Feasibility Evaluation of Novel High-Damping Rubbers as Energy-Dissipation Material under Axial Dynamic Load for Damper Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material Testing Method
2.1. Hyperelastic Composite Material
2.2. Test Procedures
3. Development of Hyperelastic Composite Material under Dynamic Axial Loads
4. HECM under Dynamic Axial Loads
4.1. Test
4.2. Testing on the Device Sample with Tension–Compression Behavior
4.3. Testing of the Device Sample with Pure Compression Behavior
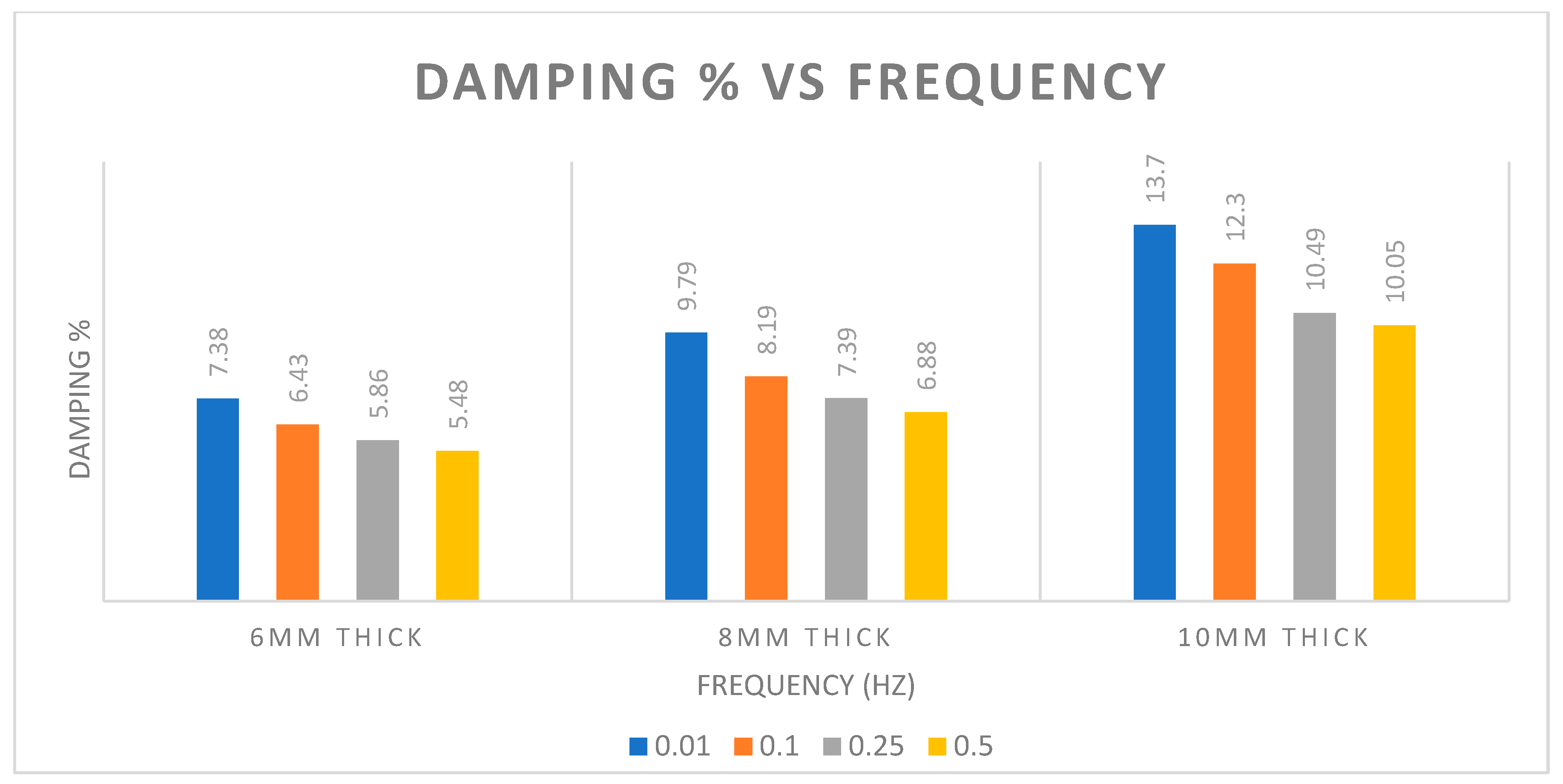
4.4. The Effects of Rubber Thickness and Load Frequency under Pure Compression
5. Finite Element Analysis of Hyperelastic Composite Damper
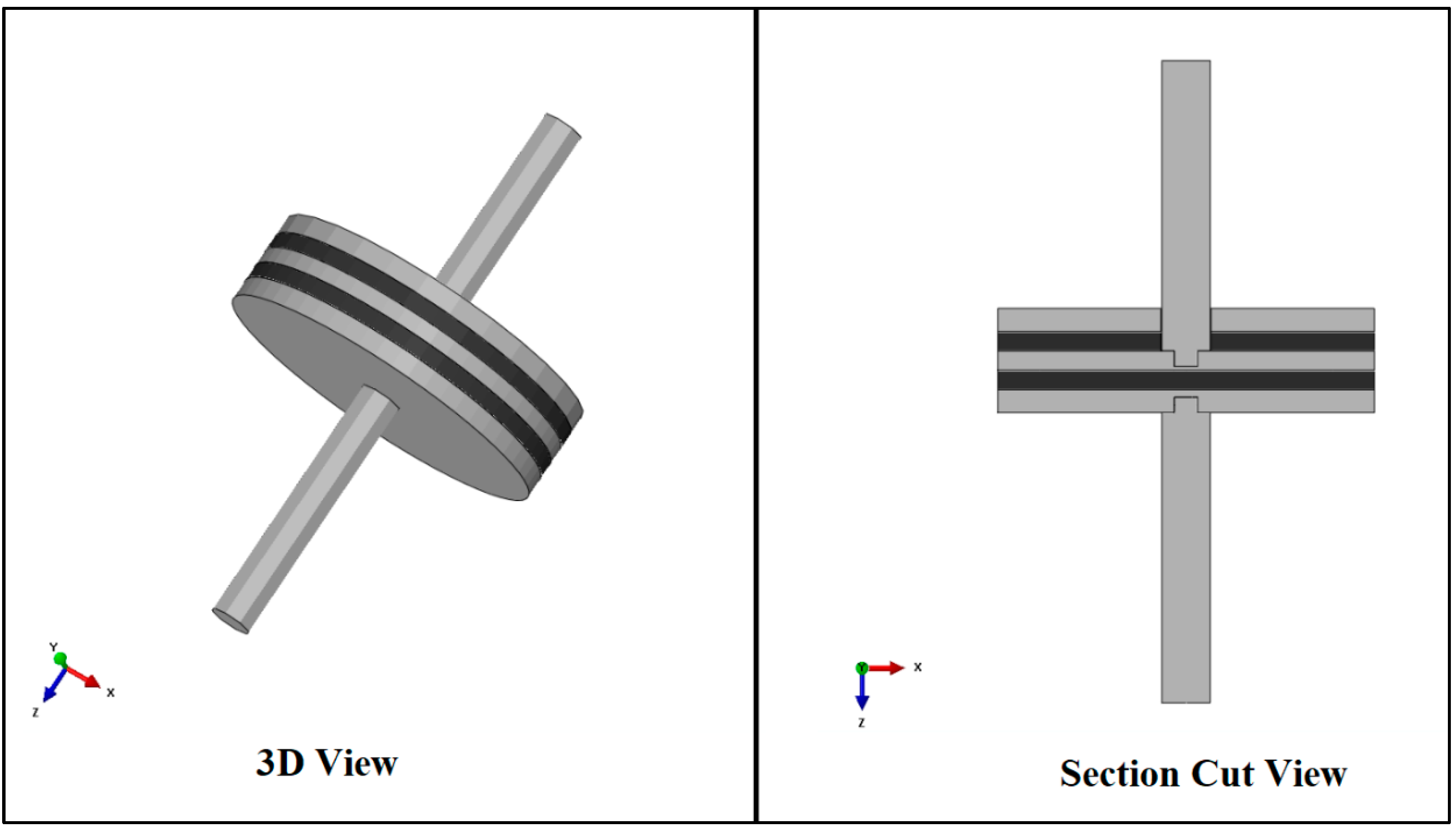
5.1. FE Modeling
5.2. Validation of FE Model
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Symbols
| G | Shear modulus |
| γ | Shear strain |
| Viscous damping ratio | |
| Effective stiffness | |
| H | Area of the hysteretic loop |
| d+ | The maximum displacement values in the cycle |
| d− | The minimum displacement values in the cycle |
| F+ | The force values at maximum displacement |
| F− | The force values at minimum displacement |
| ƒ | Frequency |
References
- Gu, H.; Itoh, Y. Ageing Behaviour of Natural Rubber and High Damping Rubber Materials Used in Bridge Rubber Bearings. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2010, 13, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerileng, K.; Dundu, M. Base Isolation Systems in Multi-Storey Structures. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Structural Engineering Research, Sydney, Australia, 20–22 November 2017; pp. 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Samadian, D.; Ghafory-Ashtiany, M.; Naderpour, H.; Eghbali, M. Seismic resilience evaluation based on vulnerability curves for existing and retrofitted typical RC school buildings. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 127, 105844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Pitilakis, K.; Tsinidis, G.; Huang, H.; Zhang, D.; Argyroudis, S. Resilience assessment of tunnels: Framework and application for tunnels in alluvial deposits exposed to seismic hazard. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 162, 107456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; John, R. Seismic performance of base isolated multi-storey building. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2015, 6, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Mazda, T.; Kajita, Y. Evaluation of mechanical properties considering hysteresis characteristic of high damping rubber bearing. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1687, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atam, E. Friction Damper-Based Passive Vibration Control Assessment for Seismically-Excited Buildings Through Comparison With Active Control: A Case Study. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 4664–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y. Influence of High Damping Rubber Bearing on Seismic Performance of The Bridge. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 510, 052058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Fujita, T.; Kasahara, Y.; Suizu, Y.; Furuya, O.; Teramoto, T.; Kitamura, H. Energy Absorption Characteristics of High Damping Rubber Damper for Vibration Control of High-Rise Buildings; SMiRT-12; IASMiRT: Anaheim, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Teramoto, T.; Kitamura, H.; Ozaki, H.; Furuya, O.; Morikawa, S.; Suzuki, S. Practical Application of high-damping rubber dampers to slender buildings. In Proceedings of the 11th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering WCEE, Acapulco, Mexico, 23–28 June 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Z.P.; Hayashikawa, T.; Matsumoto, T.; He, X.W. Seismic response analysis of base-isolated bridge subjected to long duration earthquake in low temperature environment. J. Struct. Eng. JSCE 2015, 61A, 335–343. