Abstract
Road paving costs have significantly increased in the last decades not only because of the increase in oil price globally, which has in turn increased the prices of bitumen, transportation, coarse aggregate and fine aggregate, but also due to the shortage of these virgin materials. Thus, it is essential to find more sustainable and cost-effective road paving solutions. This research focuses on the combination of recycled asphalt pavement (RAP) and crumb rubber extracted from end-life tires and new asphalt mixtures to assess the enhancement of asphalt performance and cost minimization. The optimal percentage of RAP mixed with new asphalt including crumb rubber with achieves the highest performance, stability, and durability of pavement, while considering the economic and environmental impacts was investigated. Experimental investigations, including a universal testing machine and the Marshall stability test, were implemented to evaluate different mixing percentages of RAP and the new asphalt including crumb rubber at different bitumen contents. Abaqus software was utilized to simulate a model with the new mixture to determine the stress and deformation characteristics under different loading conditions. The findings of the experimental study from testing more than 150 samples of asphalt with different percentages of mixing illustrated that a balanced mix of 50% RAP with 50% new rubberized asphalt with a 5% bitumen content achieved the optimal balance of stability, flow and density characteristics, which will offer a promising solution for more sustainable and cost-effective road-paving solutions.
1. Introduction
The concern about road paving has increased significantly in all countries in recent years due to its impact on the transportation of goods and economical aspects. As a result of the increase in oil prices on one hand and the shortage of virgin primary materials on the other hand, the cost of road paving has been increased tremendously. Consequently, it has become urgently necessary to introduce new technologies for the road-paving industry and asphalt manufacturing that not only achieve high-quality paving processes but also minimize the required cost. Recycling of the aged asphalt extracted from old roads and adding rubber as a sustainable material in the asphalt manufacturing process introduced a key solution for the problem of cost reduction. In addition, using the extracted aged asphalt in the process of new asphalt mixture manufacturing confers a positive impact on the environmental aspect by limiting the need for new material resources.
The trend of reusing solid waste materials in the manicuring of new asphalt that is utilized in the highway pavement process has been increasing in popularity in the last three decades of the twentieth century. Not only reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) but also blast furnace slag and waste plastic are employed in new asphalt manufacturing processes [1]. The performance of these recycled materials in the pavement structure and the characteristics of this structure in normal operating conditions have been assessed in many research studies. The impact of adding recycled materials has been examined in order to evaluate their appropriateness with the pavement structure and the ability of this structure to withstand high stress. It has been generally concluded that (RAP) is one of the most appropriate materials that can be used in the pavement manufacturing process. The performance of RAP mixed with asphalt mixtures depends on the quality of reclaimed materials [2,3,4].
Despite the ability to obtain waste tires from old cars, it is difficult to reclaim new tires for manufacturing due to the need to re-vulcanize the rubber process. As a result, it is environmentally recommended to enroll these tires in many industries rather than keeping them in landfills. After implementing the shredding process into old tires, they can be used in various industries such as retaining walls, trail tracks and asphalt manufacturing. Previous studies showed that the usage of crumb rubber powder extracted from waste solid tires enhances the properties of asphalt mixtures, such as durability, the ability to withstand various weather conditions and resistance to heat cracking and rutting. Moreover, it has been determined that the usage of recycled asphalt in the pavement process by adding crumb rubber powder provides an acceptable mixture structure and reduces required costs of the manufacturing process [5,6,7,8]. Other researchers concluded that adding crumb rubber to asphalt mixture increases its stability but reduces its flow. Furthermore, it has been illustrated that using rubber can help asphalt mixtures resist permanent deformation [9,10]. However, other studies stated that adding recycled asphalt to warm mix asphalt raises the resistance to rutting and moisture damage compared with warm mix asphalt mixtures without recycled asphalt [11,12]. Figure 1 illustrates the different stages of the recycled rubberized asphalt manufacturing process that starts with the extraction of old used asphalt from aged roads and shredding of old tires to obtain rubberized powder and ends with the pavement of new roads with cost reductions.
