconsolidated clay under cyclic confining pressure. Int. J. Geomech. 2022, 22, 04022197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhang, F.; Feng, D.C.; Tang, K.W.; Feng, X. Dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio of thawed saturated clay under long-term cyclic loading. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 145, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.C.; Shang, S.P.; Wang, H.D. Study of strain accumulation strengthened model for clay under cyclic loadings. Rock Soil Mech. 2018, 29, 2457–2462. [Google Scholar]





| No. of Tests | Load Modes | Effective Confining Pressure Po′ (kPa) | η | (kPa) | CSR | qampl (kPa) | Loading Cycles, N | Intermittent Time △t (s) | Drained Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C01 | Continuous cyclic loading | 100 | 0.33 | 0 | 0.20 | 40 | 4000 | / | Partially drained conditions |
| C02 | 1.00 | 27 | |||||||
| C03 | 2.00 | 67 | |||||||
| I01 | Intermittent cyclic loading | 0.33 | 0 | 1000 × 4 | 3600 | Cyclic loading period: undrained conditions Intermittent period: partially drained conditions | |||
| I02 | 1.00 | 27 | |||||||
| I03 | 2.00 | 67 |
| No. of the Loading Stage | η | a | b | D1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First loading stage | 0.33 | 2.715 | 0.592 | 0.381 | 0.935 |
| 1.00 | 4.116 | 0.743 | 0.347 | 0.972 | |
| 2.00 | 6.111 | 1.237 | 0.339 | 0.998 | |
| Second loading stage | 0.33 | 6.316 | 0.675 | 0.239 | 0.976 |
| 1.00 | 10.127 | 0.643 | 0.203 | 0.989 | |
| 2.00 | 20.233 | 0.705 | 0.147 | 0.988 | |
| Third loading stage | 0.33 | 12.805 | 0.585 | 0.200 | 0.989 |
| 1.00 | 18.742 | 0.550 | 0.166 | 0.994 | |
| 2.00 | 40.548 | 0.551 | 0.106 | 0.977 | |
| Fourth loading stage | 0.33 | 19.113 | 0.535 | 0.168 | 0.992 |
| 1.00 | 27.613 | 0.530 | 0.137 | 0.997 | |
| 2.00 | 50.117 | 0.591 | 0.083 | 0.965 |
| No. of the Loading Stage | α | β | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| First loading stage | −0.024 | 0.382 | 0.805 |
| Second loading stage | −0.055 | 0.257 | 0.999 |
| Third loading stage | −0.057 | 0.220 | 0.997 |
| Fourth loading stage | −0.052 | 0.187 | 0.998 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Meng, C.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Fu, X.; Wang, M. Evolution of the Damping Ratio Considering Cyclic Confining Pressure Under Intermittent Cyclic Loading. Buildings 2025, 15, 2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15162882
Huang J, Meng C, Zhou Y, Chen J, Fu X, Wang M. Evolution of the Damping Ratio Considering Cyclic Confining Pressure Under Intermittent Cyclic Loading. Buildings. 2025; 15(16):2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15162882
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Juehao, Chao Meng, Yongqiang Zhou, Jian Chen, Xiaodong Fu, and Mingyi Wang. 2025. "Evolution of the Damping Ratio Considering Cyclic Confining Pressure Under Intermittent Cyclic Loading" Buildings 15, no. 16: 2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15162882
APA StyleHuang, J., Meng, C., Zhou, Y., Chen, J., Fu, X., & Wang, M. (2025). Evolution of the Damping Ratio Considering Cyclic Confining Pressure Under Intermittent Cyclic Loading. Buildings, 15(16), 2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15162882







