Smart or Intelligent Assets or Infrastructure: Technology with a Purpose
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Proposal
1.2. Research Structure
2. Research Background
2.1. Models
2.2. Digital
2.3. Data
2.4. Artificial Intelligence
2.5. Blockchain
2.6. Sustainability
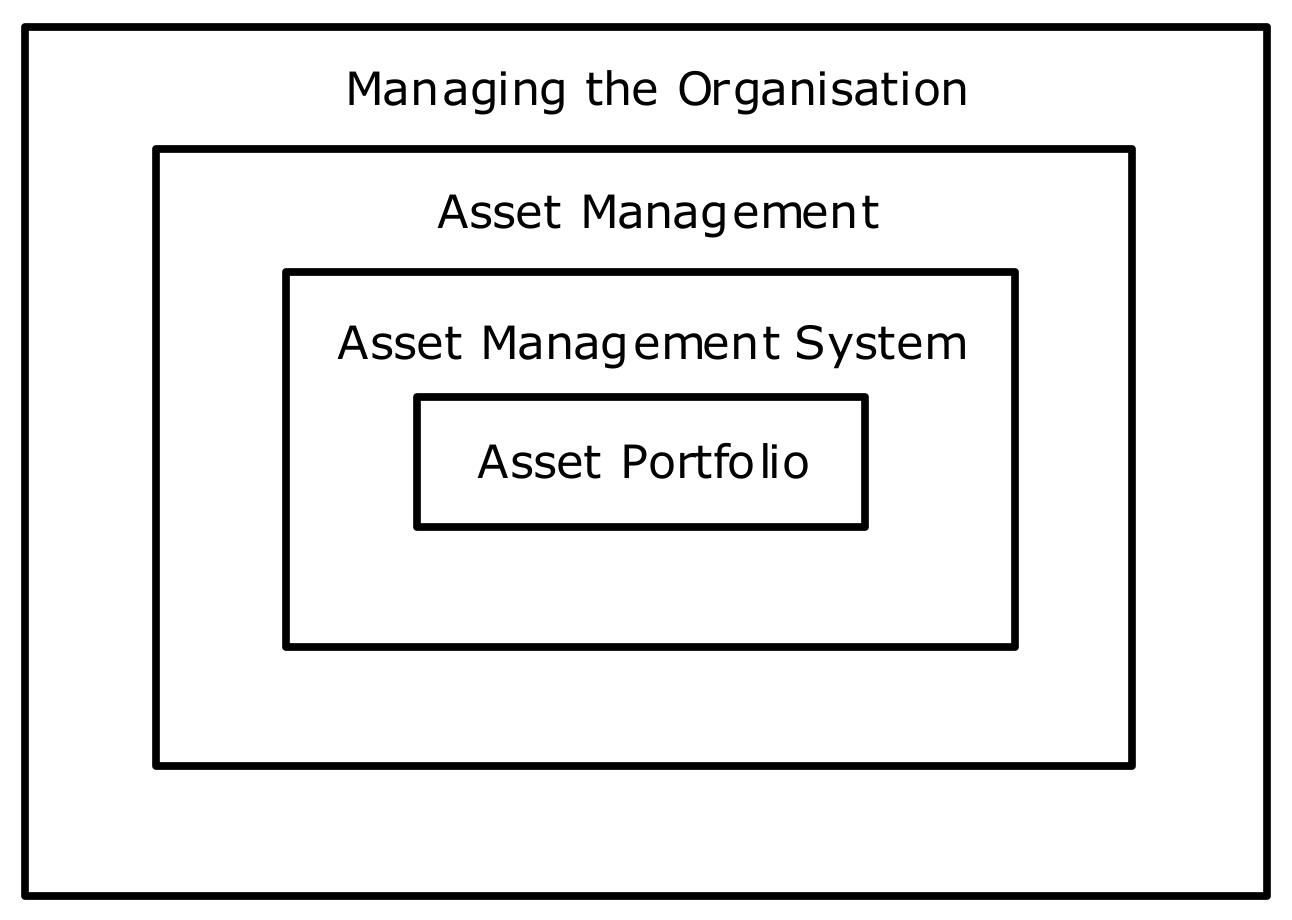
3. Asset Management
- Definition of a standard of service.