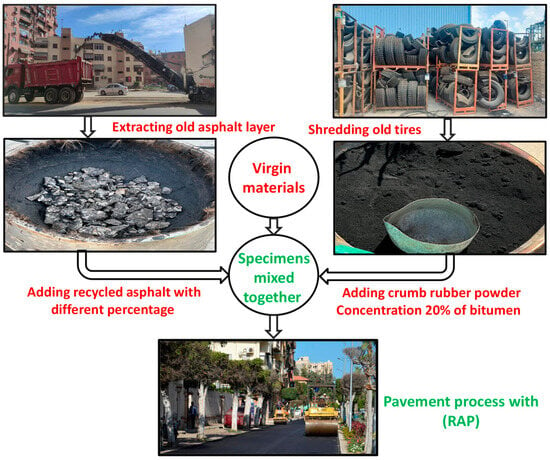
Figure 1.
Pavement of new roads using RAP and rubber powder.
Crumb rubber can be mixed with asphalt in two different processes. Firstly, dry process in which crumb rubber is added to aggregate before mixing with asphalt. Secondly, the wet process on which crumb rubber is mixed with asphalt at high temperature [13,14]. Adding rubber powder to warm asphalt mixture leads to a reduction of the required bitumen in the whole asphalt production process and consequently reduction in the overall cost. According to previous research, the best percentage concentration of rubber powder to the amount of required bitumen is 20%. The cost of crumb rubber is about 30% of the cost of bitumen; as a result, adding crumb rubber obtained from end life tires to bitumen can be considered a sustainable solution [15,16,17]. This solution introduces durable and flexible material with high resistance to wear, and weather conditions, improving asphalt stability, and reducing the deformation and maintenance cost [18,19,20].
Despite the previous research that studied the impact of adding recycled asphalt to rubberized asphalt mixture, the optimal percentage of the recycled asphalt has not been clarified intensively. As a result, the current research has investigated the effect of adding recycled asphalt with different concentration to hot mix asphalt. Moreover, the impact of adding recycled asphalt on the properties of the manufactured new asphalt has been also assessed. Different specimens of new manufactured asphalt contain different concentrations of the RAP have been examined with the using of Marshall test to analyze their ability to withstand high stress, density, and flow. Generally, the main aim of this research is to identify the optimal percentage of adding RAP extracted from old roads with new hot mix asphalt with crumb rubber. This proposed technique is a step forward minimizing the cost of paving roads in order to suit the economic situation of countries.
To evaluate the actual displacement and exact vertical stress distribution of the produced specimen that contains the optimal percentage of mixed RAP rubberized asphalt, detailed analytical analysis has been accomplished. Abaqus software has been utilized to compare two specimens. The first one contains only a new asphalt mixture; however, the second one contains new rubberized asphalt with RAP percentage. The stress strain curves of these two specimens have been obtained with the use of universal testing machine. In favor of these curves, the modulus of elasticity of the two specimens has been obtained in order to be used in Abaqus software as a way to identify the materials.
2. Methodology
This research depends on mixing the RAP and rubber with new asphalt mixture. This mixing process has been implemented with nine different percentages of RAP varies from 10% to 90% of the whole weight of the specimen. Table 1 introduces the different concentration of RAP and new asphalt (N) in each specimen. Each specimen introduced in Table 1 has been manufactured with four different bitumen percentages (4.5%, 5%, 5.5%, and 6%) from the complete weight of the specimen. The manufacturing process of tested specimens which contain RAP and rubber powder is summarized in Figure 2. It is worthy to obtain the optimal level of not only bitumen material but also RAP component. Thus, every specimen has been produced five times

Table 1.
Percentages of mixing Recycled and New asphalt.
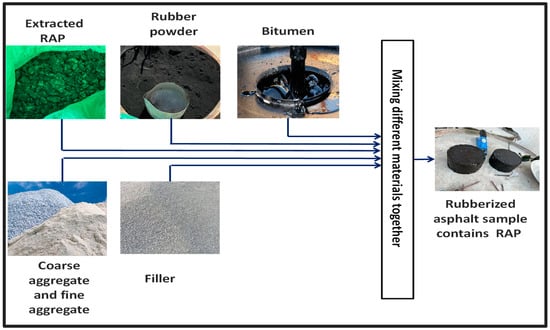
Figure 2.
Tested specimen preparation process.
