Abstract
In recent decades, university dormitories have gradually evolved from traditional residential spaces into educationally meaningful venues that support informal learning. However, limited research has explored how supportive environmental factors within dormitories influence students’ informal learning experiences. This study aims to evaluate key environmental factors that affect students’ satisfaction with informal learning in dormitory settings. Based on a comprehensive literature review, two types of informal learning behaviors—individual and collaborative—were defined, and a multi-dimensional evaluation framework comprising five categories and 26 environmental indicators was established. Field observations and structured questionnaires were employed to assess students’ satisfaction with each environmental factor and their overall informal learning experiences. Quantitative analyses were conducted to examine the relationships between environmental conditions and learning satisfaction. Results show that all five-factor categories—spatial designs, natural environments, physical settings, social aspects, and resources—positively influence informal learning, with resources being the most impactful. While environmental influences on individual and collaborative learning exhibit minor differences, the overall patterns are consistent. Compared to other informal learning spaces on campus, dormitory users place greater emphasis on spatial controllability. This study further demonstrates the cognitive and emotional value of dormitory environments and proposes targeted directions for optimizing them as informal learning spaces.
1. Introduction
In higher education, campus spaces have traditionally been constructed around two educational paradigms—lecture-based and student-centered—commonly aligned with formal and informal learning, respectively [1]. With the advancement of constructivist learning theory in pedagogy and the growing emphasis by universities on cultivating innovative talents, the importance of informal learning has become increasingly prominent. American adult educator Victoria J. Marsick conceptualizes informal learning as a loosely organized form of active learning, inherently linked to the physical environment and social context in which it occurs. Compared to formal and non-formal learning modes, informal learning is voluntary in nature and develops independently of frameworks imposed by external factors such as instructors or institutions [2].
Scholars widely acknowledge informal learning as a powerful complement to formal education [3,4], enabling the development of students’ social adaptability and emotional resilience [5]. Moreover, this form of learning aids in conveying key societal norms and expectations [6,7] and enhances social abilities through interactive and cooperative experiences [8,9]. Therefore, higher education institutions need to deliberately reimagine and optimize campus spaces to support diverse informal learning practices and ensure student success in a sustainable educational context [10,11].
College students spend a significant portion of their time in dormitories. Especially in China, almost all universities adopt a full-time boarding system for undergraduates, making dormitories one of the most frequently used spaces throughout students’ college years. Traditionally, dormitories have been treated merely as a simple living place, often lacking shared spaces for learning and social interaction. However, as the boundaries between living and learning increasingly blur in modern higher education, there is growing recognition that dormitories hold untapped potential as informal learning environments. Over the past decade, educators and designers have begun to shift perceptions, viewing dormitories as integral components of the educational ecosystem—spaces not only for living, but also for fostering social interaction, personal growth, and self-directed learning [12,13,14]. Compared with academic buildings that serve formal teaching functions, dormitories are particularly conducive to informal and non-institutionalized learning activities [15]. Nonetheless, many dormitory environments still reflect industrialized and institutionalized design logic, characterized by monotonous layouts and rigid functional configurations. Such designs often neglect the psychological needs of users and overlook the role of spatial environments in shaping students lived experiences. Existing research has shown that the physical attributes of a learning environment can significantly influence learners’ emotions, leading to important cognitive and behavioral outcomes. Spaces that offer emotional support and cognitive stimulation can effectively enhance students’ perceived experience and behavioral performance [16]. Therefore, this study advocates for a renewed understanding of the role and function of dormitories and proposes exploring targeted design strategies from the user’s perspective to unlock their unique spatial potential in supporting informal learning.
Currently, more and more studies are beginning to focus on the supportive environment design of university dormitories. Worsley et al. explored the impact of the physical and social structure of dormitories on the mental health of British college students and found that providing interactive spaces designed with diverse interactions in mind is beneficial to students’ physical and mental health [17]. Easterbrook and Vignoles found that setting up shared common areas in dormitories can promote interpersonal relationships among students, thereby improving their happiness [18]. Research by Brown et al. shows that the design of dormitory buildings affects students’ participation and their academic performance [19]. Nurul et al. found in their study that diverse space types and service facilities can improve students’ accommodation satisfaction, thus helping them achieve better academic results [20]. Huang et al. found that dormitory environment indirectly affects college students’ mental health through the mediating role of learning engagement, offering empirical support for the broader educational value of residential settings [21]. Ning and Chen constructed a framework for the POE of university dormitories in China to identify and analyze the factors that affect student accommodation satisfaction. They found that the ease of using the amenities in dormitory rooms, dormitory services, and diversified and personalized design are important factors affecting satisfaction [22]. In addition, some studies have also used POE to investigate residents’ satisfaction with student housing facilities [23,24]. While these studies affirm the influence of dormitory environments on health, behavior, and satisfaction, few have explicitly investigated their role in facilitating informal learning. Addressing this gap, this study believes that it is necessary to have a clearer understanding of dormitory environment design factors that can support informal learning behaviors from the students’ perspective, contributing to the creation of more effective and development-oriented residential learning environments.
In summary, this study highlights the prevalence and importance of informal learning in universities, explores the trend of contemporary university dormitories evolving from simple living spaces into living–learning communities, and emphasizes the need to reconceptualize student dormitories as environments that support informal learning. Based on existing literature and identified research gaps, this study aims to answer the following questions:
- Are informal learning experiences affected by the dormitory environment? Are different types of behaviors affected differently?