- Establishment of measurable specifications for the asset performance.
- Definition of a minimum condition grade.
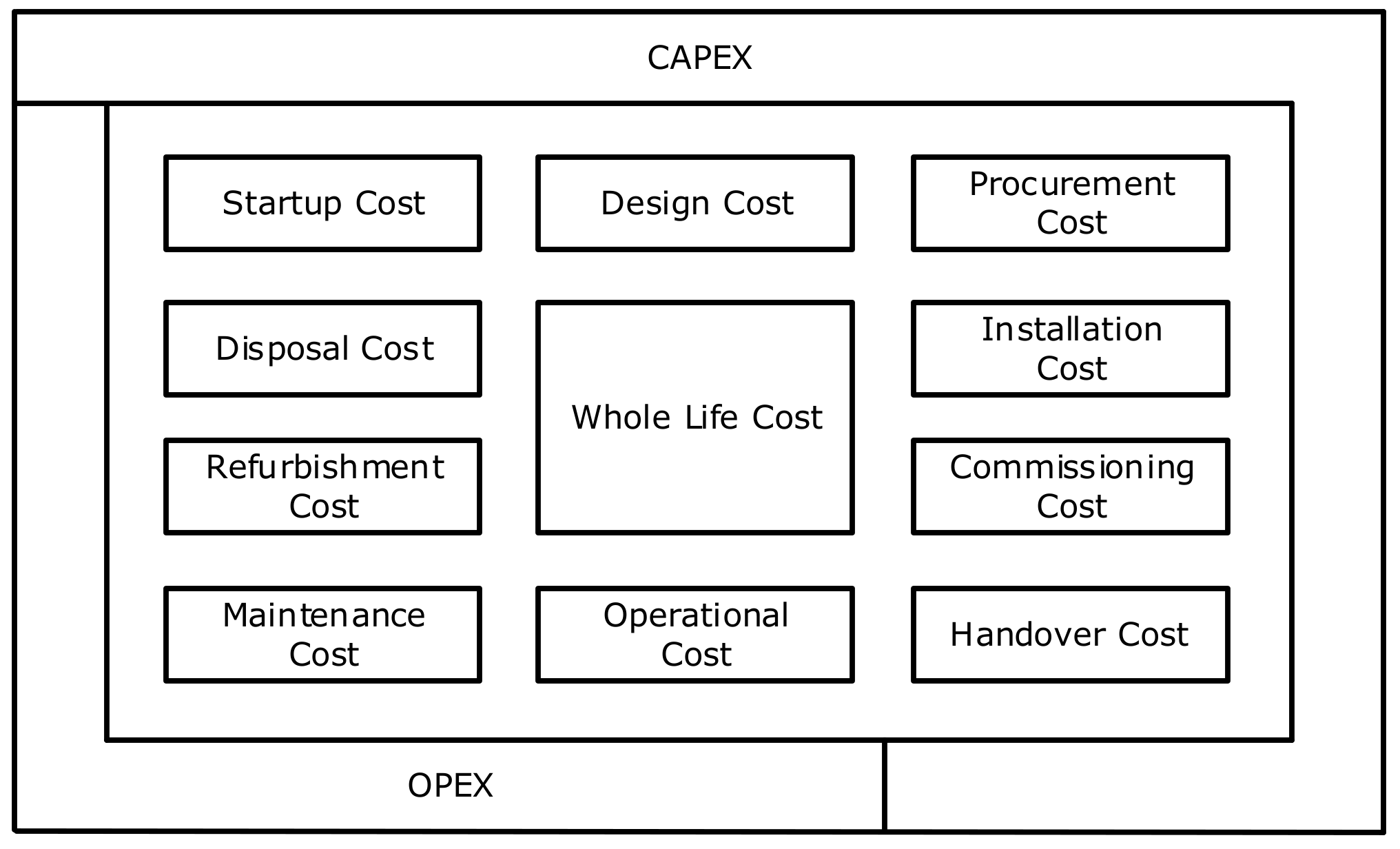
- Development of a whole-life cost approach to managing the asset.
