Research on Concrete Crack and Depression Detection Method Based on Multi-Level Defect Fusion Segmentation Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- An innovative deep learning model, Multi-level Defect Fusion Segmentation Network (MDFNet), combined with an improved U-shaped structure and target detection technique, is proposed to achieve efficient and accurate concrete defect detection.
- (2)
- The HAEConv module and SE module are introduced for feature enhancement, which improves the model’s ability to identify defective regions, such as cracks and dents, and optimizes jump connections to enhance the fusion of global features with local details. YOLOv11 is used for target detection and is combined with the Copy–Pasting strategy to optimize the segmentation task, which effectively improves the segmentation accuracy and enhances the bounding box accuracy of the target detection branch, achieving two-way optimization. And the Copy–Filing strategy reduces reliance on large amounts of data, to a certain extent.
- (3)
- A high-quality dataset covering different kinds of concrete defects is constructed and experimentally verified under multiple complex backgrounds, which provides reliable data support for subsequent research. The effectiveness of the proposed method is verified through experimental analyses, and the results show that MDFNet outperforms the existing methods in several evaluation metrics, especially in defect segmentation accuracy, which provides an efficient and robust solution for detecting concrete surface defects in complex scenarios.
2. Related Works
3. Methodology
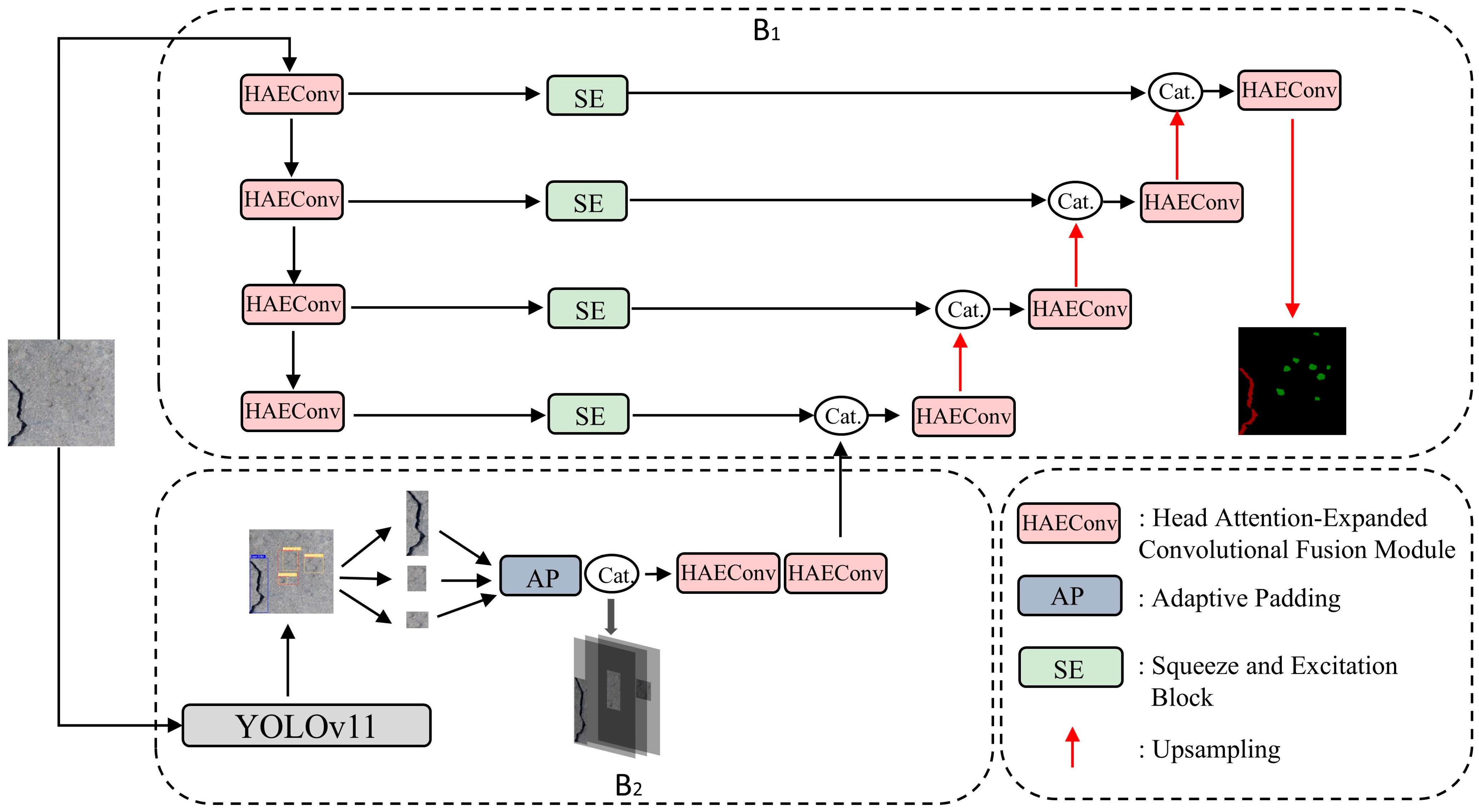
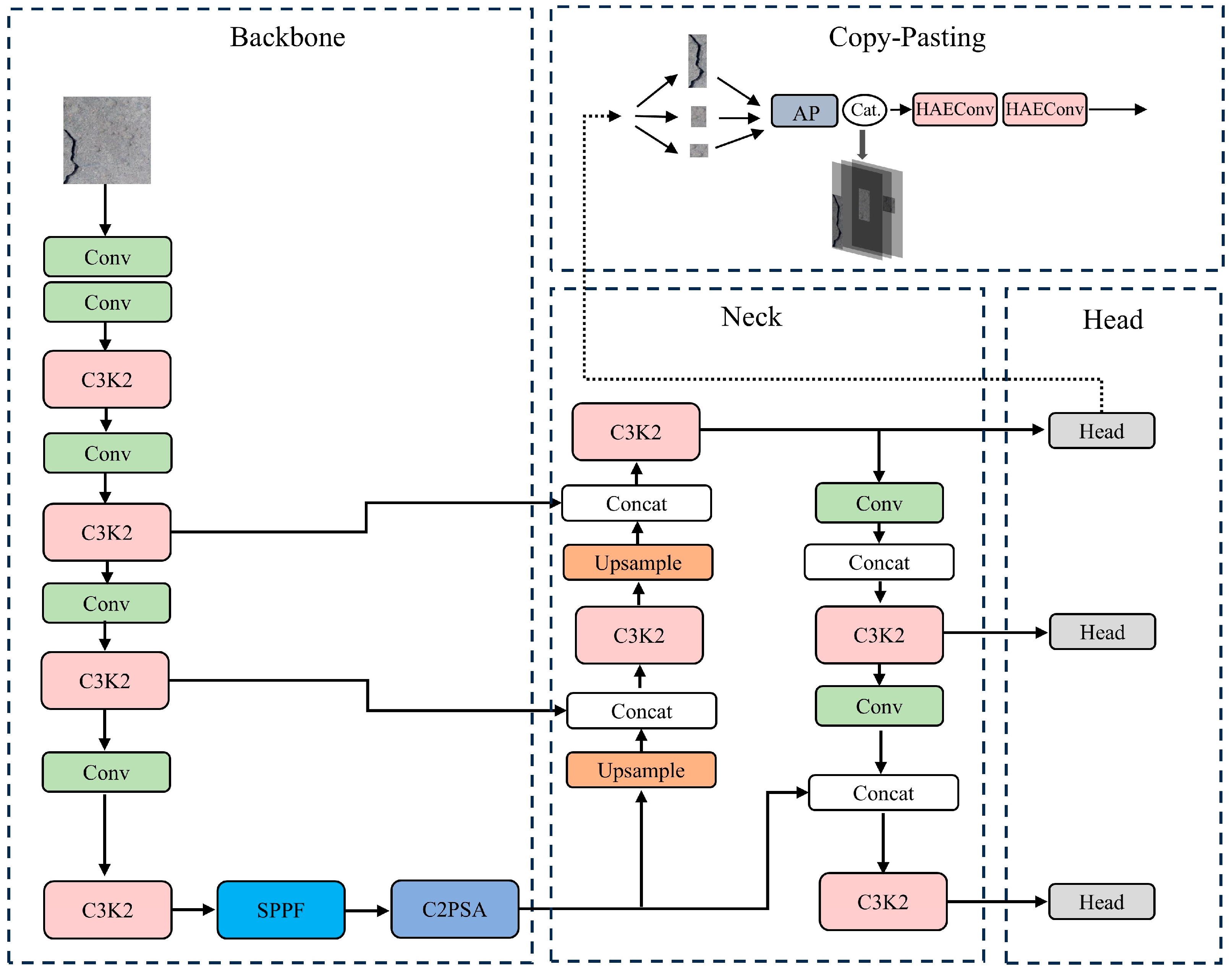
3.1. Multi-Level Defect Fusion Segmentation Network
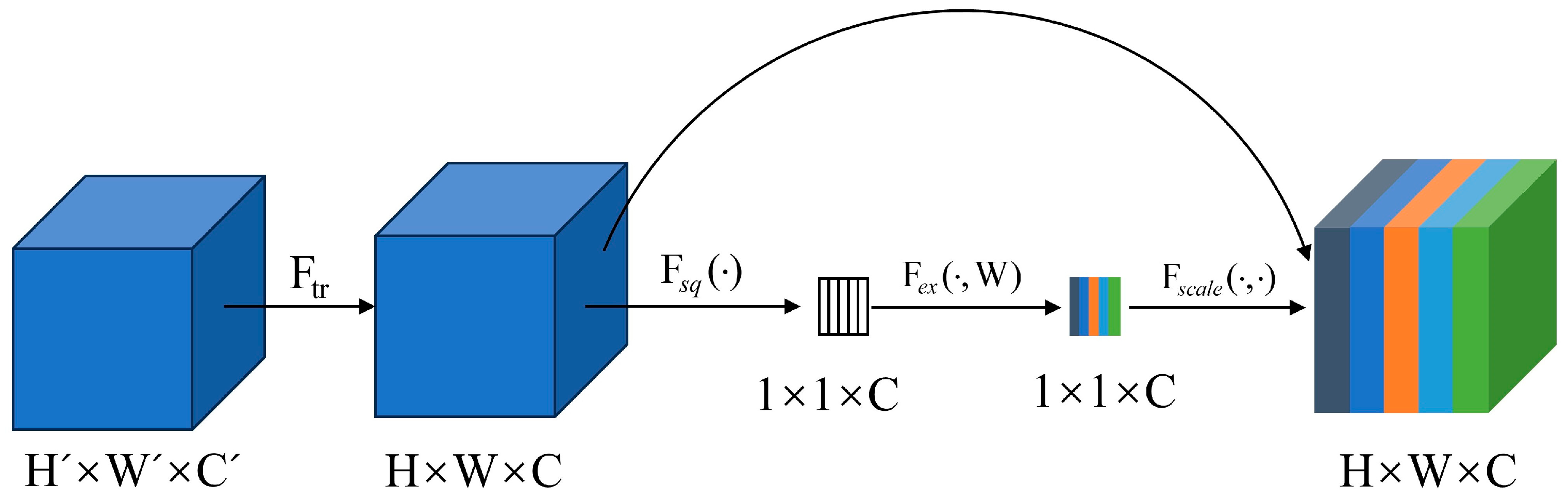
3.2. Squeeze-and-Excitation
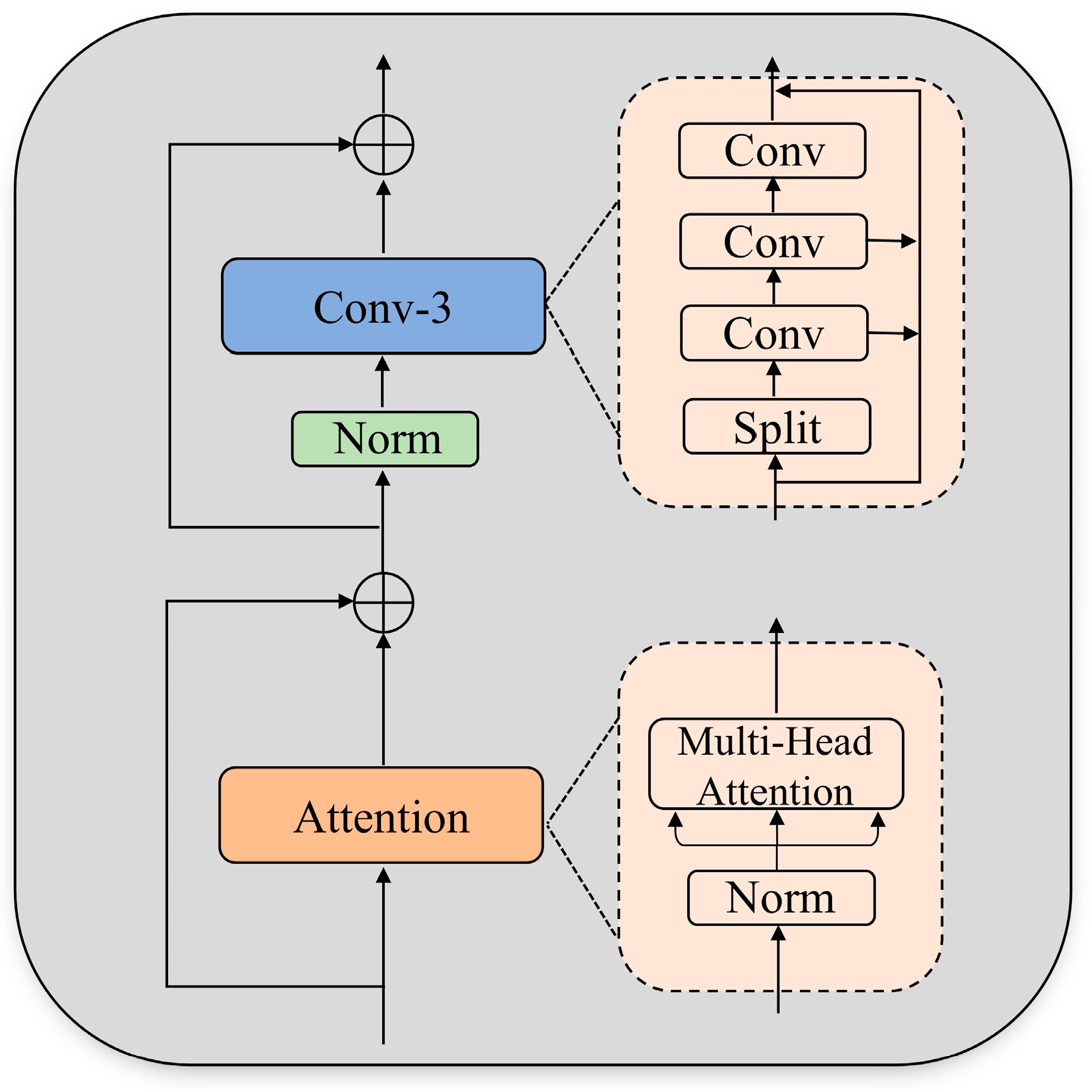
3.3. B1 Head Attention-Expander Convolutional Fusion Module
3.4. B2 Copy–Pasting
3.5. Function Loss
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Datasets
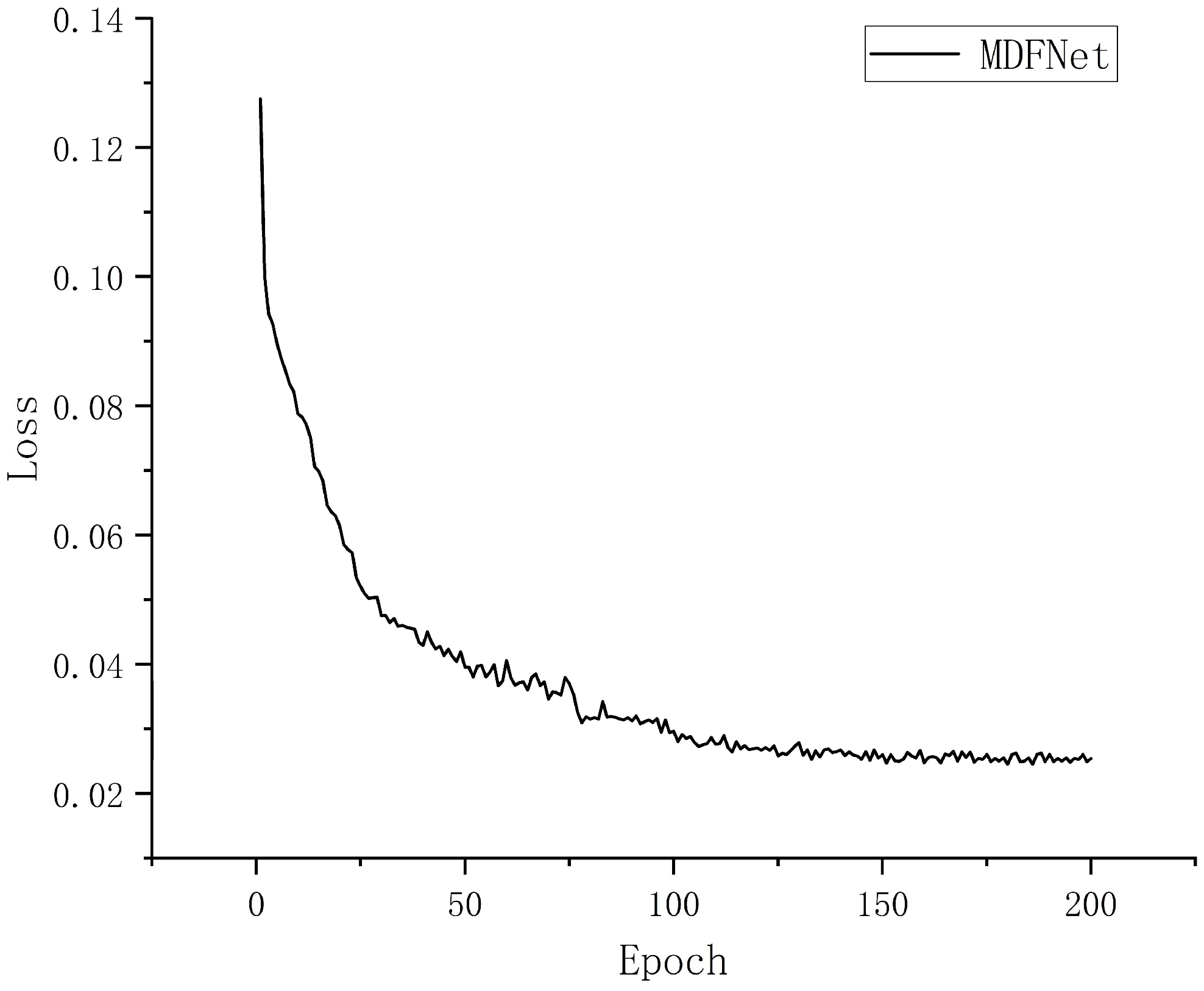
4.2. Experimental Details
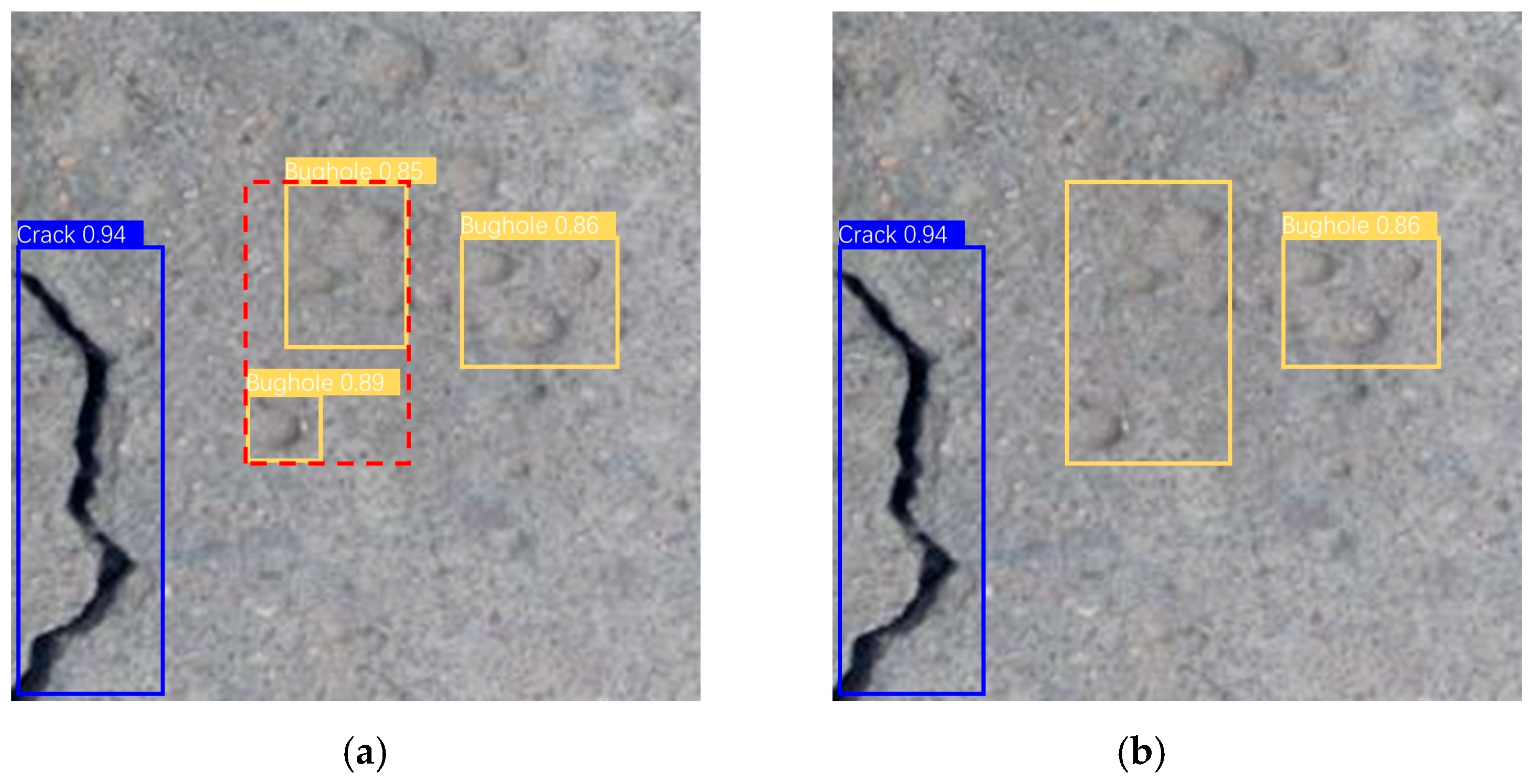
4.3. Prediction Box Fusion
4.4. Ablation Experiment
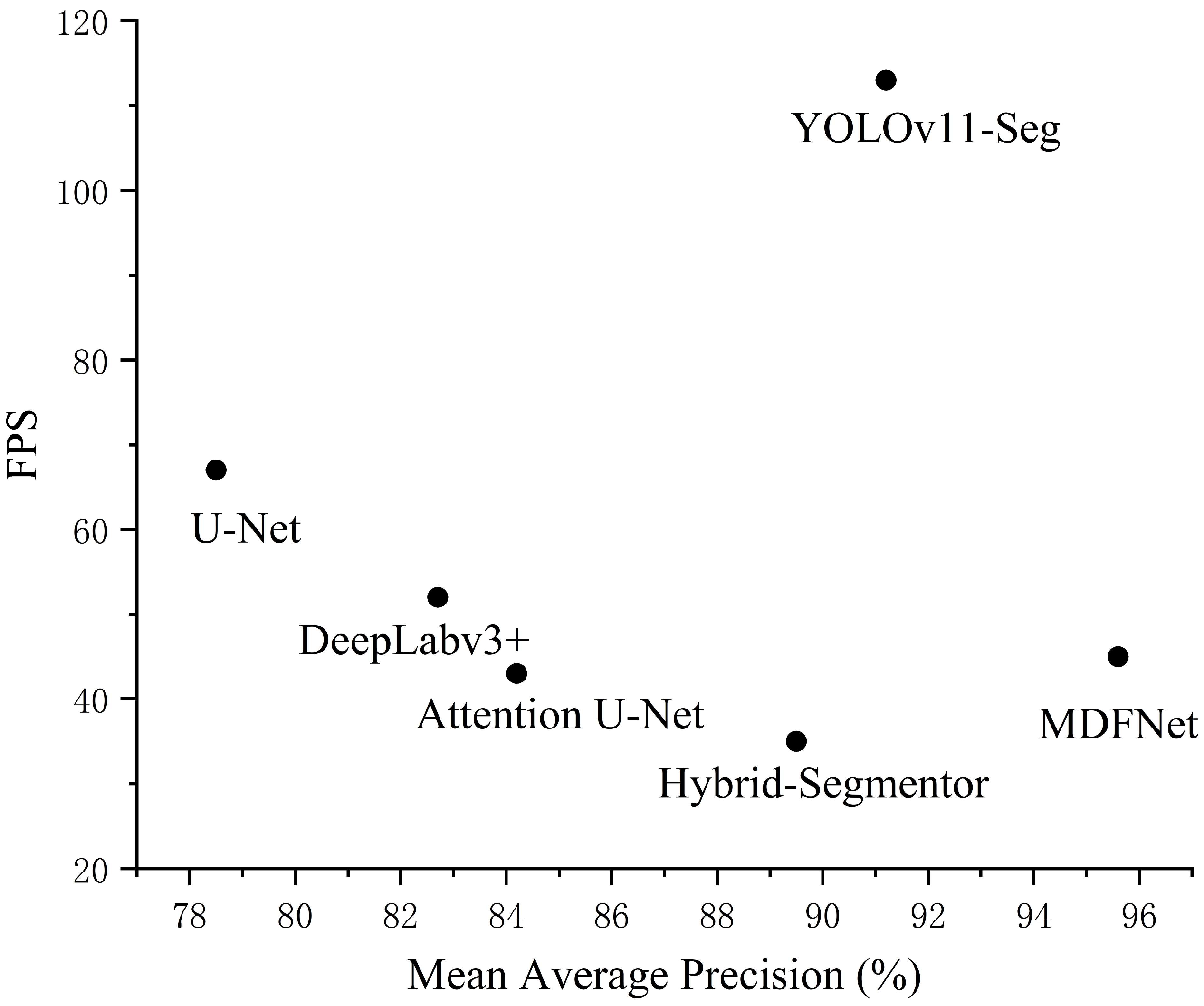
4.5. Comparison Experiment
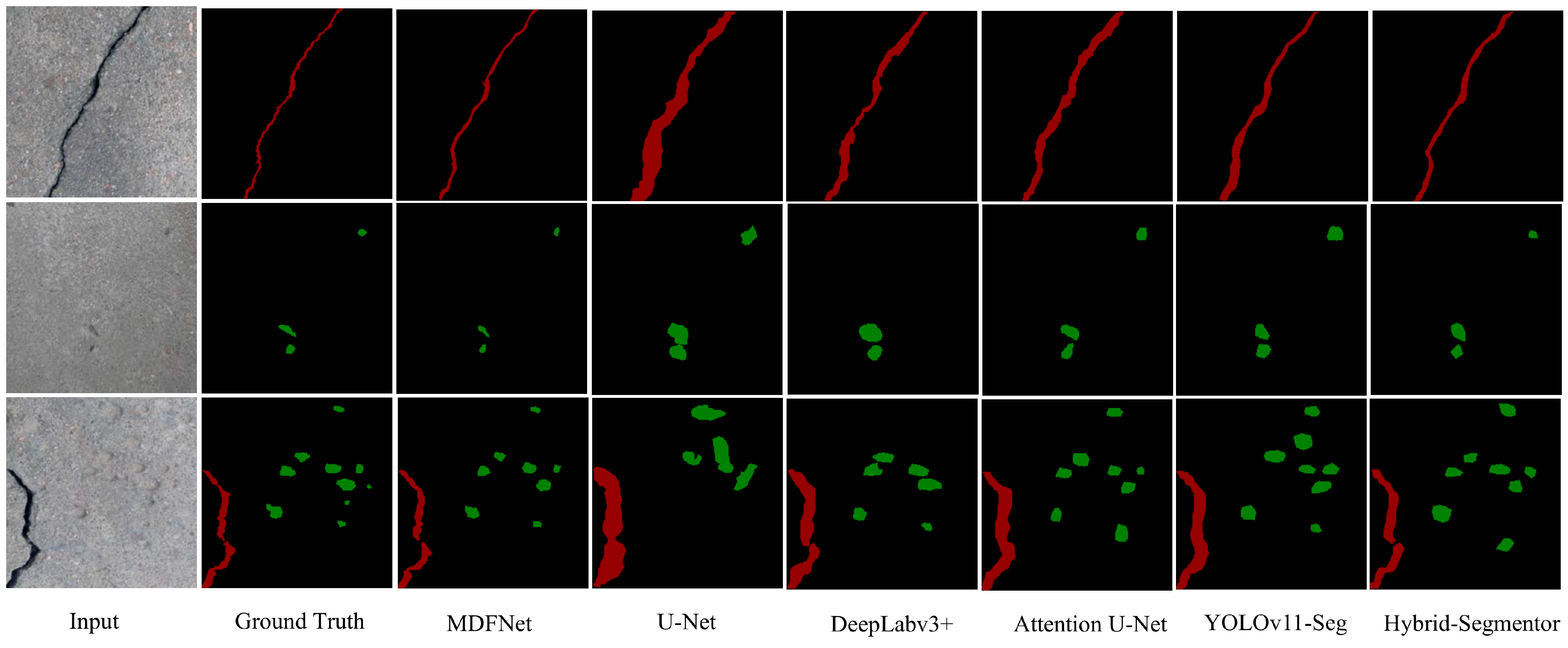
4.6. Visualization Comparison
4.7. Model Output Visualization
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Fu, H.; Tian, J.; Chin, C.-L.; Liu, H.; Yuan, J.; Tang, S.; Mai, R.; Wu, X. Axial compression behavior of GFRP-steel composite tube confined seawater sea-sand concrete intermediate long columns. Eng. Struct. 2025, 333, 120157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Guo, K.; Wu, Z.; Mai, R.; Chin, C.-L. Experimental Investigation of a Novel CFRP-Steel Composite Tube-Confined Seawater-Sea Sand Concrete Intermediate Long Column. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2024, 16, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.M.; Atamturktur, S.; Chowdhury, M.; Rahman, M. Integration of Structural Health Monitoring and Intelligent Transportation Systems for Bridge Condition Assessment: Current Status and Future Direction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 2107–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zhao, H.; Pan, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chin, C.-L.; Ma, C.-K. Behaviour of corroded circular steel tube strengthened with external FRP tube grouting under eccentric loading: Numerical study. Structures 2023, 56, 104810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Chin, C.-L.; Ma, C.-K. Nonlinear analysis of axial-compressed corroded circular steel pipes reinforced by FRP-casing grouting. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2023, 201, 107689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, J.; Jenkins, M.; Mannion, M.; Barrie, P.; Morison, G. What's cracking? A review and analysis of deep learning methods for structural crack segmentation, detection and quantification. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.03714. [Google Scholar]
- Phares, B.M.; Rolander, D.D.; Graybeal, B.A.; Washer, G.A. Reliability of visual bridge inspection. Public Roads 2001, 64, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Xia, H.; Zhou, B.; Yan, F.; Guo, R. A method to improve the accuracy of pavement crack identification by combining a semantic segmentation and edge detection model. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Deng, H.; Dong, Q.; Gu, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y. An advanced Otsu method integrated with edge detection and decision tree for crack detection in highway transportation infrastructure. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9205509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konig, J.; Jenkins, M.D.; Mannion, M.; Barrie, P.; Morison, G. Weakly-Supervised Surface Crack Segmentation by Generating Pseudo-Labels Using Localization With a Classifier and Thresholding. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 24083–24094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Gu, X.; Chen, Y. Fast and robust pavement crack distress segmentation utilizing steerable filtering and local order energy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, R.S.; Moselhi, O.; Bagchi, A. Image-based retrieval of concrete crack properties for bridge inspection. Autom. Constr. 2014, 39, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Benedetto, A.; Fiani, M.; Gujski, L.M. U-Net-based CNN architecture for road crack segmentation. Infrastructures 2023, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W., Frangi, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9351, Lecture Notes in Computer Science. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Cho, S. Automated Vision-Based Detection of Cracks on Concrete Surfaces Using a Deep Learning Technique. Sensors 2018, 18, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Pereira, F., Burges, C.J., Bottou, L., Weinberger, K.Q., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 25, Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2012/file/c399862d3b9d6b76c8436e924a68c45b-Paper.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- Kang, D.; Benipal, S.S.; Gopal, D.L.; Cha, Y.-J. Hybrid pixel-level concrete crack segmentation and quantification across complex backgrounds using deep learning. Autom. Constr. 2020, 118, 103291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Cortes, C., Lawrence, N., Lee, D., Sugiyama, M., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 28, Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2015/file/14bfa6bb14875e45bba028a21ed38046-Paper.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2020).
- Shi, Z.; Jin, N.; Chen, D.; Ai, D. A comparison study of semantic segmentation networks for crack detection in construction materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 414, 134950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Jin, L.; Wang, S.; Xu, H. Apple stem/calyx real-time recognition using YOLO-v5 algorithm for fruit automatic loading system. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 185, 111808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Weng, K.; Geng, Y.; Li, L.; Ke, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Nie, W.; et al. YOLOv6: A single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.02976. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Nyathi, M.A.; Bai, J.; Wilson, I.D. Deep Learning for Concrete Crack Detection and Measurement. Metrology 2024, 4, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terven, J.; Córdova-Esparza, D.M.; Romero-González, J.A. A comprehensive review of yolo architectures in computer vision: From yolov1 to yolov8 and yolo-nas. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2023, 5, 1680–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30, Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2017/file/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Paper.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Trans-former using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 9992–10002. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, H.; Liu, B.; Cui, J.; Zhang, H. A Convolutional-Transformer Network for Crack Segmentation with Boundary Awareness. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 8–11 October 2023; pp. 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhao, G.; Li, Y. Vison Transformer-Based Automatic Crack Detection on Dam Surface. Water 2024, 16, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zheng, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, Q.; Huang, X. Semantic segmentation model for concrete cracks based on parallel Swin-CNNs framework. Struct. Health Monit. 2024, 23, 3731–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Liu, Y.; Dai, J. Concrete Surface Crack Detection Algorithm Based on Improved YOLOv8. Sensors 2024, 24, 5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. Yolov11: An overview of the key architectural enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Fixing weight decay regularization in adam. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05101. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention U-Net: Learning Where to Look for the Pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Goo, J.M.; Milidonis, X.; Artusi, A.; Boehm, J.; Ciliberto, C. Hybrid-Segmentor: Hybrid approach for automated fine-grained crack segmentation in civil infrastructure. Autom. Constr. 2025, 170, 105960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
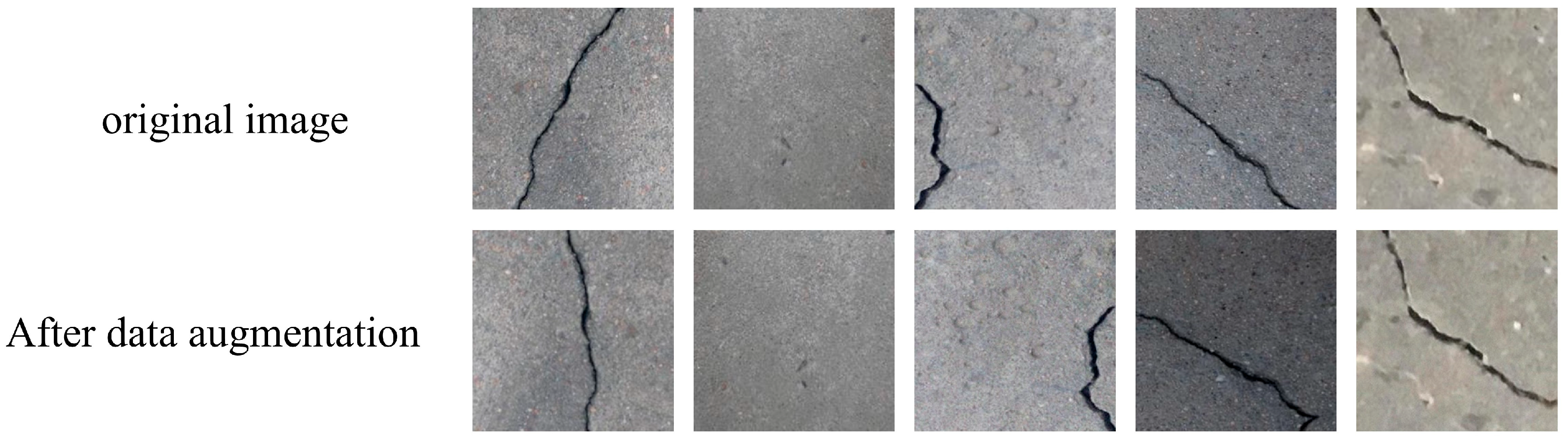
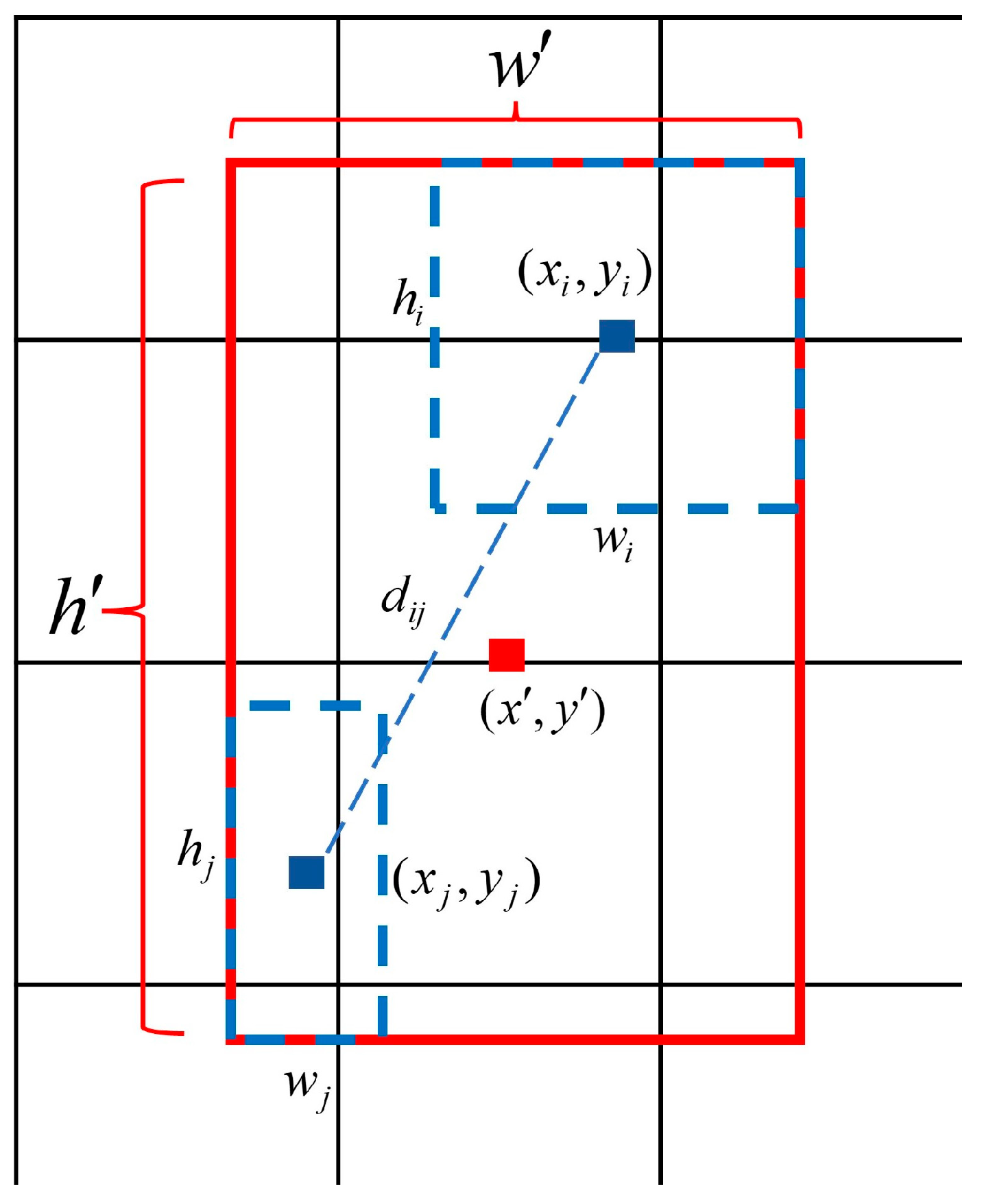


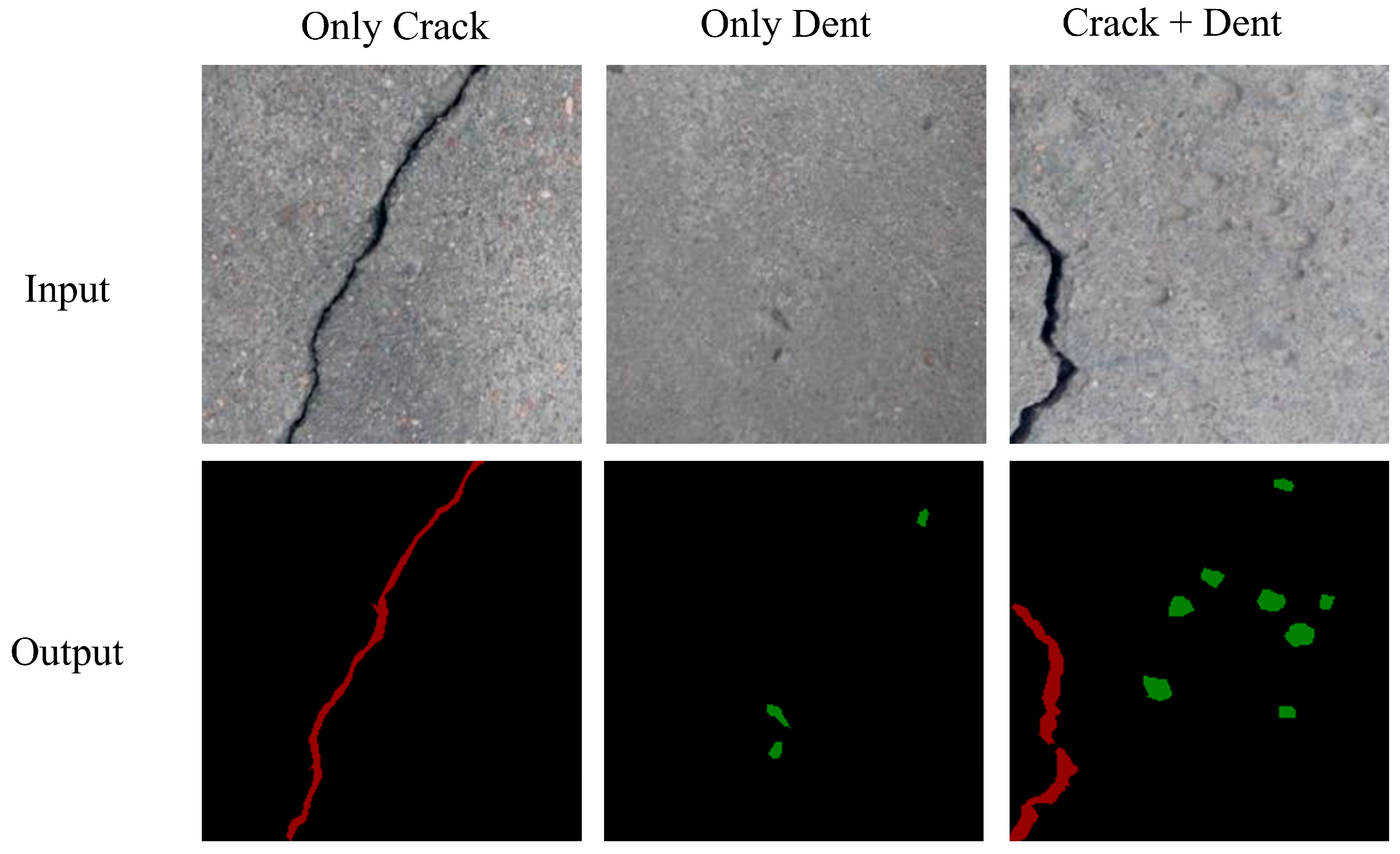
| Type | Training | Validation | Testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Only cracks | 775 | 111 | 221 |
| Only dents | 532 | 76 | 153 |
| Including cracks and dents | 443 | 63 | 126 |
| α:β | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | FP Rate | FN Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3:0.7 | 82.4% | 91.2% | 86.5 | 0.18 | 0.09 |
| 0.5:0.5 | 86.7% | 89.2% | 87.9 | 0.12 | 0.11 |
| 0.7:0.3 | 90.1% | 83.6% | 86.7 | 0.07 | 0.16 |
| Model | Module | Evaluation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAEConv | SE | B2 | Dice (%) | MAP (%) | mIoU (%) | FPS | |
| Baseline | 80.1 | 78.5 | 71.3 | 67 | |||
| M1 | √ | 86.8 | 87.2 | 76.2 | 48 | ||
| M2 | √ | 83.8 | 80.8 | 73.3 | 52 | ||
| M3 | √ | 84.5 | 85.4 | 74.8 | 51 | ||
| M4 | √ | √ | 89.5 | 91.2 | 77.6 | 46 | |
| M5 | √ | √ | 90.1 | 93.3 | 78.7 | 50 | |
| MDFNet | √ | √ | √ | 92.4 | 95.6 | 81.6 | 45 |
