1. Introduction
Why most people have a negative and inhuman image of healthcare settings? For a long time, the focus on medical technology has leaved little room for the importance of the healthcare physical environment, often characterized by deep pains and frailties of its users. However, over the past few decades, the role of architectural, spatial, and social features related to the specific needs of the users has been increasingly underlined in the healthcare domain [
1], in the light of quality-of-life concerns. In fact, the healthcare environment can both affect people’s health and convey positive information for self-esteem, security, and identity [
2], especially for those patients who are more exposed to stress, pain, dependence, helplessness, and anxiety conditions. When addressing the issue of environmental quality related to (mainly) built environments like the healthcare facilities, a reference construct is the Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ), which encompasses all aspects of the building’s environment concerning the health and wellbeing of its users, such as indoor air quality, acoustics, thermal comfort, lighting, ergonomics [
3]. The relevance of these factors in eliciting individuals’ positive responses has been demonstrated in different contexts, such as: residential [
4], educational [
5], organizational [
6], and healthcare [
7] places. For all these cases, the need to design buildings that take into account the users’ comfort and wellbeing was highlighted.
Focusing on research literature about the impact of the healthcare environment, there is evidence on the impact of features such as aesthetics, lighting, and green spaces on patients’ outcomes in terms of overall satisfaction or well-being [
8,
9,
10]. In particular, others have note the importance to take into account features such as: shape of spaces; artificial and natural light; temperature; colors and materials characterizing the building and the furnishings; acoustic environment; and green spaces [
11,
12]. Furthermore, it is important to consider that the healthcare place includes different sub-places that are interrelated and interdependent [
13,
14], in the light of the connections that their users establish with them through their place-specific activities [
15].
Following a “user-centered” design perspective [
16], the different sub-places of the healthcare setting should increase their environmental quality, in order to be perceived as “more humane” [
17] by the different place users, i.e.,: (1) fragile people who are receiving palliative treatments; (2) their relatives, who are living a painful and stressful experience [
18]; and (3) burn-out exposed staff, which could thus better support patients themselves. In this regard, the construct of “spatial-physical humanization” has often been used in research literature on healthcare places, e.g., [
19,
20]. It refers to the satisfaction of users’ psychological needs, such as spatial and sensorial comfort, orientation, sense of welcome, and privacy. In this perspective, the focus is put on the quality of those design attributes that should be provided in order to satisfy the fundamental needs of the users [
21], assuming that such factors influence how the healthcare place is experienced by its occupants [
14]. Thus, we can underline that the construct of spatial-physical humanization, which specifically refers to healthcare settings, substantially overlaps with the more general IEQ concept.
In literature, design guidelines have been proposed on the basis of the review of the empirical evidence, e.g., [
11,
12,
22,
23]. These recommendations include features of the healthcare physical environment that should satisfy users’ needs, such as presence of private rooms; colors and materials of furniture, walls, and floors; access to natural light; noise reduction; orientation; adequacy of temperature and humidity. For instance, a greater presence of natural light should improve health outcomes, since poor lighting also contributes to medication mistakes [
24]. Regarding the effect of noise, it was found as an important source of stress for both patients and staff. Consistently, the reduction of noise improves overall satisfaction and sleep quality both in patients and staff, and it lowers patients’ blood pressure [
25].
Users’ assessment of the healthcare environment features has been quantified through the development of a psychometric tool for measuring the Perceived Hospital Environment Quality Indicators (PHEQIs, [
19,
26,
27]). PHEQIs take into account the dimensions of the spatial-physical humanization, including a broad array of aspects concerning comfort, either directly (e.g., furnishings, colors, temperature, and materials) or indirectly (e.g., green spaces, lighting, orientation, and quietness), in the assessment of the main healthcare environment’s categories of users, i.e., patients, visitors/companions, and staff. In order to verify the methodological soundness of this tool, a study was carried out with patients, visitors/companions, and staff in orthopedic units of three Italian hospitals. Results indicated a different level of design quality (low vs. medium vs. high) according to the rating of design experts [
19]. The use of principal component analysis, an exploratory factorial analysis technique, allowed the following PHEQIs for the different sub-places of the hospital environment to emerge: Upkeep & care, Orientation, Building aesthetics, and Green spaces for the external hospital spaces; Spatial-physical comfort, Orientation, and Quietness for the hospital care unit; and Spatial-physical comfort (again), and Views & Lighting for specific places of the hospital care unit, i.e., inpatient and outpatient areas. These PHEQIs were substantially confirmed in subsequent studies carried out with a similar procedure in other Italian hospital units (e.g., general surgery units in [
28]); and in hospital units from a different linguistic and socio-cultural context. In fact, in such a case, participants were patients and visitors/companions in orthopedic units of four Portuguese hospitals, again varying for the level of design quality as rated by design experts [
26,
27]. Given the confirmation goal of this study, a confirmatory factor analysis was run, and reliability and validity tests were also performed.