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, K.; Ahmadi, H.; Goodchild, I.R.; Magonette, G.; Taucer, F.; Dumoulin, C. Rubber-Based Energy Dissipators for Earthquake Protection of Structures. In Proceedings of the 12th WCEE, Auckland, New Zealand, 30 January–4 February 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, Y.; Gu, H.; Satoh, K.; Yamamoto, Y. Long-Term Deterioration of High Damping Rubber Bridge Bearing. Doboku Gakkai Ronbunshuu A 2006, 62, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, P.; Tubaldi, E.; Selvi, F.; Gioiella, L. Seismic performance of an existing RC structure retrofitted with buckling restrained braces. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 33, 101688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.-W.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.-W. Design and test of tuned liquid mass dampers for attenuation of the wind responses of a full scale building. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 045020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Guo, T.; Mwangilwa, F. Development and test of a self-centering fluidic viscous damper. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2020, 23, 2835–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolati, S.S.K.; Mehrabi, A.; Dolati, S.S.K. Application of Viscous Damper and Laminated Rubber Bearing Pads for Bridges in Seismic Regions. Metals 2021, 11, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, W. Viscoelastic Material as Energy Dissipater Viscoelastic Damper for Building Structures to Mitigate the Seismic Vibration. Civ. Environ. Eng. Rep. 2019, 29, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanitkar, R.; Harms, M.; Crosby, P.; Lai, M.L. Seismic retrofit of a steel moment frame structure using vis-coe-lastic dampers. J. Earthq. Technol. 1998, 35, 207–219. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Huang, X.; Dong, Y.; Li, Q. Dynamic Properties and Energy Dissipation Study of Sandwich Viscoelastic Damper Considering Temperature Influence. Buildings 2021, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinou, M.C.; Symans, M.D. Experimental & Analytical Investigation of Seismic Response of Structures with Supplemental Fluid Viscous Dampers; NCEER-92-0032; National Center for Earthquake Engineering Research: Buffalo, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Chang, Y.H.; Lai, M.L. Temperature Rise Effect of Viscoelastically Damped Structures Under Strong Earthquake Ground Motions. J. Mech. 1998, 14, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, D.; Makris, N.; Kelly, J.M. In-situ condition assessment of seismic fluid dampers: Experimental studies and challenges. Meccanica 2014, 50, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandru, C. Variety of displacement Dependent Devices Used for Bridges and Viaducts Certified By ICECON SERT SRL. Acta Uiversitatis Cibniensis-Tech. Ser. 2017, 69, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sadek, F.; Mohraz, B.; Taylor, A.W.; Chung, R.M. Passive Energy Dissipating Devices for Sesismic Applications. In Building and Fire Research Laboratory; Report NISTIR 5923; National Institute of Standarts and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- EN 15129; Anti-Seismic Devices. Comité Européen de Normalisation (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2009.
- Reza, A.M. A study on the damping ratio of the viscous fluid dampers in the braced frames. Eur. Online J. Nat. Soc. Sci. 2014, 3, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar]
- EN 1337-3:2005; Structural Bearings—Part 3: Elastomeric Bearings. Technical Committee CEN/TC 167. BSI: London, UK, 2009.
