Calculation Method of Axial Compressive Capacity of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy Rectangular Tubes Based on Continuous Strength Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Axial Compression Test
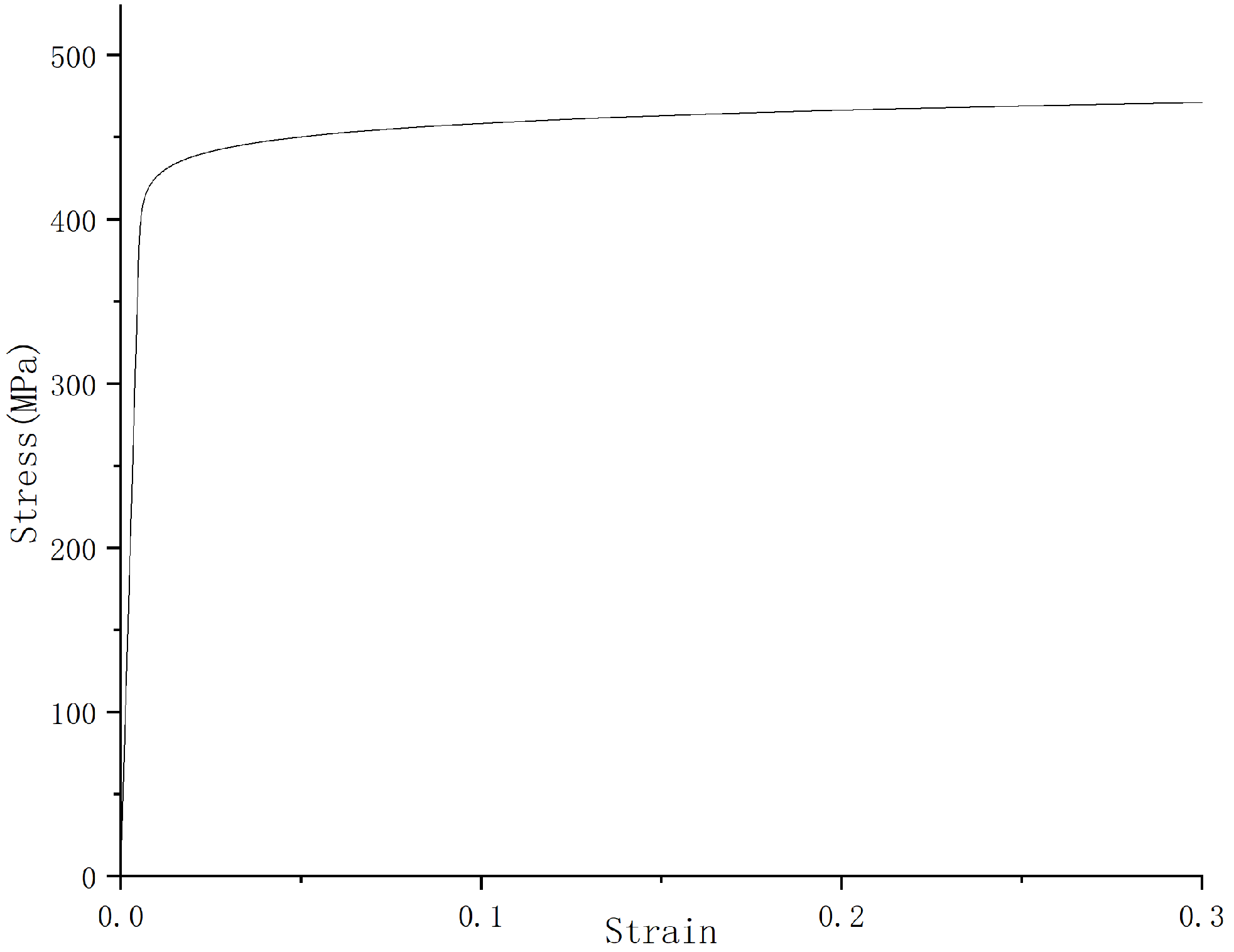
2.1. Tensile Test of Materials
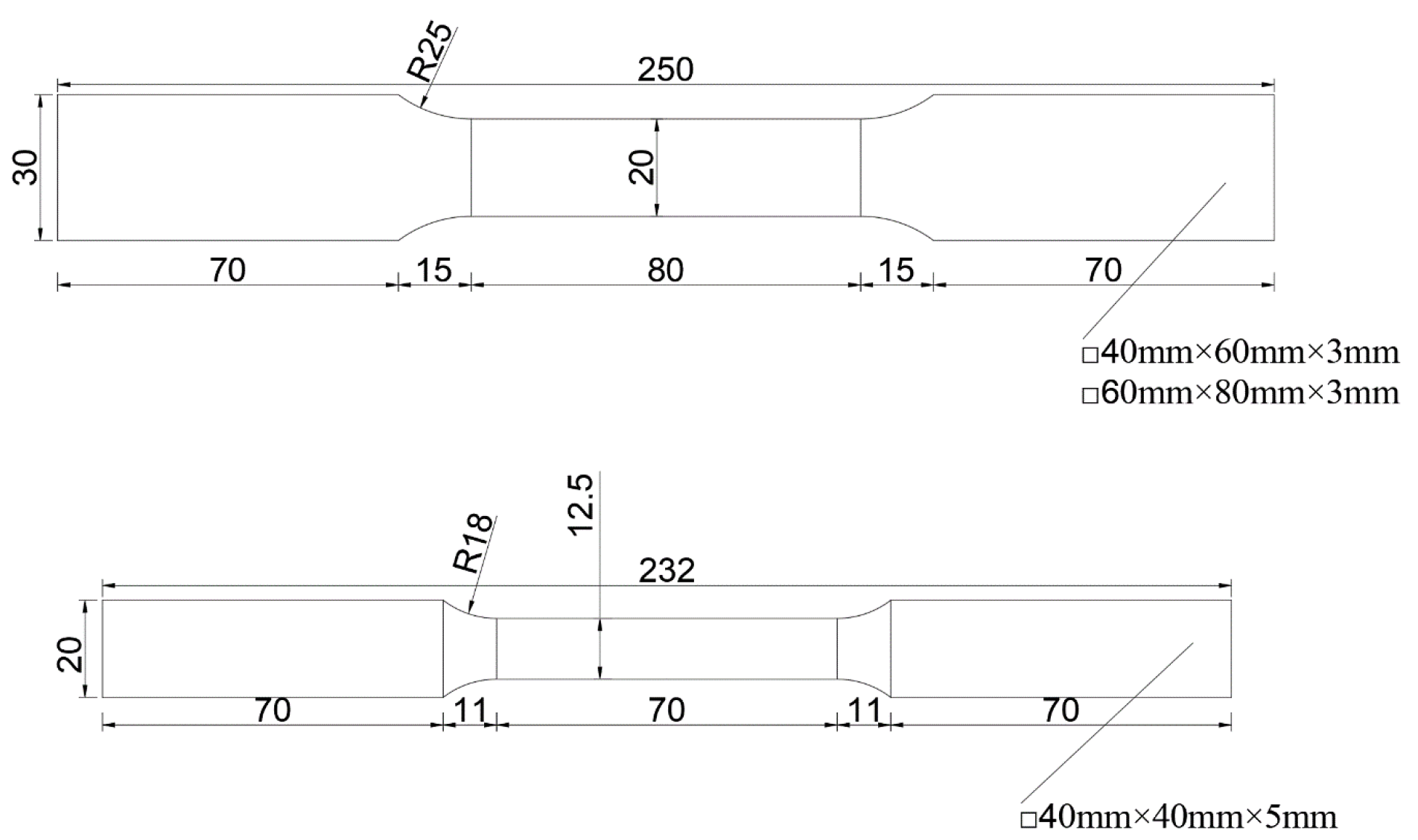
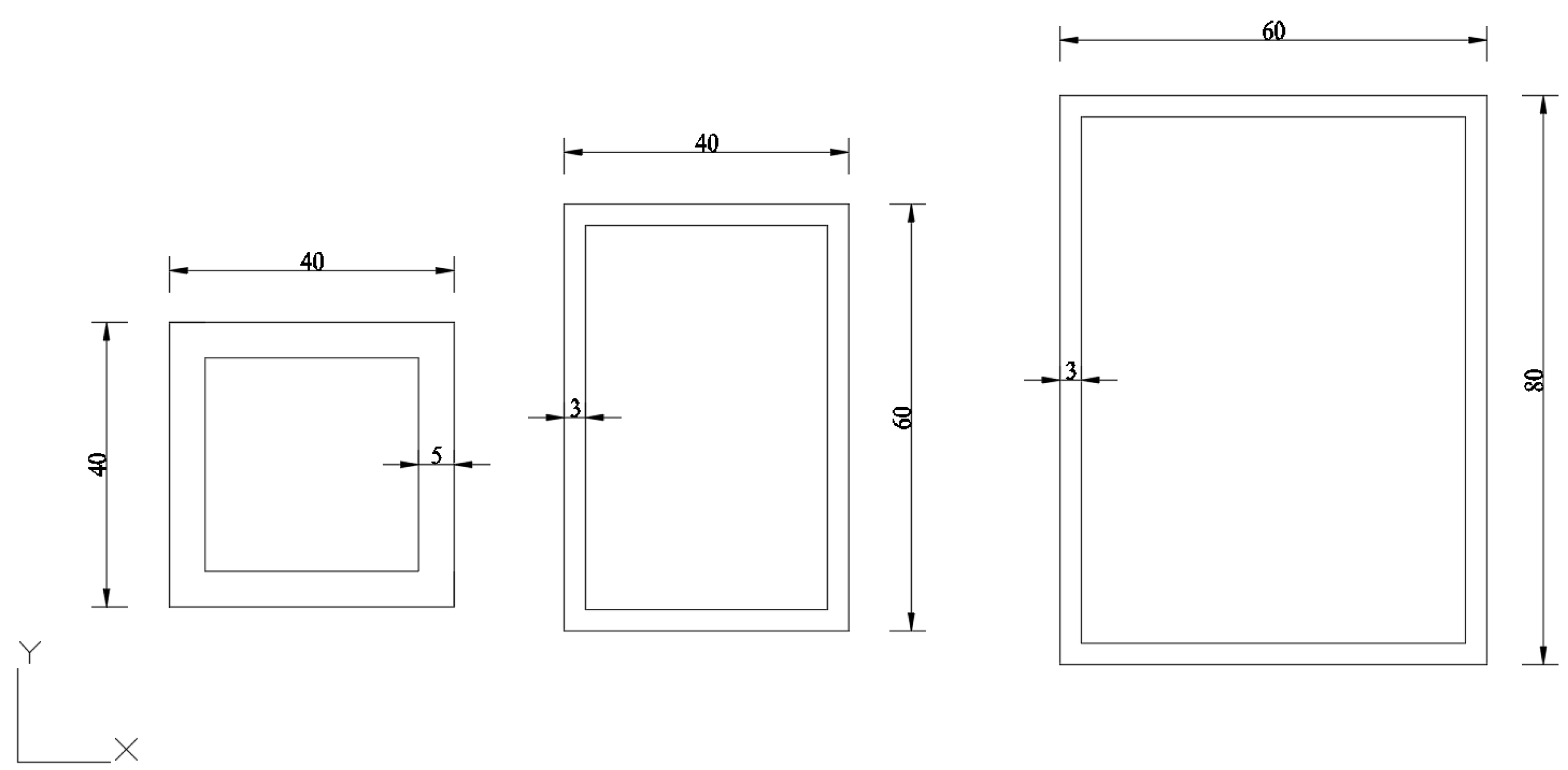