Firstly, Bitumen extraction has been obtained for RAP to know the percentage of bitumen in it. Secondly, the sieve analysis test has been applied for RAP to determine the gradation to measure it compliance with mixture design and the results have been shown in Figure 3.
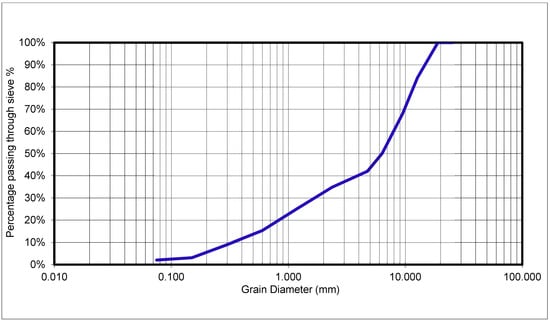
Figure 3.
Results of sieve analysis test on RAP only.
Bitumen was added to the RAP by adding the remaining percentage of bitumen to the existing percentage in RAP that has been measured from extraction test and divided into 20% of its rubber and 80% of its hot bitumen at a temperature of 180 °C. The characteristics of the bitumen used are shown in Table 2. After that, the components of the manufactured asphalt mixture were added, taking into consideration that the percentage of bitumen would also be 20% rubber and 80% hot bitumen at a temperature of 180 °C all components were mixed and then the cylindrical sample has been compacted 75 times on each side in Marshall mold with a dimension of 63.5 mm in height and 101.6 mm in diameter [21,22]. and the samples were made at the different percentages of mixing that were shown in Table 1.

Table 2.
Properties of the used bitumen in mixing according to Egyptian specifications.
3. Experimental Tests
- Marshall Test
This test is a standard method used in the design of mixture and calculating not only the stability but also the flow values and density of asphalt mixtures. The test gives the maximum load that the sample can withstand which is defined as Marshall stability, which is an indicator of the strength of the mixture. Before starting the test, all prepared samples have been weighed then immersed in a water bath at 60 °C ± 1 °C for 35 min ± 5 min as shown in Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 respectively as it’s recommended in previous literature [23]. The mechanism of the test is to subject asphalt samples to compressive load through Marshall loading machine till the failure of the asphalt sample as illustrated in Figure 7 [20,24]. The deformation happens to the sample during this test known as the flow of the mixture. These two parameters are vital to ensure that the pavement will perform suitably under high traffic loads. Marshall test is the most used test because of its simplicity, cost effectiveness, and reliability in giving the essential data for asphalt mixture design.

Figure 4.
Samples with different mix percentages.

Figure 5.
Weighting the samples before testing.

Figure 6.
Samples in the water bath before testing.

Figure 7.
Testing the samples with Marshal testing machine.
4. Experimental Results
Figure 8 represents the relationship between the bitumen content percentage on the (x-axis) and Stability on the (y-axis) for the combination of new asphalt mixture (N) with different percentages of adding RAP (R) with the addition of crumb rubber. Each line represents a different percentage of mixing RAP with rubberized asphalt mixture. Many remarkable results can be concluded from Figure 8. First, it is obvious that the increase of bitumen content leads to decrease in stability, the mixture with high percentage of RAP gives higher stability. However, this graph shows the balance between the percentage of RAP mixed with rubberized asphalt has a significant impact and gives high stability. The diagram shows that the mixing percentage between the rubberized mixture between RAP and new asphalt strongly influences the mixture stability as the bitumen content is adjusted. The mixture containing a higher percentage of RAP gives greater stability but also shows a decrease as bitumen content increases. Conversely, mixtures with a higher percentage of new asphalt in the mixture generally maintain more consistent, lower stability across different bitumen content. This shows the importance of carefully considering both mixing ratio for RAP with new asphalt mixture and bitumen content with the addition of crumb rubber to get the optimum stability, especially when balancing cost with performance.
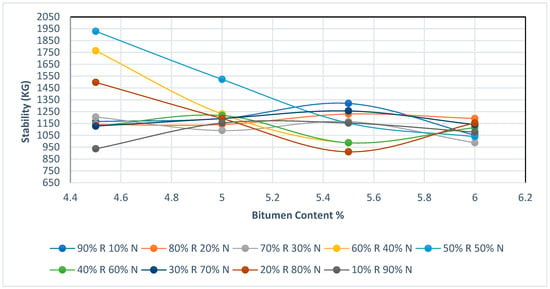
Figure 8.