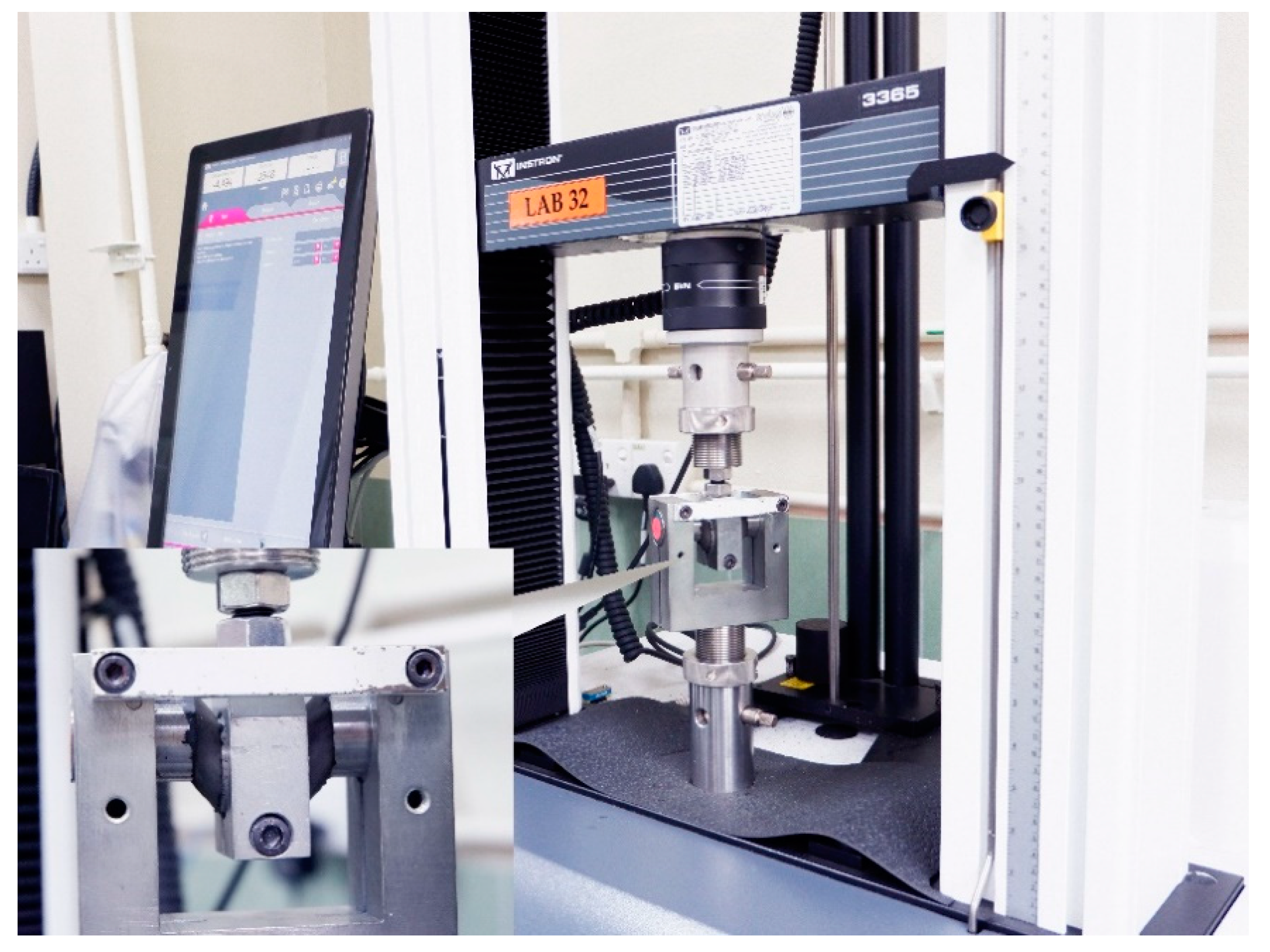
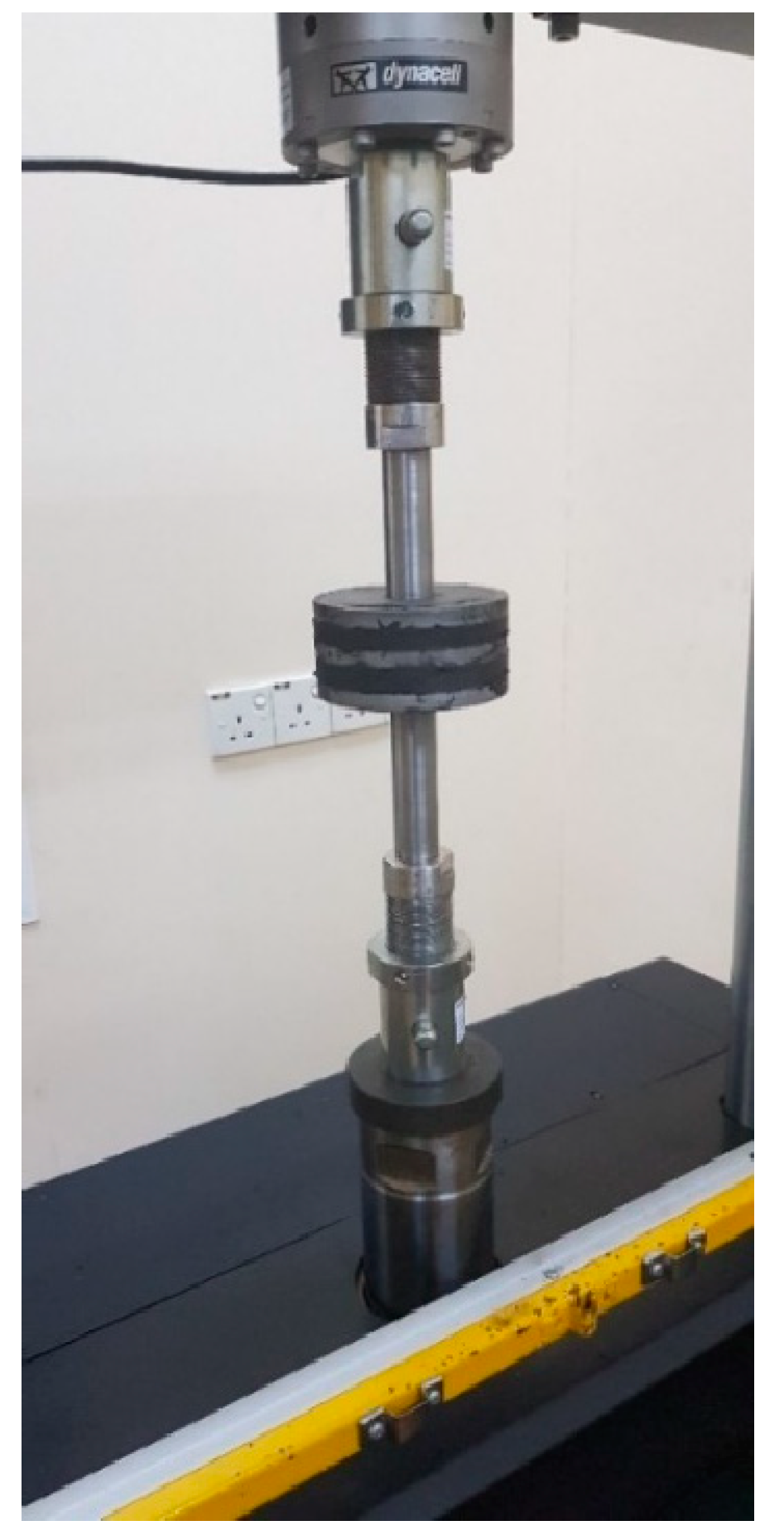
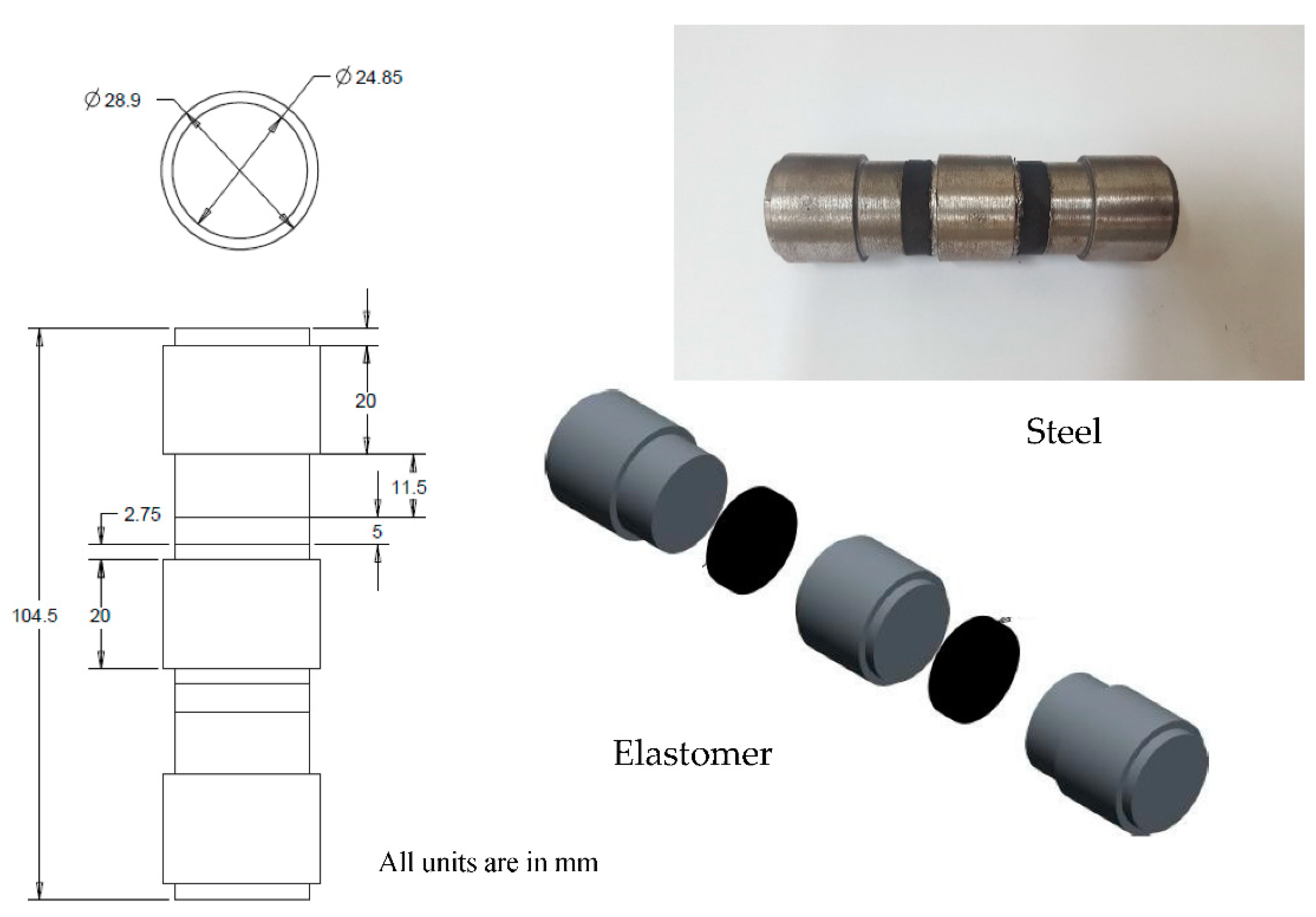

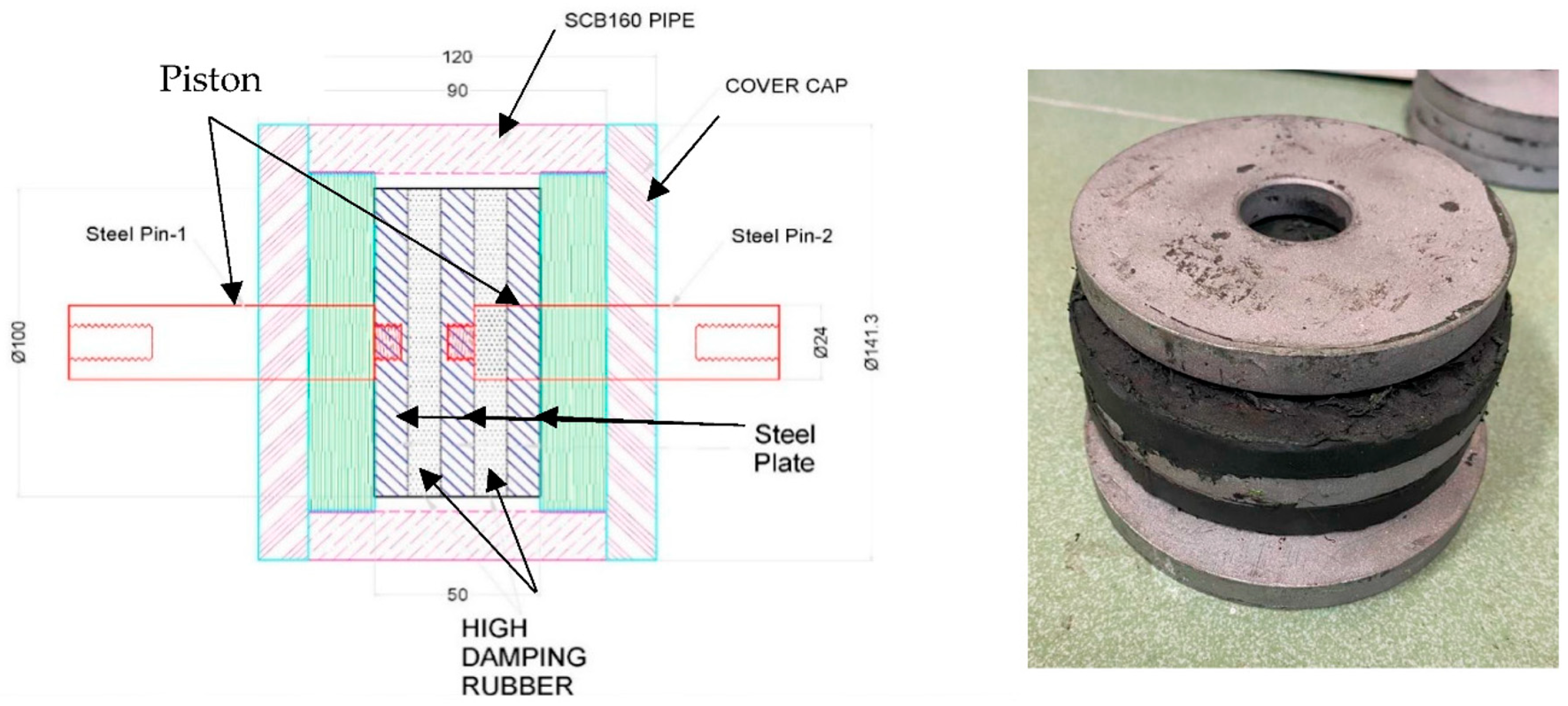

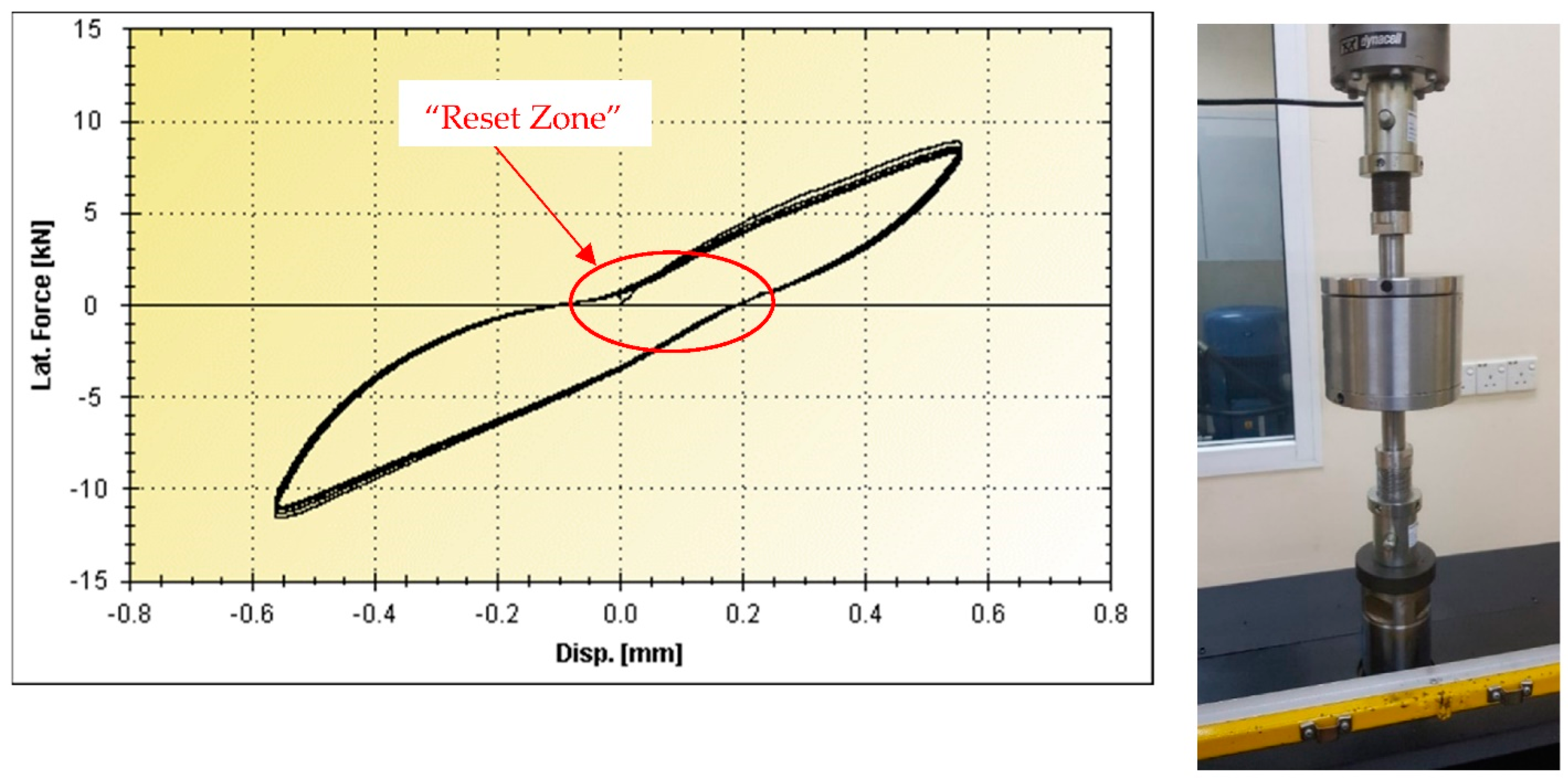
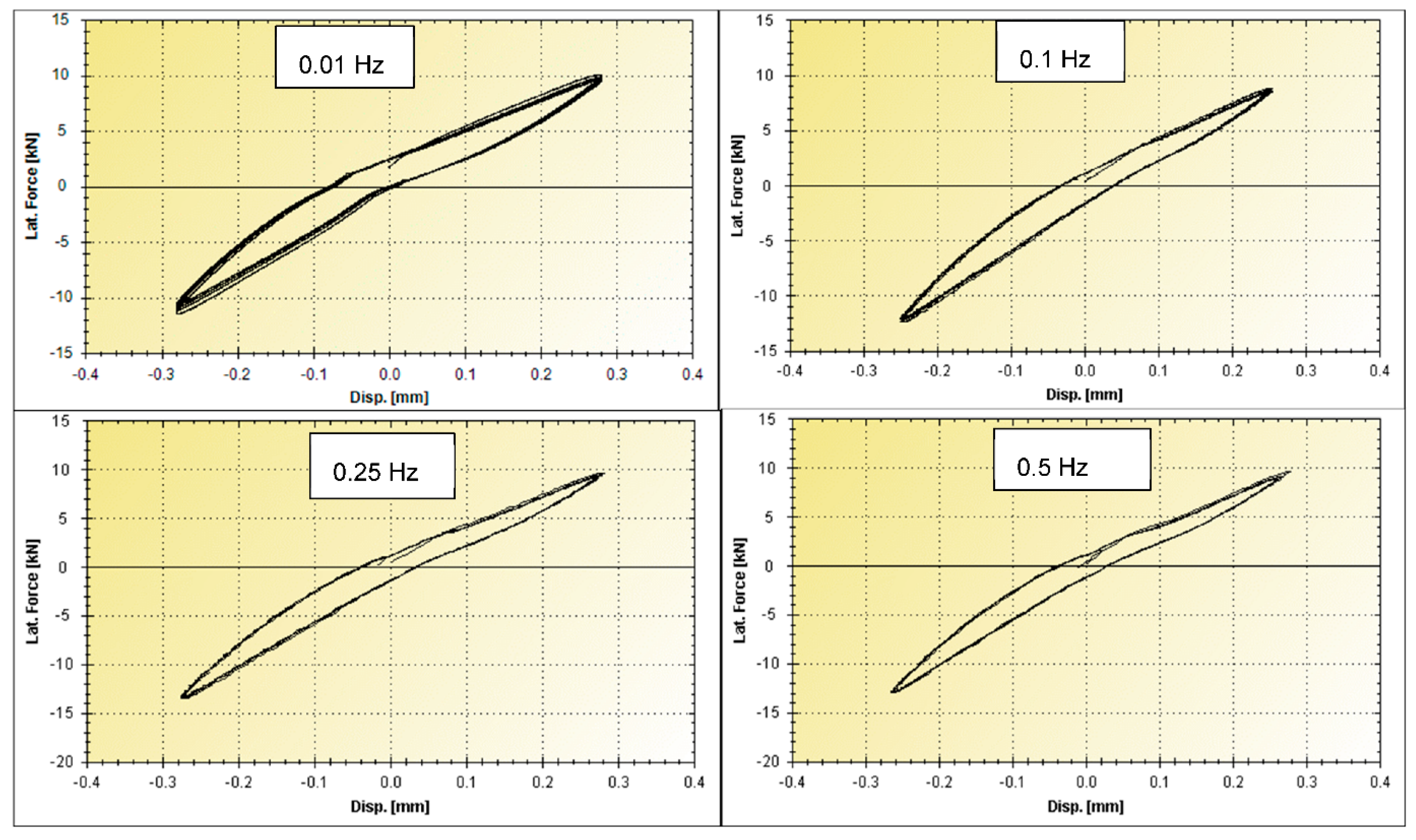
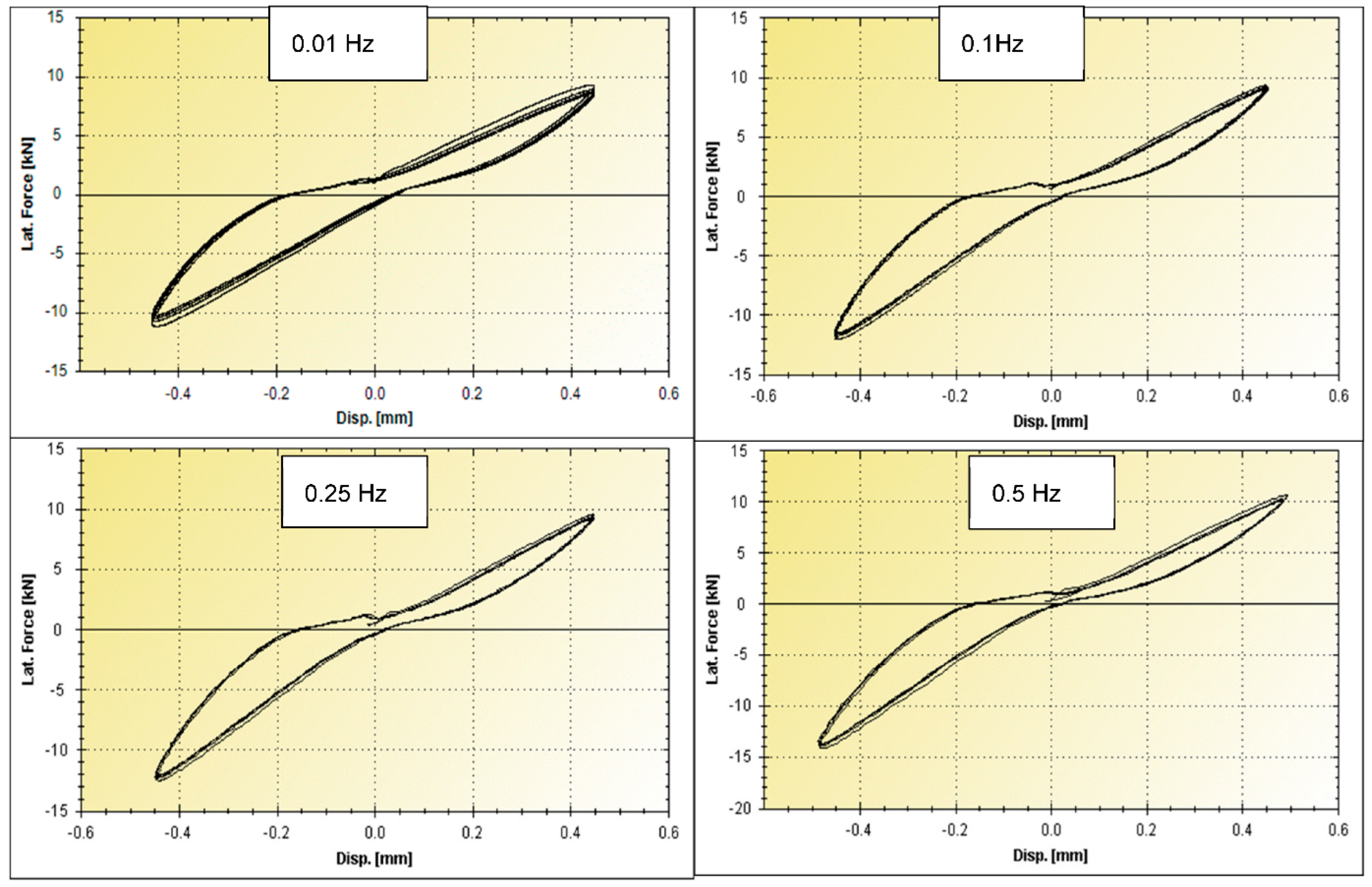
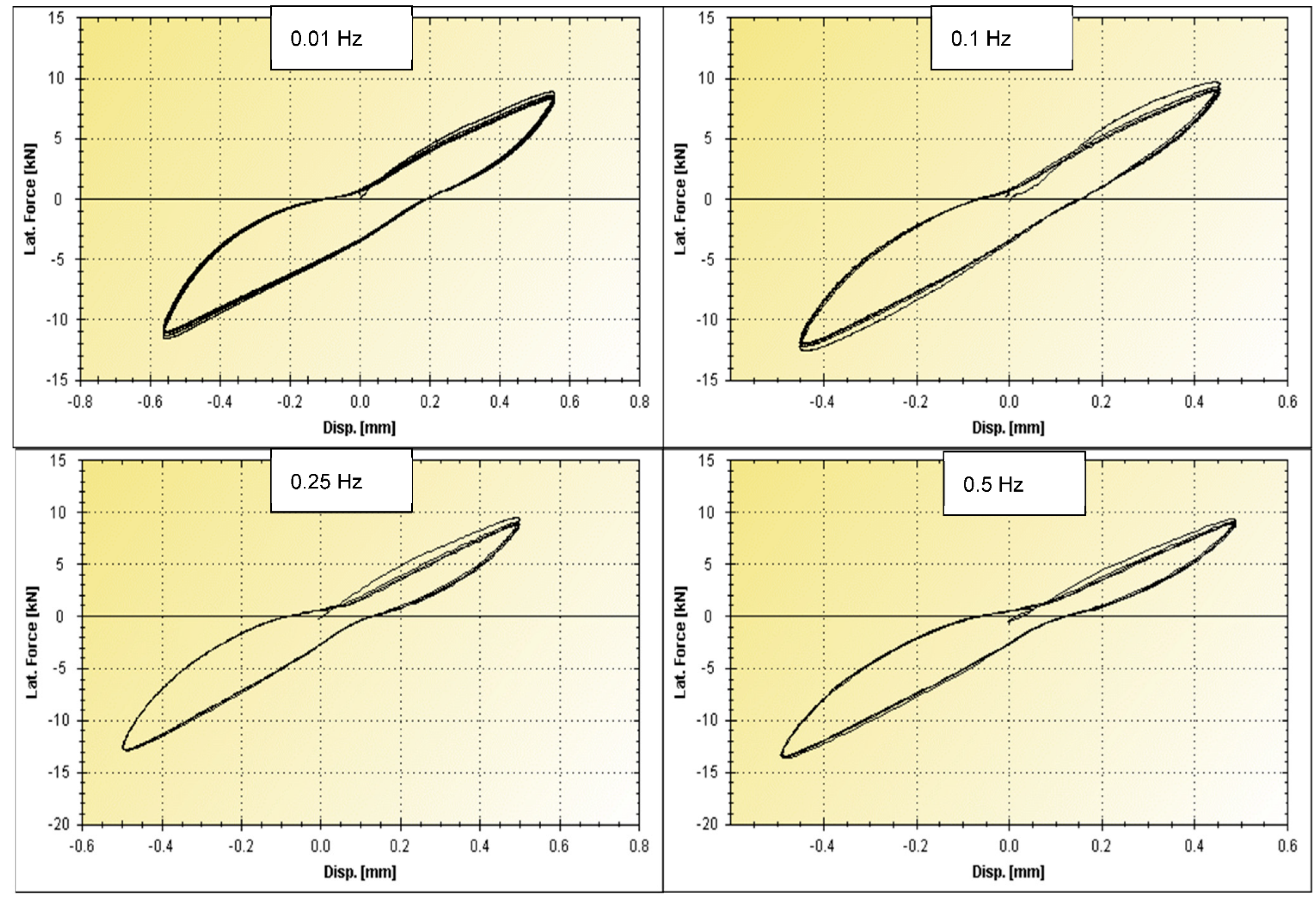


| Cycle | G | γ | d+ | d− | F+ | F− | H | Kb | ξ | ƒ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | (MPa) | (%) | (mm) | (mm) | (kN) | (kN) | (kN·mm) | (kN/mm) | (%) | (Hz) |
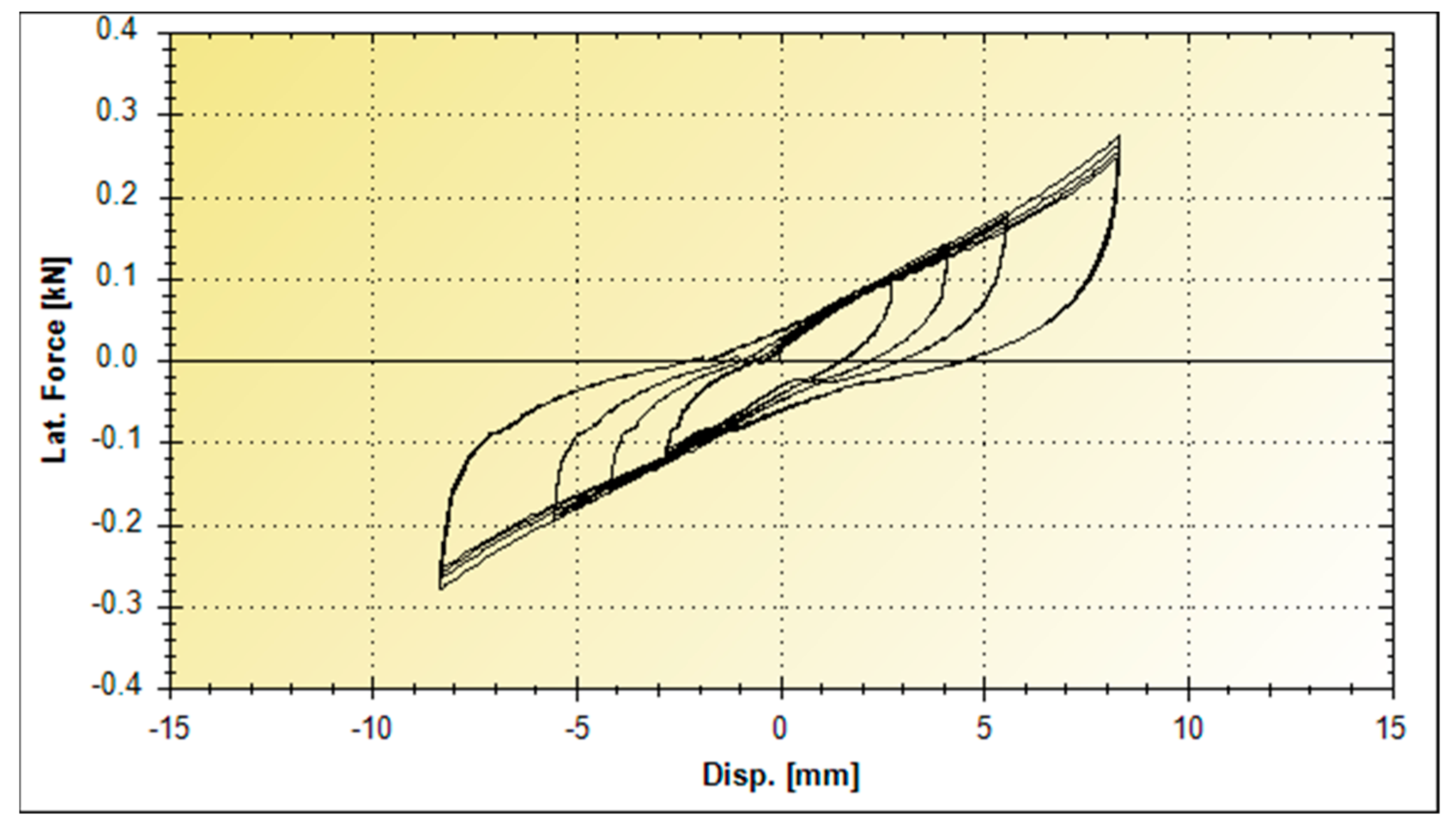
| 1 | 0.4288 | 50.6 | 2.7806 | −2.7813 | 0.10424 | −0.10863 | 0.30854 | 0.03827 | 16.59 | 0.03 |
| 2 | 0.4343 | 50.6 | 2.7806 | −2.7813 | 0.10169 | −0.1139 | 0.2941 | 0.03876 | 15.61 | 0.03 |
| 3 | 0.4401 | 50.6 | 2.7804 | −2.7812 | 0.10211 | −0.11635 | 0.29107 | 0.03928 | 15.25 | 0.03 |
| 4 | 0.4441 | 50.6 | 2.7806 | −2.7813 | 0.10261 | −0.11788 | 0.28953 | 0.03964 | 15.03 | 0.03 |
| 5 | 0.4048 | 75.8 | 4.171 | −4.1716 | 0.14277 | −0.15861 | 0.6063 | 0.03613 | 15.35 | 0.03 |
| Cycle | d+ | d− | F+ | F− | H | Kb | ξ | ƒ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | (mm) | (mm) | (kN) | (kN) | (kN·mm) | (kN/mm) | (%) | (Hz) |