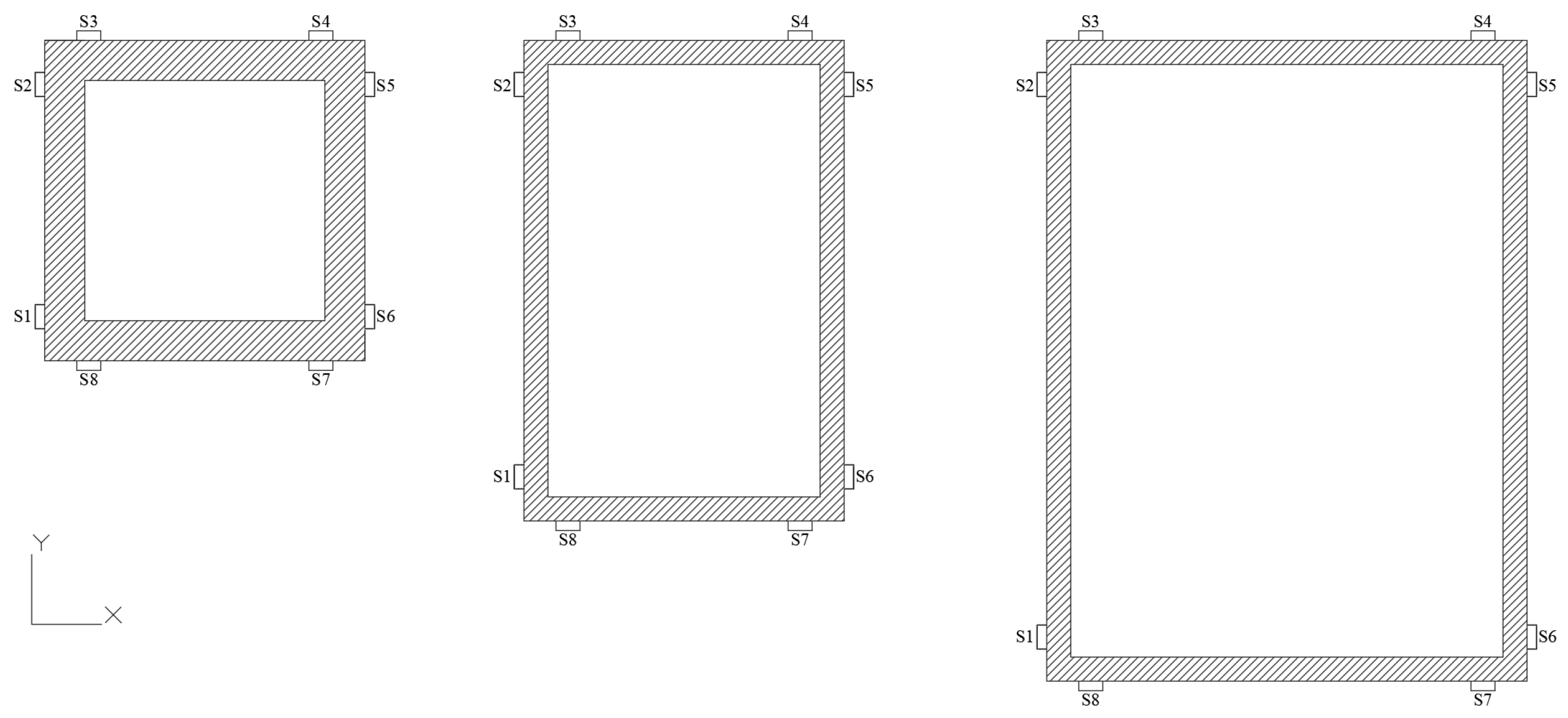
2.2. Specimen Design
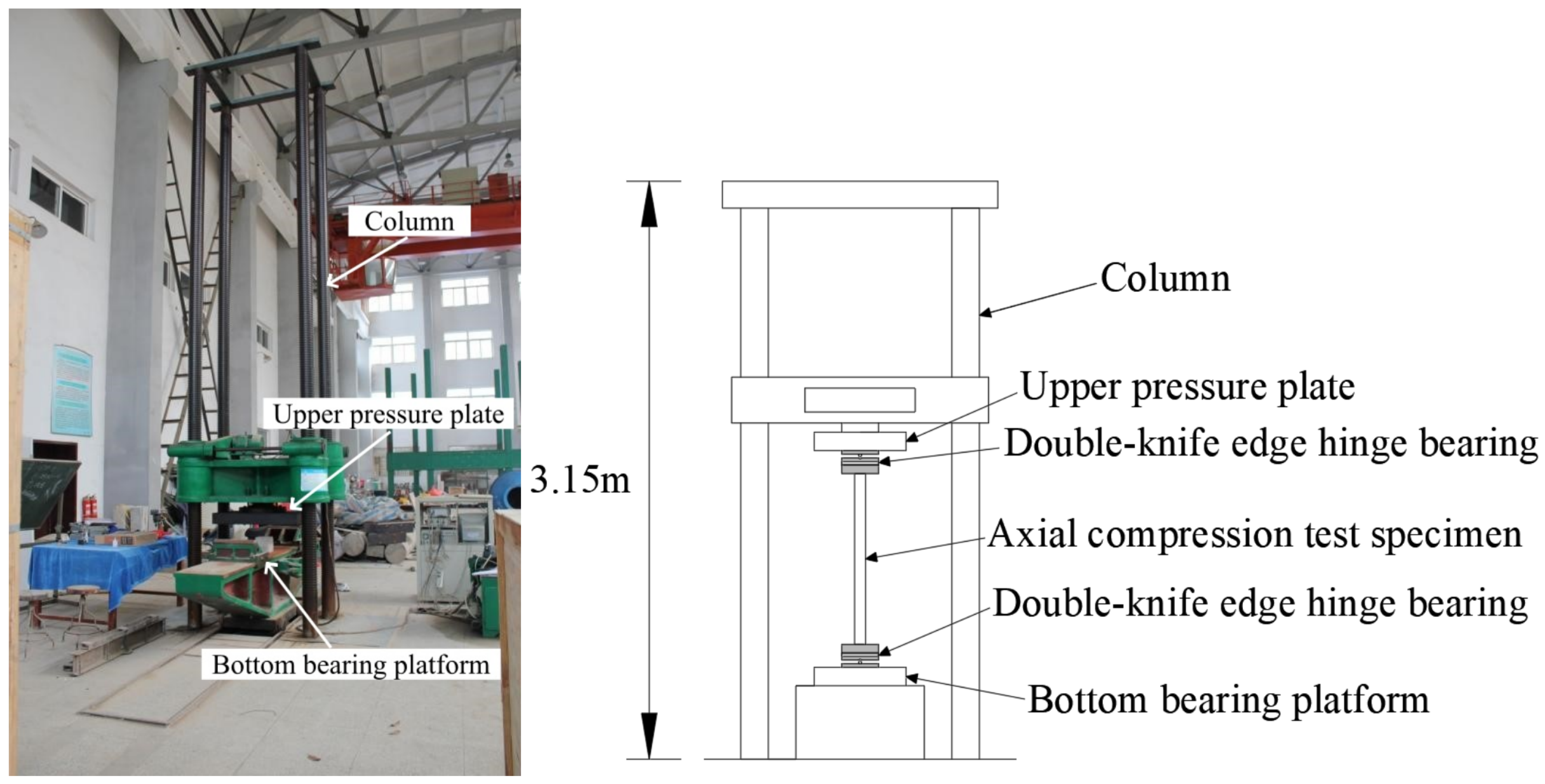
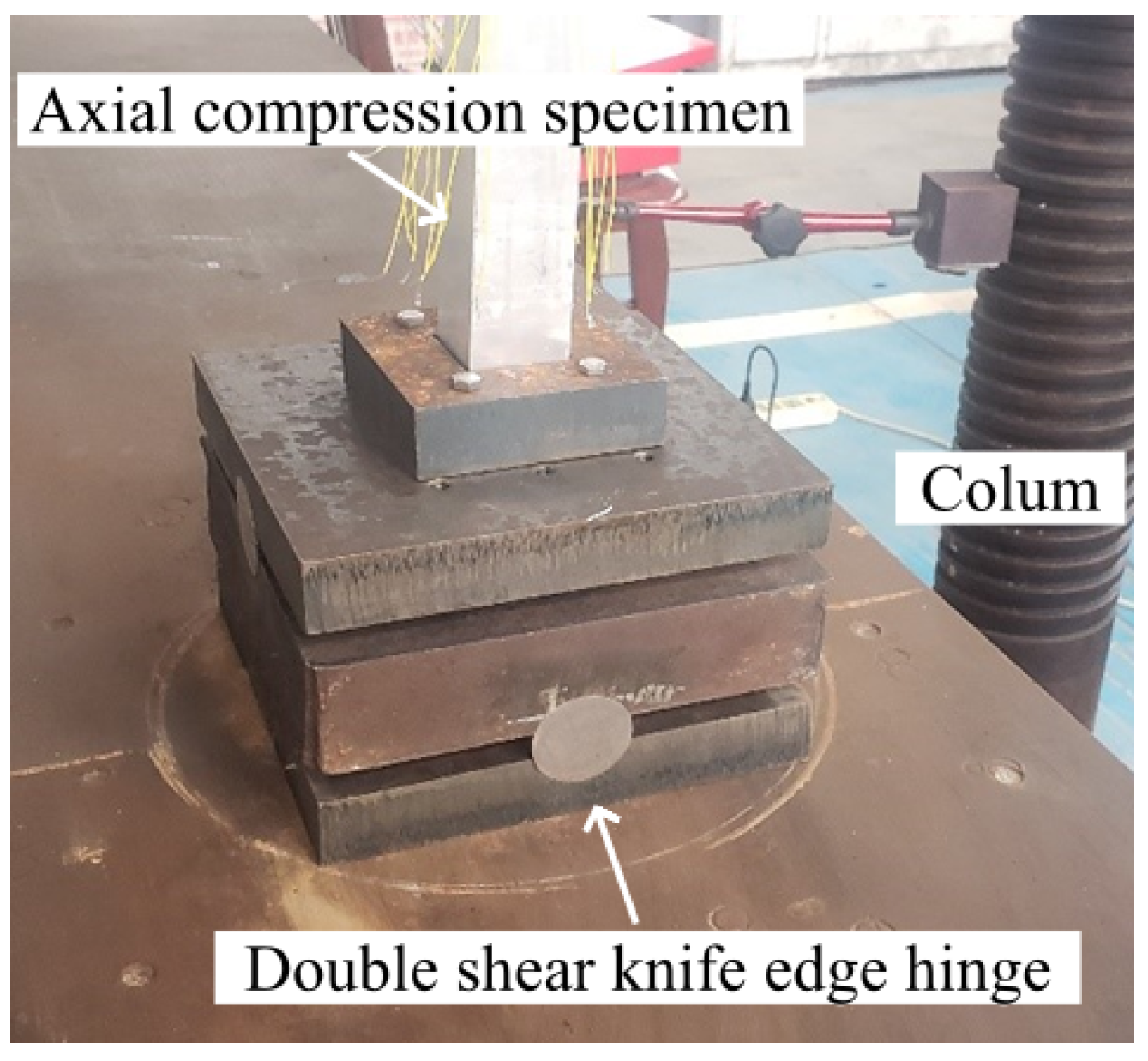
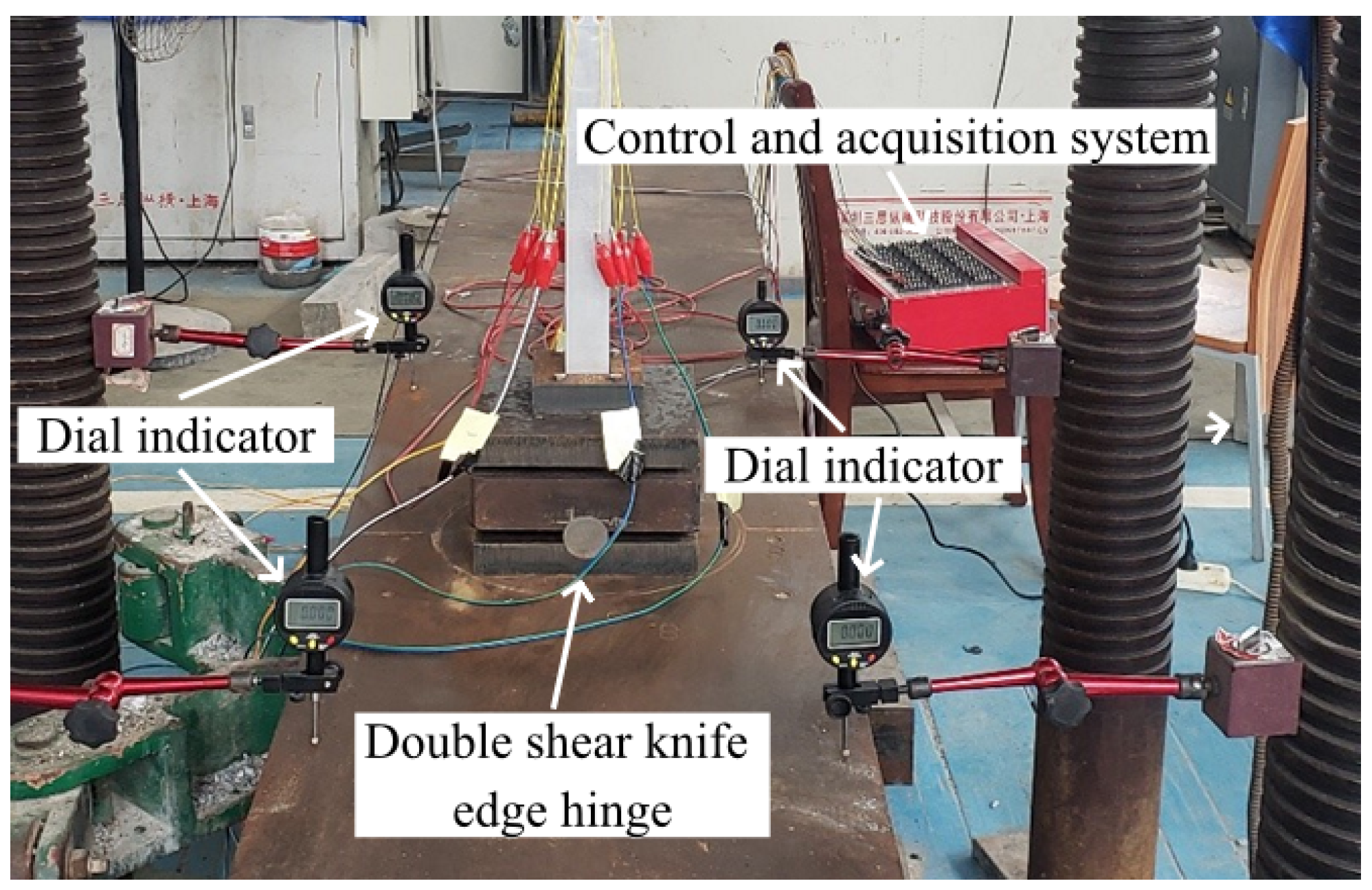