Stability diagram.
Figure 9 represents the relationship between bitumen content on the (x-axis) and the flow on the (y-axis) for the combination of new asphalt mixture (N) with different percentages of adding RAP (R) with the addition of crumb rubber. Each line represents a different percentage of mixing RAP with new asphalt mixture.
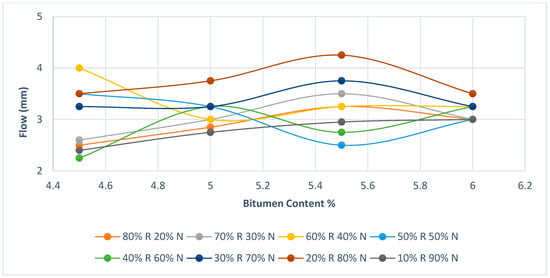
Figure 9.
Flow diagram.
- Mixtures with higher percentages of RAP mixed with rubberized asphalt mixture containing rubber (90%R 10%N and 80%R 20%N) show steady flow rates at different bitumen contents. This indicates they are quite stable.
- Mixtures with balanced mix of RAP mixed with new asphalt mixture containing rubber (50%R 50%N and 40%R 60%N) show that the optimal bitumen content is about 5.2%. They perform best at this point, but generally they are stable across the board.
- samples with low percentage of RAP (30%R 70%N, 20%R 80%N and 10%R 90%N) shows ascending manner of flow with the increase of bitumen content till the optimal point of bitumen content found which is around 5% to 5.5% then the flow shows descending manner with the increase of bitumen content than the optimal point. Consequently, it can be concluded that the mixtures with lower percentages of recycled asphalt mixed with rubberized asphalt are more sensitive to changes in bitumen content.
Figure 10 represents the relationship between bitumen content on the (x-axis) and Marshal density on the (y-axis) for the combination of new asphalt mixture (N) with different percentages of adding RAP (R) with the addition of crumb rubber. Each line represents a different percentage of mixed RAP with rubberized asphalt mixture. Marshall density graph shows that the balanced mix of recycled asphalt mixed with new asphalt mixture (50% R 50% N) gives the highest density at about 5% bitumen content. So, the blanched mix can give the best density which will be important and crucial to enhancing the road’s performance and durability. Figure 10 illustrates that the density of most of the mixtures increases slightly for around 5% bitumen content then decreases. Thus, it can be concluded that it is the optimal bitumen content to maximize the density. The percentages of mixing that gives flat lines in the graph, especially the mixtures that have high percentages of new rubberized asphalt mixtures have a more stable density despite changing in bitumen content. Generally, it is obvious that the increase of new asphalt percentage improves the density and will be more stable. And the mixtures with higher percentages of recycled asphalt go up and down in density which means that the changing in bitumen content is more sensitive for those mixtures so, higher density can be achieved with high percentage of recycled asphalt in the mixture. However, it is needed to control the bitumen content.
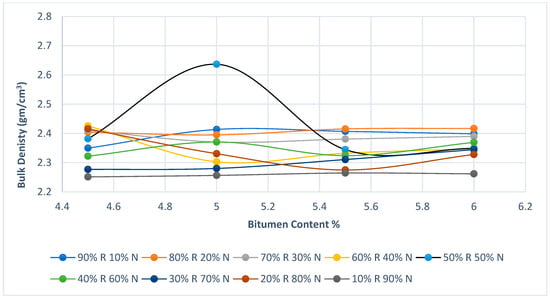
Figure 10.
Marshall Density diagram.
5. Analytical Analysis
Universal testing machine has been used to evaluate the mechanical properties of materials [25]. With the use of this machine, the stress-strain curve of any material can be obtained and the ability of this material to withstand high mechanical stress can be assessed. In this research universal machine test has been used to obtain stress-strain curve for two samples of the asphalt mixture by compression as shown in Figure 11.

Figure 11.
Universal Machine Test.
The first sample mixture with rubber and RAP was a combination between 50% new asphalt and 50% recycled asphalt with 5% bitumen content divided into 20% rubber and 80% bitumen, The stress strain curve became as shown in Figure 12. Modulus of elasticity has been calculated by Equation (1).