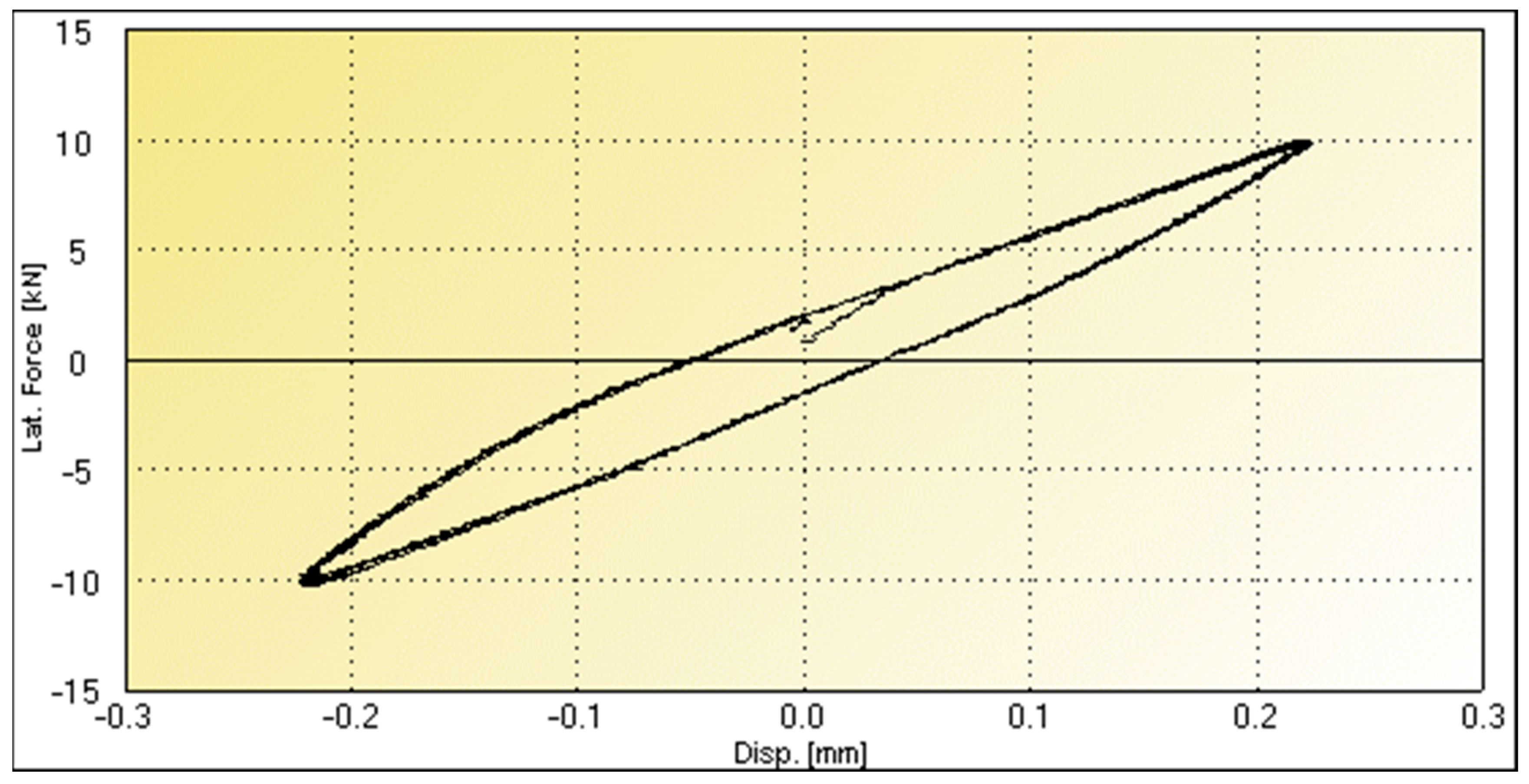
| 1 | 0.22448 | −0.22199 | 9.8674 | −10.198 | 1.1466 | 44.942 | 8.15 | 0.00995 |
| 2 | 0.22425 | −0.22182 | 9.7901 | −10.044 | 1.1687 | 44.463 | 8.41 | 0.01002 |
| 3 | 0.22486 | −0.22202 | 9.7799 | −9.8674 | 1.1700 | 43.966 | 8.48 | 0.00999 |
| Cycle | d+ | d− | F+ | F− | H | Kb | ξ | ƒ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | (mm) | (mm) | (kN) | (kN) | (kN·mm) | (kN/mm) | (%) | (Hz) |
| 1 | 0.5585 | −0.5629 | 8.6552 | −11.307 | 4.8635 | 17.801 | 13.83 | 0.01 |
| 2 | 0.5584 | −0.563 | 8.3737 | −11.055 | 4.7244 | 17.326 | 13.8 | 0.01 |
| 3 | 0.5584 | −0.5629 | 8.2284 | −10.883 | 4.6131 | 17.044 | 13.7 | 0.01 |
| 6 mm Thick Rubber Cycle | d+ | d− | F+ | F− | H | Kb | ξ | ƒ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | (mm) | (mm) | (kN) | (kN) | (kN·mm) | (kN/mm) | (%) | (Hz) |
| 1 | 0.2798 | −0.2804 | 9.9608 | −11.344 | 1.45 | 38.031 | 7.73 | 0.01 |
| 2 | 0.2799 | −0.2806 | 9.7562 | −11.047 | 1.3644 | 37.115 | 7.45 | 0.01 |
| 3 | 0.2798 | −0.2804 | 9.5962 | −10.794 | 1.3179 | 36.397 | 7.35 | 0.01 |