In spite of the growing attention on the impact that physical environment may have on health outcomes, there is a substantial lack of such systematic tools for a specific kind of healthcare environment, represented by the hospice, which is a specific category of healthcare place aimed to improve the life quality of people who are in the last phases of an incurable disease. Hospices work to manage symptoms so that patients may spend their time with dignity and quality, surrounded by their relatives [
29]. In a standard hospice, each patient is accommodated in a single room, equipped with a private bathroom and an additional bed for the permanence of family members who assist the person. Usually, rooms are fitted out with refrigerator, television, and armchairs. As concerns the external areas, the building is often surrounded by a garden, whereas inside it is made up of common areas for socialization and leisure (kitchen, living room, reading areas), specific zones dedicated to assistance (nurses’ and doctors’ offices), and patients’ rooms.
The focus of this study is on the proposal of an adapted tool for measuring hospice’s PHEQIS and on the relationship between the perception of distinct aspects of the hospice environment and the overall users’ satisfaction, bearing in mind the specific characteristics, in terms of the kind of patients and daily routine practices, which distinguish this place from other healthcare facilities.
3. Method
3.1. Places and Participants
The research involved eleven hospices located in different geographical areas of Italy (i.e., Milan, Brescia, Monza, Garbagnate Milanese and Bologna in the North; Ancona and Rome in the Centre; Bitonto in the South; Cagliari and Nuoro in the Isle of Sardinia, and Palermo in the Isle of Sicily).
The study participants (N = 135; 55% females; age range: 21–95 years; M = 55.7; SD = 14.7) were sampled from the two main categories of hospice users (i.e., patients and their relatives/companions) and were contacted in both inpatient and outpatient areas. The recruitment of participants was effected only after receiving the written approval of the hospice managers for carrying out the survey with patients, relatives, and staff (also ensuring the anonymity of the hospice). Participants were requested to provide their informed consent before taking part in the survey. A few hospice caregivers were also recruited as participants. Specifically, 30.4% were patients, 62.2% relatives/companions, and 7.4% staff.
As for the educational level, 35.8% of the participants earned a high school diploma, 27.6% had obtained an academic degree, 24.4% had a junior school certificate, and 12.2% attended primary school.
3.2. Tools and Procedure
In order to catch the specificity of the hospice environment, a self-report questionnaire, including an adapted version of the PHEQIs [
19,
