Abstract
The main causes of damage include poor site selection, such as building on fault lines or on fill soil, as well as deficiencies in design, materials, and workmanship. Damage levels are also linked to the economic conditions of the region. In the 1939 earthquake, there were high casualties due to the magnitude of the earthquake, lack of engineering design in traditional structures and unsuitable soil conditions. Similarly, in the 1992 earthquake, unexpected damage occurred due to faulty designs created by inexperienced engineers who lacked sufficient knowledge of the seismic behavior of structures, errors in craftsmanship and workmanship, and unsuitable residential area selection for construction. These problems continue today and put most of the building stock at risk in case of a major earthquake. Seismic steel isolators are used in two new buildings in the city; if they are effective, they should be made mandatory in new construction. Otherwise, consideration should be given to relocating the city to the more stable southern rocky areas, which were unaffected in both 1939 and 1992.
1. Introduction
The aim of this study is to investigate the reasons for the catastrophic consequences of earthquakes in Erzincan. For this, I think it would be good to start with the question of whether Erzincan is ready for the next earthquake.
Is Erzincan ready for the next severe earthquake? In order to answer this question, it is necessary to examine different structural damage situations and their causes as a result of previous earthquakes in Erzincan and around the world. The Erzincan residential area is located on the northern Anatolian fault zone, which crosses Turkey in an east–west direction. The Erzincan plain, located on the North Anatolian fault, is approximately 50 km long in the direction of the fault and its width is approximately 15 km [1]. Ground deformations occurring in this zone have affected the Erzincan plain. According to historical information, there have been many devastating earthquakes centered on Erzincan, as stated in Table 1. The largest of these is the 7.9 magnitude earthquake that occurred [1].

Table 1.
Earthquakes that have affected Erzincan throughout history.
The part of the Erzincan plain close to the mountain slopes consists of gravel-based, coarse-grained soils, while soils of silt, clay, and sand become more dominant in the middle part of the plain [2]. Research and practice have shown that a structure built on deformable soil may respond differently compared to one built on stable soil. This was clearly demonstrated in the 1992 Erzincan earthquake. Almost all the structures that were severely damaged or collapsed in this earthquake were constructed on silty and clay soft soils. During earthquake shaking, a structure is affected by three main factors. These factors are the structure, the foundation, and the soil under the foundation. In fact, in the case of flexible support, there is an interaction between the structure and the underlying soil that causes changes in the dynamic response [3]. The soil–structure interaction will cause an increase in the spectral period due to an increase in the fundamental period during an earthquake occurring in soft soils. This will cause an increase in acceleration and, therefore, an increase in the earthquake load acting on the structure [4]. All buildings in the Erzincan plain were built on fault zones and filling soil. The acceleration on the ground in this region is quite large. Except for earthquakes, the acceleration in the earth’s crust is zero and does not have any lateral effect on the structure. The energy waves generated during an earthquake are transmitted to the structure depending on the type of soil; strong soils absorb some of the energy and cause less force to act on the structure, while in weak soils the force increases and acts on the structure. This situation was clearly seen in the 1992 Erzincan earthquake. In 1992, almost all the buildings that collapsed or were severely damaged in Erzincan were built on silty clay soils. Ground rupture and ground shaking are the most vulnerable effects created by earthquakes, resulting in less or more severe destruction to buildings and other rigid infrastructure. A composite combination of earthquake magnitude, local geological conditions, and distance from the earthquake epicenters defines the severity of the local impact [5]. The properties of the ground on which the building sits are very important for the nonlinear earthquake behavior of buildings. These properties of the soil are important for the behavior of buildings because these properties of the soil are transmitted to the structures [6]. During an earthquake, an acceleration occurs in the earth’s crust depending on the magnitude of the earthquake and soil properties. Because of this acceleration, a force acts on the structure depending on the mass of the structure. As acceleration increases, the force acting on the structure also increases. For this reason, fault zone and fill soil is not suitable for construction, as it increases the earthquake loads on structures during an earthquake. This situation may cause the structures to suffer damage or collapse. As in the majority of places in Turkey, when choosing a residential area in Erzincan, areas close to agricultural and water resources were chosen rather than areas based on scientific facts. In general, these regions are suitable for agriculture, but not suitable for construction [7,8]. Due to the increasing effect of the ground on the earthquake loads on the structures built on the agricultural land, forces above the expected forces act on the structure and cause the structures to collapse or to be severely damaged. This effect increases even more if the structure is on the fault zone. Soil–structure interaction (SSI) effects can significantly change the behavior of structures during earthquakes. The inclusion of SSI in seismic analysis often leads to lower stresses in the structure and hence a more economical design. Consideration of SSI in design can also lead to the observation of adverse effects due to the modification of the dynamic characteristics of the structure. Examples of adverse effects are higher displacements or story drifts, increases in floor or story shear forces, higher post-elastic demands on structural members, or the collision of adjacent buildings separated by an inadequate structural connection [9].
Most earthquakes occur due to the movement of faults. Faults slowly build up stress that are suddenly released during an earthquake. The movement of the earthquake in the earth’s crust is transmitted to the structure by the ground on which the structure sits. If the structure can absorb this energy, it survives, if not, it collapses [10]. In settlements located on active fault zones, it is mandatory to check the seismic performance of existing structures and take necessary precautions, as well as to design and manufacture new structures in a strong manner against earthquakes. Especially in the buildings constructed before the 1999 Marmara earthquake, concrete production errors, faulty reinforcement details, and poor-quality workmanship, which are frequently encountered due to the lack of supervision and regulations, make the earthquake safety of such buildings highly suspicious [11]. In addition, errors in the construction details of traditional structures in rural areas cause these structures to be severely damaged and sometimes even collapse. Turkey has two fault zones capable of producing large earthquakes. One of them is the Eastern Anatolian Fault, which produced the Kahramanmaraş earthquake in 2023. Since the period of this fault is quite long (500–600 years), the earthquake phenomenon has not occurred during a period of people living in this region and they have not taken into account the earthquake phenomenon for economic reasons while designing their buildings. The other is the North Anatolian Fault, which has short return periods. Although its return period is 50–60 years, people forget the earthquake reality in a short time and the structures they have designed to reduce the building cost do not have sufficient rigidity, strength, and ductility. In the last century, more than twelve major earthquakes with a magnitude of at least 7 (Ms) have caused significant loss of life and extensive structural damage in Turkey [12]. With the increase in the incidence of natural disasters such as earthquakes along with economic development, the seismic resistance of engineering structures is being designed in larger scales with increased seismic resistance [13]. Beam–Column Joints are the most important element affecting the seismic behavior of reinforced concrete structures, especially moment-resisting frame structures, and their design is usually carried out as the last step of frame design according to well-known hierarchy principles [14]. Nowadays, the seismic design of reinforced concrete frame structures is based on hierarchy principles to exclude brittle or other undesirable collapse mechanisms and to develop a ductile global collapse mechanism. This ensures that node failure is prevented. Indeed, node failures, which are difficult to repair, are characterized by mechanisms that show strength and stiffness reduction under cyclic loading conditions [15]. Recent earthquakes around the world have shown us that structures to be built in these regions must have sufficient strength, stiffness, and ductility. The main objective of this study is to evaluate the earthquake preparedness level of Erzincan province. In this context, structural damages caused by past earthquakes (especially the 1939 and 1992 Erzincan earthquakes) will be analyzed and the adequacy of the existing building stock and urban planning against a possible earthquake will be questioned.
What types of structural damage have occurred in Erzincan in past earthquakes, and what are the main causes of this damage?
To what extent does the existing building stock in Erzincan comply with the current earthquake codes?
How do the soil structure and geological characteristics of Erzincan affect the performance of structures against earthquakes?
Are the structural and urban measures taken against earthquakes in Erzincan adequate?