- Which dormitory environmental factors have the greatest impact on informal learning experiences?
- Are there differences between dormitory environmental factors that influence informal learning experiences and those in other university spaces? If so, in what aspects are these differences reflected?
2. Materials and Methods
This study employed a three-step methodology. First, a comprehensive literature review and field investigation were conducted to inform the development and selection of questionnaire indicators. Second, on-site surveys were distributed to students from three schools to collect data on their satisfaction with informal learning experiences and various environmental factors. Finally, the collected data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics 24.0 software for descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, and priority analysis.
2.1. Case Selection
This study selected five undergraduate dormitories from three universities in Guangdong: Guangzhou International Campus of South China University of Technology (SCUT-GZIC), Beijing Normal University at Zhuhai (BNU Zhuhai), and Shantou University (STU). The case selection was based on four criteria: (1) research convenience—data could be collected without interference; (2) similar geographical location—all sites are in the same climate zone, minimizing unnecessary external climate factors; (3) availability of diverse public activity spaces—each dormitory includes numerous closed and open areas suitable for informal learning; (4) all three universities operate full-time undergraduate boarding systems, ensuring high dormitory usage and familiarity among students.
This study aims to holistically explore how dormitory environmental factors affect students’ informal learning experiences. To this end, it is necessary to obtain extensive data, including various public spaces. The survey covered all furnished public spaces in the selected dormitories, such as semi-outdoor lounge areas, study rooms, and self-service kitchens (Figure 1). For example, at SCUT-GZIC, the two dormitory buildings are connected by a second-floor corridor, with most public activity spaces located on the first and second floors. The study conducted on-site observations and administered questionnaires within these shared areas (Figure 2).

Figure 1.
Diverse public spaces in study cases.
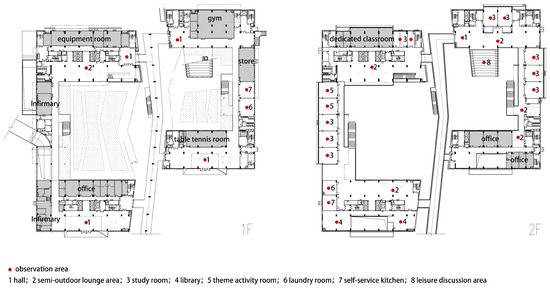
Figure 2.
Floor plan and informal learning areas in the student dormitories at SCUT-GZIC.
2.2. Questionnaire Development
Firstly, this study identified types of informal learning behaviors. Beckers et al. divided informal learning into two basic categories: individual learning necessitating concentrated attention and autonomous regulation, alongside group social collaborative learning dependent on peer interaction dynamics [25]; Guo et al. divided informal learning behaviors into personal public learning, personal private learning, teamwork learning and free and open learning according to the four-quadrant classification method [26]; Cox conceptualizes informal learning as comprising multifaceted engagements, incorporating reading, intense revision, quiet consultations with others, collaborative projects, and peer networking [27]. Chen et al. believe that informal learning behaviors include dialogue, seminars, communication, contemplation, and even rest [28]. Based on these studies, this study combines the characteristics of university student dormitories and divides informal learning behaviors into individual learning and collaborative learning. The specific contents are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The type and contents of informal learning behaviors.
Based on previous research, the environmental factors that affect informal learning behavior are divided into five basic categories: spatial design, natural environment, physical settings, social aspect, and resources [29]. Drawing on relevant studies, 24 environmental factors were identified within these five categories [4,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40]. Additionally, based on field research and expert consultation, two new indicators were added: space theme and community interaction. After screening and integration, a total of 26 environmental indicators were identified (Table 2).

Table 2.
Environmental evaluation indicators for informal learning in dormitories.
Therefore, this study developed a questionnaire to assess students’ satisfaction with their informal learning experiences in dormitory environments. It includes three parts: (1) personal background (gender, grade, and major type); (2) types of informal learning behaviors; (3) satisfaction with the dormitory spatial environment. Satisfaction was measured using a 5-point Likert scale: 1 = strongly dissatisfied; 2 = dissatisfied; 3 = neutral; 4 = satisfied; 5 = strongly satisfied. The items were developed based on the five categories and 26 environmental factors (see Appendix A: “Questionnaire Survey”).
2.3. Data Collection
Data collection was conducted over 18 days in total (in April 2025), with 6 days allocated to each participating university for field observation and questionnaire distribution. Data were collected daily from 9:00 a.m. to 9:00 p.m. Investigators patrolled the public areas of the dormitories every hour to identify student activities and invite those engaged in informal learning to complete questionnaires, thereby ensuring data authenticity and accuracy. With students’ consent, investigators also asked brief follow-up questions regarding their preferences to obtain more comprehensive insights. Participants received a small token of appreciation for completing the questionnaire. A total of 8 graduate students were recruited to assist in data collection. In total, 1502 questionnaires were distributed, and after excluding those with incomplete responses or excessive repeated answers, 1489 valid samples were retained. According to local regulations, this investigation did not require ethical approval.
2.4. Data Analysis
The evaluation was conducted using SPSS Statistics 24.0 based on 27 questionnaire items. The analysis demonstrated excellent internal consistency (Cronbach’s α = 0.940 > 0.90) and superior sampling adequacy (KMO = 0.948 > 0.85). Bartlett’s test of sphericity confirmed strong inter-variable correlations (χ2 = 5823.7, p < 0.001). Principal component analysis with varimax rotation extracted factors meeting Kaiser’s criterion (eigenvalue > 1), with a cumulative explained variance of 73.2%, indicating robust construct validity.
