Abstract
The rapidly evolving domain of artificial intelligence (AI) is significantly influencing the green building (GB) sector, acting as a catalyst for green building technology innovation (GBTI). Notably, unlike AI applications in green buildings (AI-in-GB), AI-driven GBTI positions AI as the central force, promoting and leading novel technological breakthroughs. Although research has been conducted in AI-in-GB, there remains a lack of in-depth analysis on AI-driven GBTI advancements. To address this gap, this study comprehensively reviews the existing research in AI-driven GBTI, systematically organizing and analyzing the knowledge structure, thematic evolution, research paradigms, and potential future research directions. This study conducts bibliometric analyses on 151 research publications sourced from Scopus using VOSviewer and CiteSpace, capturing the temporal characteristics, research hotspots, and frontiers of research in this area. Additionally, based on dynamic topic modeling, this study analyzes 86 representative articles, identifying three key research themes and their evolution trends, systematically elucidating the knowledge framework within the field. Through further discussion, this study reveals four core research paradigms and proposes three potential future research directions, providing theoretical support and guidance for its continued development. This study is the first to focus on AI-driven GBTI, contributing to a comprehensive understanding and expanding the knowledge domain of GBTI.
1. Introduction
Climate change and energy crises have emerged as critical global environmental challenges that necessitate immediate action [1]. The traditional construction industry is widely recognized as a major contributor to environmental pollution due to its low efficiency, high energy consumption, and resource-intensive production processes [2]. The “2024–2025 Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction” reports that the construction industry accounts for 32% of global energy consumption and generates 34% of global carbon dioxide emissions [3]. Consequently, in alignment with sustainable development frameworks like the Paris Agreement and the UN 2030 Sustainable Development Goals, countries are exploring strategies to reduce the environmental footprint of the construction sector [4,5,6].
Green building (GB) represents a key strategic approach to enhancing energy efficiency and reducing carbon emissions [7]. It is widely recognized as a fundamental pillar for achieving sustainable urban development [8,9]. In contrast to conventional construction technologies, green building technologies (GBTs) focus on resource conservation and energy efficiency, thereby promoting a balanced coexistence between the built environment and ecological systems [10,11]. While GBTs constitute the technical foundation of green buildings, green building technology innovation (GBTI) serves as the core driver that continuously advances and optimizes these technologies [12,13]. Traditionally, GBTI has been driven by several established approaches, including policy-driven mechanisms, market-based incentives, technological R&D collaborations, and knowledge diffusion networks [14,15]. These conventional methods rely primarily on institutional frameworks, stakeholder engagement, and incremental improvements in material science and engineering techniques. Additionally, the integration of building information modeling (BIM) and life cycle assessment (LCA) represents another important pathway to enhancing sustainability performance throughout the building lifecycle [16,17]. Despite strong policy and market support, green building development still faces barriers such as fragmented technology adoption and slow innovation diffusion [18]. Consequently, there is an urgent need for new tools and methods to expedite technological progress and innovation dissemination [19].
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) technology has created significant potential for promoting sustainable development in the construction industry [20,21]. This potential is now widely recognized as offering new opportunities to address the aforementioned challenges [22]. AI encompasses a collection of diverse technologies such as machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), and optimization algorithms [23]. Early applications of AI in sustainable building date from the late 1990s [24]. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) and other AI techniques were implemented in sustainability domains, particularly focusing on modeling and prediction in renewable energy systems and building energy efficiency [25,26]. These early applications demonstrated the fundamental viability of computational intelligence approaches for sustainability challenges, thereby establishing the foundation for current advanced implementations.
Through robust data processing, pattern recognition, and intelligent optimization, AI provides novel methods and tools for GB research, while also serving as a catalyst for GBTI [27]. Consequently, AI exhibits significant potential in GBTI, driving a marked rise in related studies and publications. As the field deepens, AI-driven GBTI research demonstrates characteristics of diverse themes, varied methodologies, and fragmented content. These characteristics make it difficult for researchers and practitioners to comprehend the field’s overall knowledge structure and developmental trajectory, potentially causing fundamental research questions and critical development needs to be overlooked. To address this challenge, systematic organization and analysis of AI-driven GBTI research is particularly important.
Some scholars have already conducted insightful review studies on the integration of AI with green buildings [28,29]. For example, Darko et al. focused on the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry. They used VOSviewer and CiteSpace for a scientometric analysis of the literature to assess the latest advancements in AI-in-the-AEC research [30]. Muhammad et al. investigated the use of AI and big data (BD) in design and operation of energy-efficient commercial buildings and residences, and provided a review of the latest applications of AI and BD in the field of energy-efficient buildings [31]. Abdulrazzaq et al. assessed the role of AI in contributing to green infrastructure (GI), particularly in climate change adaptation [32]. Diego et al. analyzed the application of AI in green and smart buildings [33]. Additionally, other scholars have concentrated on the potential of AI for the sustainable development of construction projects. Regona et al. investigated the application of AI in facilitating the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) across critical stages of construction projects [34]. Liu et al. conducted a review analysis of the functional advantages and contributions of AI in renewable energy systems [35]. Awuzie et al. performed a narrative review of research on applying AI in energy and building materials to transform the built environment and achieve decarbonization goals [36]. Olu-Ajayi et al. focused on AI applications in building energy prediction and reviewed nine popular AI technologies using bibliometric tools such as VOSviewer and CiteSpace [37].
While these prior reviews provide valuable insights, several limitations still exist. In terms of research paradigms, most studies rely on bibliometric methods or subjective qualitative analysis and lack systematic quantitative exploration of topic structures and their temporal evolution. From a research perspective, many works focus on AI applications in specific domains but do not sufficiently address how AI drives innovation across the entire building lifecycle. Notably, the application of AI in green buildings (AI-in-GB) differs significantly from the driving force of AI on green building technology innovation (AI-driven GBTI). The former focuses on the practical application effects of AI technology, whereas the latter explores how AI reshapes the innovation process, expands technological boundaries, and fosters systemic transformation within the field [38,39]. Currently, research on AI-driven GBTI remains limited. This gap highlights the critical need for a systematic and in-depth analysis of the field’s knowledge structure, thematic evolution, prevailing research paradigms, and future trajectories.
To address these limitations, we present an in-depth review of the current literature on AI-driven GBTI by integrating bibliometric analysis with dynamic topic modeling. Specifically, this study makes the following contributions: (1) capturing the temporal characteristics of research and systematically identifying and deconstructing research hotspots and frontiers; (2) mining the distribution and evolutionary patterns of research themes; (3) revealing the research paradigms underpinning AI-driven GBTI; and (4) delineating the focus areas for future research work. This study aims to address the following questions: (1) What are the current research focuses? (2) How have these research themes evolved over time? (3) What research paradigms should future research adopt? (4) What are the critical areas for future research?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design
To systematically explore the research trajectory and technological evolution patterns of AI-driven GBTI themes, this study proposes a four-stage framework (Figure 1). Stage 1 (data collection and processing) constructs the literature dataset from the Scopus database. Stage 2 (bibliometric analysis) identifies research hotspots and frontiers and deconstructs the field’s knowledge structure. Stage 3 (literature screening) achieves value focus by applying dual criteria to screen out core datasets. Stage 4 (literature topic analysis) reveals the distribution and evolutionary trends of research themes based on dynamic topic modeling. Finally, an in-depth discussion uncovers core research paradigms and outlines future research directions, providing theoretical guidance for the systematic advancement of this field.
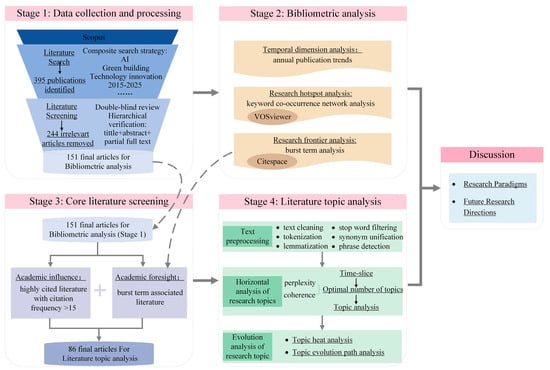
Figure 1.
Research framework.
2.2. Stage 1 Data Collection and Processing
The process of data collection and processing is shown in Figure 2.
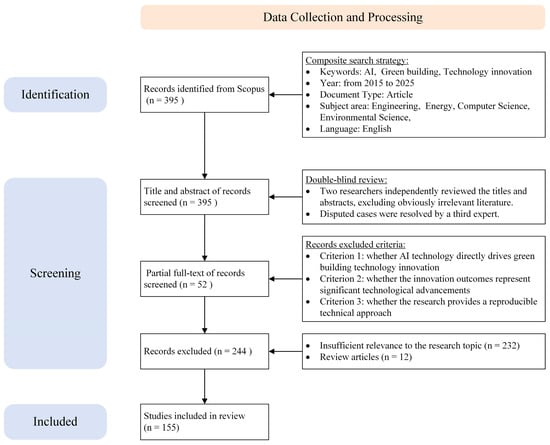
Figure 2.