2. What Is to Be Learned from Damage and Failure of Structures During Recent Earthquakes
2.1. Effects of Earthquake on Structures
In recent years, natural hazards such as earthquakes have continued to be one of the greatest challenges in the field of structural and earthquake engineering. These challenges include the revision of regulations to provide recommendations for the earthquake assessment of structures and further procedures for the renovation, rehabilitation and repair or retrofitting of buildings [16]. Every year, approximately 60,000 people worldwide lose their lives in natural disasters. The vast majority of these deaths are caused by the collapse of buildings in earthquakes, and the vast majority occur in undeveloped or developing countries. This is despite the availability of engineering solutions that can largely, if not completely, eliminate the risk of such fatalities. What is the reason for this? Engineering solutions are both expensive and technically difficult to implement. It is often the case that interventions planned for disasters remain unimplemented or ineffectively implemented. The major reason for this is the role of economic and political issues. Regulations in developing countries appear to be limited, perhaps due to limited capacity, and in many cases the impact and poverty impact. Public constructions in undeveloped and developing countries are often of low quality [17]. In the earthquakes in Turkey, public buildings suffered the most damage and collapse.
Earthquakes are uncontrollable natural events, but their effects can be minimized. No government can prevent earthquakes, but all governments can optimize regulations to reduce fatalities when disasters occur. The purpose of the regulations is to determine the necessary rules and minimum conditions for the design and construction of all public and private buildings and building-type structures to be rebuilt, altered, and enlarged, and for the design and construction of all or parts of all public and private buildings and building-type structures to be made with consideration of earthquake effect, and for the evaluation and retrofitting of the performance of existing buildings to be made with consideration of earthquake effect. After each earthquake, the regulations are revised to eliminate the deficiencies that arise. Earthquake regulations in Turkey have been revised a total of eight times, in 1947, 1953, 1961, 1968, 1975, 1998, 2007 and 2018, and the 2018 regulation is still in force. In these regulations, the minimum requirements for earthquake-resistant design and construction of buildings are given by taking into account the earthquake zone and soil properties of the building. However, earthquake mortality varies widely and systematically across countries. Earthquake-resistant construction is expensive; in poor countries, households and governments spend scarce resources on other needs rather than earthquake-resistant construction. Second, while developed countries emphasize efforts to implement and enforce earthquake-resistant construction standards, little attention is paid to them in less developed countries [18]. Since most of the buildings in undeveloped countries are not constructed in accordance with codes and standards, i.e., they are constructed using traditional methods and materials, so that the extent of damage and mortality in earthquakes increases. Earthquakes were responsible for an estimated 1.87 million deaths in the 20th century, with an average of 2052 deaths per human-affecting event between 1990 and 2010. The 8.9 magnitude earthquake in Japan in March 2011 and the subsequent tsunami killed more than 28,000 people, while a smaller 7.0 magnitude earthquake in Haiti in January 2010 killed 222,500 people. The difference is approximately 8 times. This difference is due to the level of development of the countries [19].
The main causes of earthquakes and their problems on civil engineering structures are discussed through observations of recent major earthquakes. The results show that a large damage contrast is observed between developed and underdeveloped countries. While in developed countries the damage was lower, in less developed countries the extent of damage was higher [5]. The reason for this is that the design, inspection, and supervision of structures in developed countries are much better than in underdeveloped countries. In addition, big earthquakes have shown engineers the necessity of taking into account the permanent deformations that will occur in the structure during the design of structures. Traditional buildings are poorly constructed due to lack of engineering services, use of poor materials and economic poverty. In areas close to the fault zone, these buildings are considered to be very risky buildings in terms of earthquakes [20].
Watanabe [21] concluded that most of the buildings with severe structural damage in the Hyougoken-Nanbu earthquake were constructed before 1981, and the cause of the damage was limited to the regulations. If the buildings are constructed on solid soil away from the fault zone and if the design, supervision, and controls are well performed, the buildings can be damaged, and the damage level can be limited, and the collapse of the structures can be prevented. One of the causes of earthquake damage in many settlements around the world, as in Erzincan, is the widespread use of initial soft floors by architects to provide parking space in buildings or to provide shop areas according to the wishes of the owners. However, soft and weak floors are one of the most dangerous irregularities in severe earthquakes, as historically many structures with these conditions have failed or suffered severe damage during major earthquakes worldwide [21]. The poor performance of irregular buildings has been partially documented after some strong earthquakes, as engineers are often more interested in emphasizing the spectacular damage, partial or complete collapse of individual buildings, rather than spending time and effort to document this in the context of the amount of damage observed in a city during a strong earthquake event. Several recent earthquakes, such as the 1992 Erzincan and Landers, 1994 Northridge, 1995 Kobe, and 1999 Chichi earthquakes, have caused significant damage to flexible structures close to fault lines [22].
Ulusay et al. [23] The Kocaeli and Düzce earthquakes in Turkey in 1999 caused many casualties and serious structural damage to buildings. The damage was caused partly by permanent ground displacement due to faulting and partly by liquefaction and the lateral spreading of soil, as well as poor building quality and inappropriate building materials. Arslan and Korkmaz [12] state in their research that the building stock in Turkey is generally made up of reinforced concrete structures and that in recent earthquakes, many of these structures in the epicenter regions collapsed or suffered severe damage. They state that the causes of the damage are soft stories, strong beams–weak columns, inadequate column dimensions, poor detailing practices, and insufficient concrete strength. In the PHD study, Abdelnaby states that major structural damage occurs in structures on the fault zone due to the dramatic loss of hardness and strength of structural elements as a result of material deterioration under repeated earthquake loads [24].
Bayraktar et al. [25] investigated the performance and damage of reinforced concrete buildings in the Van earthquakes of 23 October (Erciş) and 9 November (Edremit) 2011. They determined that a total of 28,000 buildings in the city center and surrounding villages were damaged or had collapsed in the Erciş earthquake. They state that this number increased to 35,000 after the Edremit earthquake. They state that a large portion of reinforced concrete buildings that did not receive engineering services completely collapsed or were severely damaged. They state the causes of damage as follows; low construction quality, low concrete strength quality and non-ribbed reinforcement steel, insufficient detailing in beam–column connections, strong beam–weak columns, soft floors, weak floors, insufficient transverse reinforcement, short column effect, etc. It is stated that the ground motions recorded close to the fault zone are different from those recorded far from the fault zone, and the fault geometry and the direction of the traveling seismic waves increase the extent of damage to the structures close to the fault zone due to the directionality effect, which may lead to serious structural damage [26,27].
In the examinations made after earthquakes around the world, the reasons for the heavy damage or collapse of structures can be listed as the distance of the structures to the fault zone, the characteristics of the soil under the structures, the quality of the structure (design, workmanship, and material quality) and the inadequacy of the regulations. As a result of the research, it is seen that the causes of damage and collapse in structures are similar all over the world. While the majority of these problems have been solved in developed countries, these problems continue in underdeveloped countries. Raghunandan and Liel [28] state that the risk of collapse of buildings will be higher when subjected to ground motions of longer duration compared to ground motions of shorter duration with the same ground motion intensity, thus the duration of ground motion will affect the collapse capacity of reinforced concrete structures. Therefore, it is recommended to consider the intensity and frequency content of ground motion as well as its duration in structural design and seismic risk assessment. Tesfamariam and Liu [29] emphasize the weakness of existing buildings and the need for seismic retrofitting of existing structures due to the damage reported from recent global earthquakes such as the 2008 Sichuan earthquake in China, the 2004 Sumatra earthquake in Indonesia, the 2003 Bingöl earthquake in Turkey, and the 1994 Northridge earthquake in the USA. The reasons for the weakness of buildings are stated as factors such as the design of buildings according to outdated codes, poor design, poor workmanship, poor materials, and the characteristics of the soil under the structure.