The methodological sequence began with descriptive statistics to profile respondents’ demographic characteristics. Subsequently, bivariate correlation analysis and multivariate linear regression were used to examine inter-variable relationships. Finally, a composite weighting method was used to determine the weights of the 26 indicators. This method integrates multiple influencing factors to enhance the accuracy and objectivity of the weight calculation [41,42]. Specifically, a multi-level indicator weighting approach was adopted, combining the entropy weight method and standardized regression analysis. It assigns weights from two complementary perspectives: the internal information disparity of individual indicators and the explanatory power of each major category with respect to overall satisfaction. All indicator weights were calculated using Formula (1), which produces the final results in a proportionally normalized form.
W′j = (ωij × βi)/[∑j₌1n (ωij × βi)] × 100%
W′j: Normalized composite weight (percentage) of indicator j.
ωij: Normalized entropy weight of indicator j within category i.
βi: Standardized regression coefficient of category i, obtained through regression analysis.
∑j₌1n (ωij × βi): Sum of the intermediate weights across all indicators.
3. Results
3.1. Respondent Characteristics
Table 3 presents the demographic profile of respondents. The gender distribution showed a balanced representation with males (n = 733, 49.2%) and females (n = 756, 50.8%), yielding a gender ratio of 0.97:1. Academic standing analysis revealed junior students constituting the largest cohort (30.4%), followed by sophomores (28.1%), freshmen (25.7%), and seniors (15.8%). Disciplinary distribution indicated predominance of science and engineering disciplines (56.9% of total respondents). Regarding learning behavioral patterns, collaborative learning emerged as the predominant mode (54.5% participation rate), surpassing individual learning engagement (45.5%).

Table 3.
Demographic and behavioral characteristics of respondents.
3.2. Correlation Analysis and Linear Regression Analysis Results
A preliminary Pearson correlation analysis was conducted using SPSS to examine the bivariate relationships between students’ satisfaction with informal learning experience and the five-factor categories. As shown in Table 4, each factor category exhibited a statistically significant positive correlation with satisfaction (r = 0.291 to 0.603, p < 0.05).

Table 4.
Pearson correlation between satisfaction and dormitory environmental factor categories.
A multivariate linear regression analysis was conducted using SPSS to quantify the influence of environmental factors on students’ satisfaction with informal learning experiences. The model showed substantial explanatory power (R2 = 0.507), accounting for 50.7% of the variance in satisfaction levels. Model significance was confirmed by an F-test (F = 305.036, p < 0.001), indicating strong statistical validity. As detailed in Table 5, all five-factor categories had significant predictive effects: spatial designs (beta = 0.124, p < 0.05), natural environments (beta = 0.235, p < 0.05), physical settings (beta = 0.197, p < 0.05), social aspects (beta = 0.041, p < 0.05), and resources (beta = 0.311, p < 0.05). Among them, the standardized beta coefficients indicated that resources were the most influential predictor, followed by natural environments and physical settings, in order to decrease the effect size.

Table 5.
Regression results of the factor categories.
To investigate the differential environmental impacts on distinct learning types, this study employed multivariate linear regression to examine associations between two learning behaviors (individual and collaborative learning) and the five-factor categories. As shown in Table 6, both learning types exhibited comparable regression patterns across the five-factor categories. Specifically, resources emerged as the predominant predictor for both individual learning (beta = 0.298) and collaborative learning (beta = 0.318), while social aspects demonstrated minimal predictive power across both modalities (individual: beta = 0.063; collaborative: beta = 0.043). The regression models revealed that collaborative learning exhibited greater environmental sensitivity (R2 = 0.589) than individual learning (R2 = 0.468). In comparison, spatial designs and physical settings exhibited greater effect sizes in the individual learning model, whereas natural environments showed stronger influence in the collaborative learning model.

Table 6.
Standardized regression coefficients for informal learning behaviors and environmental factor categories.
3.3. Weight Calculation Results
Table 7 delineates the weight distribution of 26 environmental indicators across the five-factor categories. The results demonstrate that indicators under the resources category received the highest weights, including power sockets (8.41%), wireless network (6.70%), food and beverage access (6.28%), availability of shared learning equipment (5.69%), and availability of reading materials (5.11%). Notable indicators from the spatial designs category included acoustic environment (4.63%) and furniture configuration (4.61%), followed by opening hours (4.28%) from the physical settings category. In contrast, community interaction (0.58%) and external interaction (0.53%) had the lowest weights in the assessment framework.

Table 7.
Composite weights of the 26 environmental factors.
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion on the Relationship Between Environment and Behavior
4.1.1. Discussion on Spatial Designs
The results indicate that the spatial design is a key environmental factor affecting students’ informal learning experiences, especially for individual learning, which typically involves focused, self-directed cognitive processes requiring a quiet, comfortable, and personalized setting [43].
Among the nine indicators of spatial design, the acoustic environment held the highest weight. This aligns with findings from numerous university-based studies, which have demonstrated that noise levels significantly affect learning outcomes. Un-pleasant sensory stimuli, such as sudden or intrusive noise, tend to disrupt concentration and reduce learning motivation [44,45,46]. Furniture configuration also received a relatively high weight. Observations indicated that students preferred sofas or chairs with backrests, which improve physical comfort and support prolonged study sessions. Previous studies have similarly noted that providing comfortable and personalized furniture can offer emotional value, reduce stress, and improve students’ productivity and cognitive performance [47,48]. Additionally, spatial flexibility was highly rated. Consistent with earlier research, students favored environments where layouts or furniture could be adjusted according to personal needs. Such adaptable spaces enhance one’s sense of control over the environment, encouraging both cognitive engagement and emotional responsiveness, thereby supporting attention and creativity [49].