- Specification of an asset management plan.
- Maintaining a systematic record of individual assets.
- Developing a defined program for sustaining the aggregate body of assets through deterioration modelling, planned maintenance, repair, and replacement.
- Implementing and managing information systems in support of these systems.
- Defining current and expected levels of service and linking them to maintenance and capital planning.
- Calculating life-cycle cost of assets and possible sources of finance for maintenance actions.
- Defining the standard of service that describes asset performance in objective and measurable terms against a minimum condition grade, which is established by considering the consequences of a failure of the infrastructure asset.
4. Asset Omni-Management Model
4.1. Micro-Services
4.2. Users
4.3. Spaces
4.4. Management
4.5. Technology
5. Smart or Intelligent Assets or Infrastructure
5.1. Sensor
5.2. Network
5.2.1. Software Defined Networks
5.2.2. Internet Connectivity
5.2.3. Mobile
5.2.4. Wi-Fi
5.2.5. Radio
5.2.6. Low Power Wide Area
5.2.7. Local Area Networks
5.2.8. Wide Area Networks
5.2.9. Personal Area Networks
5.3. Server
5.3.1. Systems
5.3.2. Open Standard Protocol
5.3.3. System Integrations
5.3.4. Data Structure
5.3.5. Data Formats
5.3.6. Artificial Intelligence
5.3.7. Tokenisation
5.4. Workstation
6. Discussion
6.1. Requirements
6.2. Decisions
6.3. New versus Renewal
6.4. ESG and NTZ
6.5. Cybersecurity
6.6. Hybrid Working
6.7. Services: In-House/Outsourced
6.8. Technology: Premise/Cloud
6.9. Metaverse
6.10. Datacentres
6.11. Regulation
6.12. Real Estate Data Challenges
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Akruti, K.; Dwight, R.; Zhang, T. The strategic role of Engineering Asset Management. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 146, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangreman, E.; McMahon, P.; Cabral, A. Establishing the relationship between asset management and business performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 232, 107937. [Google Scholar]
- Sangreman, E.; Cabral, A. Improving Asset Management under a regulatory view. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 190, 106523. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, A.; El-Diraby, T. A conceptual construct on value for infrastructure asset management. Util. Policy 2022, 75, 101354. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, A.; El-Diraby, T. Toward user-oriented asset management for urban railway systems. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 70, 102903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaddoost, A.; Naderpajouh, N.; Heravi, G. Integrating resilience into asset management of infrastructure systems with a focus on building facilities. J. Build. 2021, 44, 103304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, I.; Kumar, A.; Macchi, M.; Garetti, M. A Framework for implementing value-based approach in Asset Management. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Asset Management, Campo Grande, Brazil, 15–18 August 2015; pp. 487–495. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeer, M.; Wetzer, J.; van der Wielen, P.; de Haan, E.; de Meulemeester, E. Asset-management decision-support modeling, using a health and risk model. In Proceedings of the IEEE PowerTech, Eindhoven, Netherlands, 29 June–2 July 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bosisio, A.; Giustina, D.D.; Fratti, S.; Dedè, A.; Gozzi, S. A Metamodel for Multi-utilities Asset Management. In Proceedings of the IEEE Milan PowerTech, Milan, Italy, 23–27 June 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jia-xu, C.; Guan-ran, W.; Wei-xuan, M. Analysis of Key Processes and Dimensions Based on Complex Assets management Systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Urban Engineering and Management Science, Sanya, China, 29–31 January 2021; pp. 310–313. [Google Scholar]