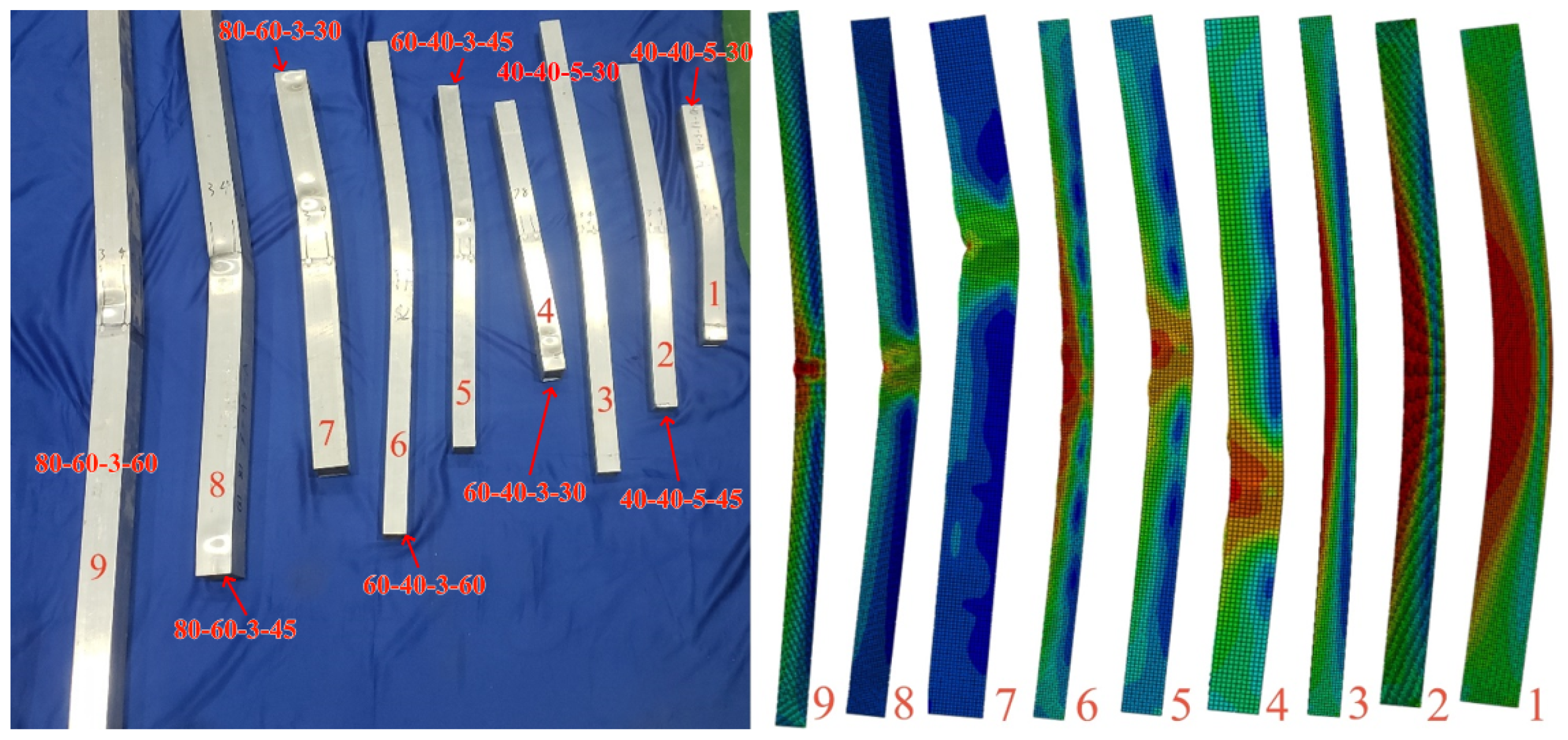
2.3. Axial Compression Test Plan
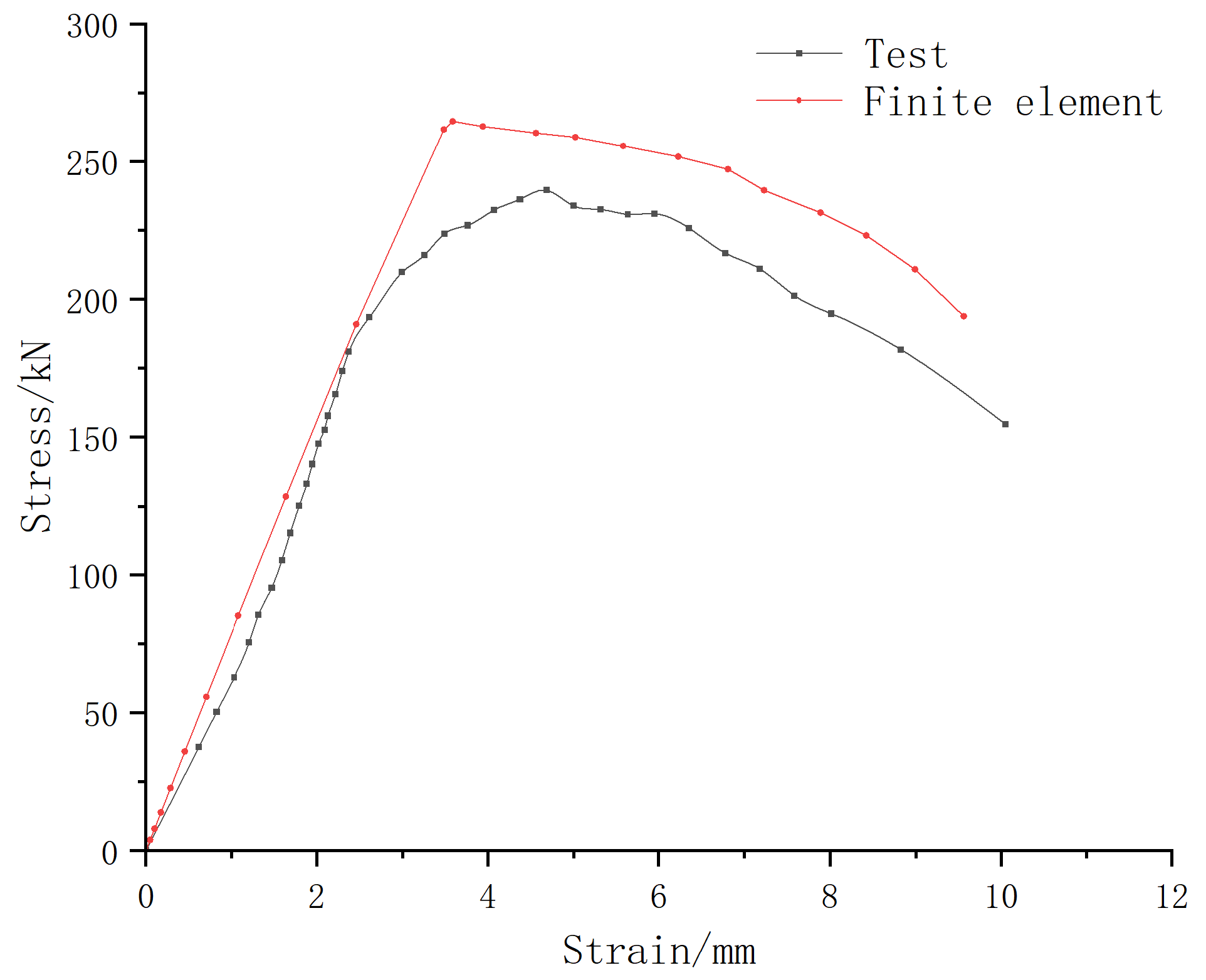
2.4. Finite Element Model Validation
3. Current Standard Calculation Method