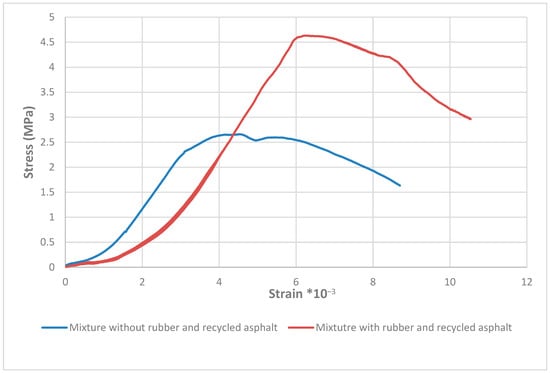
Figure 12.
Stress strain curve resulted from universal machine test for the samples.
From Figure 12 the modulus of elasticity of the first sample of asphalt equals 667 MPa.
where:
E = (σ)/(ε)
- E: represents modulus of elasticity (measured in Mega Pascals)
- σ: represents stress (Force per unit area, in Mega Pascals)
- ε: represents strain (dimensionless, as it is a ratio)
The second sample mixture without rubber and RAP was a new asphalt mixture with 5% bitumen percentage without any additions and from the stress strain curve became as shown in Figure 12:
The modulus of elasticity of the second sample of asphalt equals 750 MPa.
All these results have been used to make a simulation with Abaqus software to get the actual deformation and actual stress distribution on the two samples of asphalt. As it’s clear in Figure 13 a model has been designed with a subgrade of 50 cm and granular base layer of 30 cm and asphalt layer of 10 cm by entering the modulus of elasticity of each layer and enter the stress and strain values of asphalt layer which resulted from the universal test and applying a moving load of 8 tons in simulation.
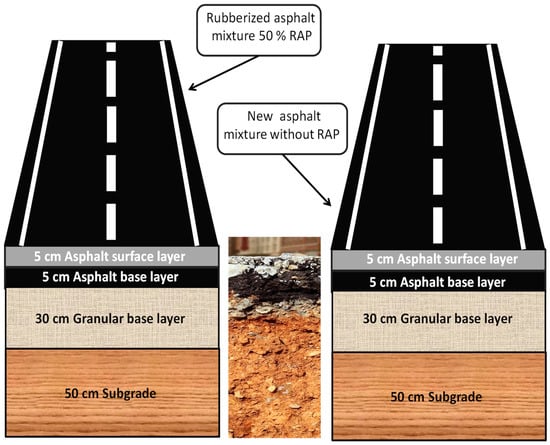
Figure 13.
Showing the model that has been simulated by Abaqus software.
Abaqus Software ©
Abaqus © is commonly used by researchers to simulate the performance of materials under different conditions such as stress levels and temperature fluctuations. The software Abaqus is adept at managing simulations across an array of sectors including biomedical and civil engineering fields. The precision of results generated by Abaqus aids in the design and testing of materials prior to deployment saving resources and time in the process. Abaqus provides a friendly user interface. Seamlessly integrates with various engineering tools making it a popular option for detailed simulations. Figure 14 represents the moving load of 8 tons on the models in simulation.
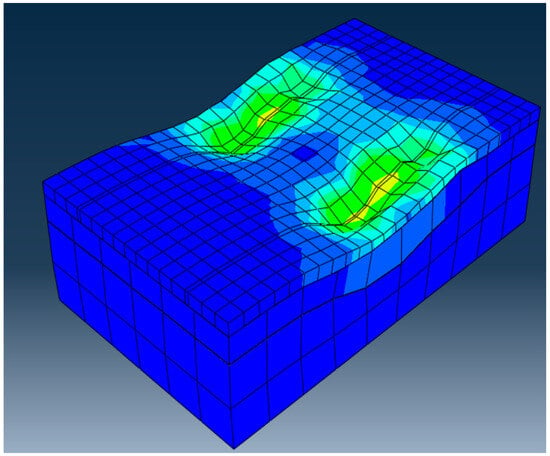
Figure 14.
Software output of simulation.
