Research on Heritage Conservation and Development of Chinese Ancient Towns and Historic Districts Based on Knowledge Graph Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis Tools
2.3. Research Framework
3. Literature Characteristics Analysis
3.1. Analysis of Research Disciplines
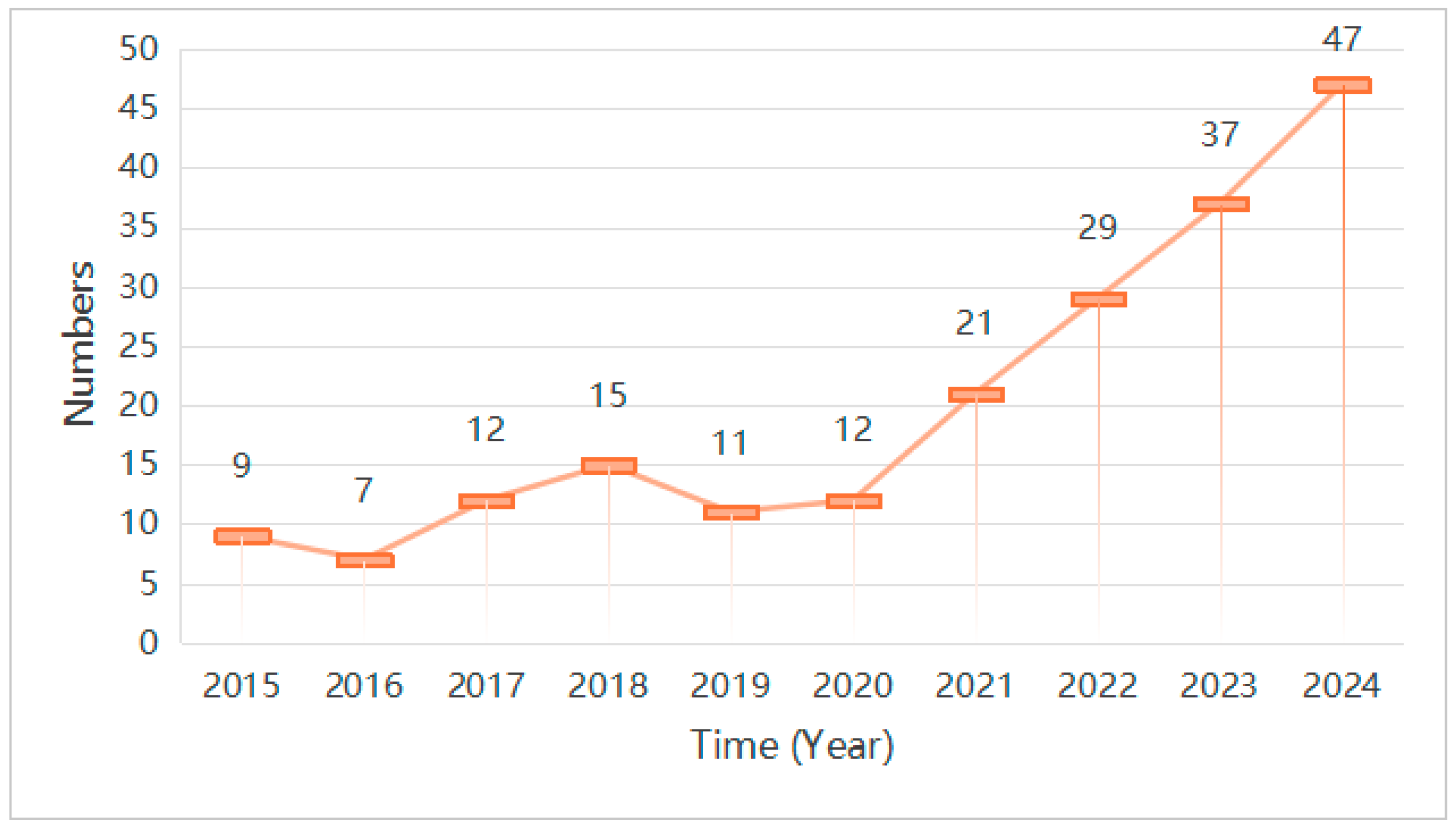
3.2. Analysis of Publication Trends and Journal Sources
3.3. Co-Word Analysis
4. Analysis of Research Directions
5. Analysis of Research Hotspots and Trends
5.1. From Cultural Heritage Conservation to Integrated Cultural and Tourism Development
5.2. From Rough Tourism Development to the Integration of Everyday Life Scenes
5.3. From the Spatial Perception of Urban Character to Enhancement of Thermal Comfort
5.4. From Single-Disciplinary Tools to the Integration of Interdisciplinary Technologies
6. Discussion and Conclusions
6.1. Discussion
- (1)
- Integrating Historical Cultural Heritage with Cultural Tourism Spatial Planning
- (2)
- Prioritizing Cultural Tourism Spatial Design and Environmental Enhancement
6.2. Conclusions
- (1)
- This study reveals that research interest in historic districts of ancient towns has been steadily increasing each year.
- (2)
- Scholars’ focus has shifted from solely heritage conservation to the integration of cultural tourism development.
- (3)
- With the increasing emphasis on cultural tourism development, historic districts should focus on spatial scene creation by designing immersive and engaging tourism experiences.
- (4)
- The comfort of public spaces, which is a major concern for both residents and tourists, has emerged as a new research hotspot.