2.2. Damage Situations of Buildings in the Erzincan Earthquake and the Reasons for This Damage
The 1939 Erzincan earthquake, or the Great Erzincan Earthquake, was a 7.8 (±0.4) magnitude earthquake with its epicenter in Erzincan. This earthquake is recorded in the literature as one of the largest earthquakes on lateral strike-slip faults in the world [30]. The rupture started from the eastern end of the settlement of Erzincan province and extended to Amasya (400 km) passing through the settlement area of the province [31]. The reasons for the great damage and loss of life in this earthquake were the fact that the settlement was on a fault zone, the buildings were constructed using traditional materials without engineering services, the magnitude of the earthquake, and the alluvial fill soil on which the buildings were built. Embankment soils magnify the energy generated during the earthquake and transmit it to the structures [7,8]. The fact that the earthquake base or epicenter is located in a residential area means that the energy released during the earthquake reaches the buildings directly without being absorbed [29]. This may have created larger than expected forces in the structure, causing serious damage or collapse [8,29]. Therefore, almost all of the buildings exposed to the 1939 earthquake in Erzincan were not earthquake-resistant structures because they were constructed with traditional methods and materials without engineering services [1]. Due to these unfavorable factors, the loss of life and property was quite high. The damaged residential area after the 1939 Erzincan earthquake is shown in Figure 1. There is a risk of collapse of traditional buildings in earthquakes above magnitude 5. Vernacular architecture in earthquake-prone areas is particularly vulnerable due to poor maintenance, linked to the general use of poor materials, scarcity of resources in poor communities, and at times the absence of good construction. Lack of structural integrity due to poor connections between building elements is one of the main causes of earthquake damage in traditional buildings. Proper connections are necessary to ensure the ‘box behavior’ of the building during earthquakes so that inertial forces can be distributed between structural elements and in-plane resisting mechanisms can develop in walls, which are typically the main structural elements in conventional buildings. However, due to the absence of solid ground and foundations, a structure is formed that causes the walls to operate individually. This situation exposes the seismic vulnerability of traditional buildings and leads to out-of-plane collapse due to inadequate wall connections and wall separation at corners. When seismic forces are transferred between vertical walls, the concentration of tensile and shear stresses at the connection leads to vertical cracking and ultimately to global collapse of the external walls [20].
In traditional buildings, clayey soils are generally used as binders for the stones used in wall construction. As these binders lose water over time, they lose their binding properties and the bond between the stones used in wall construction disappears, disrupting the integrity of the wall and causing the structure to collapse. In traditional buildings, local timbers are used as beams and these timbers are damaged by insects and lose their durability. The timber floor system resting on these walls cannot transfer the earthquake loads to the vertical elements to which it is connected (the walls on which it rests) in proportion to their stiffness, in other words, it cannot create a box effect as in the reinforced concrete floor system. A similar weakness was also reported in the study by Yardımlı et al. [32] which stated that the slabs cannot move as a mass through the beams (beams) formed at the connection points and therefore cannot withstand the earthquake load. Another problem is that since there is no roof on these buildings, soil is constantly poured and compacted on the slab platform to prevent water from dripping into the building during rainfall. For this reason, the slab thickness of traditional buildings reaches 70–80 cm. During an earthquake, the wooden beams, which have difficulty in carrying this load due to the dynamic effect, break, and the structure collapse inwards. This was one of the reasons for the high death toll in the 1939 Erzincan earthquake. Very large earthquakes are not required for the collapse of traditional buildings. The two reasons for the weakness of Erzincan buildings against earthquakes are that the binder used is very weak and loses its binding strength over time and there is no reinforced concrete slab system in the buildings. Reinforced concrete slabs have the ability to transfer the horizontal earthquake loads to vertical elements according to their stiffness during earthquakes and provide resistance to earthquake effects as a whole, in other words, reinforced concrete slabs provide box behavior of the structures. In addition, the stones used in wall construction are round and do not create a locking effect in the masonry. There are no such structures left in Erzincan except in very rural areas.

Figure 1.
A view of residential areas after the 1939 Erzincan earthquake [33].
Normally, according to the earthquake design principle, an earthquake of magnitude 5.5 should not cause damage to buildings [34]. However, although the 1983 Erzincan earthquake of magnitude 5.5 did not cause a major destruction of buildings, it caused moderate damage to many buildings. In 1983, civil engineers in Erzincan and all over Turkey did not have much knowledge about earthquakes and their damage to buildings because they had never encountered such an event before. Forty-four years had passed since the 1939 earthquake and this was enough time for many things to be forgotten. After the 1983 earthquake, buildings with moderate damage should have been reinforced, but since the engineering dimension of the event was not understood, this damage was covered with plaster and paint. In the 1992 Erzincan-centered earthquake, all the buildings that received moderate damage in the 1983 earthquake collapsed. When the epicenter of the earthquake is superficial, earthquakes with a magnitude over 5.5 may cause damage to structures [35]. The reasons for the moderate damage to the buildings in the center of Erzincan in the 1983 Erzincan earthquake include the fact that the buildings were built on fill soils and fault zones, the earthquake phenomenon was not taken into consideration in their design, the reinforced concrete workmanship was poor, and the concrete was produced in situ according to traditional methods. In this method, aggregate grain distribution, water/cement, cement amount, and mixing process were not at the desired level. For this reason, the concrete strength in reinforced concrete structures was quite low. In reinforced concrete structures, the performance of the structure depends on the working together of concrete and steel. If the concrete is too weak, the reinforced concrete element or structure will fracture or collapse below the expected performance.
In the 6.7 magnitude 13 March 1992 Erzincan earthquake, all of the buildings damaged in the 1983 earthquake were demolished. It was determined that 10% of the existing building stock was heavily damaged or had collapsed, 15% was moderately damaged and 20% was slightly damaged [36]. Many factors play an effective role in the formation of structural damage in buildings due to earthquakes occurring worldwide. These factors consist of earthquake characteristics, flawed design, distance of the structures to the fault zone, local soil conditions, old regulations, and building quality. In the 1992 Erzincan earthquake, factors such as the proximity of the epicenter to the city, the fact that the buildings were built on fill soil and fault zones, high ground acceleration, inadequate building design, workmanship, and material quality increased the extent of damage. However, it is possible to list the important reasons why the buildings were damaged more than expected such as the fact that the buildings were built on embankment soil and fault zones, non-compliance with the regulations, poor workmanship, and the fact that the strength of the concrete used in the buildings was almost negligible. Core samples taken from the surviving structures showed that the values varied between 7 and 10 MPa [36]. These concrete results alone are reason enough to explain the extent of the damage. In recent strong earthquakes, many of the engineered structures collapsed or were severely damaged. It can be said that this was due to the estimated earthquake load being lower than the effective earthquake load, or the impact on the structure exceeding the strength of the structure, or both [35]. The reasons why the damage in the buildings was higher than expected in studies carried out in the field after the 1992 earthquake are that the soil on which the buildings were built was not suitable for construction (alluvium-filled ground) and, while the magnitude of the earthquake that occurred 1992 in Erzincan was 6.7, the maximum acceleration measured (in the east–west direction) was 0.490 m/s2, which is twice the acceleration of the 6.7 magnitude earthquake [37].
The soil profile of Erzincan province is shown in Figure 2. As can be seen in the figure, the structure of the ground under the structures in Erzincan continues as alluvial fill (1–1.5 m) at the top, loose silty sand (2–4 m) below it, silty ground (1.5–3 m) below that, and loose silty sand (3–5 m) below that. From the soil profile, it is possible to say that the soil is very bad in terms of civil engineering and is an infill soil. It can be said that the acceleration increased so much due to the magnifying feature of the local soil conditions [38], the distance of structures to the fault line, and the presence of underground water. The buildings were not designed to be earthquake resistant; in other words, there is no vertical element to provide lateral deformation resistance of the building [39]. Low concrete strength may be another cause. The reasons for the low concrete properties include the absence of any design for concrete production, the aggregate used being dirty, the concrete being poured traditionally by hand or with a mixer, and the Euphrates River aggregate used not being suitable for concrete. In terms of affecting physical and mineral structure, sand and gravels were used consisting of serpentine, andesite, opal, quartz, limestone, and peridotite. These minerals decompose over time, causing the aggregate to lose its strength [40]. Several design errors were made by engineers who did not have sufficient knowledge or experience about the earthquake behavior of structures. It is possible to list the defects caused by design errors as follows:

Figure 2.
Soil profile along the foundation depth.