Based on these findings, it is recommended that future dormitory design strategies pay greater attention to providing diverse, movable furniture and multifunctional partitions (e.g., bookshelves and green walls) within public learning spaces. This would allow students to rearrange their learning areas, control levels of noise and privacy, and select furniture types that best support their preferred learning style—ultimately enabling them to create a personalized and effective informal learning environment.
4.1.2. Discussion on Natural Environments
The results show that the natural environments significantly influence students’ informal learning, with a stronger effect on collaborative learning. Collaborative learning involves communication, coordination, and negotiation, all of which benefit from a comfortable natural environment and access to greenery that helps reduce social tension and promote positive social behavior [50].
Among the evaluated indicators, thermal comfort held the highest weight, followed by natural lighting and access to greenery. These factors influence not only physiological well-being but also sustained cognitive functioning. For example, appropriate indoor temperatures help reduce stress responses and support prolonged focus [51], while natural daylight enhances alertness, emotional stability, and circadian balance [52]. Although greenery emerged as a significant factor, many current dormitory settings still lack meaningful biophilic features—limiting their potential to foster psychological restoration and mental ease. Studies have demonstrated that biophilic environments—rich in natural elements and patterns—can improve attention, reduce stress, and create a sense of safety and coherence within the space [53,54,55,56]. Introducing such features could further enhance the dormitory’s capacity to support restorative and engaging learning experiences.
To achieve this, future design strategies should combine passive and active approaches—such as insulation optimization, operable windows, dynamic shading systems, and biophilic interventions like indoor vegetation and natural textures—to foster comfort, cognitive clarity, and a balanced sensory atmosphere.
4.1.3. Discussion on Physical Settings
The findings confirm that physical settings significantly influence students’ informal learning experiences, with a notably stronger effect on individual learning. This may be attributed to the nature of individual learning, which often involves prolonged periods of sustained attention, self-regulation, and low-stimulus environments [57]. In contrast, collaborative learning tends to be more episodic, task-oriented, and socially dynamic, allowing students to adapt more flexibly to fluctuations in the physical environment [58].
Among the physical settings indicators, opening hours, facility management, and advance reservation received the highest weights—consistent with prior research [59]. When learners are able to anticipate access and control their study schedules, it reduces the cognitive load associated with uncertainty and increases intrinsic motivation. Cleanliness and effective maintenance of shared facilities further shape a sense of environmental trust and safety, which are essential psychological conditions for sustained engagement. Students who feel confident about the functionality and order of their surroundings are more likely to use the space consistently and deeply engage in their learning tasks.
Based on these insights, dormitory design should extend access hours—ideally to 24/7—and implement reservation systems for high-demand spaces to reduce conflicts. Maintaining a clean and orderly environment through regular cleaning and timely facility upkeep is essential. Efficient repair and feedback mechanisms can further enhance usability and satisfaction, contributing to a more supportive and reliable informal learning environment.
4.1.4. Discussion on Social Aspects
The analysis indicates that social aspects exert a relatively limited influence on students’ informal learning experiences within dormitories. Observations and interviews suggest that many students choose dormitory-based learning precisely because these spaces offer familiarity, privacy, and minimal distractions. As a result, community interaction is often not a primary consideration, with students focusing more on the spatial and environmental qualities of the space. Additionally, the indicator opportunities for external interaction, which reflects the openness and permeability of dormitory spaces to surrounding environments, was generally perceived as insignificant. Students reported that when seeking to expand their social networks, they prefer more public or neutral venues—such as libraries or student centers—over semi-private dormitory settings.
These findings suggest that while students are generally satisfied with the social atmosphere in their dormitories, social aspects are not a major determinant of informal learning engagement. This may reflect a spatial–functional separation between learning and socializing in student behavior: learners tend to associate dormitories with personal or academic activities, and seek social interaction elsewhere.
4.1.5. Discussion on Resources
The study results show that resources are the most influential environmental category affecting students’ informal learning experiences, with power sockets and wireless network identified as the most important indicators. In modern learning contexts, laptops, tablets, and smartphones are essential tools for both formal and informal learning [60,61]. Sustained informal learning often relies on the availability of power and stable internet access. Many students reported that accessible power outlets and reliable connectivity were primary factors in selecting a learning space. Access to food and drinks was also a significant factor. Observations revealed that many students preferred eating in the dormitory common areas rather than the cafeteria. Prior studies have shown that food and beverage availability increase dwell time and support social engagement [39,62]. In addition, such provisions are crucial for maintaining energy levels and reducing cognitive fatigue during extended learning sessions. Furthermore, the presence of shared learning equipment (e.g., printers and projectors) and reading materials (e.g., books and newspapers) also contributes to a more effective informal learning environment by supporting a variety of learning activities and improving efficiency.
Based on these findings, dormitory spaces should be equipped with abundant power outlets and robust network infrastructure. Designers should consider permitting or providing food and beverage services in designated areas, offering amenities such as microwaves, and increasing the availability of learning-related resources to better support diverse informal learning needs.