The process of data collection and processing.
2.2.1. Data Collection
Data collection serves as a critical step in ensuring research validity [30]. Scopus was selected as the data source due to its broad disciplinary coverage, high indexing quality, and timely updates, which are well-suited for interdisciplinary research in engineering and computer science [40,41].
To comprehensively collect literature related to AI-driven GBTI, this study defined three categories of keywords:
- (1)
- AI technology (e.g., “artificial intelligence”, “deep learning”);
- (2)
- green building (e.g., “green building”, “energy-efficient construction”);
- (3)
- technology innovation (e.g., “technology innovation”, “knowledge diffusion”).
This study employs previously established methodologies for keyword identification, focusing specifically on artificial intelligence applications in green building and technological innovation domains [33,42,43]. We conducted a comprehensive review of interdisciplinary research related to AI-driven GBTI by systematically expanding core terminologies to encompass the full spectrum of the relevant literature. For AI-related terms, we included various techniques such as “machine learning” and “neural network” that are commonly applied in building research [36]. Similarly, green building terms were expanded to include synonymous expressions like “sustainable build” and “eco build*” based on established green building standards in the literature [37]. Additionally, innovation terms were enhanced with phrases representing technological development based on innovation studies [38]. This systematic expansion ensured comprehensive coverage while maintaining specificity to our research focus.
Synonyms and related terms were further expanded to construct a compound search formula (Table 1). Only articles published between January 2015 and March 2025 were included. Considering the interdisciplinary nature of AI-driven GBTI, the subject areas were restricted to “Engineering”, “Environmental Science”, “Energy”, and “Computer Science”. This search resulted in an initial dataset of 395 articles.

Table 1.
Search string.
2.2.2. Stage 1: Data Screening and Processing
Literature screening employed a double-blind and hierarchical verification process to ensure the objectivity. First, two researchers independently assessed titles and abstracts, excluding obviously irrelevant literature. Disputed cases were resolved by a third expert. Second, a full-text review was conducted for articles with unclear or insufficient abstract information, focusing on three criteria: (1) whether AI technology directly drives green building technology innovation; (2) whether the innovation outcomes represent significant technological advancements; (3) whether the research provides a reproducible technical approach.
After two rounds of screening, a total of 244 publications were excluded, including 232 with insufficient relevance to the research topic and 12 review articles. Ultimately, 151 high-quality publications were retained as the foundation for this study.
2.3. Stage 2: Bibliometric Analysis
VOSviewer 1.6.17 and CiteSpace 6.3.R1 were used to conduct bibliometric analysis, aimed at systematically understanding the knowledge structure of the AI-driven GBTI field, and identifying research hotspots and frontiers.
First, annual publication trends were analyzed to identify the temporal characteristics of the literature.
Second, keyword co-occurrence analysis was performed using VOSviewer to construct a visual network map that intuitively displays the association strength between keywords and their positions within the knowledge network [44,45]. In this network, nodes represent keywords, node size reflects occurrence frequency. And links between nodes indicate co-occurrence relationships, link thickness represents co-occurrence strength, and different colors denote distinct thematic clusters [46]. Then, the Gephi tool was used to calculate centrality indicators of keywords to identify core research hotspots [47].
Finally, CiteSpace was employed to detect burst terms, thereby pinpointing emerging keywords and mapping their appearance time nodes, and change trends [48].
The complementary use of VOSviewer and CiteSpace facilitated a comprehensive view of the knowledge structure and provided empirical support for subsequent core literature selection in the research field [49,50].
2.4. Stage 3: Core Literature Screening
To precisely identify the representative core literature of AI-driven GBTI, the screening process adopted dual criteria: highly cited literature and burst term-related literature. Highly cited literature reflects the high impact, sustained academic value, and foundational role of research findings in field development [51]. Burst terms identify research focuses that have rapidly emerged over a short period; literature associated with these terms often reveals frontier hotspots and emerging trends [27].
Therefore, based on citation frequency, studies with more than 15 citations were selected, and the literature closely related to the frontier hotspots was identified using CiteSpace burst detection results, thereby addressing the limited coverage of emerging research directions by highly cited literature.
These criteria ensure both academic influence and foresight, providing a robust and reliable data foundation for the subsequent literature topic analysis.
2.5. Stage 4: Literature Topic Analysis
2.5.1. Text Preprocessing
Text preprocessing is a crucial step in ensuring the accuracy of topic modeling [52]. The retained core articles underwent a systematic preprocessing workflow as follows:
Step 1: Convert all text to lowercase and remove punctuation using Python 3.12.4.
Step 2: Tokenize and lemmatize the text with the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) to standardize word forms.
Step 3: Develop and expand a stopword list to filter out low-information words.
Step 4: Apply synonym mapping dictionaries to unify similar terms and reduce semantic redundancy.
Step 5: Use Gensim’s phrase-detection tools to identify frequent bigrams (two-word combinations like “deep learning” or “energy efficiency”) and trigrams (three-word combinations like “building information modeling”), thereby preserving meaningful multi-word expressions.
By normalizing semantics and reducing noise, this process improved text quality and established a solid foundation for reliable topic extraction.
2.5.2. Dynamic Topic Modeling
Traditional topic modeling, such as Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), effectively identifies themes in static corpora but fails to capture their temporal dynamics [53,54]. Dynamic Topic Modeling (DTM) is a temporal extension of LDA [55]. By introducing a state-space model, DTM provides a nuanced understanding of longitudinal thematic trends by capturing the evolution of topic distributions across time slices [56,57].
Considering the evident staged growth in the AI-driven GBTI field, particularly the exponential increase in the literature since 2022, DTM was preferred over traditional LDA. DTM provides insights not only into existing topic distributions but also into how they emerge, evolve, and potentially converge or diverge over time. This temporal perspective is crucial for understanding technological innovation trajectories and identifying emerging research frontiers.
The implementation comprised the following steps:
Step 1: Construct a dictionary from the preprocessed corpus and filter out terms with extreme frequencies;
Step 2: Divide the corpus into temporal windows and transform it into a bag-of-words representation;
Step 3: Evaluate model performance across different topic numbers using perplexity and coherence metrics to identify the optimal topic configuration;
Step 4: Train the DTM with Gensim’s DtmModel, tuning parameters and iterating until topic distributions converge;
Step 5: Visualize the outcomes with topic–term graphs and Sankey diagrams to illustrate dynamic flows and temporal shifts in the field’s knowledge structure.
3. Results
3.1. Bibliometric Analysis
3.1.1. Temporal Characteristics Analysis
As shown in Figure 3, the annual distribution of literature from 2015 to the present clearly indicates that AI-driven GBTI research literature has experienced staged growth. During 2015 to 2019, annual outputs ranged from 1 to 4 papers, marking an embryonic period and suggesting that this interdisciplinary field had yet to develop a systematic research trend. Between 2020 and 2021, publications increased to 8–10 per year, reflecting an emerging development phase. A significant inflection point occurred in 2022. Annual publications climbed to 20–23 per year in 2022–2023, reflecting heightened academic interest and marking a rapid growth phase. The years 2024 to 2025 represent an explosive growth phase, characterized by a dramatic spike to 55 publications in 2024—a nearly 140% increase from the previous year. The 2025 data includes 25 publications as of March. Based on this trend, it is reasonable to anticipate that future scholarly output will remain robust.
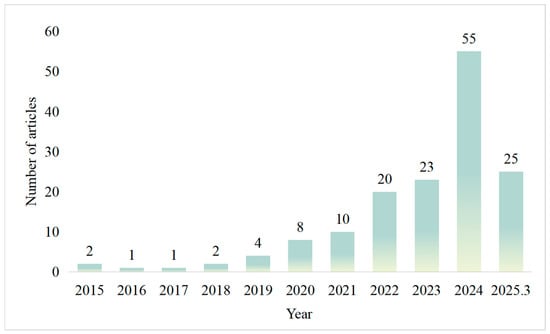
Figure 3.
Number of publications.
3.1.2. Research Hotspot Analysis: Keyword Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
From 151 papers, VOSviewer extracted 1514 keywords. By setting a minimum frequency threshold of five occurrences, 88 keywords were retained. To minimize redundancy, a synonym dictionary was applied to consolidate similar terms. The merging process primarily considered: (1) terminological variations (e.g., “artificial intelligence” and “AI”); (2) hierarchical relationships (e.g., specific neural network types merged under “neural networks”); (3) spelling variants; and (4) plural/singular forms. Each potential merger was verified through examining the original context to ensure semantic equivalence.
The resulting co-occurrence network comprises 56 nodes and 864 links, as depicted in Figure 4.