2.2.1. Soft Floor Buildings
In most of the buildings, open floors are needed for car parking, retail stores, etc., and these floors are called soft floors. The main problem faced by project engineers is that the presence of a soft floor causes structural irregularity in terms of stiffness and strength. Therefore, determining the soft floor requirements and their effects on the building is very important in the design process to predict the seismic performance of buildings [41,42].
In Erzincan, as is the case throughout Turkey, the ground floors of buildings in the city center are generally for commercial use, and the upper floors are used as home or offices. In such cases, on floors other than the ground floor, a brick infill wall is left between the frame, and on commercially used ground floors, the frame is left empty. This situation causes the formation of a soft floor on the ground floor. A soft floor has less rigidity than the floors above and this floor will have more displacement shown in Figure 3. Due to a soft floor, as in this figure, shear forces that the building elements could not withstand can cause serious damage or collapse of the structure. A soft floor can be determined by dividing the total displacement of the structure by the total building height.

Figure 3.
Soft floor building with displacement of the lower floor in Kahramanmaraş, Türkiye.
The structure is laterally pushed due to the lateral force acting on the structure during the earthquake as shown in Figure 3. While the lower ends of the column do not become displaced due to support, the free upper end becomes over-displaced. As a result of this displacement, shear force and bending moment are generated at the upper and lower ends of the column above the expected values and hinging occurs at the ends of the columns [42] shown in Figure 3.
2.2.2. Poor Reinforcement Workmanship and Inadequate Stirrups in Columns and Beams
Stirrups in reinforced concrete elements can effectively improve the mechanical properties of these elements and the concrete. However, normal strength stirrups yield prematurely as a result of their low yield strength and cannot provide sufficient restraining force to the core concrete. For this reason, low-strength stirrups cannot contribute much to the mechanical properties of reinforced concrete elements and concrete [42]. Poor reinforcement workmanship and insufficient stirrups in columns increase the slenderness of the columns, which can cause the entire structure to collapse. As a result of insufficient reinforcement and stirrups in columns, plus the use of mild steel in the structures, low lateral stiffness and large drifts can occur in the columns, causing the structures to collapse or suffer severe damage [39]. Before 1992, in Erzincan province, Turkey, building controls were either non-existent or very weak, except for important buildings. Inexperienced and uninformed reinforcement workers attached the reinforcements, but they did not do so to specifications. Especially at column and beam joints, there were missing or no stirrups, which caused such structures to suffer great damage and collapse during earthquakes. In structures where lateral deformation is not prevented, the largest shear forces occur at the column–beam node. If there is not enough reinforcement and stirrups here, large shear cracks may occur and cause the structure to collapse [36,39]. It was observed that the collapse of the majority of buildings in both the 1992 Erzincan and the 1999 Marmara earthquakes was caused by the fracture of columns [39]. Uneducated steel workers acted very carelessly in the reinforcement work, and they did not think about the result. These factors, combined with a lack of control, resulted in damage and disaster from the earthquake.
2.2.3. Short Column
Short columns are encountered due to lateral constraints on displacement. This is the case for columns in buildings whose infill walls do not extend to the full height of the story to provide space for windows. Partial height infill walls are frequently used in many types of buildings where the incomplete height is generally attributed to window openings. If the infill walls in a reinforced concrete frame are constructed shorter than the column height and they are connected to the column, i.e., there is limited or no gap between the column and infill wall, the columns are unable to bend freely under the earthquake-induced lateral loads due to the high in-plane stiffness of the infill walls. Hence, the columns are confined and can only bend between the top of the infill wall and the bottom of the beam of the bounding frame, inducing the so-called short column effect [43]. In this case, excessive shear forces occur in the short column height, especially during earthquake-induced shaking. Therefore, if the partial height infill is not separated from the bounding frame in a building, the columns can be seriously damaged during an earthquake and this situation can cause severe damage and eventually collapse of the building. This short column effect is a form of damage observed frequently in earthquake-damaged buildings all around the world. Short column conditions are an important source of severe earthquake damage. These conditions are caused by the architectural design of the building. The effects can be resolved from a multidisciplinary point of view, which can be considered as engineering, architecture, and the construction phase, since their resolution can only be achieved by an integrated approach to building design that recognizes the interaction of these three disciplines. Damages caused by these effects are frequently encountered in earthquakes that occur worldwide [42]. In the new codes, architectural decisions leading to short columns have been reviewed and situations that may affect this behavior are prohibited. The short column effect occurs where the movement of one part of the column is inhibited and the movement of another part of the column is not inhibited. Where there are window openings, the shear force at the free end of the column as a result of the shortening of the column length exceeds the shear strength of the column and creates hinges at the free end of the column. This situation can be seen in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
The reason for the formation of short columns and the situation after the earthquake [44].
As can be seen in Figure 4, since the movement of a large part of the column is prevented by the infill wall, the shear force that will occur in the movable upper part of the column may reach very large values, exceeding the shear strength of the column and causing shear damage in this part and subsequent hinging, causing the structure to lose its stability.
Hinges can minimize the vertical and horizontal load carrying capacities of the column and can cause the structure to collapse.
2.2.4. Lack of a Shear Wall
Frame systems are structural systems used in most seismic regions. However, Chile, one of the most seismically active countries in the world, is an exception to this practice. In Chile, almost all residential buildings higher than five stories consist of reinforced concrete shear walls. In the 2010 Chilean earthquake (Mw 8.8), only two percent of the exposed residential building inventory suffered severe damage, but many structures were affected by ground accelerations greater than those prescribed in the Chilean seismic design code. This observation suggests a large (and undesirable) overstrength in such buildings [45]. A shear wall is a sufficient vertical element to provide lateral deformation rigidity of the structure. Buildings with sufficient shear walls to prevent lateral deformation survived the 1992 Erzincan earthquake with minor damage. A similar situation was seen in the 1999 Marmara earthquake. In structures where lateral deformation is not prevented, columns are exposed to inelastic displacement and very large shear forces occur at the end of the column, causing sudden and brittle fracture of the column, causing the collapse of the structures. This situation is more evident in structures with vertical and horizontal element irregularities. In the 1997 and 2007 Turkish earthquake regulations, the amount of shear walls is required to be 1% of the ground floor area in both directions.
2.3. Summary of the Causes of Damage to or Collapse of Buildings and Structures in Erzincan
2.3.1. Normative Base
Problems such as inaccurate determination of the earthquake load that will affect the structure, inaccurate determination of the seismicity of the region, very low strength of the concrete used in the structure, design of the structures according to the old regulations, construction of the structures by untrained craftsmen and workers with uninformed and inexperienced engineering services, and the fact that the settlement area of the city is on the filling ground and fault zone.
2.3.2. Materials
TS EN 206 Certificate [46] is a Turkish standard that determines the production, performance, and conformity criteria of concrete and is compatible with European standards. This standard, which regulates the requirements for the quality, durability, and service life of concrete, aims to ensure the correct production and use of concrete in the construction sector. Prior to this regulation, except for very important structures, concrete was prepared on site according to the traditional method. In this method, fine and coarse aggregates were mixed and poured at the construction site; this mixture was far from the desired aggregate grain distribution and negatively affected the performance of the concrete to be produced. First, the concrete mixer was filled with aggregate, then cement and water were added, the concrete mixer was started, and the concrete was transported to the molds by lift. Since the workers using this method were paid by the cubic meter of concrete poured, they moved very fast in order to pour more concrete and did not comply with the amount of cement, water/cement ratio, and mixing time. Therefore, the concrete produced had a very heterogeneous structure. When these reasons are combined with inadequate concrete placement and maintenance, it is not possible for the concrete produced to show the expected performance. The disadvantages of concrete production by this method can be explained as the use of aggregate as if it was taken from a stream or riverbed, dirty aggregate, poor aggregate gradations, inability to adjust the water/cement ratio, and the inability to adjust the concrete mixing time [46].
2.3.3. Building Performance
Problems occurred due to a lack of shear walls, which provided insufficient lateral displacement rigidity and weakness in the column beam area; lack of reinforcement detail; low concrete strength; weak corner connections in masonry structures, etc.