4.2. Discussion on the Differences Between Dormitories and Campus Places
As demonstrated in the previous analysis, environmental factors in dormitory public areas significantly influence students’ informal learning experiences. To better understand these factors and assess their relative importance, it is useful to compare dormitories with other typical informal learning spaces on campus. While prior studies have mainly focused on learning centers, libraries, and coffee shops, this section combines previous findings with results from the current study to identify key similarities and differences in how these spaces support informal learning.
Table 8 summarizes the primary environmental factors shaping informal learning across four campus space types. Some elements—such as access to power sockets, wireless network, and shared learning equipment—consistently enhance learning convenience and efficiency. Similarly, aspects of spatial design, including acoustic environment, furniture configuration, and spatial flexibility, are widely recognized as essential for fostering supportive informal learning environments.

Table 8.
Environmental factors affecting informal learning experiences in different campus places.
However, noticeable differences also exist. Students in learning centers, libraries, and coffee shops generally place high value on natural environmental qualities—such as thermal comfort, air quality, and natural lighting—which are known to enhance focus, comfort, and cognitive engagement. In contrast, spatial openness is particularly emphasized in learning centers and libraries, where open layouts help facilitate visibility, circulation, and interaction, thereby enhancing motivation.
In contrast, coffee shops and dormitories, which serve both living and social functions, tend to offer greater familiarity and belonging. Students in these spaces prioritize autonomy over openness and focus on the ability to use the space freely and comfortably. Consequently, opening hours become a critical factor, reflecting the need for flexible, self-paced learning in familiar environments.
These findings suggest that although university dormitories share several environmental priorities with other informal learning spaces, they emphasize controllability to a greater degree. This includes ready access to essential resources, adaptable spatial configurations, low-noise conditions, and unrestricted use over time. These findings can be further interpreted through the lens of environmental psychology. Existing studies have shown that environmental controllability enhances individuals’ perceived agency and psychological safety, thereby fostering positive emotional states, stronger self-efficacy, and improved cognitive performance [66,67]. Compared with other informal learning spaces on campus, dormitories exhibit a hybrid nature—being both private and communal—and are used with high frequency. This dual functionality and prolonged occupancy heighten students’ sensitivity to both the supportive and restrictive features of their environment. When dormitory spaces enable behavioral self-regulation and spatial autonomy, they not only enhance students’ learning engagement but also reinforce place attachment and mental well-being. Therefore, future dormitory design should move beyond standardized, institutionalized models and instead create environments that are both controllable and emotion-ally resonant—such as ensuring an ample supply of power sockets and high-speed wireless networks, introducing reconfigurable furniture and movable partitions to accommodate diverse learning needs, applying acoustic zoning and intelligent noise reduction systems to maintain quietness, and offering extended or 24 h access to shared learning spaces to support flexible and self-paced use.
5. Conclusions
5.1. Main Conclusions
This study investigates the relationship between environmental factors in university dormitories and students’ informal learning experiences. Based on a questionnaire survey conducted across three universities and analyzed through rigorous quantitative methods, the following key findings are identified:
Firstly, all five categories of environmental factors—spatial designs, natural environments, physical settings, social aspects, and resources—exert statistically significant impacts on students’ informal learning satisfaction, though with differing levels of influence.
Secondly, among all indicators, resource-related factors—including power sockets, wireless network, and shared learning equipment—are found to be the most influential. Other high-weight indicators include acoustic environment, furniture configuration, opening hours, and spatial flexibility.
Thirdly, while individual and collaborative learning behaviors exhibit slight differences in environmental preferences, the overall influence patterns are largely consistent, suggesting that a well-designed dormitory environment can accommodate diverse informal learning needs.
Lastly, compared with other informal learning spaces on campus such as learning centers, libraries, and coffee shops, dormitories place greater emphasis on environmental controllability—such as privacy, accessibility, and flexibility—making them particularly suitable for personalized, sustained, and self-directed learning.
5.2. Implications for Dormitory Design and Planning
Based on our analysis of the results, we find that these effects are primarily driven by how spatial features support users’ psychological needs, such as autonomy, comfort, and cognitive stimulation. Environments that allow personal control, offer emotional and physical comfort, and provide appropriate levels of sensory engagement are more likely to enhance students’ satisfaction with informal learning. Accordingly, this study identifies three key directions for optimizing dormitory environments:
- 1.
- Controllability-Oriented Design
Dormitory spaces should offer students meaningful control over their environment. This includes spatial personalization, sensory regulation, and temporal flexibility. Rather than simply extending opening hours or adding adjustable furniture, design strategies could incorporate dynamic partitioning systems, light-modulation panels, or user-controlled microclimate zones. These affordances empower students to align space with cognitive tasks and emotional readiness, encouraging deeper learning engagement.
- 2.
- Comfort-Centered Design
Comfort in dormitory settings is not only physical but also psychological. Environments that offer emotional warmth, perceptual clarity, and low sensory stress are more conducive to focused learning. Designers might consider the use of psychologically appealing materials (e.g., textured surfaces and biophilic accents), spatial proportions that reduce crowding, and multisensory cues that enhance familiarity and security—thus reducing cognitive load and promoting task immersion. Additionally, introducing fractal patterns, organic forms, and naturalistic color palettes can enrich visual coherence and stimulate parasympathetic response, reinforcing the restorative and mood-regulating qualities of the space.
- 3.
- Stimulation-Rich Design
Beyond minimal functionality, spaces should stimulate curiosity and support diverse learning rhythms. Dormitory public spaces may incorporate layered visual perspectives, ambient learning displays, modular walls that double as writable surfaces, or shared zones designed for active experimentation. These elements encourage exploration, interdisciplinary dialogue, and social learning outside the classroom.