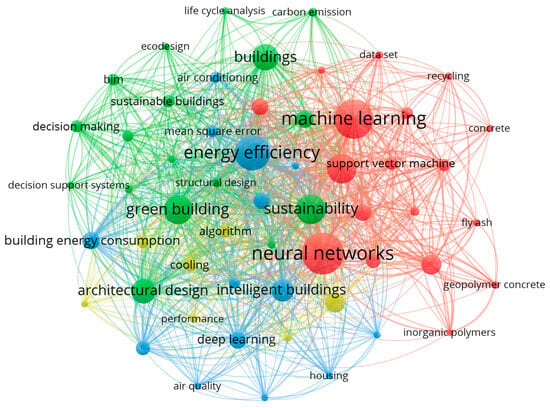
Figure 4.
Keyword co-occurrence network.
To further quantify the importance of keywords within the network, this study employed Gephi 0.10.1 software to calculate the degree centrality for each keyword. Figure 5 presents the top 30 keywords ranked by degree centrality, which reflects the number of direct connections between a keyword and other keywords. Higher degree centrality indicates a more prominent core status of the keyword within the network.
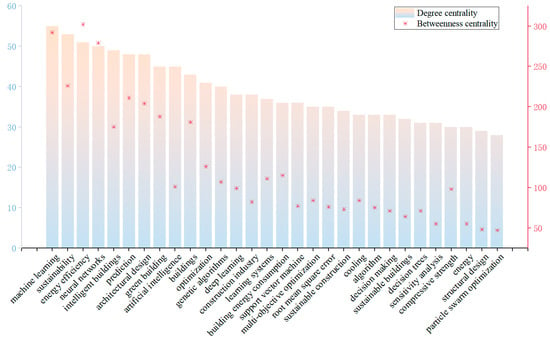
Figure 5.
Top 30 keywords.
From the co-occurrence network and degree centrality analysis, four main research clusters have formed in this field:
- (1)
- The red cluster includes terms such as “compressive strength”, “fly ash”, and “geopolymer concrete”, highlighting the role of AI in developing green building materials and evaluating their performance.
- (2)
- The blue cluster features terms such as “cooling”, “mean square error”, and “performance evaluation”, focusing on optimizing building energy performance.
- (3)
- The green cluster centers on terms such as “green building” and “sustainability”, reflecting the conceptual foundation of sustainable construction.
- (4)
- The yellow cluster includes terms such as “thermal comfort”, “air quality”, and “ventilation”, highlighting concerns regarding indoor environmental quality and occupant health.
In the degree centrality ranking, “neural networks” (55), “sustainability” (53), “energy efficiency” (51), and “machine learning” (50) occupy the top four positions, indicating the central roles of algorithmic advancement and sustainability goals in the field.
3.1.3. Research Frontier Capture: Burst Term Analysis
CiteSpace keyword burst detection (Table 2) identified seven terms with significant bursts between 2015 and 2025. The term “energy efficiency” exhibited the highest burst strength (6.74). Although it was mentioned in the earlier literature, its prominence surged from 2023 to 2025, indicating a notable rise in attention to energy efficiency in the past two years. Keywords such as “sustainable development” and “green buildings” reflect the increasing emphasis on sustainability ideals. Meanwhile, technical terms such as “genetic algorithms”, “decision trees”, and “intelligent buildings” began bursting after 2022, signaling an expansion into multi-algorithmic approaches and diverse application scenarios.

Table 2.
Burst terms.
3.2. Literature Topic Analysis
3.2.1. Core Literature Screening
To ensure the quality and representativeness of the topic analysis, a core literature collection was screened from the initial 151 publications using the dual criteria of high impact and frontier significance, as outlined in Section 2.4. Applying the citation impact standard (citation frequency > 15), 44 highly cited publications were identified as foundational research in the field. Additionally, following the frontier standard, 57 publications closely related to the key burst terms identified in Section 3.2.2 were retrieved. Following deduplication, a final core literature dataset comprising 86 publications was established, providing a robust data foundation for the subsequent topic analysis.
3.2.2. Horizontal Analysis of Research Topic Distribution
- (1)
- Determination of Optimal Topic Number
Considering the balance of publication numbers across time intervals, the literature was divided into three temporal slices: 2015–2021 (early development period), 2022–2023 (rapid growth period), and 2024–2025 (explosive period), based on the temporal analysis in Section 3.1.1. Then, DTM configurations (ranging from 2 to 10 topics) were systematically assessed using perplexity and coherence as evaluation metrics, as shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. Finally, a three-topic model was selected, which offered the best trade-off between model fit and interpretability.
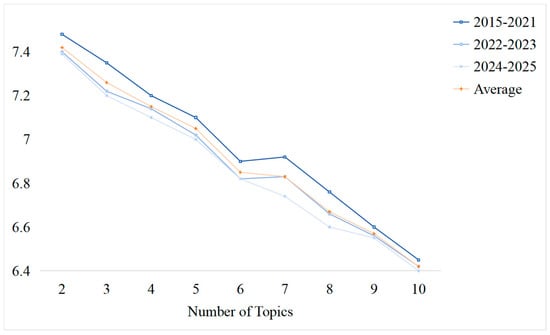
Figure 6.
Perplexity.
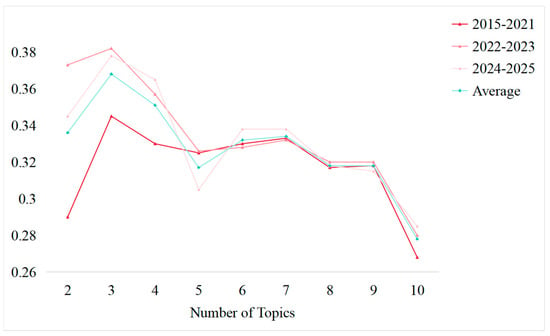
Figure 7.
Coherence.
- (2)
- Topic Analysis
In accordance with the above analysis, a three-topic model was selected, and the DTM analysis was executed by Python on the 86 core publications. The resulting output revealed three principal research topics, forming the knowledge-structure framework for AI-driven GBTI. Table 3 displays the proportion of each topic along with its top 20 salient keywords. Figure 8 illustrates the relationship between topics and their associated terms.

Table 3.
Topics and keywords.
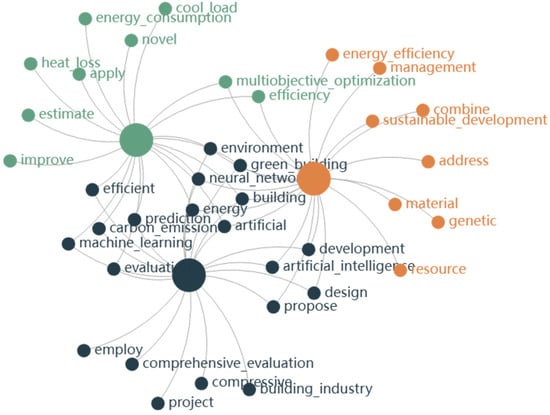
Figure 8.
Distribution of topic–keyword relationship.
Topic 1: AI-based Building Performance Prediction and Carbon Emission Assessment (40.71%)
Core keywords such as “prediction”, “machine learning”, and “neural network” underscore the field’s focus on leveraging AI to forecast project outcomes and evaluate environmental impact. Key research dimensions include:
Project performance: Techniques such as Support Vector Machines (SVM) and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) are used to improve project performance in green building projects [58,59,60]. Amos et al. integrated deep neural networks (DNN) with support vector regression (SVR) to develop models predicting project cost and duration, thereby enhancing the delivery performance [61].
Energy consumption and indoor air quality: Hybrid models such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), are widely employed to capture complex interactions among building physics, environmental conditions, and energy use [23,62]. Lu et al. integrated fuzzy clustering with a back-propagation neural network to evaluate cold-source performance, supporting energy consumption assessments during the design phase of green buildings [63].
Material sustainability: ANN and ensemble learning methods are utilized to predict the performance and sustainability of green materials, linking material composition, structure and environmental impact [64,65,66]. Shahmansouri et al. proposed an innovative hybrid ANN model to predict the compressive strength of sustainable building materials [67].
Topic 1 reflects the deep integration of AI across the green building lifecycle, from design to operation.
Topic 2: Intelligent Multi-objective Optimization of Building Energy Systems (30.23%)
Topic 2 focuses on intelligent multi-objective optimization of building energy systems, with core keywords “multiobjective optimization”, “energy consumption”, and “efficiency”. Research shows two clear technical routes:
System integration: Algorithms such as Genetic Algorithms (GA), and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) are applied to configure and optimize multi-energy systems, enabling low-carbon pathways for renewable energy use [68,69]. Zhou et al. combined supervised machine learning with advanced optimization algorithms to develop a hybrid energy-cascade system that integrates ventilation, active photovoltaic cooling, radiative cooling, and phase change material storage. This system enhances the efficiency of renewable energy utilization in green buildings [70].