The results of simulation extracted from Abaqus software are shown in the graphs of the following figures:
Figure 15 compares the displacement that happened along path with applying an axial load of 8 tons for simulation for the two different asphalt samples. The first contains RAP with 50% and rubber with new asphalt with 50% percentage of the sample weight. However, the second sample contains only asphalt without any additions and both with bitumen content of 5%. From Figure 15 the first sample with recycled asphalt and rubber showing less displacement along the path than the sample of asphalt only which indicates that the use of rubber and recycled asphalt will reduce the overall displacement along the sections of the path which may help in reducing the deformation and enhance the load bearing capacity of the road which indicates better performance of the pavement.
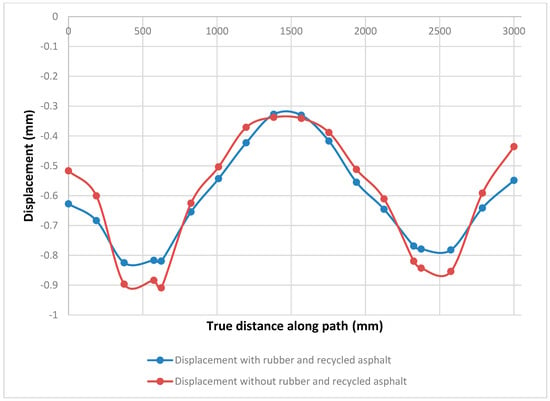
Figure 15.
Displacement graph from Abaqus.
Figure 16 compares stress distribution with depth (z) equals 10 cm along path with applying load of 8 ton for simulation for the two different asphalt samples. As shown from Figure 16 the mixture without rubber and RAP shows higher stress values than the second mixture which contains rubber and recycled asphalt which resulting that the use of RAP and rubber in the mixture enhances the performance of pavement by reducing the stress level which increases the lifespan of road and decreases the probability of the pavement failure under load repeating.
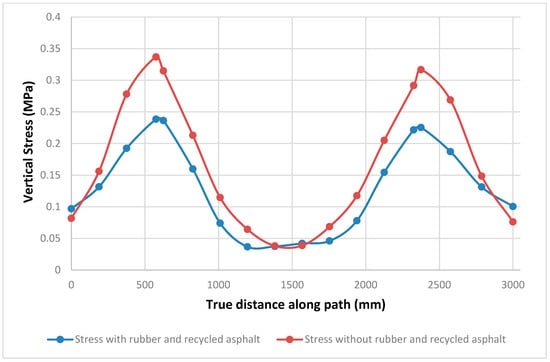
Figure 16.
Stress graph from Abaqus.
6. Conclusions
In this research it has been successfully proven the advantages of mixing the crumb rubber and RAP with the new asphalt mixtures. This combination of these materials totally enhanced the mechanical properties of the asphalt mixtures, helped in increasing stability and lower stress levels under loads and reduced the deformation. After a series of laboratory tests such as universal machine test and Marshall stability test and after testing more than 150 samples of asphalt with different percentages of mixing, it has been shown that the balanced mix of 50% RAP and 50% New asphalt mixture with 5% bitumen content including crumb rubber with 20% of the weight of bitumen offered the optimal performance. Simulation using Abaqus software also confirmed these results, showing that the modified mixture achieved high displacement and stress resistance. Both results were extracted from simulation using Abaqus software and field experiments approved that using crumb rubber and RAP can lead to constructing more sustainable and cost-effective roads. All these results and findings will make a very well foundation for future research in enhancing asphalt mixtures for different environmental and economic conditions. As s step forward to the future plan of this research, this mixture has already been utilized in three different cities that represent different climatic conditions: Desert climate, coastal climate and humid climate. The impact of these different climatic conditions will be assessed periodically in order to evaluate the performance of this mixture and compare the results of this future work with the results obtained in this research.