By shifting design thinking from a component-based improvement model toward an experience-centered framework, future dormitories can evolve into emotionally resonant, cognitively supportive ecosystems that cultivate informal learning as an everyday practice.
6. Limitations and Further Research
This study advances understanding of how dormitory environments influence students’ informal learning experiences. However, due to its broad scope, it was difficult to collect detailed data on the intensity and frequency of specific learning behaviors, limiting fine-grained analysis. Future research can build upon this foundation in the following three directions:
Firstly, narrowing the research focus to a single space type—such as semi-open communal floors or study lounges—would allow for more precise measurement of environmental impacts. Combining this with automated data collection tools, including video tracking or heat maps, could generate quantifiable evidence on behavior patterns. Additionally, future studies may incorporate physiological or neurological indicators to better capture students’ emotional and cognitive responses.
Secondly, while this study centered on student perspectives, future work should also consider other key stakeholders in dormitory environments, such as faculty and administrative staff. Their experiences, expectations, and interactions with dormitory spaces could be explored through interviews, focus groups, or structured surveys to develop a more inclusive understanding.
Thirdly, comparative studies across institutions in different climatic, cultural, or socioeconomic contexts would help test the generalizability of the findings and identify location-specific strategies for enhancing dormitory learning environments.
Continued research along these lines can deepen the theoretical and practical understanding of dormitory design, supporting the creation of more adaptable, inclusive, and pedagogically supportive living–learning spaces in higher education.
Author Contributions
W.H.: validation, resources, methodology, formal analysis, software, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, visualization. N.Z.: validation, resources, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by China Association of Higher Education, grant number 24SZ0203, entitled “Ideals and Beliefs Education for Top Innovative Talents in Chinese Universities”.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Questionnaire Survey on Dormitory Space Satisfaction
Dear Participant,
We are the research team conducting the User-Centered Informal Learning Experience in Dormitory Environments study. This survey aims to comprehensively evaluate your satisfaction with dormitory learning spaces from a user experience perspective, thereby providing evidence-based insights for optimizing student residential environments.
This survey is conducted anonymously. The questionnaire information you filled in is only for academic research and will be kept strictly confidential. Your candid responses are invaluable to this scholarly investigation. Thank you for your participation.
- [single choice] Your gender is
☐ male
☐ female
- 2.
- [single choice] Your grade is
☐ Y1
☐ Y2
☐ Y3
☐ Y4
- 3.
- [single choice] Subject of your major:
☐ science and engineering disciplines
☐ humanities and social sciences
☐ arts and design disciplines
- 4.
- [single choice] The behavior you are performing is
☐ individual learning
☐ collaborative learning
- 5.
- Your satisfaction with the following environmental factors of the space in dormitory is
| Evaluation Dimension | Evaluation Factor | Your Comments | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Spatial design | Lighting quality | |||||
| Interior decoration | ||||||
| Use of color | ||||||
| Spatial scale | ||||||
| Acoustic environment | ||||||
| Spatial flexibility | ||||||
| Furniture configuration | ||||||
| Spatial complexity | ||||||
| Space theme | ||||||
| Natural environment | Natural Lighting | |||||
| Thermal comfort | ||||||
| Access to greenery | ||||||
| Air quality | ||||||
| Physical settings | Advance reservation | |||||
| Opening hours | ||||||
| Facility management | ||||||
| Proximity and accessibility | ||||||
| Private usability | ||||||
| Safety and security | ||||||
| Social aspect | External interaction | |||||
| Community interaction | ||||||
| Resources | Food and beverage access | |||||
| Power sockets | ||||||
| Wireless network | ||||||
| Availability of reading materials | ||||||
| Availability of shared learning equipment | ||||||
- 6.