28], i.e., the Hospice PHEQIs tool, was developed.
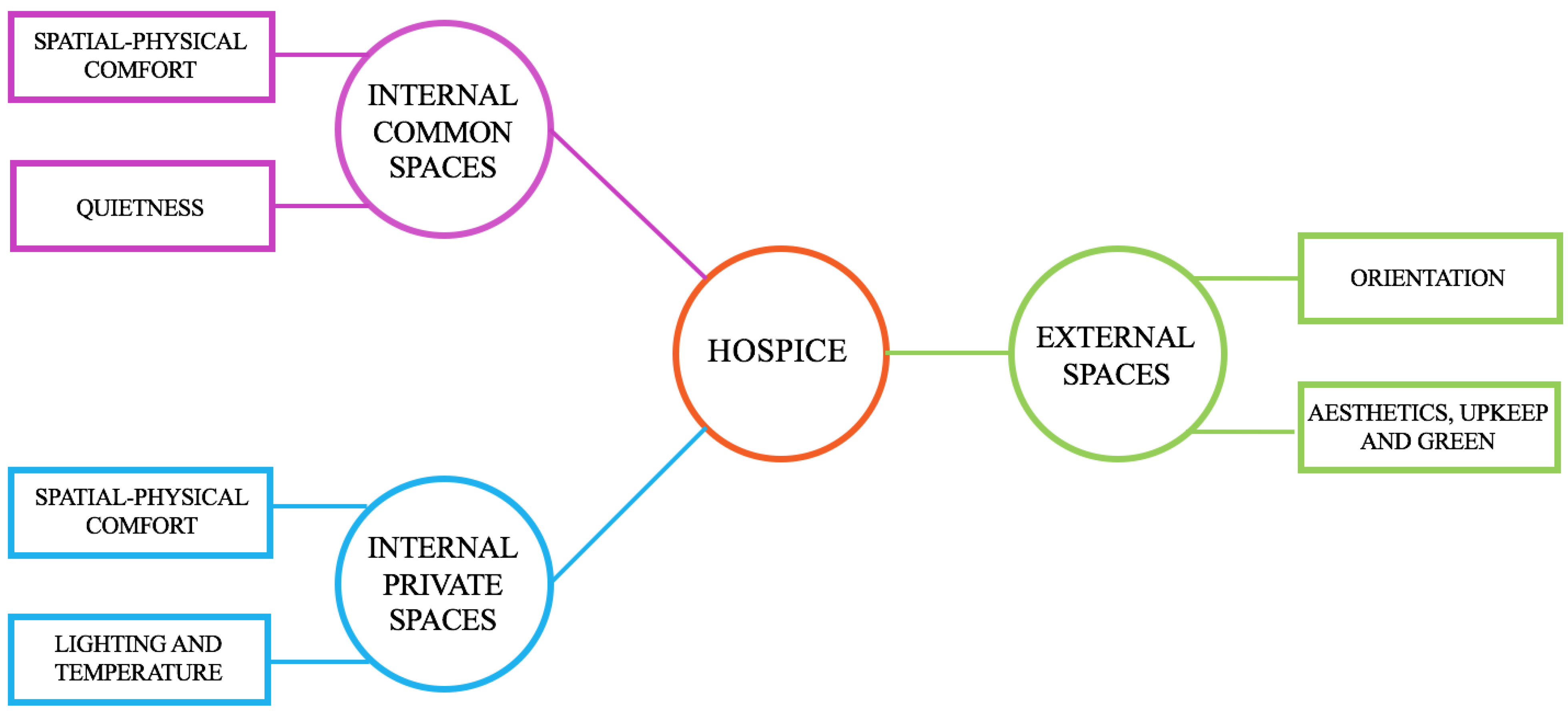
The questionnaire was structured in three sections (i.e., three scales) including items about the spatial-physical aspects of different sub-places of the hospices, that is external spaces, interior common spaces, and private spaces, i.e., patients’ rooms. A fourth section of the questionnaire included a measure of overall satisfaction towards the hospice and socio-demographic indexes.
Specifically, Hospice PHEQIs (see
Supplementary Table S1) consisted of an initial pool of 73 items including the following scales and measures:
Scale of External spaces, including 16 items on the quality of aesthetics, upkeep, green, and orientation of external spaces of the hospice;
Scale of Interior Common spaces, including 36 items on the spatial-physical comfort and the quietness of the internal common environment;
Scale of Interior Private spaces, including 21 items on the lighting, temperature, and spatial-physical comfort of the patient’s room.
Participants were asked to rate all the items on a 5-point Likert-type response scale (from “totally disagree” to “totally agree”).
The questionnaire also included an item on overall satisfaction towards the hospice environment, i.e., “Overall, how satisfied are you with this hospice?”, measured through a 5-point Likert-type response scale (from “not at all” to “completely”).
Main socio-demographic variables (i.e., gender, age, education level, role position within the hospice) were also detected.
The recruitment of participants and the delivery and collection of questionnaires were conducted by the hospices’ managers and staff.
Using the software
R (version
RStudio 0.98.1091), a Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) was performed on each Hospice PHEQIs scale for testing H1. Five indices were used in order to assess the models’ goodness of fit: the ratio between
χ2 and degrees of freedom, indicating a good fit if it is between 1 and 3 [
30], and the indices suggested by Hu and Bentler [
31], i.e., the root mean square error of approximation (
RMSEA), the standardized root mean square residual (
SRMR), the non-normed fit index (
NNFI), and the comparative fit index (
CFI). For each scale, a step-by-step iterative procedure was followed, starting from an initial solution including all the items supposed to load on each Hospice PHEQIs on the basis of the items content. In other words, we initially tested the CFAs by considering all the items inserted in the questionnaire, then we excluded those ones which lowered the model fit. Thus, the final Hospice PHEQIs included only the items which maximized the goodness of the solution. For each emerged Hospice PHEQI, the internal consistency, i.e., a measure of reliability, was then computed through the Cronbach’s
Alpha, in order to verify H2.