2.3.4. Insufficiency or Lack of Control
Failure to check the materials used in the buildings constructed in Erzincan, the suitability of the projects, and the application of the projects.
3. Results
3.1. Normative Base
Problems such as inaccurate determination of the earthquake load that will affect the structure, inaccurate determination of the seismicity of the region, very low strength of the concrete used in the structure, design of the structures according to the old regulations, construction of the structures by untrained craftsmen and workers with uninformed and inexperienced engineering services, and the fact that the settlement area of the city is on the filling ground and a fault zone.
3.2. Building Performance
Problems occurred due to lack of shear walls, which provided insufficient lateral dis-placement rigidity and weakness in the column beam area; lack of reinforcement detail; low concrete strength; weak corner connections in masonry structures, etc.
3.3. Insufficiency or Lack of Control
As in Turkey in general, except for very important buildings in Erzincan, the materials used in the buildings, the suitability of the projects, and the application of the projects are not controlled. In every major earthquake, some damage is likely to occur in residential areas, but it is possible to list the reasons for this damage to reach disaster dimensions such as workmanship errors, material errors, engineering errors, lack of supervision, and wrong residential area selection. Damage and collapse of buildings in the Erzincan earthquake was caused by these errors, if we evaluate the existing building stock in Erzincan within the scope of these errors.
3.4. Design Errors
Design errors largely continue. The fact is that civil engineers do not have sufficient knowledge or experience about the earthquake behavior of buildings. Therefore, they are under the control of the ‘software programs’ they use. It is uncertain how structures designed by engineers who do not have sufficient knowledge and experience with the earthquake behavior of reinforced concrete structures will behave during an earthquake. The biggest problem seen in the buildings constructed by inexperienced engineers in Erzincan is the use of the minimum criteria recommended by regulations. All three of the 1997, 2007, 2018 Turkish Earthquake Regulations have the same objectives, but there are very minor differences in calculation principles and application. The purpose of these codes is to prevent damage to structural and nonstructural elements in mild earthquakes, to limit and repair the damage to structural and nonstructural elements in moderate earthquakes, and to prevent permanent structural damage in severe earthquakes. The differences between the three codes are very small differences in terms of irregularities (horizontal and vertical), minimum section dimensions, minimum reinforcement ratio, lateral drift stiffness values, and minimum concrete class to be used in the structure. This situation may also pose a great risk in structures designed according to minimum criteria because earthquake loads may act much more than expected on structures built on fault zones and infill soils. Many young engineers tend to increase the lateral drift stiffness of the structure by increasing the column dimensions instead of using shear walls. It has been observed in the 1992 Erzincan, 1999 Marmara, and 2023 Kahramanmaraş earthquakes that it is not possible to provide lateral drift stiffness of a reinforced concrete structures with only column stiffness in severe earthquakes. In these earthquakes, this was observed in the structures that were severely damaged or that collapsed due to permanent deformation due to insufficient stiffness of the columns. Traditional buildings were poorly constructed due to lack of engineering services, poor use of materials, and economic poverty. In areas close to the fault zone, these buildings are considered as very risky buildings in terms of earthquakes [39].
Structures designed by a group of engineers lacking knowledge and experience on how reinforced concrete structures will behave during earthquakes and constructed by uninformed craftsmen and workers have led to the formation of a building stock whose behavior during earthquakes is uncertain. The buildings constructed in Erzincan in recent years are composed of a column–beam frame system. These structures are at great risk in places where severe earthquakes occur and where they are built on fill ground on the fault zone. In Chile, the use of sufficient shear walls in buildings of four stories or more has been made compulsory by regulation. In a later earthquake of 8.2, only two percent of the buildings were damaged [45]. In this case, the column–beam frame system of the buildings to be built in Erzincan should be prohibited and it should be ensured that the buildings with sufficient shear walls are built. Another problem is that in order to solve the car parking issue, municipalities have made it compulsory to provide a car parking area equal to the number of flats under the newly constructed buildings. This situation has led to the creation of wide span frame systems to allow vehicles to maneuver easily in the car park. As the beam span increases, the beam height also increases, which creates a strong beam–weak column situation. In order to limit the extent of damage in the regulations, it is desired that the damage should occur in ductile elements. For this reason, the strong column–weak beam philosophy has been made compulsory in 1997 and later codes in Turkey. The strong column–weak beam design philosophy is compulsorily applied in the seismic design of frame structures. The codes recommend that damage during an earthquake should occur in ductile elements [34]. Due to architectural reasons, it is often not possible to increase the column size. In this case, the weak element is the column, and the damage occurs in the column and causes collapse of the structure.
When the beam span increases, there are large increases in the shear and moment values at the ends and center of the beam. These increases generally cause the formation of hinges at the ends and center of the span; thus, the stability of the structure becomes critical. Due to the above-mentioned reasons, heavy damage or collapse occurred in the 1992 Erzincan and 1999 Marmara earthquakes in reinforced concrete structures with large span frame systems [34,38]. Another problem in large span structures is that the resonance formed in large span slabs prevents the slabs from creating a diaphragm effect during an earthquake. Thus, the distribution of earthquake loads according to the stiffness of vertical elements is prevented [39]. This situation may cause unexpected damage and collapse in structures. Shear walls cannot be placed inside the building to ensure maneuverability of vehicles or shear walls cannot be placed outside the building due to windows. Engineers have tried to ensure the stiffness of the structure by slightly increasing the column dimensions to prevent lateral deformation of the structure in severe earthquakes. This stiffness is usually low, so the structure makes inelastic deformation during the earthquake, which can cause serious structural damage or building collapse [34,35,39].
3.5. Workmanship Errors
The building control law in Turkey started to be implemented on 13 July 2001. The purpose of this law is to ensure project and construction supervision for the construction of quality buildings in accordance with the zoning plan, science, art, and health rules and standards in order to ensure the safety of life and property and to regulate the procedures and principles regarding construction supervision. Although there has been an improvement in the implementation of the project as a result of the legalization of the building supervision law, the mistakes made by inexperienced workers and craftsmen continue. In particular, the errors in the placement and maintenance of concrete will continue and the structure will not perform as expected during an earthquake. Reinforced concrete structures can show the expected performance when concrete and steel work together. Poorly compacted and poorly maintained concrete prevents the structure from showing the expected behavior.
3.6. Material Related Problems
TS EN 206 Certificate [46] is a Turkish standard that determines the production, performance, and conformity criteria of concrete and is compatible with European standards. This standard, which regulates the requirements for the quality, durability, and service life of concrete, aims to ensure the correct production and use of concrete in the construction sector. Prior to this regulation, except for very important structures, concrete was prepared on site according to the traditional method. In this method, fine and coarse aggregates were mixed and poured at the construction site, this mixture was far from the desired aggregate grain distribution and negatively affected the performance of the concrete to be produced. First, the concrete mixer was filled with aggregate, then cement and water were added, the concrete mixer was started, and the concrete was transported to the molds by lift. Since the workers using this method were paid by the cubic meter of concrete poured, they moved very fast in order to pour more concrete and did not comply with the amount of cement, water/cement ratio, and mixing time. Therefore, the concrete produced had a very heterogeneous structure. When these reasons are combined with inadequate concrete placement and maintenance, it is not possible for the concrete produced to show the expected performance. The disadvantages of concrete production by this method can be explained as the use of aggregate as if it was taken from a stream or riverbed, dirty aggregate, poor aggregate gradations, inability to adjust the water/cement ratio, and inability to adjust the concrete mixing time [46]. It is not possible to properly perform the properties such as aggregate grain distribution, aggregate cleaning, w/c ratio, amount of binder, transport or mixing and placing of concrete produced according to the traditional method at the construction site. For this reason, concrete produced by traditional methods cannot provide the expected performance. Reinforced concrete structures should behave in a ductile manner during the earthquake and absorb the energy generated in the structure during the earthquake. In order for reinforced concrete elements or structures to behave in a ductile manner, concrete and steel must work together [34,39]. If one of these two materials fails to perform its duty, the structure behaves in a brittle manner during the earthquake and the structure collapses, as shown in Figure 5. The most important indicator of the weakness of concrete is the collapse of the structure during severe earthquakes without any displacement in any direction, as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5.