- [single choice] Your overall satisfaction with the space of the dormitory is:
☐ very dissatisfied
☐ somewhat dissatisfied
☐ neither satisfied nor dissatisfied
☐ somewhat satisfied
☐ very satisfied
References
- Wu, X.; Oldfield, P.; Heath, T. Spatial Openness and Student Activities in an Atrium: A Parametric Evaluation of a Social Informal Learning Environment. Build. Environ. 2020, 182, 107141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, N.; Siol, A.; Eilks, I. The Potential of Non-Formal Laboratory Environments for Innovating the Chemistry Curriculum and Promoting Secondary School Level Students Education for Sustainability. Sustainability 2015, 7, 1798–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaste, A.-A.; Beilmann, M.; Pirk, R. Non-Formal and Informal Learning as Citizenship Education: The Views of Young People and Youth Policymakers. J. Appl. Youth Stud. 2022, 5, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, M.; Godemann, J.; Rieckmann, M.; Stoltenberg, U. Developing Key Competencies for Sustainable Development in Higher Education. Int. J. Sustain. High Educ. 2007, 8, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaukko, M.; Wilkinson, J. “Learning How to Go on”: Refugee Students and Informal Learning Practices. Int. J. Incl. Educ. 2020, 24, 1175–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldock, J.; Rowlett, P.; Cornock, C.; Robinson, M.; Bartholomew, H. The Role of Informal Learning Spaces in Enhancing Student Engagement with Mathematical Sciences. Int. J. Math. Educ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 48, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayçiçek, B. Integration of Critical Thinking into Curriculum: Perspectives of Prospective Teachers. Think. Ski. Creat. 2021, 41, 100895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, D.; Lee, S.-S.; Lim, K.Y.T. Authenticity in Learning for the Twenty-First Century: Bridging the Formal and the Informal. Educ. Tech. Res. Dev. 2012, 60, 1071–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Läänemets, U.; Kalamees-Ruubel, K.; Kiilu, K.; Sepp, A. CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT CONSIDERING FORMAL, NON-FORMAL AND INFORMAL EDUCATION. Soc. Integr. Educ. Proc. Int. Sci. Conf. 2018, 2, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, K.E.; Andrews, V.; Adams, P. Social Learning Spaces and Student Engagement. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2011, 30, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, R.; van der Voordt, T.; Dewulf, G. Learning Space Preferences of Higher Education Students. Build. Environ. 2016, 104, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark Holton A place for sharing: The emotional geographies of peer-sharing in UK University halls of residences. Emot. Space Soc. 2017, 22, 4–12. [CrossRef]
- Tajbakhsh, G.; Riahi, S. Investigating the Quality of Life of Students Living in the Student Dormitory of Razi University of Kermanshah and Its Relationship with Their Academic Performance. Sociol. Educ. 2016, 2, 61–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, M. The House System: Evaluating Its Role in the Experience of Business Students. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2017, 54, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, J. Home Experiences in Student Housing: About Institutional Character and Temporary Homes. J. Youth Stud. 2007, 10, 577–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ken, A. Chapter 6: Graetz The Psychology of Learning Environments. In Learning Spaces; Diana, G.O., Ed.; Educause: Nashville, TN, USA, 2006; pp. 74–86. [Google Scholar]
- Worsley, J.D.; Harrison, P.; Corcoran, R. Accommodation Environments and Student Mental Health in the UK: The Role of Relational Spaces. J. Ment. Health 2023, 32, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterbrook, M.J.; Vignoles, V.L. When Friendship Formation Goes down the Toilet: Design Features of Shared Accommodation Influence Interpersonal Bonds and Well-Being. Br. J. Soc. Psychol. 2015, 54, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Volk, F.; Spratto, E.M. The Hidden Structure: The Influence of Residence Hall Design on Academic Outcomes. J. Stud. Aff. Res. Pract. 2019, 56, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najib, N.U.M.; Yusof, N.A.; Sani, N.M. The Effects of Students’ Socio-Physical Backgrounds onto Satisfaction with Student Housing Facilities. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 62, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, W.; Zeng, M.; Zheng, Z. Dormitory environment, learning engagement, and college students’ mental health: An empirical study of survey data from 45 universities in China. J. Green Build. 2024, 19, 261–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Chen, J. Improving Residential Satisfaction of University Dormitories through Post-Occupancy Evaluation in China: A Socio-Technical System Approach. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, H.H.; Mohammed, M.A.; Kanu, R. A Post-Occupancy Performance Evaluation Study on User Satisfaction with University Student Housing Facilities. Facilities 2024, 43, 54–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najib, N.U.M.; Yusof, N.A.; Osman, Z. Measuring Satisfaction with Student Housing Facilities. Am. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2011, 4, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, R.; van der Voordt, T.; Dewulf, G. Why Do They Study There? Diary Research into Students’ Learning Space Choices in Higher Education. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2016, 35, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wang, L.; Caneparo, L. Research on the Factors That Influence and Improve the Quality of Informal Learning Spaces (ILS) in University Campus. Buildings 2024, 14, 3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, A.M. Space and Embodiment in Informal Learning. High. Educ. 2018, 75, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Zou, Y.; Dong, W.; Zhou, X. Optimal Design and Verification of Informal Learning Spaces (ILS) in Chinese Universities Based on Visual Perception Analysis. Buildings 2022, 12, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, S.A.; Alzamil, W.; Ajlan, A.; Azmi, A.; Ismail, S. Typology of Informal Learning Spaces (ILS) in Sustainable Academic Education: A Systematic Literature Review in Architecture and Urban Planning. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Ansari, A.N.; Khawaja, S.; Bhutta, S.M. Research Café: An Informal Learning Space to Promote Research Learning Experiences of Graduate Students in a Private University of Pakistan. Stud. Grad. Postdr. Educ. 2023, 14, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrop, D.; Turpin, B. A Study Exploring Learners’ Informal Learning Space Behaviors, Attitudes, and Preferences. New Rev. Acad. Librariansh. 2013, 19, 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Liao, J.; Ahn, A.C. Scientometric Review of Informal Learning Spaces in University Libraries: A Bibliometric Approach to Design and Trends. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfy, M.W.; Kamel, S.; Hassan, D.K.; Ezzeldin, M. Academic Libraries as Informal Learning Spaces in Architectural Educational Environment. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shi, H.; Pan, W.; Sun, D. Characterizing the Supportive Environment of Informal Spaces on Cold Region University Campuses to Enhance Social Interaction Behavior. Buildings 2024, 14, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.; Cox, A. Learning over Tea! Studying in Informal Learning Spaces. New Libr. World 2014, 115, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, O.K.T.; Chin, D.C.W.; Hsu, C.H.C. Understanding and Planning for Informal Learning Space Development: A Case Study in Hong Kong. Cogent Educ. 2023, 10, 2180863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzamil, W.; Salih, S.A.; Ismail, S.; Ajlan, A.; Azmi, A. Factors Affecting Social Learning in Nearby Pockets on Tropical Campus Grounds: Towards a Sustainable Campus. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Fadzil, N.H. Informal Setting for Learning on Campus: Usage and Preference. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 105, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramu, V.; Taib, N.; Massoomeh, H.M. Informal Academic Learning Space Preferences of Tertiary Education Learners. J. Facil. Manag. 2021, 20, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.; Birdwell, T.; Basdogan, M. Exploring Efficiencies of Informal Learning Space: A Case Study. J. Appl. Res. High. Educ. 2024, 16, 1986–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, P.; Yin, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Li, L.; Wu, D.; Li, J.; Ding, D. Evaluation of Social Stability Risk of Adjusting Goods Vehicle Calculation Method Based on Optimal Combination Weighting—Cloud Model. Sustainability 2022, 14, 17057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X. Evaluation of Urban Public Building Renovation Potential Based on Combination Weight Cloud Model—Case Study in China. Buildings 2024, 14, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Wei, W.; Fan, W.; Jin, S.; Liu, Y. Student Experience and Satisfaction in Academic Libraries: A Comparative Study among Three Universities in Wuhan. Buildings 2022, 12, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.I.; Jeon, J.Y. Influence of Indoor Soundscape Perception Based on Audiovisual Contents on Work-Related Quality with Preference and Perceived Productivity in Open-Plan Offices. Build. Environ. 2022, 208, 108598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Kim, Y.; Yang, E. Indoor Environment and Student Productivity for Individual and Collaborative Work in Learning Commons: A Case Study. Libr. Manag. 2021, 43, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, I.; Mayoral, A.M.; Navarro Pedreño, J.; Maiques, S. Acoustic Comfort in Learning Spaces: Moving Towards Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.K.; Jahin, M.A.; Rafiquzzaman, M.; Mridha, M.F. Ergonomic Design of Computer Laboratory Furniture: Mismatch Analysis Utilizing Anthropometric Data of University Students. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageb Fewella, L. The Behavioral Smart Furniture and Its Relevance to Family Emotional Dynamics. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 103030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliri Dizaj, M.; Hatami Khanghahi, T. Students’ Residential Preferences: A Case Study Is Dormitories of University of Mohaghegh Ardabili. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2022, 21, 1348–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sullivan, W.C. Impact of Views to School Landscapes on Recovery from Stress and Mental Fatigue. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 148, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, A.M.; de Paula Xavier, A.A.; Broday, E.E. Evaluating the Connection between Thermal Comfort and Productivity in Buildings: A Systematic Literature Review. Buildings 2021, 11, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foellmer, J.; Kistemann, T.; Anthonj, C. Academic Greenspace and Well-Being—Can Campus Landscape Be Therapeutic? Evidence from a German University. Wellbeing Space Soc. 2021, 2, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jin, J.; Liang, Y. The Impact of Green Space on University Students’ Mental Health: The Mediating Roles of Solitude Competence and Perceptual Restoration. Sustainability 2024, 16, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.P. The Potential of Biophilic Fractal Designs to Promote Health and Performance: A Review of Experiments and Applications. Sustainability 2021, 13, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzman, D.; Meletaki, V.; Bobrow, I.; Weinberger, A.; Jivraj, R.F.; Green, A.; Chatterjee, A. Natural Beauty and Human Potential: Examining Aesthetic, Cognitive, and Emotional States in Natural, Biophilic, and Control Environments. J. Environ. Psychol. 2025, 104, 102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann, S.; Justin, H. Cognitive Architecture: Designing for How We Respond to the Built Environment, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 136–145. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, B.J. Becoming a Self-Regulated Learner: An Overview. Theory Pract. 2002, 41, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. A Historical Review of Collaborative Learning and Cooperative Learning. TechTrends 2023, 67, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtonen, T.; Leppänen, U.; Hyypiä, M.; Kokko, A.; Manninen, J.; Vartiainen, H.; Sointu, E.; Hirsto, L. Learning Environments Preferred by University Students: A Shift toward Informal and Flexible Learning Environments. Learn. Environ. Res. 2021, 24, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.-T.; Chang, K.-E.; Liu, T.-C. The Effects of Integrating Mobile Devices with Teaching and Learning on Students’ Learning Performance: A Meta-Analysis and Research Synthesis. Comput. Educ. 2016, 94, 252–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, L. Exploring Smartphone Usage as an ICT Tool among College Students of Chaturbhujeshwar Janata Multiple Campus. Chaturbhujeshwar Acad. J. 2023, 1, 16–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, L.; Clemons, S.; Banning, J.; McKelfresh, D. The Library as Place. New Libr. World 2007, 108, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Kou, Z.; Oldfield, P.; Heath, T.; Borsi, K. Informal Learning Spaces in Higher Education: Student Preferences and Activities. Buildings 2021, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFrain, E.L.; Thoegersen, J.; Hong, M. Standing Out or Blending In: Academic Libraries in the Crowded Informal Learning Space Ecosystem. Coll. Res. Libr. 2022, 83, 45–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, S.E. Library Space Assessment: User Learning Behaviors in the Library. J. Acad. Librariansh. 2014, 40, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Remøy, H.; van den Dobbelsteen, A.; Knaack, U. Personal Control and Environmental User Satisfaction in Office Buildings: Results of Case Studies in the Netherlands. Build. Environ. 2019, 149, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansor, R.; Sheau-Ting, L.; Weng-Wai, C. The Effects of Personal Control and Perceived Thermal Comfort on Occupant Psychological Health at the Workplace. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2025, 68, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).