Finally, bivariate correlations were run between each Hospice PHEQI and Overall Satisfaction for verifying H3.
4. Results
The CFA performed for each Hospice PHEQIs scale produced, as expected (H1), two indicators of perceived quality for the external spaces, two indicators of perceived quality for the interior common spaces, and two indicators of perceived quality for the interior private spaces (i.e., the patients’ rooms).
4.1. External Spaces
The final model presents the following fit indices:
χ2 = 20.23;
df = 19;
χ2/
df = 1.065;
RMSEA = 0.023;
SRMR = 0.042;
NNFI = 0.99;
CFI = 0.99. The model includes two correlated factors (see
Figure 2). The first factor (F1), “Aesthetics, Upkeep and Green”, includes 5 items (all negative) regarding both the pleasantness and the appearance of the buildings seen from the outside and the presence of cared green spaces in the external area (
α = 0.81). The second factor (F2), “Orientation”, consists of three items (two negative and one positive) concerning wayfinding, the possibility to easily find the services, and the clearness of the signage in the external area (
α = 0.66).
Correlation between F1 and F2 is r = 0.60 (p < 0.001).
4.2. Interior Common Spaces
The final model shows the following fit indices:
χ2 = 25.97;
df = 19;
χ2/
df = 1.367;
RMSEA = 0.054;
SRMR = 0.071;
NNFI = 0.93;
CFI = 0.95. The model includes two correlated factors (see
Figure 3). The first factor (F1), “Spatial-physical comfort”, contains five items (all positive) referring to temperature, lighting, and pleasantness of furniture (
α = 0.67). The second factor (F2), “Quietness”, includes three items (two negative and one positive) concerning the presence/absence of annoying rumors coming from this area (
α = 0.75).
Correlation between F1 and F2 is r = 0.27 (p < 0.001).
4.3. Interior Private Spaces
The final model produces the following fit indices:
χ2 = 20.23;
df = 19;
χ2/
df = 1.065;
RMSEA = 0.023;
SRMR = 0.050;
NNFI = 0.98;
CFI = 0.99. The model includes two correlated factors (see
Figure 4).
The first factor (F1), “Spatial-physical comfort”, contains four items (all negative) referring to the pleasantness of and care for surfaces (i.e., floors, walls, ceilings) and furniture (α = 0.84).
The second factor (F2), “Lighting and Temperature”, includes four items (all negative) concerning the temperature and presence/absence of natural lighting (α = 0.70).
Correlation between F1 and F2 is r = 0.57 (p < 0.001).
As concerns H2, the internal consistency of the indicators is globally acceptable (Cronbach’s Alphas ranging from 0.84 to 0.66), since only two of the six indicators fall slightly below the 0.70 threshold.
Table 1 reports a synthetic picture, including, for each Hospice PHEQI, the scale of reference (i.e., the conceptual domain), the number of items, and the internal consistency.
As regards H3, the analysis of the bivariate correlations between the overall users’ satisfaction towards the hospice and each Hospice PHEQI shows significant results as expected (see
Table 2), with only two exceptions (i.e., Spatial-physical comfort in the interior common spaces—which is anyway close to significance—and Lighting and Temperature in the interior private spaces). Thus, almost all perceived quality indicators are related to the overall satisfaction pattern, with particular reference, on the basis of the magnitude of their bivariate correlation, to the orientation in the external spaces (
r = 0.38,
p < 0.01), quietness for the interior common spaces (
r = 0.37,
p < 0.01), aesthetics, upkeep and green for the external spaces (
r = 0.19,
p < 0.05), and the spatial-physical comfort for the interior private spaces (
r = 0.18,
p < 0.05). In other words, high scores of overall satisfaction toward the hospice are related to high scores of perceived quality of these indicators. Furthermore,
Table 2 shows that significant bivariate relationships of medium-high size emerged between all of the indicators.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
This study aimed to verify the factorial structure and the reliability of an adapted version of the PHEQIs for the hospice environment, and the relationships among such indicators and the overall users’ satisfaction toward the hospice.