Operational optimization: DL methods, including CNN, BiLSTM, and Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG), support real-time control and adaptive energy management in uncertain environments [71,72,73]. Aruta et al. employed GA and ANN for model predictive control and optimization of space heating operations, thereby advancing near-zero energy goal of green buildings [74].
Topic 2 emphasizes solutions that directly enhance efficiency through intelligent system design and runtime optimization.
Topic 3: Sustainable Building System Design and Intelligent Resource Management (29.07%)
Topic 3 focuses on AI applications for sustainable building design and resource management, centered on the keywords “building”, “design”, and “artificial intelligence”. Research shows two interconnected themes:
Design innovation: DL and generative design algorithms are used to establish new systematic thinking frameworks that reshape design paradigms and decision processes [75,76]. Pan et al. introduced a multi-objective optimization framework using deep reinforcement learning to adjust green building design parameters and enhance performance [77]. Techniques such as GA-ANN and NSGA-II balance CO2 emissions, energy use, and material costs in complex design tasks [78,79,80]. Additionally, Liu et al. developed an intelligent hybrid method combining BIM-DesignBuilder, Grey Wolf Optimization, Random Forest, and NSGA-II to optimize design parameters [81]. Sarfarazi et al. reviewed emerging AI trends in structural design, demonstrating how inverse machine learning and physics-informed models replace trial-and-error optimization [82].
Decision support systems: The integration of AI, IoT, and BIM enables knowledge discovery and intelligent decision-making across the building lifecycle [83]. Petrova et al. mined BIM-derived data through knowledge discovery to generate actionable insights for design decisions [84]. Liu et al. constructed a decision model that combines case-based reasoning and Random Forest to guide renovation project decisions [85].
Topic 3 demonstrates a shift from traditional design thinking toward data-driven, performance-oriented planning.
Overall, the research themes span performance prediction and assessment, multi-objective optimization, and integrated system management. These areas reflect the multidimensional application of AI-driven GBTI and underscore a data-driven research trajectory.
3.2.3. Longitudinal Analysis of Research Topic Evolution
- (1)
- Topic Heat Analysis
After horizontal analysis of research topic distribution, longitudinal analysis of topic evolution trends was conducted by calculating topic strength across different time slices. The resulting topic heat map (Figure 9) highlights each stage’s research focus and reveals distinct evolutionary patterns.
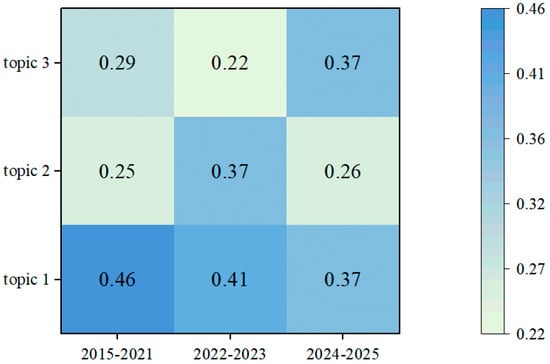
Figure 9.
Topic heat map.
In the early development period (2015–2021), Topic 1 (weight = 0.46) reflects a focus on foundational AI applications. Topic 2 and Topic 3 have relatively low weights (0.25 and 0.29), indicating that technology applications were still at an exploratory stage.
During the rapid growth period (2022–2023), Topic 1 (weight = 0.41) remained the leading theme despite a slight decline; Topic 2 (weight = 0.37) rose markedly, highlighting increased attention to energy system optimization; and Topic 3 (weight = 0.36) grew, reflecting growing interest in sustainable system design. This shift signifies the transition of research from single-point technology exploration to system optimization and integrated applications, demonstrating the in-depth development of AI technology applications in the building field.
In the explosive period (2024–2025), the three topics converged with weights of 0.37, 0.26, and 0.37, respectively, signifying thematic diversification and methodological integration.
Overall, the evolution of topic popularity reflects a gradual shift in AI-driven GBTI research, moving from an initial focus on prediction and evaluation (Topic 1) to multi-objective optimization (Topic 2), and ultimately to a balanced emphasis on prediction and evaluation (Topic 1) alongside sustainable design and decision support (Topic 3). This progression underscores the mutually reinforcing, iterative nature of research at the intersection of green building and AI, and points toward new opportunities for deeper cross-disciplinary collaboration and practical application [34].
- (2)
- Topic Evolution Path Analysis
Based on the DTM results, Figure 10 depicts the evolution path of themes, and Table 4 presents the topic–term distribution. Together, these elements illustrate the complex dynamics of content flows between research topics.
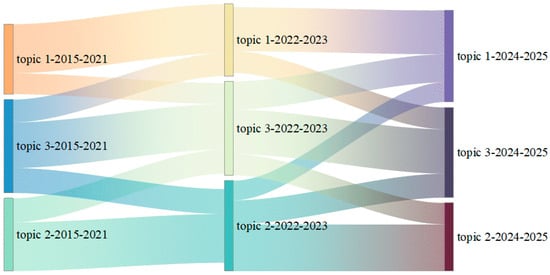
Figure 10.
The path of theme evolution.

Table 4.
The distribution of topic–word.
Topic 1 (AI-based Building Performance Prediction and Carbon Emission Assessment) shows stable and consistent development over time, reflecting a mature theoretical framework. Keywords such as “prediction” and “machine learning” have increased in prominence across all time periods, indicating a methodological trajectory that has evolved from exclusive reliance on neural networks to diverse machine learning techniques. This evolution parallels the integration of emerging technologies, such as deep learning and cloud computing, which supports precise forecasting and comprehensive evaluation [86]. The content flow (0.339) from Topic 1 to Topic 3 highlights a key transformation: performance prediction extends into sustainable building design, aligning with the construction industry’s commitment to carbon neutrality. This shift demonstrates the progression from isolated assessments to integrated applications at the system level.
Topic 2 (Intelligent Multi-objective Optimization of Building Energy Systems) shows high inter-topic fluidity, reflecting active knowledge exchange. Initially focused on multi-objective optimization and energy consumption, it has gradually incorporated machine learning, marking a shift from algorithm development to complex problem-solving in the building domain. Thanks to advances in AI methods such as deep learning, these techniques have contributed to Topic 1 (0.319) and Topic 3 (0.389), enhancing both the specificity of performance predictions and the integration of design management approaches, in line with the needs of building energy consumption research [87].
Topic-3 (Sustainable Building System Design and Intelligent Resource Management) demonstrates strong self-inheritance and ongoing content enrichment. Initially, keywords such as “building” (0.177) and “design” (0.127) dominated. Over time, new terms like “multiobjective optimization” (0.099), “energy efficiency” (0.073), and “neural network” (0.052) emerged, illustrating a shift from traditional design concepts to AI-driven system design. This evolution reflects the digital transformation of the construction industry, where widespread adoption of BIM technology has laid a solid foundation for integrating AI into architectural design [88]. Bidirectional exchanges between Topic 3 and the other topics confirm its role as a central integration platform, aligning with the growing global emphasis on buildings’ environmental impacts across their lifecycle.
Overall, this multi-dimensional evolution highlights a research landscape in which AI is increasingly embedded in green building technology innovation. This trend suggests that future research will focus more on the integration of technology and applications, interdisciplinary collaboration, and the linkage of theory and practice to establish a more mature and systematic research framework.
4. Discussion
This study employs a mixed-method approach that combines bibliometric analysis with dynamic topic modeling to systematically review recent advancements in AI-driven GBTI. Through bibliometric tools such as VOSviewer and CiteSpace, we identify key hotspots and emerging frontiers within the field. Additionally, through the application of DTM, we explore the thematic structure and evolutionary trajectories of research topics over time. Overall, these analyses address two critical questions: “What are the current research focuses?” and “How have these research themes evolved over time?” This integrated approach provides a clear scientific overview essential for a comprehensive understanding of AI-driven GBTI research.
Building upon these empirical findings, it becomes essential to extract deeper theoretical value and forward-looking perspectives. This involves examining the conceptual frameworks underlying existing studies and identifying emerging topics that may guide future innovative research directions. Consequently, this study further proceeds to analyze the research paradigms and future research directions of AI-driven GBTI, addressing two critical questions: “What research paradigms should future research adopt?” and “What research topics warrant priority in future studies?” This analysis provides the theoretical foundations and strategic guidance necessary for both deepening and systematically expanding this evolving interdisciplinary research field.
4.1. Research Paradigms of AI-Driven GBTI
4.1.1. Performance-Oriented Intelligent Design Paradigm
This paradigm establishes bidirectional mapping relationships between design parameters and performance goals based on specific objectives (such as carbon emissions and energy consumption indices). Through this approach, AI technology facilitates intelligent design scheme recommendations via iterative cycles of parameter generation and objective feedback [89,90]. AI has redefined the green building design process, transforming it into a cyclical feedback-driven process where performance objectives guide parameter generation and adjustment.