- Laue, M.; Brown, K.; Scherrer, P.; Keast, R. Integrated Strategic Asset Management: Frameworks and Dimensions. Infranomics Top. Saf. Risk Reliab. Qual. 2014, 24, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, M.; Dhakal, S.; Wiewiora, A.; Keast, R.; Brown, K. Towards an integrated maturity model of asset management capabilities. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Asset Management, Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 8–9 October 2012; pp. 431–441. [Google Scholar]
- Attwate, A.; Wang, J.; Parlikad, A.; Russell, P. Measuring the performance of asset management systems. In Proceedings of the Asset Management Conference, London, UK, 27–28 November 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, W. Whole life cost modelling in infrastructure asset management. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Quality, Reliability, Risk, Maintenance, and Safety Engineering, Chengdu, China, 15–18 July 2013; pp. 1695–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Wijnia, Y.; de Croon, J. The Asset Management Process Reference Model for Infrastructures. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Asset Management, Pretoria, South Africa, 28–31 October 2015; pp. 447–457. [Google Scholar]
- Lovea, P.; Matthews, J. The ‘how’ of benefits management for digital technology: From engineering to asset management. Autom. Constr. 2019, 107, 102930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, V.; Hsu, S.-C. An open-source and extensible platform for general infrastructure asset management system. Autom. Constr. 2021, 127, 103692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kasasbeh, M.; Abudayyeh, O.; Liu, H. An integrated decision support system for building asset management based on BIM and Work Breakdown Structure. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 34, 101959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candón, E.; Martínez-Galán, P.; De la Fuente, A.; González-Prida, V.; Márquez, A.C.; Gómez, J.; Sola, A.; Macchi, M. Implementing Intelligent Asset Management Systems within an Industry 4.0 Manufacturing Environment. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 2488–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, P.; Crespo, A.; Fuente, A.; Guillén, A. A new model to compare intelligent asset management platforms (IAMP). IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, A.; Gomez, J.; Martinez, P.; Guillen, A. Maintenance Management through Intelligent Asset Management Platforms (IAMP). Emerging Factors, Key Impact Areas and Data Models. Energies 2020, 13, 3762. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Yuan, C.; Zheng, K. A University Fixed Asset Database Information Management System Based on Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, Xi’an, China, 25–27 May 2018; pp. 2488–2491. [Google Scholar]
- Abreu, T.; Moreira, F.R.; Carvalho, C.; Cordeiro, L.; Peixoto, A.; Mendes, J.; Fernandes, M. Analytics 4 Assets—The advanced asset management project applied to power transformers. In Proceedings of the International Conference and Exhibition on Electricity Distribution, Online Conference, 20–23 September 2021; pp. 557–561. [Google Scholar]
- Polenghi, A.; Roda, I.; Macchi, M.; Pozzetti, A. A Conceptual Model of the IT Ecosystem for Asset Management in the Global Manufacturing Context. In Proceedings of the Towards Smart and Digital Manufacturing, Novi Sad, Serbia, 30 August–3 September 2020; pp. 711–719. [Google Scholar]