- (5)
- Emerging technologies are increasingly being applied in this research field, and the integration of interdisciplinary approaches has become a key future research trend.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Botao, Q.; Iskandar, Y.H.P. Tourism Augmented Reality in China. Proc. Natl. Int. Conf. 2024, 16, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Song, M. Visualizing a Field of Research: A Methodology of Systematic Scientometric Reviews. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekonnen, H.; Bires, Z.; Berhanu, K. Practices and Challenges of Cultural Heritage Conservation in Historical and Religious Heritage Sites: Evidence from North Shoa Zone, Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Herit. Sci. 2022, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Zhu, B.; Fukuda, H. Research on Ancient Town Style Construction Strategies Based on Coupled Quantitative Analysis of AI Visual Recognition and Scenic Beauty Evaluation. Front. Archit. Res. 2025, 14, 654–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knippschild, R.; Zöllter, C. Urban Regeneration between Cultural Heritage Preservation and Revitalization: Experiences with a Decision Support Tool in Eastern Germany. Land 2021, 10, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardaro, R.; La Sala, P.; De Pascale, G.; Faccilongo, N. The Conservation of Cultural Heritage in Rural Areas: Stakeholder Preferences Regarding Historical Rural Buildings in Apulia, Southern Italy. Land Use Policy 2021, 109, 105662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.J.; Leung, H.H. Becoming a Traditional Village: Heritage Protection and Livelihood Transformation of a Chinese Village. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyurkovich, M.; Gyurkovich, J. New Housing Complexes in Post-Industrial Areas in City Centres in Poland versus Cultural and Natural Heritage Protection—With a Particular Focus on Cracow. Sustainability 2021, 13, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, M.M.; Touqan, B.A.; Awad, J.; Salameh, M.M. Heritage Conservation as a Bridge to Sustainability Assessing Thermal Performance and the Preservation of Identity through Heritage Conservation in the Mediterranean City of Nablus. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchi, E.; Buda, A. Urban Green Rating Systems: Insights for Balancing Sustainable Principles and Heritage Conservation for Neighbourhood and Cities Renovation Planning. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 161, 112324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussaa, D. The Past as a Catalyst for Cultural Sustainability in Historic Cities; the Case of Doha, Qatar. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2021, 27, 470–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cong, C.; Chakraborty, A. Exploring the Institutional Dilemma and Governance Transformation in China’s Urban Regeneration: Based on the Case of Shanghai Old Town. Cities 2022, 131, 103915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, G.; Szili, G.; Huang, H. Cultural Heritage Tourism Development in Panyu District, Guangzhou: Community Perspectives on Pride and Preservation, and Concerns for the Future. J. Herit. Tour. 2022, 17, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Huang, J.; Law, A. Research Frameworks, Methodologies, and Assessment Methods Concerning the Adaptive Reuse of Architectural Heritage: A Review. Built Herit. 2021, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, X. Spatial Pattern and Micro-Location Rules of Tourism Businesses in Historic Towns: A Case Study of Pingyao, China. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2022, 25, 100721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobic, S.; Akhavan, M. Tourism Gentrification in Mediterranean Heritage Cities. Necessity Multidiscip. Planning. Cities 2022, 124, 103616. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.R.; Cao, Y.; Li, G.W. An Approach to Developing and Protecting Linear Heritage Tourism: The Construction of Cultural Heritage Corridor of Traditional Villages in Mentougou District Using GIS. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2023, 11, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, P.; Dias, A.L.; Patuleia, M. The Impacts of Tourism on Cultural Identity on Lisbon Historic Neighbourhoods. J. Ethn. Cult. Stud. 2021, 8, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruczek, Z.; Szromek, A.R.; Walas, B.; Mazanek, L. Sources of Conflict among Tourism Stakeholders in Historical Cities. J. Policy Res. Tour. Leis. Events 2024, 16, 117–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Hsu, W.-L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.-L. Service Facilities in Heritage Tourism: Identification and Planning Based on Space Syntax. Information 2021, 12, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhan, Q.; Du, G.; Wei, Y. The Effects of Involvement, Authenticity, and Destination Image on Tourist Satisfaction in the Context of Chinese Ancient Village Tourism. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2024, 60, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitušíková, A. Cultural Heritage as a Means of Heritage Tourism Development. Muzeológia A Kultúrne Dedičstvo 2021, 9, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Walsh, J. Tourist Experience, Tourist Motivation and Destination Loyalty for Historic and Cultural Tourists. Pertanika J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2021, 28, 3277–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Wei, Q.; Jin, J.; Nie, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, X.; Ma, Y. Research on Public Space Micro-Renewal Strategy of Historical and Cultural Blocks in Sanhe Ancient Town under Perception Quantification. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birer, E.; Adem, P.Ç. Role of Public Space Design on the Perception of Historical Environment: A Pilot Study in Amasya. Front. Archit. Res. 2022, 11, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Y. Preservation and Renewal: A Study on Visual Evaluation of Urban Historical and Cultural Street Landscape in Quanzhou. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Wu, Y.; Fang, K.; Liu, X. Typo-Morphological Approaches for Maintaining the Sustainability of Local Traditional Culture: A Case Study of the Damazhan and Xiaomazhan Historical Area in Guangzhou. Buildings 2023, 13, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xue, D.; Huang, G. The Effects of Residents’ Sense of Place on Their Willingness to Support Urban Renewal: A Case Study of Century-Old East Street Renewal Project in Shaoguan, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagroba, M.; Pawlewicz, K.; Senetra, A. Analysis and Evaluation of the Spatial Structure of Cittaslow Towns on the Example of Selected Regions in Central Italy and North-Eastern Poland. Land 2021, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamei, E.; Ahmadi, K.; Chau, H.W.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Horan, B.; Stojcevski, A. Urban Design and Walkability: Lessons Learnt from Iranian Traditional Cities. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Varo, I.; Delclos-Alio, X.; Miralles-Guasch, C. Jane Jacobs Reloaded: A Contemporary Operationalization of Urban Vitality in a District in Barcelona. Cities 2022, 123, 103565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shboul, B.; Koh, S.L.; Veneti, C.; Herghelegiu, A.I.; Zinca, A.E.; Pourkashanian, M. Evaluating Sustainable Development Practices in a Zero-Carbon University Campus: A Pre and Post-COVID-19 Pandemic Recovery Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Yin, B. The Impact of the Built-up Environment of Streets on Pedestrian Activities in the Historical Area. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Ricard, R.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, W. Assessing Street-Level Urban Greenery Using Google Street View and a Modified Green View Index. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Rui, Q.; Zhu, X.; Xu, H. Effect of Soundscape on Place Attachment for Historical Blocks: A Case Study of Harbin, China. Buildings 2023, 13, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z. Research on the Acoustic Environment of Heritage Buildings: A Systematic Review. Buildings 2022, 12, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Y. Effect of an Artificial Sound-Based Index on the Perception of Historical Block Environments. Buildings 2023, 13, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xie, R.; Wang, J.; Dong, Q.; Yao, W.; Lin, D. Thermal Comfort and Urban Microclimate Response: A New Thermal Environment Assessment Model for Waterfront Spaces in Historic Ancient Towns. Energy Build. 2025, 331, 115393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Guo, H.; Yin, L.; Gao, W.; Yao, W.; Sun, L. Indoor Thermal Comfort Evaluation of Traditional Dwellings in Cold Region of China: A Case Study in Guangfu Ancient City. Energy Build. 2023, 288, 113028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, L.; Liu, S.; Shi, J.; Cheng, M.; Xiang, T. The Ancient Town Residential Environment of the Elderly in Xiangxi Tujia: Survey, Questions, and Recommendations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ma, X. Research on Traditional Ecological History Experience in Site Selection of Hexia Ancient Town. Open J. Soc. Sci. 2020, 8, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Algeciras, J.A.; Gómez Consuegra, L.; Matzarakis, A. Spatial-Temporal Study on the Effects of Urban Street Configurations on Human Thermal Comfort in the World Heritage City of Camagüey-Cuba. Build. Environ. 2016, 101, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Xiong, R.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W. Traditional Architectural Heritage Conservation and Green Renovation with Eco Materials: Design Strategy and Field Practice in Cultural Tibetan Town. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isa, S.M.; Ismail, H.N.; Fuza, Z.I.M. Elderly and Heritage Tourism: A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 447, 012038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.; Brochado, A.; Correia, A. Seniors in International Residential Tourism: Looking for Quality of Life. Anatolia 2018, 29, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhao, S. Discover the Desirable Landscape Structure for Mitigating Urban Heat: The Urban-Rural Gradient Approach for an Ancient Chinese City. Cities 2022, 127, 103737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Lv, L.; Peng, X.; He, J. Sustainable Urban Regeneration with Wind and Thermal Environment Optimization: Design Roadshow of a Historic Town in China. Coatings 2024, 14, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. The Wuzhen Model: Analyzing a Strategy of Old Town Tourism in China. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
