Durability and Microstructure Analysis of Loess-Based Composite Coal Gangue Porous Vegetation Concrete
Abstract
1. Introduction
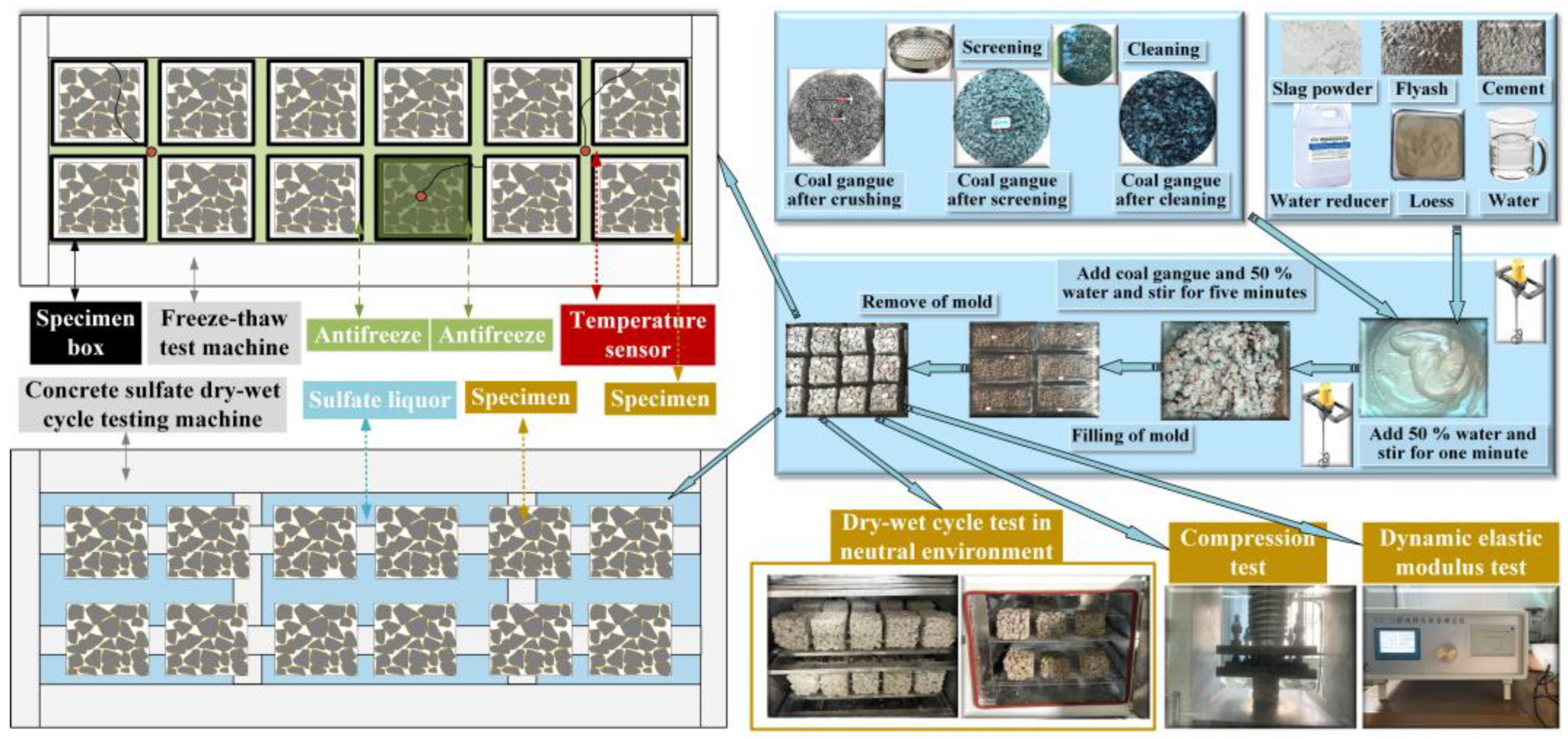
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
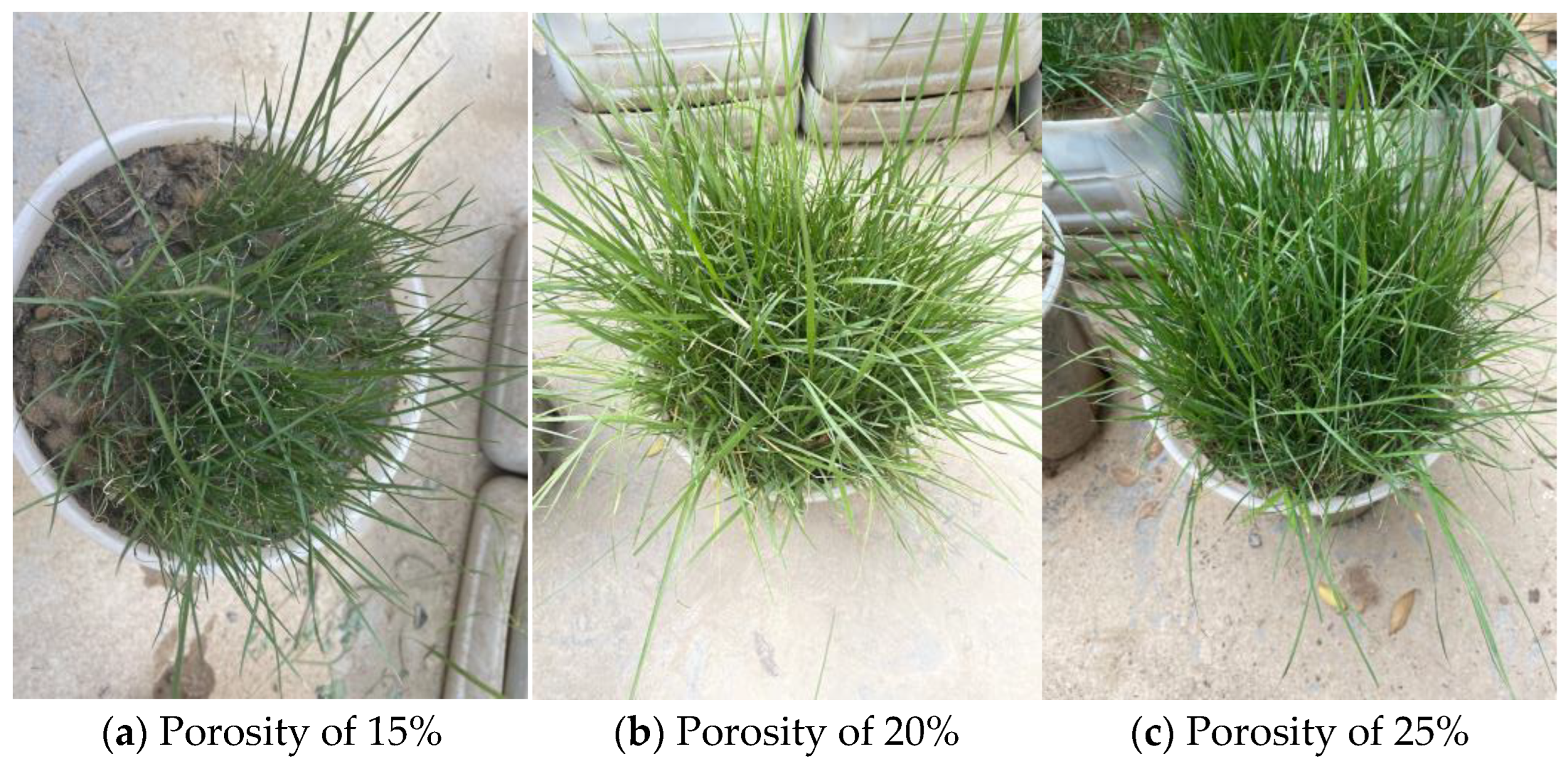
2.2. Permeability Coefficient and Planting Test
2.3. Freezing−Thawing Cycle Test
2.4. Wetting-Drying Cycle Test
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscope Test
3. Results and Discussion
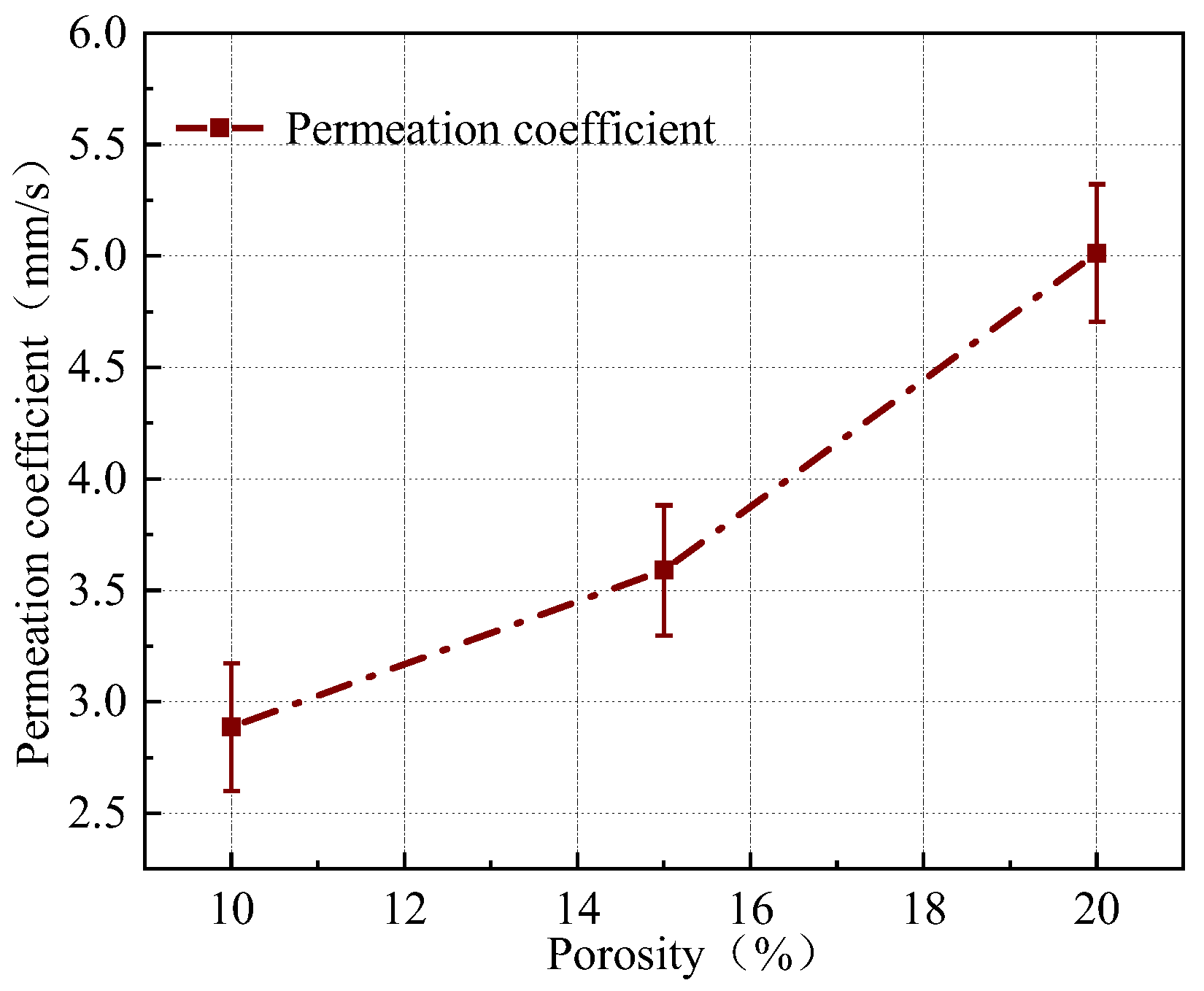
3.1. Analysis of Permeability Coefficient and Planting Test Results
3.2. Analysis of Freezing-Thawing Cycle Test Results
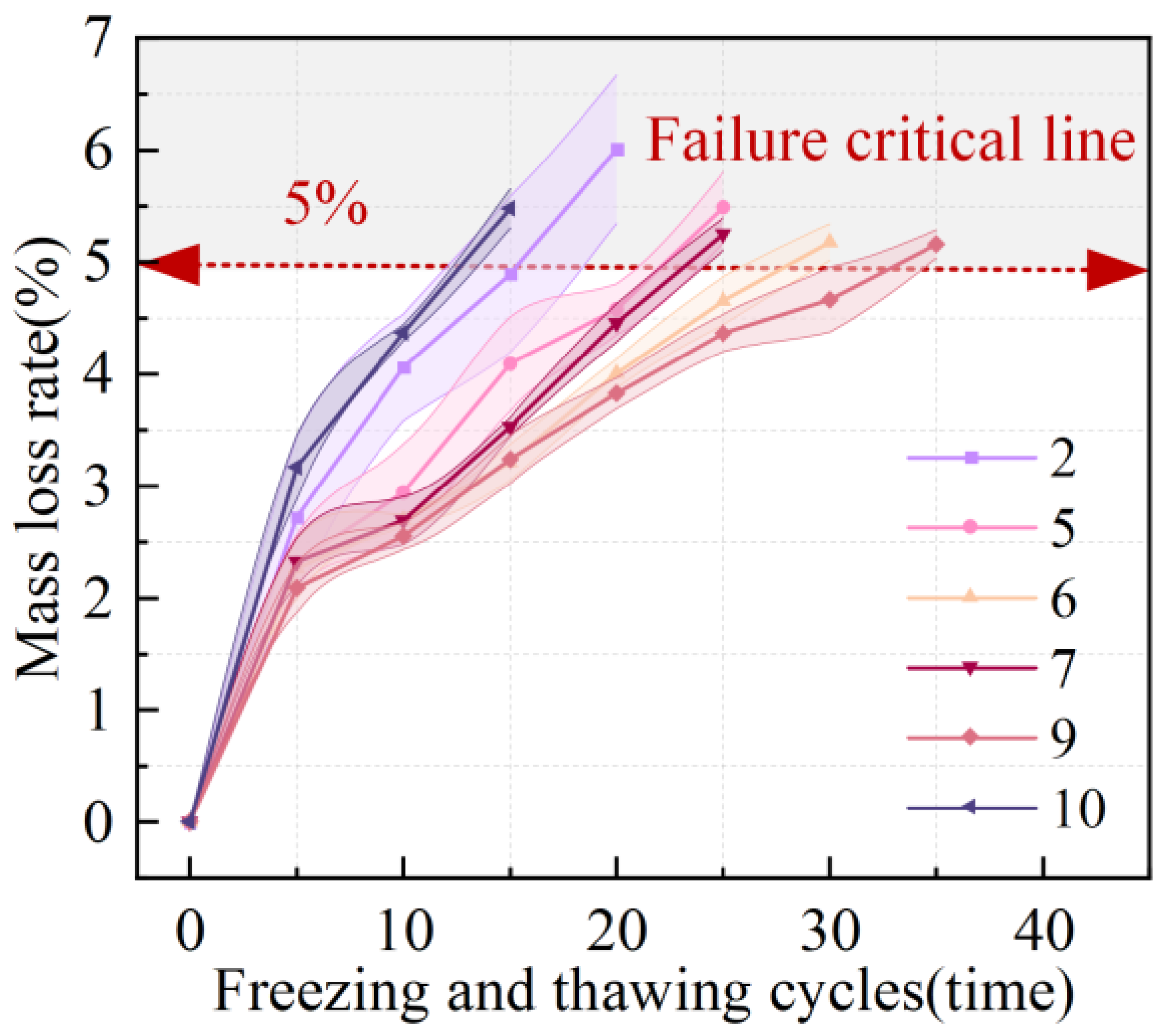
3.2.1. Mass Loss
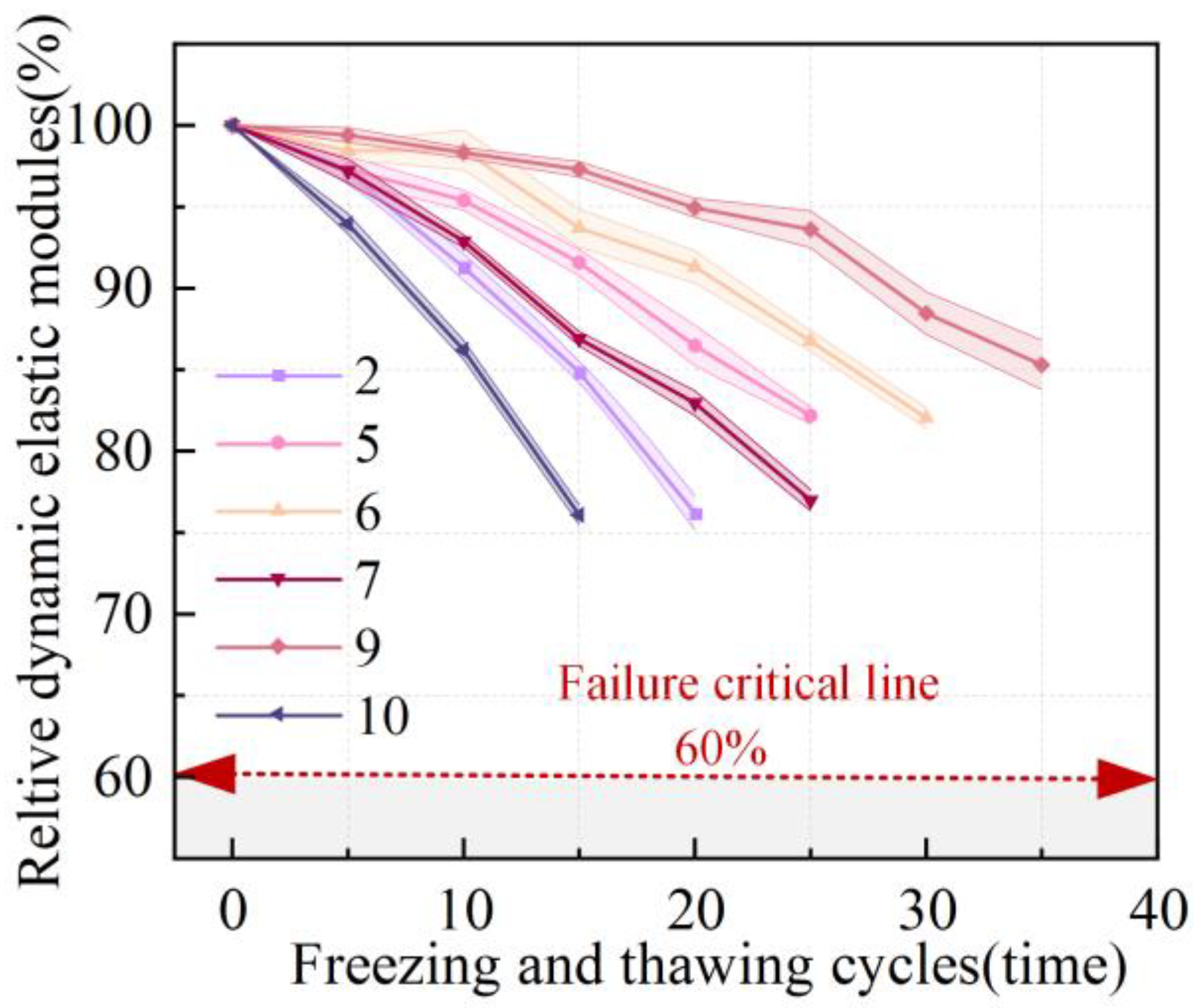
3.2.2. Relative Dynamic Elastic Modulus
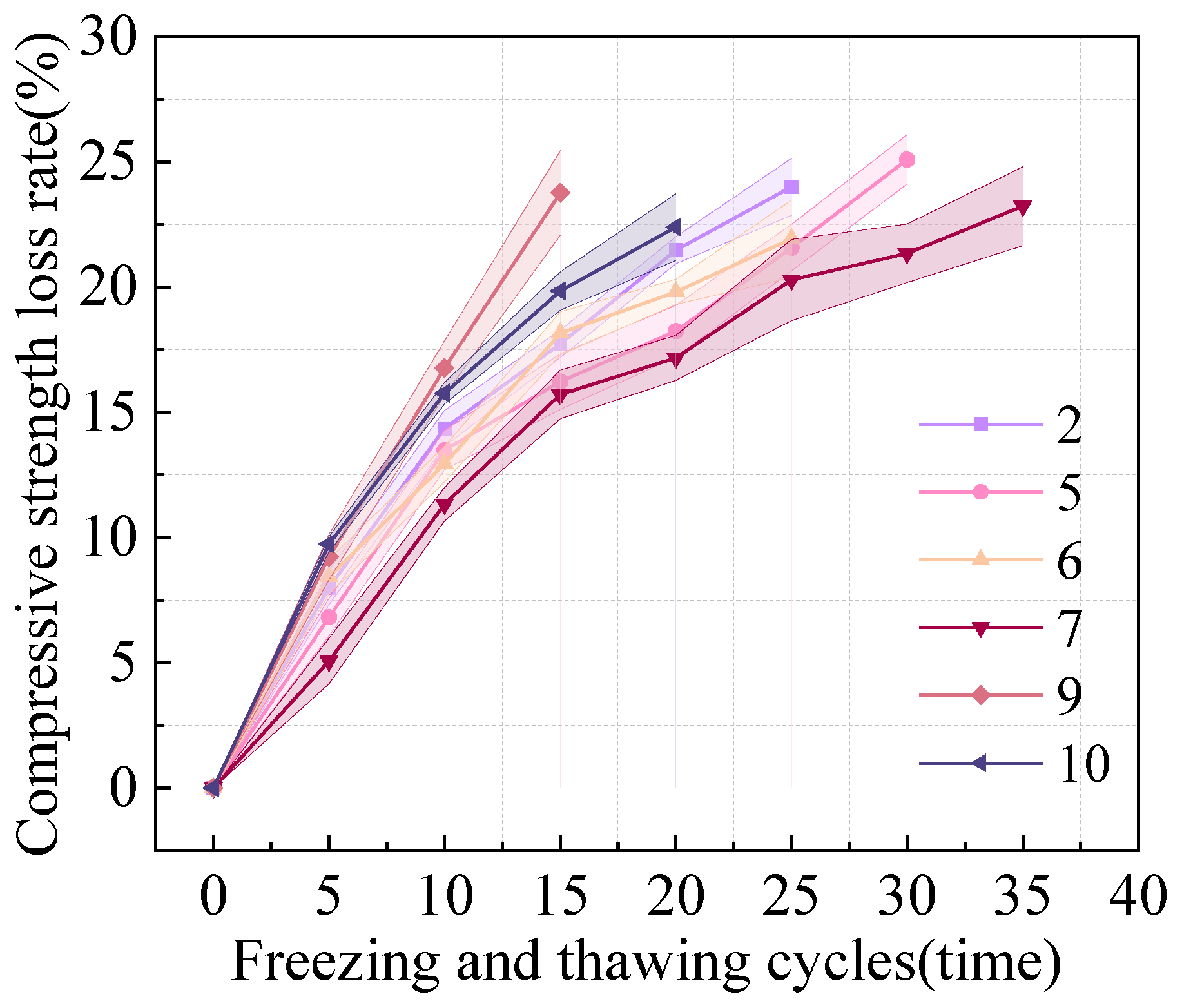
3.2.3. Compressive Strength Loss Rate
3.3. Analysis of Wetting-Drying Cycle Test Results
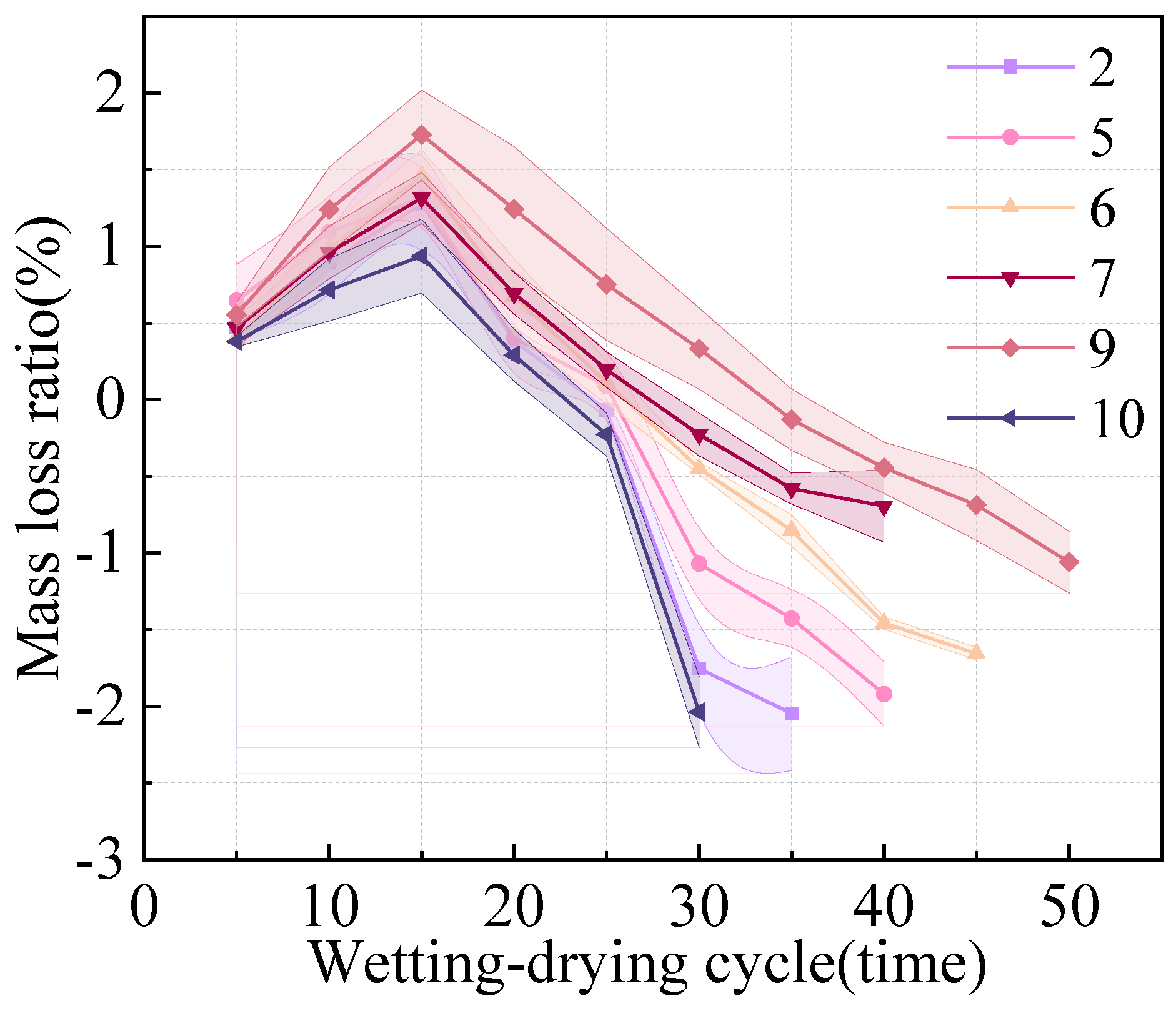
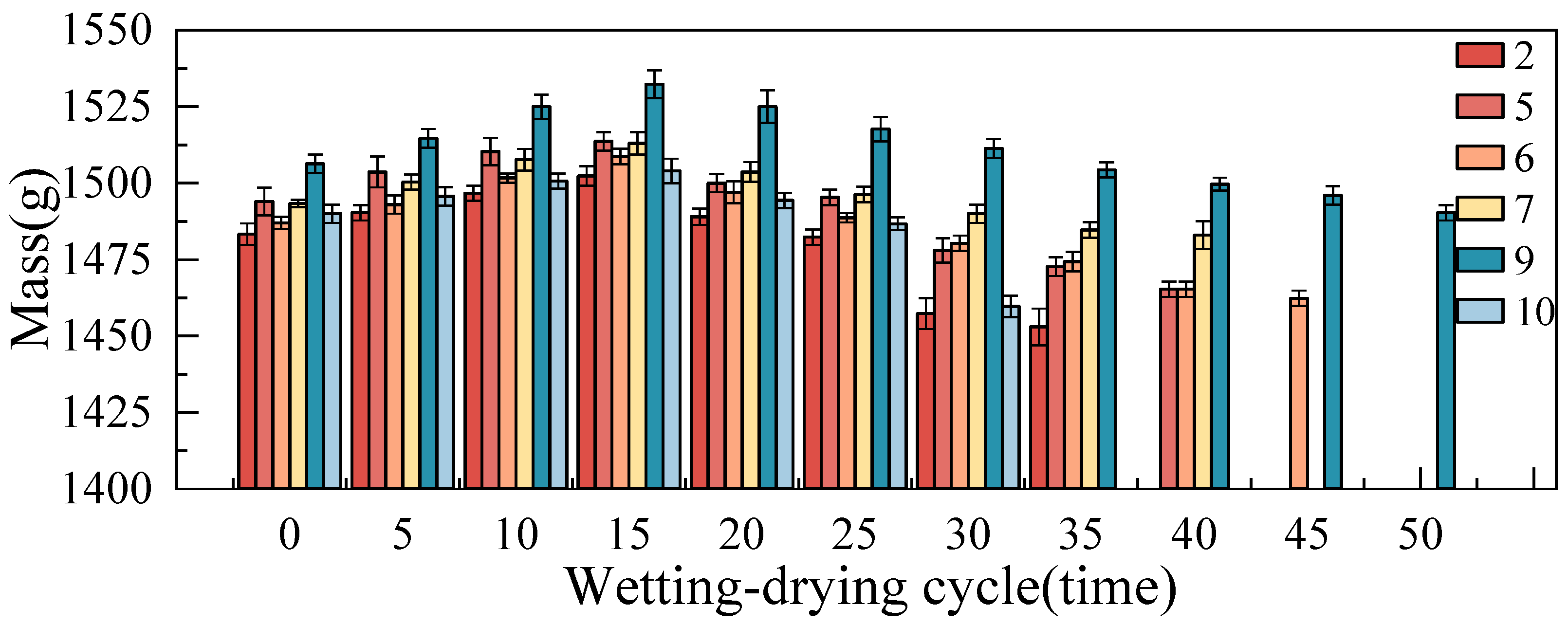
3.3.1. Mass Loss
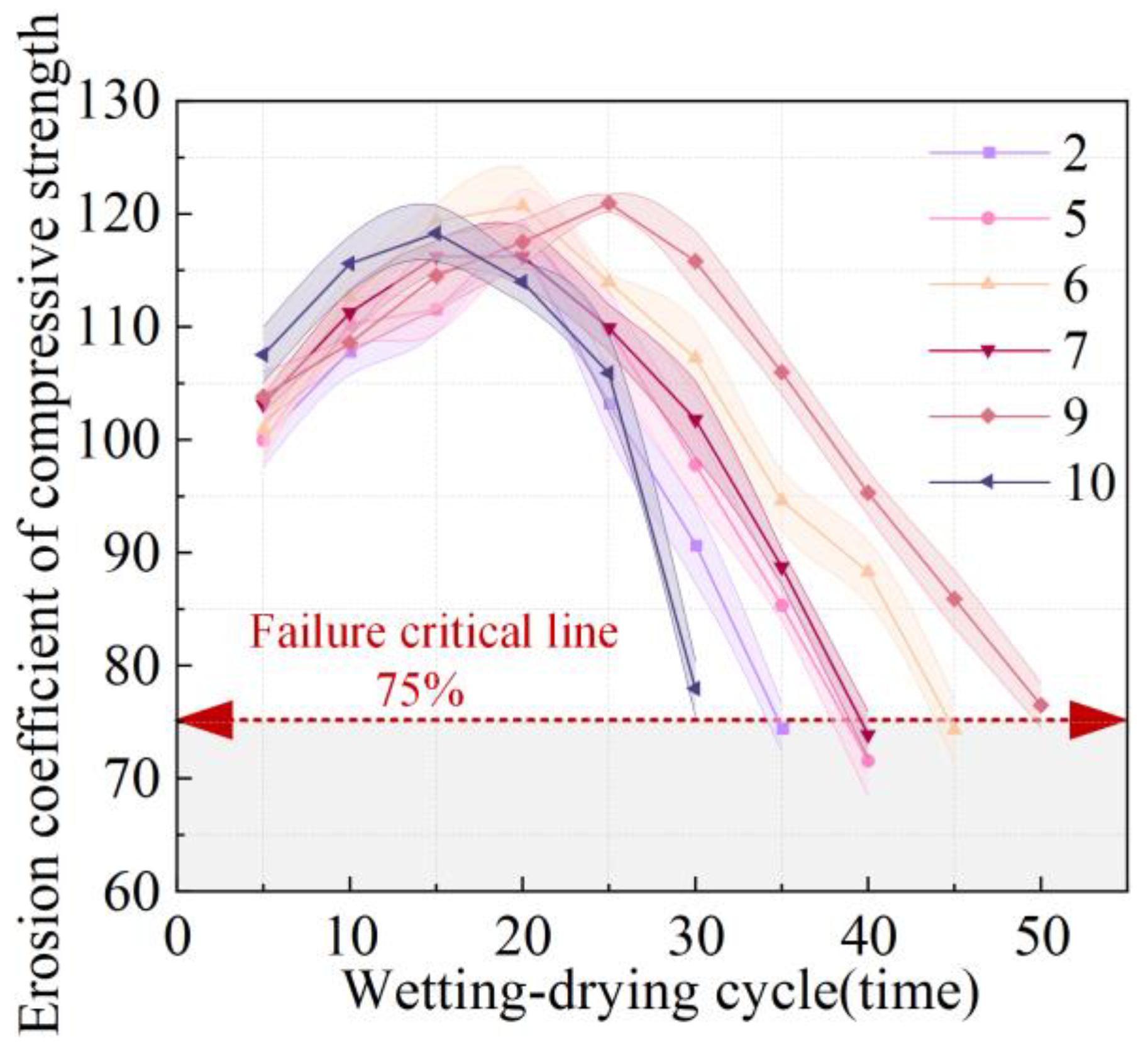
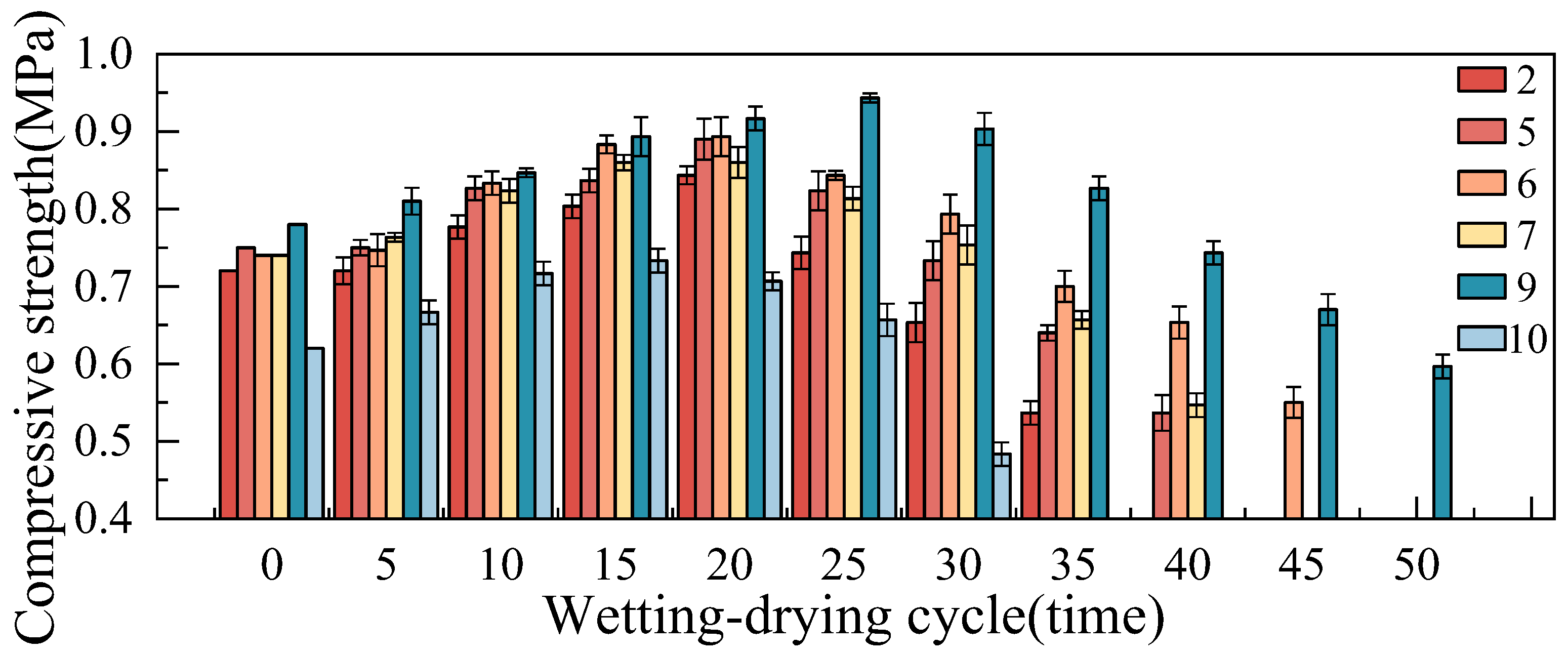
3.3.2. Erosion Coefficient of Compressive Strength
3.4. Microscopic Mechanism Analysis of LCPC
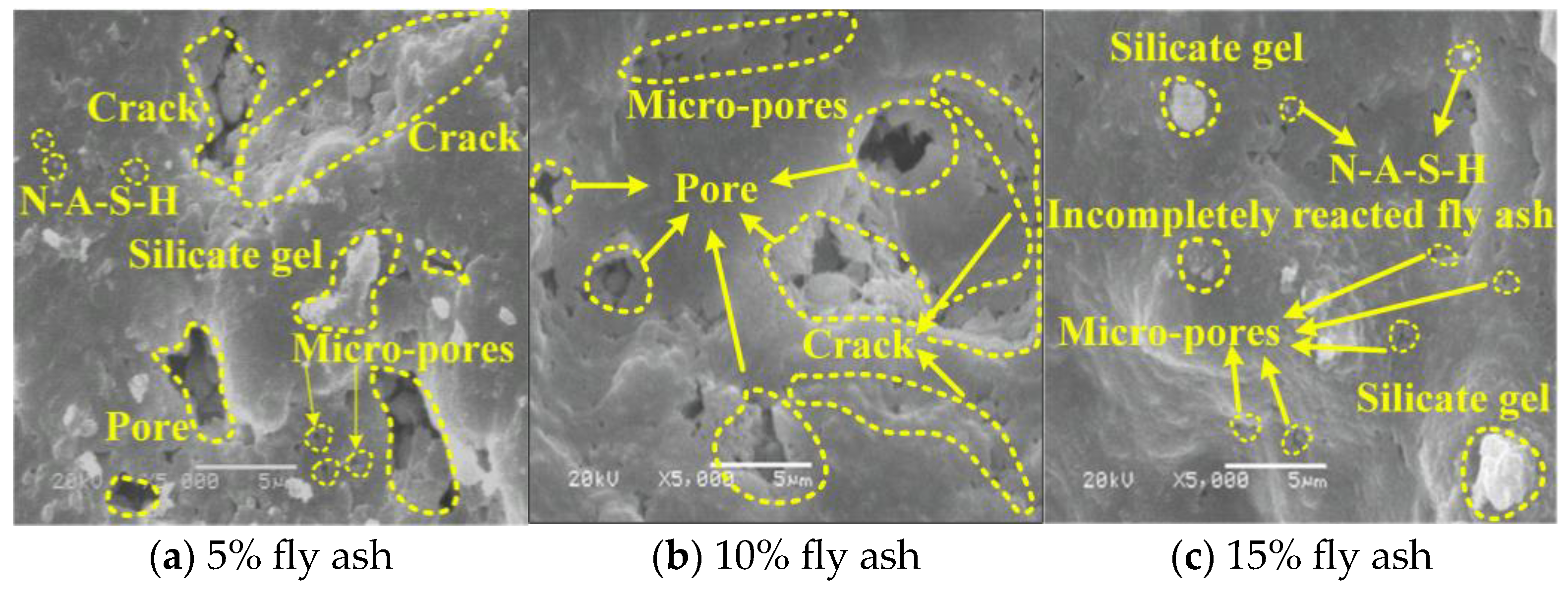
3.4.1. Analysis of Effect of Fly Ash on LCPC Microstructure
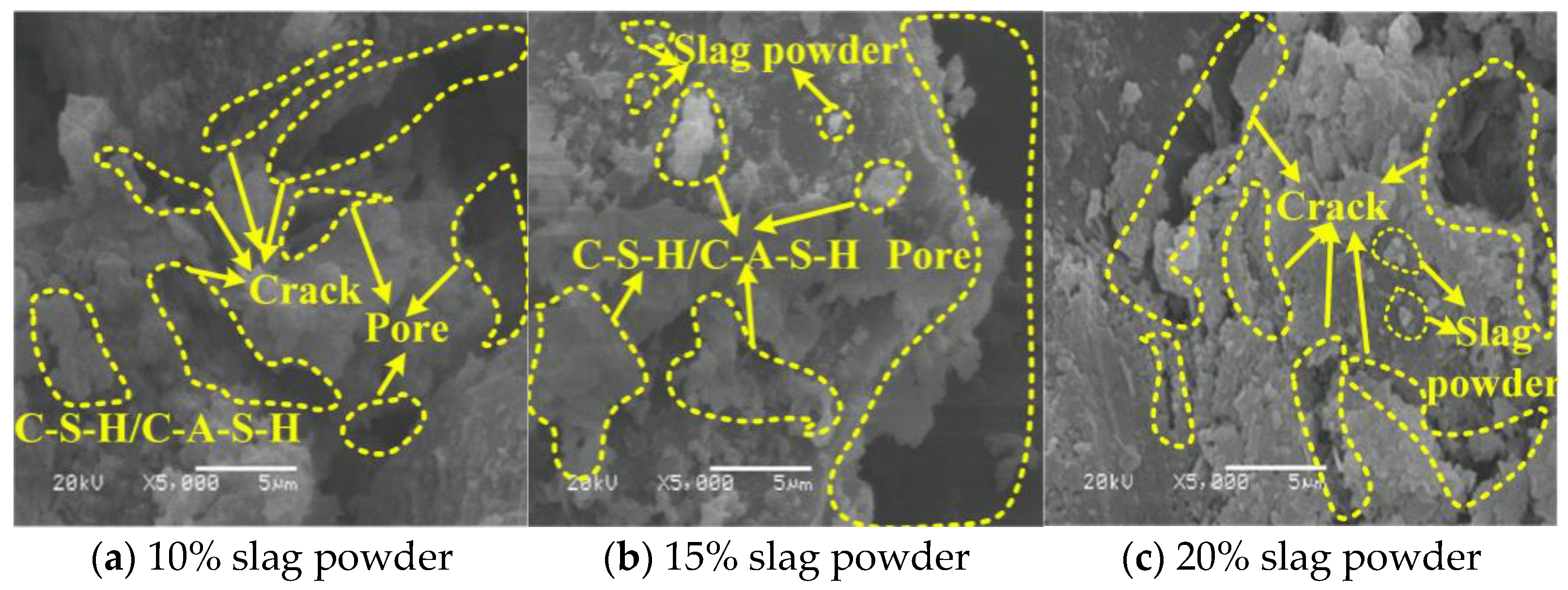
3.4.2. Analysis of the Influence of Slag Powder on LCPC Microstructure
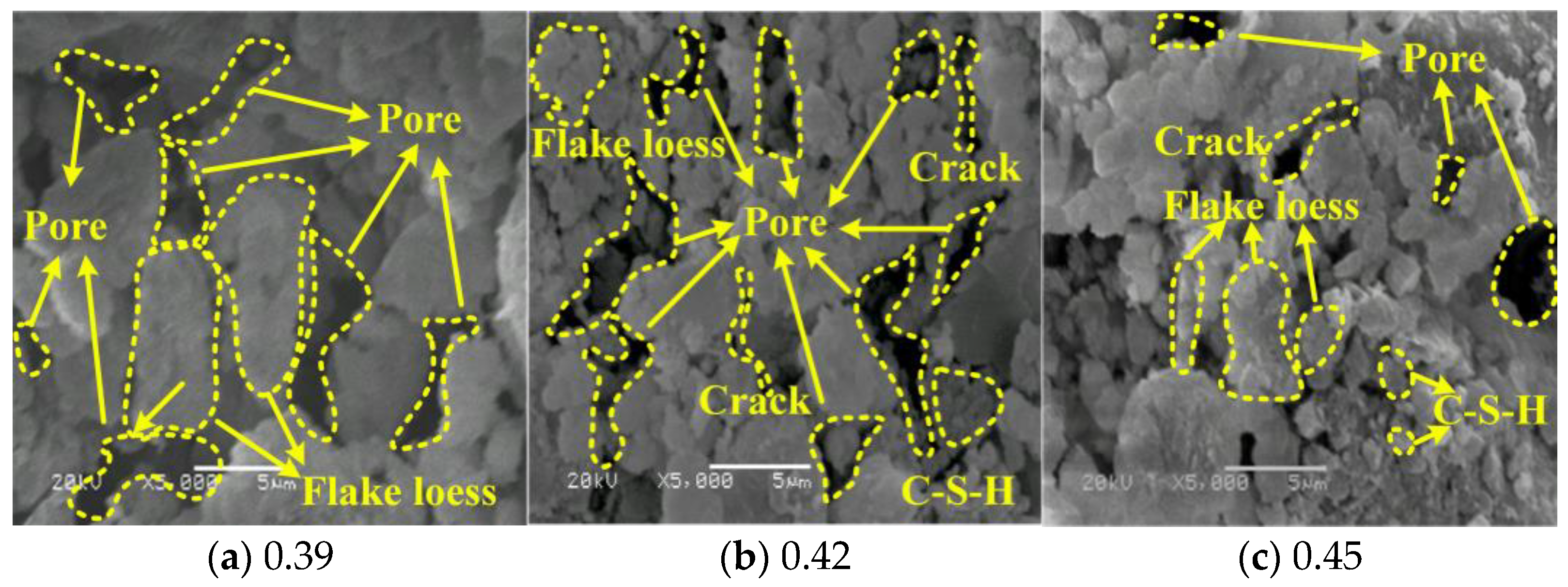