Failure of reinforced concrete structures with negligibly low concrete strength in a severe earthquake [47].
The behavior of reinforced concrete structures varies depending on the strength of steel and concrete. Steel elements offer high tensile strength and ductility, while concrete elements offer high compressive strength and stiffness. Composite elements combining steel and concrete offer the advantages of both materials [39,48].
In Turkey, almost all of the buildings collapsed without any displacement in the 1992 Erzincan, 1999 Marmara, and 2023 Kahramanmaraş earthquakes, as shown in Figure 4. With the circular dated 20 April 2004, hand pouring of concrete was banned in Turkey and the use of ready-mixed concrete was made compulsory in buildings. Since this date, the design, mixing and transport processes of concrete, which primarily affect building safety, have been carried out in accordance with scientific methods and the problems arising from concrete production have been minimized. All the buildings constructed before this date fall into the group of high-risk buildings in terms of earthquakes. According to Erzincan Municipality records, 50 percent of the existing building stock belongs to the period before 2004. The other material used in reinforced concrete structures is reinforcing steel. Two types of steel are used in structures. The first is hard steel obtained by melting scrap iron and some chemicals in a blast furnace crucible and drawing the obtained billets. This steel can give higher results in terms of strength, but its ductility is lower. The second is the soft construction steel obtained by rolling the billets obtained after melting the iron mineral in the blast furnace crucible. With the 2007 Turkish Earthquake Regulation, the use of mild steels has been made compulsory, and the use of hard steels is prohibited in places where severe earthquakes are likely to occur—in other words, in first- and second-degree earthquake zones. The reinforcement steel used in buildings was subjected to tensile tests and inspected together with the building inspection companies established with the decree dated 3 February 2007 and numbered 595. Before this date, companies preferred structural steels produced from scrap iron due to cost reasons. Scrap reinforcing steels cause the structures to be more fragile in terms of behavior and fail to show the expected flexible behavior during earthquakes. Reinforced concrete structures should exhibit ductile behavior in order to absorb the energies generated during earthquakes [32,37,39]. There is no clear information about the reinforcement used in buildings built before 2007, but these buildings may also be at risk in terms of earthquakes. In terms of materials used, approximately 60% of the existing building stock constitutes a risk in terms of earthquakes.
Most of the buildings constructed in Erzincan before 2004 were designed according to the 1977 earthquake regulations. In the 1977 earthquake code, the effective ground acceleration coefficient was 0.1 g, while this value increased to 0.4 g in 2007 and above, and 0.5 g in the 2018 earthquake code. In terms of this regulation, all of the buildings built before 1997 can be considered under risk. The reinforced concrete building stock taken from the records of Erzincan Municipality Zoning Directorate is given in Table 2. Of the building stock in Erzincan city center, 99% uses reinforced concrete and the buildings are at least three stories and above. Ugalde and Lopez-Garcia, Ersoy, and many other researchers state that reinforced concrete structures with a column–beam frame system should have a ductile structure in order to survive severe earthquakes. In order for reinforced concrete structures to behave in a ductile manner, the reinforcement and stirrup details must be very good and the concrete strength must be at least the minimum value stipulated by the regulation or above [42]. In this framework, when we evaluate the existing building stock, all of the pre-2004 frame structures have the risk of severe damage or collapse. This is because the design, reinforcement details, and concrete strength were quite bad before 2004. The majority of the buildings with a frame system built between 2004 and 2018, especially those with four stories and above, are at risk of severe damage and collapse. This is because of design and workmanship errors, and the fact that the buildings are built on fault zones and on fill soil make these buildings very risky in a severe earthquake. When Table 2 is evaluated within the scope of the structure of the soil on which the building is built, fault zone, materials, workmanship, and design errors, it can be said that 60% of the building stock is under risk in a severe earthquake (Magnitude ≥ 7).

Table 2.
Existing reinforced concrete building stock in Erzincan city center.
3.7. Defects Caused by Residential Area
Turkey has two fault zones that can produce severe earthquakes. As can be seen from the map of Turkey in Figure 5, there are two major fault zones that can produce earthquakes of magnitude 7 and above. One of these is the Northern Anatolian Fault (NAF) and the other is the Eastern Anatolian Fault (EAF). The 1939 Erzincan earthquake occurred as a result of a fault rupture of the North Anatolian Fault with a length of approximately 400 km starting from the city center of Erzincan and extending to Tokat and Amasya, with a magnitude of 8. Since the period of the EAF is very long (approximately 500–600 years) [49], it was not brought to the agenda until the 2023 Kahramanmaraş earthquake and the earthquake phenomenon was not taken into consideration in the structures built here. The North Anatolian fault starts from Lake Van and cuts across the whole northern Anatolia until the Saros Gulf. The North Anatolian fault, which is approximately 1100 km long, is a dextral-transcurrent fault and its length and strike-slip have been observed on the land during the devastating earthquakes that have occurred in the last 30 years. The fault is not a single slip plane, but a 500–1000 m wide ‘fault zone’ consisting of many parts. The residential area in the center of Erzincan is located on the North Anatolian fault zone that crosses Turkey, as shown in Figure 6 [50].
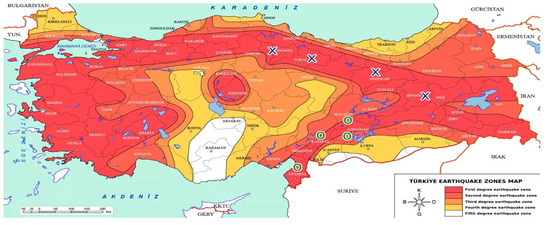
Figure 6.
Turkey fault line map [50].
As a residential area, Erzincan was founded on alluvial fill soil and a fault zone that is not suitable for construction [26,39,46]. Structures to be built in earthquake zones must have the capacity to carry a shear force of 2–2.5 times the estimated earthquake load that will affect the structure [38,51]. It is very difficult to estimate the approximate earthquake load that will affect structures built on filled soil and a fault zone [52,53,54]. Due to the increasing effects of the ground and fault zone on earthquake loads, the loads on the structure during an earthquake may be much higher than the estimated loads. In the recent earthquakes centered in Hatay and Kahramanmaraş, the effective ground acceleration coefficient was measured to be approximately twice the value specified in the 2018 Turkish earthquake regulation, especially in regions with filled soil. This situation caused severe damage and collapse in the structures. Design, material, and workmanship defects can cause the collapse of structures built on filled soil and a fault zone, but these defects can be compensated by the building of structures outside the fault zone and on strong soil. In Erzincan and surrounding regions with similar residential characteristics, all the reasons mentioned above are reasons for the heavy damage or the collapse of buildings. If the structures that are built on filled soil are 5 km or closer to the fault zone, the probability of these structures surviving is scientifically very low [52,53]. It is possible to define the effect of filled soil and fault zone as follows: you are standing in a fast-moving minibus. You feel that the minibus is about to brake. You hold on to the handles above with your hand. The minibus brakes. You shake left and right, back and forth, and you remain standing. In this case, a building designed on strong soil and outside the fault zone, taking into account the earthquake phenomenon, will shake in an earthquake, but will remain standing without collapsing. The second situation is that you are standing in the minibus again, but there is a chair under your foot, the minibus is going fast again, you feel that it is going to brake, so you hold on to the handles above with your hand. The minibus brakes, and you are thrown along with the chair. This means that even if you design structures on filled soil and on fault zone taking the earthquake into consideration, there is no scientific chance of them withstanding a severe earthquake. While Barka and Er [52] argue that earthquake-resistant buildings cannot be built scientifically on filled soil and fault zones, Tüysüz and some earth scientists argue the opposite; they claim the opposite, according to them earthquake-resistant structures can be built on fault zones and filled ground. In recent earthquakes, it has been observed that structures built on fault zones and filled soils were damaged or had collapsed beyond expectations. The North Anatolian fault produces moderate earthquakes every 30–35 years and severe earthquakes every 50–55 years in the Erzincan region [33]. This is long enough to make people forget the earthquake phenomenon. This and the cost of construction have led to higher and weaker buildings currently being built in Erzincan. In line with the negative factors mentioned above, in the event of another severe earthquake in Erzincan, there is a possibility that a large number of buildings will be severely damaged and collapse. This is not an acceptable amount because a large number of buildings destroyed means lots of deaths. When we compare Erzincan’s building stock with other provinces in terms of earthquake resistance, we can say that it has a stronger building stock. However, the fact that the Erzincan settlement is on the filled soil and fault zone makes the Erzincan building stock riskier. When we evaluate the existing building stock in Table 2, most of the buildings fall into the high-risk group. This situation creates the possibility that many buildings will collapse or be seriously damaged in a severe earthquake. After the Kahramanmaraş and Hatay major earthquake, earthquake resistance research was carried out by the commission formed by the university, governorship, and municipality, using the street scanning method on buildings built before 2000 in Erzincan. As a result, it was determined that most of the buildings were in the high-risk group. The results of this research and the study we have conducted indicate that the majority of the buildings will collapse or be severely damaged in a severe earthquake centered in Erzincan. I believe that this study will be a guide in making a new decision based on the condition of the building stock after a severe earthquake.