Author Contributions
Supervision, E.M.O.E. and T.M.M.; Project administration, A.T.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author due to privacy restrictions.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to introduce their deep thanks to the Arab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime transport, Egypt (AAST) for supporting this research and for using all the laboratories.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gkyrtis, K.; Pomoni, M. An overview of the recyclability of alternative materials for building surface courses at pavement structures. Buildings 2024, 14, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Highway Administration, U.S. Department of Transportation. Asphalt Pavement Recycling with Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP); Federal Highway Administration, U.S. Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Chen, S.; Ge, D.; Jin, D.; Zhou, X.; Liu, C.; Lv, S.; You, Z. Investigation of hot mixture asphalt with high ground tire rubber content. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 124037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocci, E.; Prosperi, E. Recyclability of reclaimed asphalt rubber pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 403, 133040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, S.; Al-Mosawe, H.; Mohammed, H. The influence of using recycled asphalt pavement and crumbed rubber on asphalt pavement: A review. Al-Nahrain J. Eng. Sci. 2023, 26, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Laboratory investigation of utilizing high percentage of RAP in rubberized asphalt mixture. Mater. Struct. 2010, 43, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfayez, S.A.; Suleiman, A.R.; Nehdi, M.L. Recycling tire rubber in asphalt pavements: State of the art. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghapour, M.; Babagoli, R. Effect of reclaimed asphalt pavement on performance of rubberised asphalt mixtures. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Constr. Mater. 2020, 173, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadim, H.M.; Al-Mosawe, H.M. Crumb rubber modification for enhanced rutting resistance in asphalt mixtures. Open Eng. 2024, 14, 20220500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabani, M.; Tahami, S.A.; Taghipoor, M. Laboratory investigation of hot mix asphalt containing waste materials. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 713–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, A.A.; Haghshenas, H.F.; Underwood, B.S.; Harvey, J.; Blankenship, P. Performance of warm asphalt mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement, an anti-stripping agent, and recycling agents: A study using a balanced mix design approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 363, 129633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, Z.; Hung, S.; Jones, D.; Harvey, J. Preliminary Investigation into the Use of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement in Gap-Graded Asphalt Rubber Mixes, and Use of Reclaimed Asphalt Rubber Pavement in Conventional Asphalt Concrete Mixes; Research Report: UCPRC-RR-2016-03; California Department of Resources, Recycling and Recovery: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2016.
- Butz, T.; Muller, J.; Riebesehl, G. Innovative method for producing crumbed rubber modified asphalt. In Proceedings of the 5th Eurasphalt & Eurobitume Congress, Istanbul, Turkey, 13–15 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, L.; Benta, A.; Picado-Santos, L. Asphalt rubber concrete fabricated by the dry process: Laboratory assessment of resistance against reflection cracking. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 160, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Song, L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y. Research progress and performance evaluation of crumb-rubber-modified asphalts and their mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 361, 129687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, M.; Azami, A. Evaluation of warm mix asphalt mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement and crumb rubber. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Segre, N.; Joekes, I. Use of tire rubber particles as addition to cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirkhanian, S.N. Utilization of crumb rubber in asphaltic concrete mixtures–South Carolina’s Experience. In Recycling and Reuse of Used Tires, Proceedings of the International Symposium Organized by the Concrete Technology Unit, Dundee, UK, 19–20 March 2001; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Gao, J.; Pei, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, R. Research on highly dissolved rubber asphalt prepared using a composite waste engine oil addition and microwave desulfurization method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 282, 122641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.H.; Zahran, E.M.; Tan, S.J. The optimal use of crumb rubber in hot-mix asphalt by dry process: A laboratory investigation using Marshall mix design. Transp. Eng. 2022, 10, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, A.; Iskender, E.; Kahraman, H.T. Application of the intuitivek-NN Estimator for prediction of the Marshall Test (ASTMD1559) results for asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 34, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroles, L.; Tumpu, M.; Rangan, P.R.; Mansyur, N. Marshall properties of LASBUTAG asphalt mixes with pertalite as a modifier. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 871, 012064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.P.; Bui, M.P.; Nguyen, Q.P.; Vo, H.L.; Du Nguyen, V. Marshall and Balanced mix design in determining the asphalt content for hot mix asphalt mixture: A comparative study. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetia Djakfar, L.; Wisnumurti, N.; Sabarudin, A. Marshall tests for asphalt concrete wearing course ASB Lawele containing capsule calsium alginate as Self-Healing Additive. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1117, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huňady, R.; Sivák, P.; Delyová, I.; Bocko, J.; Vavro, J.; Hroncová, D. Upgrade of the universal testing machine for the possibilities of fatigue tests in a limited mode. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).