| 1 | 0.25449 | −0.2496 | 8.72 | −12.377 | 1.072 | 41.852 | 6.42 | 0.099 |
| 2 | 0.25465 | −0.2499 | 8.5428 | −12.125 | 1.0607 | 40.964 | 6.48 | 0.1001 |
| 3 | 0.25407 | −0.2499 | 8.53 | −12.069 | 1.0481 | 40.873 | 6.43 | 0.0999 |
| 1 | 0.28144 | −0.2759 | 9.5915 | −13.538 | 1.1903 | 41.5 | 5.88 | 0.2447 |
| 2 | 0.27696 | −0.2754 | 9.321 | −13.344 | 1.1562 | 41.033 | 5.88 | 0.2503 |
| 3 | 0.27609 | −0.2750 | 9.3281 | −13.278 | 1.1472 | 41.019 | 5.86 | 0.2498 |
| 1 | 0.27821 | −0.2642 | 9.5691 | −12.954 | 1.0325 | 41.526 | 5.38 | 0.4871 |
| 2 | 0.2656 | −0.2656 | 9.0762 | −12.873 | 1.0025 | 41.318 | 5.47 | 0.4995 |
| 3 | 0.26711 | −0.2646 | 9.0518 | −12.9 | 1.0051 | 41.286 | 5.48 | 0.4995 |
| 8 mm Thick Rubber Cycle | d+ | d− | F+ | F− | H | Kb | ξ | ƒ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | (mm) | (mm) | (kN) | (kN) | (kN·mm) | (kN/mm) | (%) | (Hz) |
| 1 | 0.4484 | −0.4524 | 9.101 | −10.93 | 2.9893 | 22.236 | 10.55 | 0.01 |
| 2 | 0.4484 | −0.4524 | 8.7585 | −10.528 | 2.7383 | 21.411 | 10.03 | 0.01 |
| 3 | 0.4483 | −0.4524 | 8.582 | −10.31 | 2.6171 | 20.975 | 9.79 | 0.01 |