3.4.3. Effect of Water-Cement Ratio on Microstructure of LCPC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, S.; Qiu, H.; Wang, N.; Cui, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, S.; Yang, D.; Cao, M. The influence of loess cave development upon landslides and geomorphologic evolution: A case study from the northwest Loess Plateau, China. Geomorphology 2020, 359, 107167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Ni, W.; Lü, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, H.; Nie, Y. Mechanical properties and microstructure evolution of Malan loess. Quat. Int. 2022, 637, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhari, M.E.; Merroun, O.; Maalouf, C.; Bogard, F.; Kissi, B. Exploring the impact of partial sand replacement with olive waste on mechanical and thermal properties of sustainable concrete. Clean. Mater. 2023, 9, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Zhuge, Y.; Beecham, S. The relationship between porosity and strength for porous concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 4294–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Gong, C.; Wang, S.; Lu, L. Effect of aggregate coating thickness on pore structure features and properties of porous ecological concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 2019, 65, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Park, C.G. Performance evaluation and field application of porous vegetation concrete made with by-product materials for ecological restoration projects. Sustainability 2016, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Z. Review of porous vegetation eco-concrete (PVEC) technology: From engineering requirements to material design. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 279, 111442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barneyback, R.S., Jr.; Diamond, S. Expression and analysis of pore fluids from hardened cement pastes and mortar. Cem. Concr. Res. 1981, 11, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.F.; Mohan, K.; Moir, G.K. Analytical study of pure and extended Portland cement pastes: II, fly ash- and slag-cement pastes. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1985, 68, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Zhan, J.; Dong, B.; Luo, C.; Liu, Q.; Chen, D. Preparation of metal hydroxide microcapsules and the effect on pH value of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Li, F.; Guo, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, M. Research Progress of Eco-Friendly Portland Cement Porous Concrete: A Review. J. Renew. Mater. 2023, 11, 103–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Mohseni, E.; Wang, Z. Development of vegetation concrete technology for slope protection and greening. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 179, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; He, M.; Wu, Y. Mechanical properties and road performance of slag-fly ash geopolymer stabilized sludge. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 41, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhi, B.; Laskar, A.I.; Ahmed, M.A. Investigation on soil–geopolymer with slag, fly ash and their blending. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bakri, A.M.; Kamarudin, H.; Bnhussain, M.; Rafiza, A.; Zarina, Y. Effect of Na2SiO3/NaOH Ratios and NaOH Molarities on Compressive Strength of Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymer. ACI Mater. J. 2012, 109, 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Laskar, A.I.; Bhattacharjee, R. Rheology of Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2011, 108, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein Rafiean, A.; Najafi Kani, E.; Haddad, A. Mechanical and durability properties of poorly graded sandy soil stabilized with activated slag. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04019324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liang, S.; Zhang, F.; Yan, X.; Zhou, J. Feasibility analysis of loess slope improved by lime pile. Landslide Sci. A Safer Geoenviron. 2014, 2, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Zhang, F.; Wu, W.; Liang, S. Physicochemical and index properties of loess stabilized with lime and fly ash piles. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.; Chu, J. Applications of microorganisms to geotechnical engineering for bioclogging and biocementation of soil in situ. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2008, 7, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejong, J.T.; Fritzges, M.B.; Nuesselein, K. Microbially induced cementation to control sand response to undrained shear. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2006, 132, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liang, X.; Xu, L.; Tang, X.Y. Determination on representative element volume of Nanjing silty-fine sand for its spatial pore structure. Rock Soil Mech. 2019, 40, 2723–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Ding, J.; Lu, C.; Jin, Y. Experimental study on wind erosion resistance and strength of sands treated with microbial-induced calcium carbonate precipitation. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 1, 3463298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.J.; Cunningham, A.B.; Gerlach, R.; Hiebert, R.; Hwang, C.; Lomans, B.P.; Westrich, J.; Mantilla, C.; Kirksey, J.; Esposito, R.; et al. Fracture sealing with microbially-induced calcium carbonate precipitation: A field study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4111–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tan, L.; Xiao, N.; Liu, K.; Jia, P.; Zhang, W. The hydro-mechanical characteristics and micro-structure of loess enhanced by microbially induced carbonate precipitation. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2023, 34, 100469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Feng, C.; He, X.; Xu, P. Analysis of the microstructure of microbial solidified sand and engineering residue based on CT scanning. Biogeotechnics 2024, 2, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, V.C. Engineered