The extraction of good-fit models substantially let emerge factors that recall, in their content, those already found in previous studies carried out in hospital settings [
19,
26,
27], in line with H1. Such factors, showing a number of items ranging from 3 to 5, include the main aspects of the humanization construct for different sub-places of the hospice setting, consistently with the multi-place conception of places [
32] adapted to the healthcare environments [
13,
14]. In particular, for the external spaces, the outcome of a distinct PHEQI concerning orientation is confirmed, whilst aesthetics, upkeep, and green spaces emerged as combined in a unique PHEQI (whereas they were distinct in previous studies). As regards the interior spaces, the ones considered for the hospice setting (i.e., interior common spaces and interior private spaces) are different from the ones investigated for hospitals (i.e., overall care unit, inpatient, and outpatient areas). Thus, a strict direct comparison is not possible. Nevertheless, in both the hospice interior sub-places, a general indicator of spatial-physical comfort emerged, consistent with what was found in the hospital interior’s sub-places. Moreover, the indicators of quietness and lighting confirm the ones found in the hospital interior spaces. Thus, these indicators concerning the hospice interior spaces are substantially consistent with the design aspects included in the IEQ dimension [
3].
A good or at least acceptable internal consistency, and thus reliability, was found for the Hospice PHEQIs, in line with H2. In fact, Cronbach’s Alpha value was quite good, i.e., above 0.80, in two cases (i.e., for “Aesthetics, Upkeep and Green” of external spaces and “Spatial-Physical Comfort of Interior Private spaces”); quite acceptable, i.e., above 0.70, in two other cases (i.e., for “Quietness” of interior common spaces and “Lighting and Temperature” of interior private spaces); and, finally, barely acceptable, i.e., just a little below 0.70, in the last two cases (i.e., for “Orientation” of external spaces and “Spatial-Physical Comfort” of interior private spaces).
Finally, coherently with H3, users’ satisfaction toward the hospice was found to be related to the perceived quality of design features such as orientation in the external spaces; quietness in the interior common spaces; aesthetic, upkeep and green in the external spaces; and spatial-physical comfort in the interior private spaces. This is in line with previous research that highlighted the influence of design features on the wellbeing of the healthcare place users (e.g., see the reviews by Rashid & Zimring [
12], and Fornara & Andrade [
14]) and, more specifically, the positive effect on hospital users’ satisfaction of perceived spatial-physical comfort [
33], also together with orientation, quietness, and views & lighting [
27]. In fact, the satisfaction toward the hospice environment appeared, in the present study, as closely linked to the comfort related both to the perceived quality of furnishings, walls, and ceilings, and to the presence of windows and their ability to accommodate natural light in the private zones. The attribution of quietness in the common spaces and the opportunity of an easy orientation in the external zone are a further confirmation of the key role of these dimensions for eliciting users’ positive responses. Thus, the design of hospice buildings should pay specific attention to the fulfillment of places which for a certain period of time become the (last) home of patients, with their families who share the spaces and daily uses [
1].
Furthermore, the hospice environment represents a workplace for those caregivers who play the delicate role of looking after people in a delicate phase of life on a daily basis. Research literature showed that staff wellbeing is strictly connected with the healthcare physical environment where they act [
8,
12]. In particular, a high perceived comfort was found to predict job-related positive outcomes, such as organizational citizenship behaviors (OCB) in staff at facilities for the elderly [
34], and work engagement among hospital staff [
35]. Thus, the inclusion of staff needs during the design process for a healthcare facility is pretty important for improving health workers well-being, which is also supposed to positively influence the quality of the provided care.
This study presents some limitations too. First of all, a limit concerns the small size of the sample, because the target population is quite specific and hard to reach. In this regard, it should however be stressed that the participants were recruited from hospices located in eleven different cities which cover all the Italian macro-geographical areas at a national level, thus representing a small but at least representative sample in this respect. Secondly, the correlational nature of the research design does not allow to demonstrate the existence of causal links between perceived quality indicators of the spatial-physical environment and users’ satisfaction towards the hospice.
To conclude, hospice designers should pay particular attention to the significant positive relationship between perceived quality indicators of the spatial-physical environment, on the one side, and users’ satisfaction, on the other side, in order to promote positive feelings in terminally ill patients, who are living in a condition of short-term life expectancy, as well as in their relatives and in staff members, who occupy and use the hospice setting. The development and validation of place-specific tools such as the Hospice PHEQIs for measuring perceived environmental quality within a “user-centered’’ perspective [
16] could thus help to improve the design process of understudied environments such as the hospice in order to promote the creation of “more humane” healthcare settings [
17].