For example, a study on rural residential buildings in China’s hot summer and cold winter zone implemented a two-stage optimization framework [91]. The framework first established spatial energy intensity maps, and subsequently applied the SPEA-2 genetic algorithm to optimize design parameters—including room width, depth, and window-to-wall ratio. This approach achieved 11% energy savings through bidirectional mapping between design decisions and performance goals.
4.1.2. Data-Driven Prediction and Simulation Paradigm
Leveraging AI technologies such as data mining and deep learning, this paradigm constructs virtual mapping relationships from known data to research objectives. This approach enables intelligent prediction of building energy consumption, building environment, and building material performance [92,93,94]. Unlike conventional physics-based models, this AI-driven approach introduces a data-driven research model that transforms the methodological paradigm from deterministic reasoning to probabilistic inference.
A notable example is Harvard’s HouseZero, which demonstrates this paradigm through the retrofit transformation of a traditional building into a zero-energy experimental laboratory [95]. The building utilizes approximately 300 sensors that generate 17 million data points daily to power intelligent ventilation algorithms. These algorithms then optimize energy consumption and thermal comfort parameters.
4.1.3. Evolution-Driven Intelligent Optimization Paradigm
This paradigm integrates evolutionary algorithms such as Genetic Algorithms (GA) and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) with deep learning techniques to address complex multi-objective optimization problems in green building contexts [96,97,98]. The core idea is to simulate natural evolutionary processes to identify potential solutions within the parameter-objective mapping model. Solution quality improves iteratively through a hybrid model that leverages deep learning to accelerate evaluation, thereby enabling multi-objective compatibility and balance under complex constraints [32]. This approach liberates optimization from traditional path dependencies, allowing for more exploratory and adaptive search for optimal solutions.
An illustrative case study in Xiamen, China exemplifies this paradigm through multi-objective optimization of green roof layouts using the NSGA-III genetic algorithm [99]. The algorithm systematically evaluated thousands of configurations to simultaneously optimize runoff reduction (2.12–2.56%), cooling effect (0.40–0.49%), and investment costs. This approach achieved optimal ecological-economic balance in high-density urban environments.
4.1.4. Knowledge Mining-Based Systemic Decision Paradigm
By employing data mining and machine learning, this paradigm reveals latent patterns and multi-scale, cross-disciplinary knowledge relationships embedded in multidimensional green building data. These insights are integrated into intelligent decision support frameworks to enhance systemic decision-making under uncertainty [100,101,102,103]. In contrast to traditional expert-driven methods confined to a single domain, this approach integrates heterogeneous, multi-scale knowledge into a unified, data-informed structure, shifting decision-making from experience-based reasoning to systematic, knowledge-driven support.
Amsterdam’s Edge building adopts this paradigm. It integrates 28,000 sensors with a knowledge-graph analytics platform to identify correlations among occupant behavior, energy-use patterns, and environmental conditions [104]. Through continuous learning and adaptation, the system enabled the building to achieve a BREEAM score of 98.36%.
Overall, these four paradigms cover the entire green building life cycle and form the methodological basis of AI-driven GBTI. These research paradigms do not represent isolated technological applications, but rather constitute a comprehensive technological innovation system for green buildings. In this system, AI collaboration enhances the sustainability of the building life cycle.
4.2. Future Research Directions
4.2.1. AI-Powered Digital Twins for Life-Cycle Management of Green Building
The thematic analysis in the previous text reveals the fundamental shift from isolated performance evaluation to an integrated life cycle approach. This evolution echoes the growing recognition that the fragmentation of building life cycle stages seriously hinders sustainability efforts. Digital twins offer an integrated platform that unifies the isolated predictive and evaluation capabilities into a coherent life cycle management system. Building digital twins provide real-time virtual representations of physical assets or systems, specifically simulating real-world behavior across the planning, design, construction, and operation stages [105]. They have been widely adopted in studies on sustainable cities, smart buildings, and net-zero energy architecture [106,107]. Introducing AI significantly enhances the analytical capabilities of digital twins, transforming them from passive monitoring tools into predictive simulation platforms that enable accurate forecasting [108]. Debrah et al. highlighted the transformative potential of AI-enhanced digital twins in driving sustainable building practices [42].
In the green building field, AI-enhanced digital twin systems analyze climate parameters, usage patterns, and equipment performance data to identify energy flows and efficiency losses, and to generate low-carbon operational strategies. By systematically integrating building performance optimization across the planning, design, construction, and operation phases, sustainable goals can be more effectively achieved. This integrated life cycle approach aligns with the convergence trend revealed by topic evolution analysis. The analysis shows that Topic 1 predictive methodologies increasingly inform and enhance Topic 3 sustainable design frameworks. This pattern represents a critical maturation in the field, moving from isolated theoretical models to comprehensive applications that span the entire building life cycle. Additionally, BIM provides high-fidelity 3D models that support every phase of green building practice. Its synergy with digital twins and AI enhances simulation accuracy, decision-making, and adaptive learning in the sector [109]. Pan and Zhang demonstrate that integrating these three technologies enables real-time interaction between physical and virtual components and drives advances in simulation, decision support, and machine learning for green buildings [110].
However, future research confronts challenges such as the integration of heterogeneous multi-source data, safeguarding data privacy and security, and enabling cross-system interaction across the building life cycle. Achieving these objectives requires systematic solutions through interdisciplinary collaboration and advances in AI methods to meet sustainability requirements in green building applications [111].
4.2.2. Generative Artificial Intelligence Promoting Intelligent Decision Support
The topic analysis revealed that Topic 3′s progression from basic design concepts to AI-driven system design marks a pivotal shift in architectural thinking. However, persistent limitations exist in leveraging computational power for creative design, and there is a growing demand for tools that extend beyond traditional paradigms.
Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) addresses this shortfall by integrating cross-disciplinary knowledge and broadening avenues for design exploration. In contrast to predictive AI, GenAI facilitates autonomous design generation and analytical decision-making, often outperforming human experts in divergent-thinking evaluations [112,113].
GenAI excels in building form generation and spatial layout optimization. It delivers multi-constraint optimization solutions for building performance, environmental objectives, and cost considerations [114,115]. Chen et al. demonstrate that integrating standardized datasets with domain knowledge enables GenAI to support resource optimization and risk assessment on construction sites, highlighting a promising research direction [116]. Liao et al. show that GenAI can learn from historical data and leverage existing datasets to generate innovative structural design concepts, addressing inefficiencies and data scarcity [117]. Chew et al. emphasize that future work should extend beyond scheme generation to improve the interpretability of GenAI-driven decision-support systems [118].
In the green building field, generative algorithms enable simultaneous optimization of conflicting objectives, for example, daylighting, ventilation, energy efficiency and material use, by integrating multi-objective optimization techniques into the design process [119]. Topic 2′s heat-map analysis confirms this trend, revealing the progressive incorporation of machine learning within optimization frameworks. The growing prominence of “multiobjective optimization” and “energy efficiency” in Topic 3 underscores the need for tools that can navigate complex trade-offs while preserving design coherence. Liao and Zhou identify GenAI as an emerging research frontier in architecture and construction [117,118]. By transcending traditional design paradigms, GenAI expands the boundaries of sustainable architectural exploration and provides designers with quantifiable decision support and actionable insights [120,121].
Despite its promise, GenAI carries risks including hallucinations, inaccuracies, jailbreaking vulnerabilities, and challenges in handling unexpected inputs [122]. These issues require careful mitigation strategies.
4.2.3. Intelligent Construction Management Integrated with Green Construction
Longitudinal analysis traced a clear evolutionary path from theory to practice, revealing a critical implementation gap during construction. The topic heat map indicated a gradual shift toward a balanced thematic distribution in the explosive period (2024–2025), yet construction implementation remains a significant barrier to translating AI-driven innovations into built reality.
Intelligent construction management bridges advanced computational models and on-site sustainability practices. It leverages digital tools and advanced equipment, including cloud-based virtual/augmented reality (VR/AR) systems, Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) platforms, construction robotics, and automated systems [123,124]. Pan et al. emphasize the importance of further integrating AIoT and robotic technologies into the built environment to enhance automation levels [125]. Ouheri et al. identify Construction 5.0 as the industry’s latest transformation, driving a shift toward automation and robotics and offering a promising pathway for sustainable building research [126].
In the green building field, VR/AR integrated with BIM enables visualization of building information and collaborative interaction. It also facilitates virtual validation of green building plans through clash detection and process simulations, thereby minimizing material waste and rework [127]. This development aligns with the technological progress identified in the thematic analysis, which traces research from basic prediction methods to integrated intelligent systems. AIoT systems, combining AI and sensor networks, provide real-time monitoring, predictive analysis, and intelligent management of construction site data such as energy use, carbon emissions, and resource efficiency [128]. Robotics enhance construction precision and assembly efficiency while reducing material and energy consumption [129]. The integration of these smart management technologies offers significant promise for improving construction quality and supporting sustainability goals [125].
However, it is worth noting that data compatibility, data privacy, and network security present significant challenges [130].