Earthquakes are inevitable. However, their effects can be prevented from becoming catastrophic. The reasons for the catastrophic consequences of earthquakes occurring worldwide are known and most of them can be prevented with the measures to be taken. These reasons can be listed as follows:
- (a)
- The magnitude of the earthquake: There is nothing that can be done about this;
- (b)
- Design errors: Design errors can be eliminated by ensuring that the projects are carried out by experienced engineers with adequate knowledge of the earthquake behavior of structures;
- (c)
- Workmanship errors: These can be eliminated by ensuring that trained laborers and craftsmen work in the application of the projects and at the same time by making supervision very strict and serious;
- (d)
- Material faults: Errors can be eliminated by using concrete and steel reinforcements in buildings after they have been subjected to very serious tests;
- (e)
- Characteristics of the residential area (such as fault zone, filling soil): In such problems, this problem can be eliminated by changing the location of the settlement. Since this situation is quite costly, this problem is usually not solved.
3.8. Suggestion
Recently, seismic isolators were used in two reinforced concrete buildings in Erzincan. It is unclear how they will perform in a severe earthquake in a fault zone and on infill soil. If the performance of these seismic isolators meets expectations, seismic isolators should be made mandatory in buildings to be built. If these seismic isolators do not perform as expected, the city’s residential area must be moved to the rocky area south of the city. In both the 1939 and 1992 earthquakes, the damage to the buildings on the rocky bedrock 20–25 km south of Erzincan city remained at the light damage level. It is possible to say that this region is suitable for construction in terms of earthquakes. Seismic steel isolators were used in the newly constructed state hospital. It is not clear how these isolators will contribute to the structures on the infill soil and fault zone in a severe earthquake. In a severe earthquake, we do not expect the isolators to show the desired performance due to heave or settlement of the ground. Building inspection insurance companies should be established instead of building inspection companies. Building inspection companies only inspect the project’s application and materials; they have no control over the project’s compliance with the regional conditions. Implementing a building inspection insurance system whose area of responsibility covers every phase of the building, instead of building inspection companies, would mitigate the mistakes and deficiencies of inexperienced engineers, while allowing young engineers to gain experience and create good building stock. The behavior of reinforced concrete elements or structures depends on the compatibility between reinforcement and concrete [45,49]. As the concrete strength decreases, this compatibility will disappear and the extent of damage will increase, and vice versa, the compatibility will increase, and the extent of damage will decrease. Aggregate obtained by crushing physically, chemically, and mechanically suitable rocks should be used for concrete production.
4. Conclusions
As a result, the problem of being located on a fault zone as a settlement area continues, as does the negative impact of civil engineers who have poor knowledge and experience in the earthquake behavior of the structures, and the negative impact of concrete workmanship and maintenance continue to be important problems. As mentioned above, these problems are stated as the reasons for damage or collapse in structures after earthquakes around the world. Especially when the fault zone and the infill soil magnify the earthquake effect, combined with the negativity of the existing building stock, in a possible severe earthquake (magnitude ≥ 7), nearly 60% of the existing building stock as given in Table 2 will be severely damaged or will collapse. The obligation of the municipality to construct garages under the buildings leads engineers to the design of large span frame systems. More negatively, the presence of the garage prevents the design of shear walls, as maneuverability is needed for vehicles. Thus, engineers tend to provide the rigidity of the structures by increasing the column dimensions, which poses a great risk even in structures outside the fault zone, while it causes irreparable situations in structures built on fault zone and on fill soil. Another problem is that the direction of the earthquake has not been taken into consideration during parcellation. Turkish regulations suggest that the buildings should be designed parallel to the direction of the fault rupture. If the structure is not parallel or perpendicular to the fault, a torsional moment may occur in the structure during earthquake forces, and since reinforced concrete structures are very weak in terms of torsion, they may receive moderate or severe damage even in low intensity earthquakes [39,45,52]. It is seen that this rule is not followed in most of the existing building stock. This situation will cause the buildings to be damaged more than expected during an earthquake.
Funding
This research has not received any funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Çuhadaroğlu, F.; Ustaoğlu, E. Deprem ve Erzincan; T.C. Erzincan Valiliği: Istanbul, Turkey, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Öztaş, T. General engineering properties of Erzincan city vicinity. In Proceedings of the İkinci Ulusal Deprem Mühendisliği Konferansı, Erzincan, Türkiye, 10–13 March 1993; TMMOB İnşaat Mühendisleri Odası: Istanbul, Turkey, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Mekki, M.; Elachachi, S.M.; Breysse, D.; Nedjar, D.; Zoutat, M. Soil-structure interaction effects on RC structures within a performance-based earthquake engineering framework. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2014, 18, 945–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, I.; Džakić, D. Soil-Structure İnteraction Effects on Seismic Behaviour of Reinforced Concrete Frames. In Proceedings of the Skopje Earthquake-50 Years European Earthquake Engineering, Skopje, Macedonia, 28–31 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, M.; Elbaz, K.; Shen, S.L.; Chen, J. Earthquake effects on civil engineering structures and perspective mitigation solutions: A review. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalar, M.; Demirköse, M.; Mert, N. Effect of soil types on nonlinear earthquake behavior of buildings. Challenge 2024, 10, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaesmen, E. 1 Şubat 1974 İzmir Depremi Üzerine Teknik Rapor; TMMOB, İnşaat Mühendisleri odası İzmir Şubesi: İzmir, Turkey, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Erken, A.; Ansal, A.; Yıldırım, H.; Ülker, R. Erzincan kentinde yerel zemin koşulları. In Proceedings of the İkinci Ulusal Deprem Mühendisliği Konferansı, Erzincan, Türkiye, 10–13 March 1993; TMMOB İnşaat Mühendisleri Odası: Istanbul, Turkey, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Barnaure, M.; Manoli, D. Unfavourable seismic behaviour of reinforced concrete structures due to soil structure interaction. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 362, 012119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashinsky, M. Earthquake damage to structures. In Earthquake Engineering for Structural Design; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; p. 2-1. [Google Scholar]
- Damcı, E.; Temur, R.; Bekdaş, G.; Sayin, B. Damages and causes on the structures during the October 23, 2011 Van earthquake in Turkey. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2015, 3, 112–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, M.H.; Korkmaz, H.H. What is to be learned from damage and failure of reinforced concrete structures during recent earthquakes in Turkey? Eng. Fail. Anal. 2007, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, W.; Lin, R. Comparative study on the seismic behavior of precast concrete-encased CFST column to precast and cast-in-place RC beam joints. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 104, 112278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, V.; Carbonari, S.; Gara, F. Nomograms for the pre-dimensioning of RC beam-column joints according to Eurocode 8. In Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 39, pp. 958–973. [Google Scholar]