Cementitious Composites with High-Volume Fly Ash. ACI Mater. J. 2007, 104, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 50082-2009; Standard for Test Methods of Long-Term Performance and Durability of Ordinary Concrete. Architecture Publishing & Media Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Guo, S.; Li, Z.; Fa, W. Scientific management and standardized operation of field emission scanning electron microscopy. Phys. Test. Chem. Anal. (Part A Phys. Test.) 2024, 60, 20–23+28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CJJ/T 253-2016; Technical Specification for Application of Pervious Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Architecture Publishing & Media Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 50081-2019; Standard for Test Methods of Concrete Physical and Mechanical Properties. Architecture Publishing & Media Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Wang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Liu, S.; Yang, L.; Luo, S. Physical filling effect of aggregate micro fines in cement concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 41, 812–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | Others |
| Content/% | 26.1 | 6.3 | 4.0 | 58.2 | 2.1 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 2.4 |
| Compound | Na2O | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | SO3 | K2O | CaO | Fe2O3 | Others |
| Content/% | 0.60 | 0.20 | 28.10 | 59.50 | 0.38 | 0.60 | 1.40 | 5.20 | 4.02 |
| Compound | Na2O | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | SO3 | K2O | CaO | Fe2O3 | Others |
| Content/% | — | 6.21 | 17.60 | 34.2 | — | 0.51 | 34.00 | 1.11 | 6.37 |
| Compound | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | else |
| Content/% | 58.33 | 4.14 | 11.87 | 7.33 | 1.23 | — | 17.10 |
| Groups | Target Porosity | Coal Gangue | Water | Loess | Fly Ash | Slag Powder | Cement | Water Reducer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15% | 24% | 18% | 28.3% | 4.2% | 5.70% | 4.22% | 0.58% |
| 2 | 20% | 22% | 17% | 26.4% | 3.9% | 5.26% | 3.9% | 0.54% |
| 3 | 25% | 21% | 16% | 25.0% | 3.75% | 5.00% | 3.75% | 0.5% |
| Groups | Target Porosity | Coal Gangue | Water | Loess | Fly Ash | Slag Powder | Cement | Water Reducer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25% | 21% | 16% | 28.8% | 1.44% | 2.88% | 4.31% | 0.57% |
| 2 | 25% | 21% | 16% | 27.7% | 1.37% | 4.15% | 4.15% | 0.54% |
| 3 | 25% | 21% | 16% | 26.7% | 1.33% | 5.34% | 4.00% | 0.54% |
| 4 | 25% | 21% | 16% | 27.7% | 2.78% | 2.78% | 4.17% | 0.56% |
| 5 | 25% | 21% | 16% | 26.7% | 2.67% | 4.00% | 4.00% | 0.53% |
| 6 | 25% | 21% | 16% | 25.8% | 2.60% | 5.18% | 3.89% | 0.53% |
| 7 | 25% | 21% | 16% | 26.7% | 4.00% | 2.68% | 4.00% | 0.53% |
| 8 | 25% | 21% | 16% | 25.8% | 3.89% | 3.89% | 3.89% | 0.53% |
| 9 | 25% | 21% | 16% | 25.0% | 3.75% | 5.00% | 3.75% | 0.5% |
| 10 | 25% | 21% | 16% | 32.2% | 0% | 0% | 5.1% | 0.70% |