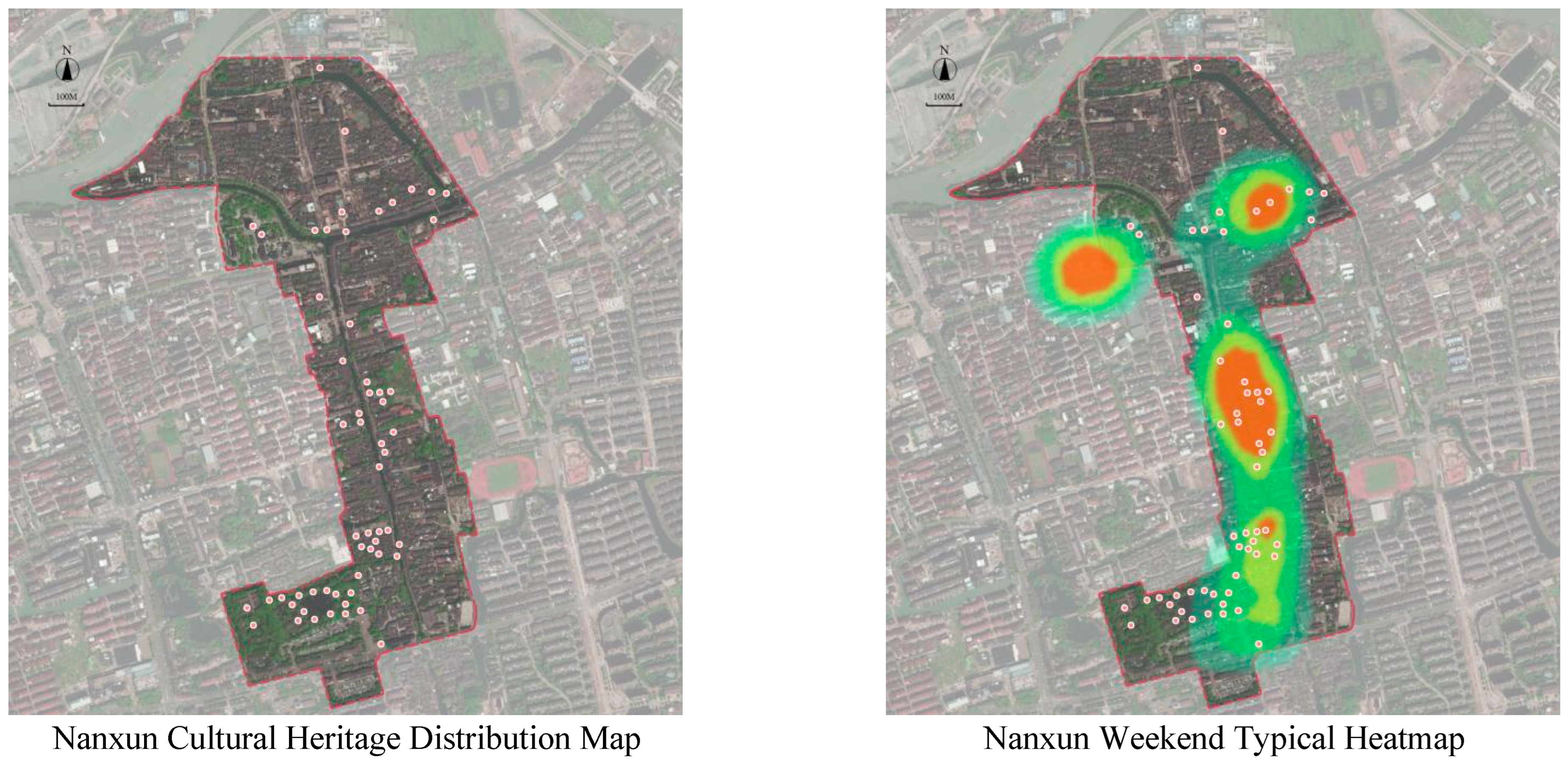
- Porfyriou, H. Urban Heritage Conservation of China’s Historic Water Towns and the Role of Professor Ruan Yisan: Nanxun, Tongli, and Wuzhen. Heritage 2019, 2, 2414–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lu, L. Probing the Long-Term Evolution of Traditional Village Tourism Destinations from a Glocalisation Perspective: A Case Study of Wuzhen in Zhejiang Province, China. Habitat Int. 2024, 148, 103073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Fukuda, H. Changes of the Northern Zhejiang Canal: Renaissance and Cultural Tourism Development of Ancient Towns. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, L.; Yin, J. Numerical Simulation of Thermal Environment in the Historical and Cultural District of Taiping Street Based on Greenbelt Microclimate. Trop. Geogr. 2023, 43, 330–342. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.-P. Extending 3D-GIS District Models and BIM-Based Building Models into Computer Gaming Environment for Better Workflow of Cultural Heritage Conservation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, L.; Zhou, J. Revitalizing Historic Districts: Identifying Built Environment Predictors for Street Vibrancy Based on Urban Sensor Data. Cities 2021, 117, 103305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, M. Cultivating Historical Heritage Area Vitality Using Urban Morphology Approach Based on Big Data and Machine Learning. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 91, 101716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
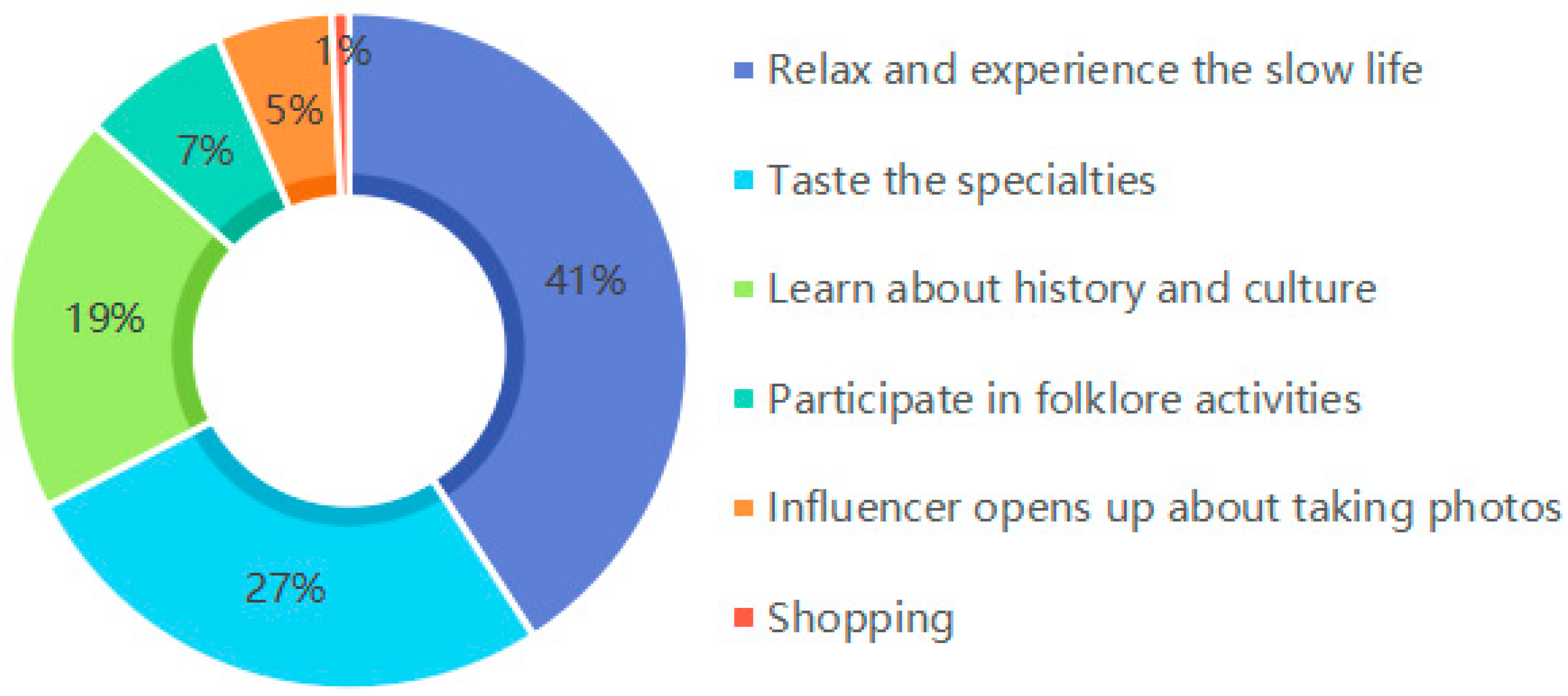
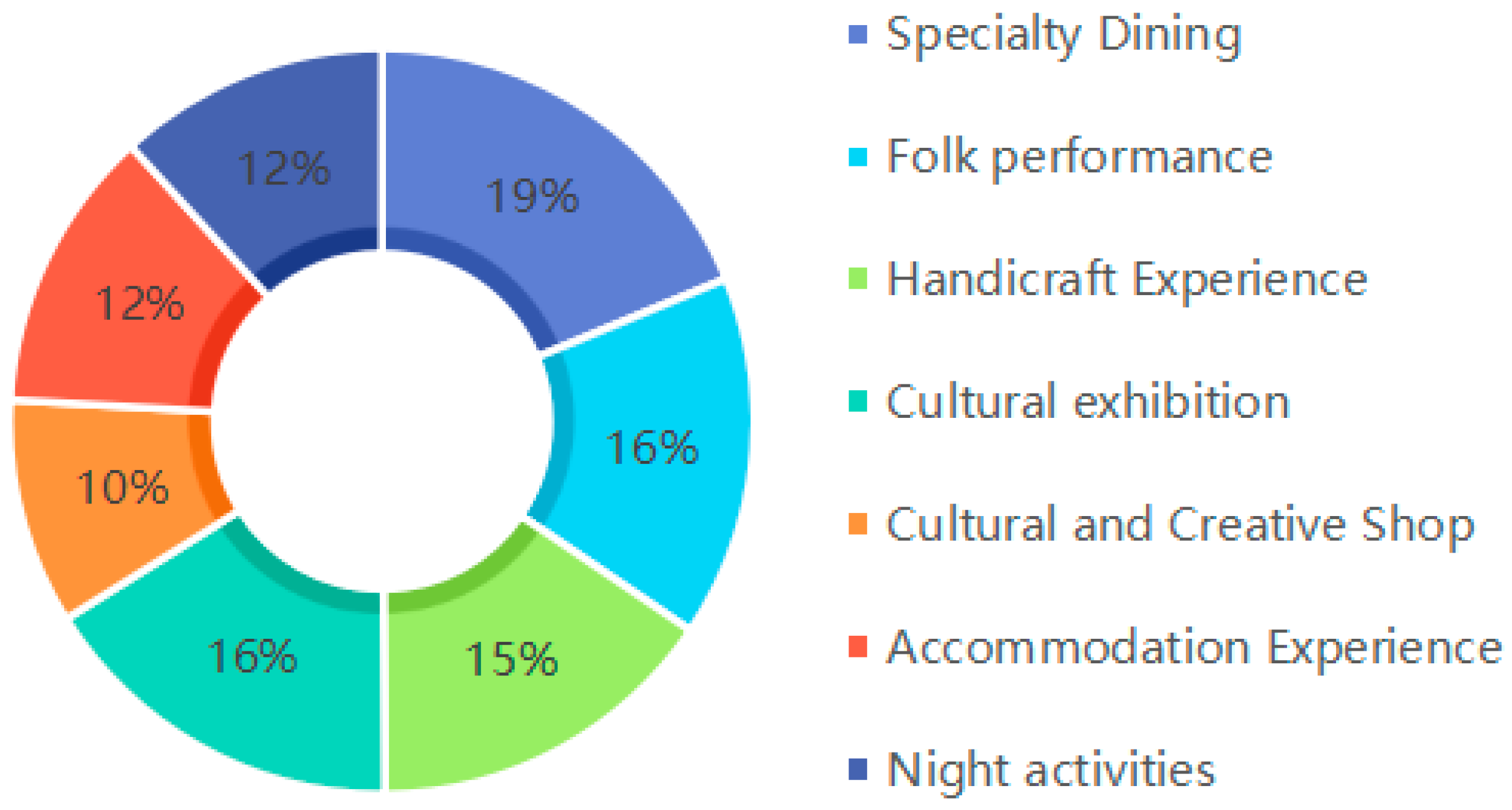
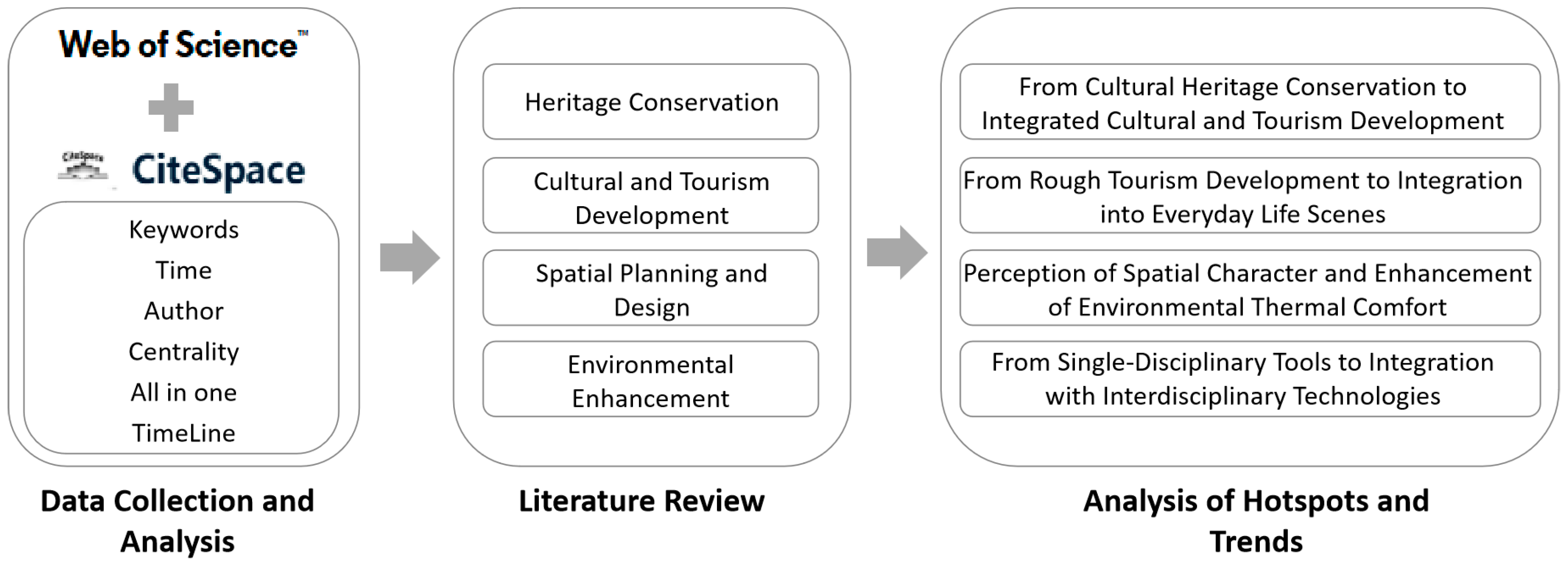
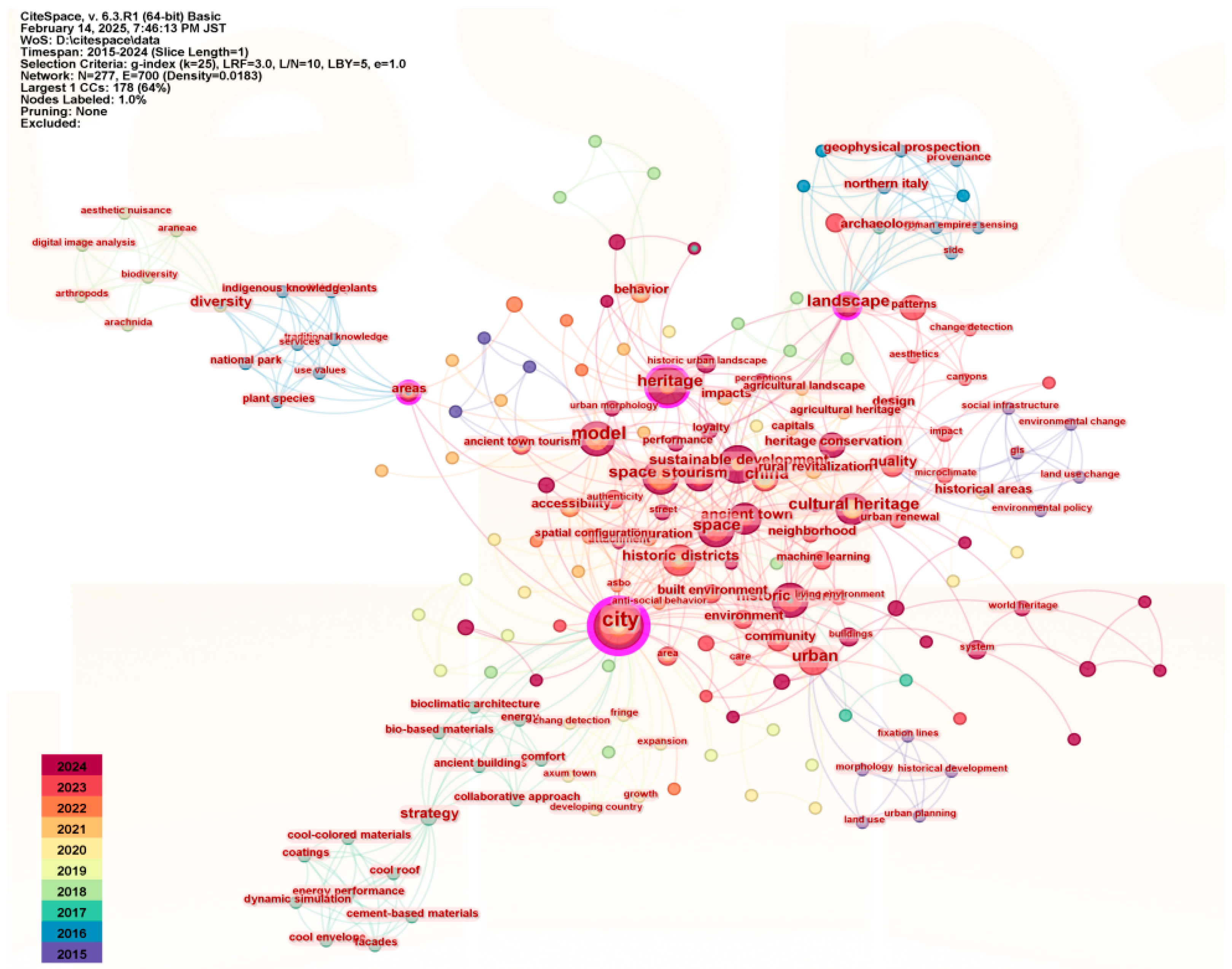
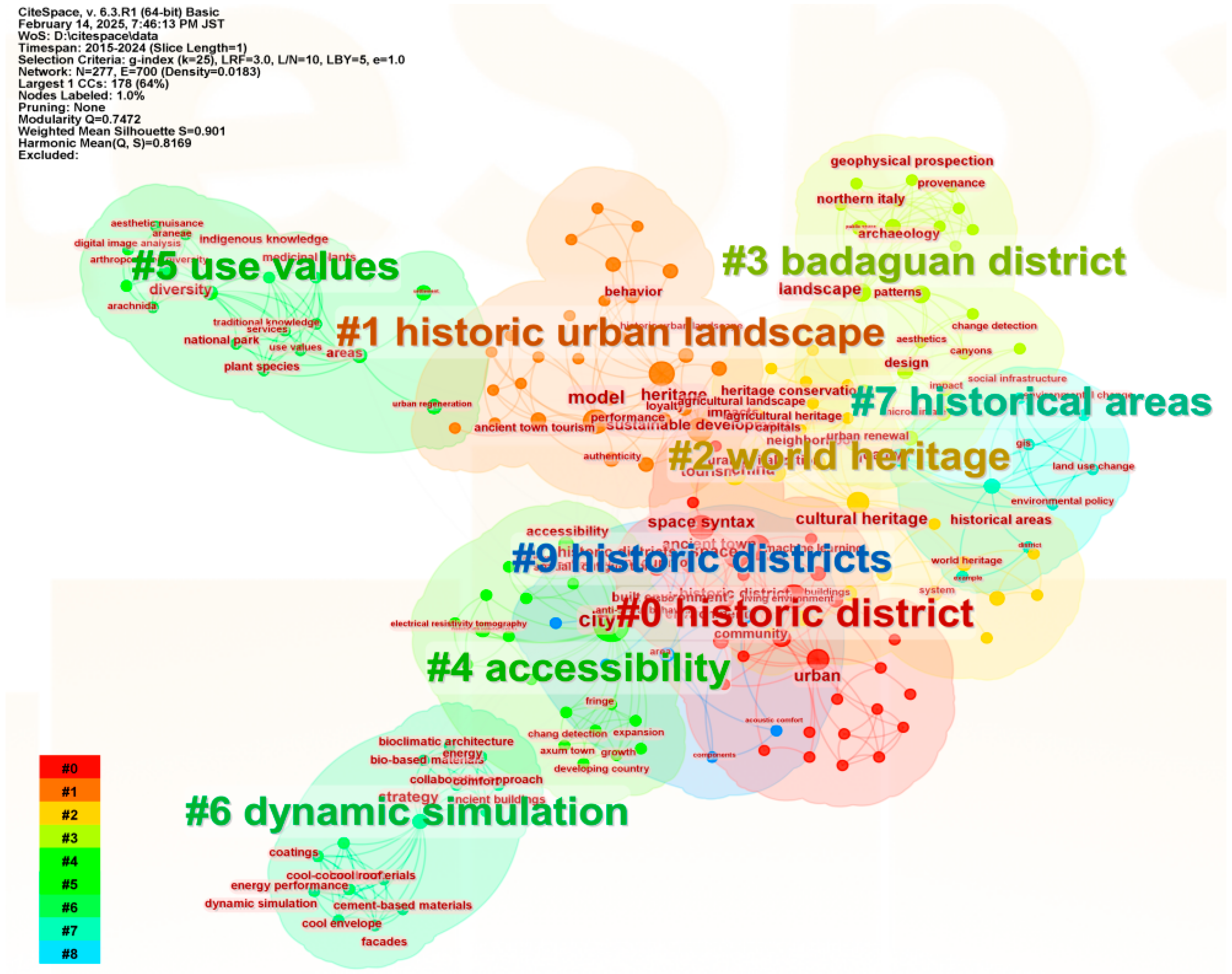
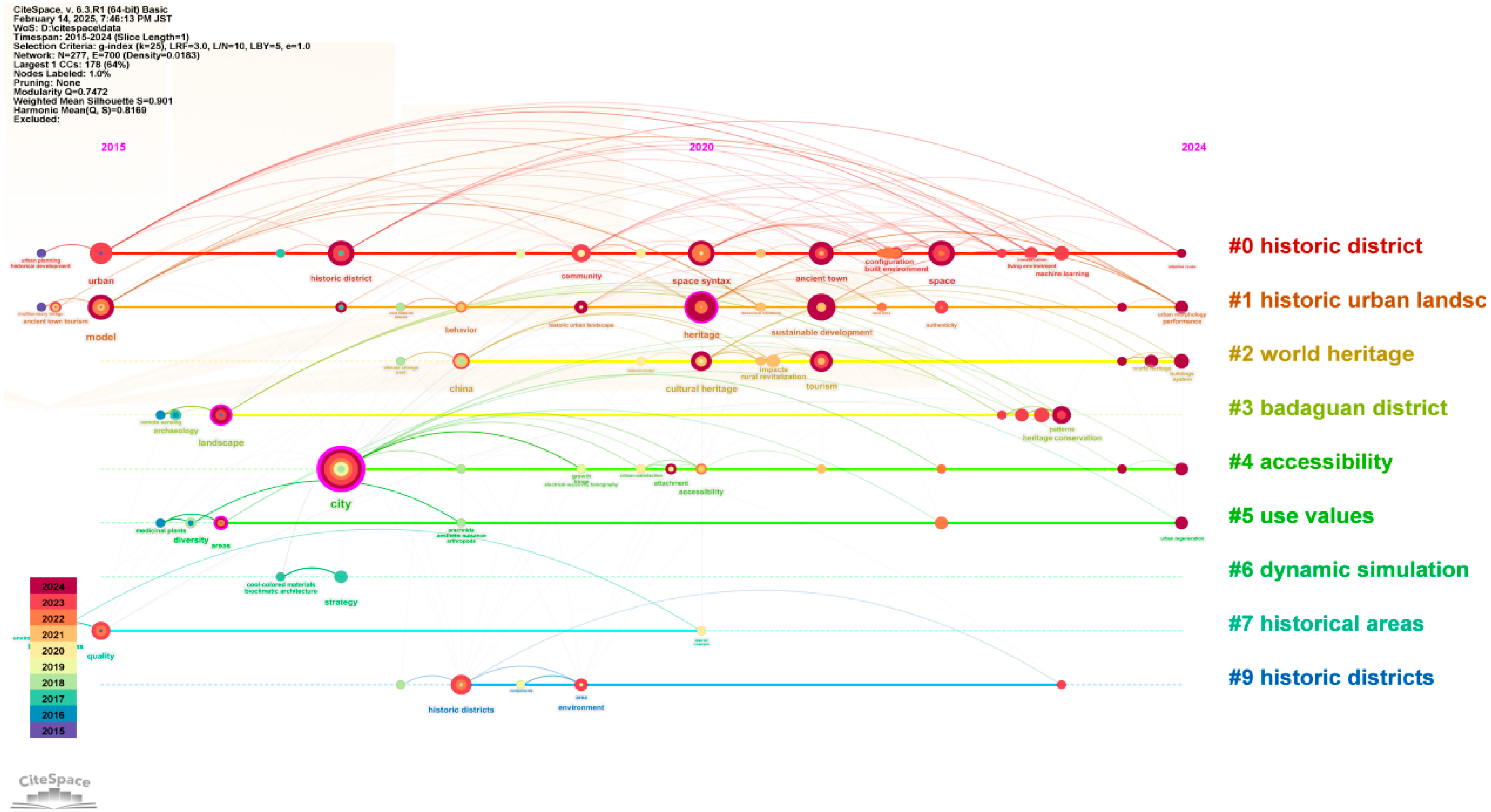
| No. | Countries (Frequency) | Countries (Centrality) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | China (109) | China (0.28) |
| 2 | England (14) | England (0.24) |
| 3 | USA (12) | Australia (0.22) |
| 4 | Italy (12) | Italy (0.15) |
| 5 | Japan (9) | USA (0.12) |
| 6 | Australia (8) | Belgium (0.09)) |
| 7 | Turkey (6) | France (0.07) |
| 8 | France (5) | Poland (0.05) |
| 9 | South Korea (5) | Greece (0.03) |
| 10 | Spain (5) | Japan (0.00) |
| No. | Keyword (Frequency) | Keyword (Centrality) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | City (22) | City (0.4) |
| 2 | Heritage (11) | Heritage (0.12) |
| 3 | Space syntax (10) | Areas (0.12) |
| 4 | Space (9) | Landscape (0.11) |