3.1. Chinese Standards
3.2. Eurocode 9
3.3. Aluminum Association AA ADM-2020
4. Calculation Method Based on the Continuous Strength Method
4.1. Base Curve
4.2. Bilinear Constitutive Model
4.3. Stability Coefficient
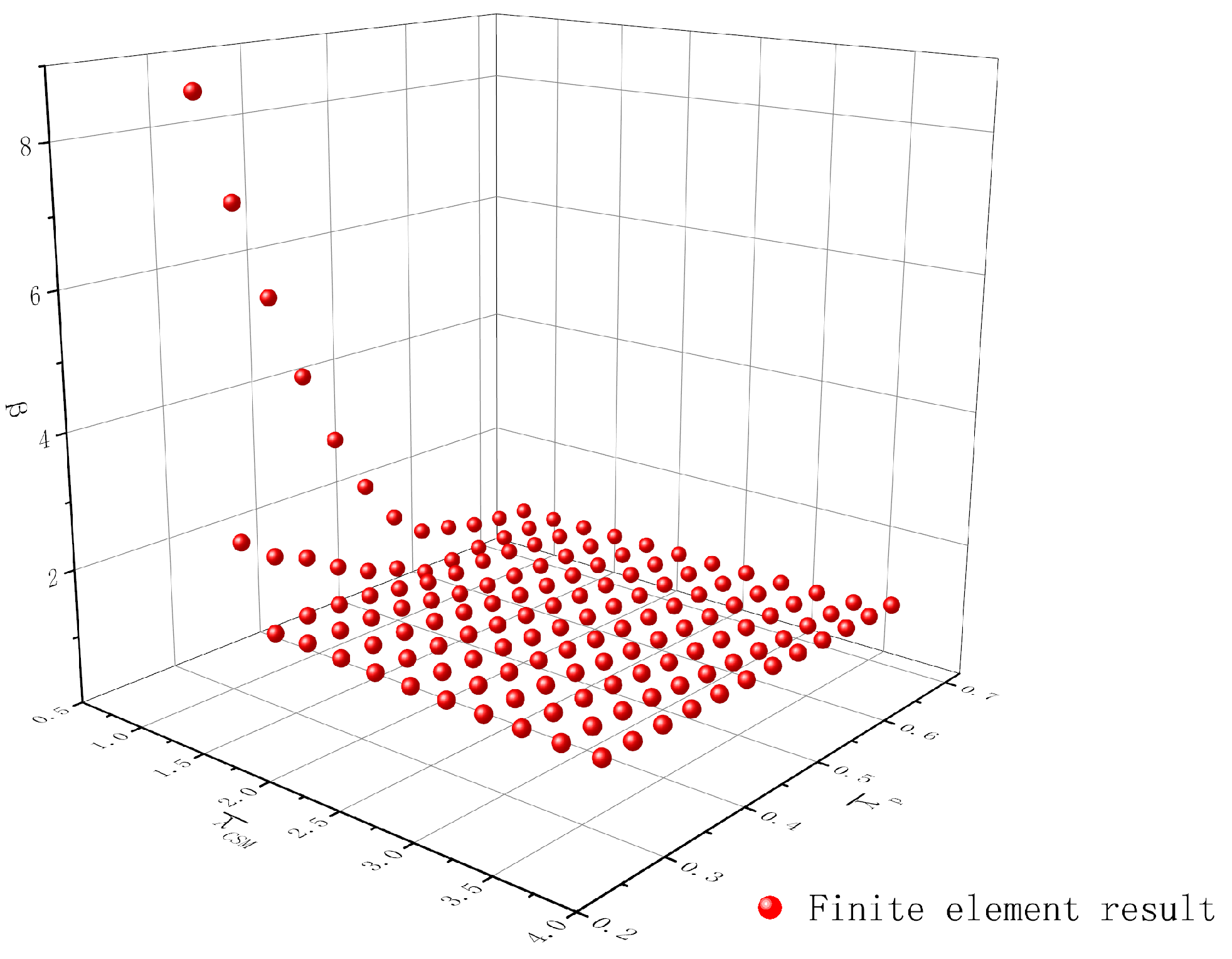
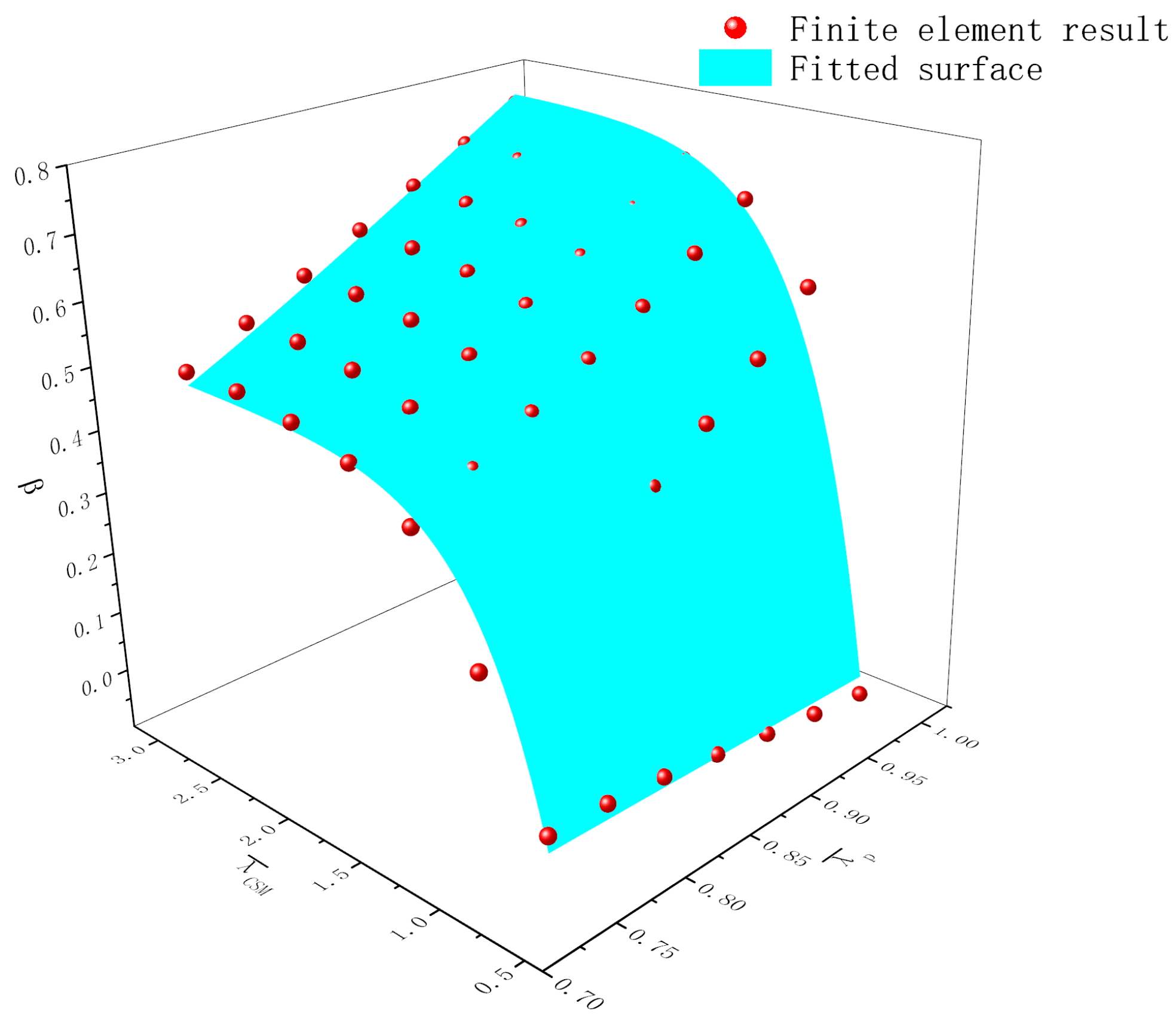
4.4. Calculation of Parameter
4.5. Computational Workflow
- 1.