| Groups | Target Porosity | Water- Cement Ratio | Cement | Water Reducer | Fly Ash | Slag Powder |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25% | 0.39 | 15% | 2.0% | 0% | 0% |
| 2 | 25% | 0.42 | 15% | 2.0% | 0% | 0% |
| 3 | 25% | 0.45 | 15% | 2.0% | 0% | 0% |
| 4 | 25% | 0.42 | 15% | 2.0% | 5% | 0% |
| 5 | 25% | 0.42 | 15% | 2.0% | 10% | 0% |
| 6 | 25% | 0.42 | 15% | 2.0% | 15% | 0% |
| 7 | 25% | 0.42 | 15% | 2.0% | 0% | 10% |
| 8 | 25% | 0.42 | 15% | 2.0% | 0% | 15% |
| 9 | 25% | 0.42 | 15% | 2.0% | 0% | 20% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, M.; Zhang, W.; Ye, S.; Li, X.; Li, J. Durability and Microstructure Analysis of Loess-Based Composite Coal Gangue Porous Vegetation Concrete. Buildings 2025, 15, 2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142531
Qiu M, Zhang W, Ye S, Li X, Li J. Durability and Microstructure Analysis of Loess-Based Composite Coal Gangue Porous Vegetation Concrete. Buildings. 2025; 15(14):2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142531
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Manman, Wuyu Zhang, Shuaihua Ye, Xiaohui Li, and Jingbang Li. 2025. "Durability and Microstructure Analysis of Loess-Based Composite Coal Gangue Porous Vegetation Concrete" Buildings 15, no. 14: 2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142531
APA StyleQiu, M., Zhang, W., Ye, S., Li, X., & Li, J. (2025). Durability and Microstructure Analysis of Loess-Based Composite Coal Gangue Porous Vegetation Concrete. Buildings, 15(14), 2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142531