- Kotsovou, G.; Mouzakis, H. Seismic design of RC external beam-column joints. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2012, 10, 645–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvnjak, I.; Ereiz, S.; Smrkić, M.F.; Damjanović, D. Post-Earthquake Dynamic Performance of Intact Masonry Building Based on Finite Element Model Updating. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, C. Why do people die in earth-quakes. The Costs, Benefits and Institutions of Disaster Risk in Developing Countries. In World Bank Policy Research Working Paper; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; p. 4823. [Google Scholar]
- Anbarci, N.; Escaleras, M.; Register, C.A. Earthquake fatalities: The interaction of nature and political economy. J. Public Econ. 2005, 89, 1907–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doocy, S.; Daniels, A.; Packer, C.; Dick, A.; Kirsch, T.D. The human impact of earthquakes: A historical review of events 1980-2009 and systematic literature review. PLoS Curr. 2013, 5, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, J.; Vasconcelos, G.; Rodrigues, H.; Correia, M.; Lourenço, P.B. Traditional earthquake resistant techniques for vernacular architecture and local seismic cultures: A literature review. J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 27, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F. Behavior of reinforced concrete buildings during the Hyougoken-Nanbu earthquake. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1997, 19, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, K.; Naimi, M. Effect of soil conditions on the response of reinforced concrete tall structures to near-fault earthquakes. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2008, 17, 541–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusay, R.; Aydan, Ö.; Hamada, M. The behaviour of structures built on active fault zones: Examples from the recent earthquakes of Turkey. Struct. Eng./Earthq. Eng. 2002, 19, 149s–167s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnaby, A. Multiple Earthquake Effects on Degrading Reinforced Concrete Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, IL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bayraktar, A.; Altunişik, A.C.; Pehlivan, M. Performance and damages of reinforced concrete buildings during the 23 October and 9 November 2011 Van, Turkey, earthquakes. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2013, 53, 49–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, G. Effects of near-fault and far-fault ground motions on nonlinear dynamic response and seismic damage of concrete gravity dams. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2013, 53, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güllü, H.; Karabekmez, M. Effect of near-fault and far-fault earthquakes on a historical masonry mosque through 3D dynamic soil-structure interaction. Eng. Struct. 2017, 152, 465–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunandan, M.; Liel, A.B. Effect of ground motion duration on earthquake-induced structural collapse. Struct. Saf. 2013, 41, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfamariam, S.; Liu, Z. Earthquake induced damage classification for reinforced concrete buildings. Struct. Saf. 2010, 32, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barka, A. Tectonics of the Erzincan basin and its vicinity and 13 March 1992 earthquake. In Proceedings of the İkinci Ulusal Deprem Mühendisliği Konferansı, Erzincan, Türkiye, 10–13 March 1993; TMMOB İnşaat Mühendisleri Odası: Istanbul, Turkey, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Gürsoy, H.; Akpınar, Z.; Tatar, O.; Koçbulut, F.; Sezen, T.F.; Mesci, B.L.; Polat, A.; Kavak, K.Ş.; Tunçer, D.; Yaman, S. 1939 Erzincan Depremi Yüzey Kırığı Haritalama Çalışmaları (Reşadiye Batısı-Koyulhisar arası)”: Ilk Gözlemlere Ait Bulgular; ATAG-10; Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi: İzmir, Türkiye, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yardımlı, S.; Dal, M.; Mıhlayanlar, E. Investigation of Earthquake Behaviour of Construction System and Materials in Traditional Turkish Architecture. ITM Web Conf. 2018, 22, 01034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Erzincan Belgeliği. 2001. Available online: https://www.avnioztopcu.com/erzincan/deprem/index.htm (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Atımtay, E. Afet Bölgelerinde Yapılacak Yapılar Hakkında Yönetmelik, Basımevi Yayın Dağtım San; Çevre, Şehircilik ve İklim Değişikliği Bakanlığı: Ankara, Turkey, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, R.T. Deprem Mühendisliginde Rasyonellik, Yapısal, İstatiksel ve Bayesien Yaklaşım. In Proceedings of the İkinci Ulusal Deprem Mühendisliği Konferansı, Erzincan, Türkiye, 10–13 March 1993; TMMOB İnşaat Mühendisleri Odası: Istanbul, Turkey, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M.S. Findings of the UK investigation of the 1992 Erzincan Earthquake. In Proceedings of the İkinci Ulusal Deprem Mühendisliği Konferansı, Erzincan, Türkiye, 10–13 March 1993; TMMOB İnşaat Mühendisleri Odası: Istanbul, Turkey, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Akyüz, S.; Uyan, M. On the qualities of concretes of the building moderately damaged during earthquake in Erzincan on March 13. In Proceedings of the İkinci Ulusal Deprem Mühendisliği Konferansı, Erzincan, Türkiye, 10–13 March 1993; TMMOB İnşaat Mühendisleri Odası: Istanbul, Turkey, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ada, E.; Ergin, N. Erzincan yöresinin depremselliğinin yeraltı koşullarına göre araştırılması ve Mart-1992 depreminin değerlendirilmesi. In Proceedings of the İkinci Ulusal Deprem Mühendisliği Konferansı, Erzincan, Türkiye, 10–13 March 1993; TMMOB İnşaat Mühendisleri Odası: Istanbul, Turkey, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ersoy, U. 1992 Erzincan depreminden alınması gereken dersler. In Proceedings of the İkinci Ulusal Deprem Mühendisliği Konferansı, Erzincan, Türkiye, 10–13 March 1993; TMMOB İnşaat Mühendisleri Odası: Istanbul, Turkey, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Tüysüz, O. Geology and Tectonic Evolution of Erzincan and Surroundings. In Proceedings of the İkinci Ulusal Deprem Mühendisliği Konferansı, Erzincan, Türkiye, 10–13 March 1993; TMMOB İnşaat Mühendisleri Odası: Istanbul, Turkey, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Alghany, M.M.; El-Kashif, K.F.; Abdalla, H.A. Seismic response of multi-storey reinforced concrete buildings with soft floor. HBRC J. 2021, 17, 407–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Shi, Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q. Seismic be-haviour of concrete columns with high-strength stirrups. Earthq. Struct. 2020, 18, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Guevara, L.T.; García, L.E. The captive-and short-column effects. Earthq. Spectra 2005, 21, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursalioğlu, D. STRASAM, Kısa Kolon Etkisi Nedir? Available online: https://strasam.org/ekonomi/teknoloji/kisa-kolon-etkisi-nedir-1212#google_vignette (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Ugalde, D.; Lopez-Garcia, D. Behavior of reinforced concrete shear wall buildings subjected to large earthquakes. Procedia Eng. 2017, 199, 3582–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TS EN 206; Concrete–Part 1: Specification, Performance, Production and Conformity. TSI: Ankara, Turkey, 2002.
- Available online: https://www.tasnimnews.com/tr/news/2023/02/25/2858546/t%C3%BCrkiye-ve-suriye-de-depremden-%C3%B6lenlerin-say%C4%B1s%C4%B1-art%C4%B1yor (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Chorafa, E.; Skrapalliou, E.; Katsimpini, P. On the Nonlinear Behavior of Composite Structures under Multiple Earthquakes Considering Soil–Structure Interaction. CivilEng 2024, 5, 673–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görür, N. Bir Bilim Adamının not Defterinden FAY’A SEYAHAT; Türkiye İş Bankası Kültür Yayınları: Istanbul, Turkey, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ketin, İ. Kuzey Anadolu Fayı Hakkında. Maden Tetk. Aram. Derg. 1969, 72, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Bayülke, N. Depremler ve Depreme Dayanıklı Betonarme Yapılar; Teknik Yayın Evi: Ankara, Turkey, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Barka, A.; Er, A. Depremini Bekleyen Şehir İstanbul; Om Yayınevi: Istanbul, Turkey, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Üşümezsoy, Ş. İstanbul Depremi; İleri Yayınevi: Istanbul, Turkey, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guéguen, P.; Astorga, A. The torsional response of civil engineering structures during earthquake from an observational point of view. Sensors 2021, 21, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).