- Refer to the calculation formula of Continuous Strength Method in reference [13], calculating the section slenderness ratio of structural members and the component section strength ;
- 2.
- Substitute the calculated into Equation (18) to compute the component’s CSM relative slenderness ratio ;
- 3.
- Calculate the component’s relative slenderness ratio using Equation (7);
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- Substitute into the following equation to compute the ultimate bearing capacity result .
5. Comparison of Calculation Methods
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, Z.; Guo, X.; Li, Y. A Brief Review of the Research Status of Aluminum Alloy Structures. J. Build. Struct. 2007, 28, 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Raabe, D.; Ponge, D.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Roscher, M.; Paolantonio, M.; Liu, C.; Antrekowitsch, H.; Kozeschnik, E.; Seidmann, D.; Gault, B.; et al. Making sustainable aluminum by recycling scrap: The science of ‘dirty’ alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 128, 100947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Xing, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Qiu, H.; Nie, R.; Yang, J.; Hui, D.; Chen, W.; et al. A Review of Research on Aluminum Alloy Materials in Structural Engineering. Dev. Built Environ. 2024, 17, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50429-2007; Code for Design of Aluminum Alloy Structures. China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Zhang, Q.; Ji, J.; Yang, L.; Wu, M. Several Important Concepts and Research Bases in the ’Code for Design of Aluminum Alloy Structures. J. Build. Struct. 2009, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- EN 1999-1-1:2007+A1; Eurocode 9: Design of Aluminium Structures–Part 1-1: General Structural Rules. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2009.
- Wang, Y.; Chang, T.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, H.; Yin, J.; Ouyang, Y. Experimental Study on Local Buckling of Short Columns with Aluminum Alloy Open Sections Under Axial Compression. J. Build. Struct. 2015, 36, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Fan, J.; Guo, R. Influence of Plate Group Effects on the Sectional Bearing Capacity of Rectangular Thin-Walled Members. J. Kunming Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2009, 34, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, J. An experimental study on dynamic constitutive relationship of 7075-T651 aluminum alloy. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 816, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, L. The continuous strength method. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.–Struct. Build. 2008, 161, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, L.; Yun, X.; Walport, F. The continuous strength method—Review and outlook. Eng. Struct. 2023, 275, 114924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Young, B.; Gardner, L. Flexural response of aluminum alloy SHS and RHS with internal stiffeners. Eng. Struct. 2016, 121, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Young, B.; Gardner, L. The continuous strength method for the design of aluminum alloy structural elements. Eng. Struct. 2016, 122, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Young, B.; Gardner, L. Deformation-based design of aluminum alloy beams. Eng. Struct. 2014, 80, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Young, B.; Gardner, L. Testing and Design of Aluminum Alloy Cross Sections in Compression. J. Struct. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Young, B.; Gardner, L. Continuous strength method for aluminium alloy structures. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 742, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, M.; Theofanous, M.; Dirar, S.; Lipitkas, N. Aluminum SHS and RHS subjected to biaxial bending: Experimental testing, modelling and design recommendations. Eng. Struct. 2021, 227, 111468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, C.; Gardner, L.; Liew, A. The continuous strength method for the design of circular hollow sections. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2016, 118, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, W.; Lu, X.; Lian, M. Study on the Stability and Bearing Capacity of Aluminum Alloy Box-Section Axial Compression Members Based on the Continuous Strength Method. J. Shenyang Jian Zhu Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 38, 401–409. [Google Scholar]
- Aluminum Design Manual: Specification & Guidelines for Aluminum Structures; The Aluminum Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2015.
- Aluminum Design Manual: Specification & Guidelines for Aluminum Structures; The Aluminum Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2020.
- Zhai, X.; Sun, L.; Zhao, Y. Comparison of Stability Bearing Capacity of High-Strength Aluminum Alloy Compression-Bending Members between Chinese and European Codes. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2015, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; Qi, R.; Zhao, Y. Calculation Methods for Flexural Bearing Capacity of 6082-T6 Aluminum Alloy Members. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2018, 50, 192–198. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; Sun, L.; Zhao, Y. Study on Stability Bearing Capacity of 6082-T6 Aluminum Alloy Box and L-Shaped Section Compression-Bending Members. J. Build. Struct. 2015, 36, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhai, X.; Sun, L. Test and design method for the buckling behaviors of 6082-T6 aluminum alloy columns with box-type and L-type sections under eccentric compression. Thin-Walled Struct. 2016, 100, 62–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhai, X. Reliability assessment of aluminum alloy columns subjected to axial and eccentric loadings. Struct. Saf. 2018, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Sun, W. A new continuous strength method for prediction of strain-hardening performance of high-strength aluminum alloy cylindrical columns. Buildings 2024, 14, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 228.1 or ISO 6892-1; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. China Iron and Steel Association: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Ramberg, W.; Osgood, W.R. Description of Stress-Strain Curves by Three Parameters; NACA TN-902: Washington, DC, USA, 1943. [Google Scholar]