5. Conclusions
This study offers the first comprehensive analysis of AI-driven GBTI research hotspots, emerging frontiers, thematic structures, and evolutionary trajectories, thereby providing a robust scientific foundation for understanding current research paradigms and for identifying future directions. From a research perspective, it clearly distinguishes AI-driven GBTI from more limited AI-in-GB applications. From a paradigmatic perspective, this work outlines core innovation modes and constructs a lifecycle blueprint linking AI with BIM and digital twin platforms. From a methodological perspective, a hybrid approach combining bibliometric mapping with dynamic topic modeling was used to minimize interpretive bias and establish a replicable framework for future investigations.
The findings indicate that the field evolved through four phases: the early incipient period (2015–2019), development period (2020–2021), rapid growth period (2022–2023), and the explosive period (2024–2025), reflecting the continuous increase in academic attention. A bibliometric analysis identified four thematic clusters centered on core keywords such as “neural networks”, “sustainability”, “energy efficiency”, and “machine learning”, corresponding to materials and structure, energy and performance prediction, sustainable design, and indoor environmental quality. This diversity establishes a multidimensional research ecosystem in which neural networks serve as a central enabling technology while sustainability and energy efficiency remain primary objectives. Burst term analysis further reveals a shift from conceptual exploration to practical implementation of AI across multiple algorithms and application scenarios, marking a move toward system integration and comprehensive application. Based on the dynamic topic model, three main topics were identified: (1) AI-based building performance prediction and carbon emission assessment; (2) intelligent multi-objective optimization of building energy systems; (3) sustainable building system design and intelligent resource management. These themes span the full innovation chain, from evaluation and optimization to holistic system management.
Building on this foundation, this study further summarizes four primary AI-driven GBTI modes: (1) performance-oriented intelligent design paradigm, (2) data-driven prediction and simulation paradigm, (3) evolution-driven intelligent optimization paradigm, (4) knowledge mining-based systemic decision paradigm. In light of these paradigms, three promising future research directions are proposed: (1) the application of AI-enhanced digital twins for life-cycle management of green building; (2) generative AI promoting intelligent design support; and (3) intelligent construction management integrated with green construction.
Although this study offers the contributions described above, it has several limitations. First, the analysis relies solely on the Scopus database and includes only journal articles, which may limit the scope of publication coverage. Second, bibliometric methods tend to favor highly cited works, potentially overlooking emerging but less-cited research. Third, the rapid pace of AI innovation means that the latest advances may not yet appear in the academic record. In future work, we will integrate multiple databases and literature types and explore alternative analytical approaches to enhance comprehensiveness and capture emerging contributions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W. and Q.W.; methodology, J.W. and Z.G.; software, J.W.; validation, J.W., C.P. and Q.W.; formal analysis, Z.G.; investigation, C.P. and Q.W.; resources, J.W. and C.P.; data curation, J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.W.; writing—review and editing, J.W. and Q.W.; visualization, J.W. and Q.W.; supervision, Z.G. and Q.W.; project administration, J.W. and Q.W.; funding acquisition, Z.G. and Q.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the funding support from the China Scholarship Council (No. 202406370135) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 72171237).
Data Availability Statement
Data availability is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for comments and recommendations from the editor and anonymous reviewers.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, L.; Mirzabeigi, S.; Soltanian-Zadeh, S.; Dong, B.; Krietemeyer, B.; Gao, P.; Wilson, N.; Zhang, J. A High-Performance Multi-Scale Modular-Based Green Design Studio Platform for Building and Urban Environmental Quality and Energy Simulations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 119, 106078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Zhao, Z.-Y. Green Building Research–Current Status and Future Agenda: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 30, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Environment Programme. Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction 2024/2025|UNEP—UN Environment Programme. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/report/global-status-report-buildings-and-construction-20242025 (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Kiss, B.M.; Visintin, C.; Garrard, G.E.; Bekessy, S.A. Evaluating Biodiversity Criteria in Green Building Rating Schemes: Toward ‘Nature Positive’ Development. Sustain. Dev. 2025; early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.F.; Esmanioto, F.; Huber, N.; Loures, E.F.R.; Junior, O.C.; Costin, A. Novel Framework for BIM Interoperability for Sustainability and Green Buildings—An Application for Concrete Structures. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2024, 29, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaashi, S.; Vilventhan, A. Development of a Building Information Modelling Based Decision-Making Framework for Green Retrofitting of Existing Buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 80, 108128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goubran, S.; Walker, T.; Cucuzzella, C.; Schwartz, T. Green Building Standards and the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, D. Strategies for Promoting Green Buildings: Integrating Evolutionary Game and SEIR Models. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanrewaju, O.I.; Enegbuma, W.I.; Donn, M.; Chileshe, N. Building Information Modelling and Green Building Certification Systems: A Systematic Literature Review and Gap Spotting. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 81, 103865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pang, Q.; Yao, J.; Zhang, M.; Arzo, S. Building Green Bridges: Unveiling the Impact of Green Technologies on Circular Practices, Resource Efficiency, and Sustainability in GVCs Influencing SDGs. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2025, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, H.; Mi, L.; Li, P.; Qi, K. Green Building Technologies Adoption Process in China: How Environmental Policies Are Reshaping the Decision-Making among Alliance-Based Construction Enterprises? Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 73, 103122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Collaborative Relationship Discovery in Green Building Technology Innovation: Evidence from Patents in China’s Construction Industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 391, 136041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-F.J.; Lin, C.-H.; Hsu, M.-W. Analysis of Intelligent Green Building Policy and Developing Status in Taiwan. Energy Policy 2016, 95, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olubunmi, O.A.; Xia, P.B.; Skitmore, M. Green Building Incentives: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, F.; Wang, Y. Comparison of Evaluation Standards for Green Building in China, Britain, United States. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Chen, H.; Du, L. A Holistic Review of Research on Carbon Emissions of Green Building Construction Industry. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2020, 27, 1065–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.W.; Zhou, J. Enhancing Environmental Sustainability over Building Life Cycles through Green BIM: A Review. Autom. Constr. 2015, 57, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gao, X.; Hua, C.; Gong, S.; Yue, A. Evolutionary Process of Promoting Green Building Technologies Adoption in China: A Perspective of Government. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, Q.; Jing, H.; Gao, Q. How to Promote the Technological Innovation Cooperation in Mega Construction Projects at the Project Level? Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2025; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, R.; Zhao, X.; Dong, K.; Wang, J.; Sharif, A. Can Artificial Intelligence Technology Innovation Boost Energy Resilience? The Role of Green Finance. Energy Econ. 2025, 142, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.; Hwang, J. The Nexus of Artificial Intelligence and Green Innovation: A Cross-Density Analysis at the Country Level. J. Knowl. Econ. 2025, 16, 1688–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; Gan, J.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y. How Does the Construction of New Generation of National AI Innovative Development Pilot Zones Drive Enterprise ESG Development? Empirical Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2024, 140, 108011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z. Research on Sustainability Evaluation of Green Building Engineering Based on Artificial Intelligence and Energy Consumption. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 11378–11391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.A. Artificial Neural Networks in Renewable Energy Systems Applications: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2001, 5, 373–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.A.; Bojic, M. Artificial Neural Networks for the Prediction of the Energy Consumption of a Passive Solar Building. Energy 2000, 25, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Rivard, H.; Zmeureanu, R. On-Line Building Energy Prediction Using Adaptive Artificial Neural Networks. Energy Build. 2005, 37, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Che, Y.; Xia, M.; Lin, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Luo, J.; Fan, G. The Evolution and Future Directions of Green Buildings Research: A Scientometric Analysis. Buildings 2024, 14, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Hao, F.; Meng, X. When Artificial Intelligence Meets Building Energy Efficiency, a Review Focusing on Zero Energy Building. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 2193–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chan, A.P.C.; Darko, A.; Chen, Z.; Li, D. Integrated Applications of Building Information Modeling and Artificial Intelligence Techniques in the AEC/FM Industry. Autom. Constr. 2022, 139, 104289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Chan, A.P.C.; Adabre, M.A.; Edwards, D.J.; Hosseini, M.R.; Ameyaw, E.E. Artificial Intelligence in the AEC Industry: Scientometric Analysis and Visualization of Research Activities. Autom. Constr. 2020, 112, 103081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, M.U.; Chun, D.; Zeeshan; Han, H.; Jeon, G.; Chen, K. A Review of the Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data to Buildings for Energy-Efficiency and a Comfortable Indoor Living Environment. Energy Build. 