| 1 | 0.45331 | −0.4527 | 9.143 | −11.712 | 2.5299 | 23.019 | 8.52 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 0.45295 | −0.4520 | 9.0148 | −11.612 | 2.4025 | 22.793 | 8.19 | 0.1 |
| 3 | 0.45308 | −0.4524 | 8.9376 | −11.29 | 2.3557 | 22.338 | 8.19 | 0.1 |
| 1 | 0.44954 | −0.4478 | 9.4756 | −12.375 | 2.3989 | 24.35 | 7.79 | 0.248 |
| 2 | 0.44757 | −0.4481 | 9.2494 | −12.255 | 2.2409 | 24.009 | 7.41 | 0.2494 |
| 3 | 0.44712 | −0.4471 | 9.199 | −12.017 | 2.2025 | 23.726 | 7.39 | 0.25 |
| 1 | 0.49519 | −0.4836 | 10.535 | −14.111 | 2.761 | 25.179 | 7.29 | 0.4924 |
| 2 | 0.48599 | −0.4849 | 10.171 | −13.889 | 2.5212 | 24.781 | 6.87 | 0.4995 |
| 3 | 0.48632 | −0.4849 | 9.9704 | −13.596 | 2.473 | 24.264 | 6.88 | 0.5 |
| 10 mm Thick Rubber Cycle | d+ | d− | F+ | F− | H | Kb | ξ | ƒ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | (mm) | (mm) | (kN) | (kN) | (kN·mm) | (kN/mm) | (%) | (Hz) |
| 1 | 0.5585 | −0.5629 | 8.6552 | −11.307 | 4.8635 | 17.801 | 13.83 | 0.01 |
| 2 | 0.5584 | −0.563 | 8.3737 | −11.055 | 4.7244 | 17.326 | 13.8 | 0.01 |
| 3 | 0.5584 | −0.5629 | 8.2284 | −10.883 | 4.6131 | 17.044 | 13.7 | 0.01 |