| 5 | Model (9) | Model (0.09) |
| 6 | Ancient town (9) | Culture heritage (0.08) |
| 7 | Sustainable development (9) | Quality (0.08) |
| 8 | Historic district (9) | Urban (0.07) |
| 9 | Culture heritage (7) | China (0.07) |
| 10 | Tourism (6) | Strategy (0.07) |
| Research Direction | Authors | Research Summary |
|---|---|---|
| Heritage Conservation | H. Mekonnen (2022) [3]; J. Fu (2021) [4]; R Knippschild (2021) [5]; R. Sardaro (2021) [6]; R.J. Qin (2021) [7]; M. Gyurkovich (2021) [8]; [9]; M.M. Salameh (2022) [9]; E. Lucchi (2022) [10]; D. Boussaa (2021) [11]; H. Zhang (2022) [12]; G. Butler (2022) [13]; Y. Li (2021) [14] | The heritage conservation of historic cultural districts primarily focuses on spatial morphology studies and architectural style preservation. Research indicates that the spatial morphology of these districts is highly distinctive, with spatial structures formed in different historical periods shaping their cultural value and residents’ experiences. The restoration and maintenance of traditional architecture remain a key aspect of historic district preservation. In recent years, the micro-renewal strategy has gained traction in academia, as it enhances urban vibrancy without compromising historical character. Additionally, the concept of multi-factor collaborative renewal has emerged as a research hotspot, emphasizing an integrated approach that considers social, cultural, and economic factors in the preservation and revitalization of historic districts. |
| Cultural and Tourism Development | M. Wang (2022) [15]; S. Bobic (2022) [16]; M.R. Li (2023) [17]; P. Daly (2021) [18]; Z. Kruczek (2024) [19]; M. Wang (2021) [20]; G. Butler (2022) [13]; Y. Zhao (2024) [21]; A. Bitušíková (2021) [22]; J. Zhang (2021) [23] | Cultural and tourism development plays a crucial role in the evolution of historic cultural districts, primarily focusing on tourist perception and satisfaction, cultural tourism development models, business formats, and spatial vitality. Studies reveal that the creation of cultural scenes and the presentation of historical architectural heritage significantly influence visitor satisfaction. Additionally, a well-planned business layout can effectively enhance the commercial vibrancy and cultural appeal of historic districts, contributing to their sustainable development. |