- Teoh, Y.; Gill, S.; Parlikad, A. IoT and Fog Computing based Predictive Maintenance Model for Effective Asset Management in Industry 4.0 using Machine Learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 1–8. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9319212 (accessed on 1 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Pai, S.; Reuland, Y.; Smith, I. Data-Interpretation Methodologies for Practical Asset-Management. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2019, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brousa, P.; Herder, P.; Janssen, M. Towards Modelling Data Infrastructures in the Asset Management Domain. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 61, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.; Sharma, P.; Gorostegui, U.; Jantunen, E.; Baglee, D. A big data analytical architecture for the Asset Management. Ind. Prod. Serv. Syst. 2017, 64, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brous, P.; Janssen, M.; Herder, P. Next Generation Data Infrastructures: Towards an Extendable Model of the Asset Management Data Infrastructure as Complex Adaptive System. Complexity 2019, 5415828, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polenghi, A.; Roda, I.; Macchi, M.; Pozzetti, A. Conceptual framework for a data model to support Asset Management decision-making process. In Proceedings of the Production Management for the Factory of the Future, Austin, TX, USA, 1–5 September 2019; pp. 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Mattioli, J.; Perico, P.; Robic, P. Artificial Intelligence based Asset Management. In Proceedings of the International Conference of System of Systems Engineering, Budapest, Hungary, 2–4 June 2020; pp. 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Idowu, S.; Strüber, D.; Berger, T. Asset Management in Machine Learning: State-of-research and State-of-practice. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, A.; Yohan, C.; Casey, J. Machine learning and optimization-based modeling for asset management: A case study. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2020, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington, M.; Lu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Airehrour, D.; Madanian, S.; Dyrkacz, A. Deep Learning Decision Support for Sustainable Asset Management. In Advances in Asset Management and Condition Monitoring; Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 166, pp. 537–547. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano, W.; Gelenbe, E.; Yin, Y. The random neural network with deep learning clusters in smart search. Neurocomputing 2020, 396, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, W.; Gelenbe, E. Intelligent search with deep learning clusters. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Systems Conference, London, UK, 7–8 September 2017; pp. 632–637. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano, W. Deep reinforcement learning algorithms in intelligent infrastructure. Infrastructures 2019, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhary, V.; Amiri, M.J.; Maiyya, S.; Agrawal, D.; El Abbadi, A. Towards Global Asset Management in Blockchain Systems. Comput. Sci. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.09359. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Tran, B.; Weber, I.; O’Connor, H.; Rimba, P.; Xu, X.; Staples, M.; Jeffery, L.Z.R. Integrated model-driven engineering of blockchain applications for business processes and asset management. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2020, 51, 1059–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleti, D.; Maleti, M.; Al-Najjar, B.; Gomišcek, B. Development of a Model Linking Physical Asset Management to Sustainability Performance: An Empirical Research. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xie, X.; Lu, Q.; Kumar, A.; Pitt, M.; Yang, J. Gemini Principles-Based Digital Twin Maturity Model for Asset Management. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 55000; Asset Management—Overview, Principles and Terminology. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Treleaven, P.; Barnett, J.; Knight, A. Real Estate Data Marketplace. AI Ethics 2021, 1, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, W. Verification and Validation for data marketplaces via a blockchain and smart contracts. Blockchain: Res. Appl. 2022, 3, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 19650; Building Information Modelling (BIM)—Organization and digitization of information about buildings and civil engineering works, including building information modelling (BIM). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Volt, J.; Toth, Z. Definition of the Digital Building Logbook; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; ISBN 978-92-9460-144-5. [Google Scholar]