2019, 202, 109383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaamala, A.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Nili, A.; Nyandega, D. Algorithmic Green Infrastructure Optimisation: Review of Artificial Intelligence Driven Approaches for Tackling Climate Change. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 101, 105182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gracia, D.; Capobianco-Uriarte, M.d.l.M.; Terán-Yépez, E.; Piedra-Fernández, J.A.; Iribarne, L.; Ayala, R. Review of Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Green/Smart Buildings. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2023, 38, 100861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regona, M.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Hon, C.; Teo, M. Artificial Intelligence and Sustainable Development Goals: Systematic Literature Review of the Construction Industry. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 108, 105499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Xing, C.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G. Artificial Intelligence Powered Large-Scale Renewable Integrations in Multi-Energy Systems for Carbon Neutrality Transition: Challenges and Future Perspectives. Energy AI 2022, 10, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awuzie, B.; Ngowi, A.; Aghimien, D. Towards Built Environment Decarbonisation: A Review of the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Improving Energy and Materials’ Circularity Performance. Energy Build. 2024, 319, 114491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olu-Ajayi, R.; Alaka, H.; Sunmola, F.; Ajayi, S.; Mporas, I. Statistical and Artificial Intelligence-Based Tools for Building Energy Prediction: A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 14733–14753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brem, A.; Giones, F.; Werle, M. The AI Digital Revolution in Innovation: A Conceptual Framework of Artificial Intelligence Technologies for the Management of Innovation. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 70, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefner, N.; Wincent, J.; Parida, V.; Gassmann, O. Artificial Intelligence and Innovation Management: A Review, Framework, and Research Agenda✰. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 162, 120392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.; Dennehy, D.; Conboy, K.; Mikalef, P. Artificial Intelligence in Information Systems Research: A Systematic Literature Review and Research Agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 60, 102383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongeon, P.; Paul-Hus, A. The Journal Coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: A Comparative Analysis. Scientometrics 2016, 106, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debrah, C.; Chan, A.P.C.; Darko, A. Artificial Intelligence in Green Building. Autom. Constr. 2022, 137, 104192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obreja, D.M.; Rughiniș, R.; Rosner, D. Mapping the Conceptual Structure of Innovation in Artificial Intelligence Research: A Bibliometric Analysis and Systematic Literature Review. J. Innov. Knowl. 2024, 9, 100465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.J.; López-Herrera, A.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. Science Mapping Software Tools: Review, Analysis, and Cooperative Study among Tools. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2011, 62, 1382–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Al-Hussein, M. Building Information Modelling for Off-Site Construction: Review and Future Directions. Autom. Constr. 2019, 101, 72–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Chan, A.P.C.; Huo, X.; Owusu-Manu, D.-G. A Scientometric Analysis and Visualization of Global Green Building Research. Build. Environ. 2019, 149, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Long, R.; Chen, H.; Chen, F.; Wang, J. Visualized Analysis of Global Green Buildings: Development, Barriers and Future Directions. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, M.; Sang, P.; Chen, P.-H.; Li, C. Stakeholder Studies of Green Buildings: A Literature Review. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 54, 104667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Fanyang, Y.; Wang, J.; Meng, S.; Tang, D. A Literature Review of Green Building Policies: Perspectives from Bibliometric Analysis. Buildings 2024, 14, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.; Santos, J.; Leite, F.; Escórcio, P. Using BIM to Improve Building Energy Efficiency—A Scientometric and Systematic Review. Energy Build. 2021, 250, 111292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, M. A Review on Application Studies of LDA Topic Models in Library and Information Science Field. Doc. Knowl. 2022, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M. Latent Dirichlet Allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, U.; Shah, A. Topic Modeling Using Latent Dirichlet Allocation: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. CSUR 2021, 54, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Lafferty, J.D. Dynamic Topic Models. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–29 June 2006; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, T.; Yang, C.; Wei, Y.; Dai, G. Carbon Reduction and Green Finance Innovations: A Scientometric Analysis Using Bibliometrics and DTM Model. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Huang, X.; Dong, K.; Liang, Z.; Wu, J. Semantic-Enhanced Topic Evolution Analysis: A Combination of the Dynamic Topic Model and Word2vec. Scientometrics 2022, 127, 1543–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, M.; Ma, G.; Jiang, S. A Hybrid Forecasting Model to Improve Cost Prediction Accuracy in Green Building Projects with Machine Learning. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2025; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, M.; Ma, G. A Machine Learning-Based Two-Stage Integrated Framework for Cost Reasonableness Prediction of Green Building Projects. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 100, 111733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.; Kim, C. Early Prediction of the Performance of Green Building Projects Using Pre-Project Planning Variables: Data Mining Approaches. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 109, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Glushakova, I.; Boateng, E.B.; Chan, A.P.C. Using Machine Learning to Improve Cost and Duration Prediction Accuracy in Green Building Projects. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2023, 149, 04023061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Chen, W.; Hu, T.; Xu, X. Evolutionary Double Attention-Based Long Short-Term Memory Model for Building Energy Prediction: Case Study of a Green Building. Appl. Energy 2021, 288, 116660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, R. Multidimensional Performance-Based Evaluation Method of High-Performance Cold Source in Green Building. Energy Build. 2021, 231, 110618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.L.; Azmi, A.M.; Dahlan, N.Y.; Woon, K.S. Predicting Life Cycle Carbon Emission of Green Office Buildings via an Integrated LCA- MLR Framework. Energy Build. 2024, 316, 114345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, A.; Das, S. Decision Support System for the Early Stage of Green Building Envelope Design Considering Energy and Maintainability. Archit. Eng. Des. Manag. 2023, 19, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harja, M.; Gencel, O.; Sarı, A.; Sutcu, M.; Erdogmus, E.; Hekimoglu, G. Production and Characterization of Natural Clay-Free Green Building Brick Materials Using Water Treatment Sludge and Oak Wood Ash. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2022, 22, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmansouri, A.A.; Yazdani, M.; Ghanbari, S.; Akbarzadeh Bengar, H.; Jafari, A.; Farrokh Ghatte, H. Artificial Neural Network Model to Predict the Compressive Strength of Eco-Friendly Geopolymer Concrete Incorporating Silica Fume and Natural Zeolite. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, G. Exergy-Based Optimisation of a Phase Change Materials Integrated Hybrid Renewable System for Active Cooling Applications Using Supervised Machine Learning Method. Sol. Energy 2020, 195, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tai, H.-W.; Cheng, K.-T.; Wei, C.-C. Consolidating Building Greening: Integrating Mobile Modular Vertical Greening Systems into Prefabricated Building. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 110983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, G. Artificial Neural Network Based Multivariable Optimization of a Hybrid System Integrated with Phase Change Materials, Active Cooling and Hybrid Ventilations. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 197, 111859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Kang, B.; Lee, S.; Park, S.; Seon Beck, J.; Hyeon Lee, S.; Park, S. Empirical Study on Optimization Methods of Building Energy Operation for the Sustainability of Buildings with Integrated Renewable Energy. Energy Build. 2024, 305, 113908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Yin, X.; Zhang, H.; Ghalandari, M. Optimal Control of Renewable Energy in Buildings Using the Machine Learning Method. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Lei, L. A Hybrid Model for Real-Time Cooling Load Prediction and Terminal Control Optimization in Multi-Zone Buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 104, 112120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruta, G.; Ascione, F.; Bianco, N.; Mauro, G.M.; Vanoli, G.P. Optimizing Heating Operation via GA- and ANN-Based Model Predictive Control: Concept for a Real Nearly-Zero Energy Building. Energy Build. 2023, 292, 113139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolucci, L.; Cordiner, S.; Mulone, V.; Pasquale, S.; Sbarra, A. Design and Management Strategies for Low Emission Building-Scale Multi Energy Systems. Energy 2022, 239, 122160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxman, R. Thinking Difference: Theories and Models of Parametric Design Thinking. Des. Stud. 2017, 52, 4–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Shen, Y.; Qin, J.; Zhang, L. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Objective Optimization in BIM-Based Green Building Design. Autom. Constr. 2024, 166, 105598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Pan, Y. BIM-Supported Automatic Energy Performance Analysis for Green Building Design Using Explainable Machine Learning and Multi-Objective Optimization. Appl. Energy 2023, 333, 120575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertosun Yıldız, M.; Beyhan, F. Prediction of Cooling Load via Machine Learning on Building Envelope Design Parameters. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 100, 111724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmetoğlu, S.; Delice, Y.; Kızılkaya Aydoğan, E.; Uzal, B. Green Building Envelope Designs in Different Climate and Seismic Zones: Multi-Objective ANN-Based Genetic Algorithm. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Huang, H.; He, B.-J. Building Information Modelling-Enabled Multi-Objective Optimization for Energy Consumption Parametric Analysis in Green Buildings Design Using Hybrid Machine Learning Algorithms. Energy Build. 