| 1 | 0.4556 | −0.4514 | 9.5276 | −12.266 | 3.9322 | 24.029 | 12.67 | 0.1002 |
| 2 | 0.4556 | −0.4507 | 9.0664 | −11.973 | 3.7401 | 23.216 | 12.49 | 0.1 |
| 3 | 0.4551 | −0.4505 | 8.9405 | −11.754 | 3.6215 | 22.853 | 12.3 | 0.1 |
| 1 | 0.5028 | −0.4989 | 9.2421 | −12.672 | 3.9203 | 21.878 | 11.37 | 0.2466 |
| 2 | 0.5000 | −0.4995 | 8.7878 | −12.607 | 3.6054 | 21.404 | 10.73 | 0.2504 |
| 3 | 0.4998 | −0.4983 | 8.6859 | −12.739 | 3.5238 | 21.466 | 10.49 | 0.2503 |
| 1 | 0.4893 | −0.4914 | 9.0509 | −13.369 | 3.5421 | 22.861 | 10.26 | 0.4916 |
| 2 | 0.4898 | −0.4896 | 8.9326 | −13.444 | 3.3499 | 22.846 | 10.18 | 0.5003 |
| 3 | 0.4894 | −0.4895 | 8.8238 | −13.193 | 3.2781 | 22.492 | 10.05 | 0.5 |
| g | τ |
|---|---|
| 0.01279 | 5.00 × 10−4 |
| 0.27523 | 0.005 |
| 0.28005 | 0.0159 |
| 0.20402 | 0.05 |
| 0.10778 | 0.159 |
| 0.05928 | 0.5 |
| 0.02867 | 1.59 |
| 0.01549 | 5 |
| 0.00753 | 15.9 |
| 0.00399 | 50 |
| 0.00195 | 159 |
| 0.00106 | 500 |
| 0.000472524 | 1590 |
| 0.000313733 | 5000 |
| 7.94 × 10−5 | 15,900 |
| 0.000121258 | 50,000 |
| 3.59 × 10−5 | 500,000 |
| 1.14 × 10−5 | 5,000,000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teh, T.W.; Tan, C.G.; Jumaat, M.Z. Feasibility Evaluation of Novel High-Damping Rubbers as Energy-Dissipation Material under Axial Dynamic Load for Damper Devices. Buildings 2022, 12, 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12111917
Teh TW, Tan CG, Jumaat MZ. Feasibility Evaluation of Novel High-Damping Rubbers as Energy-Dissipation Material under Axial Dynamic Load for Damper Devices. Buildings. 2022; 12(11):1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12111917
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeh, Tzyy Wooi, Chee Ghuan Tan, and Mohd Zamin Jumaat. 2022. "Feasibility Evaluation of Novel High-Damping Rubbers as Energy-Dissipation Material under Axial Dynamic Load for Damper Devices" Buildings 12, no. 11: 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12111917
APA StyleTeh, T. W., Tan, C. G., & Jumaat, M. Z. (2022). Feasibility Evaluation of Novel High-Damping Rubbers as Energy-Dissipation Material under Axial Dynamic Load for Damper Devices. Buildings, 12(11), 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12111917