- SteinHardt, O. Aluminum constructions in civil engineering. Aluminum 1971, 47, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X. Theoretical and Experimental Research on Aluminum Alloy Structural Members. Ph.D. Dissertation, Tongji University, Shanghai, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Seif, M.; Schafer, W.B. Local buckling of structural steel shapes. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2010, 66, 1232–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczos, P.; Pawlak, A.M. Experimental Optical Testing and Numerical Verification by CUFSM of Compression Columns with Modified Channel Section. Materials 2021, 14, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Experimental Study on the Axial Compression Performance and Bearing Capacity Calculation Method of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy Rectangle Tubes. Master’s Thesis, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]





| Tensile Specimen | E/MPa | /MPa | /MPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-1 | 74,360 | 309.43 | 322.06 | 423.77 |
| T-2 | 76,460 | 364.63 | 375.55 | 462.99 |
| T-3 | 77,000 | 472.73 | 483.79 | 575.64 |
| T-4 | 78,840 | 359.69 | 372.16 | 460.48 |
| T-5 | 79,540 | 549.03 | 557.27 | 607.44 |
| T-6 | 74,710 | 432.96 | 443.94 | 509.84 |
| T-7 | 73,210 | 463.59 | 473.82 | 541.41 |
| T-8 | 76,310 | 360.7 | 371.35 | 457.47 |
| T-9 | 73,910 | 350.92 | 362.33 | 451.02 |
| Specimen Number | Cross- Sectional Dimensions /mm | Preset Slenderness Ratio | Measured Cross- Sectional Height /mm | Measured Cross- Sectional Width /mm | Measured Cross- Sectional Thickness /mm | Actual Height /mm | Actual Slenderness Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40-40-5-30 | 40 × 40 × 5 | 30 | 39.94 | 40.01 | 4.99 | 493 | 34.2 |
| 40-40-5-45 | 40 × 40 × 5 | 45 | 40.01 | 39.96 | 5 | 710 | 49.24 |
| 40-40-5-60 | 40 × 40 × 5 | 60 | 39.98 | 39.98 | 4.99 | 926 | 64.18 |
| 60-40-3-30 | 60 × 40 × 3 | 30 | 60.01 | 40.03 | 2.99 | 562 | 35.24 |
| 60-40-3-45 | 60 × 40 × 3 | 45 | 60.01 | 40.01 | 3 | 729 | 45.75 |
| 60-40-3-60 | 60 × 40 × 3 | 60 | 60.02 | 40.1 | 2.99 | 981 | 61.42 |
| 80-60-3-30 | 80 × 60 × 3 | 30 | 79.94 | 59.95 | 2.96 | 785 | 32.51 |
| 80-60-3-45 | 80 × 60 × 3 | 45 | 80.09 | 59.88 | 2.97 | 1146 | 47.51 |
| 80-60-3-60 | 80 × 60 × 3 | 60 | 79.94 | 59.92 | 2.97 | 1509 | 62.53 |
| Specimen Number | 40-40- 5-30 | 40-40- 5-45 | 40-40- 5-60 | 60-40- 3-30 | 60-40- 3-45 | 60-40- 3-60 | 80-60- 3-30 | 80-60- 3-45 | 80-60- 3-60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Results /MPa | 388.1 | 319.6 | 192.3 | 442.6 | 262.2 | 192.9 | 297.9 | 230.1 | 172.5 |
| Form of destruction | C | C | C | L | C | C | C | C | C |
| Specimen Number | Test Results /MPa | Finite Element Results /MPa | Difference/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40-40-5-30 | 388.1 | 412.1 | 6.18 |
| 40-40-5-45 | 319.6 | 315.4 | −1.3 |
| 40-40-5-60 | 192.3 | 203.1 | 5.65 |
| 60-40-3-30 | 442.6 | 407.4 | −7.93 |
| 60-40-3-45 | 262.2 | 283.3 | 8.05 |
| 60-40-3-60 | 192.9 | 176.1 | −8.73 |
| 80-60-3-30 | 297.9 | 329.1 | 10.48 |
| 80-60-3-45 | 230.1 | 246.1 | 6.97 |
| 80-60-3-60 | 172.5 | 186.3 | 6.18 |
| Section Category | Section Dimensions | Section Slimness Ratio | Relative Slenderness Ratio of the Member |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | 80 × 80 × 10 | 0.28 | 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, 1.4, 1.6, 1.8, 2.0, 2.2, 2.4, 2.6, 2.8, 3.0, 3.2, 3.4 |
| 70 × 70 × 8 | 0.31 | ||
| 60 × 60 × 6 | 0.36 | ||
| Type 2 | 60 × 40 × 5 | 0.39 | |
| 50 × 40 × 4 | 0.42 | ||
| 60 × 60 × 5 | 0.43 | ||
| 50 × 50 × 4 | 0.45 | ||
| Type 3 | 80 × 60 × 5 | 0.54 | |
| 50 × 40 × 3 | 0.57 | ||
| 50 × 50 × 3 | 0.61 | ||
| Type | 80 × 40 × 4 | 0.65 | |
| 80 × 60 × 4 | 0.68 | ||
| 100 × 100 × 5 | 0.74 | ||
| 76 × 44 × 3 | 0.84 | ||
| 80 × 60 × 3 | 0.92 | ||
| 120 × 60 × 4 | 0.99 |
| Number of the Specimen | /MPa | /MPa | / | /MPa | / | /MPa | / | /MPa | / |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40-40-5-30 | 388.1 | 282.71 | 0.73 | 372.2 | 0.96 | 239.75 | 0.62 | 252.45 | 0.65 |
| 40-40-5-45 | 319.6 | 253.60 | 0.79 | 267.11 | 0.84 | 194.29 | 0.61 | 192.87 | 0.60 |
| 40-40-5-60 | 192.3 | 169.77 | 0.88 | 169.89 | 0.88 | 135.06 | 0.70 | 117.45 | 0.61 |
| 60-40-3-30 | 442.6 | 349.08 | 0.79 | 195.30 | 0.44 | 286.02 | 0.65 | 227.06 | 0.51 |
| 60-40-3-45 | 262.2 | 303.00 | 1.16 | 156.61 | 0.6 | 311.56 | 1.19 | 168.23 | 0.64 |
| 60-40-3-60 | 192.9 | 183.32 | 0.95 | 96.99 | 0.5 | 194.20 | 1.01 | 94.63 | 0.49 |
| 80-60-3-30 | 297.9 | 284.65 | 0.96 | 246.18 | 0.83 | 326.89 | 1.10 | 384.05 | 1.29 |
| 80-60-3-45 | 230.1 | 266.98 | 1.16 | 182.79 | 0.79 | 202.36 | 0.88 | 220.52 | 0.96 |
| 80-60-3-60 | 172.5 | 180.67 | 1.05 | 114.58 | 0.66 | 135.26 | 0.78 | 134.90 | 0.78 |
| Average | —— | —— | 0.94 | —— | 0.72 | —— | 0.84 | —— | 0.73 |
| Variance | —— | —— | 0.02 | —— | 0.03 | —— | 0.04 | —— | 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J. Calculation Method of Axial Compressive Capacity of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy Rectangular Tubes Based on Continuous Strength Method. Buildings 2025, 15, 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142387
Huang Z, Li H, Zhang C, Liu J. Calculation Method of Axial Compressive Capacity of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy Rectangular Tubes Based on Continuous Strength Method. Buildings. 2025; 15(14):2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142387
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Zhiguan, Hailin Li, Cheng Zhang, and Junli Liu. 2025. "Calculation Method of Axial Compressive Capacity of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy Rectangular Tubes Based on Continuous Strength Method" Buildings 15, no. 14: 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142387
APA StyleHuang, Z., Li, H., Zhang, C., & Liu, J. (2025). Calculation Method of Axial Compressive Capacity of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy Rectangular Tubes Based on Continuous Strength Method. Buildings, 15(14), 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142387