- Policies, Standards, Guidelines & Procedures; Centre for the Protection of National Infrastructure: London, UK, 2022.
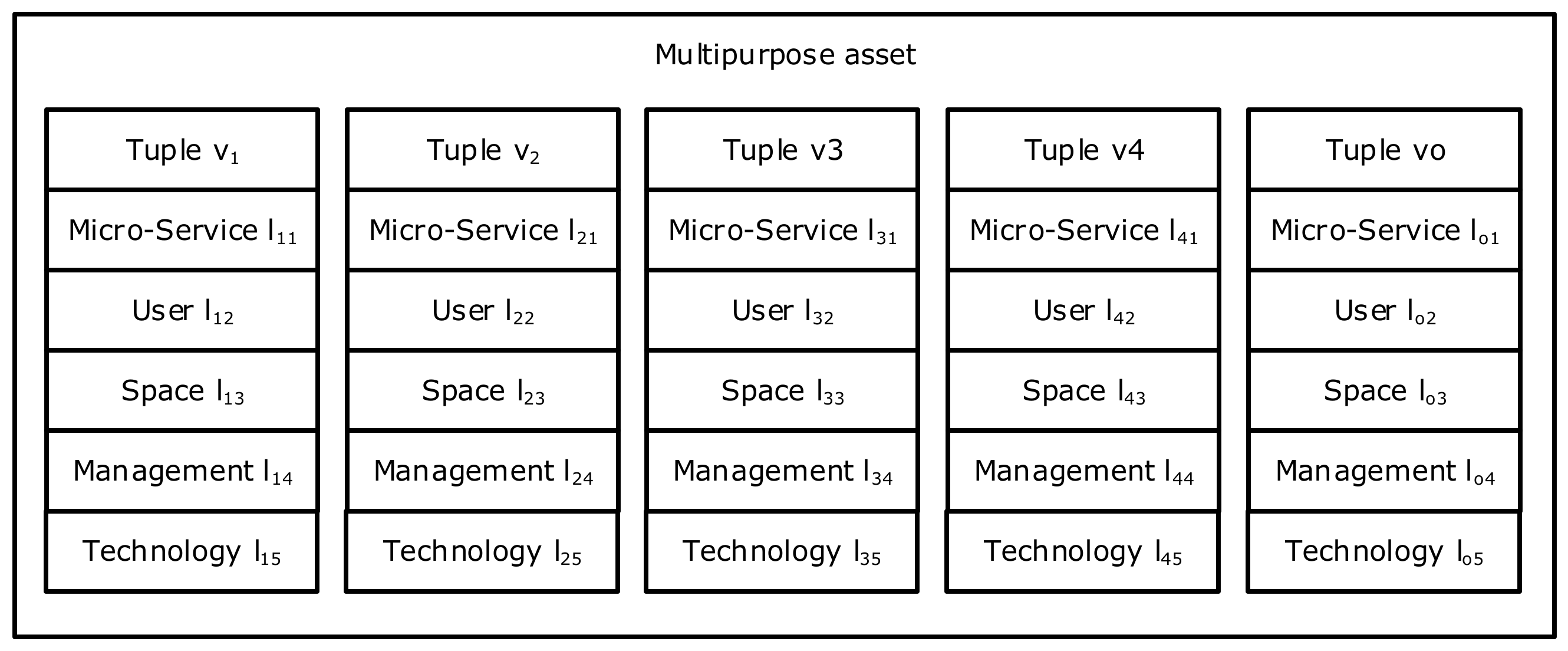
| Tuple | Micro-Service lo1 | User lo2 | Space lo3 | Management lo4 | Technology lo5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v1 | Check in visitor | Visitor | Reception | Outsourced Public cloud | Visitor Management System |
| v2 | Check in visitor | Client servicers staff | Reception | Outsourced Facilities Management provider | Visitor Management System |
| v3 | Lease collection | Asset management staff | Office | In house asset owner | Asset Management System |
| v4 | Cleaning | Facilities management staff | Washrooms | Outsourced Facilities Management provider | Smart washroom |
| v5 | Parking digital wayfinding | Asset staff | Car Park | Outsourced Public cloud | Parking Management System |
| v6 | Catering | Client Services staff | Kitchen | Outsourced Facilities Management provider | Food stock management system |
| v7 | Investor reporting | Asset management staff | Office | In house asset owner | In house asset owner |
| v8 | Energy optimisation | Asset energy performance manager | Office | Outsourced engineering services provider | Energy management system |
| v9 | HVAC maintenance | Asset maintainer | Asset back of house | Outsourced engineering services provider | Enterprise asset management |
| v10 | Network provision | Office occupier | Office | Outsourced Network services provider | Local Area Network |
| v… | … | … | … | … | … |
| Micro-Service li1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Provide return to asset investors | Design an asset | Pay electricity bill |
| Collect rent from tenants | Deliver an AM economic plan | Decide asset function |
| Collect lease from leaseholders | Maintain the HVAC | … |
| Commissioning a new asset | Change floor plan | |
| User li2 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Office occupier | Asset owner | Designer |
| Visitor | Asset manager | Cooker |
| Passenger | Facilities manager | … |
| Customer | Energy performance manager | |
| Space li3 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Office space | Bicycle rack | Washrooms |
| Reception | Retail space | Kitchen |
| Entrance | Common area | … |
| Car Park | Equipment room | |
| Management li4 | |
|---|---|
| In-house | Internal smart contracts |
| Outsourced to a third-party service provider | … |
| External data marketplace | |
| Technology li5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor | Network | Server | Workstation |
| Camera | Wi-Fi | Local Area Network | Display |
| Occupancy | 5G | Security System | Mobile App |
| Environmental | Local Area Network | Building Management System | Tablet |
| … | … | … | … |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serrano, W. Smart or Intelligent Assets or Infrastructure: Technology with a Purpose. Buildings 2023, 13, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13010131
Serrano W. Smart or Intelligent Assets or Infrastructure: Technology with a Purpose. Buildings. 2023; 13(1):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13010131
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerrano, Will. 2023. "Smart or Intelligent Assets or Infrastructure: Technology with a Purpose" Buildings 13, no. 1: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13010131
APA StyleSerrano, W. (2023). Smart or Intelligent Assets or Infrastructure: Technology with a Purpose. Buildings, 13(1), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13010131