2023, 300, 113665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfarazi, S.; Mascolo, I.; Modano, M.; Guarracino, F. Application of Artificial Intelligence to Support Design and Analysis of Steel Structures. Metals 2025, 15, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, B.; Yaman, H. Green Building Assessment Tool (GBAT) for Integrated BIM-Based Design Decisions. Autom. Constr. 2016, 70, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, E.; Pauwels, P.; Svidt, K.; Jensen, R.L. Towards Data-Driven Sustainable Design: Decision Support Based on Knowledge Discovery in Disparate Building Data. Archit. Eng. Des. Manag. 2019, 15, 334–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Ma, G.; Wang, D.; Pan, X. Intelligent Green Retrofitting of Existing Buildings Based on Case-Based Reasoning and Random Forest. Autom. Constr. 2024, 162, 105377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.; Sun, H.; El-Kenawy, E.-S.M.; Iqbal, A.; Alharbi, A.H.; Khafaga, D.S. Integrating Machine and Deep Learning Technologies in Green Buildings for Enhanced Energy Efficiency and Environmental Sustainability. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarzadeh, O.; Hamzehei, S.; Attar, H.; Amer, A.; Fasihihour, N.; Khosravi, M.R.; Solyman, A.A. Heating-Cooling Monitoring and Power Consumption Forecasting Using LSTM for Energy-Efficient Smart Management of Buildings: A Computational Intelligence Solution for Smart Homes. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2024, 29, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehraban, M.H.; Alnaser, A.A.; Sepasgozar, S.M.E. Building Information Modeling and AI Algorithms for Optimizing Energy Performance in Hot Climates: A Comparative Study of Riyadh and Dubai. Buildings 2024, 14, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Yu, P.; Yang, L. A Review of Artificial Intelligence in Enhancing Architectural Design Efficiency. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, Y.-H.; Zhang, J. Generative AIBIM: An Automatic and Intelligent Structural Design Pipeline Integrating BIM and Generative AI. Inf. Fusion 2025, 114, 102654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Shen, R.; Wu, Y. Performance-Oriented Parametric Optimization Design for Energy Efficiency of Rural Residential Buildings: A Case Study from China’s Hot Summer and Cold Winter Zone. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, Y.-K.; Lee, P.-H. Applying Data Mining Techniques to Explore Technology Adoptions, Grades and Costs of Green Building Projects. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, Z.; Fu, H. A Graph-Based Hybrid Deep Learning Approach for the Thermal Performance Potential Prediction of Green Roofs. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 84, 108554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Shen, Y.; Song, Z.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, Z.; Kusiak, A. Data-Driven Building Load Profiling and Energy Management. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 49, 101587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinham, J.; Fjeldheim, H.; Yan, B.; Helge, T.D.; Edwards, K.; Hegli, T.; Malkawi, A. Zero-Carbon Balance: The Case of HouseZero. Build. Environ. 2022, 207, 108511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Li, B.; Jia, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, D. Application of Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm to Optimize Energy Efficiency and Thermal Comfort in Building Design. Energy Build. 2015, 88, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahif, R.; Kazemi, M.; Attia, S. Overheating Analysis of Optimized Nearly Zero-Energy Dwelling during Current and Future Heatwaves Coincided with Cooling System Outage. Energy Build. 2023, 287, 112998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D. A Multi-Objective Optimization Framework for Designing Residential Green Space between Buildings Considering Outdoor Thermal Comfort, Indoor Daylight and Green View Index. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 119, 106045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Guo, R.; Lin, M.; Guo, F.; Zheng, X. Multi-Objective Optimization of Green Roof Spatial Layout in High-Density Urban Areas—A Case Study of Xiamen Island, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 115, 105827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Li, X.; Lin, B.; Zhu, Y. An Intelligent Retrofit Decision-Making Model for Building Program Planning Considering Tacit Knowledge and Multiple Objectives. Energy 2023, 263, 125704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenninger, S.; Karnebogen, P.; Lehmann, S.; Menzinger, T.; Reckstadt, M. Evidence for Residential Building Retrofitting Practices Using Explainable AI and Socio-Demographic Data. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 13514–13528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Yan, H.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y. An Integrated System of Text Mining Technique and Case-Based Reasoning (TM-CBR) for Supporting Green Building Design. Build. Environ. 2017, 124, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Lin, B.; Zhu, Y. A CBR-Based Decision-Making Model for Supporting the Intelligent Energy-Efficient Design of the Exterior Envelope of Public and Commercial Buildings. Energy Build. 2021, 231, 110625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalia, A.; Bakker, R.; Ramage, M. The Edge, Amsterdam: Showcasing an Exemplary IoT Building; Centre for Digital Built Britain: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrahman, M.; Macatulad, E.; Lei, B.; Quintana, M.; Miller, C.; Biljecki, F. What Is a Digital Twin Anyway? Deriving the Definition for the Built Environment from over 15,000 Scientific Publications. Build. Environ. 2025, 274, 112748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komninos, N. Net Zero Energy Districts: Connected Intelligence for Carbon-Neutral Cities. Land 2022, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E.; Huang, J.; Omar, O.; Kenawy, I. Synergistic Integration of Digital Twins and Zero Energy Buildings for Climate Change Mitigation in Sustainable Smart Cities: A Systematic Review and Novel Framework. Energy Build. 2025, 333, 115484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Q.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Su, C.; Wang, B. Machine Learning Based Digital Twin Framework for Production Optimization in Petrochemical Industry. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 49, 502–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Bello, A.O.; Arqam, M.; Ullah, F. Integrating Building Information Modelling and Artificial Intelligence in Construction Projects: A Review of Challenges and Mitigation Strategies. Technologies 2024, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, L. Integrating BIM and AI for Smart Construction Management: Current Status and Future Directions. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 1081–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulefki, A.; Kheddar, H.; Amira, A.; Kurugollu, F.; Himeur, Y.; Bounceur, A. Innovative AI Strategies for Enhancing Smart Building Operations through Digital Twins: A Survey. Energy Build. 2025, 335, 115567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakowski, S. Human-AI Agency in the Age of Generative AI. Inf. Organ. 2025, 35, 100560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, K.F.; Awa, K.N.; Zabelina, D.L. The Current State of Artificial Intelligence Generative Language Models Is More Creative than Humans on Divergent Thinking Tasks. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wang, W.; He, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T. Performance in Generation: An Automatic Generalizable Generative-Design-Based Performance Optimization Framework for Sustainable Building Design. Energy Build. 2023, 298, 113512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, R.; Bello, I.T.; Abdulai, S.F.; Yussif, A.-M.; Salami, B.A.; Saka, A.; Ben Seghier, M.E.A.; Zayed, T. Generative Artificial Intelligence in Construction: A Delphi Approach, Framework, and Case Study. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 116, 672–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, X.; Bao, Z.; Skibniewski, M.J.; Fang, W. Artificial Intelligence in Infrastructure Construction: A Critical Review. Front. Eng. Manag. 2025, 12, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Lu, X.; Fei, Y.; Gu, Y.; Huang, Y. Generative AI Design for Building Structures. Autom. Constr. 2024, 157, 105187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, Z.X.; Wong, J.Y.; Tang, Y.H.; Yip, C.C.; Maul, T. Generative Design in the Built Environment. Autom. Constr. 2024, 166, 105638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Y. A Graph-Enabled Parametric Modeling Approach for Façade Layout Generative Design. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 105, 112481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.Y.; Li, C.; Petzold, F.; Tiong, R.L.K.; Yang, Y. Lifecycle Framework for AI-Driven Parametric Generative Design in Industrialized Construction. Autom. Constr. 2025, 174, 106146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Lu, W.; Jia, L. Improving Knowledge Management in Building Engineering with Hybrid Retrieval-Augmented Generation Framework. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 103, 112189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taeihagh, A. Governance of Generative AI. Policy Soc. 2025, 44, puaf001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yu, M.; Hou, J. Synergistic Relationship, Agent Interaction, and Knowledge Coupling: Driving Innovation in Intelligent Construction Technology. Buildings 2024, 14, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, N.; Bled, A.; Bourgault, M.; Cousin, N.; Danjou, C.; Pellerin, R.; Roland, T. Construction 4.0: A Comparative Analysis of Research and Practice. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2024, 29, 16–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, L. Roles of Artificial Intelligence in Construction Engineering and Management: A Critical Review and Future Trends. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohueri, C.C.; Masrom, M.A.N.; Noguchi, M. Human-Robot Collaboration for Building Deconstruction in the Context of Construction 5.0. Autom. Constr. 2024, 167, 105723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baduge, S.K.; Thilakarathna, S.; Perera, J.S.; Arashpour, M.; Sharafi, P.; Teodosio, B.; Shringi, A.; Mendis, P. Artificial Intelligence and Smart Vision for Building and Construction 4.0: Machine and Deep Learning Methods and Applications. Autom. Constr. 2022, 141, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochovski, P.; Stankovski, V. Building Applications for Smart and Safe Construction with the DECENTER Fog Computing and Brokerage Platform. Autom. Constr. 2021, 124, 103562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Pan, W. Artificial Intelligence and Robotics for Prefabricated and Modular Construction: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2022, 148, 03122004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.J.; Oyekan, J.; Stergioulas, L.; Griffin, D. Utilizing Industry 4.0 on the Construction Site: Challenges and Opportunities. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).