| Spatial Planning and Design | W. Ding (2023) [24]; E. Birer (2022) [25]; Y. Zhao (2022) [26]; L. Jiao (2023) [27]; [28]; M. Zagroba (2021) [29]; E. Jamei (2021) [30]; I. Gómez-Varo (2022) [31]; Y. Xu (2021) [32]; L. Zhang (2021) [33]; M. Wang (2022) [34]; W. Zhao (2023) [35]; J. Mu (2022) [36]; J. Ye (2023) [37] | Spatial planning and design is a key direction in the planning and renewal of historic districts, encompassing environmental improvement and the enhancement of street vitality. The construction of spatial scenes has become a major research focus. Studies highlight the interaction between spatial production and place-making, which profoundly impacts the renewal of historic districts. Additionally, research that examines visual landscapes and soundscape perception suggests that the acoustic environment of streets plays a crucial role in both the visitor experience and the overall vibrancy of historic districts. |
| Environmental Enhancement | Y. Wang (2023) [38]; Yan Wang (2023) [39]; F. Zhang (2022) [40]; F. Zhang (2023) [40]; Tianchi Wang (2020) [41]; J.A.R. Algeciras (2016) [42]; K. Xie (2024) [43]; S.M. Isa (2019) [44]; Cristina Oliveira (2017) [45]; Yinuo Shi (2022) [46]; Lin, Yijie (2024) [47] | Environmental enhancement is essential for the sustainable development of historic cultural districts, primarily focusing on thermal comfort, green space optimization, and the improvement of public space quality. Studies on the thermal environment of historic districts indicate that greenery and architectural layout have a direct impact on comfort levels. Research from the perspective of urban regeneration emphasizes that optimizing the green view index in historic recreational spaces can significantly enhance the visitor experience. Furthermore, studies on age-friendly design suggest that public spaces in historic districts should incorporate barrier-free accessibility features to improve interaction experiences for both residents and tourists. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, W.; Fukuda, H. Research on Heritage Conservation and Development of Chinese Ancient Towns and Historic Districts Based on Knowledge Graph Analysis. Buildings 2025, 15, 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142459
Jin W, Fukuda H. Research on Heritage Conservation and Development of Chinese Ancient Towns and Historic Districts Based on Knowledge Graph Analysis. Buildings. 2025; 15(14):2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142459
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Wu, and Hiroatsu Fukuda. 2025. "Research on Heritage Conservation and Development of Chinese Ancient Towns and Historic Districts Based on Knowledge Graph Analysis" Buildings 15, no. 14: 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142459
APA StyleJin, W., & Fukuda, H. (2025). Research on Heritage Conservation and Development of Chinese Ancient Towns and Historic Districts Based on Knowledge Graph Analysis. Buildings, 15(14), 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142459