| Model | Dice (%) | MAP (%) | mIoU (%) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 80.1 | 78.5 | 71.3 | 67 |
| DeepLabv3+ | 82.3 | 82.7 | 75.9 | 52 |
| Attention U-Net | 85.1 | 84.2 | 74.4 | 43 |
| YOLOv11-Seg | 88.6 | 91.2 | 76.1 | 113 |
| Hybrid-Segmentor | 87.6 | 89.5 | 78.4 | 35 |
| MDFNet | 92.4 | 95.6 | 81.6 | 45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Z.; Li, Y.; Fu, H.; Tian, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chin, C.-L.; Ma, C.-K. Research on Concrete Crack and Depression Detection Method Based on Multi-Level Defect Fusion Segmentation Network. Buildings 2025, 15, 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101657
Yao Z, Li Y, Fu H, Tian J, Zhou Y, Chin C-L, Ma C-K. Research on Concrete Crack and Depression Detection Method Based on Multi-Level Defect Fusion Segmentation Network. Buildings. 2025; 15(10):1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101657
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Zhaochen, Yanjuan Li, Hao Fu, Jun Tian, Yang Zhou, Chee-Loong Chin, and Chau-Khun Ma. 2025. "Research on Concrete Crack and Depression Detection Method Based on Multi-Level Defect Fusion Segmentation Network" Buildings 15, no. 10: 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101657
APA StyleYao, Z., Li, Y., Fu, H., Tian, J., Zhou, Y., Chin, C.-L., & Ma, C.-K. (2025). Research on Concrete Crack and Depression Detection Method Based on Multi-Level Defect Fusion Segmentation Network. Buildings, 15(10), 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101657








